Abstract
The state of well-being and health of our body is regulated by the fine osmotic and biochemical balance established between the cells of the different tissues, organs, and systems. Specific districts of the human body are defined, kept in the correct state of functioning, and, therefore, protected from exogenous or endogenous insults of both mechanical, physical, and biological nature by the presence of different barrier systems. In addition to the placental barrier, which even acts as a linker between two different organisms, the mother and the fetus, all human body barriers, including the blood–brain barrier (BBB), blood–retinal barrier, blood–nerve barrier, blood–lymph barrier, and blood–cerebrospinal fluid barrier, operate to maintain the physiological homeostasis within tissues and organs. From a pharmaceutical point of view, the most challenging is undoubtedly the BBB, since its presence notably complicates the treatment of brain disorders. BBB action can impair the delivery of chemical drugs and biopharmaceuticals into the brain, reducing their therapeutic efficacy and/or increasing their unwanted bioaccumulation in the surrounding healthy tissues. Recent nanotechnological innovation provides advanced biomaterials and ad hoc customized engineering and functionalization methods able to assist in brain-targeted drug delivery. In this context, lipid nanocarriers, including both synthetic (liposomes, solid lipid nanoparticles, nanoemulsions, nanostructured lipid carriers, niosomes, proniosomes, and cubosomes) and cell-derived ones (extracellular vesicles and cell membrane-derived nanocarriers), are considered one of the most successful brain delivery systems due to their reasonable biocompatibility and ability to cross the BBB. This review aims to provide a complete and up-to-date point of view on the efficacy of the most varied lipid carriers, whether FDA-approved, involved in clinical trials, or used in in vitro or in vivo studies, for the treatment of inflammatory, cancerous, or infectious brain diseases.
1. Introduction
One of the main functions of the vascular system is to deliver oxygen and nutrients from the heart to all functional districts and, at the same time, remove carbon dioxide and metabolic waste from tissues. This system is composed of arteries and arterioles, which deliver blood to the tissues of the capillary bed and assist gas and nutrient exchange within tissues, and venules and veins, which drain blood from tissues. The microvasculature, comprising capillaries and postcapillary venules, is the constitutive component for the establishment and maintenance of tissue health via blood perfusion and a dynamic interaction between tissues and the extracellular environment [1].
The unique microvasculature system present in the brain is the blood–brain barrier (BBB). Its peculiarity relies on the presence of continuous non-fenestrated capillaries, allowing at the same time precise regulation of brain homeostasis and protection from physical, chemical, and biological external agents.
However, although the strict selectivity of BBB is necessary for proper brain functioning, it undoubtedly represents an obstacle to the effective delivery of drugs in the case of neurodegenerative diseases or cancer, excluding more than 98% of therapeutic molecules from entering the brain [2]. This BBB feature makes the treatments of many brain diseases, such as brain tumors, Alzheimer’s disease (AD), Parkinson’s disease (PD), and Huntington’s disease (HD), difficult and sometimes ineffective.
There are different methods to increase the efficacy of drug delivery across the BBB, but each of them has some disadvantages. The lipid solubility of the drug can be improved, but it can also affect its pharmacological activity. The BBB could be temporarily and reversibly disrupted in a non-specific manner and could either damage endothelial cells or brain tissues, allowing at the same time the access of harmful or toxic compounds. The BBB could also be bypassed through the intranasal route, limiting drug administration, and by means of invasive approaches, causing patient discomfort and possible sites of pathogen entry [3].
However, new targeted drug delivery approaches based on inorganic and organic nanoparticles (NPs) use provide a systemic brain-targeted administration with limited off-target effects and damages to the BBB. Inorganic NPs are non-degradable, have intrinsic toxicity, and are frequently used as contrast agents in imaging. Organic NPs characterized by higher biocompatibility, lower toxicity, and extensive loading and functionalization possibilities are often employed as nanocarriers for BBB crossing.
This field develops very rapidly, and in this updated review, we give an overview of the BBB structure and physiopathology, shedding light on the universally recognized mechanisms regarding the different ways to approach this barrier. Among the various strategies developed to deliver drugs to the brain, besides methods that use ligand conjugation for active targeting and techniques allowing temporary BBB disruption, many recent nanotechnological solutions have been designed to enhance the efficacy of the available pharmacological treatments for brain diseases. Many nanocarriers have been designed and tested as central nervous system (CNS) delivery systems, both for diagnosis and/or therapy [4,5,6], and in this review, we focused our attention on the lipid-based ones. Nanocarriers such as liposomes, solid lipid nanoparticles (SLNs), nanoemulsions (NEs), nanostructured lipid carriers (NLCs), niosomes, proniosomes, cubosomes, extracellular vesicles (EVs), and cell membrane-derived nanocarriers were described. For each of these categories of lipid nanocarriers, a table containing the experimental studies published from 2016 to date referring to specific brain diseases for both in vitro and in vivo studies was reported. For each nanocarrier, we combined a detailed description not only regarding its therapeutic cargoes but also all the functionalization methods and/or solutions applied to target the brain, highlighting the nanocarriers that have already undergone clinical trials.
2. The Blood–Brain Barrier
Between the end of the 19th century and the beginning of the 20th century, microbiologists Paul Ehrlich and his student Edwin Goldmann observed during histological labeling experiments that when a dye is injected systemically, it does not reach the brain, while if injected in the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), it does not spread to the other organs. However, in 1898, Max Lewandowsky was the first researcher to postulate the existence of a specialized barrier in the brain; thus, he coined the term BBB. Only in the late 1960s did Reese and Karnovsky visualize the BBB during electron microscopy experiments [7,8].
The BBB strictly controls the permeability of cerebral capillaries and, selectively filtering what should enter the brain and what should not, ensures that the right concentrations of ions, amino acids, and peptides are maintained, preserving the homeostasis of the brain microenvironment [9].
2.1. BBB Structure
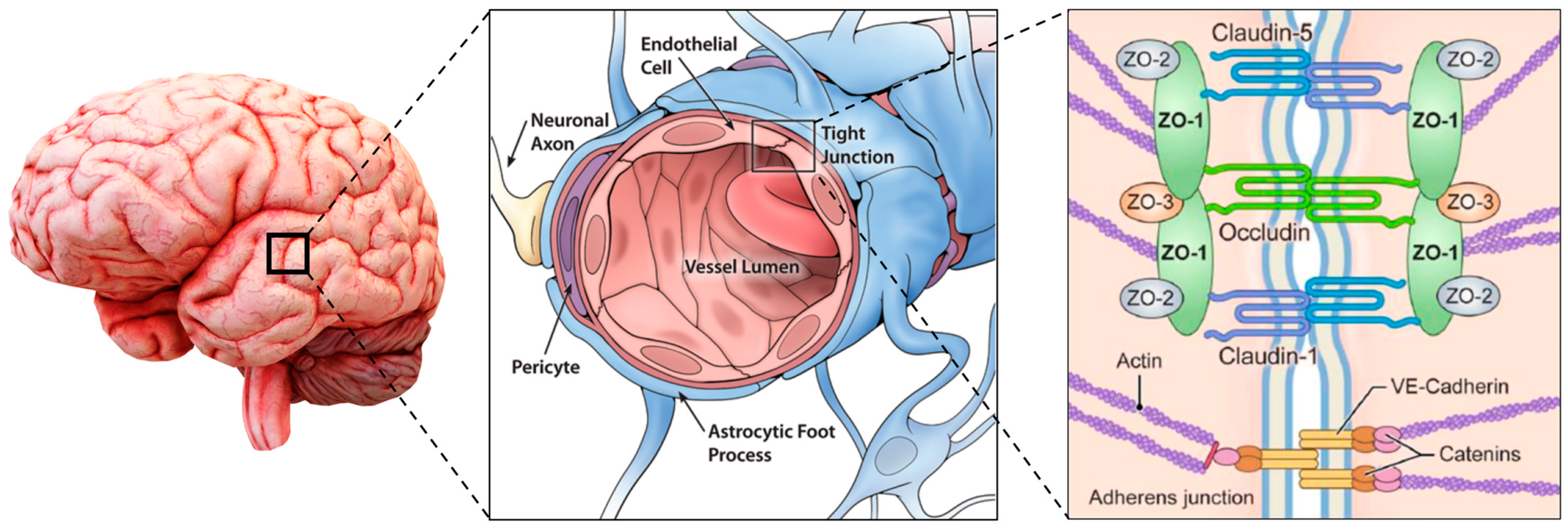
The physiological filtering properties of the BBB are conferred by the interactions between different cell lines: those constituting the blood vessels, endothelial (ECs) and mural (MCs) cells, glial and neural cells, and those of the immune system. The structure of the BBB is represented in Figure 1.
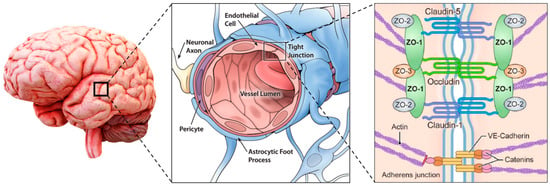
Figure 1.
Scheme of the BBB neurovascular unit, modified from [10,11].
2.1.1. Endothelial Cells and Junctions
The endothelial cells are squamous epithelial cells forming the walls of the vessels, and, in the central nervous system, they are phenotypically different from the ones located in other parts of the body. They have a luminal/abluminal polarization and tightly regulate the ions, molecules, and cell exchange through the tight junctions (TJs), which strictly limit the paracellular flux of solutes. In addition, CNS ECs have extremely low rates of transcytosis if compared with other ECs, greatly restricting vesicle-mediated transcellular transport. CNS ECs have peculiar features that could be found only in BBB and allow them to tightly regulate CNS homeostasis. In detail, they express efflux transporters for lipophilic molecules and highly specific transporters for the conveyance of nutrients and the removal of waste products.
If compared to ECs from other tissues, CNS ECs have a higher number of mitochondria to generate the adenosine triphosphate (ATP) needed for transport functions, low levels of leukocyte adhesion molecules to limit immune cell entry, and a different metabolism to alter the physical properties of molecules, changing their reactivity, solubility, and transport properties [12].
ECs are sealed in their conjunction sites by different types of junctions. Tight junctions, which include integral membrane proteins such as claudin, occludin, junction adhesion molecules, and various cytoplasmic accessory proteins, are close to the apical membrane and limit the paracellular diffusion of solutes across the BBB [13]. TJs proteins are connected to the actin and vinculin-based cytoskeletal filaments via scaffolding proteins of the membrane-associated guanylate kinase family zonula occludens (ZO)-1, -2, and -3 [14].
TJs are stabilized by adherens junctions (AJs), which are close to the basolateral membrane and comprise cadherin, catenin, alpha-actinin, and vinculin, forming homophilic endothelial-to-endothelial contacts roughly 20 nm wide and participating in the development and preservation of TJs [15]. AJs are connected to the EC cytoskeleton, modulate receptor signaling, and regulate the transendothelial migration of immune cells [14]. AJs are crucial for the integrity of TJs, and their damage leads to disruption of the BBB. The reduction in TJs increases the probability of tumor metastasis since they are on the frontlines as the structure that cancer cells must overcome to metastasize [16].
In addition to the previous ones, there are also the gap junctions, which include connexin-37, 40, and 43, and they establish hemichannels between ECs, allowing endothelial intercellular communications, but also maintaining the TJs integrity [14].
The restrictions on the paracellular movement of ions and charged molecules cause a high transendothelial electrical resistance measurable across the BBB [17].
2.1.2. Basement Membrane
The basement membrane (BM) surrounds the blood vessels and can be divided into the inner vascular BM, secreted by ECs and pericytes (PCs), and the outer parenchymal BM, secreted by astrocytes. It is composed of different molecules, such as type IV collagens, laminin, nidogen, heparin sulfate proteoglycans, and other glycoproteins. Besides the support function, the BM also acts as an additional barrier. During different neurological diseases, BM is impaired by matrix metalloproteinases, leading to leakage in its barrier functions.
2.1.3. Pericytes
Pericytes are contractile MCs that partially wrap around the abluminal surface of ECs with their long cellular processes and are included in the BM. They can tune the diameter of the capillary and thus the blood flow in response to neural activity, thanks to contractile proteins. They also play a key role in angiogenesis, deposition of extracellular matrix, wound healing, and immune cell infiltration. They closely interact with ECs, and a disruption of these interactions may lead to BBB dysfunction and neuroinflammation.
2.1.4. Astrocytes
The major type of glial cells in the BBB are astrocytes (ACs), and their end-feet, surrounding ECs, BMs, and PCs, provide a link between the neuronal circuitry and the bloodstream.
Moreover, ASs can also increase the level of TJ proteins and inhibit the differentiation of pericytes, essential functions to maintain BBB integrity and low permeability.
In the BBB, there are different types of ACs, depending on their morphology, origin, density, and function, and eventually adapting to the needs of the microenvironment. The most abundant types are protoplasmic astrocytes in the gray matter, with many radially extending processes, and fibrous astrocytes in the white matter, with smoother and longer processes [18].
2.1.5. Microglia
Microglia are monocyte-resident cells throughout the brain and spinal cord. Being the resident macrophage cells, their main functions are immune defense and CNS preservation, but they can also modulate the expression of TJs [19].
2.2. BBB Transport Mechanisms
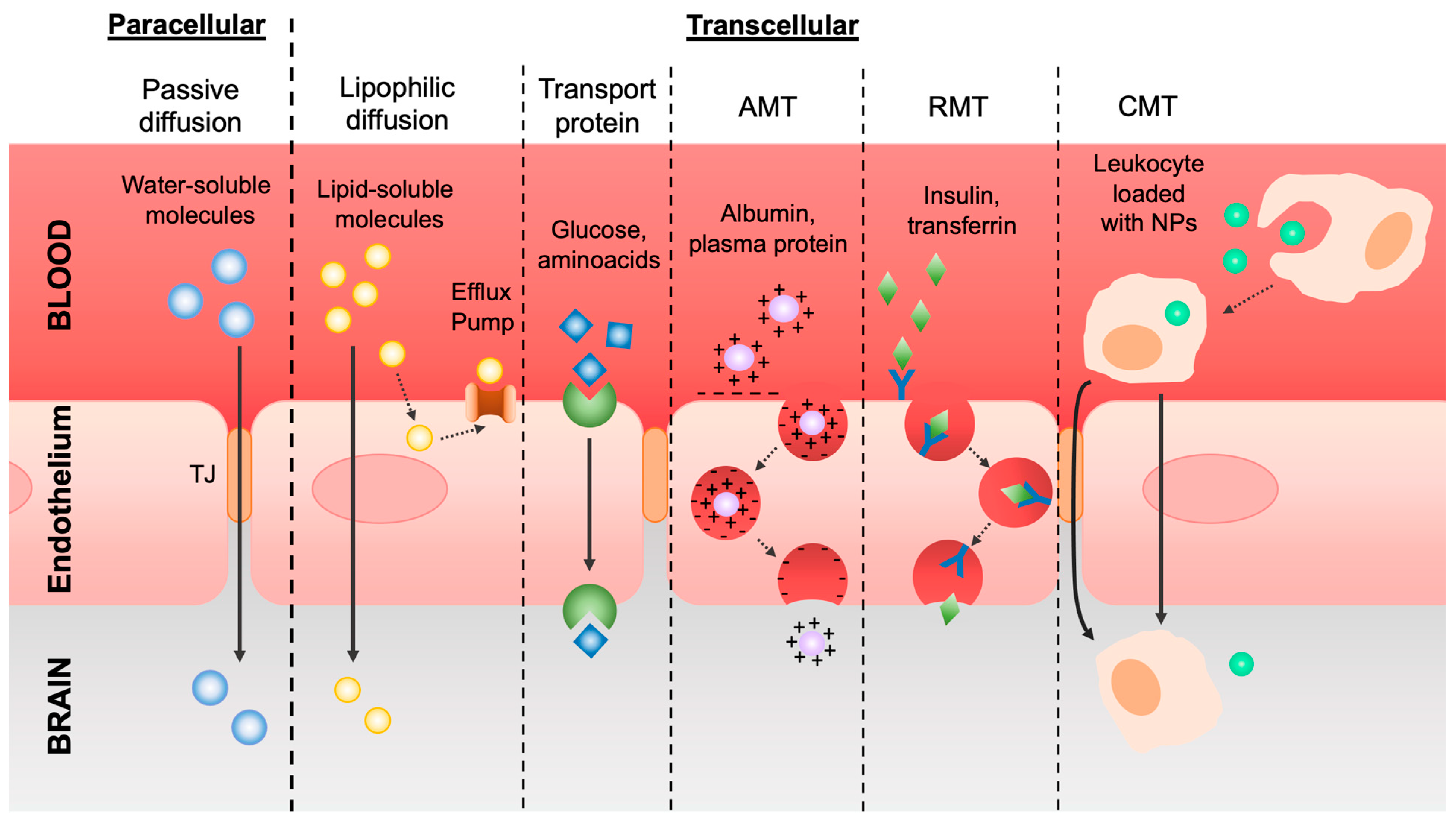
Flow across the BBB is regulated through different transport mechanisms (Figure 2).
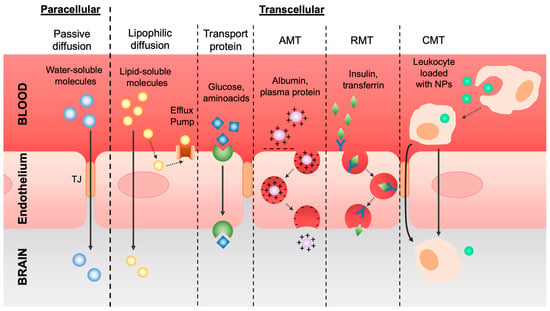
Figure 2.
The different molecules’ transport mechanisms in the BBB are divided into paracellular and transcellular.
The first mechanism of transport is the one referred to as the diffusion of molecules via the paracellular or transcellular pathways. Small water-soluble molecules can cross the BBB through paracellular passive diffusion following the negative gradient of concentration across the TJs. In addition, the presence of particular enzymes in the abluminal part of the vessels causes the degradation of unwanted small molecules that eventually infiltrate by this mechanism. Lipophilic, non-polar, and low-molecular-weight molecules, such as oxygen and carbon dioxide, but also alcohol and anesthetics, can cross the membranes of the ECs, entering the BBB via a transcellular pathway.
To eventually remedy harmful lipophilic molecules permeation, on the membranes of ECs there are efflux pumps able to drain these substances out of the cerebral tissue into the bloodstream. The most important one is the active drug efflux transporter of the ATP-binding cassette (ABC) gene family, which is notably responsible for drug distribution and elimination from the CNS and is understandably one of the major obstacles to effective drug delivery to the brain [20].
In contrast, polar and high-molecular-weight molecules, such as glucose and amino acids, which cannot easily cross the BBB through passive diffusion, exploit transport proteins or carriers. These types of solutes bind to a transporter on the luminal side of the EC membrane and, triggering a conformational change in the protein, are released by the abluminal side in the brain. This active transport depends on Na+ gradients such as sodium-dependent glucose transporters and amino acid transporters of glutamate and aspartate [21].
Regarding ions, their permeability is driven by an electrostatic interaction between the macromolecules’ positive charge and the negatively charged membranes, following a pathway called adsorptive-mediated transcytosis (AMT), or pinocytosis. Cationic molecules, such as cationized albumin and cell-penetrating peptides, bind to the luminal surface of ECs and are then exocytozed at the abluminal surface [22].
Another type of transcytosis is receptor-mediated transcytosis (RMT), for the selective delivery of macromolecules, including transferrin, melanotransferrin, insulin, leptin, TNF-alpha, and epidermal growth factor. In detail, the specific macromolecules (ligands) bind to the specific receptors in clathrin-coated pits, specialized areas of the plasma membrane. Then, these coated pits invaginate into the cytoplasm, forming coated vesicles. The ligand can dissociate from the receptor once the acidification of the endosome is complete and cross to the other side of the membrane [20,23].
In addition to these mechanisms, there is also cell-mediated transcytosis (CMT), which is usually exploited by pathogens to enter the CNS but can also be exploited for drug transport. In brief, pathogens or drugs can be easily phagocytized by leukocytes and then cross the BBB through diapedesis and chemotaxis. The infiltration of the immune cells is a dynamic and complex procedure that requires a series of stages such as tethering, rolling, crawling, arrest, and diapedesis across the ECs. However, in pathological conditions, the TJs among ECs may be disturbed by cytokines and other proinflammatory factors, letting macrophages and monocytes enter the brain by paracellular and transcellular pathways [12,24].
3. Brain Diseases
Besides the recent advancement in medicine, brain diseases remain one of the most important causes of death, health loss, and disability worldwide; according to the World Health Organization, 3.4 billion people are affected by neurological pathologies or disorders [25]. The difficulty of treatment of brain diseases mainly relies on their heterogeneity, the lack of proper preclinical models, and, overall, the presence of the BBB, which rejects more than 98% of the substances used for therapeutic treatment [26].
The role of the BBB is key for the diagnosis and especially for the treatment of brain diseases. Its integrity is physiologically related to the health status and the age of the patients, and it could be directly impaired by some brain diseases, such as stroke, tumors, or neurodegenerative diseases. An impaired BBB can cause an alteration to brain homeostasis, such as ion imbalance and the entry of immune cells and molecules, potentially leading to neuronal dysfunction and degeneration [1]. Many studies have shown that plasma proteins can be neurotoxic, suggesting that even if a compromised BBB does not cause these disorders, it can exacerbate them [13]. Furthermore, BBB, by using standard drug delivery administration methods, mechanically and biochemically prevents the efficient delivery of therapeutics in the brain to the injured sites, and, if locally delivered, its presence notably limits the diffusion of the active molecules. In the following paragraphs, we give an overview of the most diffused brain pathologies.
3.1. Stroke
Stroke is one of the most common causes of adult disability and/or death. After an ischemic or hemorrhagic stroke, the intense neuroinflammation unleashes a cascade of events, such as acute BBB breakdown, cytotoxic and vasogenic edema, and hemorrhagic transformation, to remove the damaged tissue and prepare the brain for repair. It also contributes to neuronal injury and worsens neurological outcomes. Besides, in an early phase, neuroinflammation causes brain damage; it could later promote recovery by facilitating neurogenesis, angiogenesis, and neuronal plasticity [27].
A cerebral stroke leads to a hypoxic state, causing an increase in BBB permeability and TJ alterations. This increased permeability could be continuous, monophasic, or biphasic, with an early phase just after the onset of hypoxia/ischemia and a later one after several days. The degree of the altered permeability depends on the type, degree, and duration of occlusion [13].
The presence of comorbidities, such as hypertension and hyperglycemia, can induce anatomical and functional changes to the brain vasculature and often exacerbate BBB disruption after ischemia.
Currently, therapies for acute ischemic stroke are mostly based on tissue plasminogen activator-mediated thrombolysis, even if they are not always applicable [28].
3.2. Neurodegenerative Diseases
Alzheimer’s disease is one of the most common dementia disorders and is associated with cognitive decline and memory loss. AD is characterized by the presence of insoluble plaques of amyloid beta protein (Aβ) and neurofibrillary tangles constituted by hyperphosphorylated intraneuronal deposits of microtubule-associated protein tau (τ), which lead to neuronal cell death and loss of synapse [29]. This peptide aggregation is due to dysfunctional mitochondrial production of reactive oxygen species and dyshomeostasis of metals from oxidative stress [30]. Many studies have highlighted an increased extravasation of plasma proteins in AD brains, suggesting dysfunctional BBB properties. This dysfunction is probably caused by Aβ and τ accumulation in the perivascular areas and includes increased BBB permeability, microbleeds, reduced TJs’ expression, impaired transporter expression, accumulation of blood-derived products, and degeneration of PCs and ECs. Thus, toxic molecules, cells, and pathogens can enter the brain and trigger the inflammatory response, leading to disease progression and eventually causing cerebral amyloid angiopathy [31].
Parkinson’s disease is another common neurodegenerative disease affecting 2–3% of the population over 65 years old with motor dysfunctions, including tremor, rigidity, akinesia or bradykinesia, and postural instability. It is characterized by neural loss in the substantia nigra causing striatal dopamine deficiency, and Lewy is made of misfolded α-synuclein, neurofilaments, and ubiquitin in dopaminergic neurons and glial cells [32].
In PD, there is a BBB disruption detected by the increase in albumin level and immunoglobulin G in CSF, erythrocytes, hemoglobin, and fibrin extravasation in the striatum, and the reduction in ZO-1 and occludin [13]. There is no cure for PD, but some treatments could prevent the progression of the disease, such as the administration of DOPA agonists, DOPA precursors (or L-DOPA), amantadine, and anticholinergics [33].
Huntington’s disease is caused by an autosomal-dominant mutation: an expanded trinucleotide repetition of the CAG sequence in the gene HTT5 on chromosome 4 due to the abnormal pathogenic multifunctional protein huntingtin. It results in a progressive loss of neural function, resulting in movement, cognitive, and psychiatric problems, influenced by epigenetic, oxidative stress, metabolic, and nutritional factors. Post-mortem magnetic resonance (MR) studies showed increased BBB permeability, fibrin deposition, and a reduction in occludin and claudin-5 expression [13]. Currently, there is no effective therapy for the treatment or the reduction in HD progression [33].
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is the most common non-traumatic disabling disease affecting young adults, with an increasing incidence worldwide.
The onset of MS is associated with peripheral immune activation followed by CNS immune aggression, which causes demyelination and axonal loss, leading to neurodegeneration and irreversible neurological impairment. The most important pathological hallmarks of MS are BBB disruption, changes in the BBB endothelium, and lymphocyte trafficking [34]. It is generally considered a two-stage disease, characterized by early inflammation responsible for relapsing–remitting disease and then delayed neurodegeneration causing non-relapsing progression [35].
