Physiologically-Based Pharmacokinetic Modeling and In Vitro–In Vivo Correlation of TV-46000 (Risperidone LAI): Prediction from Dog to Human
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data
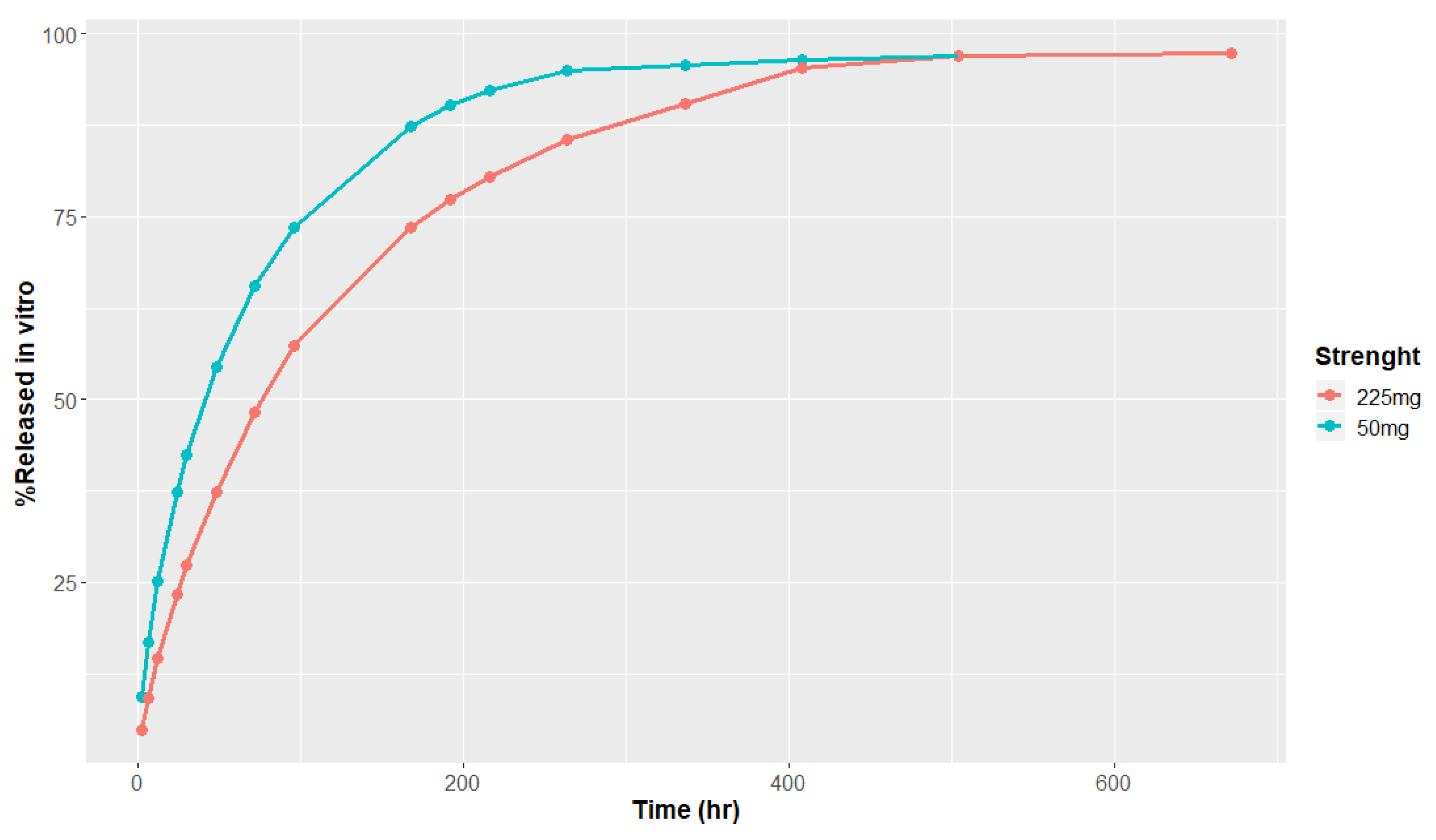
2.1.1. In Vitro Release Data
2.1.2. In Vitro Metabolism Data
2.1.3. Dog Data
2.1.4. Human Data
2.2. Physiologically-Based Pharmacokinetic Modeling and Simulation
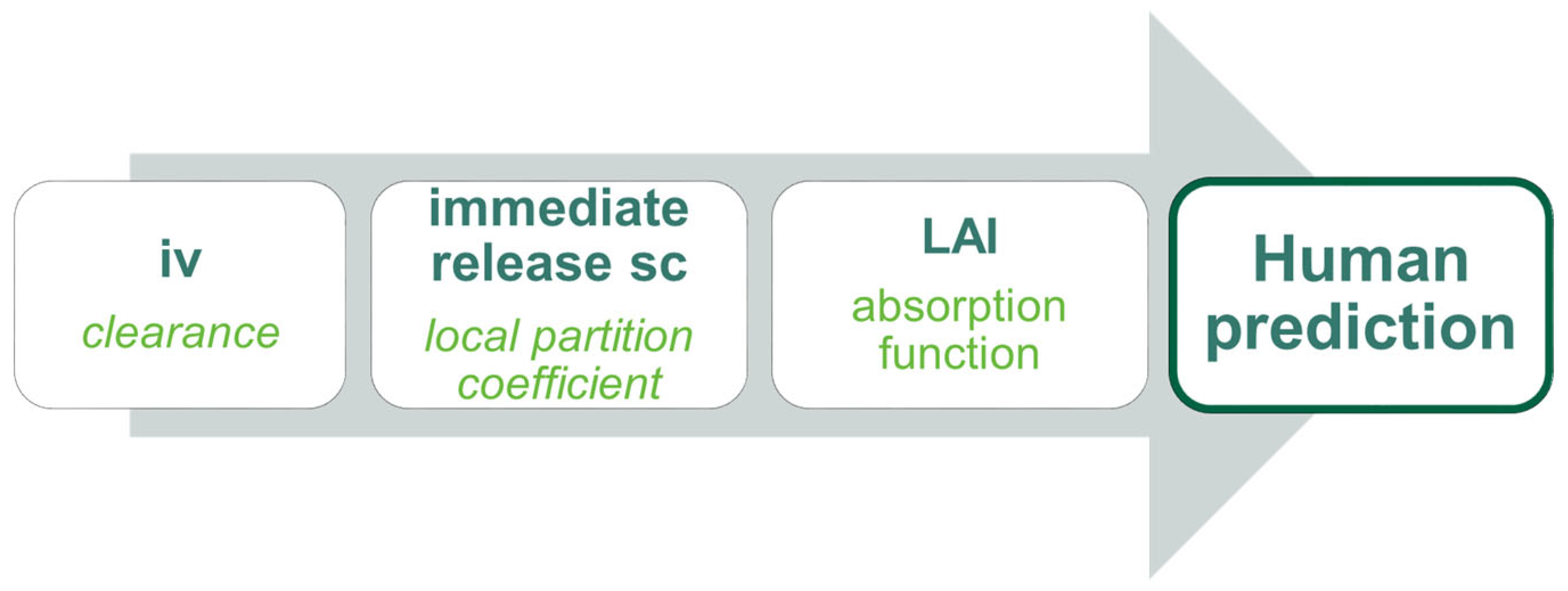
2.2.1. Modeling Strategy
2.2.2. Physicochemical Properties
2.2.3. Intravenous Model in Dogs
2.2.4. Immediate-Release sc Model in Dogs
2.2.5. Long-Acting Injectable sc Model in Dogs
2.2.6. Physiologically-Based Pharmacokinetic Model for TV-46000 in Humans
2.3. In Vitro–In Vivo Correlation
2.3.1. Mechanistic Deconvolution
2.3.2. In Vitro Time Scaling
2.3.3. Correlation
2.3.4. Convolution and Model Assessment
2.4. Software
3. Results
3.1. In Vitro Release and Metabolism Data
