Abstract
Cimicifuga racemosa (CR) extracts contain diverse constituents such as saponins. These saponins, which act as a defense against herbivores and pathogens also show promise in treating human conditions such as heart failure, pain, hypercholesterolemia, cancer, and inflammation. Some of these effects are mediated by activating AMP-dependent protein kinase (AMPK). Therefore, comprehensive screening for activating constituents in a CR extract is highly desirable. Employing machine learning (ML) techniques such as Deep Neural Networks (DNN), Logistic Regression Classification (LRC), and Random Forest Classification (RFC) with molecular fingerprint MACCS descriptors, 95 CR constituents were classified. Calibration involved 50 randomly chosen positive and negative controls. LRC achieved the highest overall test accuracy (90.2%), but DNN and RFC surpassed it in precision, sensitivity, specificity, and ROC AUC. All CR constituents were predicted as activators, except for three non-triterpene compounds. The validity of these classifications was supported by good calibration, with misclassifications ranging from 3% to 17% across the various models. High sensitivity (84.5–87.2%) and specificity (84.1–91.4%) suggest suitability for screening. The results demonstrate the potential of triterpene saponins and aglycones in activating AMP-dependent protein kinase (AMPK), providing the rationale for further clinical exploration of CR extracts in metabolic pathway-related conditions.
1. Introduction
Extracts of Cimicifuga racemosa L., NUTT. (also known as Actaea racemosa L. or black cohosh) are widely accepted [1,2,3,4] and have been granted “well-established use” status in the treatment of postmenopausal (i.e., climacteric) complaints by the European Medicines Agency [5]. This monograph predominantly includes vasomotor symptoms such as hot flushes and sweating, as well as nervousness, irritability, and metabolic changes. Although characteristic postmenopausal complaints have been known for a very long time and the beneficial effects of Cimicifuga extracts on climacteric symptoms are well accepted [3,4], the mechanism of actions has not yet been fully elucidated.
As well as clinical studies involving female patients, Seidlova-Wuttke et al. (2012) [6] undertook a comprehensive investigation aimed at delving into the beneficial impacts of a CR extract on postmenopausal symptoms in ovariectomized rats. In addition to the commonly reported climacteric effects, the authors were able to discern noteworthy reductions in fat accumulation and a decrease in the manifestations of metabolic syndrome in these animals. As AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) plays a pivotal role in regulating cellular metabolism [7], Moser et al. [8] investigated the effect of a CR extract Ze 450 and three of its isolated components (23-epi-26-deoxyactein, protopine, and Cimiracemoside C) on AMPK activity and carbohydrate metabolism in HepaRG cells and male ob/ob mice.
The extract and its components activated AMPK to the same extent as the AMPK activator metformin. The results also showed the extract led to significant reductions in body weight and plasma glucose levels, while improving glucose metabolism and insulin sensitivity in male diabetic ob/ob mice [8]. These findings broadened the mechanism of action of Cimicifuga in various domains to include the activation of AMPK and the subsequent effect on cellular metabolism, as indicated by a recent review discussion [9]. This new perspective brings new areas of application such as metabolic disorders, cardiovascular diseases, obesity, anti-aging, antioxidative, and supportive antiproliferative therapy into the focus of future clinical developments.
When examining the literature on published AMPK activators, the substantial chemical and pharmacological heterogeneity of the activators becomes evident. While only a handful of these (naturally occurring) activators directly target the enzyme itself, such as salicylate or AMP, the majority exert their effects indirectly. They achieve this by either influencing upstream kinases that subsequently phosphorylate AMPK or by reducing cellular ATP levels, leading to AMPK phosphorylation and subsequent activation. In particular, a variety of plant extracts or isolated plant constituents have been described in the literature to activate the enzyme [10,11,12].
The primary class of naturally occurring metabolites that may activate AMPK is the class of triterpene saponins and polyphenols such as flavonoids, courcumin, stilbenes, and others may also do so [13,14,15]. The class of triterpene saponins is widely distributed throughout the plant kingdom and constitutes a large and diverse group of secondary metabolites. They consist of a hydrophobic (water-repelling) aglycone, which can be steroidal or triterpenoid in nature, and one or more hydrophilic sugar moieties known as glycosides. These sugar moieties can be either monosaccharides or oligosaccharides and exhibit variations in their structure, size, and composition. The most common sugar moieties in steroidal saponins include glucose, galactose, rhamnose, xylose, and arabinose, which can undergo further metabolic processes. The type and number of sugar moieties attached to the steroid or triterpenoid aglycone affect the physicochemical properties and biological activities of the saponins, such as their solubility, stability, and bioavailability [16]. Saponins usually have unfavorable physiochemical properties for oral absorption due to their large molecular mass and hydrophilicity, which hinders enteral absorption and cellular uptake [17]. Hence, biotransformation to aglycones by cleavage of the glycosidic sugars may significantly alter cellular availability and consequently affect their pharmacological effects. Notably, certain saponins undergo deglycosidation by colonic microflora leading to enhanced intestinal absorption of the lipophilic aglycones. This is observed in the cases of certain ginsenosides and soybean saponins [18,19,20]. These compounds may also have a higher probability of entering their target cells.
When investigating herbal remedies, experiments can be challenging. The herbal extracts are complex and often contain multiple substances. Additionally, obtaining pure isolated compounds from these extracts can be difficult.
This presents an opportunity where machine learning models can significantly enhance the classification of activator constituents. Machine learning offers the possibility of thorough screening of these complex mixtures so that key compounds can be accurately identified, thereby streamlining subsequent detailed analysis and testing.
Recently, we have published research about sensitive and accurate machine learning models for the classification of AMPK activators [12]. In the present study, an extended and updated version of this applied database of known activators and controls has been used to classify all chemically characterized constituents of the Cimicifuga extract Ze 450 to estimate its ability to activate AMPK.
2. Materials and Methods
The flow and structure of experiments are illustrated in the following Figure 1:
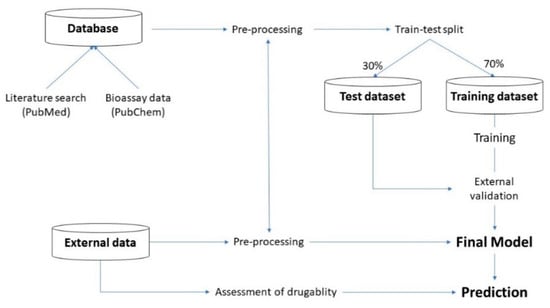
Figure 1.
Flow and structure of experiments.
2.1. Data
A highly detailed AMPK dataset was compiled in 2021 [13] and recently updated in August 2023. It was compiled by a thorough literature review of AMPK activators and inhibitors, conducted on PubMed (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/, accessed on 4 April 2024) using the search terms “AMPK AND activation” and “AMPK AND inhibition”. Compounds were included if they were confirmed activators or inhibitors by at least one publication listed on PubMed. Additionally, the Bioassay database of PubChem Substance and Compound databases (https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/, accessed on 4 April 2024) was consulted, particularly when compounds exhibited an EC50 of ≤0.1 µM, indicating activation. Conversely, compounds that were tested and found to be inactive for AMPK activation or exhibited inhibitory activity were used as the control group for this analysis. In total, the database comprised N = 1120 and N = 815 active compounds or controls, respectively.
To comprehensively characterize the power of Cimicifuga racemosa, 95 chemically defined compounds from the rhizome were included for analysis [21] (see Table A1, Appendix B).
2.2. Data Preprocessing
Chemical structures were coded using the simplified molecular-input line-entry system (isomeric SMILES taken from PubChem). Data were used to calculate MACCS fingerprint descriptors (Molecular ACCess System, [22]). MACCS fingerprint descriptors are binary representations encoding the presence or absence of specific structural features or substructures within a molecule. They are represented by a fixed-length vector of 166 bits with “0” values indicating absence and “1” values indicating presence. They do not encode information about bond order, stereochemistry, or spatial arrangement of atoms. Despite these limitations, fingerprint descriptors are commonly used in cheminformatics and computational chemistry. Since MACCS fingerprints focus on specific structural features, they are effective at capturing chemical diversity in a dataset [23].
Finally, data preprocessing (curation) entailed eliminating duplicate entries, salts, mixtures, smaller fragments, and proteins from SMILES structures, with a focus on low molecular weight drug-like compounds (molecular weight < 1000). Lastly, tautomers were not standardized during this process.
To reduce computational effort and noise, the VarianceThreshold feature selection method was used to remove features with low variance (<0.01%).
The unbalanced distribution of activators and controls was compensated for by the Synthetic Minority Oversampling Technique (SMOTE, [24]), which generates synthetic samples for the minority class by interpolating between existing samples. It creates new samples that are combinations of neighboring samples, resulting in an even class distribution (1122 members for each class). SMOTE was only applied in the training and not in the test phase.
2.3. Validation
Validation of models was based on OECD Principles for (Q)SAR Validation [25] using the 2:1 random split of the 2244 total data into 1570 training and 674 test data. These training data were further split (5:1 ratio) into a validation training dataset (N = 1258) and a validation test dataset (N = 314) to optimize model hyperparameters and train the models (using the sklearn train-test split method). After completion of training, the test data served as an external control using 5-fold cross-validation. Furthermore, the training was repeated after randomization of the response variable (Y-randomization [26]).
The high-dimensional data of activators and controls were transformed into a two-dimensional space using the t-distributed stochastic neighbor embedding technique (tSNE). This method offers a visual representation of the structural relationship between various compounds, aiding in the interpretation of the database’s applicability domain [27].
2.4. Machine Learning Models
The following three machine learning techniques were applied: Deep Neural Networks, Logistic Regression Classification, and Random Forest Classification.
All calculations were performed using Python 3.11.2 (https://www.python.org/, accessed on 4 April 2024). Graphical analysis was carried out using OriginPro, version 2023, OriginLab Corporation, Northampton, MA, USA, or Matplotlib, version 3.3.3 (https://matplotlib.org/#, accessed on 5 April 2024).
2.4.1. Deep Neural Network (DNN)
DNNs are sophisticated computational models with multiple interconnected layers, allowing them to automatically learn hierarchical representations of complex patterns from data [28]. Their depth enables effective feature extraction and is a key factor in their success across various machine learning tasks.
The data were assessed using a sequential DNN model, featuring a variable number of dense, hidden, and dropout layers, with HeNormal as the kernel initializer and Constant (value = 0) as the bias initializer. The activation functions employed were the exponential linear unit (ELU) for positive values and sigmoid for the output layers. Binary cross-entropy was utilized as the loss function. Details of the model are given in Appendix A.
2.4.2. Logistic Regression Classification (LRC)
LRC [29] is a powerful and widely used statistical method for modeling the probability of a binary outcome based on one or more independent variables.
LRC is used to estimate the probability that an instance belongs to a class:
using the logistic function:
Binary classification for two classes denoted with 0 and 1 was obtained by
The scikit-learn procedure was used (https://scikit-learn.org/stable/modules/generated/sklearn.linear_model.LogisticRegression.html, accessed on 4 April 2024).
2.4.3. Random Forest Classification (RFC)
RFC, an ensemble method (https://scikit-learn.org/stable/modules/generated/sklearn.ensemble.RandomForestClassifier.html, accessed on 4 April 2024), enhances generalizability and robustness by aggregating multiple base estimators, surpassing the performance of individual estimators such as decision trees. Each base estimator in the sequence aims to minimize the bias of the combined estimator. Renowned for classification tasks, RFCs are adept decision tree algorithms. Hyperparameters were optimized through grid search analysis, covering the number of estimators, maximum features utilized, maximum tree depth, minimum samples for split and leaf, and impurity criterion. Notably, no bootstrap sampling was employed in the process.
2.5. Hyperparameter Tuning
The hyperparameter tuning was performed on both the validation training dataset (N = 1258) and a validation test dataset (N = 314), which was derived with a 5:1 split using the train-test split method to optimize model hyperparameters and train the models.
Some of the adjustable hyperparameters of the investigated models were tuned by grid search, which was coupled with a 5-fold cross-validation (using sklearn GridSearchCV module), the others were kept in their default settings. Specifically for logistic regression, we focused on two key hyperparameters: the inverse of the regularization strength, denoted as “C”, and the penalty functions, which could be either “l1” (Lasso), “l2” (Ridge) regression, or “elasticnet” (a combination of “l1” (Lasso) and “l2” (Ridge)). These penalty functions help to control the impact of large coefficients in the model, thereby discouraging it from fitting noise into the data. Additionally, we determined the optimal solver among various options, which included the Newton-conjugate gradient optimization method (“Newton-cg”), the Limited-memory Broyden–Fletcher–Goldfarb–Shanno optimization method (“lbfgs”), a linear programming approach (“liblinear”).