Prion diseases, or transmissible spongiform encephalopathies, are rare and fatal neurodegenerative disorders, including Creutzfeldt–Jakob disease, Gerstmann–Sträussler–Scheinker syndrome, fatal familial insomnia, and kuru in humans. Prions are nucleic acid-free structures, mainly composed of scrapie prion protein, a misfolded isoform of the host-derived cellular prion protein, and this transition is a key event for prion infection and propagation. The etiology of prion diseases can be sporadic, inherited, or caused by iatrogenic or dietary prion assumptions and lead to spongiform changes, neuronal loss, and neuroinflammatory responses [36].
3.3. Brain Tumors
Brain tumors are a heterogeneous group of both benign and malignant cancers in the brain parenchyma and surrounding tissues. They have relevant morbidity and mortality in both adults and children, often generating severe disabilities [37]. They can be classified as primary, when they arise from the glia and are usually called gliomas, or metastatic, when they originate from systemic cancers and further form metastasis in the brain parenchyma.
The most common ones are astrocytomas, oligodendrogliomas, and oligoastrocytomas. Astrocytoma arises from the ACs and is classified from grade I to grade IV, depending on histological findings. Grades I and II are low-grade, grade III is high-grade or anaplastic astrocytoma, and grade IV is also called glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) or malignant astrocytic glioma and is the most aggressive type. Oligodendrogliomas originate from oligodendrocytes or a glial precursor cell, while oligoastrocytomas have a mixed appearance of glial cell origin, astrocytoma, and oligodendroglioma.
The major hurdles in effective gliomas’ treatments are related to the complex anatomy of the brain, to the difficulties in identifying tumor burdens, to chemoresistance, and to the concrete possibility of reaching the tumor sites in a therapeutic dose, avoiding overtreatments, and reducing the incidence and severity of adverse effects [38].
3.4. Infectious Diseases
Infections of the brain are caused by pathogens entering the BBB that normally prevent microbial invasions. Bacteria, viruses, fungi, and parasites can cause infections in the meningeal or parenchymal compartments, leading to meningitis or encephalitis, respectively [39,40,41].
Bacterial infections could be limited to localized focal infections, such as brain abscesses, or spread to meningoencephalitis. Bacteria could reach the brain from the upper airways, through the bloodstream from another primary site, or from a direct inoculation due to an injury or surgery. The most typical bacteria affecting the human brain are Streptococcus pneumoniae, Neisseria meningitidis, Hemophilus influenzae, and Listeria monocytogenes, while Escherichia coli and group B Streptococcus can affect neonates [42].
Viral meningitis and encephalitis are the most frequent brain infections, mostly caused by enteroviruses, parechoviruses, herpes simplex, varicella-zoster, Epstein–Barr virus, rabies, human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), measles, and COVID-19. These viral infections could potentially lead to neurological disorders [43,44]. Viruses can affect the brain in three different ways: by a direct invasion, causing encephalitis, inflammation, or necrosis, leading to permanent disability or death, as a result of a viral infection elsewhere in the body, from where inflammatory cytokines reach and cross the BBB, or this infection in another site may damage the brain through a long-range action through other mechanisms [45].
Fungal brain infections are usually opportunistic in immunocompromised patients, even though immunocompetent people with predisposing environmental and iatrogenic factors can be possible hosts. These infections originate from the direct inoculation of fungal spores, coming from yeasts, molds, and dimorphic fungi, after trauma or surgery. The most common infection is cryptococcal meningoencephalitis; candidiasis is a typical nosocomial infection; aspergillosis and mucormycosis, although rare, are devastating in immunosuppressed patients; and cerebral phaeohyphomycosis strike immunocompetent people [46,47].
Brain parasitic diseases are a huge issue, especially in low- and middle-income countries. The symptoms are very unspecific, such as meningitis, encephalitis, ventriculitis, myelitis, or brain abscess, with fever and headaches. Nematode infections cause eosinophilic meningoencephalitis, Taenia solium neurocysticercosis, which leads to epileptic seizures, some protozoan species, and free-living amoebae [47,48].
4. Drug Delivery across the BBB
At this point in the discussion, it should be clear that the BBB plays a key role in determining the success or failure of a therapy for any brain pathology. The role of this barrier is crucial because it must allow a specific drug to reach the exact site to be treated in the brain in the right dose and because, at the same time, it must prevent drugs used to treat pathologies in other areas of the human body from causing neurological damage.
Below is a list and description of all the ways in which it is possible to carry out therapies in the brain across the BBB by bypassing it, temporarily disrupting it, or by means of ligand conjugation.
4.1. Bypassing the BBB
4.1.1. Intracerebroventricular
The intracerebroventricular (ICV) administration route consists of the direct injection of the drug into the CSF of the lateral cerebral ventricle after the penetration of the skull, using a catheter with an implantable reservoir or a pump. The pump is the most used since it guarantees a more continuous and elevated concentration of drug in the CSF. This method of administration allows a reduction in systemic side effects and avoids drug metabolism in blood serum and opsonization [49]. However, ICV administration has some significant drawbacks and risks. The CSF is turned over every 4–5 h via bulk flow and absorbed into the bloodstream; conversely, the ICV-infused drug can penetrate the brain by diffusion. The rate of CSF bulk flow is orders of magnitude greater than diffusion, so drugs often exit the ventricles faster than they can diffuse into the brain. In addition, the process is invasive and is often associated with other risks. For instance, catheter placement risks include hemorrhage, postoperative infection, and mispositioning. Some drugs could cause seizures and chemical arachnoiditis that could turn into leukoencephalopathy, but infections remain an important adverse effect that occurs either during the insertion of the device or for improper aseptic reservoir access [50,51,52].
4.1.2. Intracerebral/Intraparenchymal
Intracerebral or intraparenchymal (IC/IP) administration is the most direct method since it delivers the drugs directly to the brain site through an implant or injection, and it spreads with a passive diffusion mechanism [53]. As with ICV, the process is very slow, and the drug can diffuse only up to 2 mm from the site of injection.
4.1.3. Convection-Enhanced Delivery
Convection-enhanced delivery (CED) is a stereotactically guided drug delivery method in which the drug is delivered directly into targeted brain parenchymal cells. After a minimally invasive surgical exposure of the brain, one or more small catheters or micro-infusion pumps are placed into the parenchyma, allowing the delivery of drugs and ensuring a sustained therapeutic concentration [54]. CED has demonstrated potential utility in treating brain malignancies, but there are two main problems: the first is the high-flow-rate infusion for a uniform distribution across a large volume, and the second is the use of a large cannula to achieve this flux. The high flow rate induces damage to tissues at the infusion site and induces backflow along the insertion tract. At the same time, the large cannula can lead to inflammation, tissue damage, and scarring around the device [55].
4.1.4. Implants
Polymeric implants and interstitial wafers are often used, for example, for glioblastoma’s treatment. However, they have poor drug penetration beyond the resection cavity, drug dosage is limited by the implant size, and they are associated with high intracranial pressures and local toxicity, causing infections and brain trauma [54,56,57].
4.1.5. Intranasal Delivery
Intranasal delivery is a non-invasive approach for the delivery of therapeutics to the brain across the olfactory mucosa and along the connective tissue around the olfactory nerve bundle or axons of olfactory neurons, thus bypassing the BBB. This approach, guaranteeing a nose-to-brain direct delivery, enhances drug targeting and bioavailability with a faster brain delivery and, avoiding the metabolism of the liver, decreases drug accumulation in non-targeting tissues, minimizing side effects [58].
Once the intranasal-administered molecules reach the origins of the olfactory and trigeminal nerves in the cerebrum and pons, respectively, they are dispersed throughout the brain following different mechanisms: intracellular and extracellular. In the intracellular one, the molecule is internalized by an olfactory neuron, transported by an endocytic vesicle to the neuron’s projection site, and then exocytosed. Conversely, in the extracellular pathway, the molecule crosses the nasal epithelium, reaching the lamina propria, where the neurons are located, and it is transported externally along the neuronal axon by bulk flow processes [59,60].
Besides the advantages of this administration method, it also has some drawbacks due to the poor permeability of drugs from the nasal mucosa, their enzymatic degradation and mucociliary clearance, the low retention time, and nasomucosal toxicity. The clinical application of intranasal delivery is limited by the necessary high and frequent doses since each human nostril has an administration volume <200 μL and at most, 1% of the drug reaches the brain, moreover, strongly irritating the nasal mucosa [61]. In addition, the formulations have a short residence time in the nose (15–30 min), which confines the drug adsorption. Furthermore, the enzymes of the nasal cavities can enzymatically metabolize many sensitive drugs, and the formulations must have pH values and viscosities compatible with those of the nasal mucosa, such as not inducing irritation or inflammation of the nasal epithelium [62].
The most commonly used nanocarriers for intranasal delivery are SLNs and NLCs for their improved nasal retention, biocompatibility, drug solubility and permeability, reduced mucociliary clearance, and drug enzymatic degradation.
4.2. Temporary Disruption of the BBB
The temporary disruption of the BBB is the most commonly used method to deliver drugs from the bloodstream to the CNS.
Besides the pathological degradation of the BBB, where a therapeutic nanocarrier administered intravenously could, in theory, directly accumulate in these diseased regions, temporary induced BBB permeability could be achieved with some strategies, such as the administration of chemical agents, ultrasounds (US), and magnetic fields [63].
4.2.1. Osmotic Disruption
The temporary osmotic BBB disruption is based on the high osmotic pressure induced by the administration of chemical substances such as mannitol, fructose, milk amide, urea, and glycerol. The injection of hyperosmolar agents at a flow rate sufficient to allow a complete filling of the vessel without producing significant reflux in the common carotid artery leads to the reversible dehydration of brain ECs and subsequent disruption of the TJs. This method intervenes in the overcoming of the sink effect, which is the accumulation of the chemotherapeutic drug in tumor necrotic areas, seizing them from the periphery of the tumor, such as the highly proliferative tumor edges with neoplastic cells. In fact, ensuring a more uniform delivery to the entire CNS vascular territory, including tumor edges, osmotic disruption (OD) provides longer tumor cell exposure to higher concentrations of the drugs [64]. However, BBB’s OD temporarily increases the fluid influx, potentially leading to a transient cerebral edema and the entrance of not only molecular components, which can cause neuropathological changes, neurological toxicity, aphasia, and hemiparesis, but also toxic and harmful agents, possibly resulting in a change in the normal functions of the CNS [58,64].
4.2.2. Ultrasound Disruption
The transient disruption of the BBB using high-intensity focused US is based on the combination of US, that can pass through the skull and converge at a specific focal point inside the brain and intravenously injected microbubbles (MBs). These MBs, excited by the rarefactions and compressions provided by US, start to oscillate, exerting a mechanical stress on the cells, leading to the opening of TJs. This BBB disruption effect lasts usually for 4–6 h, but it can vary according to the patient, the intensity of US, and the size and concentration of the MBs [58,64]. In addition, these US favor the active transport of molecules across the BBB, for example, by enhancing the delivery through vesicles and carrier proteins or modulating mechanosensitive ion channels, they can cause convective flux in the tumor interstitial space, and they can remodel brain vasculature and stimulate the development of new neurons [65,66,67]. This approach is currently on clinical trials for gliomas (NCT03322813, NCT02343991, NCT03616860, and NCT03551249) [68,69,70], recurrent GBM (NCT02253212, NCT03626896, and NCT03712293) [71,72,73], amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (NCT03321487) [74], PD (NCT03608553 and NCT04370665) [75], and AD (NCT02986932, NCT03671889, NCT03739905, and NCT04118764) [76,77,78]. Although undoubtedly advantageous, especially for big molecules (500–2000 kDa), BBB US disruption also provides inherent risks, such as large volumetric oscillations of the MBs and, potentially, their collapse, which can generate extra mechanical stresses on the capillaries in the form of micro-jets that can damage the surrounding capillary and brain parenchyma [64,79].
4.2.3. Optical Disruption
The optical disruption of BBB consists in the illumination of a brain region, inducing the internalization of junction molecules and locally opening the BBB for up to 48 h. This optical disruption can be obtained in two different ways: using photodynamic or laser interstitial thermal therapy (LITT) [80]. In the first way, the light activates some photosensitizers (such as fluorescent dyes), which generate reactive oxygen species, inducing changes in junction morphology and increasing BBB permeability with high spatiotemporal selectivity [81]. LITT uses laser energy to generate heat in the target tissue, and it can temporally increase the BBB permeability, enhancing the secretion of heat shock proteins and nitric oxide [80]. LITT, applied to enhance BBB permeability, has undergone some clinical trials, such as NCT01851733 in combination with doxorubicin [82] or NCT02311582 with pembrolizumab [83]. The optical disruption of the BBB requests the exposition of the brain by creating an optical window in the skull.
4.2.4. Electrical Disruption
The electrical disruption of the BBB can be achieved either by transcranial stimulation applying electrodes to the skull or by using penetrating electrodes to generate pulsed electric fields (PEF) to provoke and electroporation (EP) of the BBB. In transcranial stimulation, there is increased permeability, probably due to the increased convection through the gaps between TJs. When PEFs are applied to cells or tissue, they change the innate electrical potential across the cell membranes. The destabilization of membrane potential creates nanoscale aqueous pores in the lipid bilayers, resulting in an increased membrane’s permeability, termed electroporation. After the EP, if membranes reseal, it is called a reversible EP, while if it leads to cell death, it is an irreversible EP [84]. Electrical stimulation has shown cognitive and therapeutic effects, but its safety, efficacy, and the potential risk of increased exposure to toxins and pathogens have not been fully evaluated. In addition, EP probes are highly invasive, and if they must be inserted in deep brain regions, they could cause long-term damage [80].
4.2.5. Radiation Therapy Disruption
Since ECs and oligodendrocytes are radiation-responsive, ionizing radiation can be used in a controlled and targeted way to selectively damage BBB tissues, increasing their permeability. High doses of radiation can favor BBB permeability through TJ modifications, cell density reduction, and the formation of actin stress fibers. Few clinical trials, such as NCT02974803, have been conducted using this method despite showing promising results; the optimal radiation dose and therapeutic window are still not determined, and the side effects remain serious [85].
4.3. Ligands Conjugation for Active Brain Targeting
Besides the just-described methods to bypass or temporarily disrupt the BBB for drug delivery to the brain, many nanotechnological solutions have been designed to enhance BBB penetration [86]. In the following paragraph, some of the most commonly used functionalization approaches have been reported. The delivery of drugs to the brain occurs through different mechanisms, according to molecules’ physicochemical properties, such as adsorptive-mediated transcytosis, receptor-mediated transcytosis, transporter-mediated transcytosis (TMT), and cell-mediated transcytosis [4,87].
4.3.1. Adsorptive-Mediated Transcytosis
Cardiolipin
Cardiolipin is a component of the mitochondrial membrane and is necessary for numerous enzymatic activities for mitochondrial energy metabolism. Since cardiolipin is positively charged, it can cross the BBB through AMT. Interestingly, in the case of AD, nanocarriers functionalized with cardiolipin cannot by themselves decrease Aβ fibrils in the brain, but they reveal a high affinity for these fibrils, opening new perspectives for the generation of new vehicles for imaging and new therapeutic agents [87].
Heparin
Heparin is a polyanionic polysaccharide of the glycosaminoglycans family widely used in nanomedicine in the oncological, coagulation, tissue engineering, and drug delivery fields. It demonstrated an innate ability to compete with Aβ peptides in binding to proteoglycans, properties particularly interesting for AD therapy [87].
Cell-Penetrating Peptides
Cell-penetrating peptides (CPPs) are small cationic or amphipathic peptides that can be translocated across cell membranes, delivering the associated compounds inside cells without compromising their properties, exploiting the presence of peptide sequences called protein transduction domains. They also have a positive charge, which can favor electrostatic interactions with membranes.
An example of CPP is poly-l-Arginine, which is a synthetic cationic peptide constituted by eight or more arginine residues and is one of the most widely used peptides in drug delivery. Another CPP is penetratin, which enhances internalization across epithelial cells in a two-step mechanism: penetratin binds cell-surface lipids through electrostatic interactions and is translocated via tryptophan-induced destabilization [88]. Other CPPs are penetratin, SynB, HIV-1 trans-activator of transcription (TAT) protein, and octa-arginine (R8) [4].
4.3.2. Receptor-Mediated Transcytosis
Transferrin Receptor
Transferrin (Tf) receptors (TfR) are transmembrane glycoproteins constituted of two subunits of 90 kDa linked by a disulfide bridge, and each of them can bind one molecule of transferrin [88]. TfR can be exploited for brain delivery since it is overexpressed on brain capillary endothelial cells, but it must be considered that TfR is also expressed on other cells, such as hepatocytes and monocytes, besides BBB, that the high concentration of endogenous serum transferrin typically saturates all the receptors, and that it can lead to an overdose of iron transport into the brain [89,90]. To overcome these limitations, NPs can be conjugated with the transferrin monoclonal antibody (OX-26), since they bind to a different site than the transferrin protein, interfering less with endogenous transferrin [90]. Another alternative is T7 (HAIYPRH), which is a heptapeptide that can bind to TfR with high affinity without any competitive inhibition with endogenous Tf since they bind to different sites of TfR [88].
Lactoferrin Receptor
The lactoferrin (Lf) receptor (LfR), a single-chain cationic-iron-binding glycoprotein of the TfR family, is constituted by a homodimer and has anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, and immunomodulatory functions. The LfR has two binding sites, a high-affinity and a low-affinity one, and their sizes and features change depending on the cell types, opening the possibility of targeting a particular LfR [58,91]. Tf and Lf have similar characteristics, but lactoferrin has a lower plasma concentration and a unidirectional brain uptake mechanism [88]. In addition, LfRs are overexpressed on the BBB in several neurological conditions, such as AD, PD, and HD [92].
Lipoproteins Receptor
Low-density lipoprotein (LDL) receptor (LDLR) is the removal of highly atherogenic LDL from the circulation; in particular, LDLR, LDLR-related protein (LRP) 1, and very low-density lipoprotein receptor are overexpressed on brain ECs. Alipoproteins B and E (ApoB and ApoE) are soluble apolipoproteins that bind to the LDL receptor and, thus, can be exploited to cross the BBB. ApoE and apoB have demonstrated efficacy but have innate protein instability and compete with LDL [88]. An alternative to ApoE functionalization is the coating of NPs with Tween 80, since it induces the adsorption of ApoE present in the bloodstream’s systemic circulation.
Angiopep-2 is a 19 amino acid peptide derived from the Kunitz domains of aprotinin and other human proteins, which are ligands for LRP1 and LRP2, and it can induce the crossing of the BBB through the recognition of LDL receptors. Angiopep-2. It has a high transcytosis capacity, bypassing the P-glycoprotein efflux pump. Functionalization with angiopep-2 can increase the concentration of the nanocarrier in the brain tumor site, probably attracted by the acidic tumor microenvironment.
Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors
The nicotinic acetylcholine receptor binds the neurotransmitter acetylcholine and is widely expressed in not only the brain in pre- and postsynaptic sites of neurons but also the BBB. They are a very promising tool for drug delivery since they allow the passage of the BBB but also target neuronal cells. This receptor could be exploited by the rabies virus glycoprotein (RVG) 29 peptide, a 29 amino acid fragment from the rabies virus glycoprotein.
4.3.3. Transporter-Mediated Transport
Glutathione
Glutathione (GSH) is a hydrophilic tripeptide known as an antioxidant useful to maintain cellular redox homeostasis and suppress oxidative stresses. GSH has been evaluated for brain drug delivery by exploiting the TMT via GSH transporters.
Acetycholine
Acetycholine is an essential neurotransmitter that requires choline to be synthesized and transported to the brain via choline transporters.
Glucose
Glucose is the essential fuel of the brain that must be transported from the bloodstream to the brain by dedicated transmembrane proteins, the glucose transporters (GLUT), since neurons are unable to synthesize or store glucose. GLUT is expressed in the BBB to mediate the uptake of the metabolites but is overexpressed in brain cancer cells, making them attractive for glioma treatment. GLUT1, which transports glucose from the blood to the extracellular spaces, and GLUT3, which transports glucose from the extracellular space to neurons, are the main transporters in the human brain and are present in approximately equal amounts. Although there are some concerns regarding the number of these transporters in some pathologies, such as AD and hyperglycemia, GLUT can be effectively used for brain targeting [88].
4.3.4. RGD Peptides
RGD (arginine–glycine–aspartic acid) tripeptide has been widely studied for drug delivery applications for its affinity with the ECM proteins, fibronectin and vitronectin, and integrin αvβ3/αvβ5. Cyclic forms of RGD such as c(RGDyK), c(RGDfC), c(RGDfK), RGD4C (KACDCRGDCFCG), and iRGD (CRGDK/RGPD/EC) have higher stability in biological environments. Moreover, iRGD can also act as a tumor-penetrating peptide, binding to the neuropilin-1 (NRP-1) receptors on tumor cells [93].
4.3.5. Antibodies
Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and its type II receptor, VEGFR2, are highly expressed in brain tumors, playing a key role in angiogenesis and metastasis. Thus, gliomas’ and GBMs’ antiangiogenic therapies aim to inhibit angiogenesis by using anti-VEGF monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) like bevacizumab or avoid VEGF binding to the receptor by blocking VEGFR2 with an mAb such as ramucirumab [93].
4.3.6. Aptamers
Aptamers are short, single-stranded sequences of DNA or RNA that can bind to their receptors with high affinity and specificity. If compared to antibodies, aptamers have higher stability, lower immunogenicity, a small size (5–30 kDa), and a simple synthesis and modification procedure [93].
4.3.7. Polyethylene Glycol
Coating lipid-based nanocarriers (NCs) with polyethylene glycol (PEG) is a widely known method to prolong the NCs circulation time in plasma and their chemical stability. In the case of brain delivery, PEG confers a BBB crossing ability depending on the chain length; longer chains demonstrated better efficiencies in a time-dependent manner [89].
5. Lipid-Based Nanocarriers
The major hurdle in drug delivery to the brain is the presence of the BBB and enzymes, which strictly select the substances that could enter the brain. There are several factors that could be controlled to drive the entry of compounds into the brain, such as binding the drug to a transporter, opening and closing ion channels, lipophilicity, enzymatic degradation of drugs, functional groups, and charged residues of the molecules.
Furthermore, after penetration inside the brain, the drug faces other hurdles, such as inactivation by catabolic enzymes, drug resistance, and affinity towards multidrug ABC transporters, making the drug less bioavailable to the target site. Some studies estimate that almost 98% of small-molecule drugs and mostly all the large-molecule ones are excluded from entering the BBB [54]. Thus, alternative strategies are required to enable the treatment of CNS disease. The growing number of patients with CNS diseases urgently requires the development of new and non-invasive drug delivery methods as alternatives to traditional surgery, radiotherapy, and chemotherapy. In this vision, nanotechnologies are emerging as a good alternative to classical treatments for their ability to directly alleviate oxidative stress and inflammation, overcome the BBB, deliver therapeutics in a targeted manner to the site of disease, enhance the dose efficacy, control the release profiles, and avoid side effects.
Thanks to the many advances in nanotechnology, nanomedicine has a wide array of organic, inorganic, or NCs for therapeutic applications [94,95]. Among the organic NCs, those that seem to be most used for brain drug delivery are the lipid-based ones, that is, liposomes, SLNs, NEs, NLCs, niosomes, proniosomes, cubosomes, EVs, cell membrane-derived nanocarriers, and organic nanocarriers with high lipophilicity and ability to cross the BBB through passive diffusion [86,96].
5.1. Liposomes
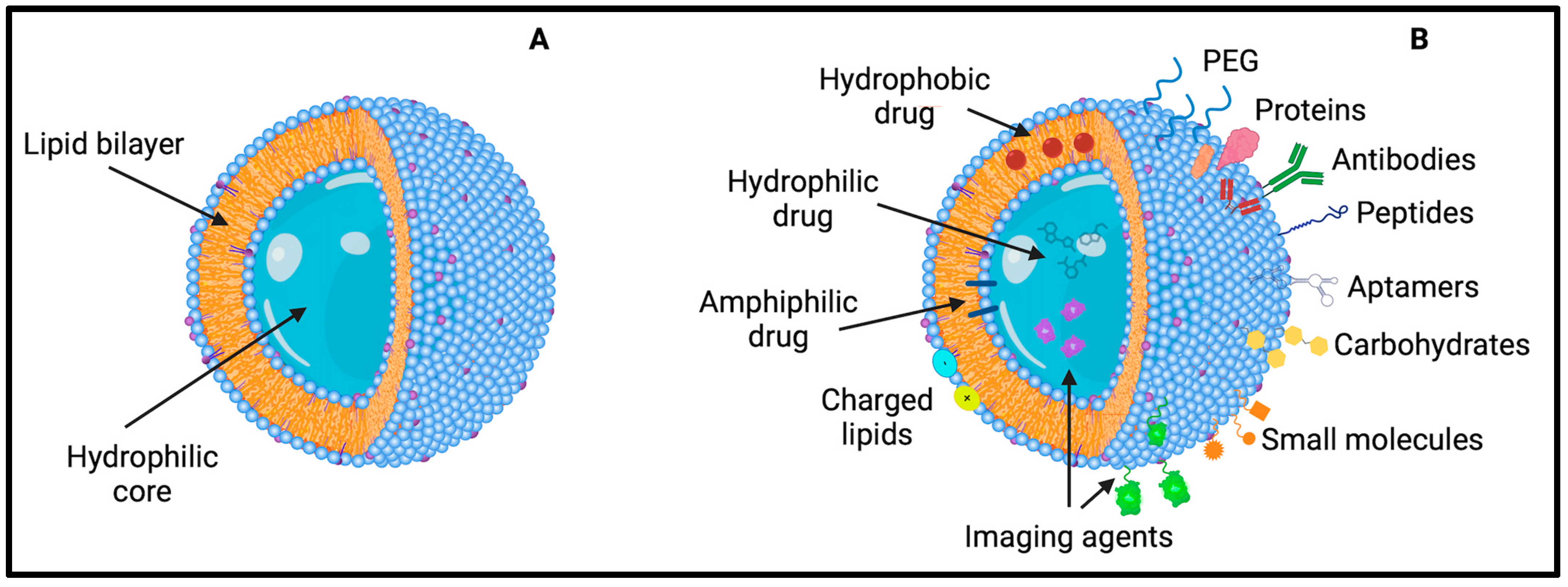
Liposomes are synthetic or natural self-assembled lipid bilayers deeply studied since 1960 for their applicability as drug delivery vehicles thanks to their structural similarity to biologic membranes. They are biocompatible, non-toxic, and biodegradable, making them suitable for drug delivery, preventing drugs’ degradation and immune responses [97]. They are composed of a hydrophobic bilayer and a hollow aqueous core, allowing the encapsulation and delivery of hydrophilic, hydrophobic, and amphiphilic molecules, such as proteins, peptides, nucleic acids, small molecules, and drugs (Figure 3).