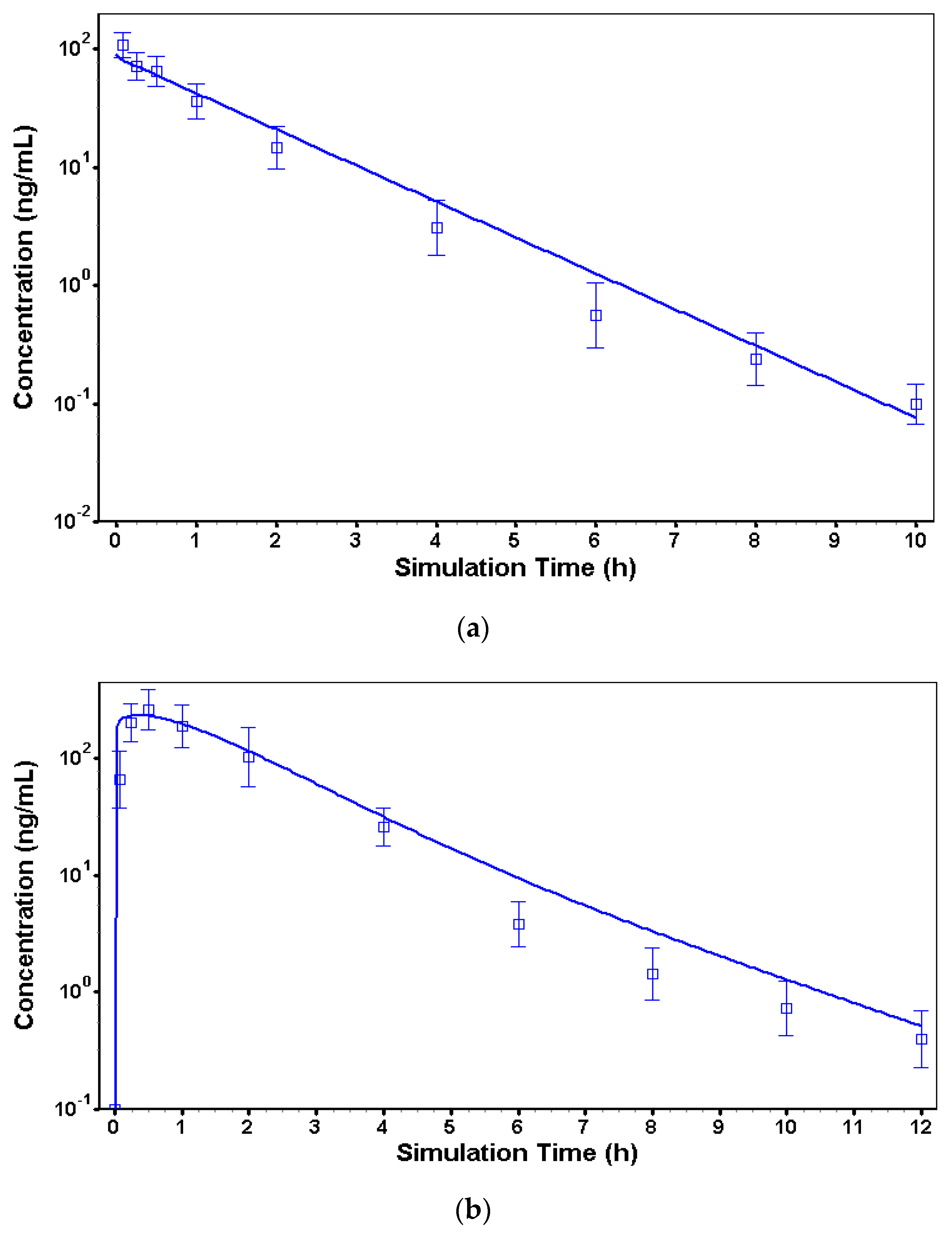
3.2. In Vivo Models to Characterize Risperidone Pharmacokinetics following Different Routes of Administration in Dogs
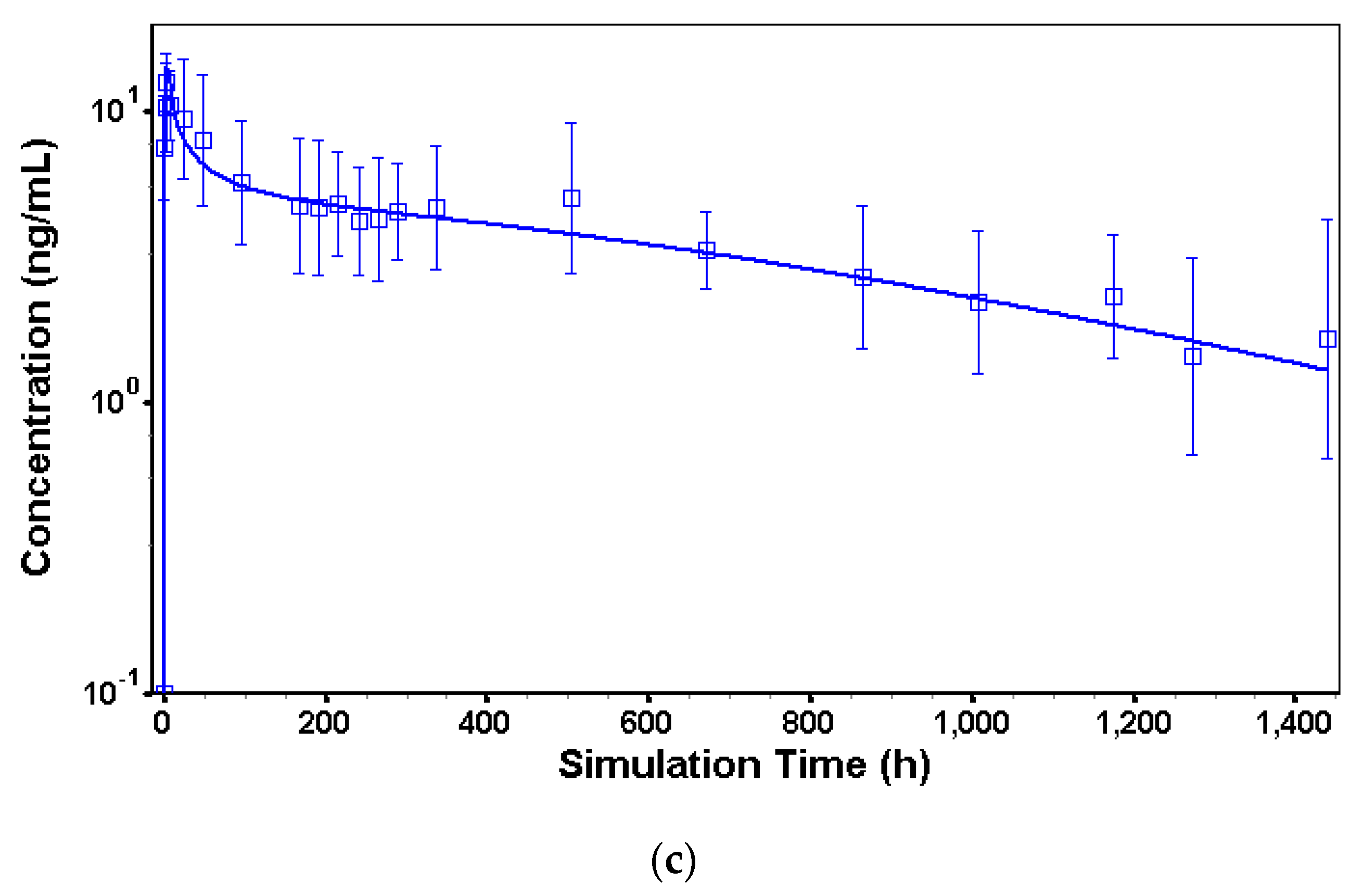
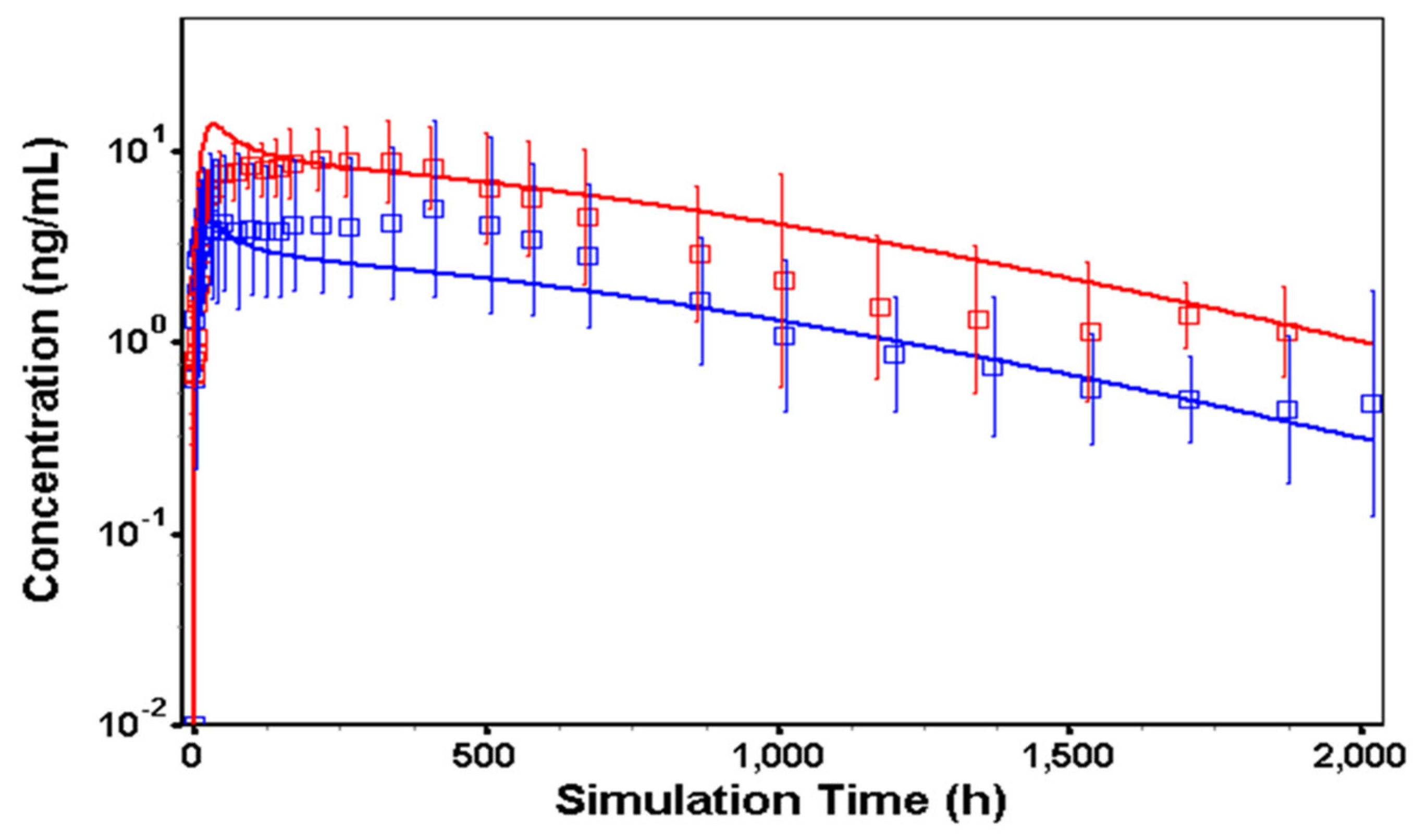
3.3. In Vivo Model in Humans
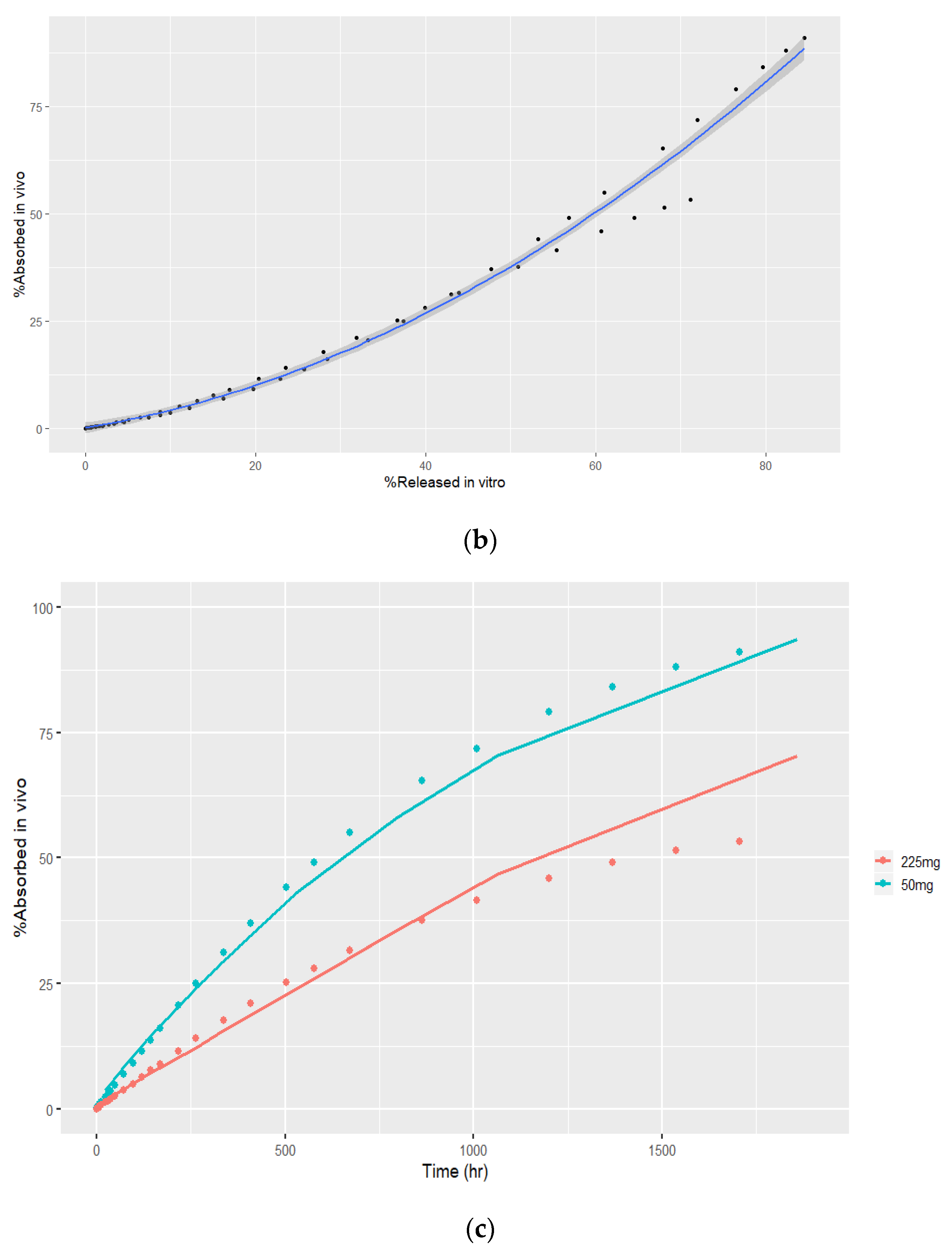
3.4. In Vivo–In Vitro Correlation Modeling
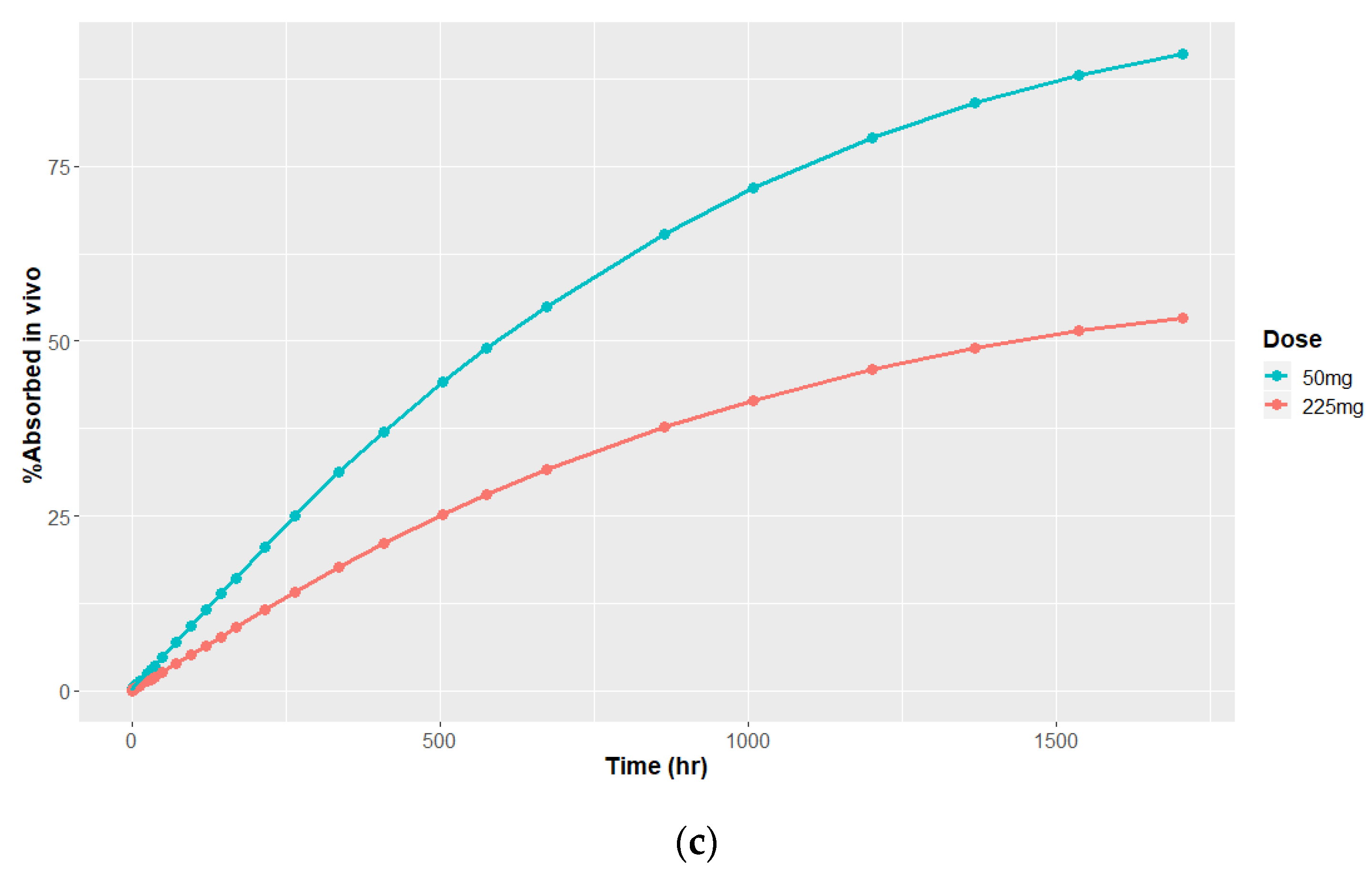
3.4.1. Deconvolution
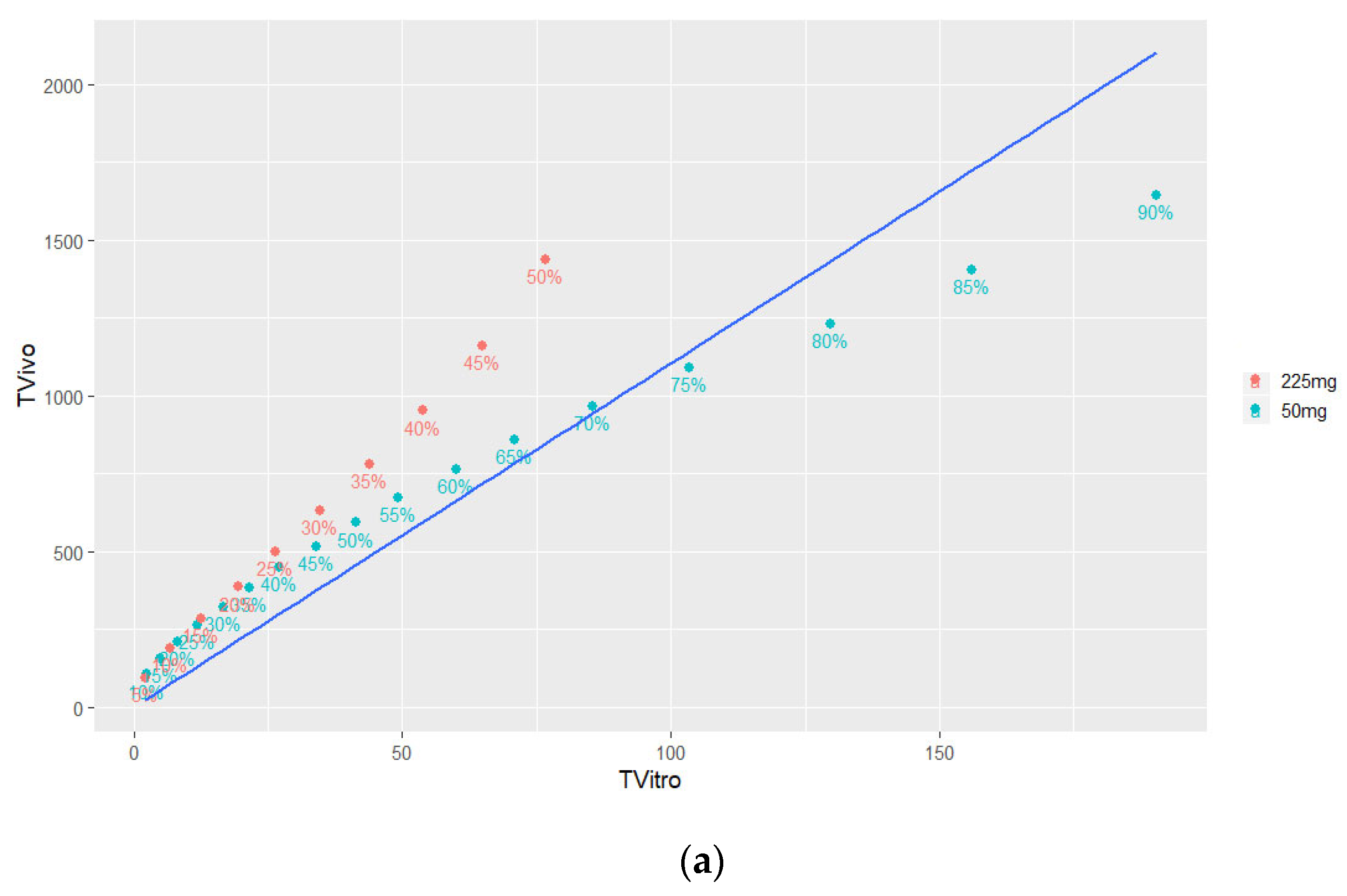
3.4.2. Time Scaling and Correlation
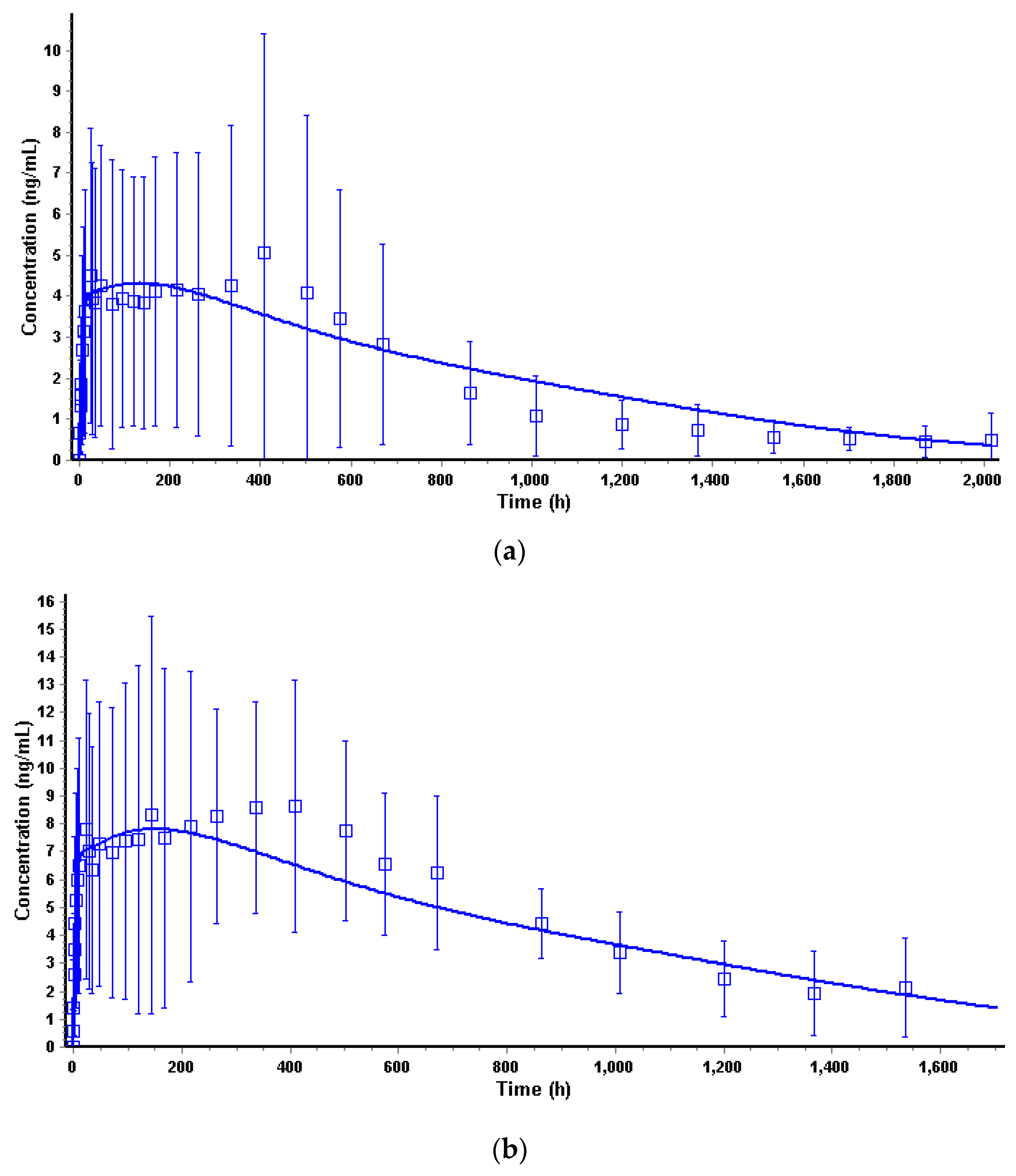
3.4.3. Convolution and Internal Prediction Errors
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Owen, A.; Rannard, S. Strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and challenges for long-acting injectable therapies: Insights for ap-plications in HIV therapy. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2016, 103, 144–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartzokis, G.; Lu, P.H.; Amar, C.P.; Raven, E.P.; Detore, N.R.; Altshuler, L.L.; Mintz, J.; Ventura, J.; Casaus, L.R.; Luo, J.S.; et al. Long-acting injection versus oral risperidone in first-episode schizophrenia: Differential impact on white matter myelination trajectory. Schizophr. Res. 2011, 132, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rhee, Y.-S.; Park, C.-W.; DeLuca, P.P.; Mansour, H.M. Sustained release injectable drug delivery. A review on the current status of long-acting injectables, including commercially marketed products. Pharm. Technol. 2010, 11 (Suppl. S6), 16–22. [Google Scholar]
- Ravi, S.; Peh, K.K.; Darwis, Y.; Murthy, B.K.; Singh, T.R.; Mallikarjun, C. Development and characterization of polymeric microspheres for controlled release protein loaded drug delivery system. Indian. J. Pharm. Sci. 2008, 70, 303–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitragotri, S.; Burke, P.A.; Langer, R. Overcoming the challenges in administering biopharmaceuticals: Formulation and delivery strategies. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2014, 13, 655–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brissos, S.; Veguilla, M.R.; Taylor, D.; Balanzá-Martinez, V. The role of long-acting injectable antipsychotics in schizophrenia: A critical appraisal. Ther. Adv. Psychopharmacol. 2014, 4, 198–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guzman, F. Mechanism of Action of Risperidone. Available online: https://psychopharmacologyinstitute.com/antipsychotics/risperidone/mechanism-of-action-pharmacodynamics-risperidone/ (accessed on 9 August 2018).
- Kane, J.M.; Harary, E.; Eshet, R.; Tohami, O.; Weiser, M.; Leucht, S.; Merenlender-Wagner, A.; Sharon, N.; Davis, G.L.; Suett, M.; et al. Efficacy and safety