For DNN, a grid search was performed on learning rate, batch size, number of hidden layers, and dropout layers.
2.6. Model Evaluation
The dataset underwent partitioning using the sklearn.model_selection preprocessing method train_test_split, allocating 30% for testing and 70% for training. Subsequently, a 5-fold cross-validation (CV) was performed.
To compare data distributions and assess the application domain, t-distributed stochastic neighbor embedding analysis was conducted via the sklearn.manifold.TSNE procedure. This technique transforms high-dimensional data into a 2-dimensional representation, facilitating graphical evaluation of applicability domains.
Machine learning model performance was evaluated using the following metrics:
- Accuracy: (TP + TN)/(TP + TN + FP + FN);
- Precision: TP/(TP + FP);
- Sensitivity: TP/(TP + FN);
- Specificity: TN/(TN + FP).
Here, TP represents true positives (correctly predicted activators), FP denotes false positives (incorrectly predicted activators), TN signifies true negatives (correctly predicted controls), and FN stands for false negatives (incorrectly predicted controls).
2.7. Prevention of Overfitting
Overfitting is a common problem in machine learning and statistical modeling, and it occurs when a model learns to perform very well on the training data but fails to generalize its predictions to new, unseen data.
One important risk factor is an unbalanced distribution of activators and controls in our database. This is an inherent problem in AMPK activation. Due to the importance of this activation, many potential activator compounds have been tested experimentally, whereas a much smaller number of negative controls (often inhibitors) have been investigated. This leads to a bias in the reported results within the literature. To significantly minimize the risk of overfitting, various methodical precautions were undertaken.
2.7.1. Feature Selection
Since more complex models have a greater risk of model noise and are prone to overfitting, we simplified our models by eliminating those features that contribute information only marginally (e.g., have a variance threshold below 0.01).
2.7.2. Cross-Validation
Cross-validation, especially the 5-fold variant during hyperparameter tuning followed by a 10-fold variant coupled to the ROC analysis (see below), is a machine learning technique that gauges predictive model performance and generalization. It does this by splitting the dataset into ten roughly equal parts or “folds”. The model is trained on nine of these parts and tested on the remaining one. This process is repeated ten times, with each fold serving as the test set once.
The performance metrics (in our case accuracy) from these ten rounds were then averaged to judge the model’s overall performance. It is a powerful method for comprehensively evaluating a model’s capabilities. It is more robust than a single train-test split because it examines how well the model generalizes different subsets of data.
2.7.3. Regularization
For logistic regression: an application of regularization techniques like L1 (Lasso) or L2 (Ridge) regression or elastic net option was used to penalize large coefficients in the model. This discourages the model from fitting noise into the data. The parameter C denotes the inverse of the regularization strength. The choice between these techniques was made in the tuning of hyperparameters by the grid search procedure. For DNN, dropout layers were evaluated.
2.7.4. Early Stopping
For DNN training, an early stopping procedure (keras.callbacks module EarlyStopping, https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/keras/callbacks/EarlyStopping, accessed on 4 April 2024) was applied to monitor the training loss and halt training if there was no improvement for five consecutive epochs.
2.8. Receiver Operating Characteristic (ROC)
To assess the performance of a binary classifier regardless of thresholds, the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve and its corresponding area under the curve (AUC) scores were computed [30]. This evaluation was complemented with a 10-fold cross-validation to ensure the robustness and generalizability of the results.
2.9. y-Randomization
A final aspect of method validation is y-randomization. In this step, the DNN was applied to the molecular descriptors (denoted by X) unchanged, while the target y was randomized (null model). The performance was then measured. If the original model significantly outperformed the null model, it suggested a meaningful relationship between the molecular descriptors (X) and biological activity (denoted by y) in our dataset. In such a scenario, it provided confidence in the predictive power of our model. To enhance confidence further, this process was repeated 50 times.
2.10. Classification of Cimicifuga racemosa (CR) Constituents
Using the SMILES of the CR constituents, the same molecular descriptors were calculated for the database. While the database was fitted to a standardizer and transformed, the CR descriptors were only transformed using the same standardizer. Using the best-performing model of the training, the CR constituents were predicted as either AMPK activators or controls.
To calibrate these classifications, 50 randomly chosen samples of the positive and negative controls of the database were each also classified in the same run. The models were ranked by the number of misclassifications.
2.10.1. Comparison of Cimicifuga racemosa (CR) Metabolites with Database
The best-performing model from the analysis was then employed to classify the transformed CR constituent descriptors. For each CR constituent, the five most similar members of the database were determined through pairwise calculation of cosine similarity scores (k) using scikit-learn (https://scikit-learn.org/stable/modules/generated/sklearn.metrics.pairwise.cosine_similarity.html, accessed on 4 April 2024):
where denotes the Euclidian norm and <x,y> denotes the dot product of vectors x and y. It ranges from −1 to 1. Values of k > 0.8 were regarded as similar.
2.10.2. Comparison of Cimicifuga racemosa (CR) Saponins with Their Estimated Aglycones
In total, 46 of the CR constituents were identified as saponins. Their original SMILES codes were theoretically deglycosylated, following the approach suggested by SwissADME [31], to generate new SMILES codes for their corresponding aglycones. These new SMILES codes were then used to generate descriptors from the estimated aglycones for classification.
2.10.3. Assessment of Markers for Oral Absorption
A comparison between triterpene saponin constituents and their aglycones was conducted using the web tool SwissADME [31] available at http://www.swissadme.ch, accessed on 4 April 2024. This tool utilizes robust and predictive models for physicochemical properties, pharmacokinetics, and drug-likeness. It allowed us to estimate several parameters considered as indicators for the oral bioavailability of drugs, including molecular weight (MW), water solubility [32], topological polar surface area (TPSA; [33]), distribution coefficient XlogP [34], the number of violations of Lipinski’s rule of five [35], and the estimated lead-likeness [31].
3. Results
3.1. t-SNE Analysis
The t-SNE graphical analysis indicates a clear separation between the two classes, namely activators and controls, across the MACCS fingerprint descriptors (Figure 2):
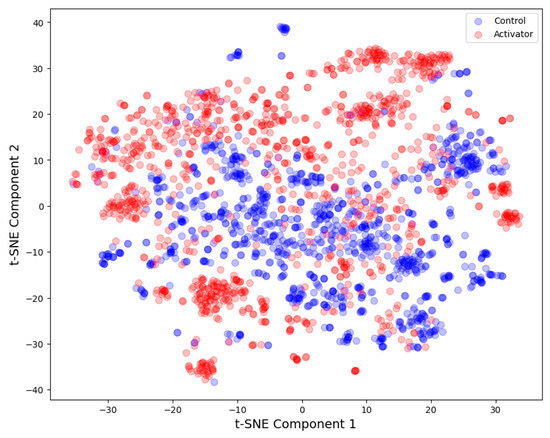
Figure 2.
tSNE analysis: AMPK activators and controls. MACCS fingerprint descriptors (N = 2242, perplexity = 100, number of iterations = 5000).
For illustration, the distribution of four important parameters between activators and controls is displayed in Figure 3:
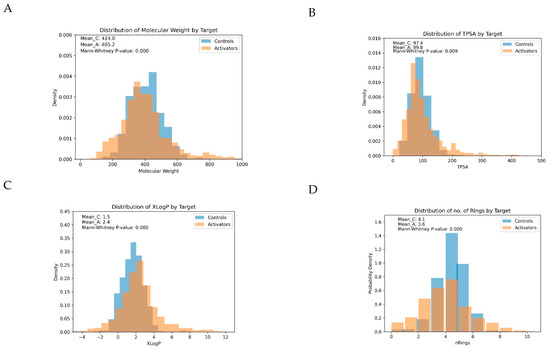
Figure 3.
Distribution of four important physicochemical parameters between activators and controls: (A) Molecular Weight, (B) Total Polar Surface Area (TPSA), (C) Number of Rings in the Molecules, and (D) Predicted Octanol/Water Partition Coefficients (XLogP). Significant differences in the distributions of these parameters were observed (Mann–Whitney test): Activators had lower molecular weights (p < 0.0001), higher lipophilicity (median XLogP 2.4 for activators vs. 1.5 for controls; p < 0.0001), lower Total Polar Surface Area (TPSA) (p < 0.009), and fewer rings in the molecules, on average (3.6 for activators vs. 4.1 for controls; p < 0.0001), than controls.
3.2. Feature Reduction
Variance threshold reduction simplified the models by reducing the number of features to 139 for the MACCS fingerprint descriptors from their initial counts of 166.
3.3. Hyperparameter Tuning
For the MACCS fingerprint descriptors a batch size of 16, no dropout layers, a learning rate of 0.001, and three hidden layers were found to be optimal for the DNN model. As a solver, the Adam optimizer and the binary cross-entropy as loss functions were used.
For the LRC model, a regularization strength C of 0.5, a L2 penalty, and the liblinear solver were selected, and “newton-cg” for the solver was estimated to be optimal parameters. For RFC, the gini criterion was chosen, the maximum features were set to log2 (number of features), the min_samples_leaf and min_samples_split were set to 1 and 4, respectively, and the number of estimators was set to 110.
All other parameters were left at their default settings.
3.4. Test Performances
In evaluating the performance of various machine learning techniques, all models demonstrated a commendable accuracy level of approximately 90%. Notably, the DNN model exhibited superior performance compared with other models by minimizing the number of misclassifications on the calibration data. With DNN, there were only three misclassifications, in contrast to 17 for LRC and 9 for the RFC model.
While the LRC model achieved the highest overall test accuracy at 90.2%, both the DNN and RFC models surpassed it in terms of precision, sensitivity, specificity, and ROC AUC, as summarized in Table 1.

Table 1.
Summary of results of classification of different machine learning methods.
All models utilized the MinMax Scaler for data scaling prior to modeling. As a side note, the RFC model was also evaluated without prior scaling, producing identical results to those obtained with scaled data.
The area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (ROC AUC) assesses a model’s capacity to differentiate between activator and control classes across various thresholds. These curves (Figure 4) were combined using a 10-fold cross-validation. A higher ROC AUC value indicates better class discrimination, with the optimal value being 1.0 or −1.0.
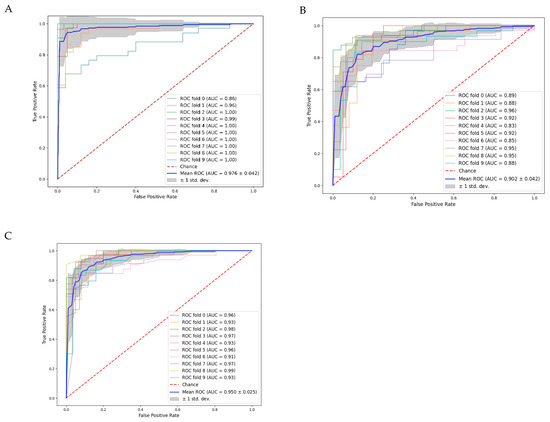
Figure 4.
(ROC) analysis coupled with 10-fold cross-validation: (A) Deep Neural Network (DNN); (B) Logistic Regression Classification (LRC); and (C) Random Forest Classification (RFC).
3.5. y-Randomization
Notably, in none of the 50 shuffled models could a distinction be made between activators and controls (see Table 1). The mean accuracy ranged from 57.6% ± 1.8% to 57.8% ± 1.8%. These results suggest that the unchanged models are statistically significant and are unlikely to have arisen by chance. This provides confidence in the predictive power of our models.
3.6. Classification of Cimicifuga racemosa (CR) Constituents
For classification, 103 chemically defined CR root compounds were identified [21] and checked for isomeric SMILES codes by using the PubChem database (https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/, accessed on 4 April 2024). In total, 95 distinct compounds with all information available were used for analysis (see Table A1, Appendix B).
All compounds with triterpene and triterpenoid structures were classified as active. This classification is supported by the literature for 23-Epi-26-deoxyactein and cimiracemoside C [8]. From the non-triterpene compounds, the cinnamic, benzoic, or fukiic acid derivatives were clearly classified as active. A literature search supported this classification for synaptic acid [36], P-coumaric acid [11], isoferulic acid [37], protocatechuic acid [37], and protocatechuic aldehyde [38]. Compounds such as cimiracemates, cimiphenones, cimifugic acid derivatives, and actealactone were likewise classified as active. Among the chromones—angelicain, cimifugin, and visnagin—only angelicain and cimifugin were classified as active, whereas visnagin was classified as inactive, possibly due to the absence of a propan-2-ol group. Interestingly, the glycoside cimidahurin was classified as active. However, its aglycone hydroxytyrosol, and not the compound itself, was identified in the literature as an activator of AMPK [39]. For the chemical structures, see Appendix B: Table A1.