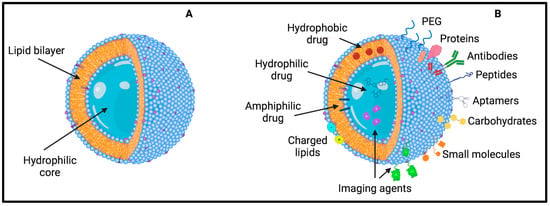
Figure 3.
Representation of (A) liposomes’ structure made of a lipid bilayer encapsulating an aqueous core and (B) their possible load and functionalization.
Liposomes are widely used to overcome some limitations of bare therapeutics. Some liposomes have already been approved by the FDA for the treatment of many brain pathologies or are undergoing some clinical trials, as follows:
- -
- AmBisome® for the treatment of cryptococcal meningitis, composed of amphotericin B encapsulated in a lipid bilayer of hydrogenated soy phosphatidylcholine (HSPC), 1,2-distearoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphoglycerol (DSPG), and cholesterol (Chol);
- -
- Abelcet® for the treatment of cryptococcal meningitis, composed of amphotericin B encapsulated in a liposome made of 1,2-dimyristoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine (DMPC), and 1,2-dimyristoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphoglycerol (DMPG);
- -
- Daunoxome®, composed of distearoylphosphatidylcholine (DSPC) and Chol liposomes carrying daunorubicin for the treatment of pediatric brain tumors;
- -
- Depocyt®, cytarabine encapsulated in Chol, triolein, 1,2-dioleoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine (DOPC), and 1,2-dipalmitoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphoglycerol (DPPG) liposomes for the treatment of lymphomatous meningitis;
- -
- Doxil®/Caelyx® also proposed for the treatment of GBM and pediatric brain tumors by encapsulating doxorubicin in HSPC, Chol, and 1,2-distearoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphoethanolamine poly(ethylene glycol) 2000 (DSPE-PEG2000) liposomes;
- -
- Myocet® liposome composed of egg phosphatidylcholine (EPC) and Chol-encapsulating doxorubin were also proposed for the GBM [8].
Some already-approved liposomal formulations have been repurposed, such as Depocyt® for the treatment of patients with recurrent GBM [98], liposomal amphotericin B for CNS infections with azole-resistant Aspergillus [99], or recurrent Candida albicans meningitis [100], and liposomal cytarabine for pediatric malignant brain tumors [101], administering them through ICV or IC.
Besides all the benefits, liposomes also display some limitations. That is, fast clearance and degradation and stability issues after prolonged storage times [89]. To face these hurdles, different formulations and strategies have been studied to enhance drug delivery across the BBB. Besides the lipophilic features of liposomes, they are too large to simply diffuse across or between cells, but they must exploit transport systems such as AMT, RMT, and CMT. To cross the BBB via the abovementioned routes, liposomes can be functionalized to enhance their blood circulation time or to improve their targeting ability in the CNS [85,89].
The first modification is the formulation of cationic liposomes to use the AMT. They display a positive surface charge to favor the electrostatic interaction with negatively charged glycocalyx at the luminal BBB membrane. Moreover, the liposomal positive charge enhances the adsorption of polyanions, such as DNA and RNA. The brain uptake of liposomes strongly depends also on their adhesion force to BBB, which must overcome the hydrodynamic force of cerebral blood flow, which can be affected by the administration routes and pathologies. For instance, a large cationic liposome (~200 nm) is preferred when the wall shear rate is low, such as in the case of transient cerebral hypoperfusion due to intra-arterial injection. On the contrary, a smaller one is better when the blood flow is faster and the hemodynamic stress is high. Thus, liposomes’ particle size must be optimized, considering the hemodynamic stress factors [102].
To avoid the problem of fast clearance, PEG can be covalently conjugated to liposomes to enhance their stability and prolong their circulation half-life. PEGylation inhibits liposomes’ clearance by the mononuclear phagocytic cells in the liver and spleen, preventing their opsonization. However, PEG chains can hinder the uptake of liposomes by target cells by impeding the binding of surface-targeting ligands with the matching cell surface receptor [103,104].
Furthermore, liposomes can be functionalized by targeting biological moieties, such as proteins, antibodies, carbohydrates, aptamers, and polypeptide sequences, through covalent or non-covalent bonds. Covalent bonding includes thioether, hydrazone, carboxamide, amide, and disulfide bonds, while non-covalent or physical bonding relies on attractive forces such as electrostatic interactions, hydrogen bonding, and van der Waals forces. However, non-covalent bonding has some problems in the control of the orientation of the ligands, hindering the liposome’s stability and activity, and of the environmental conditions required since changes in ionic strength, pH, or the isoelectric point of the ligand can lead to the detachment of the ligand from the surface [104].
Some liposomes are currently undergoing clinical trials, as follows:
NCT05034497, NCT01906385, and NCT05460507: Rhenium-186-NanoLiposome are administered through CED [105,106] or ICV injection to allow localized GBM therapy.
- -
- NCT05768919: liposomal curcumin is associated with radiotherapy and temozolomide for patients with newly diagnosed high-grade gliomas (HGG).
- -
- NCT00944801: pegylated liposomal doxorubicine and temozolomide in addition to radiotherapy in newly diagnosed GBM [107].
- -
- NCT04573140: RNA-lipid particle vaccines are used for the therapy of newly diagnosed pediatric HGG and GBM [108].
- -
- NCT00019630 and NCT00465673: liposomal doxorubicin HCl for the pediatric treatment of refractory brain tumors or brain metastases from breast cancer.
- -
- NCT00992602: IC injection of liposomal cytarabine combined with methotrexate for breast cancer brain metastasis.
- -
- NCT01386580 and NCT01818713: a GSH-functionalized pegylated liposome loaded with doxorubicin hydrochloride is administered in patients with HGG and leptomeningeal breast cancer metastasis [109].
- -
- NCT04590664: a repurposing of the drug verteporfin for the treatment of recurrent high-grade EGFR-mutated GBM [110].
- -
- NCT05864534: liposomal doxorubicin is administered in combination with a device with nine US emitters to disrupt the BBB and enhance drug penetration into the brain tumor.
- -
- NCT01044966: ICV administration of liposomes encapsulating Ara-C (DepoCyt®) in patients with recurrent GBM.
- -
- NCT00734682: liposomal irinotecan for recurrent HGG [111,112].
- -
- NCT03086616 and NCT02022644: CED of irinotecan liposome with real-time imaging with gadolinium in children with diffuse intrinsic pontine glioma and adults with HGG [113].
- -
- NCT01356290: oral thalidomide, fenofibrate, celecoxib, and alternating 21-day cycles of oral etoposide and cyclophosphamide, supplemented by intravenous bevacizumab and intraventricular therapy via an Ommaya reservoir consisting of alternating etoposide and liposomal cytarabine for children with medulloblastoma and ependydoma [114].
- -
- NCT01222780: Marqibo® (liposomal Vincristine) for children and adolescents with refractory tumors.
- -
- NCT05496894: mitoxantrone hydrochloride is encapsulated in a liposomal formulation for the treatment of MS.
- -
- NCT01039103: intravenous PEG-liposomal prednisolone sodium phosphate (Nanocort®) for the treatment of MS.
- -
- NCT02686853: intrathecal administration of liposomal amphotericin B in cryptococcal meningitis in immunocompetent patients;
- -
- NCT05453539: a novel liposomal device constituted by DSPE-DOTA-Gadolinium for contrast-enabled MR imaging of amyloid plaques for the diagnosis of AD.
- -
- NCT04976127: liposomal talineuren for PD.
Otherwise, many liposomal formulations are still undergoing preclinical studies, and some examples are reported in Table 1.

Table 1.
Liposomes for the treatment of brain diseases.
5.2. Solid–Lipid NPs
Similar to liposomes, solid–lipid NPs are nanometric lipid-based constructs, but they have a solid hydrophobic lipid core, in which both hydrophilic and lipophilic drugs can be encapsulated. They were developed for the first time in the early 1990s by Müller et al. and found application, especially in the cosmetic field [156].
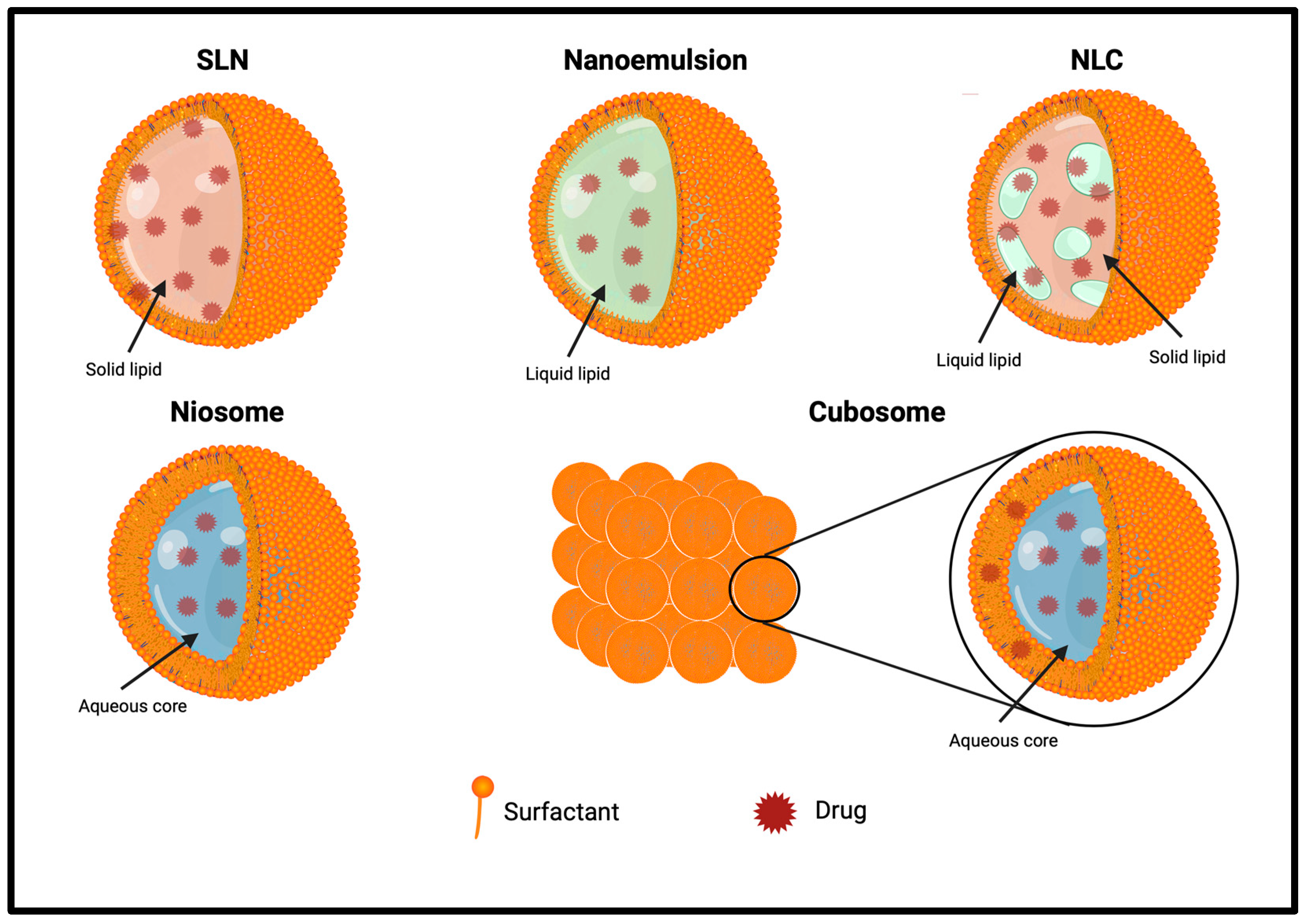
The main feature of SLNs is that they contain solid lipids at room temperature (Figure 4). Its solid lipidic core, instead of an aqueous one, protects drugs from biochemical degradation. SLNs have excellent physicochemical stability that allows them to escape the reticuloendothelial system by bypassing liver and spleen filtration; they are physiological and biodegradable, with a high biocompatibility; and their fabrication is scalable, fast, and economic.
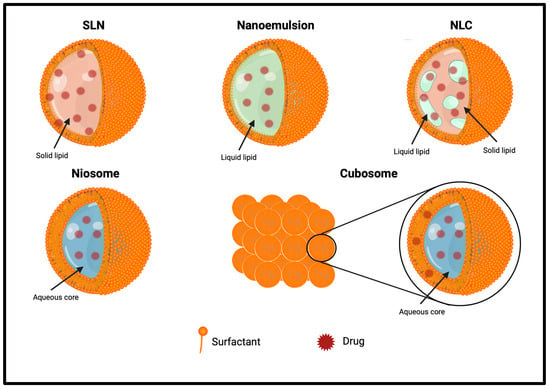
Figure 4.
Structure of other synthetic lipid-based delivery systems.
The solid lipid core allows SLNs’ storage for a long time in aqueous solutions, which is impossible with liposomes for the establishment of degradation phenomena.
However, SLNs also have some drawbacks, such as poor drug loading due to the limited space in the organized solid lipid core and the possible interaction of the drug with the lipid matrix, resulting in a failure of the formulation [157,158].
Some SLN formulations are undergoing promising preclinical studies, as listed in Table 2.

Table 2.
SLN for the treatment of brain diseases.
5.3. Other Synthetic Lipid Nanocarriers
Besides liposomes and SLNs, there are other lipid-based synthetic NCs, such as nanoemulsions, nanostructured lipid carriers, niosomes, proniosomes, and cubosomes, that are studied for brain delivery applications (Table 3, Figure 3).
5.3.1. Nanoemulsions
Emulsions are biphasic liquid systems constituted by two phases, the internal one dispersed as a small droplet in the external or continuous one. Their main feature, making them extremely useful in the food, pharmaceutical, and cosmetic fields, is the possibility to mix non-polar and polar molecules. Among them, NEs are nanosized emulsions where surfactants are employed to lower the surface tension and act as a barrier to emulsion coalescence at the interface between the two phases. NEs are widely used in nanomedicine to solubilize hydrophobic drugs, reducing side effects [169].
5.3.2. Nanostructured Lipid Carriers
NLCs are the second generation of SLNs, developed in 1999, and they are defined as nanometric (50–500 nm) colloidal drug delivery systems, containing a lipid mixture of both solid and liquid lipids in their core. Compared to SLNs, which have a solid lipid core in a highly organized fashion, NLCs contain liquid and solid lipid, forming an unorganized drug matrix. This unorganized nature allows the encapsulation of more drugs in the core and prevents crystallization and drug leakage during storage. They are biocompatible, non-toxic, and safe, with high stability and drug loading ability if compared to other lipid-based delivery tools [170].
5.3.3. Niosomes and Proniosomes
Niosomes are nonionic surfactant vesicles, like liposomes, used to improve the solubility and stability of poorly soluble drugs. Proniosomes are water-soluble nonionic dehydrated powdered or gelated structured provesicles that can be immediately rehydrated before use, avoiding many issues related to aqueous vesicular dispersions [171]. They are constituted by a lipid compound, cholesterol, or L-α-soya phosphatidylcholine, and nonionic surfactants, such as spans, tweens, and Brij [172].
5.3.4. Cubosomes
Cubosomes are composed of amphiphilic lipids and surfactants organized in a cubic nanostructure. The presence of liquid–crystal phases favors the dissolution of hydrosoluble peptides. They have some advantages, such as easy formulations, biocompatibility, prevention from degradation, and stability [33].

Table 3.
Nanoemulsions, nanostructured lipid carriers, niosomes, proniosomes, and cubosomes for the treatment of brain diseases.
Table 3.
Nanoemulsions, nanostructured lipid carriers, niosomes, proniosomes, and cubosomes for the treatment of brain diseases.
| LNC | Composition | Drug | Surface Functionalization | Size (nm) | ZP (mV) | Disease | Administration Route | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NE | Capmul MCM + Tween 80 + Transcutol P + propylene glycol | Quetiapine fumarate | - | 144.0± 0.5 | −8.1 ± 1.8 | Brain delivery | Intranasal | [173] |
| Capryol PGMC + Kolliphore® RH40 + Transcutol®-P | Zolmitriptan | Chitosan | 43.5 ± 1.9 | +5.2 ± 0.9 | Migraine | Intranasal | [174] | |
| Isopropyl myristate + Capryol + Cremophor EL + Labrasol | Huperzine A | Lf | 15.2 ± 0.7 | −4.5 ± 1.0 | AD | Intranasal | [175] | |
| oleic acid + α-tocopherol + Span 8 + olive oil + Tween 80 | Indinavir | 112 ± 4 | −33 ± 3 | HIV | Intravenous | [176] | ||
| NLCs | Precirol ATO 5+ Capmul MCM + Tween 80 + Span 20 | Carbamazepine | - | 132.8 | −29 ± 6 | Epilepsy | Intranasal inside gel | [177] |
| Compritol + Sweet almond oil + L-PC + gelucire 44/14 | Flibanserin | - | 115 | - | Brain delivery | Intranasal inside gel | [178] | |
| Precirol ATO 5 + Lauroglycol 90 + Tween 80 | Escitalopram and paroxetine | - | 165 ± 2 | +11.2 ± 0.4 | Depression | Intravenous and intranasal | [179] | |
| Cetyl palmitate + oleic acid + Tween 80 + Polaxomer 188 | Sesamol | - | 92 ± 6 | −27.9 ± 0.6 | Ischemic stroke | Intravenous | [180] | |
| Compritol + Labrafil + Tween 80 + lauroglycol | Almotriptan malate | Chitosan | 254.9 ± 1.9 | +34.1 ± 0.1 | Migraine | Intranasal | [181] | |
| Glyceryl monostearate + oleic acid + Tween 80 + pluronic F127 | Lorazepam | 72 ± 5 | −20 ± 3 | Epilepsy | Intranasal | [182] | ||
| Palmityl palmitate + Miglyol® + sphingosylphosphorylcholine + Solutol HS15® + DSPE-PEG2000 | Nimodipine | Lf | 170 ± 14 | −15.9 ± 1.1 | Ischemic stroke | Intravenous | [183] | |
| PC + chol oleate + glycerol trioleate + S100-COOH | Curcumin | 103.8 ± 0.6 | −5.8 ± 0.7 | AD | IC | [184] | ||
| Niosomes | Span60 + Chol | Bromocriptine mesylate | - | 180 ± 5 | −14.2 ± 1.8 | Brain delivery | Intranasal | [185] |
| DOTMA + lycopene + polysorbate 60 | pCMS-EGFP plasmid | - | 119 ± 3 | +23 ± 2 | Brain delivery | IC | [186] | |
| Chol + Tween60 | Thymoquinone | - | 78 | −5 | Ischemic stroke | Intravenous | [187] | |
| SUR II + Chol + PEG2000 | Pramipexole | - | 103 ± 0.4 | −13.8 ± 0.2 | PD | Intraperitoneal | [120] | |
| Tween60 + Chol | Oleuropein | - | 79.37 ± 0.12 | +1.38 ± 0.07 | Metastatic brain tumors | Intravenous | [188] | |
| Span 60 + Solulan C24 | Albumin | Glucopyranose and alanine | 94 ± 10 | −3.8 ± 1.0 | Brain delivery | Intravenous | [189] | |
| Span + Chol | Olanzapine | Chitosan | 250 ± 5 | - | Schizophrenia | Intranasal | [190] | |
| Span 60 + Chol | Lacosamide | 194 | +36 | Epilepsy | Intravenous | [191] | ||
| Dicetyl phosphate + Chol + Tween20 | Pentamidine | 118 ± 2 | −26.7 ± 0.7 | Brain delivery | Intranasal | [192] | ||
| Cubosomes | Phytantriol + Tween80 | - | - | 170–250 | - | Brain delivery | Intravenous | [193] |
| Gold NPs | - | 196 ± 3 | - | Intravenous | [194] | |||
| Selachyl alcohol + Tween80 | Phenytoin | - | 144 ± 4 | - | Seizure | Intravenous | [195] | |
| Glycerol mono-oleate + poloxamer 407 | Donepezil HCl | - | 138–231 | −40 | AD | Intranasal | [196] | |
| Glycerol monooleate + Poloxamer 407 + Tween 80 | Granisetron | - | 267 ± 3 | −27 ± 2 | Chemotherapy-induced emesis | Intranasal | [197] | |
| Glyceryl monooleate + poloxamer 407 + ethanol + polyethylene glycol 200 | Tizanidine hydrochloride | - | 50.2 | −6.4 | Brin delivery | Intranasal | [198] | |
| Monoolein + Tween80 | Paliperidone palmitate | Chitosan | 306 ± 23 | +42.4 ± 0.2 | Schizophrenia | Intranasal | [199] | |
| Glyceryl monooleate + Pluronic 127 | Gambogenic acid and PLHSpT | Angiopep-2 | 128.7 ± 1.0 | >30 | GBM | Intravenous | [200] | |
| Monoolein + amphiphilic polymer | Temozolomide or cisplatin | ∼280 | +18 | GBM | Intravenous | [201] |
DOTMA: 1,2-di-O-octadecenyl-3-trimethylammonium propane.
5.4. Extracellular Vesicles
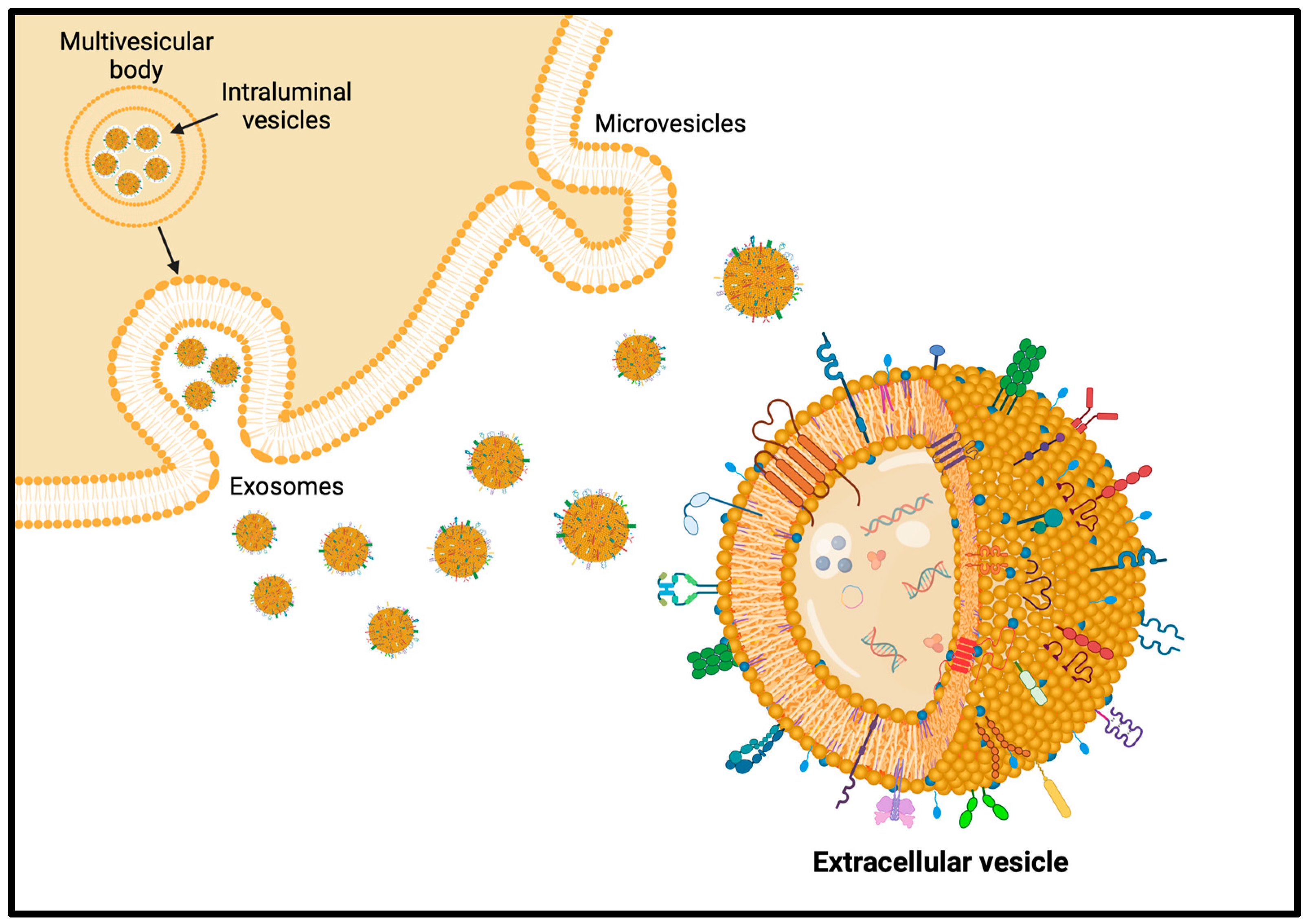
Extracellular vesicles (EVs) are phospholipid bilayer-delimited vesicles naturally produced by cells in both physiological and pathological conditions. Their membrane and cargo composition mirror the cell of origin and can modulate many physiological and pathological cellular processes, acting as effective intercellular communication mediators (Figure 5). In this way, EVs modulate immune reactions, tissue regeneration, tumor niche establishment, and tumor metastatization, triggering phenotypic changes in acceptor cells. This key role of EVs demonstrates their potential as vehicles for the delivery of therapeutic cargoes or as hybrid nanosized tools engineered ad hoc to regulate a physio-pathological condition or a disease progression. In addition to their delivery capabilities, EVs have intrinsic targeting abilities towards the parental or pathological tissue [202]. The increasing interest of researchers in EVs mainly relies on their potential diagnostic and therapeutic applications in many medical fields such as cancer, neurodegenerative, and immunological diseases, and many clinical trials involving different types of EVs, even from plants, are already on the go [203].
