Investigating Laser Ablation Process Parameters for the Fabrication of Customized Microneedle Arrays for Therapeutic Applications
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Research Design
2.2.1. Pilot Study
2.2.2. Design of Experiment
2.2.3. Predictive Model
- y denotes the predicted response for the experiments (diameter and height).
- b0 denotes the intercept coefficient.
- b1–b5 denote the coefficients of the respective input factors waveform, power, pulse width, repetition, and interval, respectively.
- x1–x5 denote the predictor values for the respective experiment input factors: waveform, power, pulse width, repetition, and interval, respectively.
2.2.4. Mechanical Characterization
3. Results and Discussions
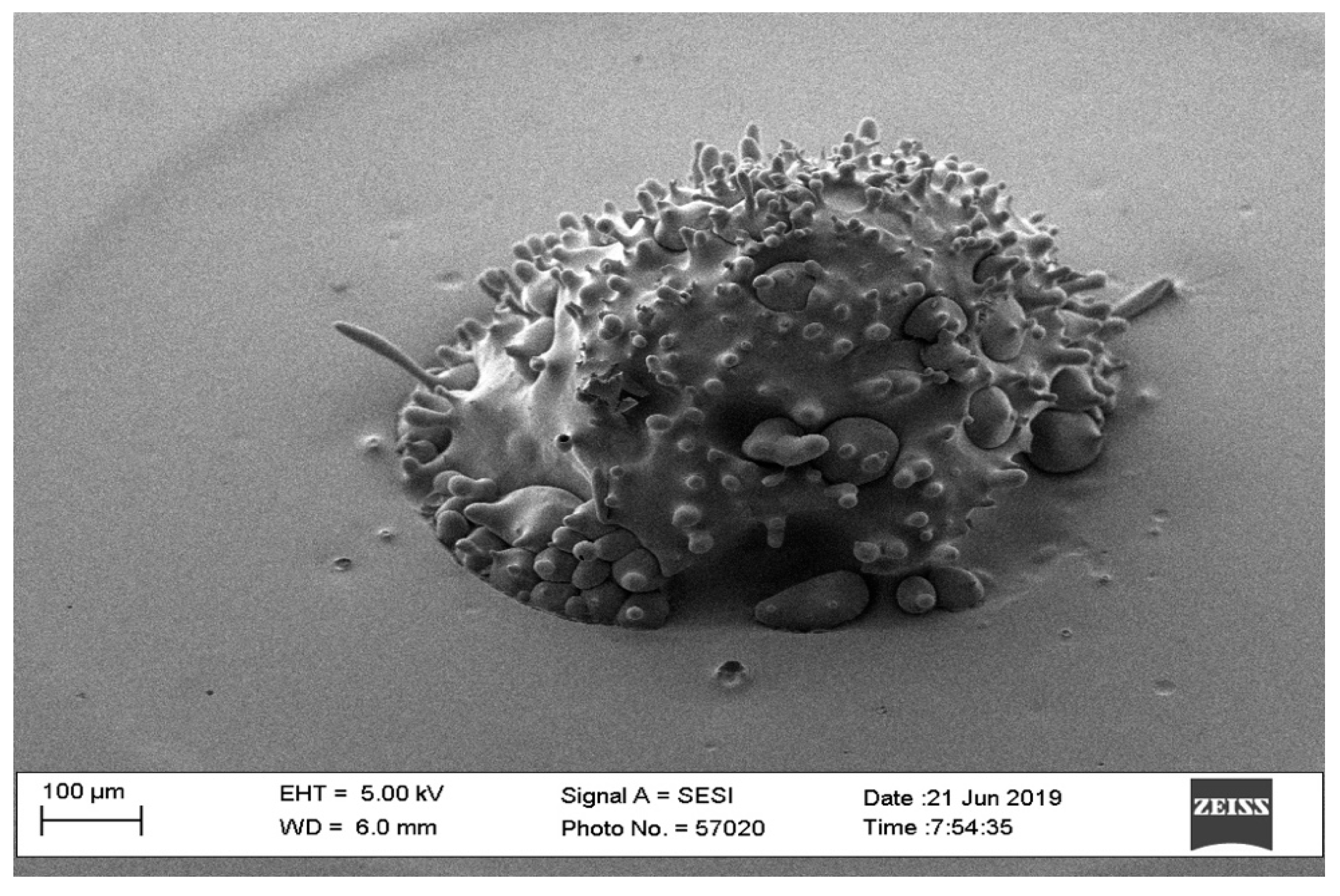
3.1. Pilot Study
3.1.1. Waveform
3.1.2. Laser Power
3.1.3. Pulse Width
3.1.4. Number of Repetitions
3.1.5. Interval Time
3.2. Design of Experiments
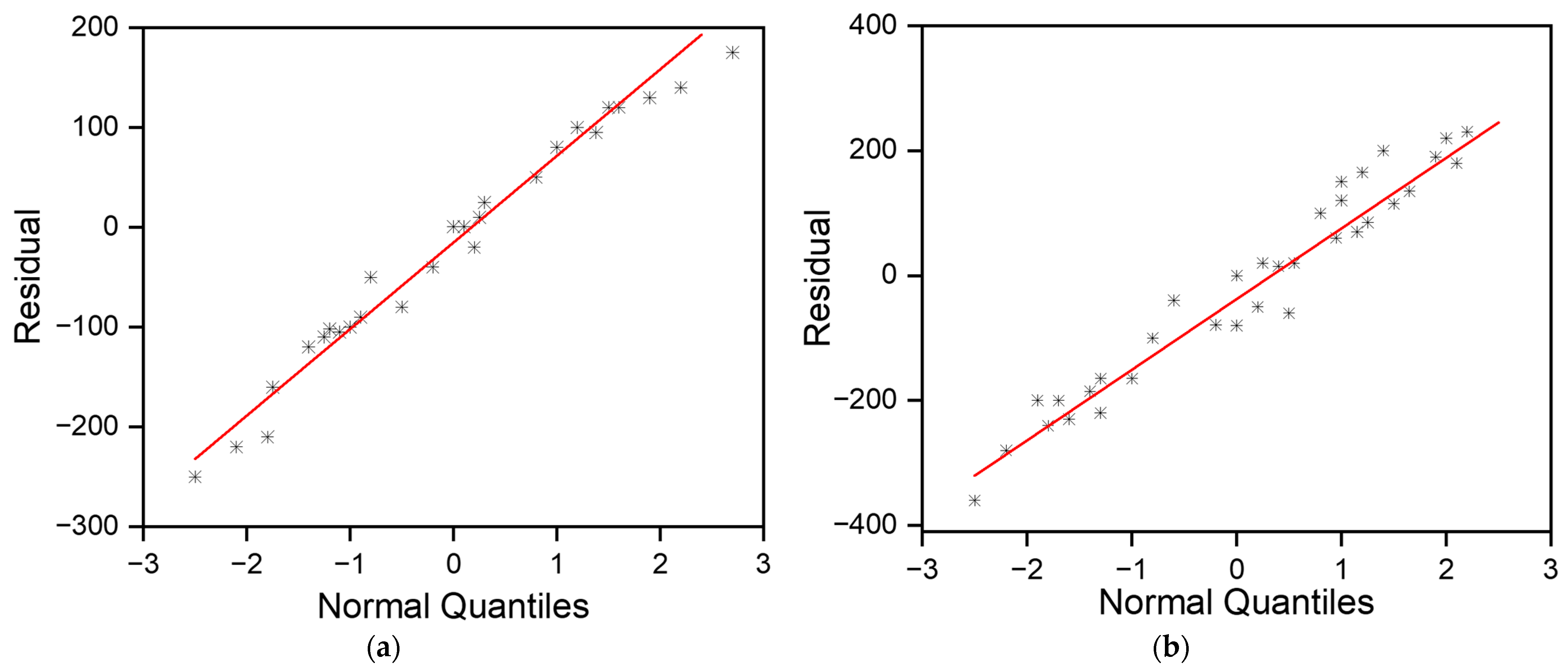
3.2.1. Normality Check
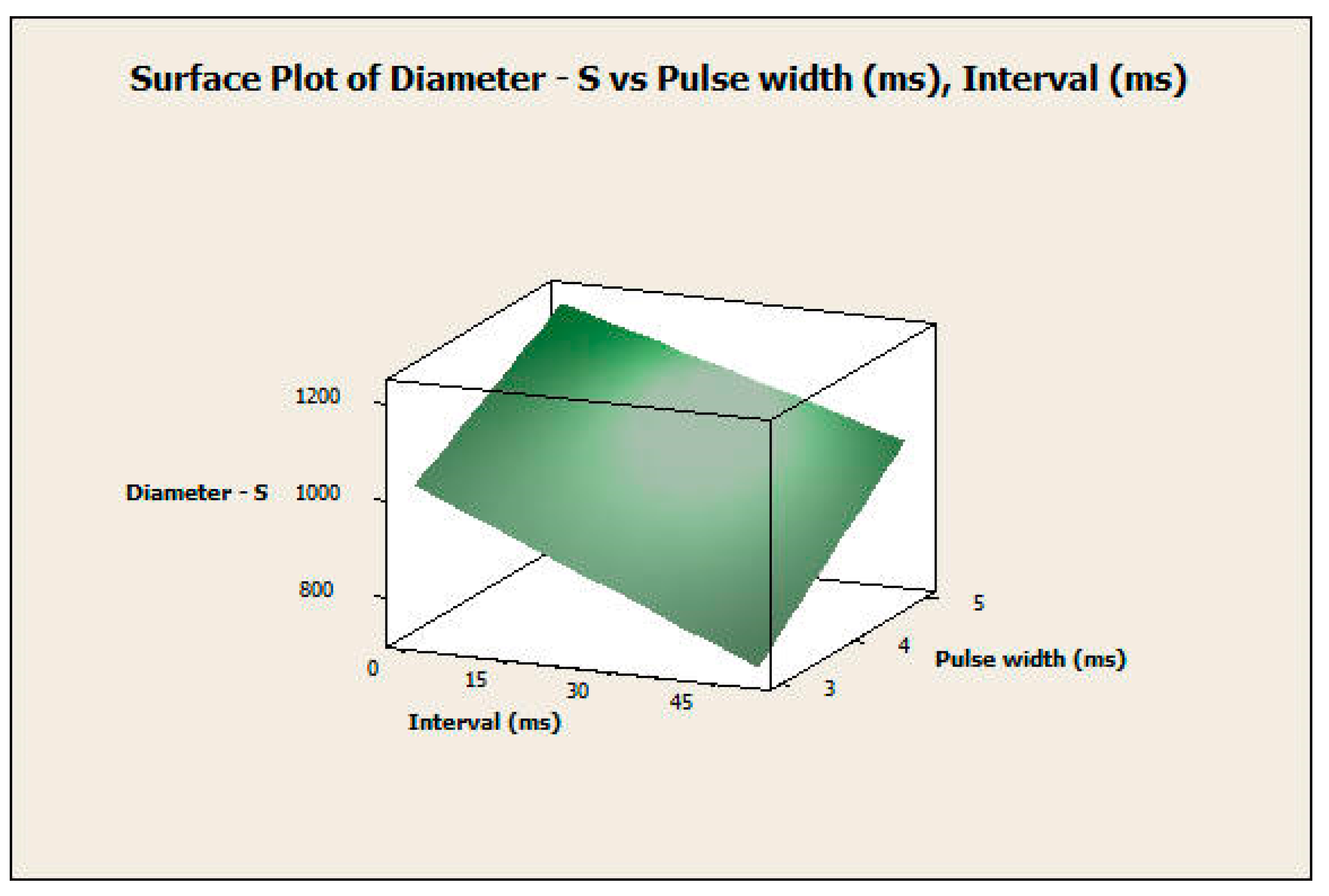
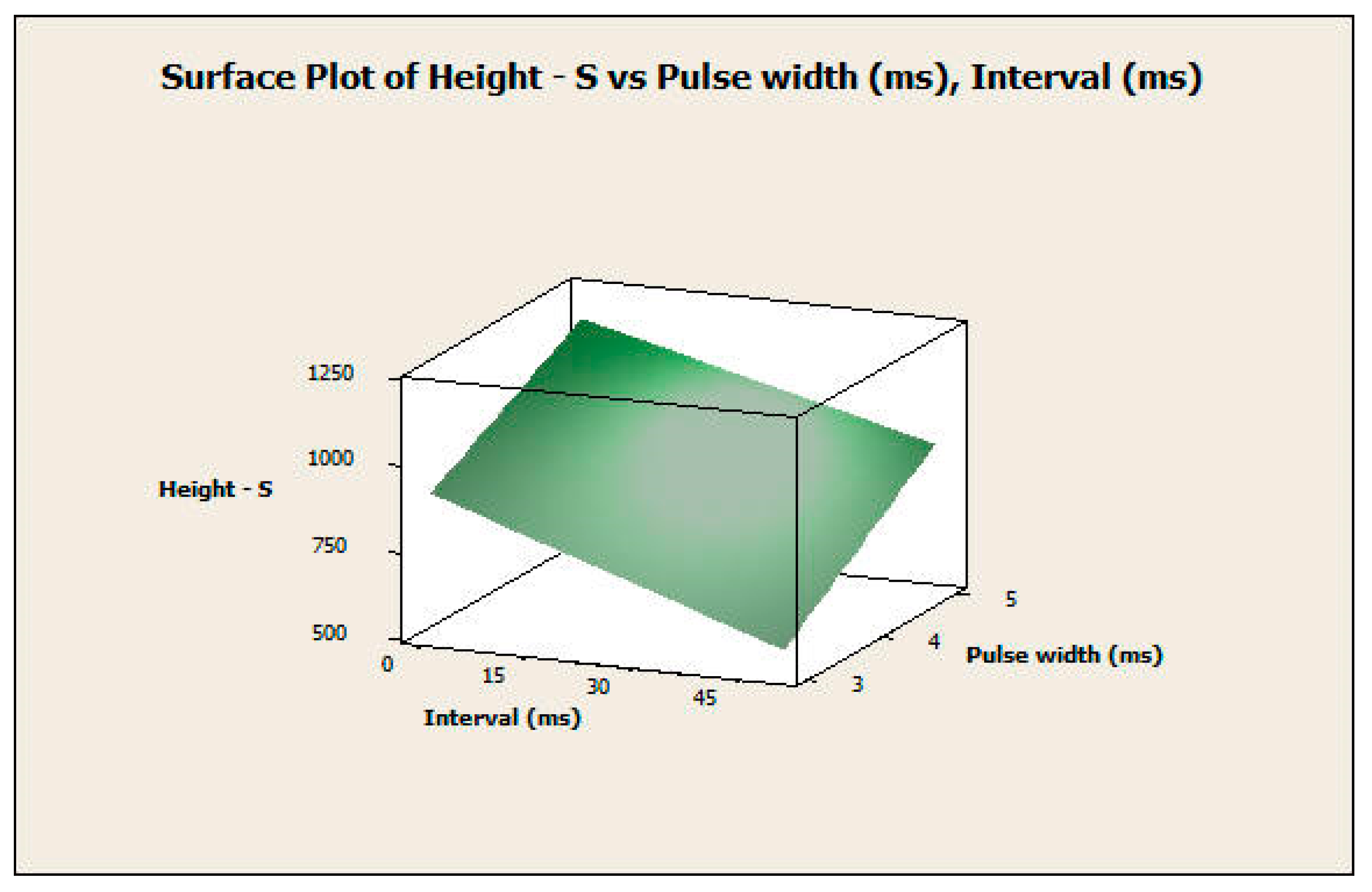
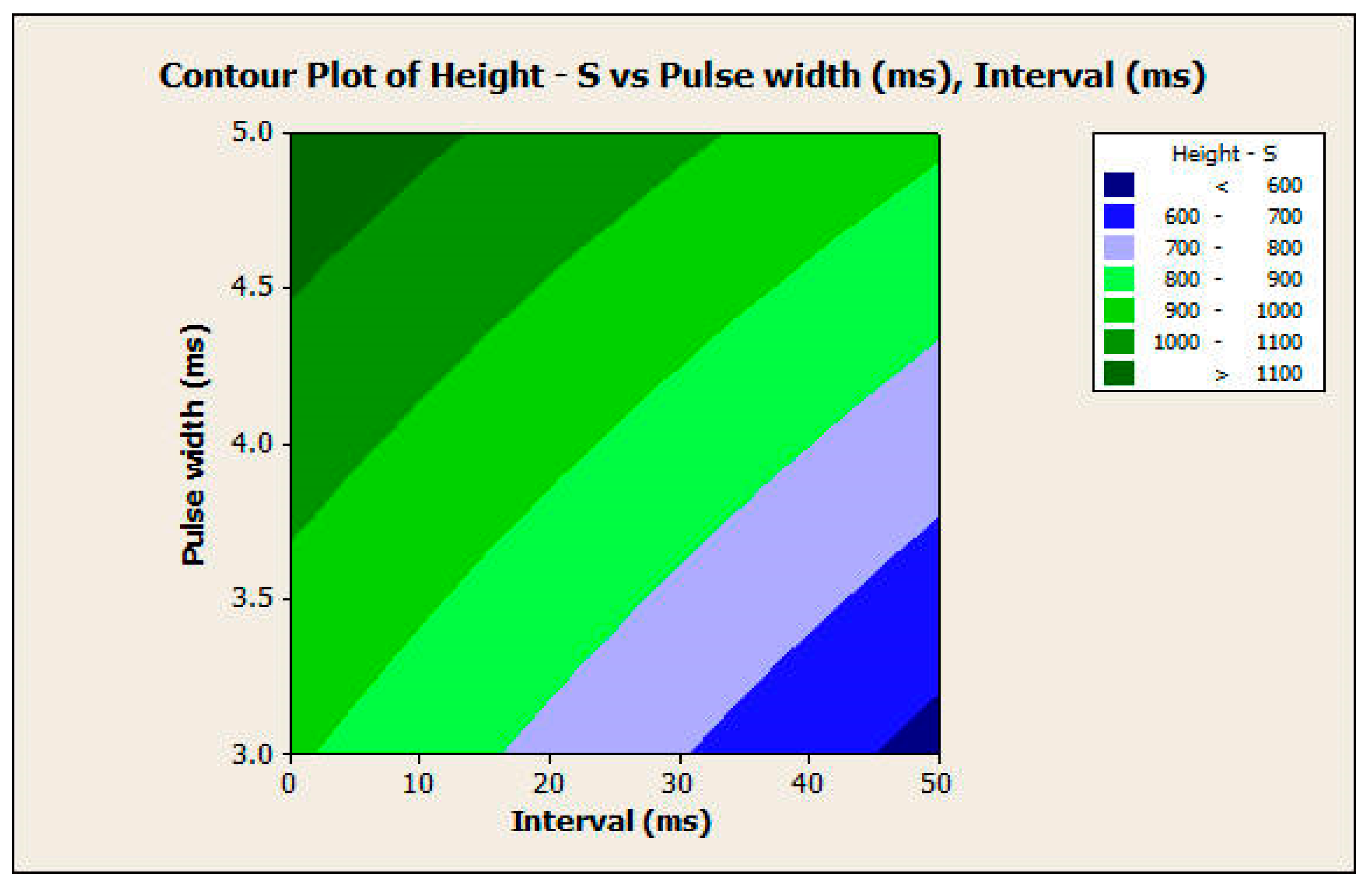
3.2.2. Response Surface Analysis
3.2.3. Predictive Model
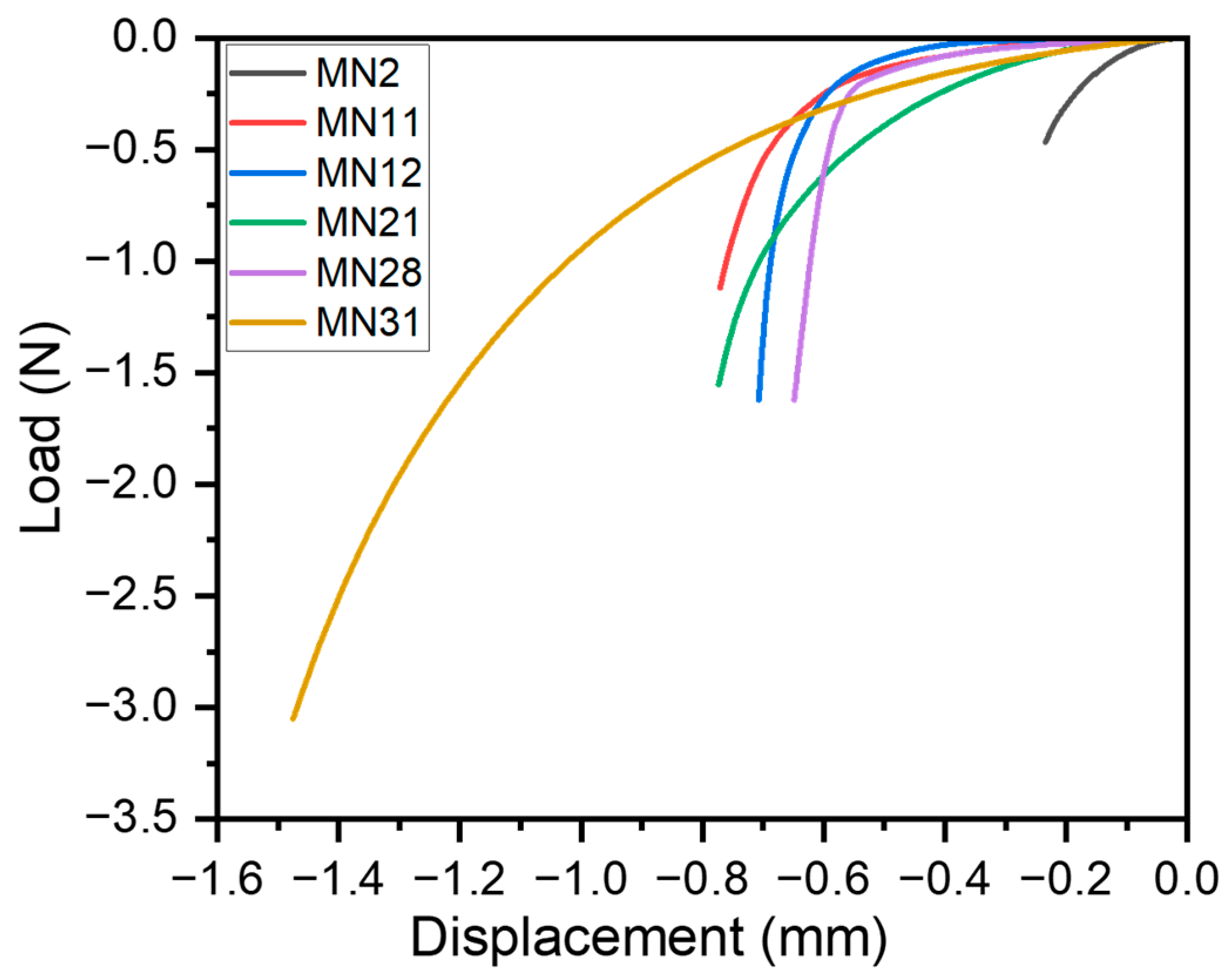
3.3. Mechanical Characterization of Microneedles
3.4. Discussion and Future Directions
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Donnelly, R.F.; Prausnitz, M.R. The promise of microneedle technologies for drug delivery. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2024, 14, 573–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le, Z.; Yu, J.; Quek, Y.J.; Bai, B.; Li, X.; Shou, Y.; Myint, B.; Xu, C.; Tay, A. Design principles of microneedles for drug delivery and sampling applications. Mater. Today 2023, 63, 137–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Yang, L.; Cui, Y. Microneedles: Materials, fabrication, and biomedical applications. Biomed. Microdevices 2023, 25, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Kong, H.; Zhang, J.; Chan, H.F.; Wang, J.; Shao, D.; Tao, Y.; Li, M. Microneedle system for tissue engineering and regenerative medicine. Exploration 2023, 3, 20210170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nanda, A.; Nanda, S.; Ghilzai, N.M.K. Current Developments Using Emerging Transdermal Technologies In Physical Enhancement Methods. Curr. Drug Deliv. 2006, 3, 233–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Sharma, P.K.; Malviya, R.; Alam, A.; Sagar, S. Advances in Microneedle-Based Approaches for Skin Diseases: A Comprehensive Review of Therapeutic Applications and Future Perspectives. Anti-Infect. Agents 2024, 22, 17–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paolino, D.; Sinha, P.; Fresta, M.; Ferrari, M. Drug Delivery Systems. In Encyclopedia of Medical Devices and Instrumentation; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mooney, K.; McElnay, J.C.; Donnelly, R.F. Parents’ perceptions of microneedle-mediated monitoring as an alternative to blood sampling in the monitoring of their infants. Int. J. Pharm. Pract. 2015, 23, 429–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trimzi, M.A.; Ham, Y.-B. A Needle-Free Jet Injection System for Controlled Release and Repeated Biopharmaceutical Delivery. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giudice, E.L.; Campbell, J.D. Needle-free vaccine delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2006, 58, 68–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ledesma-Feliciano, C.; Chapman, R.; Hooper, J.W.; Elma, K.; Zehrung, D.; Brennan, M.B.; Spiegel, E.K. Improved DNA Vaccine Delivery with Needle-Free Injection Systems. Vaccines 2023, 11, 280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Generotti, A.; Contreras, R.; Zounes, B.; Schade, E.; Kemme, A.; Rane, Y.; Liu, X.; Elwood, D.; Schultheis, K.; Marston, J.; et al. Intradermal DNA vaccine delivery using vacuum-controlled, needle-free electroporation. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2023, 34, 102070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tettey, F.; Parupelli, S.K.; Desai, S. A Review of Biomedical Devices: Classification, Regulatory Guidelines, Human Factors, Software as a Medical Device, and Cybersecurity. Biomed. Mater. Devices 2024, 2, 316–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birchall, J.C.; Clemo, R.; Anstey, A.; John, D.N. Microneedles in Clinical Practice—An Exploratory Study Into the Opinions of Healthcare Professionals and the Public. Pharm. Res. 2011, 28, 95–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Museau, M.; Butdee, S.; Vignat, F. Design and Manufacturing of Microneedles Toward Sustainable Products. KMUTNB Int. J. Appl. Sci. Technol. 2013, 4, 41–51. [Google Scholar]
- Avcil, M.; Çelik, A. Microneedles in Drug Delivery: Progress and Challenges. Micromachines 2021, 12, 1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manoj, H.; Gupta, P.; Mohan, L.; Nagai, M.; Wankhar, S.; Santra, T.S. Microneedles: Current Trends and Applications. In Microfluidics and Bio-MEMS; Jenny Stanford Publishing: Dubai, United Arab Emirates, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, J.; Xu, D.; Xuan, X.; He, H. Advances of Microneedles in Biomedical Applications. Molecules 2021, 26, 5912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Lu, G.; Liu, W.; Liao, L.; Ban, J.; Lu, Z. Formulation and Evaluation of PLGA Nanoparticulate-Based Microneedle System for Potential Treatment of Neurological Diseases. Int. J. Nanomed. 2023, 18, 3745–3760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhao, M.; Yan, Y.; Li, P.; Huang, W. Flexible Monitoring, Diagnosis, and Therapy by Microneedles with Versatile Materials and Devices toward Multifunction Scope. Research 2023, 6, 0128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.; Jung, H. Drawing lithography for microneedles: A review of fundamentals and biomedical applications. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 7309–7326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yung, K.L.; Xu, Y.; Kang, C.; Liu, H.; Tam, K.F.; Ko, S.M.; Kwan, F.Y.; Lee, T.M.H. Sharp tipped plastic hollow microneedle array by microinjection moulding. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2011, 22, 015016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parupelli, S.K.; Desai, S. Hybrid additive manufacturing (3D printing) and characterization of functionally gradient materials via in situ laser curing. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2020, 110, 543–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olowe, M.; Parupelli, S.K.; Desai, S. A Review of 3D-Printing of Microneedles. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 2693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parupelli, S.K.; Desai, S. The 3D Printing of Nanocomposites for Wearable Biosensors: Recent Advances, Challenges, and Prospects. Bioengineering 2024, 11, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kochhar, J.S.; Goh, W.J.; Chan, S.Y.; Kang, L. A simple method of microneedle array fabrication for transdermal drug delivery. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2013, 39, 299–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Liu, B.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, Z.; Jiang, L.; Yuan, W.; Liang, L. Fabrication of a Ti porous microneedle array by metal injection molding for transdermal drug delivery. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0172043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aldawood, F.K.; Parupelli, S.K.; Andar, A.; Desai, S. 3D Printing of Biodegradable Polymeric Microneedles for Transdermal Drug Delivery Applications. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khaled, F.; Desai, S.; Parupelli, S.K.; Andar, A. Polymeric Microneedles Using Additive Manufacturing for Therapeutic Applications. In Proceedings of the IISE Annual Conference & Expo, New Orleans, LA, USA, 21–23 May 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, A.R.; Procopio, A.T. Low cost additive manufacturing of microneedle masters. 3D Print. Med. 2019, 5, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krieger, K.J.; Bertollo, N.; Dangol, M.; Sheridan, J.T.; Lowery, M.M.; O’cearbhaill, E.D. Simple and customizable method for fabrication of high-aspect ratio microneedle molds using low-cost 3D printing. Microsyst. Nanoeng. 2019, 5, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, J.; Tay, F.E.; Miao, J.; Iliescu, C. Microfabricated Silicon Microneedle Array for Transdermal Drug Delivery. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2006, 34, 1127–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, R.E.; Mao, X.L.; Yoo, J.; Gonzalez, J.J. Chapter 3-Laser ablation. In Laser-Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy, 2nd ed.; Singh, J.P., Thakur, S.N., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2007; pp. 41–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, R. Laser ablation in analytical chemistry—A review. Talanta 2002, 57, 425–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeggy, C. Micro-Injection Moulding: From Process to Modelling; Presses Universitaires de Louvain: Louvain-la-Neuve, Belgium, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Guillot, A.J.; Cordeiro, A.S.; Donnelly, R.F.; Montesinos, M.C.; Garrigues, T.M.; Melero, A. Microneedle-Based Delivery: An Overview of Current Applications and Trends. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tu, K.-T.; Chung, C.-K. Fabrication of biodegradable polymer microneedle array via CO2 laser ablation. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE 10th International Conference on Nano/Micro Engineered and Molecular Systems, NEMS, Xi’an, China, 7–11 April 2015; pp. 494–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, K.T.; Chung, C.K. Rapid prototyping of biodegradable microneedle arrays by integrating CO2laser processing and polymer molding. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2016, 26, 065015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evens, T.; Van Hileghem, L.; Dosso, F.D.; Lammertyn, J.; Malek, O.; Castagne, S.; Seveno, D.; Van Bael, A. Producing Hollow Polymer Microneedles Using Laser Ablated Molds in an Injection Molding Process. J. Micro Nano-Manuf. 2021, 9, 030902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dharadhar, S.; Majumdar, A.; Dhoble, S.; Patravale, V. Microneedles for transdermal drug delivery: A systematic review. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2019, 45, 188–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.-W.; Chen, M.-C.; Wu, K.-W.; Tu, T.-Y. A Facile Approach for Rapid Prototyping of Microneedle Molds, Microwells and Micro-Through-Holes in Various Substrate Materials Using CO2 Laser Drilling. Biomedicines 2020, 8, 427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phipps, C. Laser Ablation and Its Applications; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.-T.; Ma, K.-J.; Tseng, A.A.; Chen, P. Projection ablation of glass-based single and arrayed microstructures using excimer laser. Opt. Laser Technol. 2005, 37, 271–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Lam, Y.; Sundarraman, C.; Tran, D. Influence of substrate cooling on femtosecond laser machined hole depth and diameter. Appl. Phys. A 2007, 89, 559–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintino, L.; Costa, A.; Miranda, R.; Yapp, D.; Kumar, V.; Kong, C. Welding with high power fiber lasers–A preliminary study. Mater. Des. 2007, 28, 1231–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotov, Y.A.; Samatov, O.M.; Ivanov, M.G.; Murzakaev, A.M.; Medvedev, A.I.; Timoshenkova, O.R.; Demina, T.M.; V’yukhina, I.V. Production and characteristics of composite nanopowders using a fiber ytterbium laser. Tech. Phys. 2011, 56, 652–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarp, A.S.K.; Gülsoy, M. Ceramic bracket debonding with ytterbium fiber laser. Lasers Med Sci. 2011, 26, 577–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldawood, F.K.; Andar, A.; Desai, S. A Comprehensive Review of Microneedles: Types, Materials, Processes, Characterizations and Applications. Polymers 2021, 13, 2815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becker, H.; Gärtner, C. Polymer microfabrication technologies for microfluidic systems. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2008, 390, 89–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, U.; Karim, K.J.B.A.; Buang, N.A. A Review of the Properties and Applications of Poly (Methyl Methacrylate) (PMMA). Polym. Rev. 2015, 55, 678–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janphuang, P.; Laebua, M.; Sriphung, C.; Taweewat, P.; Sirichalarmkul, A.; Sukjantha, K.; Promsawat, N.; Leuasoongnoen, P.; Suphachiaraphan, S.; Phimol, K.; et al. Polymer based microneedle patch fabricated using microinjection moulding. MATEC Web Conf. 2018, 192, 01039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ainslie, K.M.; Kraning, C.M.; Desai, T.A. Microfabrication of an asymmetric, multi-layered microdevice for controlled release of orally delivered therapeutics. Lab Chip 2008, 8, 1042–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demir, Y.K.; Akan, Z.; Kerimoglu, O. Characterization of Polymeric Microneedle Arrays for Transdermal Drug Delivery. PLOS ONE 2013, 8, e77289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.