Further support for these classifications came from a similarity comparison of the CR constituents against our database. The constituents demonstrated high similarity to database compounds, with median similarity scores descending from 0.94 to 0.91. However, five compounds—cimipromidine (0.78), cimipromidine methyl ester (0.74), dopargine (0.77), and N-methylcytisine (0.797)—recorded the lowest similarity scores, aligning with their lower probability estimates of AMPK activation, as indicated in Figure 5. These findings, including individual similarity scores, are detailed in Table A2 in Appendix B, underscoring the data supporting the classification outcomes.
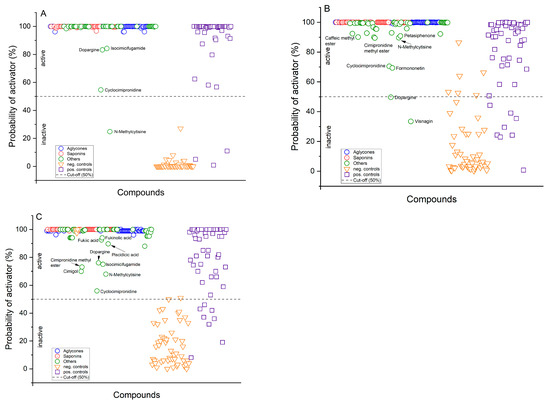
Figure 5.
Classification of Cimicifuga racemosa root constituents was performed using three different methods: (A) Deep Neural Network (DNN); (B) Logistic Regression Classification (LRC); and (C) Random Forest Classification (RFC). Saponins and their aglycones are clearly classified as activators of AMPK. Saponins and their aglycones were unequivocally identified as activators of AMPK. While other constituents were also categorized similarly, albeit with lower probabilities. Among these constituents, cyclocimipronidine and dopargine were classified with uncertainty, along with N-methylcytisine, which the DNN model classified as inactive.
3.7. Comparison of Saponins with Their Aglycones
The 46 theoretical aglycones showed no systematic and significant differences in their probability compared with the saponins from which they were derived [31].
Saponins and their corresponding aglycones were analyzed for several markers indicative of oral bioavailabilities and drug-likeness (Figure 6). Data were applied to open source Webtool SwissADME [31], available at http://www.swissadme.ch, accessed on 4 April 2014.
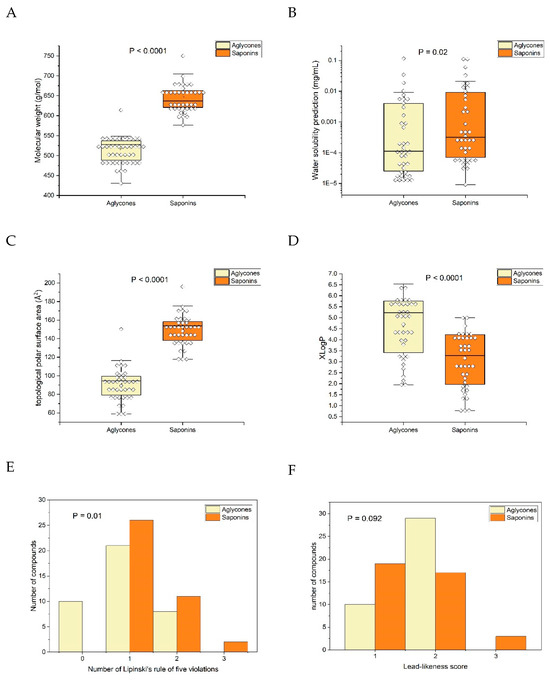
Figure 6.
Comparison of triterpene saponin constituents with their theoretically derived aglycones (applied from open source SwissAMDE Webtool, [31]): (A) molecular weight of aglycones was significantly smaller than that of saponins (p < 0.0001, paired two-sided t-test); (B) water solubility surprisingly showed high overlap but was significantly smaller (p = 0.02); (C) topological polar surface area (TPSA) was clearly significantly smaller in the aglycones (p < 0.0001; paired two-sided t-test); (D) lipophilicity, as expressed by XLogP, increased significantly (p < 0.0001; paired two-sided t-test); (E) Lipinski’s rule of five violations was significantly differently distributed (p = 0.01; Wilcoxon signed-rank test), with aglycones having a smaller number of violations; and (F) estimation of the lead-likeness score was not significantly different.
As constructed, the molecular weight of aglycones was consistently lower than their corresponding saponins. While water solubility exhibited a significant decrease, on average (p = 0.02, paired two-sided t-test), compared with the solubility of saponins, there was a notable overlap between the two groups. In contrast, the topological polar surface area showed minimal overlap and a highly significant difference (p < 0.0001, paired two-sided t-test) between aglycones and saponins. An increase in lipophilicity, as indicated by the significant elevation of XLogP (p < 0.0001, paired two-sided t-test), was evident.
Assessing oral bioavailability using Lipinski’s rule of five [35], which indicates improved bioavailability if all five conditions are met, revealed significantly fewer violations for the aglycones (p = 0.01, Wilcoxon signed-rank test). Despite expectations that the observed effects on topological polar surface area (TPSA) and XLogP would manifest as clear differences in water solubility, the substantial overlap in solubility suggests that various physicochemical parameters exert opposing effects. This phenomenon cannot be solely explained by lipophilicity in a monocausal manner. Concerning drugability (lead-likeness), no clear advantage of the aglycones over the saponins could be demonstrated (p = 0.09, Wilcoxon signed-rank test).
4. Discussion
Herbal preparations encompass complex mixtures of potentially active chemical compounds. Nevertheless, comprehensive in vitro experiments often necessitate pure, isolated substances for each identified constituent. Regrettably, such isolated constituents are frequently insufficiently available. Hence, our extended approach uses machine learning tools, offering novel opportunities to screen these multi-substance preparations and identify promising lead compounds. These can then undergo rigorous subsequent testing.
Even when availability problems are set to one side, directly assessing each ingredient in vitro is a resource-intensive and time-consuming endeavor. A swifter, more cost-effective solution could be employing diverse machine learning models. These models, based on an established structure–activity database, can predict the AMPK activation potential of numerous so far uncharacterized substances “in a single run”.
All models investigated showed very good performance in discriminating AMPK activators from controls. Surprisingly, with the exception of three compounds (cyclocimipronidine, dopargine, and N-methylcytisine), all of the 95 investigated CR constituents were clearly predicted activators. It was therefore necessary to rule out a technical artifact caused by the overfitting of the model. Overfitting is a common problem in machine learning and statistical modeling, and it occurs when a model learns to perform very well on the training data but fails to generalize its predictions to new, yet unseen data. In other words, an overfitted model has focused on capturing the noise or random fluctuations in the training data instead of accurately capturing the underlying patterns or relationships.
A risk factor for overfitting is an unbalanced distribution of activators and controls in our database. This is an inherent problem in pharmacology. Due to the importance of AMPK activation, many potential activator compounds have been experimentally tested, whereas a much smaller number of negative controls (often inhibitors) have been investigated. This leads to a bias in the reported results within the literature.
In mitigating the challenge of overfitting, various methodological measures have been implemented to minimize this risk:
- Balancing unevenly distributed dataset classes;
- Employing simpler models;
- Implementing cross-validation;
- Utilizing regularization techniques;
- Employing early stopping techniques.
All of these precautions were rigorously applied to ensure that technical and methodological safeguards had been implemented.
As we have previously demonstrated [12], the positive controls within our dataset, which serve as activators, exhibit a notable structural diversity. This diversity arises from the fact that a significant proportion of activators exert their effects indirectly. They interact with regulatory sites upstream in the biological pathways. When these sites are activated, they, in turn, trigger the phosphorylation and activation of AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK). AMPK is a critical enzyme responsible for sensing and regulating energy supply, as well as various cellular functions. These functions include controlling carbohydrate entry and metabolism, generating reactive oxygen species (ROS), regulating apoptosis, modulating cellular growth, and influencing processes like mitochondrial biogenesis and autophagy.
While we achieved an excellent predictive performance on our unseen test dataset, it is important to acknowledge that the presence of unaccounted-for mechanisms cannot be ruled out. It is also worth noting that machine learning models have inherent limitations. They provide classification probabilities that ideally should be validated through direct in vitro or in vivo experiments or by other evidence. Another limitation is the research process itself. It focuses on AMPK activators rather than inhibitors or inactive substances. As a result, significantly fewer substances have been identified that inhibit AMPK, or, perhaps even more importantly, are confirmed not to interact with it. This leads to a selection bias in our database and unbalanced distribution and thus poses a theoretical risk of over-identifying active substances. This suggests that external evidence should also be sought.
A point that clearly supports the validity of the classifications is the calibration of the data, each consisting of 50 randomly selected positive and negative controls. Their classifications were clearly separated, with only 3% to 17% misclassifications across the three models under investigation. Another point to consider is the high sensitivity (84.5–87.2%) and specificity (84.1–91.4%), which provide strong indications for suitability as a screening tool.
To further substantiate our model’s predictive accuracy regarding the classification of the 95 CR constituents as either activators or controls, a comprehensive similarity analysis against all compounds in our database was performed. This involved computing the structural similarities of the CR constituents to every database entry and identifying the five most closely matching compounds for each metabolite (details provided in Table A2 in Appendix B). Notably, each of the CR constituents displayed considerable structural similarity to the positive control compounds within our database. The constituents showed high similarity to compounds in the database, with median similarity scores ranging from 0.94 down to 0.91. Nonetheless, a subset of compounds—specifically, cimipromidine (0.78), cimipromidine methyl ester (0.74), dopargine (0.77), and N-methylcytisine (0.797)—registered the lowest similarity scores. This correlates with their diminished likelihood of activating AMPK, as reflected in the probability estimates presented in Figure 4. These observations, including individual similarity scores, are thoroughly documented in Table A2 in Appendix B, providing a robust data foundation supporting our classification results.
Studying herbal drugs presents a unique set of challenges due to the complexity of herbal extracts, which consist of multiple substances. Additionally, obtaining pure substances from these extracts is often a challenging task, resulting in limited availability. Consequently, our improved method offers exciting new prospects for conducting thorough analyses of these complex mixtures. It enables the examination of multi-component herbal extracts to identify particular compounds of interest. Subsequently, these compounds can undergo more extensive assessments and evaluations, followed by further refinement of the extracts to enhance the concentration of the desired components.
Our results indicate that the models clearly classified all constituents of Cimicifuga racemosa as activators apart from three non-triterpenes. This suggests a high probability of their ability to activate AMPK. However, we cannot determine the strength of this activation from our findings. Moreover, it is plausible that this activation is a collaborative or even synergistic effect, considering that many constituents were classified as active. The overall effect is certainly influenced by the concentrations of these active compounds at the site of action, which is hard to predict.
It is perplexing that the models made no distinction between triterpene saponins and their aglycones in terms of the probability of classifying the compounds as activators. Although it is conceivable that aglycones, due to their higher lipophilicity, have a greater likelihood of being absorbed into tissues and reaching the site of action [40], our model merely predicts whether the compounds are capable of activating AMPK at all. It does not take into account the dose–response relationship and kinetics.
Triterpene saponins, known for their high hydrophilicity, exhibit limited oral absorption from the gastrointestinal tract, especially when compared to their respective lipophilic aglycones (for a review, see [40]). In our experiments, the range of water solubility values of CR triterpene saponins significantly overlapped the range of the values of their corresponding aglycones, suggesting that this statement likely needs to be assessed individually for each saponin and aglycone. Consequently, it is difficult to predict the overall oral absorption of a multicomponent mixture as an herbal extract.
In current Cimicifuga racemosa extracts, the aglycone content is relatively low. Nevertheless, research has demonstrated that a significant portion of the dose of triterpene saponin, as observed with 23-epi-26 dihydroxyactein, is orally absorbed in both rats [41] and humans [42]. Nonetheless, following oral administration, certain triterpene saponins have the potential to reach the large intestine, where they might undergo degradation by the colonic microbiome. This process, similar to what has been observed for other triterpene saponins [40]), could also contribute to the overall effect.
This study has some limitations: While MACCS (Molecular Access System) descriptors are widely utilized in cheminformatics and machine learning for representing chemical compounds [23], it is essential to acknowledge their inherent limitations and potential biases. Being rooted in predefined substructures, there is a possibility of bias towards specific compound types or functional groups, potentially overlooking less common or innovative structural motifs. The reliance on a fixed set of molecular features may impede the generalizability of machine learning models across diverse chemical datasets. Furthermore, some MACCS descriptors may exhibit high correlation or redundancy, leading to multicollinearity in the feature space. Addressing such issues is crucial as it can impact the stability and interpretability of machine learning models, often necessitating feature selection or dimensionality reduction techniques, as we applied in our study.