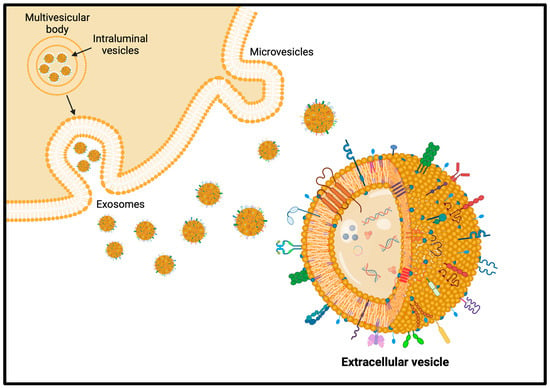
Figure 5.
Representation of extracellular vesicles and their production and release mechanisms.
In addition to the just-described properties, EVs have the outstanding, and still not totally understood, ability to cross the BBB bidirectionally, influencing neurons or peripheral tissues through the bloodstream. The comprehension of this phenomenon becomes essential for the use of EVs as drug delivery vehicles in pharmacology and therapeutics. In the last decade, the effects of EVs have been evaluated in preclinical models of brain diseases such as AD, stroke, traumatic brain injury, and intracerebral hemorrhage. Similarly to other body compartments, EVs in the brain also play a key role in the communication between neurons, glia, and vascular cells, especially in the maintenance of homeostasis and the progression of pathologies. In the last decade, there has been a shift from cell-based therapeutics to EV-based ones, and in this regard, many studies have shown the potential of EVs as nanotherapeutics for brain pathologies. Native EVs have neuroprotective and regenerative effects, but they can also be engineered in terms of payload and surface functionalization to enhance their bioactivity and targeting [204].
Although EVs have unique properties to advance smart drug delivery systems in terms of pharmacokinetics, targeting, and safety against those of synthetic nanocarriers, clinical translation of these results is still challenging. The EVs’ intrinsic size heterogeneity, batch-to-batch differences, and the risks of the biogenesis procedure are higher than in synthetic nanocarriers. Moreover, effective and reproducible methods to load them with therapeutic drugs are still needed, and the current EV purification methods limit the development of standardized and large-scale production [205].
Therapeutic effects of native EVs on different brain pathologies have been reported since 2011; most of them use EVs derived from mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) for the treatment of stroke, traumatic brain injury, or AD. MSC-derived EVs show a homing mechanism toward injured brain tissue driven by inflammation. Other studies use EVs from neural stem cells (NSCs) isolated from mice or humans after the differentiation of induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSC), opening the perspective of a very personalized medicine by isolating iPSC from the patient himself. In this last case, the patient may benefit from his own cells after the generation of iPSCs [25,53]. NSCs-derived EVs demonstrate an outstanding innate tropism to make the brain capable of reaching the injury site [204]. In addition, dendritic cell-derived EVs have been proven to be promising for the treatment of brain cancers, which are resistant to immune cell recruitment, proposing them for immunotherapy against GBM [206].
To date, some EV-based treatments have undergone clinical trials:
- -
- NCT03384433: EVs from allogenic placenta MSCs are IC injected to ameliorate the brain injury by promoting neurogenesis after an ischemic stroke [207];
- -
- NCT05490173: MSC-derived EVs are intranasally administered to low-birth-weight infants to mitigate neurodevelopmental outcomes;
- -
- NCT04202770: MSCs-derived EVs with transcranial focused US in patients with refractory, treatment-resistant depression, anxiety, and neurodegenerative dementia;
- -
- NCT06138210: intravenous injection of EVs derived from human-induced pluripotent stem cells for ischemic stroke;
- -
- NCT04388982: intranasal administration of allogenic adipose MSC-EVs in the treatment of mild to moderate dementia due to AD [208].
Besides the ongoing clinical trials, many other applications of EVs at the preclinical stage are listed in Table 4.

Table 4.
Native EVs for the treatment of brain diseases.
Although it has been demonstrated that EVs have clear potential for therapeutic applications already used in their native state, that is, being isolated from the cellular fluids in which they are dispersed after being secreted by a specific cell line, there are an increasing number of pharmaceutical applications of EVs engineered or functionalized after their isolation (Table 5).

Table 5.
Engineered EVs for the management of brain diseases.
5.5. Cell-Membrane-Derived Nanocarriers
Cell-derived EV-mimetic nanocarriers have been used as an alternative to EVs, taking advantage of a much higher production yield for the drug delivery of different therapeutic molecules and NPs to the brain (Table 6).
The first membranes used were derived from red blood cells (RBCs), trying to exploit their prolonged circulating time due to the presence of membrane-oriented CD47. However, RBCs do not expose specific targeting, limiting their application to specific targets.
Trying to achieve enhanced targeting ability, other sources of cell membranes have been evaluated to favor the therapeutic effects of the nanocarriers and their side effects. Hence, tumor cells, neutrophils, macrophages, and leukocytes, stem cells, natural killer cells, platelets, and bacteria have been assessed as cell membrane sources [312,313].

Table 6.
Cell membrane-derived nanocarriers for the management of brain diseases.
Table 6.
Cell membrane-derived nanocarriers for the management of brain diseases.
| Membranes’ Origin | Carrier | Cargo | Surface Functionalization | Disease | Administration Route | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4T1 and platelet hybrid | Polymetformin + hyaluronic acid liposomes | Paeonol | - | Ischemic stroke | Intravenous | [314] |
| Aorta endothelial cells | HOP NPs | Rapamycin | CXCR4 | Ischemic stroke | Intravenous | [315] |
| Brain microvasculature endothelial cells | Mesoporous silica NPs | Dihydroartemisinin | - | Cerebral malaria | Intravenous | [316] |
| PLGA-PEG NPs | Doxorubicin | - | GBM | Intravenous | [317] | |
| Dendritic cells | PLGA NPs | Rapamycin | Glioma | Intravenous | [318] | |
| Macrophages | - | Molybdenum disulfide quantum dots | - | AD | Intravenous | [319] |
| - | Cannabidiol | - | Post-traumatic stress disorder | Intravenous and US | [320] | |
| - | aPD-L1 and CXCL10 | Angiopep-2 | GBM | Intravenous | [321] | |
| Liposomes (DSPE-PEG2000) | IR-792 | - | PTT of GBM | Intravenous | [322] | |
| Liposomes (DPPC, Chol, and DSPE-PEG2000) | Oxytocin | - | AD | Intranasal | [323] | |
| Mesoporous silica NPs | anti-NF-κB peptides | - | GBM | Intravenous | [324] | |
| Poly(N-vinylcaprolactam) nanogel | Manganese dioxide and cisplatin | - | Glioma | Intravenous | [325] | |
| Liposomes (Chol and soybean lecithin) | Baicalin | - | Ischemic stroke | Intravenous | [326] | |
| Cu2−x Se and PVP NPs | Curcumin | DSPE-PEG2000-TPP | PD | Intravenous | [327] | |
| SLN (glycerol monostearate, Tween 80, and soya lecithin) | Genistein | RVG29 and TPP | AD | Intravenous | [328] | |
| PLGA | Rapamycin | PD-1 | GBM | Intravenous | [329] | |
| Microglia cells | Poly(propylene glycol dithiopropionate) | Zoledronate | - | GBM | Intravenous | [330] |
| PLGA NPs | PLX3397 | DSPE-PEG2000 | Cognitive impairment | Intravenous | [331] | |
| MSCs | Liposomes (PC) | Curcumin | - | Ischemic stroke | Intravenous | [332] |
| Monocytes | PLGA | Rapamycin | - | Ischemic stroke | Intravenous | [333] |
| Neutrophil | - | Fingolimod hydrochloride | - | Intravenous | [334] | |
| - | Mesoporous Prussian blue nanozyme | - | Intravenous | [335] | ||
| PLGA NPs | Superparamagnetic iron oxide NPs | - | Neuroinflammation imaging | Intravenous | [336] | |
| Liposomes (DPPC + Chol + DSPE-PEG2000) | Leonurine | - | Ischemic stroke | Intravenous | [337] | |
| Dendrigraft poly-L-lysine and PEG NPs | Catalase | N-acetyl Pro-Gly-Pro | Intravenous | [338] | ||
| β-cyclodextrin PBAP | Edaravone | SHp-PEG-DSPE | Intravenous | [339] | ||
| PEI NPs | Octanoic acid | RVG29 | Intravenous | [340] | ||
| Neural stem cells | - | Oncolytic adenovirus A4/k37 | - | GBM | Intravenous | [341] |
| Zein NPs | Antisense oligonucleotide | Aptamer 19S | PD | Intravenous | [342] | |
| NK cells | PLGA NPs | Temozolomide and IL-15 | cRGD peptide | GBM | Intravenous | [343] |
| Neuron cells | Cu2–xSe-PVP | Quercetin | VCAM-1 | PD | Intravenous and US | [344] |
| Platelets | - | L-arginine and γ-Fe2O3 magnetic nanoparticles | - | Ischemic stroke | Intravenous | [345] |
| T7-PEG-poly-histidine-poly-lysine | miRNA-Let-7c | Intravenous | [346] | |||
| PLGA NPs | Human fat extract | RGD peptide | Intravenous | [347] | ||
| Dextran NPs | Neuroprotectant (ZL006e) | Recombinant tissue plasminogen activator (rtPA) and thrombin-cleavable Tat-peptide | Intravenous | [348] | ||
| RBCs | - | Celecoxib | - | AD | Intranasal | [349] |
| Mesoporous silica NPs + upconversion NPs | S-nitrosoglutathione | - | PD | Intravenous | [350] | |
| - | Doxorubicin | CDX peptide | Glioma | Intravenous | [351] | |
| - | Docetaxel nanocrystals | pHA-VAP peptide | [352] | |||
| Surfactant | Docetaxel | cRGDyK peptide | [353] | |||
| pH-sensitive NPs of acetal-dextran | Doxorubicin and lexiscan | Angiopep-2 | GBM | Intravenous | [354] | |
| PEI + Poly-L-lysine NPs | siRNA | Intravenous | [355] | |||
| Nanogel (Poly(deca-4,6-diynedioic acid) + Puilulan) | Temozolomide and indocyanine green | ApoE | Intravenous | [356] | ||
| Acetal dextran | Temozolomide and OTX015 | Intravenous | [357] | |||
| ABT + A12 inhibitors | Intravenous | [358] | ||||
| NLC (Tween 80 + cetyl palmitate + oleic acid + chol + DSPE-PEG2000) | Resveratrol | RVG29 and TPP | AD | Intravenous | [359] | |
| Human serum albumin NPs | Curcumin | T807 and TPP | Intravenous | [360] | ||
| - | Curcumin nanocrystals | RVG29 | PD | Intravenous | [361] | |
| Boronic ester-Dextran | NR2B9C | Stroke-homing peptide | Ischemic stroke | Intravenous | [362] | |
| NLC (Chol oleate + Chol + soybean lecithin + triolein) | PARP inhibitor olaparib | C3 and SS31 peptides | Traumatic brain injury | Intravenous | [363] | |
| Cancer cell-derived | PCL NPs | Indocyanine green | - | Fluorescent imaging and phototherapy of GBM | Intravenous | [364] |
| Brain cancer | Nanocomposite of PDPP3T + PLGA + PVA | Ultrasmall iron oxide NPs | cRGD peptide | Brain tumors | Intravenous | [365] |
| Breast cancer | PEG–PDPA | Succinobucol | - | Ischemic stroke | Intravenous | [366] |
| Brain metastatic breast cancer cell | mPEG-PLGA | Doxorubicin | - | Brain delivery | Intravenous | [367] |
| GBM cell line | pH-sensitive biomimetic NPs of acetal dextran | Temozolomide and cisplatin | - | GBM | Intravenous | [368] |
| pH-sensitive polyglutamic acid | Doxorubicin | - | Intravenous + US | [369] | ||
| PEI | pDNA (pHSVtk) | - | Intravenous/Intranasal | [370] | ||
| Boron nitride nanotubes | Doxorubicin | - | Intravenous | [371] | ||
| - | CuFeSe2 nanocrystals | - | Photothermal therapy GBM | Intravenous | [372] | |
| Nanosuspension | 10-hydroxycamptothecin | - | Glioma | Intravenous | [373] | |
| PVP K30 + Sodium deoxycholate | Paclitaxel | WSW peptide | Intravenous | [374] | ||
| Poly(MIs)-PEI | Paclitaxel | siPGK1 | GBM | Intravenous | [375] | |
| GBM from the patient | - | Au Nanorods | - | GBM | Intravenous | [376] |
| Glioma cell line | Cu2−x Se NPs | Cinobufotalin | - | GBM | Intravenous | [377] |
| Liposomes (DPPC, DSPC, DOPC, and Chol) | Indocyanine green | - | PTT of glioma | Intravenous | [378] | |
| Metastatic melanoma | Citraconic anhydride grafted poly-lysine and polyethyleneimine xanthate | siPGK1 | - | GBM | Intravenous | [356] |
| Brain metastatic breast cancer cells and glioma cells | Oleic acid, TPGS, and lanthanide-doped NPs | Gambogic acid and indocyanine green | - | Glioma | Intravenous | [379] |
| Dendritic cells and glioma cells | NE (lecithin) | Docetaxel | - | Glioma | Intravenous | [380] |
| GBM, macrophage, and microglia cells | Amphiphilic polymer chlorin e6, cucurbit[7]urils, and PEG | 5-(3-methyltriazene-1-yl)imidazole-4-carboxamide | - | GBM | Intravenous | [381] |
| Mitochondria and GBM cells | PEG-PHB | Gboxin | - | GBM | Intravenous | [382] |
| Neutrophils and macrophages | PLGA NPs | Rapamycin | - | Glioma | Intravenous | [383] |
| Platelets and glioma cells | PLGA NPs | β-mangostin | - | Glioma | Intravenous | [384] |
| Platelets and RBCs | - | Hypoxia inducible factor-1α inhibitor YC-1 | - | Ischemic stroke | Intravenous | [385] |
CXCR4: C-X-C motif chemokine receptor 4; HOP: ROS-responsive amphiphilic copolymer HBA-OC-PEG2000; PBAP: phenylboronic acid pinacol ester; VCAM: vascular cell adhesion protein; pHA: p-hydroxybenzoic acid; PARP: poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase; PCL: polycaprolactone; PDPA: poly(2-(diisopropylamino)ethyl methacrylate; PVP: polyvinylpyrrolidone; PGK1: phosphoglycerate kinase-1; PEG-PHB: poly (ethylene glycol)-poly (4-(4,4,5,5-Tetramethyltetramethyl-1,3,2-dioxaborolan-2-yl) benzyl acrylate).
6. Conclusions
This review pointed out that nanomedicine is a significant tool for the development of efficient and safe brain disease treatments. The BBB, due to its structure, poses a formidable challenge to achieving effective drug delivery.
Nanosystems can be designed to reach the BBB and specifically deliver the cargo, thus increasing drug retention at the target site. For an efficacious design of drug delivery systems, a deep knowledge of the BBB structure and physiopathology is mandatory.
The lipid-based nanocarriers here described are versatile platforms, and several efforts have been made in the past years for the treatment of several BBB diseases.
Some liposomal formulations are currently used or are undergoing clinical trials, especially for tumor treatments. Some clinical trials are already active for the treatment of brain diseases with EVs. A relevant number of other nanocarriers were able to overcome the in vitro/vivo bottleneck since their activity was shown in animal models, paving the way for future clinical translation.
Nanotechnologies for therapeutic and diagnosis applications allow not only to enhance the availability of active anti-stroke, anticancer, antimicrobics, and neuroprotective agents for targeting e/o personalized brain drug delivery applications but also to empower the reengineering of a wide variety of small molecules and biologic drugs to assist neurodevelopment and face neurological diseases.
Funding
This research receives no funding.
Acknowledgments
T.L. and F.S. want to thank More Care S.r.l. for their support and for the fruitful and stimulating discussions on the topics covered in this review.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Daneman, R.; Prat, A. The blood-brain barrier. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2015, 7, a020412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, D.; Chen, Q.; Chen, X.; Han, F.; Chen, Z.; Wang, Y. The blood–brain barrier: Structure, regulation, and drug delivery. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, Q.; Zhao, S.; Xu, T.; Wang, Q.; Lan, M.; Yan, L.; Chen, X. Getting drugs to the brain: Advances and prospects of organic nanoparticle delivery systems for assisting drugs to cross the blood–brain barrier. J. Mater. Chem. B 2022, 10, 9314–9333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teixeira, M.I.; Lopes, C.M.; Amaral, M.H.; Costa, P.C. Surface-modified lipid nanocarriers for crossing the blood-brain barrier (BBB): A current overview of active targeting in brain diseases. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2023, 221, 112999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alotaibi, B.S.; Buabeid, M.; Ibrahim, N.A.; Kharaba, Z.J.; Ijaz, M.; Noreen, S.; Murtaza, G. Potential of nanocarrier-based drug delivery systems for brain targeting: A current review of literature. Int. J. Nanomed. 2021, 16, 7517–7533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, F.; Varghese, R.; Panda, S.; Ramamoorthy, S.; Areeshi, M.Y.; Fagoonee, S.; Haque, S. Smart Nanoformulations for Brain Cancer Theranostics: Challenges and Promises. Cancers 2022, 14, 5389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadry, H.; Noorani, B.; Cucullo, L. A blood–brain barrier overview on structure, function, impairment, and biomarkers of integrity. Fluids Barriers CNS 2020, 17, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vieira, D.B.; Gamarra, L.F. Getting into the brain: Liposome-based strategies for effective drug delivery across the blood–brain barrier. Int. J. Nanomed. 2016, 11, 5381–5414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasmussen, M.K.; Mestre, H.; Nedergaard, M. Fluid transport in the brain. Physiol. Rev. 2022, 102, 1025–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murayi, R.; Chittiboina, P. Glucocorticoids in the management of peritumoral brain edema: A review of molecular mechanisms. Childs Nerv. Syst. 2016, 32, 2293–2302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendricks, B.K.; Cohen-Gadol, A.A.; Miller, J.C. Novel delivery methods bypassing the blood-brain and blood-tumor barriers. Neurosurg. Focus. FOC 2015, 38, E10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alahmari, A. Blood-Brain Barrier Overview: Structural and Functional Correlation. Neural Plast. 2021, 2021, 6564585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lochhead, J.J.; Yang, J.; Ronaldson, P.T.; Davis, T.P. Structure, Function, and Regulation of the Blood-Brain Barrier Tight Junction in Central Nervous System Disorders. Front. Physiol. 2020, 11, 914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sweeney, M.D.; Zhao, Z.; Montagne, A.; Nelson, A.R.; Zlokovic, B.V. Blood-Brain Barrier: From Physiology to Disease and Back. Physiol. Rev. 2019, 99, 21–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, M.; Sharma, P.; Maheshwari, R.; Tekade, M.; Shrivastava, S.K.; Tekade, R.K. Chapter 15—Beyond the Blood–Brain Barrier: Facing New Challenges and Prospects of Nanotechnology-Mediated Targeted Delivery to the Brain. In Nanotechnology-Based Targeted Drug Delivery Systems for Brain Tumors; Kesharwani, P., Gupta, U., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2018; pp. 397–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, A.H.; Erly, W.; Moser, F.G.; Maya, M.; Nael, K. Differentiation of solitary brain metastasis from glioblastoma multiforme: A predictive multiparametric approach using combined MR diffusion and perfusion. Neuroradiology 2015, 57, 697–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Bock, M.; Van Haver, V.; Vandenbroucke, R.E.; Decrock, E.; Wang, N.; Leybaert, L. Into rather unexplored terrain—Transcellular transport across the blood–brain barrier. Glia 2016, 64, 1097–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilhelm, I.; Nyúl-Tóth, Á.; Suciu, M.; Hermenean, A.; Krizbai, I.A. Heterogeneity of the blood-brain barrier. Tissue Barriers 2016, 4, e1143544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, S.; Khan, A.I.; Cai, X.; Song, Y.; Lyu, Z.; Du, D.; Dutta, P.; Lin, Y. Overcoming blood–brain barrier transport: Advances in nanoparticle-based drug delivery strategies. Mater. Today 2020, 37, 112–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gawdi, R.; Shumway, K.R.; Emmady, P.D. Physiology, Blood Brain Barrier; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Zaragozá, R. Transport of Amino Acids Across the Blood-Brain Barrier. Front. Physiol. 2020, 11, 973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Shi, T.; Zhang, L.; Zhu, P.; Deng, M.; Huang, C.; Hu, T.; Jiang, L.; Li, J. Mammalian drug efflux transporters of the ATP binding cassette (ABC) family in multidrug resistance: A review of the past decade. Cancer Lett. 2016, 370, 153–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harilal, S.; Jose, J.; Parambi, D.G.T.; Kumar, R.; Unnikrishnan, M.K.; Uddin, M.S.; Mathew, G.E.; Pratap, R.; Marathakam, A.; Mathew, B. Revisiting the blood-brain barrier: A hard nut to crack in the transportation of drug molecules. Brain Res. Bull. 2020, 160, 121–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terstappen, G.C.; Meyer, A.H.; Bell, R.D.; Zhang, W. Strategies for delivering therapeutics across the blood–brain barrier. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2021, 20, 362–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinmetz, J.D.; Seeher, K.M.; Schiess, N.; Nichols, E.; Cao, B.; Servili, C.; Cavallera, V.; Cousin, E.; Hagins, H.; Moberg, M.E.; et al. Global, regional, and national burden of disorders affecting the nervous system, 1990–2021: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021. Lancet Neurol. 2024, 23, 344–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhunia, S.; Kolishetti, N.; Vashist, A.; Yndart Arias, A.; Brooks, D.; Nair, M. Drug Delivery to the Brain: Recent Advances and Unmet Challenges. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 2658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Candelario-Jalil, E.; Dijkhuizen, R.M.; Magnus, T. Neuroinflammation, stroke, blood-brain barrier dysfunction, and imaging modalities. Stroke 2022, 53, 1473–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, X.; Andjelkovic, A.V.; Zhu, L.; Yang, T.; Bennett, M.V.L.; Chen, J.; Keep, R.F.; Shi, Y. Blood-brain barrier dysfunction and recovery after ischemic stroke. Prog. Neurobiol. 2018, 163–164, 144–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kisler, K.; Nelson, A.R.; Montagne, A.; Zlokovic, B.V. Cerebral blood flow regulation and neurovascular dysfunction in Alzheimer disease. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2017, 18, 419–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, A.; Tyson, J.; Patel, S.; Patel, M.; Katakam, S.; Mao, X.; He, W. Emerging Nanotechnology for Treatment of Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s Disease. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2021, 9, 672594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Z.; Wong, L.-W.; Su, Y.; Huang, X.; Wang, N.; Chen, H.; Yi, C. Blood-brain barrier integrity in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease. Front. Neuroendocrinol. 2020, 59, 100857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poewe, W.; Seppi, K.; Tanner, C.M.; Halliday, G.M.; Brundin, P.; Volkmann, J.; Schrag, A.-E.; Lang, A.E. Parkinson disease. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2017, 3, 17013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.T.; Nguyen, T.T.D.; Tran, N.-M.-A.; Van Vo, G. Lipid-Based Nanocarriers via Nose-to-Brain Pathway for Central Nervous System Disorders. Neurochem. Res. 2022, 47, 552–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balasa, R.; Barcutean, L.; Mosora, O.; Manu, D. Reviewing the Significance of Blood–Brain Barrier Disruption in Multiple Sclerosis Pathology and Treatment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobson, R.; Giovannoni, G. Multiple sclerosis—A review. Eur. J. Neurol. 2019, 26, 27–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Chen, M.; Zhu, C. Neuroinflammation in Prion Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Robles, P.; Fiest, K.M.; Frolkis, A.D.; Pringsheim, T.; Atta, C.; St. Germaine-Smith, C.; Day, L.; Lam, D.; Jette, N. The worldwide incidence and prevalence of primary brain tumors: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Neuro-Oncol. 2014, 17, 776–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonali; Viswanadh, M.K.; Singh, R.P.; Agrawal, P.; Mehata, A.K.; Pawde, D.M.; Narendra; Sonkar, R.; Muthu, M.S. Nanotheranostics: Emerging Strategies for Early Diagnosis and Therapy of Brain Cancer. Nanotheranostics 2018, 2, 70–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Condos, A.M.; Wangaryattawanich, P.; Rath, T.J. Bacterial, Viral, and Prion Infectious Diseases of the Brain. Magn. Reson. Imaging Clin. N. Am. 2024, 32, 289–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mastrangelo, A.; Gama, L.; Cinque, P. Strategies to target the central nervous system HIV reservoir. Curr. Opin. HIV AIDS 2024, 19, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barani, M.; Mukhtar, M.; Rahdar, A.; Sargazi, G.; Thysiadou, A.; Kyzas, G.Z. Progress in the Application of Nanoparticles and Graphene as Drug Carriers and on the Diagnosis of Brain Infections. Molecules 2021, 26, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Guennec, L.; Coureuil, M.; Nassif, X.; Bourdoulous, S. Strategies used by bacterial pathogens to cross the blood–brain barrier. Cell. Microbiol. 2020, 22, e13132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayala-Nunez, N.V.; Gaudin, R. A viral journey to the brain: Current considerations and future developments. PLoS Pathog. 2020, 16, e1008434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wouk, J.; Rechenchoski, D.Z.; Rodrigues, B.C.D.; Ribelato, E.V.; Faccin-Galhardi, L.C. Viral infections and their relationship to neurological disorders. Arch. Virol. 2021, 166, 733–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunter, P. Viral diseases and the brain. EMBO Rep. 2022, 23, e54342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strickland, A.B.; Shi, M. Mechanisms of fungal dissemination. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2021, 78, 3219–3238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Govic, Y.; Demey, B.; Cassereau, J.; Bahn, Y.S.; Papon, N. Pathogens infecting the central nervous system. PLoS Pathog. 2022, 18, e1010234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia, H.H.; Nath, A.; Del Brutto, O.H. Parasitic infections of the nervous system. Semin. Neurol. 