Synthesis, Radiolabeling, and Biodistribution Study of a Novel DOTA-Peptide for Targeting Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Receptors in the Molecular Imaging of Breast Cancer
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
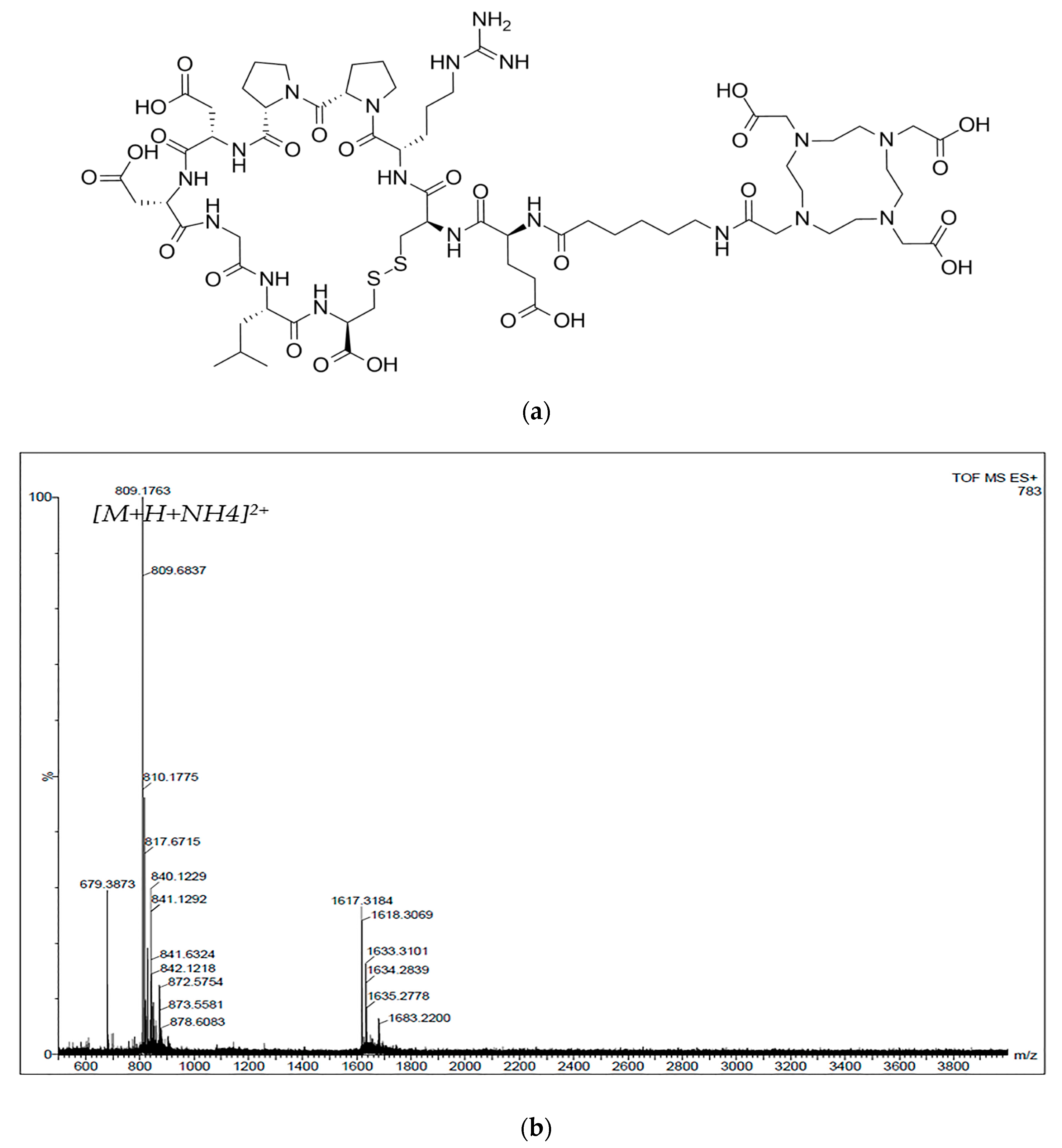
2.2. Synthesis of DOTA-Ahx-VGB3 and 68Ga-Radiolabeling
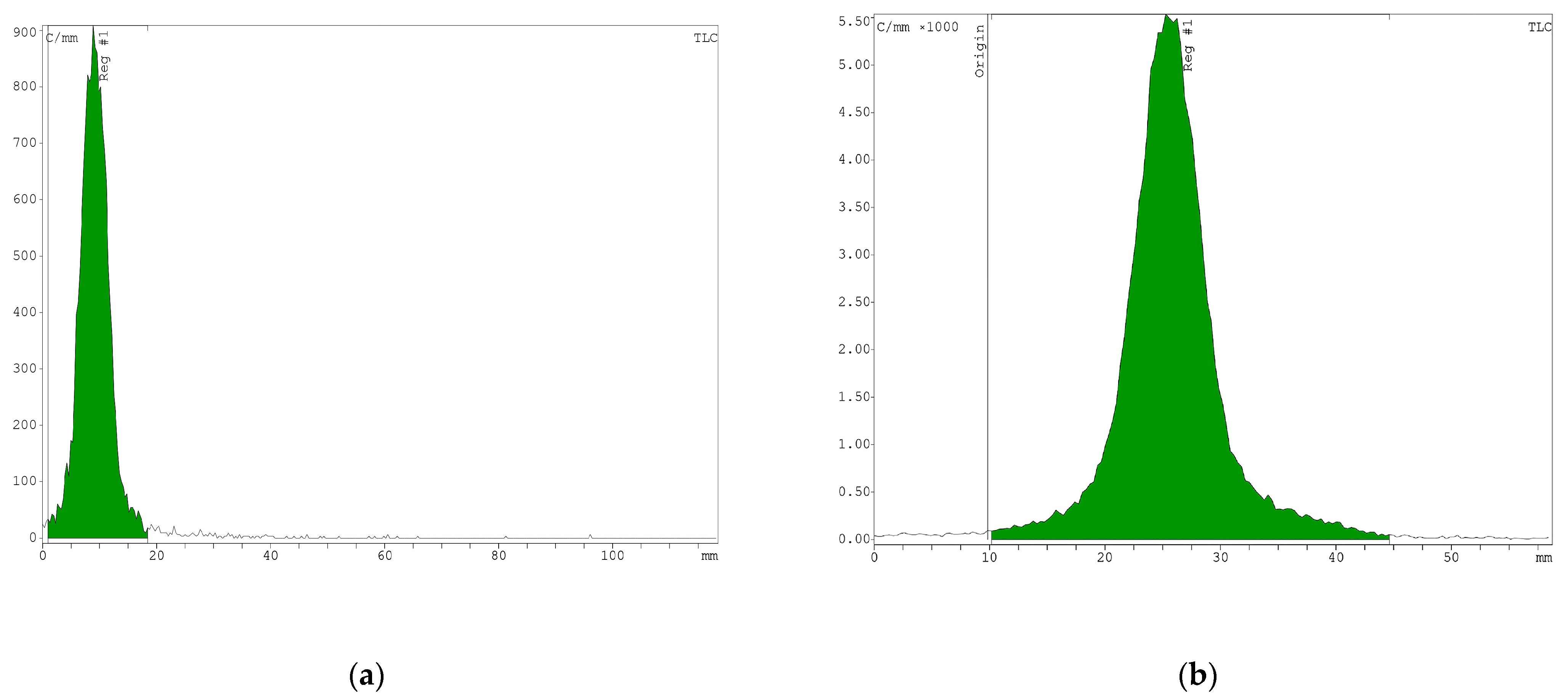