Moreover, MACCS descriptors are primarily tailored for small organic molecules and may not adequately represent complex biomolecules or materials. Hence, to ensure compatibility with the descriptor’s scope, we constrained our dataset to small compounds (molecular weight ≤ 1000).
A PubMed search using the terms “AMPK” and “QSAR” reveals that various QSAR models for predicting AMPK activation have been documented [43,44]. These models predominantly rely on pharmacophore docking, homology modeling, and structure-, ligand-, or fragment-based design strategies, focusing solely on compounds that activate AMPK directly. Diverging from these methodologies, our research appears to be the first to comprehensively incorporate compounds that activate AMPK, regardless of whether the activation is direct or indirect. This inclusive approach enables a broader understanding and captures the diverse mechanisms of AMPK activation more effectively, addressing the enzyme’s activation heterogeneity.
5. Conclusions
The results of this study confirm that all triterpene saponins, as well as their aglycones, tested may contribute to activating the AMP-dependent protein kinase (AMPK). With regard to the mechanism, this may suggest a collaborative or even synergistic action on the enzyme. Since AMPK plays a pivotal role in various interconnected metabolic pathways, our results further underscore the rationale for clinically investigating the therapeutic benefits of Cimicifuga racemosa extracts in conditions associated with disturbances in these metabolic pathways.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/pharmaceutics16040511/s1; Table S1: DB_descript_MACCS; Table S2: Cimi_descript_MACCS; Table S3. Experiments.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.D., V.S. and G.B.; methodology, V.S.; software and validation, J.D., V.S. and O.D.; formal analysis, J.D.; data curation, J.D.; writing—original draft preparation, J.D.; writing—review and editing, V.S., G.B., O.D. and A.S.; supervision, J.D. and G.B.; funding acquisition, G.B. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable, since the studies did not involve humans or animals.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable, since the studies did not involve humans or animals.
Data Availability Statement
A complete list of used activators and controls is given in Supplementary Materials as Tables S1–S3, and source codes of all models are given in Table A1 and Table A2.
Conflicts of Interest
J.D., O.D., A.S. and G.B. work at Max Zeller Söhne AG, a phytopharmaceutical company. V.S. declares no conflicts of interest. The design of this study was the sole responsibility of the authors. The funders/company had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analysis, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Appendix A. Details of the Deep Neural Networks Model
- Details of the Deep Neural Networks model;
- Python code: Model.ipynb;
- Database: database.csv.
| from sklearn.model_selection import KFold |
| from sklearn.metrics import make_scorer, accuracy_score |
| from keras.models import Sequential |
| from keras.callbacks import ModelCheckpoint |
| from keras.models import load_model |
| from sklearn.model_selection import GridSearchCV |
| from sklearn.model_selection import cross_val_score |
| n_features = X_train.shape [1] |
| n_targets = 1 |
| learning_rate = 0.01 |
| n_hidden = 4 |
| batch_size = 32 |
| epochs = 10 |
| def create_model (n_features: int, learning_rate: float, n_hidden: int, batch_size: int, |
| dropout: float) -> Sequential:inputs = Input (shape = (number of features)) |
| x = Dense (1_500, kernel_initializer = init_w, bias_initializer = init_b) (inputs) |
| x = Activation (“elu”)(x) |
| x = Dropout (dropout)(x) |
| for i in range (0,n_hidden): |
| (x) = Dense (1_500-i*300, kernel_initializer = init_w, bias_initializer = init_b) (x) |
| (x) = Activation (“elu”) (x) |
| (x) = Dropout (dropout) (x) |
| outputs = Dense (n_targets, activation = “sigmoid”) (x) |
| model = Model (inputs = inputs, outputs = outputs) |
| model.compile (loss = ‘binary_crossentropy’, optimizer = Adam(learning_rate = learning_rate), metrics = [‘accuracy’]) |
| return model |
Appendix B

Table A1.
Major constituents of Cimicifuga racemosa extracts.
Table A1.
Major constituents of Cimicifuga racemosa extracts.
Shengmanol type (16-ketone type)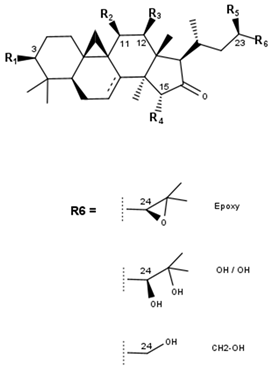 | ||||||||
| Compounds | R1 | R2 | R3 | R4 | R5 | R6 | Δ7,8 | CID |
| 23-O-Acetylshengmanol | OH | H | H | OH | O-Ac | Epoxy | - | 91827092 |
| 23-O-Acetylshengmanol-3- O-β-D-xylopyranoside | O-Xyl | H | H | OH | O-Ac | Epoxy | - | 56962372 |
| 23-O-Acetylshengmanol-3-O-α-L- arabinopyranoside | O-Ara | H | H | OH | O-Ac | Epoxy | - | 10865257 |
| Bugbanoside C | O-Ara | H | O-Ac | OH | =O | OH/OH | + | 15894670 |
| Bugbanoside D | O-Ara | H | O-Ac | OH | =O | Epoxy | + | 15894671 |
| Bugbanoside E | O-Ara | H | O-Ac | H | =O | Epoxy | + | 15894672 |
| Cimicifugoside H-1 | O-Xyl | OH | H | H | =O | Epoxy | + | 15241163 |
| Cimicifugoside H-3 | O-Xyl | OH | H | H | =O | CH2OH | + | 15241164 |
| Cimiracemoside L | 4′-O-Ac-Xyl | H | H | OH | O-Ac | Epoxy | - | 10952624 |
| Cimicidanol | OH | OH | H | H | =O | Epoxy | + | 10413064 |
Hydroxyshengmanol type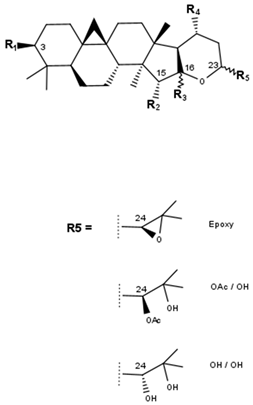 | |||||||||
| Compounds | R1 | R2 | R3 | R4 | R5 | 16 | 23 | 24 | CID |
| 24-Acetylhydroshengmanol-3-O-β-D- xylopyranoside | O-Xyl | OH | OH | CH3 | O-Ac/OH | S | S | S | 157168 |
| Cimiracemoside E | O-Xyl | =O | H | CH2OH | O-Ac/OH | R | R | S | 91827210 |
| Shengmanol | OH | OH | OH | CH3 | Epoxy | S | R | S | 101133349 |
| Shengmanol-3-O-β-D-xylopyranoside | O-Xyl | OH | OH | CH3 | Epoxy | S | R | S | 158275 |
Cimigenol type (A)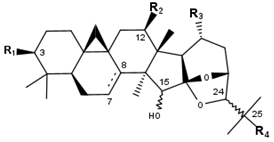 | ||||||||
| Compounds | R1 | R2 | R3 | R4 | Δ7,8 | 15 | 24 | CID |
| Cimigenol | OH | H | CH3 | OH | - | R | S | 16020000 |
| Cimigol | OH | H | CH3 | OH | - | S | R | 101596828 |
| 25-O-Acetylcimigenol | OH | H | CH3 | O-Ac | - | R | S | 46881255 |
| 25-O-Acetylcimigenol 3-O-α-L- arabinopyranoside | O-Xyl | H | CH3 | O-Ac | - | R | S | 24721386 |
| 25-O-Methylcimigenol | OH | H | CH3 | O-CH3 | - | R | S | 146027510 |
| 25-O-Methylcimigenol-3-O-β-D- xylopyranoside | O-Xyl | H | CH3 | O-CH3 | - | R | S | 146027510 |
| 25-O-Ethylcimigenol-3-O-β-D- xylopyranoside | O-Xyl | H | CH3 | O-CH2CH3 | - | R | S | 16091662 |
| 12-β-Acetoxycimigenol | OH | O-Ac | CH3 | OH | - | R | S | 16104912 |
| 12-β-Acetylcimigenol-3-O-β-D- xylopyranoside | O-Xyl | O-Ac | CH3 | OH | - | R | S | 44418831 |
| 12-β-Hydroxycimigenol | OH | OH | CH3 | OH | - | R | S | 10006332 |
| Bugbanoside F | O-Ara | OH | CH3 | OH | + | R | S | 101096469 |
| Cimiracemoside B | O-Xyl | H | CH2OH | OH | - | R | S | 91826883 |
| Cimiracemoside C (=Cimifugoside M) | O-Ara | H | CH3 | OH | - | R | S | 15541911 |
| Cimiracemoside D | O-Ara | O-Ac | CH3 | OH | - | R | S | 70698290 |
| Cimiside A | O-Xyl | OH | CH3 | OH | - | R | S | 91827183 |
| Cimiside B | 3′-O-Xyl-3-O-Xyl | H | CH3 | OH | - | R | S | 10054869 |
Cimigenol type (B)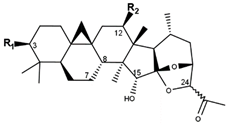 | ||||
| Compounds | R1 | R2 | 24 | CID |
| 25-AnhydroCimigenol-3-O-α-L- arabinopyranoside | O-Ara | H | R | 70698285 |
| Cimiracemoside J | O-Ara | O-Ac | S | 10952455 |
| Cimiracemoside K | O-Xyl | O-Ac | S | 10930352 |
| Cimiside E | O-Xyl | H | S | 102147078 |
Acteol type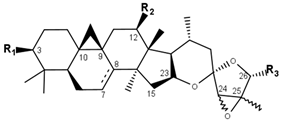 | |||||||
| Compounds | R1 | R2 | R3 | Δ7,8 | 24 | 25 | CID |
| Acteol | OH | OH | OH | - | S | R | 59595161 |
| Actein | O-Xyl | O-Ac | OH | - | R | S | 10032468 |
| 23-Epi-26-deoxyactein | O-Xyl | O-Ac | H | - | R | R | 10974362 |
| Cimiracemoside N | O-Ara | O-Ac | H | - | S | S | 21591918 |
| Cimiracemoside P | O-Xyl | O-Ac | =O | - | S | R | 91827183 |
| 12-O-Acetylacteol | OH | O-Ac | OH | - | S | S | 23640137 |
Cimiracemoside type | |||
| Compounds | R1 | Δ7,8 | CID |
| Cimiracemoside A (=F) | O-Xyl | + | 21606551 |
| Cimiracemoside H | O-Xyl | - | 21606553 |
Neocimigenoside type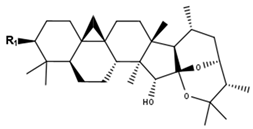 | ||
| Compounds | R1 | CID |
| Neocimicigenoside A | O-Ara | 44583839 |
| Neocimicigenoside B | O-Xyl | 44583840 |
Cimilactone type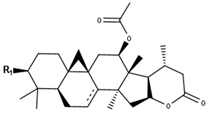 | |||
| Compounds | R1 | Δ7,8 | CID |
| Cimilactone A | O-Xyl | - | 10908062 |
Podocarpaside type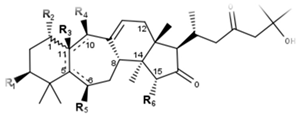 | ||||||||||||
| Compounds | R1 | R2 | R3 | R4 | R5 | R6 | Δ5,6 | Δ5,11 | Δ10,11 | 5 | 11 | CID |
| Podocarpaside A | O-Ara | OH | - | H | H | H | - | + | - | - | - | 16110015 |
| Podocarpaside B | O-Ara | H | H | OH | H | H | - | - | - | R | S | 16110011 |