-H.; Allen, M.G.; Prausnitz, M.R. Biodegradable polymer microneedles: Fabrication, mechanics and transdermal drug delivery. J. Control. Release 2005, 104, 51–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yadav, S.; Singh, A. Microneedling: Advances and widening horizons. Indian Dermatol. Online J. 2016, 7, 244–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, N.-W.; Kim, S.; Lee, J.-Y.; Kim, K.-T.; Choi, Y.; Oh, Y.; Kim, J.; Kim, D.-D.; Park, J.-H. Microneedles for drug delivery: Recent advances in materials and geometry for preclinical and clinical studies. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2021, 18, 929–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kochhar, J.S.; Quek, T.C.; Soon, W.J.; Choi, J.; Zou, S.; Kang, L. Effect of Microneedle Geometry and Supporting Substrate on Microneedle Array Penetration into Skin. J. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 102, 4100–4108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, S.A.; Oakes, R.S.; Kapnick, S.M.; Jewell, C.M. Mapping the Mechanical and Immunological Profiles of Polymeric Microneedles to Enable Vaccine and Immunotherapy Applications. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 843355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ning, X.; Wiraja, C.; Lio, D.C.S.; Xu, C. A Double-Layered Microneedle Platform Fabricated through Frozen Spray-Coating. Adv. Heal. Mater. 2020, 9, e2000147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chi, Y.; Huang, Y.; Kang, Y.; Dai, G.; Liu, Z.; Xu, K.; Zhong, W. The effects of molecular weight of hyaluronic acid on transdermal delivery efficiencies of dissolving microneedles. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2022, 168, 106075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osipov, V.V.; Lisenkov, V.V.; Platonov, V.V. Ablation of oxide materials and production of nanopowders by ytterbium fiber laser. Appl. Phys. A 2015, 118, 1133–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldawood, F.; Desai, S.; Andar, A. Laser Fabrication of Polymeric Microneedles for Transdermal Drug Delivery. In Proceedings of the 2021 IISE Annual Conference, Online, 22–25 May 2021; Available online: https://par.nsf.gov/biblio/10297495-laser-fabrication-polymeric-microneedles-transdermal-drug-delivery (accessed on 5 June 2024).
- Aoyagi, S.; Izumi, H.; Isono, Y.; Fukuda, M.; Ogawa, H. Laser fabrication of high aspect ratio thin holes on biodegradable polymer and its application to a microneedle. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2007, 139, 293–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, G.; Liu, Z.; Kong, F.; Tam, H.; Shori, R.K.; Dong, L. Highly efficient ytterbium-doped phosphosilicate fiber lasers operating below 1020 nm. Opt. Express 2015, 23, 17693–17700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilsson, J.; Sahu, J.K.; Jeong, Y.; Clarkson, W.A.; Selvas, R.; Grudinin, A.B.; Alam, S. High-power fiber lasers: New developments. In Advances in Fiber Lasers; SPIE: Washington, DC, USA, 2003; pp. 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