2019, 39, 358–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fahoum, F.; Eyal, S. Intracerebroventricular administration for delivery of antiseizure therapeutics: Challenges and opportunities. Epilepsia 2023, 64, 1750–1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atkinson, A.J., Jr. Intracerebroventricular drug administration. Transl. Clin. Pharmacol. 2017, 25, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slavc, I.; Cohen-Pfeffer, J.L.; Gururangan, S.; Krauser, J.; Lim, D.A.; Maldaun, M.; Schwering, C.; Shaywitz, A.J.; Westphal, M. Best practices for the use of intracerebroventricular drug delivery devices. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2018, 124, 184–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furtado, D.; Björnmalm, M.; Ayton, S.; Bush, A.I.; Kempe, K.; Caruso, F. Overcoming the Blood–Brain Barrier: The Role of Nanomaterials in Treating Neurological Diseases. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1801362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teleanu, D.M.; Chircov, C.; Grumezescu, A.M.; Volceanov, A.; Teleanu, R.I. Blood-Brain Delivery Methods Using Nanotechnology. Pharmaceutics 2018, 10, 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandit, R.; Chen, L.; Götz, J. The blood-brain barrier: Physiology and strategies for drug delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2020, 165–166, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramadi, K.B.; Bashyam, A.; Frangieh, C.J.; Rousseau, E.B.; Cotler, M.J.; Langer, R.; Graybiel, A.M.; Cima, M.J. Computationally Guided Intracerebral Drug Delivery via Chronically Implanted Microdevices. Cell Rep. 2020, 31, 107734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cesca, F.; Limongi, T.; Accardo, A.; Rocchi, A.; Orlando, M.; Shalabaeva, V.; Di Fabrizio, E.; Benfenati, F. Fabrication of biocompatible free-standing nanopatterned films for primary neuronal cultures. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 45696–45702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limongi, T.; Rocchi, A.; Cesca, F.; Tan, H.; Miele, E.; Giugni, A.; Orlando, M.; Perrone Donnorso, M.; Perozziello, G.; Benfenati, F. Delivery of brain-derived neurotrophic factor by 3D biocompatible polymeric scaffolds for neural tissue engineering and neuronal regeneration. Mol. Neurobiol. 2018, 55, 8788–8798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Shen, Z.; Anraku, Y.; Kataoka, K.; Chen, X. Nanomaterial-based blood-brain-barrier (BBB) crossing strategies. Biomaterials 2019, 224, 119491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdő, F.; Bors, L.A.; Farkas, D.; Bajza, Á.; Gizurarson, S. Evaluation of intranasal delivery route of drug administration for brain targeting. Brain Res. Bull. 2018, 143, 155–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crowe, T.P.; Greenlee, M.H.W.; Kanthasamy, A.G.; Hsu, W.H. Mechanism of intranasal drug delivery directly to the brain. Life Sci. 2018, 195, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, S.U.; Shehzad, A.; Ahmed, M.B.; Lee, Y.S. Intranasal Delivery of Nanoformulations: A Potential Way of Treatment for Neurological Disorders. Molecules 2020, 25, 1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.-T.-L.; Maeng, H.-J. Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of Intranasal Solid Lipid Nanoparticles and Nanostructured Lipid Carriers for Nose-to-Brain Delivery. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umlauf, B.J.; Shusta, E.V. Exploiting BBB disruption for the delivery of nanocarriers to the diseased CNS. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2019, 60, 146–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinkiewicz, M.; Pinkiewicz, M.; Walecki, J.; Zaczyński, A.; Zawadzki, M. Breaking Barriers in Neuro-Oncology: A Scoping Literature Review on Invasive and Non-Invasive Techniques for Blood–Brain Barrier Disruption. Cancers 2024, 16, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, K.-T.; Wei, K.-C.; Liu, H.-L. Theranostic strategy of focused ultrasound induced blood-brain barrier opening for CNS disease treatment. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thombre, R.; Mess, G.; Kempski Leadingham, K.M.; Kapoor, S.; Hersh, A.; Acord, M.; Kaovasia, T.; Theodore, N.; Tyler, B.; Manbachi, A. Towards standardization of the parameters for opening the blood–brain barrier with focused ultrasound to treat glioblastoma multiforme: A systematic review of the devices, animal models, and therapeutic compounds used in rodent tumor models. Front. Oncol. 2023, 12, 1072780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorick, C.M.; Breza, V.R.; Nowak, K.M.; Cheng, V.W.; Fisher, D.G.; Debski, A.C.; Hoch, M.R.; Demir, Z.E.; Tran, N.M.; Schwartz, M.R. Applications of focused ultrasound-mediated blood-brain barrier opening. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2022, 191, 114583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anastasiadis, P.; Gandhi, D.; Guo, Y.; Ahmed, A.K.; Bentzen, S.M.; Arvanitis, C.; Woodworth, G.F. Localized blood-brain barrier opening in infiltrating gliomas with MRI-guided acoustic emissions-controlled focused ultrasound. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2103280118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mainprize, T.; Lipsman, N.; Huang, Y.; Meng, Y.; Bethune, A.; Ironside, S.; Heyn, C.; Alkins, R.; Trudeau, M.; Sahgal, A.; et al. Blood-Brain Barrier Opening in Primary Brain Tumors with Non-invasive MR-Guided Focused Ultrasound: A Clinical Safety and Feasibility Study. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, Y.; Pople, C.B.; Suppiah, S.; Llinas, M.; Huang, Y.; Sahgal, A.; Perry, J.; Keith, J.; Davidson, B.; Hamani, C.; et al. MR-guided focused ultrasound liquid biopsy enriches circulating biomarkers in patients with brain tumors. Neuro Oncol. 2021, 23, 1789–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpentier, A.; Canney, M.; Vignot, A.; Reina, V.; Beccaria, K.; Horodyckid, C.; Karachi, C.; Leclercq, D.; Lafon, C.; Chapelon, J.-Y.; et al. Clinical trial of blood-brain barrier disruption by pulsed ultrasound. Sci. Transl. Med. 2016, 8, 343re2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.-T.; Chai, W.-Y.; Lin, Y.-J.; Lin, C.-J.; Chen, P.-Y.; Tsai, H.-C.; Huang, C.-Y.; Kuo, J.S.; Liu, H.-L.; Wei, K.-C. Neuronavigation-guided focused ultrasound for transcranial blood-brain barrier opening and immunostimulation in brain tumors. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eabd0772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.H.; Kim, M.J.; Jung, H.H.; Chang, W.S.; Choi, H.S.; Rachmilevitch, I.; Zadicario, E.; Chang, J.W. One-Year Outcome of Multiple Blood-Brain Barrier Disruptions With Temozolomide for the Treatment of Glioblastoma. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abrahao, A.; Meng, Y.; Llinas, M.; Huang, Y.; Hamani, C.; Mainprize, T.; Aubert, I.; Heyn, C.; Black, S.E.; Hynynen, K.; et al. First-in-human trial of blood–brain barrier opening in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis using MR-guided focused ultrasound. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 4373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pineda-Pardo, J.A.; Gasca-Salas, C.; Fernández-Rodríguez, B.; Rodríguez-Rojas, R.; Del Álamo, M.; Obeso, I.; Hernández-Fernández, F.; Trompeta, C.; Martínez-Fernández, R.; Matarazzo, M.; et al. Striatal Blood-Brain Barrier Opening in Parkinson’s Disease Dementia: A Pilot Exploratory Study. Mov. Disord. 2022, 37, 2057–2065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lipsman, N.; Meng, Y.; Bethune, A.J.; Huang, Y.; Lam, B.; Masellis, M.; Herrmann, N.; Heyn, C.; Aubert, I.; Boutet, A.; et al. Blood–brain barrier opening in Alzheimer’s disease using MR-guided focused ultrasound. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 2336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehta, R.I.; Carpenter, J.S.; Mehta, R.I.; Haut, M.W.; Wang, P.; Ranjan, M.; Najib, U.; D’Haese, P.F.; Rezai, A.R. Ultrasound-mediated blood-brain barrier opening uncovers an intracerebral perivenous fluid network in persons with Alzheimer’s disease. Fluids Barriers CNS 2023, 20, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, Y.; Goubran, M.; Rabin, J.S.; McSweeney, M.; Ottoy, J.; Pople, C.B.; Huang, Y.; Storace, A.; Ozzoude, M.; Bethune, A.; et al. Blood-brain barrier opening of the default mode network in Alzheimer’s disease with magnetic resonance-guided focused ultrasound. Brain 2023, 146, 865–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Li, Z.; Pan, M.; Fiaz, M.; Hao, Y.; Yan, Y.; Sun, L.; Yan, F. Ultrasound-mediated blood-brain barrier opening: An effective drug delivery system for theranostics of brain diseases. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2022, 190, 114539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stamp, M.E.M.; Halwes, M.; Nisbet, D.; Collins, D.J. Breaking barriers: Exploring mechanisms behind opening the blood–brain barrier. Fluids Barriers CNS 2023, 20, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Feng, W.; Vodovozova, E.; Tretiakova, D.; Boldyrevd, I.; Li, Y.; Kürths, J.; Yu, T.; Semyachkina-Glushkovskaya, O.; Zhu, D. Photodynamic opening of the blood-brain barrier to high weight molecules and liposomes through an optical clearing skull window. Biomed. Opt. Express 2018, 9, 4850–4862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butt, O.H.; Zhou, A.Y.; Huang, J.; Leidig, W.A.; Silberstein, A.E.; Chheda, M.G.; Johanns, T.M.; Ansstas, G.; Liu, J.; Talcott, G.; et al. A phase II study of laser interstitial thermal therapy combined with doxorubicin in patients with recurrent glioblastoma. Neurooncol. Adv. 2021, 3, vdab164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, H.; Huang, J.; Khaddour, K.; Butt, O.H.; Ansstas, G.; Chen, J.; Katumba, R.G.; Kim, A.H.; Leuthardt, E.C.; Campian, J.L. Prolonged response of recurrent IDH-wild-type glioblastoma to laser interstitial thermal therapy with pembrolizumab. CNS Oncol. 2022, 11, Cns81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharabi, S.; Bresler, Y.; Ravid, O.; Shemesh, C.; Atrakchi, D.; Schnaider-Beeri, M.; Gosselet, F.; Dehouck, L.; Last, D.; Guez, D. Transient blood–brain barrier disruption is induced by low pulsed electrical fields in vitro: An analysis of permeability and trans-endothelial electric resistivity. Drug Deliv. 2019, 26, 459–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Upton, D.H.; Ung, C.; George, S.M.; Tsoli, M.; Kavallaris, M.; Ziegler, D.S. Challenges and opportunities to penetrate the blood-brain barrier for brain cancer therapy. Theranostics 2022, 12, 4734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saraiva, C.; Praça, C.; Ferreira, R.; Santos, T.; Ferreira, L.; Bernardino, L. Nanoparticle-mediated brain drug delivery: Overcoming blood–brain barrier to treat neurodegenerative diseases. J. Control. Release 2016, 235, 34–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinheiro, R.G.R.; Coutinho, A.J.; Pinheiro, M.; Neves, A.R. Nanoparticles for Targeted Brain Drug Delivery: What Do We Know? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 11654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Gailani, M.; Liu, M.; Wen, J. Ligands for oral delivery of peptides across the blood-brain-barrier. Acta Mater. Medica 2022, 1, 106–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, X.; Chen, J.; Gao, J. Nanocarriers as a powerful vehicle to overcome blood-brain barrier in treating neurodegenerative diseases: Focus on recent advances. Asian J. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 14, 480–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, G.; Lakkadwala, S.; Modgil, A.; Singh, J. The Role of Cell-Penetrating Peptide and Transferrin on Enhanced Delivery of Drug to Brain. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agwa, M.M.; Sabra, S. Lactoferrin coated or conjugated nanomaterials as an active targeting approach in nanomedicine. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 167, 1527–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradi, S.Z.; Momtaz, S.; Bayrami, Z.; Farzaei, M.H.; Abdollahi, M. Nanoformulations of Herbal Extracts in Treatment of Neurodegenerative Disorders. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 8, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mojarad-Jabali, S.; Farshbaf, M.; Walker, P.R.; Hemmati, S.; Fatahi, Y.; Zakeri-Milani, P.; Sarfraz, M.; Valizadeh, H. An update on actively targeted liposomes in advanced drug delivery to glioma. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 602, 120645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scicluna, M.C.; Vella-Zarb, L. Evolution of Nanocarrier Drug-Delivery Systems and Recent Advancements in Covalent Organic Framework–Drug Systems. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2020, 3, 3097–3115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, M.J.; Billingsley, M.M.; Haley, R.M.; Wechsler, M.E.; Peppas, N.A.; Langer, R. Engineering precision nanoparticles for drug delivery. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2021, 20, 101–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aslam, M.; Javed, M.N.; Deeb, H.H.; Nicola, M.K.; Mirza, M.; Alam, M.S.; Akhtar, M.H.; Waziri, A. Lipid nanocarriers for neurotherapeutics: Introduction, challenges, blood-brain barrier, and promises of delivery approaches. CNS Neurol. Disord.-Drug Targets 2022, 21, 952–965. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Susa, F.; Bucca, G.; Limongi, T.; Cauda, V.; Pisano, R. Enhancing the preservation of liposomes: The role of cryoprotectants, lipid formulations and freezing approaches. Cryobiology 2021, 98, 46–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frankel, B.M.; Cachia, D.; Patel, S.J.; Das, A. Targeting Subventricular Zone Progenitor Cells with Intraventricular Liposomal Encapsulated Cytarabine in Patients with Secondary Glioblastoma: A Report of Two Cases. SN Compr. Clin. Med. 2020, 2, 836–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schauwvlieghe, A.F.A.D.; Bredius, R.G.M.; Verdijk, R.M.; Smiers, F.J.W.; van der Beek, M.T.; Goemans, B.F.; Zwaan, C.M.; Brüggemann, R.J.; Rijnders, B.J.A. Management of cerebral azole-resistant Aspergillus fumigatus infection: A role for intraventricular liposomal-amphotericin B. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2020, 22, 354–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toprak, D.; Öcal Demir, S.; Kadayifci, E.K.; Türel, Ö.; Soysal, A.; Bakir, M. Recurrent Candida albicans Ventriculitis Treated with Intraventricular Liposomal Amphotericin B. Case Rep. Infect. Dis. 2015, 2015, 340725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stepien, N.; Peyrl, A.; Azizi, A.; Gojo, J.; Mayr, L.; Reisinger, D.; Haberler, C.; Czech, T.; Slavc, I. DDEL-03. Long-term intraventricular therapy alternating etoposide and liposomal cytarabine: Experience in 75 children and adolescents with malignant brain tumors. Neuro-Oncol. 2020, 22, iii284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juhairiyah, F.; de Lange, E.C.M. Understanding Drug Delivery to the Brain Using Liposome-Based Strategies: Studies that Provide Mechanistic Insights Are Essential. AAPS J. 2021, 23, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zalba, S.; Ten Hagen, T.L.; Burgui, C.; Garrido, M.J. Stealth nanoparticles in oncology: Facing the PEG dilemma. J. Control. Release 2022, 351, 22–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raju, R.; Abuwatfa, W.H.; Pitt, W.G.; Husseini, G.A. Liposomes for the Treatment of Brain Cancer-A Review. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- William, P.; Ande, B.; John, F.; Vibhudutta, A.; Toral, P.; Marc, H.; Norman, L.; Cheri, R.; Joel, M.; Jeffrey, W.; et al. Rhenium-186-NanoLiposome (186RNL) in the treatment of relapse/recurrent glioblastoma (rGBM): A novel approach for cancer therapy. J. Nucl. Med. 2022, 63, 2488. [Google Scholar]
- Woodall, R.T.; Hormuth Ii, D.A.; Wu, C.; Abdelmalik, M.R.A.; Phillips, W.T.; Bao, A.; Hughes, T.J.R.; Brenner, A.J.; Yankeelov, T.E. Patient specific, imaging-informed modeling of rhenium-186 nanoliposome delivery via convection-enhanced delivery in glioblastoma multiforme. Biomed. Phys. Eng. Express 2021, 7, 045012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beier, C.P.; Schmid, C.; Gorlia, T.; Kleinletzenberger, C.; Beier, D.; Grauer, O.; Steinbrecher, A.; Hirschmann, B.; Brawanski, A.; Dietmaier, C.; et al. RNOP-09: Pegylated liposomal doxorubicine and prolonged temozolomide in addition to radiotherapy in newly diagnosed glioblastoma—A phase II study. BMC Cancer 2009, 9, 308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melnick, K.; Dastmalchi, F.; Mitchell, D.; Rahman, M.; Sayour, E.J. Contemporary RNA Therapeutics for Glioblastoma. Neuromolecular Med. 2022, 24, 8–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brandsma, D.; Kerklaan, B.M.; Diéras, V.; Altintas, S.; Anders, C.K.; Ballester, M.A.; Gelderblom, H.; Soetekouw, P.M.M.B.; Gladdines, W.; Lonnqvist, F.; et al. 472P—Phase 1/2A Study of Glutathione Pegylated Liposomal Doxorubicin (2B3-101) in Patients with Brain Metastases (Bm) from Solid Tumors or Recurrent High Grade Gliomas (Hgg). Ann. Oncol. 2014, 25, iv157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Read, R.D. Repurposing the drug verteporfin as anti-neoplastic therapy for glioblastoma. Neuro Oncol. 2022, 24, 708–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clarke, J.L.; Molinaro, A.M.; Cabrera, J.R.; DeSilva, A.A.; Rabbitt, J.E.; Prey, J.; Drummond, D.C.; Kim, J.; Noble, C.; Fitzgerald, J.B.; et al. A phase 1 trial of intravenous liposomal irinotecan in patients with recurrent high-grade glioma. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2017, 79, 603–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, J.L.; Molinaro, A.M.; DeSilva, A.A.; Rabbitt, J.E.; Drummond, D.C.; Chang, S.M.; Butowski, N.A.; Prados, M. A phase I trial of intravenous liposomal irinotecan in patients with recurrent high-grade gliomas. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 2029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, J.S.; Aghi, M.K. Chronic convection-enhanced intratumoural delivery of chemotherapy for glioblastoma. Lancet Oncol. 2022, 23, 1347–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peyrl, A.; Chocholous, M.; Sabel, M.; Lassaletta, A.; Sterba, J.; Leblond, P.; Nysom, K.; Torsvik, I.; Chi, S.N.; Perwein, T.; et al. Sustained Survival Benefit in Recurrent Medulloblastoma by a Metronomic Antiangiogenic Regimen: A Nonrandomized Controlled Trial. JAMA Oncol. 2023, 9, 1688–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Q.; Mao, K.-L.; Tian, F.-R.; Yang, J.-J.; Chen, P.-P.; Xu, J.; Fan, Z.-L.; Zhao, Y.-P.; Li, W.-F.; Zheng, L.; et al. Brain tumor-targeted delivery and therapy by focused ultrasound introduced doxorubicin-loaded cationic liposomes. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2016, 77, 269–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghaferi, M.; Raza, A.; Koohi, M.; Zahra, W.; Akbarzadeh, A.; Ebrahimi Shahmabadi, H.; Alavi, S.E. Impact of PEGylated liposomal doxorubicin and carboplatin combination on glioblastoma. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 2183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, M.; Fortin, D.; Paquette, B.; Sanche, L. Convection-enhancement delivery of liposomal formulation of oxaliplatin shows less toxicity than oxaliplatin yet maintains a similar median survival time in F98 glioma-bearing rat model. Investig. New Drugs 2016, 34, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashizawa, A.T.; Holt, J.; Faust, K.; Liu, W.; Tiwari, A.; Zhang, N.; Ashizawa, T. Intravenously Administered Novel Liposomes, DCL64, Deliver Oligonucleotides to Cerebellar Purkinje Cells. Cerebellum 2019, 18, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirunagi, T.; Sahashi, K.; Tachikawa, K.; Leu, A.I.; Nguyen, M.; Mukthavaram, R.; Karmali, P.P.; Chivukula, P.; Tohnai, G.; Iida, M. Selective suppression of polyglutamine-expanded protein by lipid nanoparticle-delivered siRNA targeting CAG expansions in the mouse CNS. Mol. Ther.-Nucleic Acids 2021, 24, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunay, M.S.; Ozer, A.Y.; Erdogan, S.; Bodard, S.; Baysal, I.; Gulhan, Z.; Guilloteau, D.; Chalon, S. Development of nanosized, pramipexole-encapsulated liposomes and niosomes for the treatment of Parkinson’s disease. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2017, 17, 5155–5167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Kong, Q.; Chen, Y.; Yang, Z.; Wu, Z.; Xiao, Y.; Chen, Y.; Yu, Z.; Luo, X.; Qu, W. Liposome-based loading enhances the distribution of nicotinamide riboside chloride into the brain and its neuroprotective effects in cerebral ischemic mice. J. Neurorestoratology 2024, 12, 100111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Cao, W.; Xing, H.; Guo, S.; Huang, L.; Wang, L.; Sui, X.; Lu, K.; Luo, Y.; Wang, Y.; et al. A mix & act liposomes of phospholipase A2-phosphatidylserine for acute brain detoxification by blood–brain barrier selective-opening. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2024, 14, 1827–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Li, X.; Liu, L.; Chen, Y.-H.; You, Y.; Gao, Y.; Liu, Y.-Y.; Yang, L.; Tong, K.; Chen, D.-S. Transferrin-Pep63-liposomes accelerate the clearance of Aβ and rescue impaired synaptic plasticity in early Alzheimer’s disease models. Cell Death Discov. 2021, 7, 256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopalco, A.; Cutrignelli, A.; Denora, N.; Lopedota, A.; Franco, M.; Laquintana, V. Transferrin Functionalized Liposomes Loading Dopamine HCl: Development and Permeability Studies across an In Vitro Model of Human Blood–Brain Barrier. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lam, F.C.; Morton, S.W.; Wyckoff, J.; Vu Han, T.-L.; Hwang, M.K.; Maffa, A.; Balkanska-Sinclair, E.; Yaffe, M.B.; Floyd, S.R.; Hammond, P.T. Enhanced efficacy of combined temozolomide and bromodomain inhibitor therapy for gliomas using targeted nanoparticles. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, L.; Li, X.-T.; Ni, Y.-N.; Xiao, H.-H.; Yao, Y.-J.; Wang, Y.-Y.; Ju, R.-J.; Li, H.-Y.; Liu, J.-J.; Fu, M. Transferrin-modified osthole PEGylated liposomes travel the blood-brain barrier and mitigate Alzheimer’s disease-related pathology in APP/PS-1 mice. Int. J. Nanomed. 2020, 15, 2841–2858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Zeng, H.; You, Y.; Wang, R.; Tan, T.; Wang, W.; Yin, L.; Zeng, Z.; Zeng, Y.; Xie, T. Active targeting of orthotopic glioma using biomimetic liposomes co-loaded elemene and cabazitaxel modified by transferritin. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2021, 19, 289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.-S.; Rait, A.; Kim, E.; DeMarco, J.; Pirollo, K.F.; Chang, E.H. Encapsulation of temozolomide in a tumor-targeting nanocomplex enhances anti-cancer efficacy and reduces toxicity in a mouse model of glioblastoma. Cancer Lett. 2015, 369, 250–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.-S.; Rait, A.; Garrido-Sanabria, E.R.; Pirollo, K.F.; Harford, J.B.; Chang, E.H. Nanotherapeutics for gene modulation that prevents apoptosis in the brain and fatal neuroinflammation. Mol. Ther. 2018, 26, 84–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregori, M.; Orlando, A.; Re, F.; Sesana, S.; Nardo, L.; Salerno, D.; Mantegazza, F.; Salvati, E.; Zito, A.; Malavasi, F.; et al. Novel Antitransferrin Receptor Antibodies Improve the Blood–Brain Barrier Crossing Efficacy of Immunoliposomes. J. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 105, 276–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.-S.; Jung, H.-J.; Oh, J.-S.; Song, D.-Y. Use of PEGylated Immunoliposomes to Deliver Dopamine Across the Blood–Brain Barrier in a Rat Model of Parkinson’s Disease. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2016, 22, 817–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnsen, K.B.; Burkhart, A.; Melander, F.; Kempen, P.J.; Vejlebo, J.B.; Siupka, P.; Nielsen, M.S.; Andresen, T.L.; Moos, T. Targeting transferrin receptors at the blood-brain barrier improves the uptake of immunoliposomes and subsequent cargo transport into the brain parenchyma. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 10396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shein, S.A.; Kuznetsov, I.I.; Abakumova, T.O.; Chelushkin, P.S.; Melnikov, P.A.; Korchagina, A.A.; Bychkov, D.A.; Seregina, I.F.; Bolshov, M.A.; Kabanov, A.V.; et al. VEGF- and VEGFR2-Targeted Liposomes for Cisplatin Delivery to Glioma Cells. Mol. Pharm. 2016, 13, 3712–3723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, H.; Qiao, G.; Liu, M.; Zhang, C.; Cui, D.; Ma, L. Dual-modified cationic liposomes loaded with paclitaxel and survivin siRNA for targeted imaging and therapy of cancer stem cells in brain glioma. Drug Deliv. 2018, 25, 1718–1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.-J.; Chuang, E.-Y.; Cheng, Y.-H.; Anilkumar, T.; Chen, H.-A.; Chen, J.-P. Thermosensitive magnetic liposomes for alternating magnetic field-inducible drug delivery in dual targeted brain tumor chemotherapy. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 373, 720–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grafals-Ruiz, N.; Rios-Vicil, C.I.; Lozada-Delgado, E.L.; Quiñones-Díaz, B.I.; Noriega-Rivera, R.A.; Martínez-Zayas, G.; Santana-Rivera, Y.; Santiago-Sánchez, G.S.; Valiyeva, F.; Vivas-Mejía, P.E. Brain targeted gold liposomes improve RNAi delivery for glioblastoma. Int. J. Nanomed. 2020, 15, 2809–2828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajora, M.; Ding, L.; Valic, M.; Jiang, W.; Overchuk, M.; Chen, J.; Zheng, G. Tailored theranostic apolipoprotein E3 porphyrin-lipid nanoparticles target glioblastoma. Chem. Sci. 2017, 8, 5371–5384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, B.; Zhao, Y.; Dong, S.; Sun, Y.; Hao, F.; Xie, J.; Teng, L.; Lee, R.J.; Fu, Y.; Bi, Y. Cell-penetrating peptide-coated liposomes for drug delivery across the blood–brain barrier. Anticancer Res. 2019, 39, 237–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Mei, L.; Xu, C.; Yu, Q.; Shi, K.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Gao, H.; Zhang, Z. Dual receptor recognizing cell penetrating peptide for selective targeting, efficient intratumoral diffusion and synthesized anti-glioma therapy. Theranostics 2016, 6, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, Y.-C.; Chen, C.-L.; Rajesh, R. Optimized liposomes with transactivator of transcription peptide and anti-apoptotic drugs to target hippocampal neurons and prevent tau-hyperphosphorylated neurodegeneration. Acta Biomater. 2019, 87, 207–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, S.; Layek, B.; Singh, J. Design and validation of liposomal ApoE2 gene delivery system to evade blood–brain barrier for effective treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Mol. Pharm. 2020, 18, 714–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, M.; Lin, Q.; He, S.; Wang, L.; Fu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, L. A brain targeting functionalized liposomes of the dopamine derivative N-3, 4-bis (pivaloyloxy)-dopamine for treatment of Parkinson’s disease. J. Control. Release 2018, 277, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, Y.-C.; Tsai, H.-C.; Rajesh, R. Glutathione liposomes carrying ceftriaxone, fk506, and nilotinib to control overexpressed dopamine markers and apoptotic factors in neurons. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2021, 7, 3242–3255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, K.-H.; Hong, S.-T.; Wang, H.-T.; Lo, Y.-L.; Lin, A.M.-Y.; Yang, J.C.-H. Enhancing Anticancer Effect of Gefitinib across the Blood–Brain Barrier Model Using Liposomes Modified with One α-Helical Cell-Penetrating Peptide or Glutathione and Tween 80. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Shi, K.; Tang, X.; Wei, J.; Cun, X.; Chen, X.; Yu, Q.; Zhang, Z.; He, Q. pH-sensitive folic acid and dNP2 peptide dual-modified liposome for enhanced targeted chemotherapy of glioma. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 124, 240–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, Y.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, L.; Xiao, W.; Yang, J.; Guo, L.; Wu, Y. Dual-targeting for brain-specific liposomes drug delivery system: Synthesis and preliminary evaluation. Bioorganic Med. Chem. 2018, 26, 4677–4686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vijayakumar, M.R.; Vajanthri, K.Y.; Balavigneswaran, C.K.; Mahto, S.K.; Mishra, N.; Muthu, M.S.; Singh, S. Pharmacokinetics, biodistribution, in vitro cytotoxicity and biocompatibility of Vitamin E TPGS coated trans resveratrol liposomes. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2016, 145, 479–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, R.P.; Sharma, G.; Kumari, L.; Koch, B.; Singh, S.; Bharti, S.; Rajinikanth, P.S.; Pandey, B.L.; Muthu, M.S. RGD-TPGS decorated theranostic liposomes for brain targeted delivery. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2016, 147, 129–141. [Google Scholar]