| Podocarpaside C | O-Ara | H | H | OH | H | OH | - | - | - | R | S | 16110016 |
| Podocarpaside D | O-Ara | H | OH | H | H | H | - | - | - | S | S | 16110012 |
| Podocarpaside E | O-Ara | H | - | OH | OH | OH | - | + | - | - | - | 139071967 |
| Podocarpaside F | O-Ara | H | - | - | H | OH | - | - | + | R | - | 16110017 |
| Podocarpaside G | O-Ara | H | - | - | - | OH | + | - | + | - | - | 16110014 |
Podocarpaside type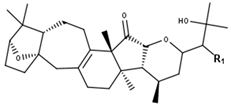 | ||||||||||||
| Compounds | R1 | R2 | R3 | R4 | R5 | R6 | Δ5,6 | Δ5,11 | Δ10,11 | 5 | 11 | CID |
| Podocarpaside A | O-Ara | OH | - | H | H | H | - | + | - | - | - | 16110015 |
| Podocarpaside B | O-Ara | H | H | OH | H | H | - | - | - | R | S | 16110011 |
| Podocarpaside C | O-Ara | H | H | OH | H | OH | - | - | - | R | S | 16110016 |
| Podocarpaside D | O-Ara | H | OH | H | H | H | - | - | - | S | S | 16110012 |
| Podocarpaside E | O-Ara | H | - | OH | OH | OH | - | + | - | - | - | 139071967 |
| Podocarpaside F | O-Ara | H | - | - | H | OH | - | - | + | R | - | 16110017 |
| Podocarpaside G | O-Ara | H | - | - | - | OH | + | - | + | - | - | 16110014 |
Acerinol type | ||
| Compounds | R1 | CID |
| 24-O-Acetylacerionol | O-Ac | 101596791 |
| Acerinol | OH | 73347277 |
Cimicinol | |
| Compound | CID |
| Cimicinol | 102146755 |
Actaeaepoxide-3-O-beta-D-xylopyranoside | |
| Compound | CID |
| Actaeaepoxide-3-O--D-xylopyranoside | 15515494 |
Friedelin | |
| Compound | CID |
| Friedelin | 91472 |
Cinnamic acid derivatives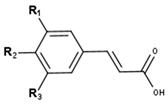 | ||||
| Compounds | R1 | R2 | R3 | CID |
| Sinapic acid | O-Me | OH | O-Me | 637775 |
| p-Coumaric acid | H | OH | H | 637542 |
| Isoferulic acid | OH | O-Me | H | 736186 |
| 3,4-Dimethoxycinnamic acid | O-Me | O-Me | H | 717531 |
Cimiracemate type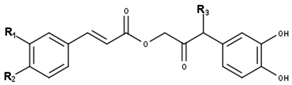 | ||||
| Compounds | R1 | R2 | R3 | CID |
| Cimiracemate A | OH | O-Me | H | 5315874 |
| Cimiracemate B | O-Me | OH | H | 5315876 |
| Cimiracemate C | OH | O-Me | O-Me * | 5315877 |
| Cimiracemate D | O-Me | OH | O-Me * | 5315878 |
| * Stereochemistry not known. | ||||
Cimiciphenone type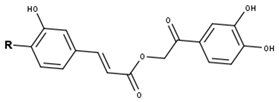 | ||
| Compounds | R | CID |
| Cimiciphenone | O-Me | 71487912 |
| Petasiphenone | OH | 16066851 |
Protocatechuic acid type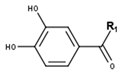 | ||
| Compounds | R1 | CID |
| Protocatechuic acid | OH | 72 |
| Protocatechuic aldehyde | H | 637542 |
Fukiic acid derivatives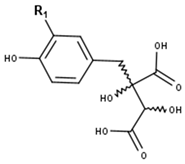 | ||
| Compounds | R1 | CID |
| Fukiic acid | OH | 161871 |
| Piscidic acid | H | 120693 |
Cimicifugic acid derivatives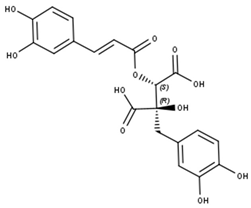 | |||||
| Compounds | R1 | R2 | R3 | R4 | CID |
| Cimicifugic acid A (2-Feruloyl fukinolic acid) | OH | OH | O-Me | OH | 6449879 |
| Cimicifugic acid B (2-Isoferuloyl piscidic acid) | OH | OH | OH | O-Me | 6449880 |
| Cimicifugic acid C (2-p Coumaric fukinolic acid) | OH | OH | H | OH | 6401178 |
| Cimicifugic acid D (2-Caffeoyl piscidic acid) | OH | H | OH | OH | 11742743 |
| Cimicifugic acid E (2-Feruloyl piscidic acid) | OH | H | O-Me | OH | 10002902 |
| Cimicifugic acid F (2-Isoferuloyl piscidic acid) | OH | H | OH | O-Me | 6450179 |
| Cimicifugic acid G (2-Feruloyl piscidic acid) | OH | OH | O-Me | O-Me | 11655574 |
| Fukinolic acid | OH | OH | OH | OH | 6441059 |
Actealactone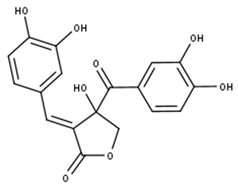 | |
| Compound | CID |
| Actealactone | 11537736 |
Astilbin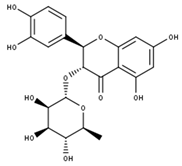 | |
| Compound | CID |
| Astilbin | 119258 |
Chromones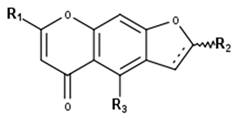 | ||||||
| Compound | R1 | R2 | R3 | Δ7a−7b | 7b | CID |
| Angelicain | CH2-OH | propan-2-ol | OH | - | S | 46240156 |
| Cimifugin | O-Me | propan-2-ol | O-Me | - | S | 4411960 |
| Visnagin | Me | H | O-Me | + | - | 6716 |
Cimidahurine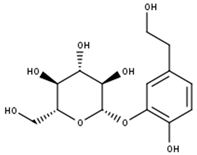 | |
| Compound | CID |
| Cimidahurine | 5315870 |
Cimipronidine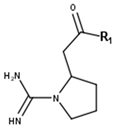 | ||
| Compounds | R1 | CID |
| Cimipronidine | OH | 21594000 |
| Cimipronidine methylester | O-Me | 101467166 |
Dopargine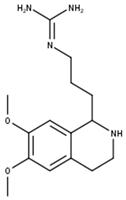 | |
| Compound | CID |
| Dopargine | 10357001 |
Cyclocimipronidine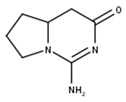 | |
| Compound | CID |
| Cyclocimipronidine | 101467165 |
N-Methycytisine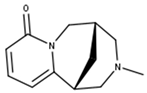 | |
| Compound | CID |
| N-Methycytisine | 670971 |

Table A2.
Support of classification: similarity of Cimicifuga constituents to database elements.
Table A2.
Support of classification: similarity of Cimicifuga constituents to database elements.
| (Cosine-Similarity Score) | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No | Generic Name | Top 1 | Score | Top 2 | Sore | Top 3 | Score | Top 4 | Score | Top 5 | Score |
| Cimi_1 | 12-beta-Acetoxy-Cimigenol | DMAT | 0.902 | 2-Hydroxyestradiol | 0.899 | CHEMBL3393133 | 0.899 | CHEMBL3133762 | 0.899 | CHEMBL196759 | 0.899 |
| Cimi_2 | 12-beta-Acetyl-Cimigenol-3-O-beta-D-xylopyranoside | CHEMBL3393133 | 0.951 | CHEMBL3133762 | 0.951 | CHEMBL196759 | 0.951 | 2-Hydroxyestradiol | 0.951 | Ezetimibe | 0.940 |
| Cimi_3 | 12-beta-Hydroxy-Cimigenol | DMAT | 0.900 | CHEMBL196759 | 0.899 | CHEMBL3133762 | 0.899 | 2-Hydroxyestradiol | 0.899 | CHEMBL3393133 | 0.899 |
| Cimi_4 | 12-O-Acetylacteol | DMAT | 0.903 | CHEMBL3133762 | 0.900 | CHEMBL196759 | 0.900 | CHEMBL3393133 | 0.900 | 2-Hydroxyestradiol | 0.900 |
| Cimi_5 | 15-O-Methyl-Cimigenol | CHEMBL3393133 | 0.899 | 2-Hydroxyestradiol | 0.899 | CHEMBL3133762 | 0.899 | CHEMBL196759 | 0.899 | CHEMBL3361128 | 0.887 |
| Cimi_6 | 23-epi-26-Deoxyactein=27-Deoxyactein | CHEMBL3393133 | 0.952 | CHEMBL196759 | 0.952 | CHEMBL3133762 | 0.952 | 2-Hydroxyestradiol | 0.952 | CHEMBL2325901 | 0.931 |
| Cimi_7 | 23-O-Acetylshengmanol | Compound C2 | 0.909 | CHEMBL2017214 | 0.899 | CHEMBL383246 | 0.895 | CHEMBL3963444 | 0.894 | 6 Paradol | 0.894 |
| Cimi_8 | 23-O-Acetylshengmanol 3-O-beta-D-xylopyranoside | CHEMBL2325901 | 0.951 | CHEMBL371968 | 0.934 | CHEMBL2420899 | 0.934 | Polydatin | 0.934 | Teneligliptin | 0.934 |
| Cimi_9 | 23-O-Acetylshengmanol xyloside | CHEMBL2325901 | 0.951 | CHEMBL371968 | 0.934 | CHEMBL2420899 | 0.934 | Polydatin | 0.934 | Teneligliptin | 0.934 |
| Cimi_10 | 24-Acetylhydroshengmanol xyloside | CHEMBL196759 | 0.941 | CHEMBL3393133 | 0.941 | CHEMBL3133762 | 0.941 | 2-Hydroxyestradiol | 0.941 | CHEMBL2325901 | 0.939 |
| Cimi_11 | 24-O-Acetylacerionol | CHEMBL3746293 | 0.923 | GW275944X | 0.921 | Theasinensis A | 0.917 | CHEMBL1078665 | 0.901 | Mogrol | 0.897 |
| Cimi_12 | 25-AnhydroCimigenol-3-O-alpha-L-arabinoside | 6-O-Cinnamoyl-D-glucopyranose | 0.952 | GW290597X | 0.952 | GW458787A | 0.952 | delphinidin-3-glucoside | 0.952 | Ezetimibe | 0.952 |
| Cimi_13 | 25-O-AcetylCimigenol | CHEMBL383246 | 0.901 | CHEMBL3963444 | 0.900 | 6 Paradol | 0.900 | CHEMBL4112013 | 0.900 | Ascofuranone | 0.878 |
| Cimi_14 | 25-O-AcetylCimigenol 3-o-alpha-L-arabinoside | CHEMBL3393133 | 0.951 | CHEMBL3133762 | 0.951 | CHEMBL196759 | 0.951 | 2-Hydroxyestradiol | 0.951 | Ezetimibe | 0.940 |
| Cimi_15 | 25-O-Acetyl-cimigenol xyloside | CHEMBL3393133 | 0.951 | CHEMBL3133762 | 0.951 | CHEMBL196759 | 0.951 | 2-Hydroxyestradiol | 0.951 | Ezetimibe | 0.940 |
| Cimi_16 | 25-O-Ethyl-cimigenol-3-O-beta-D-xylopyranoside | 2-Hydroxyestradiol | 0.951 | CHEMBL3393133 | 0.951 | CHEMBL3133762 | 0.951 | CHEMBL196759 | 0.951 | GYY4137 | 0.928 |
| Cimi_17 | 25-O-Methyl-cimigenol | CHEMBL3393133 | 0.899 | 2-Hydroxyestradiol | 0.899 | CHEMBL3133762 | 0.899 | CHEMBL196759 | 0.899 | CHEMBL3361128 | 0.887 |
| Cimi_18 | 25-O-Methyl-cimigenol-3-O-beta-D-xyloside | 2-Hydroxyestradiol | 0.951 | CHEMBL3393133 | 0.951 | CHEMBL3133762 | 0.951 | CHEMBL196759 | 0.951 | GYY4137 | 0.928 |
| Cimi_20 | 3,4-Dimethoxycinnamic acid | 4a-Isoalantolactone | 0.958 | Nootkatone | 0.958 | Gemcitabine | 0.957 | Fenoldopam | 0.936 | GW439255X | 0.913 |
| Cimi_22 | Acerinol | Theasinensis A | 0.917 | GW275944X | 0.895 | Folic caid | 0.892 | 6-O-cinnamoyl-D-glucopyranose | 0.890 | Karaviloside X | 0.886 |
| Cimi_23 | Actaeaepoxide 3-O-beta-D-xylopyranoside | GSK978744A | 0.945 | CHEMBL2338231 | 0.943 | LCZ696 | 0.943 | Tadalafil | 0.943 | Berteroin | 0.943 |
| Cimi_24 | Actaealactone | C129 | 0.859 | GW644007X | 0.827 | Clozapin | 0.827 | CHEMBL1081678 | 0.813 | CHEMBL4092508 | 0.812 |
| Cimi_25 | Actein | CHEMBL196759 | 0.941 | CHEMBL3133762 | 0.941 | 2-Hydroxyestradiol | 0.941 | CHEMBL3393133 | 0.941 | Ezetimibe | 0.931 |
| Cimi_26 | Acteol | DMAT | 0.902 | CHEMBL3133762 | 0.899 | 2-Hydroxyestradiol | 0.899 | CHEMBL3393133 | 0.899 | CHEMBL196759 | 0.899 |