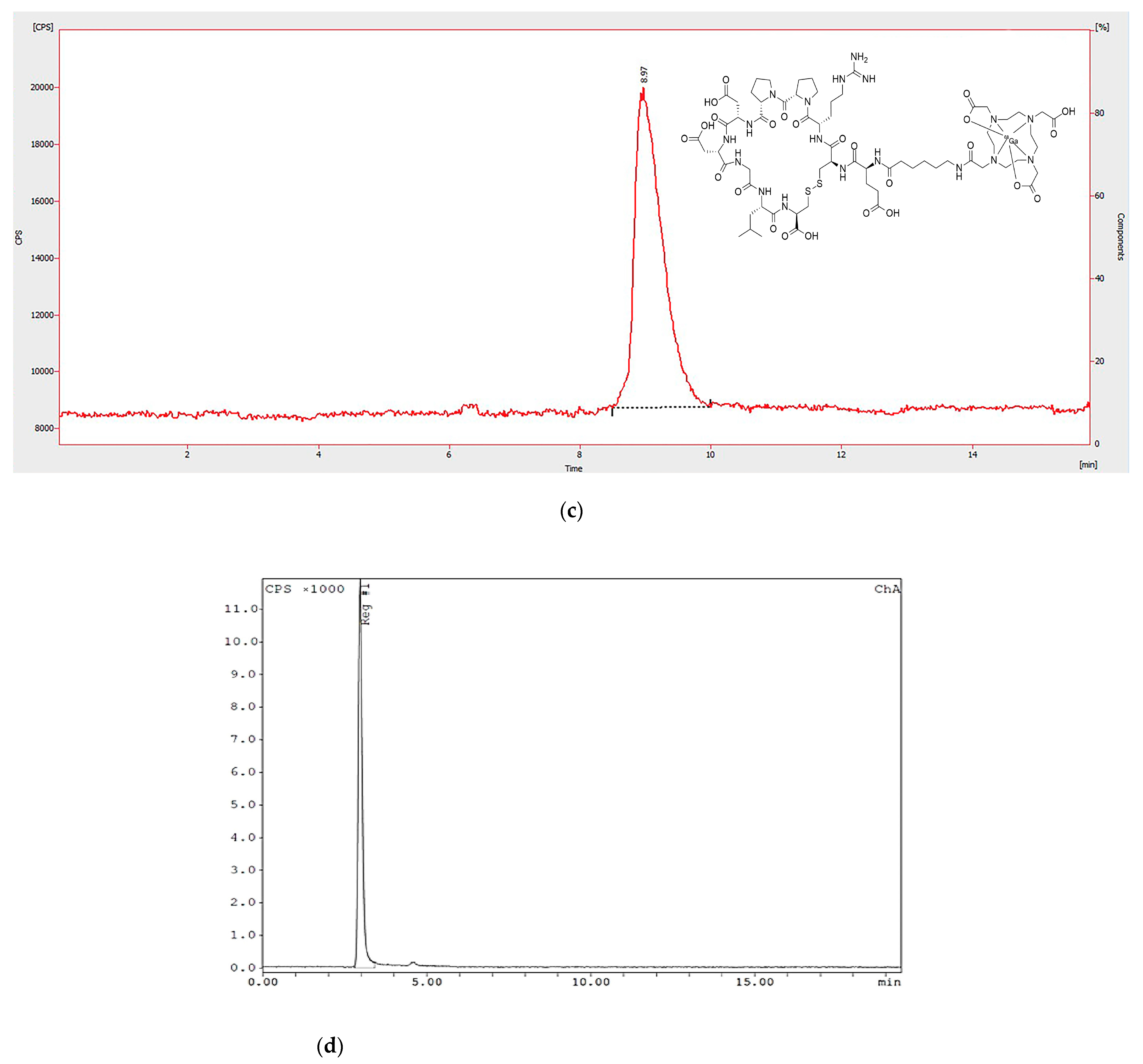
2.3. Quality Control
2.4. Determination of n-Octanol/Water Partition Coefficient (Log p)
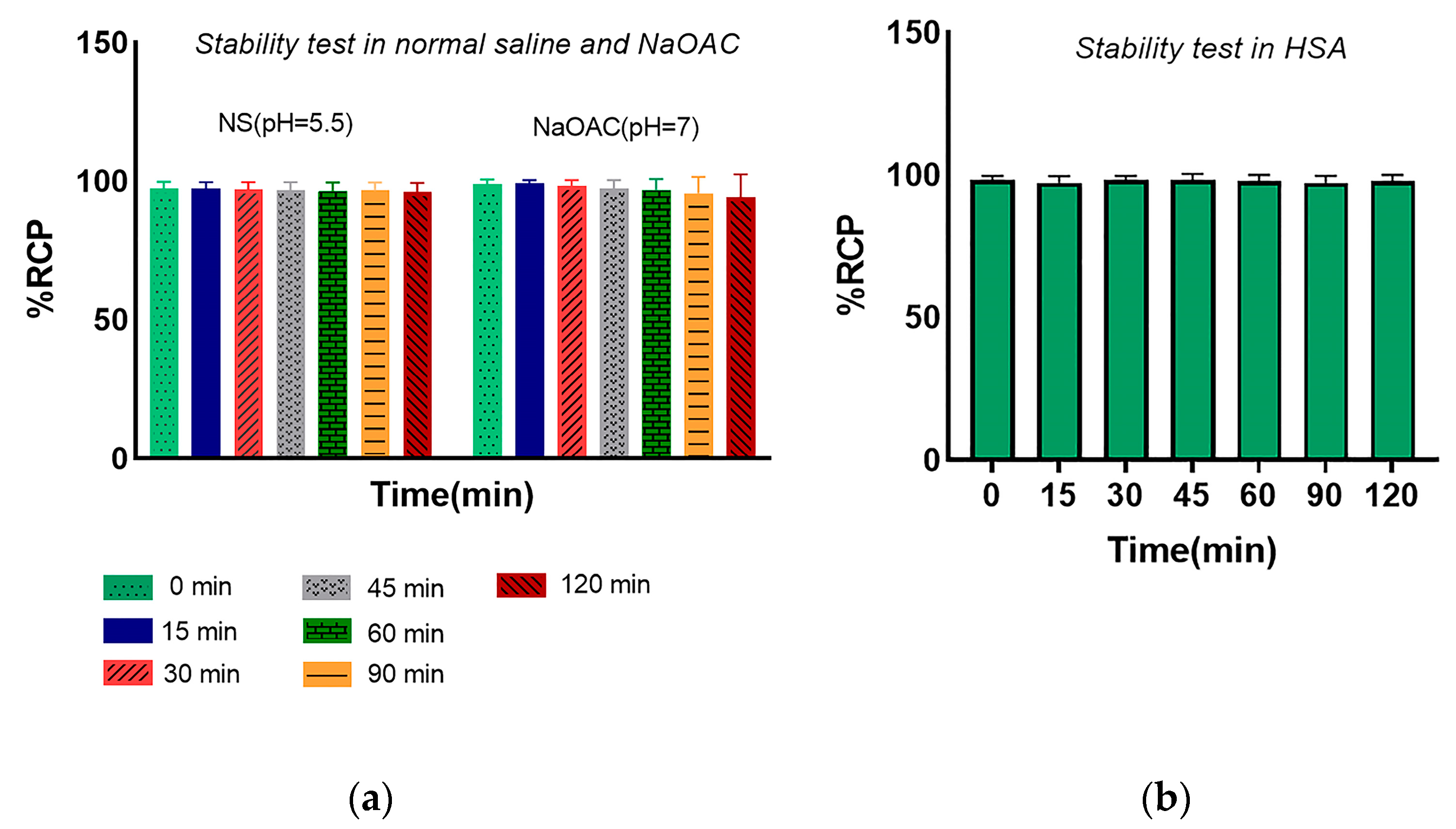