- Sonkar, R.; Sonali; Jha, A.; Viswanadh, M.K.; Burande, A.S.; Narendra; Pawde, D.M.; Patel, K.K.; Singh, M.; Koch, B.; et al. Gold liposomes for brain-targeted drug delivery: Formulation and brain distribution kinetics. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2021, 120, 111652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuo, Y.-C.; Chen, I.-Y.; Rajesh, R. Astragaloside IV-and nesfatin-1-encapsulated phosphatidylserine liposomes conjugated with wheat germ agglutinin and leptin to activate anti-apoptotic pathway and block phosphorylated tau protein expression for Parkinson’s disease treatment. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2021, 129, 112361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Ying, X.; Xu, H.; Yan, H.; Li, X.; Tang, H. The functional curcumin liposomes induce apoptosis in C6 glioblastoma cells and C6 glioblastoma stem cells in vitro and in animals. Int. J. Nanomed. 2017, 12, 1369–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewicky, J.D.; Fraleigh, N.L.; Boraman, A.; Martel, A.L.; Nguyen, T.M.-D.; Schiller, P.W.; Shiao, T.C.; Roy, R.; Montaut, S.; Le, H.-T. Mannosylated glycoliposomes for the delivery of a peptide kappa opioid receptor antagonist to the brain. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2020, 154, 290–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.-Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Guo, R.-B.; Liu, Y.; Li, X.-T.; Ma, L.-Y.; Kong, L. Menthol-modified paclitaxel multifunctional cationic liposomes cross the blood-brain barrier and target glioma stem cells for treatment of glioblastoma. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2024, 93, 105387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.-Y.; Zhang, C.-X.; Liu, L.; Mu, L.-M.; Zeng, F.; Ju, R.-J.; Xie, H.-J.; Yan, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Lu, W.-L. Construction of functional targeting daunorubicin liposomes used for eliminating brain glioma and glioma stem cells. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2016, 12, 1404–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omar, S.H.; Osman, R.; Mamdouh, W.; Abdel-Bar, H.M.; Awad, G.A.S. Bioinspired lipid-polysaccharide modified hybrid nanoparticles as a brain-targeted highly loaded carrier for a hydrophilic drug. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 165, 483–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, I.; Yasir, M.; Verma, M.; Singh, A.P. Nanostructured Lipid Carriers: A Groundbreaking Approach for Transdermal Drug Delivery. Adv. Pharm. Bull. 2020, 10, 150–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Satapathy, M.K.; Yen, T.-L.; Jan, J.-S.; Tang, R.-D.; Wang, J.-Y.; Taliyan, R.; Yang, C.-H. Solid Lipid Nanoparticles (SLNs): An Advanced Drug Delivery System Targeting Brain through BBB. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, H.; Zhang, S.; Wang, J.; Chen, Q. A Review on Polymer and Lipid-Based Nanocarriers and Its Application to Nano-Pharmaceutical and Food-Based Systems. Front. Nutr. 2021, 8, 783831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hady, M.A.; Sayed, O.M.; Akl, M.A. Brain uptake and accumulation of new levofloxacin-doxycycline combination through the use of solid lipid nanoparticles: Formulation; Optimization and in-vivo evaluation. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2020, 193, 111076. [Google Scholar]
- Rassu, G.; Soddu, E.; Posadino, A.M.; Pintus, G.; Sarmento, B.; Giunchedi, P.; Gavini, E. Nose-to-brain delivery of BACE1 siRNA loaded in solid lipid nanoparticles for Alzheimer’s therapy. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2017, 152, 296–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinheiro, R.; Granja, A.; Loureiro, J.A.; Pereira, M.; Pinheiro, M.; Neves, A.R.; Reis, S. Quercetin lipid nanoparticles functionalized with transferrin for Alzheimer’s disease. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2020, 148, 105314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muntoni, E.; Martina, K.; Marini, E.; Giorgis, M.; Lazzarato, L.; Salaroglio, I.C.; Riganti, C.; Lanotte, M.; Battaglia, L. Methotrexate-Loaded Solid Lipid Nanoparticles: Protein Functionalization to Improve Brain Biodistribution. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, I.; Swami, R.; Pooja, D.; Jeengar, M.K.; Khan, W.; Sistla, R. Lactoferrin bioconjugated solid lipid nanoparticles: A new drug delivery system for potential brain targeting. J. Drug Target. 2016, 24, 212–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuo, Y.-C.; Cheng, S.-J. Brain targeted delivery of carmustine using solid lipid nanoparticles modified with tamoxifen and lactoferrin for antitumor proliferation. Int. J. Pharm. 2016, 499, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Topal, G.R.; Mészáros, M.; Porkoláb, G.; Szecskó, A.; Polgár, T.F.; Siklós, L.; Deli, M.A.; Veszelka, S.; Bozkir, A. ApoE-Targeting Increases the Transfer of Solid Lipid Nanoparticles with Donepezil Cargo across a Culture Model of the Blood–Brain Barrier. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadari, A.; Pooja, D.; Gora, R.H.; Gudem, S.; Kolapalli, V.R.M.; Kulhari, H.; Sistla, R. Design of multifunctional peptide collaborated and docetaxel loaded lipid nanoparticles for antiglioma therapy. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2018, 132, 168–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loureiro, J.A.; Andrade, S.; Duarte, A.; Neves, A.R.; Queiroz, J.F.; Nunes, C.; Sevin, E.; Fenart, L.; Gosselet, F.; Coelho, M.A.N.; et al. Resveratrol and Grape Extract-loaded Solid Lipid Nanoparticles for the Treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease. Molecules 2017, 22, 277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandomi, N.; Varshochian, R.; Atyabi, F.; Ghahremani, M.H.; Sharifzadeh, M.; Amini, M.; Dinarvand, R. Solid lipid nanoparticles surface modified with anti-Contactin-2 or anti-Neurofascin for brain-targeted delivery of medicines. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2017, 22, 426–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karami, Z.; Zanjani, M.R.S.; Hamidi, M. Nanoemulsions in CNS drug delivery: Recent developments, impacts and challenges. Drug Discov. Today 2019, 24, 1104–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, S.; Sharma, A.; Jain, V. An Overview of Nanostructured Lipid Carriers and its Application in Drug Delivery through Different Routes. Adv. Pharm. Bull. 2023, 13, 446–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Limongi, T.; Susa, F.; Marini, M.; Allione, M.; Torre, B.; Pisano, R.; di Fabrizio, E. Lipid-Based Nanovesicular Drug Delivery Systems. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 3391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gharbavi, M.; Amani, J.; Kheiri-Manjili, H.; Danafar, H.; Sharafi, A. Niosome: A promising nanocarrier for natural drug delivery through blood-brain barrier. Adv. Pharmacol. Sci. 2018, 2018, 6847971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boche, M.; Pokharkar, V. Quetiapine nanoemulsion for intranasal drug delivery: Evaluation of brain-targeting efficiency. AAPS PharmSciTech 2017, 18, 686–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdou, E.M.; Kandil, S.M.; El Miniawy, H.M. Brain targeting efficiency of antimigrain drug loaded mucoadhesive intranasal nanoemulsion. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 529, 667–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.; Liu, C.; Zhai, W.; Zhuang, N.; Han, T.; Ding, Z. The Optimization Design Of Lactoferrin Loaded HupA Nanoemulsion For Targeted Drug Transport Via Intranasal Route. Int. J. Nanomed. 2019, 14, 9217–9234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karami, Z.; Saghatchi Zanjani, M.R.; Rezaee, S.; Rostamizadeh, K.; Hamidi, M. Neuropharmacokinetic evaluation of lactoferrin-treated indinavir-loaded nanoemulsions: Remarkable brain delivery enhancement. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2019, 45, 736–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deshkar, S.S.; Jadhav, M.S.; Shirolkar, S.V. Development of carbamazepine nanostructured lipid carrier loaded thermosensitive gel for intranasal delivery. Adv. Pharm. Bull. 2021, 11, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahmy, U.A.; Ahmed, O.A.; Badr-Eldin, S.M.; Aldawsari, H.M.; Okbazghi, S.Z.; Awan, Z.A.; Bakhrebah, M.A.; Alomary, M.N.; Abdulaal, W.H.; Medina, C. Optimized nanostructured lipid carriers integrated into in situ nasal gel for enhancing brain delivery of flibanserin. Int. J. Nanomed. 2020, 15, 5253–5264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, S.; Bicker, J.; Fonseca, C.; Ferreira, N.R.; Vitorino, C.; Alves, G.; Falcão, A.; Fortuna, A. Encapsulated escitalopram and paroxetine intranasal co-administration: In vitro/in vivo evaluation. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 751321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassanzadeh, P.; Atyabi, F.; Dinarvand, R.; Dehpour, A.-R.; Azhdarzadeh, M.; Dinarvand, M. Application of nanostructured lipid carriers: The prolonged protective effects for sesamol in in vitro and in vivo models of ischemic stroke via activation of PI3K signalling pathway. DARU J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 25, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salem, L.H.; El-Feky, G.S.; Fahmy, R.H.; El Gazayerly, O.N.; Abdelbary, A. Coated Lipidic Nanoparticles as a New Strategy for Enhancing Nose-to-Brain Delivery of a Hydrophilic Drug Molecule. J. Pharm. Sci. 2020, 109, 2237–2251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taymouri, S.; Minaiyan, M.; Ebrahimi, F.; Tavakoli, N. In-vitro and in-vivo evaluation of chitosan-based thermosensitive gel containing lorazepam NLCs for the treatment of status epilepticus. Iet Nanobiotechnol. 2020, 14, 148–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Zhang, J.; Hu, H.; Qiao, M.; Chen, D.; Zhao, X.; Yang, C. Design of lactoferrin modified lipid nano-carriers for efficient brain-targeted delivery of nimodipine. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2018, 92, 1031–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, F.; Asghar, S.; Gao, S.; Su, Z.; Song, J.; Huo, M.; Meng, W.; Ping, Q.; Xiao, Y. A novel LDL-mimic nanocarrier for the targeted delivery of curcumin into the brain to treat Alzheimer’s disease. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2015, 134, 88–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sita, V.G.; Jadhav, D.; Vavia, P. Niosomes for nose-to-brain delivery of bromocriptine: Formulation development, efficacy evaluation and toxicity profiling. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2020, 58, 101791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mashal, M.; Attia, N.; Soto-Sánchez, C.; Martínez-Navarrete, G.; Fernández, E.; Puras, G.; Pedraz, J.L. Non-viral vectors based on cationic niosomes as efficient gene delivery vehicles to central nervous system cells into the brain. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 552, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatami Nemati, S.; Bigdeli, M.R.; Mortazavi Moghadam, F.; Sharifi, K. Neuroprotective effects of niosomes loaded with thymoquinone in the cerebral ischemia model of male Wistar rats. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2023, 48, 102637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Jammal, A.; Bigdeli, M.R.; Mortazavi Moghadam, F. pH-sensitive oleuropein-loaded niosome: Efficient treatment for metastatic brain tumors in initial steps in-vivo. OpenNano 2022, 8, 100095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mészáros, M.; Porkoláb, G.; Kiss, L.; Pilbat, A.-M.; Kóta, Z.; Kupihár, Z.; Kéri, A.; Galbács, G.; Siklós, L.; Tóth, A.; et al. Niosomes decorated with dual ligands targeting brain endothelial transporters increase cargo penetration across the blood-brain barrier. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 123, 228–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khallaf, R.A.; Aboud, H.M.; Sayed, O.M. Surface modified niosomes of olanzapine for brain targeting via nasal route; preparation, optimization, and in vivo evaluation. J. Liposome Res. 2020, 30, 163–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tulbah, A.S.; Elkomy, M.H.; Zaki, R.M.; Eid, H.M.; Eissa, E.M.; Ali, A.A.; Yassin, H.A.; Aldosari, B.N.; Naguib, I.A.; Hassan, A.H. Novel nasal niosomes loaded with lacosamide and coated with chitosan: A possible pathway to target the brain to control partial-onset seizures. Int. J. Pharm. X 2023, 6, 100206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rinaldi, F.; Hanieh, P.N.; Chan, L.K.N.; Angeloni, L.; Passeri, D.; Rossi, M.; Wang, J.T.-W.; Imbriano, A.; Carafa, M.; Marianecci, C. Chitosan Glutamate-Coated Niosomes: A Proposal for Nose-to-Brain Delivery. Pharmaceutics 2018, 10, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azhari, H.; Strauss, M.; Hook, S.; Boyd, B.J.; Rizwan, S.B. Stabilising cubosomes with Tween 80 as a step towards targeting lipid nanocarriers to the blood–brain barrier. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2016, 104, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azhari, H.; Younus, M.; Hook, S.M.; Boyd, B.J.; Rizwan, S.B. Cubosomes enhance drug permeability across the blood–brain barrier in zebrafish. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 600, 120411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammad, Y.; Prentice, R.N.; Boyd, B.J.; Rizwan, S.B. Comparison of cubosomes and hexosomes for the delivery of phenytoin to the brain. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 605, 146–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patil, R.P.; Pawara, D.D.; Gudewar, C.S.; Tekade, A.R. Nanostructured cubosomes in an in situ nasal gel system: An alternative approach for the controlled delivery of donepezil HCl to brain. J. Liposome Res. 2019, 29, 264–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eissa, E.M.; Elkomy, M.H.; Eid, H.M.; Ali, A.A.; Abourehab, M.A.S.; Alsubaiyel, A.M.; Naguib, I.A.; Alsalahat, I.; Hassan, A.H. Intranasal Delivery of Granisetron to the Brain via Nanostructured Cubosomes-Based In Situ Gel for Improved Management of Chemotherapy-Induced Emesis. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakkar, H.; Modi, B.; Patel, B. Intranasal spray of cubosomal tizanidine hydrochloride for brain targeting: In vitro and in vivo characterisation. J. Microencapsul. 2023, 40, 366–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deruyver, L.; Rigaut, C.; Gomez-Perez, A.; Lambert, P.; Haut, B.; Goole, J. In vitro Evaluation of Paliperidone Palmitate Loaded Cubosomes Effective for Nasal-to-Brain Delivery. Int. J. Nanomed. 2023, 18, 1085–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.; Wei, Q.; Zhang, H.; Yang, Y.; Jiang, B.; Wang, Z.; Li, S.; Wang, Q.; Hu, M.; Chen, W.; et al. Novel dual targeting cubosomes modified with angiopep-2 for co-delivery GNA and PLHSpT to brain glioma. J. Biomater. Appl. 2023, 38, 743–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, X.; Refaat, A.; Gan, P.-Y.; Fan, B.; Yu, H.; Thang, S.H.; Drummond, C.J.; Voelcker, N.H.; Tran, N.; Zhai, J. Angiopep-2-Functionalized Lipid Cubosomes for Blood–Brain Barrier Crossing and Glioblastoma Treatment. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2024, 16, 12161–12174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limongi, T.; Susa, F.; Dumontel, B.; Racca, L.; Perrone Donnorso, M.; Debellis, D.; Cauda, V. Extracellular Vesicles Tropism: A Comparative Study between Passive Innate Tropism and the Active Engineered Targeting Capability of Lymphocyte-Derived EVs. Membranes 2021, 11, 886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos-Zaldívar, H.M.; Polakovicova, I.; Salas-Huenuleo, E.; Corvalán, A.H.; Kogan, M.J.; Yefi, C.P.; Andia, M.E. Extracellular vesicles through the blood–brain barrier: A review. Fluids Barriers CNS 2022, 19, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lino, M.M.; Simões, S.; Tomatis, F.; Albino, I.; Barrera, A.; Vivien, D.; Sobrino, T.; Ferreira, L. Engineered extracellular vesicles as brain therapeutics. J. Control. Release 2021, 338, 472–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaie, J.; Feghhi, M.; Etemadi, T. A review on exosomes application in clinical trials: Perspective, questions, and challenges. Cell Commun. Signal. 2022, 20, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katakowski, M.; Chopp, M. Exosomes as Tools to Suppress Primary Brain Tumor. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2016, 36, 343–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehghani, L.; Khojasteh, A.; Soleimani, M.; Oraee-Yazdani, S.; Keshel, S.H.; Saadatnia, M.; Saboori, M.; Zali, A.; Hashemi, S.M.; Soleimani, R. Safety of Intraparenchymal Injection of Allogenic Placenta Mesenchymal Stem Cells Derived Exosome in Patients Undergoing Decompressive Craniectomy Following Malignant Middle Cerebral Artery Infarct, A Pilot Randomized Clinical Trial. Int. J. Prev. Med. 2022, 13, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Song, Q.; Dai, C.; Cui, S.; Tang, R.; Li, S.; Chang, J.; Li, P.; Wang, J.; Li, J.; et al. Clinical safety and efficacy of allogenic human adipose mesenchymal stromal cells-derived exosomes in patients with mild to moderate Alzheimer’s disease: A phase I/II clinical trial. Gen. Psychiatr. 2023, 36, e101143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pei, X.; Li, Y.; Zhu, L.; Zhou, Z. Astrocyte-derived exosomes suppress autophagy and ameliorate neuronal damage in experimental ischemic stroke. Exp. Cell Res. 2019, 382, 111474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Hu, G.; Chen, Y.; Yuan, J.; Zhang, J.; Wang, S.; Li, Q.; Wang, Y.; Deng, Z. Embryonic Stem Cell Derived Small Extracellular Vesicles Modulate Regulatory T Cells to Protect against Ischemic Stroke. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 7370–7385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elia, C.A.; Tamborini, M.; Rasile, M.; Desiato, G.; Marchetti, S.; Swuec, P.; Mazzitelli, S.; Clemente, F.; Anselmo, A.; Matteoli, M. Intracerebral injection of extracellular vesicles from mesenchymal stem cells exerts reduced Aβ plaque burden in early stages of a preclinical model of Alzheimer’s disease. Cells 2019, 8, 1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Godoy, M.A.; Saraiva, L.M.; de Carvalho, L.R.; Vasconcelos-dos-Santos, A.; Beiral, H.J.; Ramos, A.B.; de Paula Silva, L.R.; Leal, R.B.; Monteiro, V.H.; Braga, C.V. Mesenchymal stem cells and cell-derived extracellular vesicles protect hippocampal neurons from oxidative stress and synapse damage induced by amyloid-β oligomers. J. Biol. Chem. 2018, 293, 1957–1975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bodart-Santos, V.; de Carvalho, L.R.; de Godoy, M.A.; Batista, A.F.; Saraiva, L.M.; Lima, L.G.; Abreu, C.A.; De Felice, F.G.; Galina, A.; Mendez-Otero, R. Extracellular vesicles derived from human Wharton’s jelly mesenchymal stem cells protect hippocampal neurons from oxidative stress and synapse damage induced by amyloid-β oligomers. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2019, 10, 332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Losurdo, M.; Pedrazzoli, M.; D’Agostino, C.; Elia, C.A.; Massenzio, F.; Lonati, E.; Mauri, M.; Rizzi, L.; Molteni, L.; Bresciani, E.; et al. Intranasal delivery of mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles exerts immunomodulatory and neuroprotective effects in a 3xTg model of Alzheimer’s disease. Stem Cells Transl. Med. 2020, 9, 1068–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cone, A.S.; Yuan, X.; Sun, L.; Duke, L.C.; Vreones, M.P.; Carrier, A.N.; Kenyon, S.M.; Carver, S.R.; Benthem, S.D.; Stimmell, A.C.; et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles ameliorate Alzheimer’s disease-like phenotypes in a preclinical mouse model. Theranostics 2021, 11, 8129–8142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, X.; Huang, M.; Zheng, M.; Dai, C.; Song, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Li, Q.; Gu, X.; Chen, H.; Jiang, G.; et al. ADSCs-derived extracellular vesicles alleviate neuronal damage, promote neurogenesis and rescue memory loss in mice with Alzheimer’s disease. J. Control. Release 2020, 327, 688–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonafede, R.; Turano, E.; Scambi, I.; Busato, A.; Bontempi, P.; Virla, F.; Schiaffino, L.; Marzola, P.; Bonetti, B.; Mariotti, R. ASC-Exosomes Ameliorate the Disease Progression in SOD1(G93A) Murine Model Underlining Their Potential Therapeutic Use in Human ALS. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geffen, Y.; Perets, N.; Horev, R.; Yudin, D.; Oron, O.; Elliott, E.; Marom, E.; Danon, U.; Offen, D. Exosomes derived from adipose mesenchymal stem cells: A potential non-invasive intranasal treatment for autism. Cytotherapy 2020, 22, S49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Duan, L.; Xu, X.; Li, X.; Liu, M.; Chen, H.; Lu, J.; Xia, J. Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes for Treatment of Autism Spectrum Disorder. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2020, 3, 6384–6393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perets, N.; Oron, O.; Herman, S.; Elliott, E.; Offen, D. Exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem cells improved core symptoms of genetically modified mouse model of autism Shank3B. Mol. Autism 2020, 11, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, Q.; Upadhya, D.; Hattiangady, B.; Kim, D.-K.; An, S.Y.; Shuai, B.; Prockop, D.J.; Shetty, A.K. Intranasal MSC-derived A1-exosomes ease inflammation, and prevent abnormal neurogenesis and memory dysfunction after status epilepticus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E3536–E3545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Y.; Chen, B.; Sun, E.; Lu, X.; Li, Z.; Wang, R.; Fang, D. Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Alleviate Brain Damage Following Subarachnoid Hemorrhage via the Interaction of miR-140-5p and HDAC7. Mol. Neurobiol. 