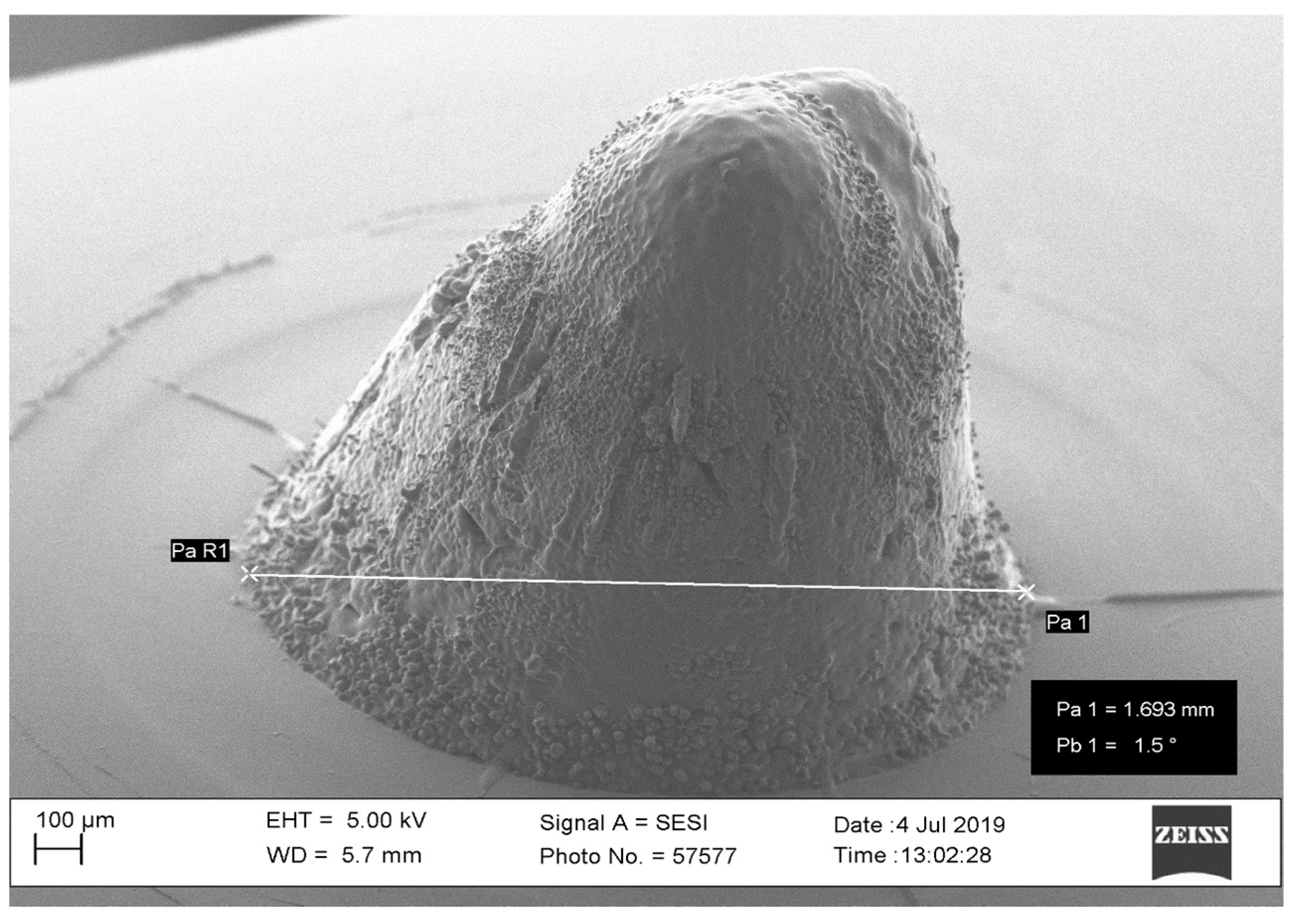

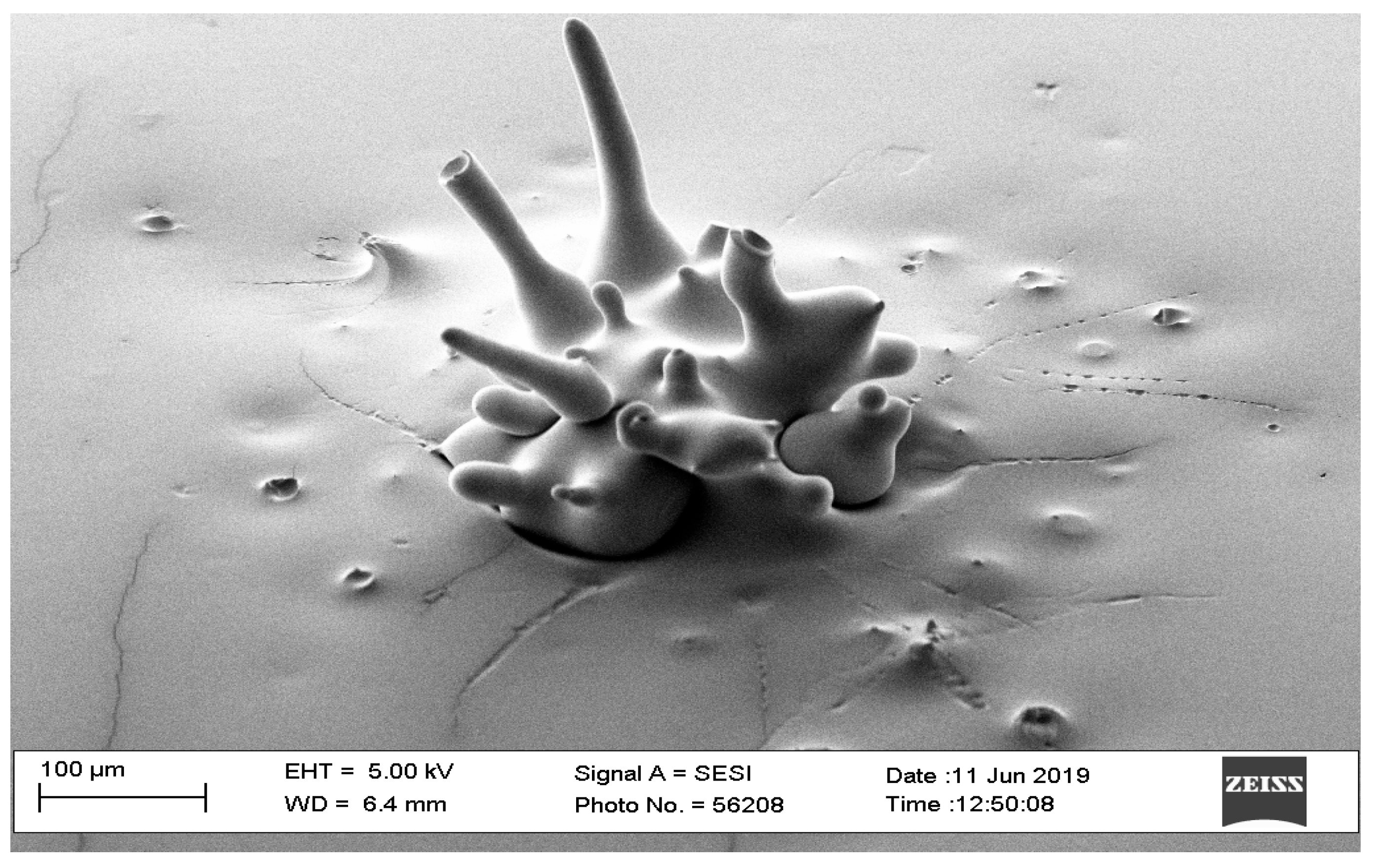
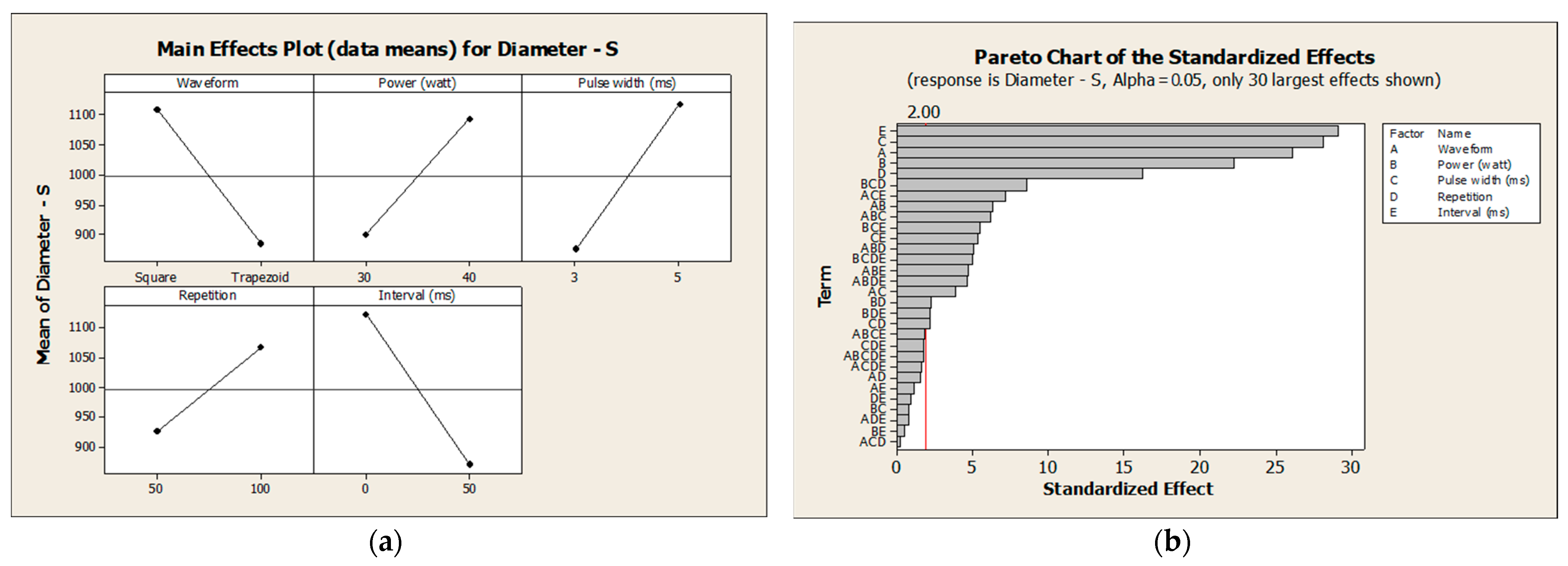
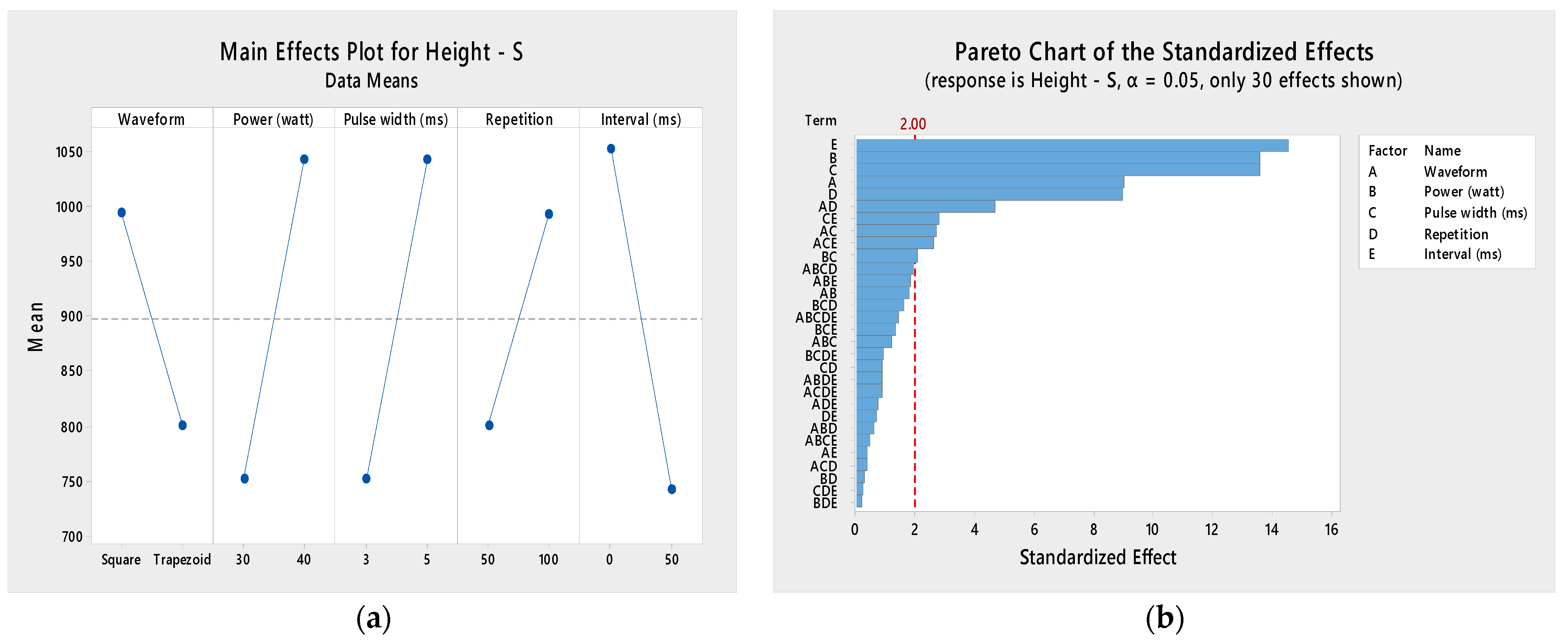




| Parameters | Level 1 | Level 2 |
|---|---|---|
| Waveform | Square | Trapezoid |
| Laser power | 30 w | 40 w |
| Laser pulse width | 3 ms | 5 ms |
| Number of repetitions | 50 times | 100 times |
| Interval time | 0 ms | 50 ms |
| Parameter | Values Available | Optimal Choice | Reason | Values to Exclude |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Waveform | Square, triangle, or trapezoid shape | Trapezoid or Square | A trapezoid will result in having a pyramid or cone shape. A square will result in a fair needle shape. | Triangle form required high laser power values, which resulted in a large diameter of the needle. |
| Power (watts) | 0 watts to 200 watts | 30 watts to 40 watts | Seek desired outcomes | Power below 30 watts will not result in any holes and is too low to create a needle. Higher power will cause a larger diameter. |
| Pulse Width (ms) | 0 to 10 ms | 3 to 5 ms | Seek desired outcomes | Values higher than 5 ms will cause a larger diameter. |
| Number of repetitions | 0 to 500 times | 50 to 100 times | Seek desired outcomes | Values higher than 100 times will cause a larger diameter. |
| Interval time (ms) | 0 to 200 ms | 0 to 50 ms | Seek desired outcomes | Values higher than 50 ms will cause a larger diameter. |
| Parameters | Run 1 | Run 2 | Run 3 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. | Waveform | Power (watts) | Pulse Width (ms) | Repetitions | Interval (ms) | Diameter (μm) | Height (μm) | Diameter (μm) | Height (μm) | Diameter (μm) | Height (μm) |
| 1 | Square | 30 | 3 | 50 | 0 | 917 | 800 | 931 | 796 | 958 | 762 |
| 2 | 30 | 3 | 50 | 50 | 687 | 456 | 782 | 492 | 593 | 505 | |
| 3 | 30 | 3 | 100 | 0 | 1083 | 995 | 1193 | 1033 | 1068 | 917 | |
| 4 | 30 | 3 | 100 | 50 | 897 | 691 | 858 | 788 | 887 | 673 | |
| 5 | 30 | 5 | 50 | 0 | 1144 | 1105 | 1013 | 1089 | 1175 | 1153 | |
| 6 | 30 | 5 | 50 | 50 | 922 | 871 | 997 | 893 | 940 | 821 | |
| 7 | 30 | 5 | 100 | 0 | 1278 | 1171 | 1235 | 1002 | 1193 | 1155 | |
| 8 | 30 | 5 | 100 | 50 | 1004 | 856 | 952 | 876 | 964 | 924 | |
| 9 | 40 | 3 | 50 | 0 | 1100 | 1011 | 1287 | 945 | 1161 | 1057 | |
| 10 | 40 | 3 | 50 | 50 | 933 | 808 | 939 | 829 | 948 | 766 | |
| 11 | 40 | 3 | 100 | 0 | 1250 | 1094 | 1267 | 1154 | 1319 | 1213 | |
| 12 | 40 | 3 | 100 | 50 | 1013 | 860 | 1027 | 949 | 1019 | 877 | |
| 13 | 40 | 5 | 50 | 0 | 1441 | 1481 | 1377 | 1057 | 1456 | 1532 | |
| 14 | 40 | 5 | 50 | 50 | 1009 | 997 | 1049 | 933 | 1038 | 998 | |
| 15 | 40 | 5 | 100 | 0 | 1638 | 1485 | 1638 | 1461 | 1663 | 1422 | |
| 16 | 40 | 5 | 100 | 50 | 1372 | 1157 | 1350 | 1095 | 1320 | 1103 | |
| 17 | Trapezoid | 30 | 3 | 50 | 0 | 843 | 577 | 806 | 545 | 808 | 560 |
| 18 | 30 | 3 | 50 | 50 | 230 | 0 | 195 | 0 | 254 | 0 | |
| 19 | 30 | 3 | 100 | 0 | 928 | 785 | 934 | 779 | 937 | 844 | |
| 20 | 30 | 3 | 100 | 50 | 605 | 323 | 597 | 374 | 607 | 323 | |
| 21 | 30 | 5 | 50 | 0 | 1018 | 810 | 932 | 800 | 903 | 803 | |
| 22 | 30 | 5 | 50 | 50 | 827 | 610 | 892 | 605 | 916 | 598 | |