2.5. In Vitro Stability of Radiopeptide
2.6. Radionuclide Identification and Activity Measurements
2.7. Cell Culture and Animal Models
2.8. Internalization and Surface Binding in the Breast Cancer Cell Line
2.9. In Vitro Competitive Binding Study
2.10. Biodistribution Studies and Analysis
2.11. PET/CT Imaging
3. Results
3.1. Synthesis and 68Ga-Labeling of the Peptide
3.2. n-Octanol/Water Partition Coefficient (Log p)
3.3. In Vitro Stability of the Radiopeptide
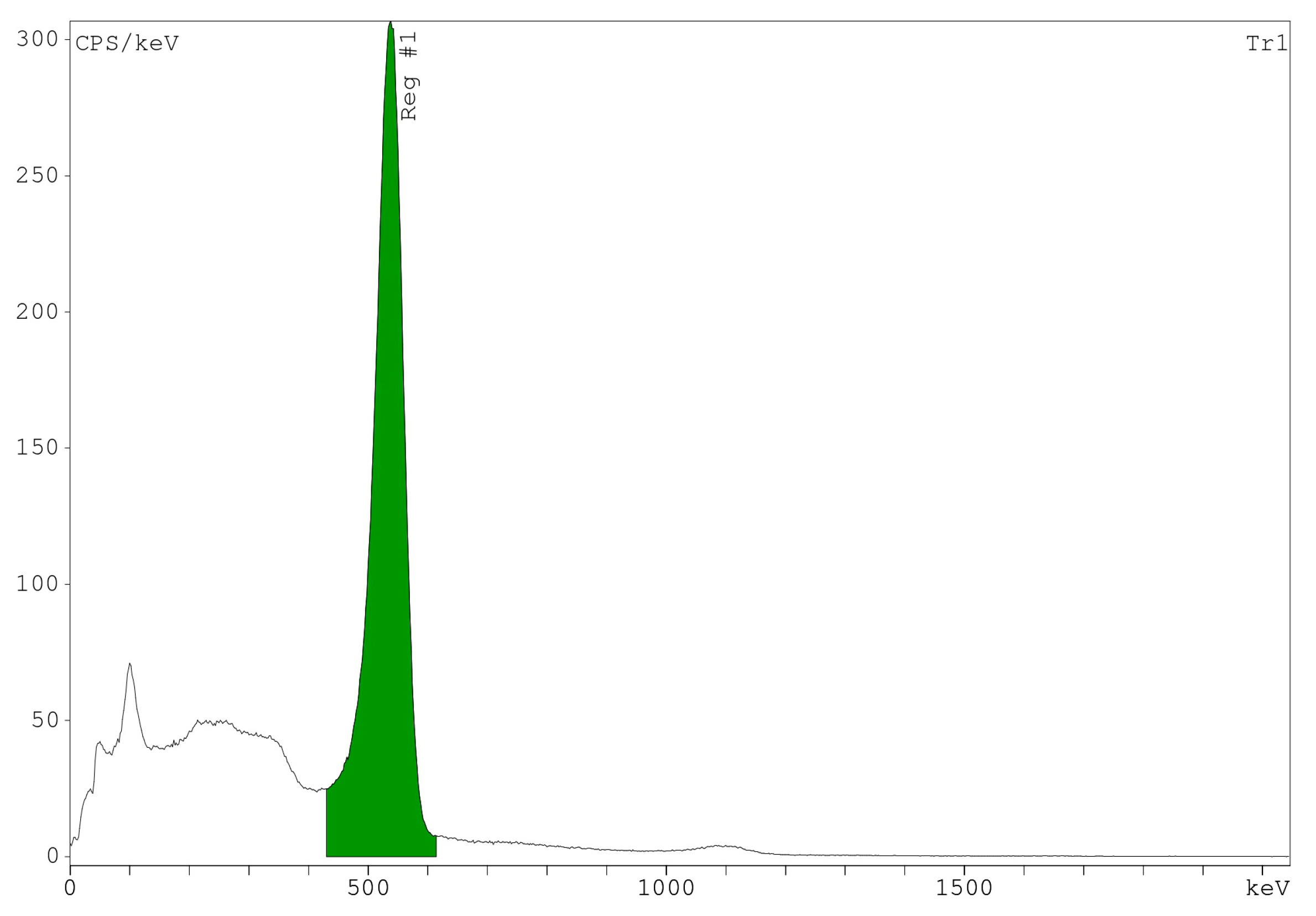
3.4. Radionuclide Identification and Activity Measurements