| Cimi_27 | Angelicain | GW644007X | 0.899 | CHEMBL3730916 | 0.864 | CHEMBL2338229 | 0.857 | CHEMBL204420 | 0.838 | CHEMBL4217199 | 0.834 |
| Cimi_28 | Bugbanoside E | CHEMBL2420899 | 0.954 | Teneligliptin | 0.954 | Polydatin | 0.954 | CHEMBL371968 | 0.954 | Cinacalcet | 0.954 |
| Cimi_29 | Bugbanoside F | Folic acid | 0.961 | GSK978744A | 0.954 | GW290597X | 0.952 | SC4 | 0.952 | 6-O-cinnamoyl-D-glucopyranose | 0.952 |
| Cimi_30 | Caffeic acid | 3-O-methylquercetin | 1.000 | CHEMBL208286 | 0.977 | CHEMBL2408232 | 0.934 | 4a-Isoalantolactone | 0.914 | Nootkatone | 0.914 |
| Cimi_31 | Caffeic methyl ester | Nootkatone | 0.980 | 4a-Isoalantolactone | 0.980 | Fenoldopam | 0.959 | 3-O-methylquercetin | 0.938 | CHEMBL208286 | 0.917 |
| Cimi_32 | Cimicfugoside M | CHEMBL196759 | 0.961 | 2-Hydroxyestradiol | 0.961 | CHEMBL3133762 | 0.961 | CHEMBL3393133 | 0.961 | GYY4137 | 0.938 |
| Cimi_33 | Cimicidanol | Gamma linolenic acid | 0.924 | Fluvastatin | 0.923 | CHEMBL1078665 | 0.913 | CHEMBL4114120 | 0.912 | Compound C2 | 0.912 |
| Cimi_34 | Cimicifugic acid C | Glyceolin | 0.957 | GW780056X | 0.926 | Oligomycin | 0.926 | Ibuprofen | 0.926 | CHEMBL4092508 | 0.878 |
| Cimi_35 | Cimicifugic acid D | Glyceolin | 0.957 | GW780056X | 0.926 | Oligomycin | 0.926 | Ibuprofen | 0.926 | CHEMBL4092508 | 0.878 |
| Cimi_36 | Cimicifugic acid E | Glyceolin | 0.930 | GW780056X | 0.900 | Oligomycin | 0.900 | Ibuprofen | 0.900 | Melatonin | 0.885 |
| Cimi_37 | Cimicifugic acid F | Glyceolin | 0.930 | GW780056X | 0.900 | Oligomycin | 0.900 | Ibuprofen | 0.900 | Melatonin | 0.885 |
| Cimi_38 | Cimicifugoside H-1 | CHEMBL2420899 | 0.954 | Teneligliptin | 0.954 | Polydatin | 0.954 | CHEMBL371968 | 0.954 | Cinacalcet | 0.954 |
| Cimi_39 | Cimicifugoside H-2 | CHEMBL1230171 | 0.962 | Meriolin 1 | 0.962 | CHEMBL2420899 | 0.953 | Polydatin | 0.953 | Cinacalcet | 0.953 |
| Cimi_40 | Cimicifugoside H-3 | CHEMBL1230171 | 0.982 | Polydatin | 0.973 | Teneligliptin | 0.973 | CHEMBL371968 | 0.973 | GW576924A | 0.973 |
| Cimi_41 | Cimicinol | Folic acid | 0.939 | GSK978744A | 0.934 | SC4 | 0.932 | GW290597X | 0.932 | 6-O-cinnamoyl-D-glucopyranose | 0.932 |
| Cimi_42 | Cimiciphenone | Paroxetine | 0.969 | CHEMBL4112741 | 0.921 | Melatonin | 0.919 | CHEMBL4066628 | 0.904 | Ibuprofen | 0.904 |
| Cimi_43 | Cimidahurine | Gamma-oryzanol | 0.973 | Atractylenolide III | 0.960 | Sirtinol | 0.937 | Zidovudine | 0.933 | Compound 59 | 0.926 |
| Cimi_44 | Cimifugin | CHEMBL3930006 | 0.858 | GW644007X | 0.858 | GW708336X | 0.852 | Palbociclib | 0.849 | CHEMBL204420 | 0.844 |
| Cimi_45 | Cimigenol | DMAT | 0.900 | CHEMBL196759 | 0.899 | CHEMBL3133762 | 0.899 | 2-Hydroxyestradiol | 0.899 | CHEMBL3393133 | 0.899 |
| Cimi_46 | Cimigenol xyloside | CHEMBL196759 | 0.961 | 2-Hydroxyestradiol | 0.961 | CHEMBL3133762 | 0.961 | CHEMBL3393133 | 0.961 | GYY4137 | 0.938 |
| Cimi_47 | Cimigol | DMAT | 0.900 | CHEMBL196759 | 0.899 | CHEMBL3133762 | 0.899 | 2-Hydroxyestradiol | 0.899 | CHEMBL3393133 | 0.899 |
| Cimi_48 | Cimilactone B | GW576924A | 0.953 | Teneligliptin | 0.953 | CHEMBL2420899 | 0.953 | polydatin | 0.953 | Cinacalcet | 0.953 |
| Cimi_49 | Cimipronidine | CHEMBL1933279 | 0.778 | Cheletyrine | 0.764 | Pinosylvin | 0.758 | Nordihydroguaiaretic acid | 0.755 | CHEMBL3730146 | 0.723 |
| Cimi_50 | Cimipronidine methyl ester | CHEMBL1933279 | 0.743 | Pinosylvin | 0.741 | GSK182497A | 0.713 | Cheletyrine | 0.710 | BDE-209 | 0.705 |
| Cimi_51 | Cimiracemate A | Paroxetine | 0.954 | Oligomycin | 0.922 | GW780056X | 0.922 | Ibuprofen | 0.922 | CHEMBL4112741 | 0.907 |
| Cimi_52 | Cimiracemate B | Paroxetine | 0.954 | Oligomycin | 0.922 | GW780056X | 0.922 | Ibuprofen | 0.922 | CHEMBL4112741 | 0.907 |
| Cimi_53 | Cimiracemate C | Paroxetine | 0.956 | CHEMBL4066628 | 0.926 | Melatonin | 0.910 | CHEMBL4112741 | 0.880 | CHEMBL4092508 | 0.878 |
| Cimi_54 | Cimiracemate D | Paroxetine | 0.956 | CHEMBL4066628 | 0.926 | Melatonin | 0.910 | CHEMBL4112741 | 0.880 | CHEMBL4092508 | 0.878 |
| Cimi_55 | Cimiracemoside A (=F) | GSK978744A | 0.963 | Ezetimibe | 0.962 | Monensin | 0.952 | Folic acid | 0.952 | GSK192082A | 0.945 |
| Cimi_56 | Cimiracemoside B | CHEMBL3393133 | 0.990 | CHEMBL3133762 | 0.990 | CHEMBL196759 | 0.990 | 2-Hydroxyestradiol | 0.990 | GYY4137 | 0.970 |
| Cimi_57 | Cimiracemoside C | CHEMBL196759 | 0.961 | 2-Hydroxyestradiol | 0.961 | CHEMBL3133762 | 0.961 | CHEMBL3393133 | 0.961 | GYY4137 | 0.938 |
| Cimi_58 | Cimiracemoside D | CHEMBL3393133 | 0.951 | CHEMBL3133762 | 0.951 | CHEMBL196759 | 0.951 | 2-Hydroxyestradiol | 0.951 | Ezetimibe | 0.940 |
| Cimi_59 | Cimiracemoside E | CHEMBL2325901 | 0.981 | Cinacalcet | 0.962 | Teneligliptin | 0.962 | Polydatin | 0.962 | CHEMBL371968 | 0.962 |
| Cimi_60 | Cimiracemoside G | GSK978744A | 0.963 | Ezetimibe | 0.962 | Monensin | 0.952 | Folic acid | 0.952 | GSK192082A | 0.945 |
| Cimi_61 | Cimiracemoside H | CHEMBL3393133 | 0.951 | CHEMBL3133762 | 0.951 | CHEMBL196759 | 0.951 | 2-Hydroxyestradiol | 0.951 | Ezetimibe | 0.940 |
| Cimi_62 | Cimiracemoside J | Ezetimibe | 0.962 | Monensin | 0.952 | CHEMBL3975011 | 0.952 | CHEMBL4246000 | 0.952 | GSK978744A | 0.945 |
| Cimi_63 | Cimiracemoside K | Ezetimibe | 0.962 | Monensin | 0.952 | CHEMBL3975011 | 0.952 | CHEMBL4246000 | 0.952 | GSK978744A | 0.945 |
| Cimi_64 | Cimiracemoside L | CHEMBL2325901 | 0.929 | CDN1163 | 0.918 | Cinacalcet | 0.914 | CHEMBL2420899 | 0.914 | polydatin | 0.914 |
| Cimi_65 | Cimiracemoside N | CHEMBL3393133 | 0.952 | CHEMBL196759 | 0.952 | CHEMBL3133762 | 0.952 | 2-Hydroxyestradiol | 0.952 | CHEMBL2325901 | 0.931 |
| Cimi_66 | Cimiracemoside P | CHEMBL3133762 | 0.932 | CHEMBL196759 | 0.932 | 2-Hydroxyestradiol | 0.932 | CHEMBL3393133 | 0.932 | CHEMBL2325901 | 0.931 |
| Cimi_67 | Cimiside A | CHEMBL196759 | 0.961 | 2-Hydroxyestradiol | 0.961 | CHEMBL3133762 | 0.961 | CHEMBL3393133 | 0.961 | GYY4137 | 0.938 |
| Cimi_68 | Cimiside B | CHEMBL196759 | 0.971 | 2-Hydroxyestradiol | 0.971 | CHEMBL3133762 | 0.971 | CHEMBL3393133 | 0.971 | GYY4137 | 0.949 |
| Cimi_69 | Cimiside E | 6-O-Cinnamoyl-D-glucopyranose | 0.952 | GW290597X | 0.952 | GW458787A | 0.952 | delphinidin-3-glucoside | 0.952 | Ezetimibe | 0.952 |
| Cimi_70 | Cyclocmipronidine | Cheletyrine | 0.801 | 15,16-dihydrotanshinone I | 0.800 | CHEMBL3730933 | 0.800 | Nordihydroguaiaretic acid | 0.791 | CHEMBL188282 | 0.757 |
| Cimi_71 | Dahurinol | CHEMBL383246 | 0.901 | CHEMBL4094080 | 0.897 | 2G11 | 0.897 | Gamma linolenic acid | 0.884 | CHEMBL3735890 | 0.884 |
| Cimi_72 | Dopargine | Tangeretin | 0.768 | GSK182497A | 0.751 | SC-202671 | 0.748 | CHEMBL3927465 | 0.748 | Oleic acid | 0.747 |
| Cimi_73 | Ferulic acid methyl ester | 4a-Isoalantolactone | 0.958 | Nootkatone | 0.958 | Gemcitabine | 0.957 | Fenoldopam | 0.936 | GW439255X | 0.913 |
| Cimi_74 | Formononetin | CHEMBL3774632 | 1.000 | SB-409514 | 0.984 | PP487 | 0.969 | CHEMBL3393131 | 0.969 | CHEMBL207674 | 0.969 |
| Cimi_75 | Friedelin | Procyanidin B2 | 0.891 | CHEMBL4112013 | 0.857 | GSK635416A | 0.857 | CHEMBL3727865 | 0.850 | CHEMBL3859268 | 0.840 |
| Cimi_76 | Fukiic acid | Glyceolin | 0.924 | Adenine | 0.861 | CHEMBL2408232 | 0.861 | Icaritin | 0.859 | Oligomycin | 0.853 |
| Cimi_77 | Fukinolic acid | Glyceolin | 0.957 | GW780056X | 0.926 | Oligomycin | 0.926 | Ibuprofen | 0.926 | CHEMBL4092508 | 0.878 |
| Cimi_78 | IsoCimicifugamide | Compound 59 | 0.869 | Nummularic acid | 0.858 | Sirtinol | 0.858 | Bupivacaine | 0.849 | CHEMBL3931350 | 0.837 |
| Cimi_79 | Isoferulic acid | Nootkatone | 1.000 | 4a-Isoalantolactone | 1.000 | fenoldopam | 0.979 | 3-O-methylquercetin | 0.914 | Gemcitabine | 0.914 |
| Cimi_80 | Neocimicigenoside A | CHEMBL196759 | 0.941 | CHEMBL3393133 | 0.941 | CHEMBL3133762 | 0.941 | 2-Hydroxyestradiol | 0.941 | CHEMBL2325901 | 0.939 |
| Cimi_81 | Neocimicigenoside B | CHEMBL196759 | 0.941 | CHEMBL3393133 | 0.941 | CHEMBL3133762 | 0.941 | 2-Hydroxyestradiol | 0.941 | CHEMBL2325901 | 0.939 |
| Cimi_82 | N-Methylcytisine | TBB | 0.797 | CHEMBL3967075 | 0.784 | Soyasapogenol C | 0.780 | Momordicoside Q | 0.780 | GW827396X | 0.738 |
| Cimi_83 | p-Coumaric acid | Sulforaphane | 1.000 | 3-O-Methylquercetin | 0.879 | GW782612X | 0.868 | CHEMBL3736320 | 0.849 | CHEMBL208286 | 0.847 |
| Cimi_84 | Petasiphenone | CHEMBL4112741 | 0.951 | Paroxetine | 0.936 | Ibuprofen | 0.933 | GW780056X | 0.933 | Oligomycin | 0.933 |
| Cimi_85 | Piscidic acid | Glyceolin | 0.892 | Adenine | 0.891 | Icaritin | 0.831 | Ibuprofen | 0.814 | Oligomycin | 0.814 |
| Cimi_86 | Podocarpaside A | CHEMBL1230171 | 0.962 | Meriolin | 0.962 | CHEMBL2420899 | 0.953 | Polydatin | 0.953 | Cinacalcet | 0.953 |
| Cimi_87 | Podocarpaside B | CHEMBL1230171 | 0.962 | Meriolin | 0.962 | CHEMBL2420899 | 0.953 | Polydatin | 0.953 | Cinacalcet | 0.953 |