of TV-46000, a long-acting, subcutaneous, injectable formulation of risperidone, for schizophrenia: A randomised clinical trial in the USA and Bulgaria. Lancet Psychiatry 2023, 10, 934–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberge, C.; Cros, J.-M.; Serindoux, J.; Cagnon, M.-E.; Samuel, R.; Vrlinic, T.; Berto, P.; Rech, A.; Richard, J.; Lopez-Noriega, A. BEPO®: Bioresorbable diblock mPEG-PDLLA and triblock PDLLA-PEG-PDLLA based in situ forming depots with flexible drug delivery kinetics modulation. J. Control. Release 2020, 319, 416–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhuang, X.; Lu, C. PBPK modeling and simulation in drug research and development. Acta Pharm. Sin. B. 2016, 6, 430–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markowicz-Piasecka, M.; Kubisiak, M.; Asendrych-Wicik, K.; Kołodziejczyk, M.; Grzelińska, J.; Fabijańska, M.; Pietrzak, T. Long-Acting Injectable Antipsychotics-A Review on Formulation and In Vitro Dissolution. Pharmaceutics 2023, 16, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perlstein, I.; Merenlender-Wagner, A.; Gomeni, R.; Lamson, M.; Harary, E.; Spiegelstein, O.; Kalmanczhelyi, A.; Tiver, R.; Loupe, P.; Levi, M.; et al. Population Pharmacokinetic Modeling and Simulation of TV-46000: A Long-Acting Injectable Formulation of Risperidone. Clin. Pharmacol. Drug Dev. 2022, 11, 865–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharan, S.; Lanyan Fang, L.; Viera Lukacova, V.; Xiaomei Chen, X.; Andrew, C.; Hooker, A.C.; Karlsson, M.O. Model-Informed Drug Development for Long-Acting Injectable Products: Summary of American College of Clinical Pharmacology Symposium. Clin. Pharmacol. Drug Dev. 2021, 10, 220–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson and Johnson. Risperidal New Drug Application. Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/nda/2006/020272Orig1s036,s041,020588Orig1s024,s028,s029,21444Orig1s008,s015.pdf (accessed on 20 June 2024).
- Kneller, L.A.; Abad-Santos, F.; Hempel, G. Physiologically Based Pharmacokinetic Modelling to Describe the Pharmacokinetics of Risperidone and 9-Hydroxyrisperidone According to Cytochrome P450 2D6 Phenotypes. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2020, 59, 51–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mannens, G.; Meuldermans, W.; Snoeck, E.; Heykants, J. Plasma protein binding of risperidone and its distribution in blood. Psychopharmacology 1994, 114, 566–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Invega: EPAR—Procedural Steps Taken before Authorization, EMA 2007. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/scientific-discussion/invega-epar-scientific-discussion_en.pdf (accessed on 23 February 2024).
