Evaluation of Drug Blood-Brain-Barrier Permeability Using a Microfluidic Chip
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Cell Culture
2.3. BBB-on-a-Chip Assembly in the Device
2.4. Confirmation of Cell Seeding
2.5. Immunofluorescence
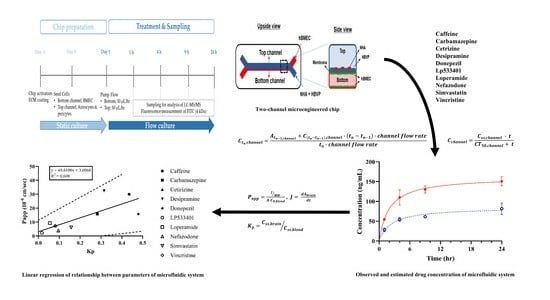
2.6. Drug Treatment and Sampling
2.7. LC-MS/MS Analysis
2.8. Data Analysis
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Schematic Diagram and Functional Validation of hBBB Models
3.2. Assessment of hBBB Permeability Using Microfluidic Model
3.3. In Vitro BBB Models for Drug Transport Screening
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ramirez-Velez, I.; Belardi, B. Storming the gate: New approaches for targeting the dynamic tight junction for improved drug delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2023, 199, 114905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, W.J.; Asselin, M.-C.; Hinz, R.; Parkes, L.M.; Allan, S.; Schiessl, I.; Boutin, H.; Dickie, B.R. In vivo methods for imaging blood–brain barrier function and dysfunction. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2023, 50, 1051–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Hou, Y.; Ai, X.; Sun, J.; Xu, B.; Meng, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, S. Potential applications of microfluidics based blood brain barrier (BBB)-on-chips for in vitro drug development. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 132, 110822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, X. Current Strategies for Brain Drug Delivery. Theranostics 2018, 8, 1481–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, A.D.; Ye, M.; Levy, A.F.; Rothstein, J.D.; Bergles, D.E.; Searson, P.C. The blood-brain barrier: An engineering perspective. Front. Neuroeng. 2013, 6, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonner, M.G.; Gudapati, H.; Mou, X.; Musah, S. Microfluidic systems for modeling human development. Development 2022, 149, dev199463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Koo, B.-K.; Knoblich, J.A. Human organoids: Model systems for human biology and medicine. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2020, 21, 571–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Festing, S.; Wilkinson, R. The ethics of animal research. Talking Point on the use of animals in scientific research. EMBO Rep. 2007, 8, 526–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhopadhyay, C.; Paul, M.K. Organoid-based 3D in vitro microphysiological systems as alternatives to animal experimentation for preclinical and clinical research. Arch. Toxicol. 2023, 97, 1429–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Sun, L.; Zhang, H.; Shang, L.; Zhao, Y. Microfluidics for Drug Development: From Synthesis to Evaluation. Chem. Rev. 2021, 121, 7468–7529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beißner, N.; Lorenz, T.; Reichl, S. Organ on Chip. In Microsystems for Pharmatechnology: Manipulation of Fluids, Particles, Droplets, and Cells; Dietzel, A., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 299–339. [Google Scholar]
- Ingber, D.E. Developmentally inspired human ‘organs on chips’. Development 2018, 145, dev.156125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingber, D.E. From mechanobiology to developmentally inspired engineering. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2018, 373, 20170323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damiati, S.; Kompella, U.B.; Damiati, S.A.; Kodzius, R. Microfluidic Devices for Drug Delivery Systems and Drug Screening. Genes 2018, 9, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajal, C.; Campisi, M.; Mattu, C.; Chiono, V.; Kamm, R.D. In vitro models of molecular and nano-particle transport across the blood-brain barrier. Biomicrofluidics 2018, 12, 042213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sei, Y.; Justus, K.; LeDuc, P.; Kim, Y. Engineering living systems on chips: From cells to human on chips. Microfluid. Nanofluidics 2014, 16, 907–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawakita, S.; Mandal, K.; Mou, L.; Mecwan, M.M.; Zhu, Y.; Li, S.; Sharma, S.; Hernandez, A.L.; Nguyen, H.T.; Maity, S.; et al. Organ-On-A-Chip Models of the Blood–Brain Barrier: Recent Advances and Future Prospects. Small 2022, 18, 2201401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vatine, G.D.; Barrile, R.; Workman, M.J.; Sances, S.; Barriga, B.K.; Rahnama, M.; Barthakur, S.; Kasendra, M.; Lucchesi, C.; Kerns, J.; et al. Human iPSC-Derived Blood-Brain Barrier Chips Enable Disease Modeling and Personalized Medicine Applications. Cell Stem Cell 2019, 24, 995–1005.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pediaditakis, I.; Kodella, K.R.; Manatakis, D.V.; Le, C.Y.; Barthakur, S.; Sorets, A.; Gravanis, A.; Ewart, L.; Rubin, L.L.; Manolakos, E.S.; et al. A microengineered Brain-Chip to model neuroinflammation in humans. iScience 2022, 25, 104813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nehlig, A.; Daval, J.L.; Debry, G. Caffeine and the central nervous system: Mechanisms of action, biochemical, metabolic and psychostimulant effects. Brain Res. Brain Res. Rev. 1992, 17, 139–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjork, M.H.; Zoega, H.; Leinonen, M.K.; Cohen, J.M.; Dreier, J.W.; Furu, K.; Gilhus, N.E.; Gissler, M.; Halfdanarson, O.; Igland, J.; et al. Association of Prenatal Exposure to Antiseizure Medication with Risk of Autism and Intellectual Disability. JAMA Neurol. 2022, 79, 672–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirsch, A.; Wanounou, M.; Perlman, A.; Hirsh-Raccah, B.; Muszkat, M. The effect of multidrug exposure on neurological manifestations in carbamazepine intoxication: A nested case-control study. BMC Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2020, 21, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akanuma, S.I.; Han, M.; Murayama, Y.; Kubo, Y.; Hosoya, K.I. Differences in Cerebral Distribution between Imipramine and Paroxetine via Membrane Transporters at the Rat Blood-Brain Barrier. Pharm. Res. 2022, 39, 223–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vandenbossche, J.; Huisman, M.; Xu, Y.; Sanderson-Bongiovanni, D.; Soons, P. Loperamide and P-glycoprotein inhibition: Assessment of the clinical relevance. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2010, 62, 401–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamei, J.; Hirano, S.; Miyata, S.; Saitoh, A.; Onodera, K. Effects of first- and second-generation histamine-H1-receptor antagonists on the pentobarbital-induced loss of the righting reflex in streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2005, 97, 266–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greig, N.H.; Soncrant, T.T.; Shetty, H.U.; Momma, S.; Smith, Q.R.; Rapoport, S.I. Brain uptake and anticancer activities of vincristine and vinblastine are restricted by their low cerebrovascular permeability and binding to plasma constituents in rat. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 1990, 26, 263–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pagire, S.H.; Pagire, H.S.; Park, K.Y.; Bae, E.J.; Kim, K.E.; Kim, M.; Yoon, J.; Parameswaran, S.; Choi, J.H.; Park, S.; et al. Identification of New Non-BBB Permeable Tryptophan Hydroxylase Inhibitors for Treating Obesity and Fatty Liver Disease. Molecules 2022, 27, 3417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nacca, A.; Guiso, G.; Fracasso, C.; Cervo, L.; Caccia, S. Brain-to-blood partition and in vivo inhibition of 5-hydroxytryptamine reuptake and quipazine-mediated behaviour of nefazodone and its main active metabolites in rodents. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1998, 125, 1617–1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsui, K.; Mishima, M.; Nagai, Y.; Yuzuriha, T.; Yoshimura, T. Absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion of donepezil (Aricept) after a single oral administration to Rat. Drug Metab. Dispos. 1999, 27, 1406–1414. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Johnson-Anuna, L.N.; Eckert, G.P.; Keller, J.H.; Igbavboa, U.; Franke, C.; Fechner, T.; Schubert-Zsilavecz, M.; Karas, M.; Müller, W.E.; Wood, W.G. Chronic administration of statins alters multiple gene expression patterns in mouse cerebral cortex. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2005, 312, 786–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowland, M.; Tozer, T.N. Time to reach plateau. In Clinical Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics: Concepts and Applications, 5th ed.; Wolters Kluwer Health/Lippincott William & Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2017; pp. 290–297. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.S.; Im, S.H.; Yang, J.Y.; Lee, Y.R.; Kim, G.R.; Chae, J.S.; Shin, D.S.; Song, J.S.; Ahn, S.; Lee, B.H.; et al. Zebrafish as a Screening Model for Testing the Permeability of Blood–Brain Barrier to Small Molecules. Zebrafish 2017, 14, 322–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, N.J.; Hughes, C.C.; Revest, P.A.; Greenwood, J. Development and characterisation of a rat brain capillary endothelial culture: Towards an in vitro blood-brain barrier. J. Cell Sci. 1992, 103 Pt 1, 23–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naik, P.; Cucullo, L. In Vitro Blood–Brain Barrier Models: Current and Perspective Technologies. J. Pharm. Sci. 2012, 101, 1337–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seebach, J.; Dieterich, P.; Luo, F.; Schillers, H.; Vestweber, D.; Oberleithner, H.; Galla, H.-J.; Schnittler, H.-J. Endothelial Barrier Function under Laminar Fluid Shear Stress. Lab. Investig. 2000, 80, 1819–1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinitz, A.; DeStefano, J.; Ye, M.; Wong, A.D.; Searson, P.C. Human brain microvascular endothelial cells resist elongation due to shear stress. Microvasc. Res. 2015, 99, 8–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeda-Murakami, K.; Tani, N.; Ikeda, T.; Aoki, Y.; Ishikawa, T. Central Nervous System Stimulants Limit Caffeine Transport at the Blood-Cerebrospinal Fluid Barrier. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, C.; Marchi, N.; Hossain, M.; Rasmussen, P.; Alexopoulos, A.V.; Gonzalez-Martinez, J.; Yang, H.; Janigro, D. A pro-convulsive carbamazepine metabolite: Quinolinic acid in drug resistant epileptic human brain. Neurobiol. Dis. 2012, 46, 692–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holtzman, C.W.; Wiggins, B.S.; Spinler, S.A. Role of P-glycoprotein in statin drug interactions. Pharmacotherapy 2006, 26, 1601–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez-Figueroa, M.J.; Pessoa-Mahana, C.D.; Palavecino-González, M.E.; Mella-Raipán, J.; Espinosa-Bustos, C.; Lagos-Muñoz, M.E. Evaluation of the membrane permeability (PAMPA and skin) of benzimidazoles with potential cannabinoid activity and their relation with the Biopharmaceutics Classification System (BCS). AAPS PharmSciTech 2011, 12, 573–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozoya-Agullo, I.; Araújo, F.; González-Álvarez, I.; Merino-Sanjuán, M.; González-Álvarez, M.; Bermejo, M.; Sarmento, B. Usefulness of Caco-2/HT29-MTX and Caco-2/HT29-MTX/Raji B Coculture Models To Predict Intestinal and Colonic Permeability Compared to Caco-2 Monoculture. Mol. Pharm. 2017, 14, 1264–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, S.I.; Sei, Y.J.; Park, H.-J.; Kim, J.; Ryu, Y.; Choi, J.J.; Sung, H.-J.; MacDonald, T.J.; Levey, A.I.; Kim, Y. Microengineered human blood–brain barrier platform for understanding nanoparticle transport mechanisms. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Chemicals | Target | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Caffeine (CAF) | CNS stimulant | [20] |