2024, 15, 5253–5264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, K.H.; Chen, C.H.; Wallace, C.G.; Yuen, C.M.; Kao, G.S.; Chen, Y.L.; Shao, P.L.; Chen, Y.L.; Chai, H.T.; Lin, K.C.; et al. Intravenous administration of xenogenic adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells (ADMSC) and ADMSC-derived exosomes markedly reduced brain infarct volume and preserved neurological function in rat after acute ischemic stroke. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 74537–74556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xin, H.; Li, Y.; Cui, Y.; Yang, J.J.; Zhang, Z.G.; Chopp, M. Systemic administration of exosomes released from mesenchymal stromal cells promote functional recovery and neurovascular plasticity after stroke in rats. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2013, 33, 1711–1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moon, G.J.; Sung, J.H.; Kim, D.H.; Kim, E.H.; Cho, Y.H.; Son, J.P.; Cha, J.M.; Bang, O.Y. Application of Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles for Stroke: Biodistribution and MicroRNA Study. Transl. Stroke Res. 2019, 10, 509–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikeda, T.; Kawabori, M.; Zheng, Y.; Yamaguchi, S.; Gotoh, S.; Nakahara, Y.; Yoshie, E.; Fujimura, M. Intranasal Administration of Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosome Alleviates Hypoxic-Ischemic Brain Injury. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, C.; Li, X.; Ba, L.; Zhang, M.; Yang, Y.; Gao, Y.; Sun, Z.; Han, Q.; Zhao, R.C. MSC-Derived Exosomes can Enhance the Angiogenesis of Human Brain MECs and Show Therapeutic Potential in a Mouse Model of Parkinson’s Disease. Aging Dis. 2021, 12, 1211–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomi, G.; Surbek, D.; Haesler, V.; Joerger-Messerli, M.; Schoeberlein, A. Exosomes derived from umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells reduce microglia-mediated neuroinflammation in perinatal brain injury. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2019, 10, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsivion-Visbord, H.; Perets, N.; Sofer, T.; Bikovski, L.; Goldshmit, Y.; Ruban, A.; Offen, D. Mesenchymal stem cells derived extracellular vesicles improve behavioral and biochemical deficits in a phencyclidine model of schizophrenia. Transl. Psychiatry 2020, 10, 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Chopp, M.; Zhang, Z.G.; Katakowski, M.; Xin, H.; Qu, C.; Ali, M.; Mahmood, A.; Xiong, Y. Systemic administration of cell-free exosomes generated by human bone marrow derived mesenchymal stem cells cultured under 2D and 3D conditions improves functional recovery in rats after traumatic brain injury. Neurochem. Int. 2017, 111, 69–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Bai, W.; Peng, Y.; Lin, Y.; Tian, M. Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes provide neuroprotection in traumatic brain injury through the lncRNA TUBB6/Nrf2 pathway. Brain Res. 2024, 1824, 148689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, A.M.; Dennahy, I.S.; Bhatti, U.F.; Halaweish, I.; Xiong, Y.; Chang, P.; Nikolian, V.C.; Chtraklin, K.; Brown, J.; Zhang, Y. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes provide neuroprotection and improve long-term neurologic outcomes in a swine model of traumatic brain injury and hemorrhagic shock. J. Neurotrauma 2019, 36, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.; Mahmood, A.; Chopp, M. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles as a cell-free therapy for traumatic brain injury via neuroprotection and neurorestoration. Neural Regen. Res. 2024, 19, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Li, Z.; He, T.; Qu, M.; Jiang, L.; Li, W.; Shi, X.; Pan, J.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Y. M2 microglia-derived exosomes protect the mouse brain from ischemia-reperfusion injury via exosomal miR-124. Theranostics 2019, 9, 2910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Webb, R.L.; Kaiser, E.E.; Jurgielewicz, B.J.; Spellicy, S.; Scoville, S.L.; Thompson, T.A.; Swetenburg, R.L.; Hess, D.C.; West, F.D.; Stice, S.L. Human neural stem cell extracellular vesicles improve recovery in a porcine model of ischemic stroke. Stroke 2018, 49, 1248–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webb, R.L.; Kaiser, E.E.; Scoville, S.L.; Thompson, T.A.; Fatima, S.; Pandya, C.; Sriram, K.; Swetenburg, R.L.; Vaibhav, K.; Arbab, A.S. Human neural stem cell extracellular vesicles improve tissue and functional recovery in the murine thromboembolic stroke model. Transl. Stroke Res. 2018, 9, 530–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Jung, J.-H.; Arvola, O.; Santoso, M.R.; Giffard, R.G.; Yang, P.C.; Stary, C.M. Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes Protect Astrocyte Cultures From in vitro Ischemia and Decrease Injury as Post-stroke Intravenous Therapy. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Zhang, L.; Kuang, Y.; Venkataramani, V.; Jin, F.; Hein, K.; Zafeiriou, M.P.; Lenz, C.; Moebius, W.; Kilic, E. Extracellular vesicles derived from neural progenitor cells––A preclinical evaluation for stroke treatment in mice. Transl. Stroke Res. 2021, 12, 185–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdavipour, M.; Hassanzadeh, G.; Seifali, E.; Mortezaee, K.; Aligholi, H.; Shekari, F.; Sarkoohi, P.; Zeraatpisheh, Z.; Nazari, A.; Movassaghi, S. Effects of neural stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles on neuronal protection and functional recovery in the rat model of middle cerebral artery occlusion. Cell Biochem. Funct. 2020, 38, 373–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apodaca, L.A.; Baddour, A.A.D.; Garcia, C.; Alikhani, L.; Giedzinski, E.; Ru, N.; Agrawal, A.; Acharya, M.M.; Baulch, J.E. Human neural stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles mitigate hallmarks of Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s Res. Ther. 2021, 13, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thome, A.D.; Thonhoff, J.R.; Zhao, W.; Faridar, A.; Wang, J.; Beers, D.R.; Appel, S.H. Extracellular Vesicles Derived From Ex Vivo Expanded Regulatory T Cells Modulate In Vitro and In Vivo Inflammation. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 875825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, S.; Wang, D.; Zhang, S.; Xia, J.; Li, S.; Qiu, Q.; Lee, H.; Wang, J. Anti-glioma effect of ginseng-derived exosomes-like nanoparticles by active blood–brain-barrier penetration and tumor microenvironment modulation. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2023, 21, 253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, L.; Zhang, Z.; Tan, X.; Wang, Z.; Tang, B.; Wang, Z.; Li, M.; Mi, T.; Shen, L.; Long, C.; et al. Antitumor effect of Escherichia coli-derived outer membrane vesicles on neuroblastoma in vitro and in vivo. Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin. 2022, 54, 1301–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Gao, Z.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, H.; Yang, X.; Fang, X.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Ouyang, F. Lactobacillus plantarum-derived extracellular vesicles protect against ischemic brain injury via the microRNA-101a-3p/c-Fos/TGF-β axis. Pharmacol. Res. 2022, 182, 106332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.; Kim, Y.-K.; Han, P.-L. Extracellular vesicles derived from Lactobacillus plantarum increase BDNF expression in cultured hippocampal neurons and produce antidepressant-like effects in mice. Exp. Neurobiol. 2019, 28, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fei, X.; Wang, L.; Dou, Y.-n.; Fei, F.; Zhang, Y.; Lv, W.; He, X.; Wu, X.; Chao, W.; Chen, H. Extracellular vesicle encapsulated Homer1a as novel nanotherapeutics against intracerebral hemorrhage in a mouse model. J. Neuroinflammation 2024, 21, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kutchy, N.A.; Ma, R.; Liu, Y.; Buch, S.; Hu, G. Extracellular vesicle-mediated delivery of ultrasmall superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles to mice brain. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 819516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Liu, H.; Hu, Q.; Wang, J.; Zhang, S.; Cui, W.; Shi, Y.; Bai, H.; Zhou, J.; Han, L.; et al. Astrocyte-Derived Extracellular Vesicular miR-143-3p Dampens Autophagic Degradation of Endothelial Adhesion Molecules and Promotes Neutrophil Transendothelial Migration after Acute Brain Injury. Adv. Sci. 2024, 11, 2305339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, M.; Lin, Q.; Huang, L.; Fu, Y.; Wang, L.; He, S.; Fu, Y.; Yang, S.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, L. Dopamine-loaded blood exosomes targeted to brain for better treatment of Parkinson’s disease. J. Control. Release 2018, 287, 156–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Fogarty, B.; LaForge, B.; Aziz, S.; Pham, T.; Lai, L.; Bai, S. Delivery of Small Interfering RNA to Inhibit Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor in Zebrafish Using Natural Brain Endothelia Cell-Secreted Exosome Nanovesicles for the Treatment of Brain Cancer. AAPS J. 2017, 19, 475–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen Cao, T.G.; Kang, J.H.; Kang, S.J.; Truong Hoang, Q.; Kang, H.C.; Rhee, W.J.; Zhang, Y.S.; Ko, Y.T.; Shim, M.S. Brain endothelial cell-derived extracellular vesicles with a mitochondria-targeting photosensitizer effectively treat glioblastoma by hijacking the blood–brain barrier. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2023, 13, 3834–3848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamshiripour, P.; Rahnama, M.; Nikoobakht, M.; Rad, V.F.; Moradi, A.-R.; Ahmadvand, D. Extracellular vesicles derived from dendritic cells loaded with VEGF-A siRNA and doxorubicin reduce glioma angiogenesis in vitro. J. Control. Release 2024, 369, 128–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Li, Y.; Peng, H.; Liu, R.; Ji, W.; Shi, Z.; Shen, J.; Ma, G.; Zhang, X. Targeted exosome coating gene-chem nanocomplex as “nanoscavenger” for clearing α-synuclein and immune activation of Parkinson’s disease. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaba3967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izco, M.; Blesa, J.; Schleef, M.; Schmeer, M.; Porcari, R.; Al-Shawi, R.; Ellmerich, S.; de Toro, M.; Gardiner, C.; Seow, Y. Systemic exosomal delivery of shRNA minicircles prevents parkinsonian pathology. Mol. Ther. 2019, 27, 2111–2122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalani, A.; Chaturvedi, P.; Kamat, P.K.; Maldonado, C.; Bauer, P.; Joshua, I.G.; Tyagi, S.C.; Tyagi, N. Curcumin-loaded embryonic stem cell exosomes restored neurovascular unit following ischemia-reperfusion injury. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2016, 79, 360–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Q.; Ling, X.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Li, Q.; Niu, X.; Hu, G.; Chen, B.; Li, H.; Wang, Y. Embryonic stem cells-derived exosomes endowed with targeting properties as chemotherapeutics delivery vehicles for glioblastoma therapy. Adv. Sci. 2019, 6, 1801899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Chen, S.; Zhang, W.; Chen, Y.; Bihl, J.C. Exosomes from miRNA-126-modified endothelial progenitor cells alleviate brain injury and promote functional recovery after stroke. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2020, 26, 1255–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortega-Pineda, L.; Sunyecz, A.; Salazar-Puerta, A.I.; Rincon-Benavides, M.A.; Alzate-Correa, D.; Anaparthi, A.L.; Guilfoyle, E.; Mezache, L.; Struckman, H.L.; Duarte-Sanmiguel, S.; et al. Designer Extracellular Vesicles Modulate Pro-Neuronal Cell Responses and Improve Intracranial Retention. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2022, 11, 2100805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, Z.; Zhang, T.; He, W.; Jin, H.; Liu, C.; Yang, Z.; Ren, J. Methotrexate-Loaded Extracellular Vesicles Functionalized with Therapeutic and Targeted Peptides for the Treatment of Glioblastoma Multiforme. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 12341–12350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monfared, H.; Jahangard, Y.; Nikkhah, M.; Mirnajafi-Zadeh, J.; Mowla, S.J. Potential Therapeutic Effects of Exosomes Packed With a miR-21-Sponge Construct in a Rat Model of Glioblastoma. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Zhai, Y.; Hao, Y.; Wang, Q.; Han, F.; Zheng, W.; Hong, J.; Cui, L.; Jin, W.; Ma, S.; et al. Specific anti-glioma targeted-delivery strategy of engineered small extracellular vesicles dual-functionalised by Angiopep-2 and TAT peptides. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2022, 11, e12255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Si, Y.; Guan, J.-S.; Zhou, Z.; Kim, S.; Kim, T.; Shan, L.; Willey, C.D.; Zhou, L.; Liu, X. Targeted Extracellular Vesicles Delivered Verrucarin A to Treat Glioblastoma. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, G.; Kim, M.; Lee, Y.; Byun, J.W.; Lee, M. Systemic delivery of microRNA-21 antisense oligonucleotides to the brain using T7-peptide decorated exosomes. J. Control. Release 2020, 317, 273–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Bai, Y.; Han, B.; Ju, M.; Tang, T.; Shen, L.; Li, M.; Yang, L.; Zhang, Z.; Hu, G.; et al. Extracellular vesicle-mediated delivery of circDYM alleviates CUS-induced depressive-like behaviours. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2022, 11, e12185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.; Zhao, Y.; Xue, F.; Zheng, Y.; Huang, H.; Wang, W.; Chang, Y.; Yang, H.; Zhang, J. Exosomal DNA aptamer targeting α-synuclein aggregates reduced neuropathological deficits in a mouse Parkinson’s disease model. Mol. Ther.-Nucleic Acids 2019, 17, 726–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Han, B.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, S.; Bai, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Tang, Y.; Du, L.; Xu, L.; Wu, F. Extracellular vesicle–mediated delivery of circular RNA SCMH1 promotes functional recovery in rodent and nonhuman primate ischemic stroke models. Circulation 2020, 142, 556–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Wu, S.; Hou, L.; Zhu, D.; Yin, S.; Yang, G.; Wang, Y. Therapeutic effects of simultaneous delivery of nerve growth factor mRNA and protein via exosomes on cerebral ischemia. Mol. Ther.-Nucleic Acids 2020, 21, 512–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, H.; Pang, Y.; Ren, Z.; Fu, X.; Jia, L. Delivering synaptic protein mRNAs via extracellular vesicles ameliorates cognitive impairment in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. BMC Med. 2024, 22, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, W.; Li, X.; Guo, X.; Sun, Y.; Chai, W.; Chang, Y.; Huang, Q.; Wang, P.; Wang, X. Ultrasound-Assisted CRISPRi-Exosome for Epigenetic Modification of α-Synuclein Gene in a Mouse Model of Parkinson’s Disease. ACS Nano 2024, 18, 7837–7851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.-K.; Liu, L.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Z.; Xu, H.; Bai, W.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, D.; Chen, Z. Hippocampal-derived extracellular vesicle synergistically deliver active adenosine hippocampus targeting to promote cognitive recovery after stroke. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2024, 234, 113746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, W.; Luozhong, S.; Cai, S.; Londhe, K.; Elkasri, N.; Hawkins, R.; Yuan, Z.; Su-Greene, K.; Yin, Y.; Cruz, M.; et al. Extracellular vesicles incorporating retrovirus-like capsids for the enhanced packaging and systemic delivery of mRNA into neurons. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2024, 8, 415–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haney, M.J.; Klyachko, N.L.; Harrison, E.B.; Zhao, Y.; Kabanov, A.V.; Batrakova, E.V. TPP1 delivery to lysosomes with extracellular vesicles and their enhanced brain distribution in the animal model of batten disease. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2019, 8, 1801271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Sui, H.; Zheng, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Shi, Y.; Liang, J.; Zhao, L. Curcumin-primed exosomes potently ameliorate cognitive function in AD mice by inhibiting hyperphosphorylation of the Tau protein through the AKT/GSK-3β pathway. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 7481–7496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, D.; Zhao, Y.; Banks, W.A.; Bullock, K.M.; Haney, M.; Batrakova, E.; Kabanov, A.V. Macrophage exosomes as natural nanocarriers for protein delivery to inflamed brain. Biomaterials 2017, 142, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Haney, M.J.; Fallon, J.K.; Rodriguez, M.; Swain, C.J.; Arzt, C.J.; Smith, P.C.; Loop, M.S.; Harrison, E.B.; El-Hage, N.; et al. Using Extracellular Vesicles Released by GDNF-Transfected Macrophages for Therapy of Parkinson Disease. Cells 2022, 11, 1933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, L.; Cao, Y.; Yuan, W.; Guo, J.; Sun, G. Exosomal circRNA BTG2 derived from RBP-J overexpressed-macrophages inhibits glioma progression via miR-25-3p/PTEN. Cell Death Dis. 2022, 13, 506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, G.; Han, Y.; An, Y.; Ding, Y.; He, C.; Wang, X.; Tang, Q. NRP-1 targeted and cargo-loaded exosomes facilitate simultaneous imaging and therapy of glioma in vitro and in vivo. Biomaterials 2018, 178, 302–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, L.; Liu, Y.; Guo, K.; Zhang, K.; Liu, Q.; Wang, P.; Wang, X. Ultrasound Facilitates Naturally Equipped Exosomes Derived from Macrophages and Blood Serum for Orthotopic Glioma Treatment. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 14576–14587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, G.-H.; Guo, H.-D.; Li, H.; Zhai, Y.; Gong, Z.-B.; Wu, J.; Liu, J.-S.; Dong, Y.-R.; Hou, S.-X.; Liu, J.-R. RVG-modified exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem cells rescue memory deficits by regulating inflammatory responses in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Immun. Ageing 2019, 16, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarkar, S.N.; Corbin, D.; Simpkins, J.W. Brain-Wide Transgene Expression in Mice by Systemic Injection of Genetically Engineered Exosomes: CAP-Exosomes. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izadpanah, M.; Dargahi, L.; Ai, J.; Asgari Taei, A.; Ebrahimi Barough, S.; Mowla, S.J.; TavoosiDana, G.; Farahmandfar, M. Extracellular Vesicles as a Neprilysin Delivery System Memory Improvement in Alzheimer’s Disease. Iran. J. Pharm. Res. 2020, 19, 45–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Deng, X.; Liu, M.; He, M.; Long, W.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, K.; Liu, T.; So, K.-F.; Fu, Q.-L.; et al. Intranasal delivery of BDNF-loaded small extracellular vesicles for cerebral ischemia therapy. J. Control. Release 2023, 357, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, W.; Tang, H.; Luo, S.; Lv, Y.; Liang, D.; Kang, X.; Hong, W. Exosomes from miRNA-126-modified ADSCs promotes functional recovery after stroke in rats by improving neurogenesis and suppressing microglia activation. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2019, 11, 780. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.Y.; Kim, T.J.; Kang, L.; Kim, Y.-J.; Kang, M.K.; Kim, J.; Ryu, J.H.; Hyeon, T.; Yoon, B.-W.; Ko, S.-B.; et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived magnetic extracellular nanovesicles for targeting and treatment of ischemic stroke. Biomaterials 2020, 243, 119942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Luo, S.; Zhang, J.; Yu, T.; Fu, Z.; Zheng, Y.; Xu, X.; Liu, C.; Fan, M.; Zhang, Z. Exosome-mediated delivery of antisense oligonucleotides targeting α-synuclein ameliorates the pathology in a mouse model of Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol. Dis. 2021, 148, 105218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Ye, Y.; Kong, C.; Su, X.; Zhang, X.; Bai, W.; He, X. MiR-124 Enriched Exosomes Promoted the M2 Polarization of Microglia and Enhanced Hippocampus Neurogenesis After Traumatic Brain Injury by Inhibiting TLR4 Pathway. Neurochem. Res. 2019, 44, 811–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Guo, X.; Guo, X.; Yu, R.; Qian, M.; Wang, S.; Gao, X.; Qiu, W.; Guo, Q.; Xu, J. MicroRNA-29a-3p delivery via exosomes derived from engineered human mesenchymal stem cells exerts tumour suppressive effects by inhibiting migration and vasculogenic mimicry in glioma. Aging 2021, 13, 5055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.; Yao, X.; Li, H.; Li, X.; Zhang, T.; Sun, Q.; Ji, C.; Chen, G. Role of exosomes derived from miR-133b modified MSCs in an experimental rat model of intracerebral hemorrhage. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2018, 64, 421–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, T.; Zhang, H.-X.; He, C.-P.; Fan, S.; Zhu, Y.-L.; Qi, C.; Huang, N.-P.; Xiao, Z.-D.; Lu, Z.-H.; Tannous, B.A. Surface functionalized exosomes as targeted drug delivery vehicles for cerebral ischemia therapy. Biomaterials 2018, 150, 137–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Wu, J.; Wu, J.; Fan, Q.; Zhou, J.; Wu, J.; Liu, S.; Zang, J.; Ye, J.; Xiao, M. Exosome-mediated targeted delivery of miR-210 for angiogenic therapy after cerebral ischemia in mice. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2019, 17, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Zhang, X.; Chen, X.; Wang, L.; Yang, G. Exosome mediated delivery of miR-124 promotes neurogenesis after ischemia. Mol. Ther.-Nucleic Acids 2017, 7, 278–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.; Li, Y.; Ji, W.; Zhao, R.; Lu, Z.; Shen, J.; Wu, Y.; Wang, J.; Hao, Q.; Wang, J.; et al. Intranasal Administration of Self-Oriented Nanocarriers Based on Therapeutic Exosomes for Synergistic Treatment of Parkinson’s Disease. ACS Nano 2022, 16, 869–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, H.; Li, Y.; Wang, C.; Jiang, Y.; Han, Y.; Li, Y.; Zheng, D.; Ye, J.; Chen, G.; Yang, G.-y.; et al. Click chemistry extracellular vesicle/peptide/chemokine nanocarriers for treating central nervous system injuries. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2023, 13, 2202–2218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, K.; Niu, F.; Dagur, R.S.; He, M.; Tian, C.; Hu, G. Intranasal delivery of lincRNA-Cox2 siRNA loaded extracellular vesicles decreases lipopolysaccharide-induced microglial proliferation in mice. J. Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2020, 15, 390–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, X.; Guo, M.; Hu, T.; Li, W.; Huang, S.; Yin, Z.; Li, Y.; Chen, F.; Zhu, L.; Kang, C. Increased microglial exosomal miR-124-3p alleviates neurodegeneration and improves cognitive outcome after rmTBI. Mol. Ther. 2020, 28, 503–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haroon, K.; Zheng, H.; Wu, S.; Liu, Z.; Tang, Y.; Yang, G.-Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Z. Engineered exosomes mediated targeted delivery of neuroprotective peptide NR2B9c for the treatment of traumatic brain injury. Int. J. Pharm. 2024, 649, 123656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haroon, K.; Ruan, H.; Zheng, H.; Wu, S.; Liu, Z.; Shi, X.; Tang, Y.; Yang, G.-Y.; Zhang, Z. Bio-clickable, small extracellular vesicles-COCKTAIL therapy for ischemic stroke. J. Control. Release 2023, 363, 585–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Huo, Y.; Zhao, C.; Liu, H.; Shao, Y.; Zhu, C.; An, L.; Chen, X.; Chen, Z. Engineered exosomes with enhanced stability and delivery efficiency for glioblastoma therapy. J. Control. Release 2024, 368, 170–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, T.; Cao, L.; He, C.; Ye, Q.; Liang, R.; You, W.; Zhang, H.; Wu, J.; Ye, J.; Tannous, B.A.; et al. Targeted delivery of neural progenitor cell-derived extracellular vesicles for anti-inflammation after cerebral ischemia. Theranostics 2021, 11, 6507–6521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, T.; Liang, R.; Erel-Akbaba, G.; Saad, L.; Obeid, P.J.; Gao, J.; Chiocca, E.A.; Weissleder, R.; Tannous, B.A. Immune Checkpoint Inhibition in GBM Primed with Radiation by Engineered Extracellular Vesicles. ACS Nano 2022, 16, 1940–1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.-Y.; Liao, B.-Y.; Xiao, D.; Wu, W.-C.; Xiao, Y.; Alexander, T.; Song, S.-J.; Zhao, Z.-H.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Z.-H. Encapsulation of bryostatin-1 by targeted exosomes enhances remyelination and neuroprotection effects in the cuprizone-induced demyelinating animal model of multiple sclerosis. Biomater. Sci. 2022, 10, 714–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Kumar, U.S.; Sadeghipour, N.; Massoud, T.F.; Paulmurugan, R. A Microfluidics-Based Scalable Approach to Generate Extracellular Vesicles with Enhanced Therapeutic MicroRNA Loading for Intranasal Delivery to Mouse Glioblastomas. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 18327–18346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Tang, W.; Yang, M.; Yin, Y.; Li, H.; Hu, F.; Tang, L.; Ma, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y. Inflammatory tumor microenvironment responsive neutrophil exosomes-based drug delivery system for targeted glioma therapy. Biomaterials 2021, 273, 120784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira Silva, R.; Counil, H.; Rabanel, J.