- Kesisoglou, F.; Xia, B.; Agrawal, N.G.B. Comparison of Deconvolution-Based and Absorption Modeling IVIVC for Extended Release Formulations of a BCS III Drug Development Candidate. AAPS J. 2015, 17, 1492–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomeni, R.; Bressolle-Gomeni, F. Modeling Complex Pharmacokinetics of Long-Acting Injectable Products Using Convolution-Based Models with Nonparametric Input Functions. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2021, 61, 1081–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- FDA CDER. Guidance for Industry, Extended Release Oral Dosage Forms: Development, Evaluation, and Application of In Vitro/In Vivo Correlations. 1997. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/media/70939/download (accessed on 23 February 2024).
| Parameter | Risperidone | 9-OH-Risperidone |
|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight (g/mol) | 410.49 | 426.48 |
| LogP | 3.04 | 2.32 |
| Solubility (pH 7.4, mg/mL) | 0.171 | 0.171 |
| pKa (Base) | 8.24 | 8.24 |
| pKa (Acid) | 3.11 | 3.11 |
| Enzyme | Vm (pmol/min/pmolCYP) | Km (µM) |
|---|---|---|
| CYP2D6 1 | 13.9 | 40.4 |
| CYP2D6 2 | 3.155 | 0.534 |
| CYP3A4 | 12.4 ± 0.5 | 37.4 ± 3.2 |
| Model Parameters | Observed Value | Predicted Value | Error (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Calibrated iv model | |||
| Cmax (ng/mL) | 109.1 | 88.4 | 18.9 |
| AUC0–∞ (h × ng/mL) | 115.7 | 121.7 | 5.2 |
| Calibrated IR model | |||
| Cmax (ng/mL) | 264.3 | 234.8 | 11.1 |
| AUC0–∞ (h × ng/mL) | 510.6 | 560.3 | 9.7 |
| Calibrated LAI sc model | |||
| Cmax (ng/mL) | 12.7 | 14.2 | 11.8 |
| AUC0–∞ (h × ng/mL) | 5552.1 | 5730.6 | 3.2 |
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Time lag (h) | 0 |
| Total released (%) | 100 |
| Phase 1—fraction | 0.142 |
| Phase 1—time scale | 30.88 |
| Phase 1—shape | 0.717 |
| Phase 2—fraction | 0.858 |
| Phase 2—time scale | 6370.7 |
| Phase 2—shape | 1.285 |
| Parameter | Observed Value | Predicted Value | Error (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cmax (ng/mL) | 5.0 | 5.6 | 12.0 |
| AUC0–∞ (h × ng/mL) | 4566.7 | 3196.2 | 30.0 |
| Model Parameters | Observed Value | Predicted Value | Error (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| TV-46000 50 mg | |||
| Cmax (ng/mL) | 5.05 | 4.31 | 13.6 |
| AUC0–∞ (h × ng/mL) | 4566.7 | 4414.1 | 3.3 |
| TV-46000 250 mg | |||
| Cmax (ng/mL) | 8.6 | 7.8 | 9.3 |
| AUC0–∞ (h × ng/mL) | 9365.8 | 8392.1 | 10.4 |
| Parameter | 50 mg | 225 mg |
|---|---|---|
| Time lag (h) | 0.090 | 0.095 |
| Total released (%) | 99.75 | 60.0 |
| Phase 1—fraction | 0.197 | 0.187 |
| Phase 1—time scale | 102.1 | 107.2 |
| Phase 1—shape | 0.68 | 0.65 |
| Phase 2—fraction | 0.367 | 0.367 |
| Phase 2—time scale | 2745.8 | 2745.8 |
| Phase 2—shape | 1.32 | 1.32 |
| Phase 3—fraction | 0.436 | 0.446 |
| Phase 3—time scale | 1,823,000 | 1,914,000 |
| Phase 3—shape | 2.05 | 2.05 |
| Strength | Observed | Predicted | Prediction Error (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cmax (ng/mL) | 50 mg | 5.0 | 4.3 | 14.0 |
| 225 mg | 8.7 | 7.0 | 19.5 | |
| AUC0-t (h × ng/mL) | 50 mg | 3839 | 2876 | 25.0 |
| 225 mg | 8296 | 9440 | 13.8 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bibi, D.; Bilgraer, R.; Steiner, L.; Hallak, H. Physiologically-Based Pharmacokinetic Modeling and In Vitro–In Vivo Correlation of TV-46000 (Risperidone LAI): Prediction from Dog to Human. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 896. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16070896
Bibi D, Bilgraer R, Steiner L, Hallak H. Physiologically-Based Pharmacokinetic Modeling and In Vitro–In Vivo Correlation of TV-46000 (Risperidone LAI): Prediction from Dog to Human. Pharmaceutics. 2024; 16(7):896. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16070896
Chicago/Turabian StyleBibi, David, Raphael Bilgraer, Lilach Steiner, and Hussein Hallak. 2024. "Physiologically-Based Pharmacokinetic Modeling and In Vitro–In Vivo Correlation of TV-46000 (Risperidone LAI): Prediction from Dog to Human" Pharmaceutics 16, no. 7: 896. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16070896
APA StyleBibi, D., Bilgraer, R., Steiner, L., & Hallak, H. (2024). Physiologically-Based Pharmacokinetic Modeling and In Vitro–In Vivo Correlation of TV-46000 (Risperidone LAI): Prediction from Dog to Human. Pharmaceutics, 16(7), 896. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16070896