| Cimi_88 | Podocarpaside C | CHEMBL1230171 | 0.962 | Meriolin | 0.962 | CHEMBL2420899 | 0.953 | Polydatin | 0.953 | Cinacalcet | 0.953 |
| Cimi_89 | Podocarpaside D | CHEMBL1230171 | 0.962 | Meriolin | 0.962 | CHEMBL2420899 | 0.953 | Polydatin | 0.953 | Cinacalcet | 0.953 |
| Cimi_90 | Podocarpaside F | CHEMBL1230171 | 0.962 | Meriolin | 0.962 | CHEMBL2420899 | 0.953 | Polydatin | 0.953 | Cinacalcet | 0.953 |
| Cimi_91 | Podocarpaside G | CHEMBL1230171 | 0.952 | Meriolin | 0.952 | Teneligliptin | 0.944 | Polydatin | 0.944 | CHEMBL371968 | 0.944 |
| Cimi_92 | Protocatechualdehyde | CHEMBL208286 | 0.951 | 3-O-Methylquercetin | 0.929 | Belinostat | 0.923 | CHEMBL2408232 | 0.909 | GW782612X | 0.872 |
| Cimi_93 | Protocatechuic acid | CHEMBL208286 | 1.000 | 3-O-Methylquercetin | 0.977 | CHEMBL2408232 | 0.956 | Fenoldopam | 0.910 | Nootkatone | 0.891 |
| Cimi_94 | Shengmanol | CHEMBL196759 | 0.910 | DMAT | 0.892 | CHEMBL3133762 | 0.889 | CHEMBL3393133 | 0.889 | 2-Hydroxyestradiol | 0.889 |
| Cimi_95 | Shengmanol xyloside | CHEMBL196759 | 0.951 | CHEMBL3133762 | 0.931 | 2-Hydroxyestradiol | 0.931 | CHEMBL3393133 | 0.931 | Ezetimibe | 0.920 |
| Cimi_96 | Sinapic acid | Nootkatone | 0.961 | 4a-Isoalantolactone | 0.961 | Fenoldopam | 0.941 | Gemcitabine | 0.920 | CHEMBL4066628 | 0.895 |
| Cimi_97 | Visnagin | Prednisolone | 0.938 | CHEMBL3976646 | 0.889 | Rifampicin | 0.889 | CHEMBL208118 | 0.889 | Monascus | 0.889 |
| Cimi_2_ metab | 12-beta-Acetoxycimigenol | DMAT | 0.902 | 2-Hydroxyestradiol | 0.899 | CHEMBL3393133 | 0.899 | CHEMBL3133762 | 0.899 | CHEMBL196759 | 0.899 |
| Cimi_6_ metab | Cimi_6_metab | CHEMBL3393133 | 0.910 | CHEMBL196759 | 0.910 | 2-Hydroxyestradiol | 0.910 | CHEMBL3133762 | 0.910 | Monensin | 0.908 |
| Cimi_8_ metab | 23-O-Acetylshengmanol | Compound C2 | 0.909 | CHEMBL2017214 | 0.899 | CHEMBL383246 | 0.895 | CHEMBL3963444 | 0.894 | 6 Paradol | 0.894 |
| Cimi_9_ metab | Cimi_9_metab | Compound C2 | 0.909 | CHEMBL2017214 | 0.899 | CHEMBL383246 | 0.895 | CHEMBL3963444 | 0.894 | 6 Paradol | 0.894 |
| Cimi_10_ metab | Cimi_10_metab | CHEMBL196759 | 0.899 | 2-Hydroxyestradiol | 0.899 | CHEMBL3133762 | 0.899 | CHEMBL3393133 | 0.899 | CHEMBL4094080 | 0.899 |
| Cimi_12_ metab | Cimi_12_metab | Ascofuranone | 0.919 | AKOS007865932 | 0.907 | CHEMBL4246000 | 0.907 | CHEMBL3975011 | 0.907 | delphinidin-3-glucoside | 0.898 |
| Cimi_14_ metab | Cimi_14_metab | DMAT | 0.902 | 2-Hydroxyestradiol | 0.899 | CHEMBL3393133 | 0.899 | CHEMBL3133762 | 0.899 | CHEMBL196759 | 0.899 |
| Cimi_15_ metab | Cimi_15_metab | DMAT | 0.902 | 2-Hydroxyestradiol | 0.899 | CHEMBL3393133 | 0.899 | CHEMBL3133762 | 0.899 | CHEMBL196759 | 0.899 |
| Cimi_16_ metab | 25- O-Methylcimigenol | CHEMBL3393133 | 0.899 | 2-Hydroxyestradiol | 0.899 | CHEMBL3133762 | 0.899 | CHEMBL196759 | 0.899 | CHEMBL3361128 | 0.887 |
| Cimi_18_ metab | 25-O-Methylcimigenol | CHEMBL3393133 | 0.899 | 2-Hydroxyestradiol | 0.899 | CHEMBL3133762 | 0.899 | CHEMBL196759 | 0.899 | CHEMBL3361128 | 0.887 |
| Cimi_19_ metab | Cimi_19_metab | DMAT | 0.903 | CHEMBL3133762 | 0.900 | CHEMBL196759 | 0.900 | CHEMBL3393133 | 0.900 | 2-Hydroxyestradiol | 0.900 |
| Cimi_22_ metab | Cimi_22_metab | Monensin | 0.909 | GSK978744A | 0.905 | CHEMBL2338231 | 0.903 | Berteroin | 0.903 | LCZ696 | 0.903 |
| Cimi_23_ metab | Cimi_23_metab | Monensin | 0.909 | GSK978744A | 0.905 | CHEMBL2338231 | 0.903 | Berteroin | 0.903 | LCZ696 | 0.903 |
| Cimi_25_ metab | Cimi_25_metab | DMAT | 0.903 | CHEMBL3133762 | 0.900 | CHEMBL196759 | 0.900 | CHEMBL3393133 | 0.900 | 2-Hydroxyestradiol | 0.900 |
| Cimi_28_ metab | Cimi_28_metab | CHEMBL3746293 | 0.925 | CHEMBL1078665 | 0.925 | Compound C2 | 0.924 | CHEMBL4114120 | 0.902 | GW275944X | 0.902 |
| Cimi_29_ metab | Cimi_29_metab | CHEMBL2376144 | 0.899 | CHEMBL2041962 | 0.898 | CHEMBL3427184 | 0.898 | Epiberberine | 0.898 | GW275944X | 0.898 |
| Cimi_32_ metab | Cimi_32_metab | DMAT | 0.900 | CHEMBL196759 | 0.899 | CHEMBL3133762 | 0.899 | 2-Hydroxyestradiol | 0.899 | CHEMBL3393133 | 0.899 |
| Cimi_38_ metab | Cimicidanol | Gamma linolenic acid | 0.924 | Fluvastatin | 0.923 | CHEMBL1078665 | 0.913 | CHEMBL4114120 | 0.912 | Compound C2 | 0.912 |
| Cimi_39_ metab | Cimi_39_metab | Gamma linolenic acid | 0.966 | Fluvastatin | 0.966 | CHEMBL2337767 | 0.955 | Epiberberine | 0.955 | CHEMBL1078665 | 0.933 |
| Cimi_40_ metab | Cimi_40_metab | C128 | 0.956 | Pitavastatin | 0.955 | Xanthohumol | 0.928 | Fluvastatin | 0.920 | CHEMBL4114120 | 0.909 |
| Cimi_41_ metab | Cimi_41_metab | GW631581B | 0.894 | Theasinensis A | 0.884 | Compound C2 | 0.884 | GW275944X | 0.881 | Folic acid | 0.880 |
| Cimi_43_ metab | Hydroxytyrosol | CHEMBL1233881 | 1.000 | CHEMBL4112741 | 0.830 | CHEMBL3909286 | 0.823 | gamma-oryzanol | 0.802 | CHEMBL4215572 | 0.793 |
| Cimi_46_ metab | Cimigenol | DMAT | 0.900 | CHEMBL196759 | 0.899 | CHEMBL3133762 | 0.899 | 2-Hydroxyestradiol | 0.899 | CHEMBL3393133 | 0.899 |
| Cimi_56_ metab | Cimi_56_metab | CHEMBL3393133 | 0.941 | 2-Hydroxyestradiol | 0.941 | CHEMBL3133762 | 0.941 | CHEMBL196759 | 0.941 | CHEMBL4278763 | 0.917 |
| Cimi_57_ metab | Cimigenol | DMAT | 0.900 | CHEMBL196759 | 0.899 | CHEMBL3133762 | 0.899 | 2-Hydroxyestradiol | 0.899 | CHEMBL3393133 | 0.899 |
| Cimi_58_ metab | 12beta-acetoxycimigenol | DMAT | 0.902 | 2-Hydroxyestradiol | 0.899 | CHEMBL3393133 | 0.899 | CHEMBL3133762 | 0.899 | CHEMBL196759 | 0.899 |
| Cimi_59_ metab | Cimi_59_metab | CHEMBL2325901 | 0.939 | CHEMBL2420899 | 0.923 | CHEMBL371968 | 0.923 | Teneligliptin | 0.923 | Polydatin | 0.923 |
| Cimi_61_ metab | Cimi_61_metab | CHEMBL3393133 | 0.920 | CHEMBL3133762 | 0.920 | CHEMBL196759 | 0.920 | 2-Hydroxyestradiol | 0.920 | Monensin | 0.917 |
| Cimi_62_ metab | Cimi_62_metab | Ascofuranone | 0.923 | AKOS007865932 | 0.911 | Monensin | 0.908 | CHEMBL3975011 | 0.908 | CHEMBL4246000 | 0.908 |
| Cimi_63_ metab | Cimi_63_metab | Ascofuranone | 0.923 | AKOS007865932 | 0.911 | Monensin | 0.908 | CHEMBL3975011 | 0.908 | CHEMBL4246000 | 0.908 |
| Cimi_64_ metab | 23-O-Acetylshengmanol | Compound C2 | 0.909 | CHEMBL2017214 | 0.899 | CHEMBL383246 | 0.895 | CHEMBL3963444 | 0.894 | 6 Paradol | 0.894 |
| Cimi_65_ metab | Cimi_65_metab | CHEMBL3393133 | 0.910 | CHEMBL196759 | 0.910 | 2-Hydroxyestradiol | 0.910 | CHEMBL3133762 | 0.910 | Monensin | 0.908 |
| Cimi_66_ metab | Cimi_66_metab | CHEMBL2017214 | 0.911 | DMAT | 0.903 | CHEMBL3735890 | 0.889 | CHEMBL383246 | 0.885 | CHEMBL3393133 | 0.879 |
| Cimi_67_ metab | 12beta-Hydroxycimigenol | DMAT | 0.900 | CHEMBL196759 | 0.899 | CHEMBL3133762 | 0.899 | 2-Hydroxyestradiol | 0.899 | CHEMBL3393133 | 0.899 |
| Cimi_68_ metab | Cimigenol | DMAT | 0.900 | CHEMBL196759 | 0.899 | CHEMBL3133762 | 0.899 | 2-Hydroxyestradiol | 0.899 | CHEMBL3393133 | 0.899 |
| Cimi_69_ metab | Cimi_69_metab | Ascofuranone | 0.919 | AKOS007865932 | 0.907 | CHEMBL4246000 | 0.907 | CHEMBL3975011 | 0.907 | delphinidin-3-glucoside | 0.898 |
| Cimi_78_ metab | Cimi_78_metab | SB-732941 | 0.924 | CHEMBL3933251 | 0.875 | CHEMBL3728128 | 0.870 | Corosolic acid | 0.852 | Hernandezine | 0.800 |
| Cimi_80_ metab | Cimi_80_metab | Urolithin A | 0.907 | CHEMBL2017214 | 0.897 | CHEMBL383246 | 0.891 | DMAT | 0.890 | CHEMBL3963444 | 0.890 |
| Cimi_81_ metab | Cimi_81_metab | Urolithin A | 0.907 | CHEMBL2017214 | 0.897 | CHEMBL383246 | 0.891 | DMAT | 0.890 | CHEMBL3963444 | 0.890 |
| Cimi_86_ metab | Cimi_86_metab | Gamma linolenic acid | 0.955 | CHEMBL1078665 | 0.944 | CHEMBL4114120 | 0.943 | GW780159X | 0.942 | Crocin | 0.941 |
| Cimi_87_ metab | Cimi_87_metab | CHEMBL4114120 | 0.953 | Crocin | 0.952 | Gamma linolenic acid | 0.943 | Fluvastatin | 0.941 | Fucoxanthin | 0.940 |
| Cimi_88_ metab | Cimi_88_metab | Gamma linolenic acid | 0.955 | Fluvastatin | 0.954 | CHEMBL1078665 | 0.944 | CHEMBL4114120 | 0.943 | Epiberberine | 0.942 |
| Cimi_89_ metab | Cimi_89_metab | CHEMBL4114120 | 0.953 | Crocin | 0.952 | Gamma linolenic acid | 0.943 | Fluvastatin | 0.941 | Fucoxanthin | 0.940 |
| Cimi_90_ metab | Cimi_90_metab | CHEMBL1230171 | 0.962 | Meriolin 1 | 0.962 | CHEMBL2420899 | 0.953 | polydatin | 0.953 | Cinacalcet | 0.953 |
| Cimi_91_ metab | Cimi_91_metab | Gamma linolenic acid | 0.943 | Fluvastatin | 0.941 | CHEMBL1078665 | 0.932 | CHEMBL4114120 | 0.930 | Epiberberine | 0.929 |
| Cimi_92_ metab | Cimi_92_metab | CHEMBL196759 | 0.910 | DMAT | 0.892 | CHEMBL3133762 | 0.889 | CHEMBL3393133 | 0.889 | 2-Hydroxyestradiol | 0.889 |
| Median | 0.941 | 0.923 | 0.922 | 0.912 | 0.907 | ||||||
Highlighted in blue are the constituents for which no comparison molecule was found in the database with a cosine similarity score > 0.8.