| 23 | 30 | 5 | 100 | 0 | 1157 | 1035 | 1084 | 1108 | 1151 | 1125 | |
| 24 | 30 | 5 | 100 | 50 | 1000 | 815 | 964 | 934 | 950 | 902 | |
| 25 | 40 | 3 | 50 | 0 | 953 | 835 | 927 | 735 | 913 | 824 | |
| 26 | 40 | 3 | 50 | 50 | 760 | 575 | 820 | 543 | 801 | 496 | |
| 27 | 40 | 3 | 100 | 0 | 992 | 1206 | 1029 | 1165 | 981 | 1267 | |
| 28 | 40 | 3 | 100 | 50 | 649 | 728 | 692 | 770 | 624 | 770 | |
| 29 | 40 | 5 | 50 | 0 | 1039 | 1148 | 1040 | 1051 | 1022 | 1076 | |
| 30 | 40 | 5 | 50 | 50 | 930 | 924 | 946 | 788 | 909 | 797 | |
| 31 | 40 | 5 | 100 | 0 | 1286 | 1223 | 1248 | 1734 | 1184 | 1005 | |
| 32 | 40 | 5 | 100 | 50 | 1101 | 1224 | 1009 | 1126 | 1015 | 1154 | |
| Observation | Effect | est1 | Effects |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | A | −113.30 | −226.60 |
| 2 | B | 96.61 | 193.22 |
| 3 | C | 121.76 | 243.52 |
| 4 | D | 70.11 | 140.22 |
| 5 | E | −126.11 | −252.22 |
| 6 | AB | −27.19 | −54.39 |
| 7 | AC | 16.53 | 33.06 |
| 8 | AD | −6.78 | −13.56 |
| 9 | AE | 4.82 | 9.64 |
| 10 | BC | −3.51 | −7.02 |
| 11 | BD | −9.94 | −19.89 |
| 12 | BE | 2.40 | 4.81 |
| 13 | CD | 9.49 | 18.97 |
| 14 | CE | 23.21 | 46.43 |
| 15 | DE | −4.30 | −8.60 |
| 16 | ABC | −26.94 | −53.89 |
| 17 | ACD | 1.13 | 2.27 |
| 18 | ABD | −22.13 | −44.27 |
| 19 | ABE | 20.63 | 41.27 |
| 20 | ACE | 31.19 | 62.39 |
| 21 | ADE | −3.49 | −6.97 |
| 22 | BCD | 37.34 | 74.68 |
| 23 | BCE | −23.84 | −47.68 |
| 24 | BDE | −9.65 | −19.31 |
| 25 | CDE | −7.55 | −15.10 |
| 26 | ABCD | 0.53 | 1.06 |
| 27 | ABCE | −8.07 | −16.14 |
| 28 | ABDE | −20.13 | −40.27 |
| 29 | ACDE | −7.03 | −14.06 |
| 30 | BCDE | 21.67 | 43.35 |
| 31 | ABCDE | 7.40 | 14.81 |
| Observation | Effect | est1 | Effects |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | A | −96.62 | −193.25 |
| 2 | B | 145.37 | 290.75 |
| 3 | C | 145.31 | 290.62 |
| 4 | D | 96.10 | 192.20 |
| 5 | E | −155.41 | −310.83 |
| 6 | AB | 19.39 | 38.79 |
| 7 | AC | 29.08 | 58.16 |
| 8 | AD | 50.12 | 100.25 |
| 9 | AE | −4.18 | −8.37 |
| 10 | BC | −22.25 | −44.50 |
| 11 | BD | −3.41 | −6.83 |
| 12 | BE | −0.85 | −1.70 |
| 13 | CD | −9.60 | −19.20 |
| 14 | CE | 29.79 | 59.58 |
| 15 | DE | 7.79 | 15.58 |
| 16 | ABC | −13.14 | −26.29 |
| 17 | ACD | 4.00 | 8.00 |
| 18 | ABD | 6.35 | 12.70 |
| 19 | ABE | 19.87 | 39.75 |
| 20 | ACE | 28.10 | 56.20 |
| 21 | ADE | −7.89 | −15.79 |
| 22 | BCD | 17.20 | 34.41 |
| 23 | BCE | −14.31 | −28.62 |
| 24 | BDE | −2.18 | −4.37 |
| 25 | CDE | 2.83 | 5.66 |
| 26 | ABCD | −20.60 | −41.20 |
| 27 | ABCE | −5.00 | −10.00 |
| 28 | ABDE | −9.45 | −18.91 |
| 29 | ACDE | 9.39 | 18.79 |
| 30 | BCDE | 9.77 | 19.54 |
| 31 | ABCDE | 15.41 | 30.83 |
| Coefficients | Standard Error | t Stat | p-Value | Lower 95% | Upper 95% | Lower 95.0% | Upper 95.0% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intercept | 89.13 | 91.36 | 0.97 | 0.33 | −92.36 | 270.63 | −92.36 | 270.63 |
| Waveform | −226.60 | 19.81 | −11.43 | 0.00 | −265.97 | −187.23 | −265.97 | −187.23 |
| Power | 19.32 | 1.98 | 9.74 | 0.00 | 15.38 | 23.26 | 15.38 | 23.26 |
| Pulse width | 121.76 | 9.90 | 12.28 | 0.00 | 102.07 | 141.44 | 102.07 | 141.44 |
| Repetition | 2.80 | 0.39 | 7.07 | 0.00 | 2.01 | 3.59 | 2.01 | 3.59 |
| Interval | −5.04 | 0.39 | −12.72 | 0.00 | −5.83 | −4.25 | −5.83 | −4.25 |