-M.; Haddad, M.; Zaouter, C.; Ben Khedher, M.R.; Patten, S.A.; Ramassamy, C. Donepezil-Loaded Nanocarriers for the Treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease: Superior Efficacy of Extracellular Vesicles Over Polymeric Nanoparticles. Int. J. Nanomed. 2024, 19, 1077–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mattera, V.; Occhiuzzi, F.; Correale, J.; Pasquini, J.M. Remyelinating effect driven by transferrin-loaded extracellular vesicles. Glia 2024, 72, 338–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, Y.; Guo, L.; Jiang, Y.; Shi, Y.; Sui, H.; Zhao, L. Brain delivery of quercetin-loaded exosomes improved cognitive function in AD mice by inhibiting phosphorylated tau-mediated neurofibrillary tangles. Drug Deliv. 2020, 27, 745–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Huang, Z.; Huang, L.; Liang, J.; Wang, P.; Zhao, L.; Shi, Y. Surface-modified engineered exosomes attenuated cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury by targeting the delivery of quercetin towards impaired neurons. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2021, 19, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, W.; Xiao, Q.; Wang, X.; Zhu, J.; Li, J.; Liang, X.; Peng, Y.; Wu, C.; Lu, R.; Pan, Y.; et al. A Biomimetic Drug Delivery System by Integrating Grapefruit Extracellular Vesicles and Doxorubicin-Loaded Heparin-Based Nanoparticles for Glioma Therapy. Nano Lett. 2021, 21, 1484–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhuang, X.; Teng, Y.; Samykutty, A.; Mu, J.; Deng, Z.; Zhang, L.; Cao, P.; Rong, Y.; Yan, J.; Miller, D. Grapefruit-derived nanovectors delivering therapeutic miR17 through an intranasal route inhibit brain tumor progression. Mol. Ther. 2016, 24, 96–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Wang, Z.; Huang, X.; Xue, J.; Zhang, S.; Guo, X.; Zhou, S. Bacteria-Derived Outer-Membrane Vesicles Hitchhike Neutrophils to Enhance Ischemic Stroke Therapy. Adv. Mater. 2023, 35, 2301779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, Z.; Yao, Q.; Qi, Y.; Zheng, J.; Liu, J.; Liu, Z.; Tan, H.; Ma, X.; Zhou, W.; Rong, P. Salmonella-mediated blood–brain barrier penetration, tumor homing and tumor microenvironment regulation for enhanced chemo/bacterial glioma therapy. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2023, 13, 819–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Feng, N. Cell membrane-coated nanosized active targeted drug delivery systems homing to tumor cells: A review. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2020, 106, 110298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Yang, L.; He, W.; Zheng, M.; Zou, Y. Cell Membrane Camouflaged Biomimetic Nanoparticles as a Versatile Platform for Brain Diseases Treatment. Small Methods 2024, 2400096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, L.; Yin, Y.; Liu, H.; Zhu, M.; Cao, Y.; Feng, J.; Fu, C.; Li, Z.; Shu, W.; Gao, J.; et al. Blood–Brain Barrier-Penetrating and Lesion-Targeting Nanoplatforms Inspired by the Pathophysiological Features for Synergistic Ischemic Stroke Therapy. Adv. Mater. 2024, 36, 2312897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, L.; Zang, G.; Liu, B.; Qin, X.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, H.; Wu, W.; Wang, G. Bioengineering CXCR4-overexpressing cell membrane functionalized ROS-responsive nanotherapeutics for targeting cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury. Theranostics 2021, 11, 8043–8056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.; Cheng, W.; Dai, W.; Lu, F.; Cheng, Y.; Jiang, T.; Ren, Z.; Xie, Y.; Xu, J.; Zhao, Q.; et al. A Nanodrug Coated with Membrane from Brain Microvascular Endothelial Cells Protects against Experimental Cerebral Malaria. Nano Lett. 2022, 22, 211–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Ji, J.; Zhang, L.; Luo, C.; Chen, T.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, C.; Ke, Y.; Wang, J. Nanoparticles Coated with Brain Microvascular Endothelial Cell Membranes can Target and Cross the Blood–Brain Barrier to Deliver Drugs to Brain Tumors. Small 2024, 2306714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, X.; Kuang, L.; Yin, Y.; Tang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Fan, Q.; Wang, B.; Dong, Z.; Wang, W.; Yin, T.; et al. Tumor–Antigen Activated Dendritic Cell Membrane-Coated Biomimetic Nanoparticles with Orchestrating Immune Responses Promote Therapeutic Efficacy against Glioma. ACS Nano 2023, 17, 2341–2355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, X.; Li, L.; Ye, P.; Xie, M. Macrophage Membrane-Modified MoS2 Quantum Dots as a Nanodrug for Combined Multi-Targeting of Alzheimer’s Disease. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2024, 13, 2303211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Wang, C.; Hu, J.; Jiao, W.; Tang, Z.; Song, X.; Wu, Y.; Dai, J.; Gao, P.; Du, L.; et al. Cannabidiol–loaded biomimetic macrophage membrane vesicles against post–traumatic stress disorder assisted by ultrasound. Int. J. Pharm. 2023, 637, 122872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Zhang, Z.; Du, J.; Xue, Y.; Chen, X.; Zhang, J.; Yang, X.; Chang, D.; Xie, J.; Ju, S. Recruiting T-Cells toward the Brain for Enhanced Glioblastoma Immunotherapeutic Efficacy by Co-Delivery of Cytokines and Immune Checkpoint Antibodies with Macrophage-Membrane-Camouflaged Nanovesicles. Adv. Mater. 2023, 35, 2209785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, J.; Deng, G.; Sun, Z.; Peng, X.; Li, J.; Gong, P.; Zhang, P.; Cai, L. Scaffolds biomimicking macrophages for a glioblastoma NIR-Ib imaging guided photothermal therapeutic strategy by crossing Blood-Brain Barrier. Biomaterials 2019, 211, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, M.; Ye, C.; Tian, C.; Zhao, D.; Li, H.; Sun, Z.; Miao, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, J.; Dou, Y. Engineered macrophage-biomimetic versatile nanoantidotes for inflammation-targeted therapy against Alzheimer’s disease by neurotoxin neutralization and immune recognition suppression. Bioact. Mater. 2023, 26, 337–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, R.; Chen, L.; Ji, Q.; Liang, Q.; Zhu, Y.; Fu, W.; Chen, T.; Duan, H.; He, W.; Xu, Z.; et al. Macrophage Membrane-Coated Nanoparticles Sensitize Glioblastoma to Radiation by Suppressing Proneural–Mesenchymal Transformation in Glioma Stem Cells. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 33, 2213292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, T.; He, M.; Xu, F.; Fan, Y.; Jia, B.; Shen, M.; Wang, H.; Shi, X. Macrophage Membrane-Camouflaged Responsive Polymer Nanogels Enable Magnetic Resonance Imaging-Guided Chemotherapy/Chemodynamic Therapy of Orthotopic Glioma. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 20377–20390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, Y.; Xiang, Y.; Liu, S.; Zhang, Y.; Wan, J.; Ci, Z.; Cui, M.; Shen, L.; Li, N.; Guan, Y. Macrophage membrane modified baicalin liposomes improve brain targeting for alleviating cerebral ischemia reperfusion injury. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2022, 43, 102547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Q.; Liu, H.; Zhang, H.; Han, Y.; Yuan, J.; Wang, T.; Gao, Y.; Li, Z. Ameliorating Mitochondrial Dysfunction of Neurons by Biomimetic Targeting Nanoparticles Mediated Mitochondrial Biogenesis to Boost the Therapy of Parkinson’s Disease. Adv. Sci. 2023, 10, 2300758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Gao, C.; Wang, H.; Sun, J.; Liang, M.; Feng, Y.; Liu, Q.; Fu, S.; Cui, L.; Gao, C.; et al. Macrophage membrane-coated nanocarriers Co-Modified by RVG29 and TPP improve brain neuronal mitochondria-targeting and therapeutic efficacy in Alzheimer’s disease mice. Bioact. Mater. 2021, 6, 529–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, T.; Fan, Q.; Hu, F.; Ma, X.; Yin, Y.; Wang, B.; Kuang, L.; Hu, X.; Xu, B.; Wang, Y. Engineered Macrophage-Membrane-Coated Nanoparticles with Enhanced PD-1 Expression Induce Immunomodulation for a Synergistic and Targeted Antiglioblastoma Activity. Nano Lett. 2022, 22, 6606–6614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, S.; Cheng, Y.; Liu, M.; Ji, Q.; Zhang, B.; Mei, Q.; Liu, D.; Zhou, S. Chemoattractants driven and microglia based biomimetic nanoparticle treating TMZ-resistant glioblastoma multiforme. J. Control. Release 2021, 336, 54–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Chen, H.; Ding, L.; Huang, J.; Zhang, M.; Liu, Y.; Ma, R.; Zheng, S.; Gong, J.; Piña-Crespo, J.C.; et al. Microglial targeted therapy relieves cognitive impairment caused by Cntnap4 deficiency. Exploration 2023, 3, 20220160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.; Jiang, X.; Li, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, T.; Zhi, P.; Gao, J. Engineering Stem Cell Derived Biomimetic Vesicles for Versatility and Effective Targeted Delivery. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 2006169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, S.; Cui, Y.; Liang, X.; Shan, J.; Gu, W.; Qiu, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, G. Functionalized nanoparticles with monocyte membranes and rapamycin achieve synergistic chemoimmunotherapy for reperfusion-induced injury in ischemic stroke. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2021, 19, 331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Li, Q.; Niu, J.; Guo, E.; Zhao, C.; Zhang, J.; Liu, X.; Wang, L.; Rao, L.; Chen, X.; et al. Neutrophil Membrane-Camouflaged Polyprodrug Nanomedicine for Inflammation Suppression in Ischemic Stroke Therapy. Adv. Mater. 2024, 36, 2311803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, L.; Dou, C.; Xia, Y.; Li, B.; Zhao, M.; Yu, P.; Zheng, Y.; El-Toni, A.M.; Atta, N.F.; Galal, A. Neutrophil-like cell-membrane-coated nanozyme therapy for ischemic brain damage and long-term neurological functional recovery. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 2263–2280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.; Wang, Q.; Li, K.; Li, X.; Wang, C.; Xue, L.; Ju, C.; Zhang, C. A neutrophil-mimetic magnetic nanoprobe for molecular magnetic resonance imaging of stroke-induced neuroinflammation. Biomater. Sci. 2021, 9, 5247–5258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.; Meng, S.; Song, Z.; Yang, X.; Li, X.; Guo, H.; Du, M.; Chen, J.; Zhu, Y.Z.; Wang, X. Neutrophil membrane fusogenic nanoliposomal leonurine for targeted ischemic stroke therapy via remodeling cerebral niche and restoring blood-brain barrier integrity. Mater. Today Bio 2023, 20, 100674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Ling, C.-L.; Pang, L.; Wang, Q.; Liu, J.-X.; Wang, B.-S.; Liang, J.-M.; Guo, Y.-Z.; Qin, J.; Wang, J.-X. Direct Macromolecular Drug Delivery to Cerebral Ischemia Area using Neutrophil-Mediated Nanoparticles. Theranostics 2017, 7, 3260–3275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.; Tang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, X.; Yin, Y.; Kuang, L.; Fan, Q.; Wang, B.; Hu, X.; Yin, T.; et al. A Homing Peptide Modified Neutrophil Membrane Biomimetic Nanoparticles in Response to ROS/inflammatory Microenvironment for Precise Targeting Treatment of Ischemic Stroke. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2024, 34, 2309167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Wang, P.; Jiang, X.; Xu, J.; Zhang, M.; Liu, F.; Lin, Y.; Tao, J.; He, J.; Zhou, X.; et al. A Nanotherapy of Octanoic Acid Ameliorates Cardiac Arrest/Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation-Induced Brain Injury via RVG29- and Neutrophil Membrane-Mediated Injury Relay Targeting. ACS Nano 2023, 17, 3528–3548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, X.; Wang, L.; Feng, X.; Liu, W.; Wang, X.; Li, F.; Liu, X.; Yu, J.; Yu, B.; Yu, X. Cell Membrane-Coated Oncolytic Adenovirus for Targeted Treatment of Glioblastoma. Nano Lett. 2023, 23, 11120–11128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Kong, J.; Ge, X.; Mao, M.; Yu, H.; Wang, Y. An Antisense Oligonucleotide-Loaded Blood–Brain Barrier Penetrable Nanoparticle Mediating Recruitment of Endogenous Neural Stem Cells for the Treatment of Parkinson’s Disease. ACS Nano 2023, 17, 4414–4432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhou, Y.; Qi, J.; Gu, L.; Zhao, Q.; Yu, R.; Zhou, X. A Trojan-Horse-Like Biomimetic Nano-NK to Elicit an Immunostimulatory Tumor Microenvironment for Enhanced GBM Chemo-Immunotherapy. Small 2023, 19, 2301439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Han, Y.; Wang, T.; Zhang, H.; Xu, Q.; Yuan, J.; Li, Z. Targeting Microglia for Therapy of Parkinson’s Disease by Using Biomimetic Ultrasmall Nanoparticles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 21730–21742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Li, J.; Chen, J.; Liu, Y.; Cheng, X.; Yang, F.; Gu, N. Platelet Membrane Biomimetic Magnetic Nanocarriers for Targeted Delivery and in Situ Generation of Nitric Oxide in Early Ischemic Stroke. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 2024–2035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, C.; Chen, Q.; Li, W.; Zhang, J.; Yang, C.; Chen, D. Multi-functional platelet membrane-camouflaged nanoparticles reduce neuronal apoptosis and regulate microglial phenotype during ischemic injury. Appl. Mater. Today 2022, 27, 101412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Yang, X.; Jiang, Y.; Qi, L.; Zhuge, D.; Xu, T.; Guo, Y.; Deng, M.; Zhang, W.; Tian, D.; et al. Targeted delivery of fat extract by platelet membrane-cloaked nanocarriers for the treatment of ischemic stroke. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2022, 20, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Wang, X.; Yin, H.; Cao, X.; Hu, Q.; Lv, W.; Xu, Q.; Gu, Z.; Xin, H. Sequentially Site-Specific Delivery of Thrombolytics and Neuroprotectant for Enhanced Treatment of Ischemic Stroke. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 8577–8588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.-W.; Guan, P.-P.; Ding, W.-Y.; Wang, S.-L.; Huang, X.-S.; Wang, Z.-Y.; Wang, P. Erythrocyte membrane-encapsulated celecoxib improves the cognitive decline of Alzheimer’s disease by concurrently inducing neurogenesis and reducing apoptosis in APP/PS1 transgenic mice. Biomaterials 2017, 145, 106–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Z.; Hu, B.; Xiang, B.; Fang, H.; Zhang, B.; Wang, Y.; Zhuo, Y.; Deng, D.; Wang, X. Biomimetic Biomembrane Encapsulation and Targeted Delivery of a Nitric Oxide Release Platform for Therapy of Parkinson’s Disease. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2023, 9, 2545–2557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, Z.; Hu, X.; Wei, X.; Zhan, C.; Lu, L.; Jiang, K.; Su, B.; Ruan, H.; Ran, D.; Fang, R.H.; et al. A facile approach to functionalizing cell membrane-coated nanoparticles with neurotoxin-derived peptide for brain-targeted drug delivery. J. Control. Release 2017, 264, 102–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Xu, Q.; Chai, Z.; Wu, S.; Xu, W.; Wang, J.; Zhou, J.; Luo, Z.; Liu, Y.; Xie, C.; et al. All-stage targeted red blood cell membrane-coated docetaxel nanocrystals for glioma treatment. J. Control. Release 2024, 369, 325–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, Z.; Ran, D.; Lu, L.; Zhan, C.; Ruan, H.; Hu, X.; Xie, C.; Jiang, K.; Li, J.; Zhou, J. Ligand-modified cell membrane enables the targeted delivery of drug nanocrystals to glioma. Acs Nano 2019, 13, 5591–5601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.; Liu, Y.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, D.; Lu, Y.; Zheng, M.; Xue, X.; Geng, J.; Chung, R.; Shi, B. Effective and Targeted Human Orthotopic Glioblastoma Xenograft Therapy via a Multifunctional Biomimetic Nanomedicine. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1803717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zou, Y.; Feng, C.; Lee, A.; Yin, J.; Chung, R.; Park, J.B.; Rizos, H.; Tao, W.; Zheng, M.; et al. Charge Conversional Biomimetic Nanocomplexes as a Multifunctional Platform for Boosting Orthotopic Glioblastoma RNAi Therapy. Nano Lett. 2020, 20, 1637–1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Tian, S.; Liu, Y.; Zheng, M.; Yang, X.; Zou, Y.; Shi, B.; Luo, L. Near infrared-activatable biomimetic nanogels enabling deep tumor drug penetration inhibit orthotopic glioblastoma. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 6835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, W.; Zhang, D.; Sun, Y.; Li, F.; Zheng, M.; Lovejoy, D.B.; Zou, Y.; Shi, B. Brain co-delivery of first-line chemotherapy drug and epigenetic bromodomain inhibitor for multidimensional enhanced synergistic glioblastoma therapy. Exploration 2022, 2, 20210274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.; Li, X.; Morsch, M.; Ismail, M.; Liu, Y.; Rehman, F.U.; Zhang, D.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, M.; Chung, R.; et al. Brain-Targeted Codelivery of Bcl-2/Bcl-xl and Mcl-1 Inhibitors by Biomimetic Nanoparticles for Orthotopic Glioblastoma Therapy. ACS Nano 2022, 16, 6293–6308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Chu, X.; Cui, L.; Fu, S.; Gao, C.; Li, Y.; Sun, B. Neuronal mitochondria-targeted therapy for Alzheimer’s disease by systemic delivery of resveratrol using dual-modified novel biomimetic nanosystems. Drug Deliv. 2020, 27, 502–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, C.; Wang, Y.; Sun, J.; Han, Y.; Gong, W.; Li, Y.; Feng, Y.; Wang, H.; Yang, M.; Li, Z.; et al. Neuronal mitochondria-targeted delivery of curcumin by biomimetic engineered nanosystems in Alzheimer’s disease mice. Acta Biomater. 2020, 108, 285–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Luo, J.; Liu, Y.; Liu, W.; Yu, G.; Huang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Chen, X.; Chen, T. Brain-targeted biomimetic nanodecoys with neuroprotective effects for precise therapy of Parkinson’s disease. ACS Cent. Sci. 2022, 8, 1336–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, W.; Xu, J.; Wang, X.; Li, X.; Xu, Q.; Xin, H. Bioengineered boronic ester modified dextran polymer nanoparticles as reactive oxygen species responsive nanocarrier for ischemic stroke treatment. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 5417–5426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Liu, J.; Gao, C.; Zheng, J.; Zhang, J.; Ding, Y.; Gong, W.; Yang, M.; Li, Z.; Wang, Y.; et al. Targeted delivery of PARP inhibitors to neuronal mitochondria via biomimetic engineered nanosystems in a mouse model of traumatic brain injury. Acta Biomater. 2022, 140, 573–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Wu, B.; Wu, Y.; Song, X.; Zhang, S.; Liu, Z. Camouflaging Nanoparticles with Brain Metastatic Tumor Cell Membranes: A New Strategy to Traverse Blood–Brain Barrier for Imaging and Therapy of Brain Tumors. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 1909369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y.; Wu, M.; Hu, D.; Pan, Y.; Hu, F.; Liu, X.; Thakor, N.; Ng, W.H.; Liu, X.; Sheng, Z. Biomimetic nanocomposites cloaked with bioorthogonally labeled glioblastoma cell membrane for targeted multimodal imaging of brain tumors. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 2004346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.; Mei, Q.; Li, J.; Zhai, Y.; Chen, Y.; Wang, R.; Lu, E.; Zhang, X.-Y.; Zhang, Z.; Sha, X. Preferential Targeting Cerebral Ischemic Lesions with Cancer Cell-Inspired Nanovehicle for Ischemic Stroke Treatment. Nano Lett. 2021, 21, 3033–3043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, P.; Treuren, T.V.; Ranjan, A.P.; Chaudhary, P.; Vishwanatha, J.K. In vivo imaging and biodistribution of near infrared dye loaded brain-metastatic-breast-cancer-cell-membrane coated polymeric nanoparticles. Nanotechnology 2019, 30, 265101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.; Wang, Y.; Xu, S.; Liu, Y.; Yin, J.; Lovejoy, D.B.; Zheng, M.; Liang, X.J.; Park, J.B.; Efremov, Y.M. Brain co-delivery of temozolomide and cisplatin for combinatorial glioblastoma chemotherapy. Adv. Mater. 2022, 34, 2203958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Zhang, S.; Fang, Q.; He, H.; Ren, J.; Sun, D.; Lai, J.; Ma, A.; Chen, Z.; Liu, L.; et al. Biomimetic Nanosonosensitizers Combined with Noninvasive Ultrasound Actuation to Reverse Drug Resistance and Sonodynamic-Enhanced Chemotherapy against Orthotopic Glioblastoma. ACS Nano 2023, 17, 421–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, S.; Lee, Y.; Lee, M. Biomimetic cell membrane-coated DNA nanoparticles for gene delivery to glioblastoma. J. Control. Release 2021, 338, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Pasquale, D.; Marino, A.; Tapeinos, C.; Pucci, C.; Rocchiccioli, S.; Michelucci, E.; Finamore, F.; McDonnell, L.; Scarpellini, A.; Lauciello, S.; et al. Homotypic targeting and drug delivery in glioblastoma cells through cell membrane-coated boron nitride nanotubes. Mater. Des. 2020, 192, 108742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Xu, C.; Deng, H.; You, Q.; Zhao, C.; Li, Y.; Gao, Q.; Akakuru, O.U.; Li, J.; Zhang, J.; et al. Localized NIR-II laser mediated chemodynamic therapy of glioblastoma. Nano Today 2022, 43, 101435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Hao, W.; Cui, Y.; Chen, M.; Chu, X.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Gao, C. Cancer cell membrane-coated nanosuspensions for enhanced chemotherapeutic treatment of glioma. Molecules 2021, 26, 5103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Cui, Y.; Hao, W.; Chen, M.; Liu, Q.; Wang, Y.; Yang, M.; Li, Z.; Gong, W.; Song, S.; et al. Carrier-free highly drug-loaded biomimetic nanosuspensions encapsulated by cancer cell membrane based on homology and active targeting for the treatment of glioma. Bioact. Mater. 2021, 6, 4402–4414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Tang, X.-L.; Zhao, M.-J.; Zhang, Y.-D.; Xiao, Y.; Liu, Y.-Y.; Qian, C.-F.; Xie, Y.-D.; Liu, Y.; Zou, Y.-J.; et al. Biomimetic hypoxia-triggered RNAi nanomedicine for synergistically mediating chemo/radiotherapy of glioblastoma. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2023, 21, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Guan, S.; Wei, T.; Wang, T.; Zhang, J.; You, Y.; Wang, Z.; Dai, Z. Homotypic Membrane-Enhanced Blood–Brain Barrier Crossing and Glioblastoma Targeting for Precise Surgical Resection and Photothermal Therapy. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2023, 145, 5930–5940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Z.; Zhao, L.; Fang, W.; Guo, S.; Xu, A.; Zhan, Z.; Cai, Y.; Xue, S.; Chai, P.; Jiang, Q.; et al. Glioma cell membrane camouflaged cinobufotalin delivery system for combinatorial orthotopic glioblastoma therapy. Nano Res. 2023, 16, 11164–11175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.; Wang, X.; Hu, D.; Wang, P.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, X.; Jiang, J.; Liu, X.; Sheng, Z.; Liu, B.; et al. Phototheranostics: Active Targeting of Orthotopic Glioma Using Biomimetic Proteolipid Nanoparticles. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 386–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chi, S.; Zhang, L.; Cheng, H.; Chang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, X.; Liu, Z. Biomimetic Nanocomposites Camouflaged with Hybrid Cell Membranes for Accurate Therapy of Early-Stage Glioma. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2023, 62, e202304419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, W.; Cui, Y.; Fan, Y.; Chen, M.; Yang, G.; Wang, Y.; Yang, M.; Li, Z.; Gong, W.; Yang, Y.; et al. Hybrid membrane-coated nanosuspensions for multi-modal anti-glioma therapy via drug and antigen delivery. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2021, 19, 378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Mu, N.; Ding, Y.; Huang, R.; Wu, W.; Li, L.; Chen, T. Tumor microenvironment targeting for glioblastoma multiforme treatment via hybrid cell membrane coating supramolecular micelles. J. Control. Release 2024, 366, 194–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.; Sun, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, D.; Yang, H.; Wang, X.; Zheng, M.; Shi, B. Cancer cell-mitochondria hybrid membrane coated Gboxin loaded nanomedicines for glioblastoma treatment. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 4557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Y.; Tang, W.; Ma, X.; Tang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, M.; Hu, F.; Li, G.; Wang, Y. Biomimetic neutrophil and macrophage dual membrane-coated nanoplatform with orchestrated tumor-microenvironment responsive capability promotes therapeutic efficacy against glioma. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 433, 133848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Li, Q.; Deng, J.; Shen, J.; Xu, W.; Yang, W.; Chen, B.; Du, Y.; Zhang, W.; Ge, F. Platelet-tumor cell hybrid membrane-camouflaged nanoparticles for enhancing therapy efficacy in glioma. Int. J. Nanomed. 2021, 16, 8433–8446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Geng, X.; Shi, Y.; Liang, J.; Zhao, L. Biomimetic oxygen-boosted hybrid membrane nanovesicles as the treatment strategy for ischemic stroke with the concept of the neurovascular unit. Biomater. Adv. 2023, 148, 213379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).