References
- Wuttke, W.; Seidlová-Wuttke, D.; Gorkow, C. The Cimicifuga preparation BNO 1055 vs. conjugated estrogens in a double-blind placebo-controlled study: Effects on menopause symptoms and bone markers. Maturitas 2003, 44, S67–S77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osmers, R.; Friede, M.; Liske, E.; Schnitker, J.; Freudenstein, J.; Henneicke von Zepelin, H.H. Efficacy and safety of isopropanolic black cohosh extract for climacteric symptoms. Obstet. Gynecol. 2005, 105, 1074–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schellenberg, R.; Saller, R.; Hess, L.; Melzer, J.; Zimmermann, C.; Drewe, J.; Zahner, C. Dose-dependent effects of the Cimicifuga racemosa extract Ze450 in the treatment of climacteric complaints: A randomized, placebo-controlled study. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2012, 2012, 260301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drewe, J.; Zimmermann, C.; Zahner, C. The effect of a Cimicifuga racemosa extracts Ze 450 in the treatment of climacteric complaints—An observational study. Phytomed. Int. J. Phytother. Phytopharm. 2013, 20, 659–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- HMPC. European Union Herbal Monograph on Cimicifuga racemosa (L.) Nutt., Rhizoma; European Medicines Agency: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Seidlova-Wuttke, D.; Eder, N.; Stahnke, V.; Kammann, M.; Stecher, G.; Haunschild, J.; Wessels, J.T.; Wuttke, W. Cimicifuga racemosa and its triterpene-saponins prevent the Metabolic Syndrome and deterioration of cartilage in the knee joint of ovariectomized rats by similar mechanisms. Phytomed. Int. J. Phytother. Phytopharm. 2012, 19, 846–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hardie, D.G. Keeping the home fires burning: AMP-activated protein kinase. J. R. Soc. Interface 2018, 15, 20170774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moser, C.; Vickers, S.P.; Brammer, R.; Cheetham, S.C.; Drewe, J. Antidiabetic effects of the Cimicifuga racemosa extract Ze 450 in vitro and in vivo in ob/ob mice. Phytomed. Int. J. Phytother. Phytopharm. 2014, 21, 1382–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drewe, J.; Boonen, G.; Culmsee, C. Treat more than heat New therapeutic implications of Cimicifuga racemosa through AMPK-dependent metabolic effects. Phytomed. Int. J. Phytother. Phytopharm. 2022, 100, 154060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardie, D.G. Regulation of AMP-activated protein kinase by natural and synthetic activators. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2016, 6, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, H.; Kumar, S. Natural AMPK Activators: An Alternative Approach for the Treatment and Management of Metabolic Syndrome. Curr. Med. Chem. 2017, 24, 1007–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drewe, J.; Küsters, E.; Hammann, F.; Kreuter, M.; Boss, P.; Schöning, V. Modeling Structure-Activity Relationship of AMPK Activation. Molecules 2021, 26, 6508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vazirian, M.; Nabavi, S.M.; Jafari, S.; Manayi, A. Natural activators of adenosine 5′-monophosphate (AMP)-activated protein kinase (AMPK) and their pharmacological activities. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2018, 122, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Francini, F.; Schinella, G.R.; Rios, J.L. Activation of AMPK by Medicinal Plants and Natural Products: Its Role in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 2019, 19, 880–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anjum, J.; Mitra, S.; Das, R.; Alam, R.; Mojumder, A.; Emran, T.B.; Islam, F.; Rauf, A.; Hossain, M.J.; Aljohani, A.S.M.; et al. A renewed concept on the MAPK signaling pathway in cancers: Polyphenols as a choice of therapeutics. Pharmacol. Res. 2022, 184, 106398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Francis, G.; Kerem, Z.; Makkar, H.P.; Becker, K. The biological action of saponins in animal systems: A review. Br. J. Nutr. 2002, 88, 587–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, K.; Chen, F.; Li, C. Absorption, disposition, and pharmacokinetics of saponins from Chinese medicinal herbs: What do we know and what do we need to know more? Curr. Drug Metab. 2012, 13, 577–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tawab, M.A.; Bahr, U.; Karas, M.; Wurglics, M.; Schubert-Zsilavecz, M. Degradation of ginsenosides in humans after oral administration. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2003, 31, 1065–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Setchell, K.D.; Brown, N.M.; Desai, P.B.; Zimmer-Nechimias, L.; Wolfe, B.; Jakate, A.S.; Creutzinger, V.; Heubi, J.E. Bioavailability, disposition, and dose-response effects of soy isoflavones when consumed by healthy women at physiologically typical dietary intakes. J. Nutr. 2003, 133, 1027–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Setchell, K.D.; Brown, N.M.; Zimmer-Nechemias, L.; Brashear, W.T.; Wolfe, B.E.; Kirschner, A.S.; Heubi, J.E. Evidence for lack of absorption of soy isoflavone glycosides in humans, supporting the crucial role of intestinal metabolism for bioavailability. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2002, 76, 447–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.X.; Yu, Z.Y. Cimicifugae rhizoma: From origins, bioactive constituents to clinical outcomes. Curr. Med. Chem. 2006, 13, 2927–2951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durant, J.L.; Leland, B.A.; Henry, D.R.; Nourse, J.G. Reoptimization of MDL keys for use in drug discovery. J. Chem. Inf. Comput. Sci. 2002, 42, 1273–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orosz, A.; Heberger, K.; Racz, A. Comparison of Descriptor- and Fingerprint Sets in Machine Learning Models for ADME-Tox Targets. Front. Chem. 2022, 10, 852893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chawla, N.V.; Bowyer, K.W.; Hall, L.O.; Kegelmeyer, W.P. SMOTE: Synthetic Minority Over-sampling Technique. J. Artif. Intellig. Res. 2002, 16, 321–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OECD. OECD Principles for the Validation, for Regulatory Purposes, of (Quantitative) Structure-Activity Relationship Models; OECD: Paris, France, 2004; Available online: https://www.oecd.org (accessed on 4 April 2024).
- Tropsha, A. Best Practices for QSAR Model Development, Validation, and Exploitation. Mol. Inf. 2010, 29, 476–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Maaten, L.J.P.; Hinton, G.E. Visualizing high-dimensional data using t-SNE. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2008, 9. [Google Scholar]
- Goodfellow, L.; Bengio, Y.; Courville, A. Deep Learning; MIT Press: Cambridge, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Tolles, J.; Meurer, W.J. Logistic Regression: Relating Patient Characteristics to Outcomes. JAMA 2016, 316, 533–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fawcett, T. An introduction to ROC analysis. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2006, 27, 861–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daina, A.; Michielin, O.; Zoete, V. SwissADME: A free web tool to evaluate pharmacokinetics, drug-likeness and medicinal chemistry friendliness of small molecules. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 42717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delaney, J.S. ESOL: Estimating aqueous solubility directly from molecular structure. J. Chem. Inf. Comput. Sci. 2004, 44, 1000–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, J.; Camilleri, P.; Brown, M.B.; Hutt, A.J.; Kirton, S.B. Revisiting the general solubility equation: In silico prediction of aqueous solubility incorporating the effect of topographical polar surface area. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2012, 52, 420–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, T.; Zhao, Y.; Li, X.; Lin, F.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Li, Y.; Wang, R.; Lai, L. Computation of octanol-water partition coefficients by guiding an additive model with knowledge. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2007, 47, 2140–2148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipinski, C.A.; Lombardo, F.; Dominy, B.W.; Feeney, P.J. Experimental and computational approaches to estimate solubility and permeability in drug discovery and development settings. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2012, 64, 4–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, I.S.; Kim, S.H. Sinapic Acid Promotes Browning of 3T3-L1 Adipocytes via p38 MAPK/CREB Pathway. Biomed. Res. Int. 2020, 2020, 5753623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.S.B.; Patil, K.N. trans-ferulic acid attenuates hyperglycemia-induced oxidative stress and modulates glucose metabolism by activating AMPK signaling pathway in vitro. J. Food Biochem. 2022, 46, e14038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, B.; Wan, H.; Yang, J.; Yu, L.; Zhou, H.; Wan, H. Lipid regulation of protocatechualdehyde and hydroxysafflor yellow A via AMPK/SREBP2/PCSK9/LDLR signaling pathway in hyperlipidemic zebrafish. Heliyon 2024, 10, e24908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.Z.; Li, L.; Espe, M.; Lu, K.L.; Rahimnejad, S. Hydroxytyrosol Attenuates Hepatic Fat Accumulation via Activating Mitochondrial Biogenesis and Autophagy through the AMPK Pathway. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 9377–9386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro del Hierro, J.; Herrera, T.; Fornari, T.; Reglero, G. The gastrointestinal behavior of saponins and its significance for their bioavailability and bioactivities. J. Funct. Food 2018, 40, 484–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Disch, L.; Forsch, K.; Siewert, B.; Drewe, J.; Fricker, G. In vitro and in situ characterization of triterpene glycosides from Cimicifuga racemosa extract. J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 106, 3642–3650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Breemen, R.B.; Liang, W.; Banuvar, S.; Shulman, L.P.; Pang, Y.; Tao, Y.; Nikolic, D.; Krock, K.M.; Fabricant, D.S.; Chen, S.N.; et al. Pharmacokinetics of 23-epi-26-deoxyactein in women after oral administration of a standardized extract of black cohosh. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2010, 87, 219–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramesh, M.; Vepuri, S.B.; Oosthuizen, F.; Soliman, M.E. Adenosine Monophosphate-Activated Protein Kinase (AMPK) as a Diverse Therapeutic Target: A Computational Perspective. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2016, 178, 810–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Peng, J.; Li, P.; Du, H.; Li, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhang, L.; Wang, L.L.; Zuo, Z. Identification of potential AMPK activator by pharmacophore modeling, molecular docking and QSAR study. Comput. Biol. Chem. 2019, 79, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).