| Carbamazepine (CBZ) | Anticonvulsant drug | [21,22] |
| Desipramine (DES) | Anti-depressant | [23] |
| Loperamide (LPM) | P-gp substrate | [24] |
| Cetirizine (CET) | Antihistamine drug | [25] |
| Vincristine (VIN) | Anticancer drug | [26] |
| LP533401 (LP) | Tryptophan hydroxylase 1 inhibitor | [27] |
| Nefazodone (NZD) | Serotonin antagonist | [28] |
| Donepezil (DPZ) | Cholinesterase inhibitor | [29] |
| Simvastatin (SIM) | Antihyperlipidemic drug | [30] |
| Chemicals | MRM Transition | Collision Energy | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Precursor Ion [M + H]+ | Product Ion | ||
| Caffeine (CAF) | 195.1 | 138.0 | 18.0 |
| Carbamazepine (CBZ) | 237.1 | 194.1 | 14.0 |
| Desipramine (DES) | 266.8 | 72.2 | 31.0 |
| Loperamide (LPM) | 477.1 | 266.1 | 25.0 |
| Cetirizine (CET) | 389.2 | 201 | 25.0 |
| Vincristine (VIN) | 825.4 | 807.4 | 539 |
| LP533401 (LP) | 527.1 | 253.0 | 30.0 |
| Nefazodone (NZD) | 281.3 | 86 | 14.0 |
| Donepezil (DPZ) | 311 | 143 | 10.0 |
| Simvastatin (SIM) | 345.2 | 143 | 18.0 |
| Chemicals | (Brain/Blood) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Caffeine | 2.91 | 114.47 | 2.39 | 49.79 | 0.4349 |
| Carbamazepine | 1.98 | 112.88 | 3.27 | 31.86 | 0.2823 |
| Cetirizine | 2.37 | 314.91 | 4.46 | 24.27 | 0.0771 |
| Desipramine | 57.44 | 234.83 | 34.47 | 73.93 | 0.3148 |
| Donepezil | 16.55 | 106.64 | 14.43 | 51.12 | 0.4794 |
| LP533401 | 6.80 | 573.66 | 0.16 | 9.77 | 0.0170 |
| Loperamide | 58.46 | 684.09 | 20.04 | 37.75 | 0.0552 |
| Nefazodone | 9.01 | 161.89 | 37.79 | 15.43 | 0.0953 |
| Simvastatin | 1.83 | 139.52 | 8.72 | 21.91 | 0.1570 |
| Vincristine | 2.99 | 626.20 | 0.00 | 51.41 | 0.0821 |
| Chemicals | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Caffeine | 44.8098 | 21.52 | 29.9873 |
| Carbamazepine | 28.6749 | 29.41 | 15.7719 |
| Cetirizine | 21.8407 | 40.16 | 7.2984 |
| Desipramine | 66.5383 | 310.22 | 32.4598 |
| Donepezil | 46.0063 | 129.86 | 15.7542 |
| LP533401 | 8.7886 | 1.42 | 2.1693 |
| Loperamide | 33.9736 | 180.32 | 9.2550 |
| Nefazodone | 13.8908 | 340.10 | 3.8408 |
| Simvastatin | 19.7183 | 78.50 | 6.1221 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, J.Y.; Shin, D.-S.; Jeong, M.; Kim, S.S.; Jeong, H.N.; Lee, B.H.; Hwang, K.-S.; Son, Y.; Jeong, H.-C.; Choi, C.-H.; et al. Evaluation of Drug Blood-Brain-Barrier Permeability Using a Microfluidic Chip. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 574. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16050574
Yang JY, Shin D-S, Jeong M, Kim SS, Jeong HN, Lee BH, Hwang K-S, Son Y, Jeong H-C, Choi C-H, et al. Evaluation of Drug Blood-Brain-Barrier Permeability Using a Microfluidic Chip. Pharmaceutics. 2024; 16(5):574. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16050574
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Jung Yoon, Dae-Seop Shin, Moonkyu Jeong, Seong Soon Kim, Ha Neul Jeong, Byung Hoi Lee, Kyu-Seok Hwang, Yuji Son, Hyeon-Cheol Jeong, Chi-Hoon Choi, and et al. 2024. "Evaluation of Drug Blood-Brain-Barrier Permeability Using a Microfluidic Chip" Pharmaceutics 16, no. 5: 574. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16050574
APA StyleYang, J. Y., Shin, D.-S., Jeong, M., Kim, S. S., Jeong, H. N., Lee, B. H., Hwang, K.-S., Son, Y., Jeong, H.-C., Choi, C.-H., Lee, K.-R., & Bae, M. A. (2024). Evaluation of Drug Blood-Brain-Barrier Permeability Using a Microfluidic Chip. Pharmaceutics, 16(5), 574. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16050574