| Coefficients | Standard Error | t Stat | p-Value | Lower 95% | Upper 95% | Lower 95.0% | Upper 95.0% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intercept | −544.87 | 121.12 | −4.49 | 0.00 | −785.50 | −304.24 | −785.50 | −304.24 |
| Waveform | −193.25 | 26.27 | −7.35 | 0.00 | −245.45 | −141.04 | −245.45 | −141.04 |
| Power | 29.07 | 2.62 | 11.06 | 0.00 | 23.85 | 34.29 | 23.85 | 34.29 |
| Pulse width | 145.31 | 13.13 | 11.06 | 0.00 | 119.21 | 171.41 | 119.21 | 171.41 |
| Repetition | 3.84 | 0.52 | 7.31 | 0.00 | 2.80 | 4.88 | 2.80 | 4.88 |
| Interval | −6.21 | 0.52 | −11.83 | 0.00 | −7.26 | −5.17 | −7.26 | −5.17 |
| Multiple R | 0.931 |
| R Square | 0.867 |
| Adjusted R Square | 0.860 |
| Standard Error | 97.091 |
| Observations | 96 |
| df | SS | MS | F | p Value | |
| Regression | 31 | 6,283,437.91 | 202,691.55 | 112.28 | <0.0001 |
| Residual | 64 | 115,533.33 | 1805.21 | ||
| Total | 95 | 6,398,971.24 |
| Multiple R | 0.919 |
| R Square | 0.845 |
| Adjusted R Square | 0.836 |
| Standard Error | 128.721 |
| Observations | 96 |
| df | SS | MS | F | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Regression | 31 | 8,949,791.96 | 288,702.96 | 26.43 | <0.0001 |
| Residual | 64 | 699,162.00 | 10,924.41 | ||
| Total | 95 | 9,648,953.96 |
| Tukey’s Studentized Range (HSD) Test for Output | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alpha | 0.05 | |||
| Error Degrees of Freedom | 64 | |||
| Error Mean Square | 10,924.41 | |||
| Critical Value of Studentized Range | 2.82522 | |||
| Minimum Significant Difference | 42.622 | |||
| Means with the same letter are not significantly different. | ||||
| Tukey Grouping | Mean | N | Waveform | |
| A | 993.65 | 48 | 1 | |
| B | 800.40 | 48 | 2 | |
| Tukey Grouping | Mean | N | Power | |
| A | 1042.40 | 48 | 40 | |
| B | 751.65 | 48 | 30 | |
| Tukey Grouping | Mean | N | Pulse | |
| A | 1042.33 | 48 | 5 | |
| B | 751.71 | 48 | 3 | |
| Tukey Grouping | Mean | N | Repetition | |
| A | 993.13 | 48 | 100 | |
| B | 800.92 | 48 | 50 | |
| Tukey Grouping | Mean | N | Interval | |
| A | 800.40 | 48 | 0 | |
| B | 800.40 | 48 | 50 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aldawood, F.K.; Andar, A.; Desai, S. Investigating Laser Ablation Process Parameters for the Fabrication of Customized Microneedle Arrays for Therapeutic Applications. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 885. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16070885
Aldawood FK, Andar A, Desai S. Investigating Laser Ablation Process Parameters for the Fabrication of Customized Microneedle Arrays for Therapeutic Applications. Pharmaceutics. 2024; 16(7):885. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16070885
Chicago/Turabian StyleAldawood, Faisal Khaled, Abhay Andar, and Salil Desai. 2024. "Investigating Laser Ablation Process Parameters for the Fabrication of Customized Microneedle Arrays for Therapeutic Applications" Pharmaceutics 16, no. 7: 885. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16070885
APA StyleAldawood, F. K., Andar, A., & Desai, S. (2024). Investigating Laser Ablation Process Parameters for the Fabrication of Customized Microneedle Arrays for Therapeutic Applications. Pharmaceutics, 16(7), 885. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16070885