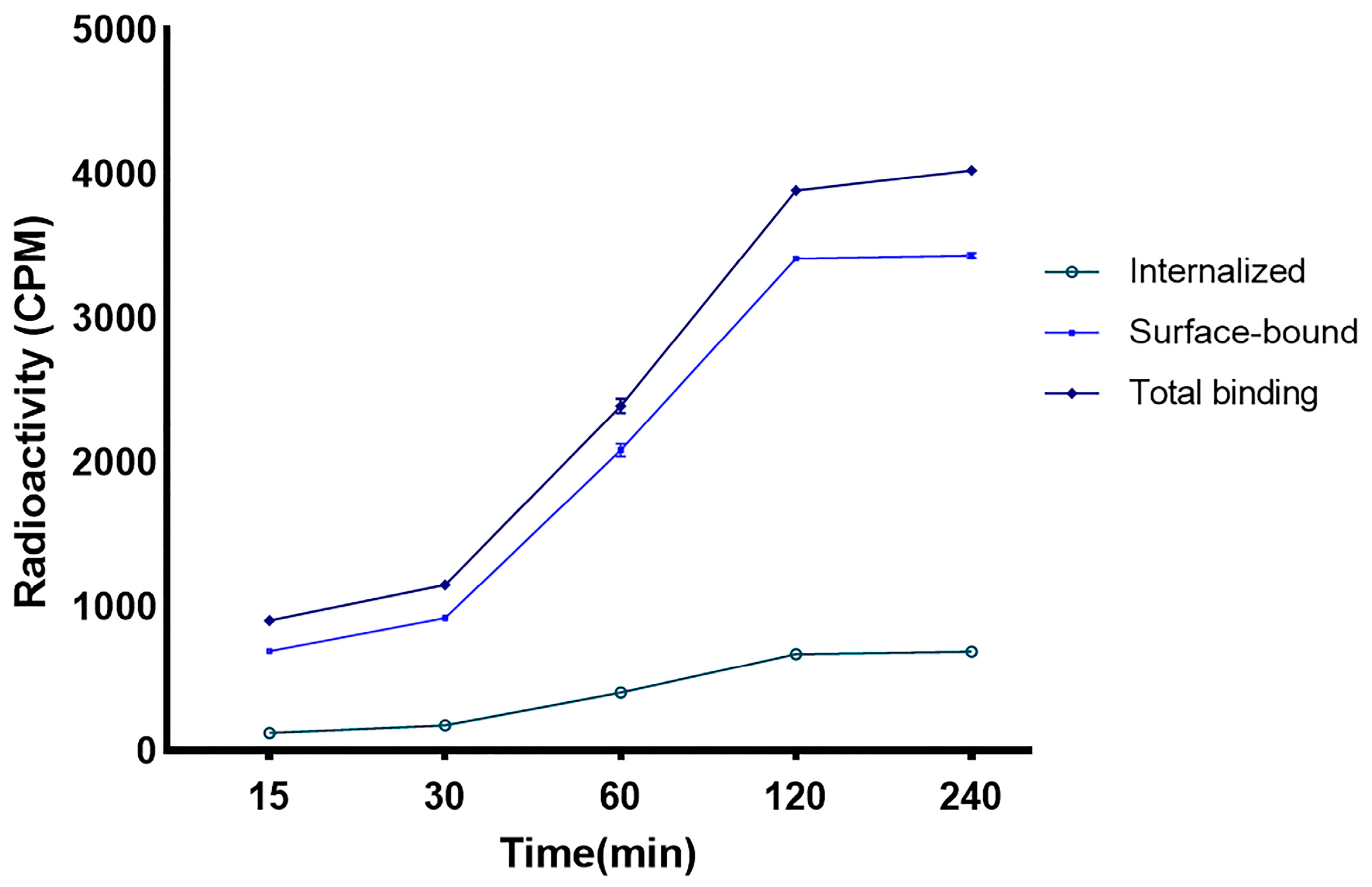
3.5. Internalization and Surface Binding in the Breast Cancer Cell Line
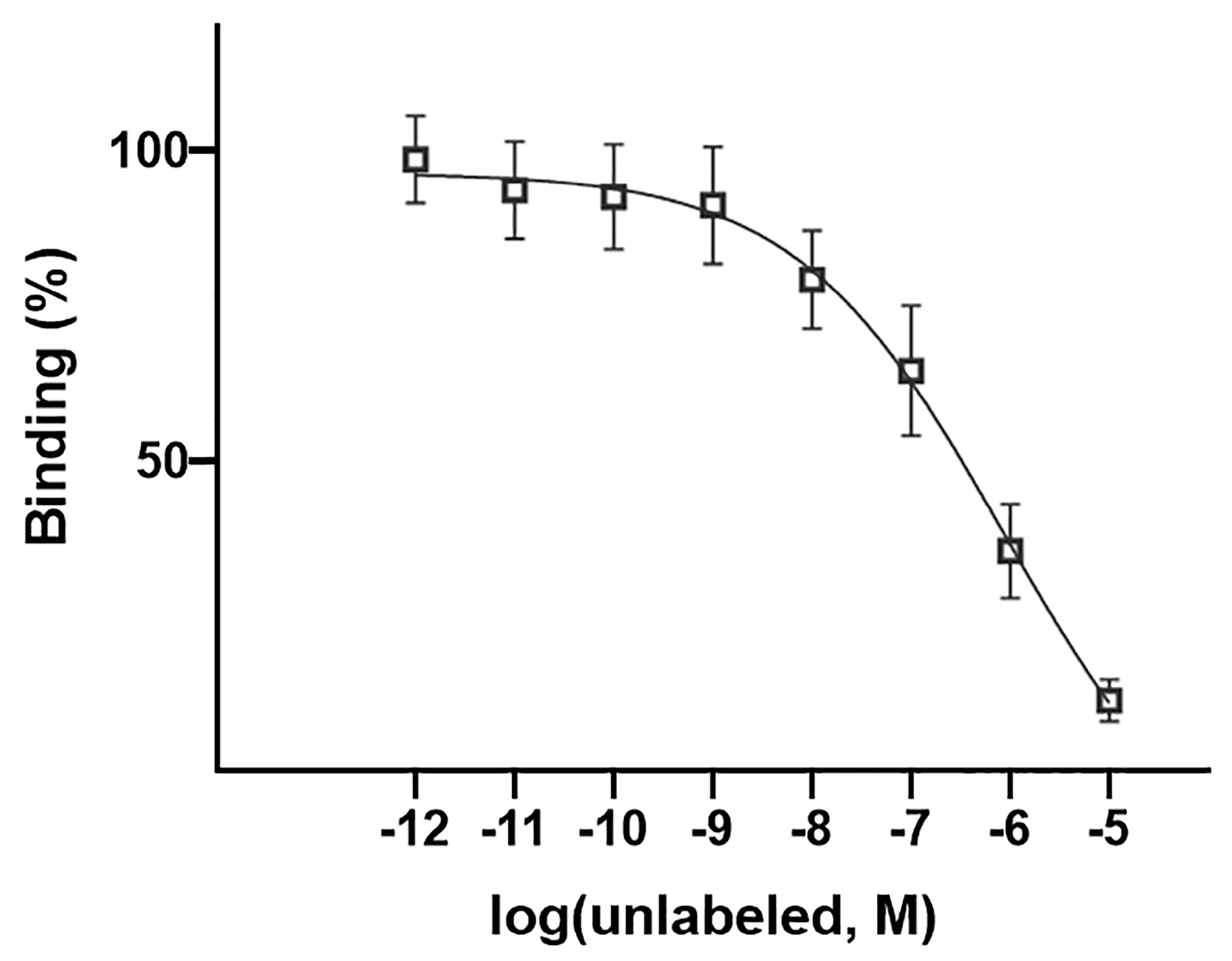
3.6. Competitive Cell Binding
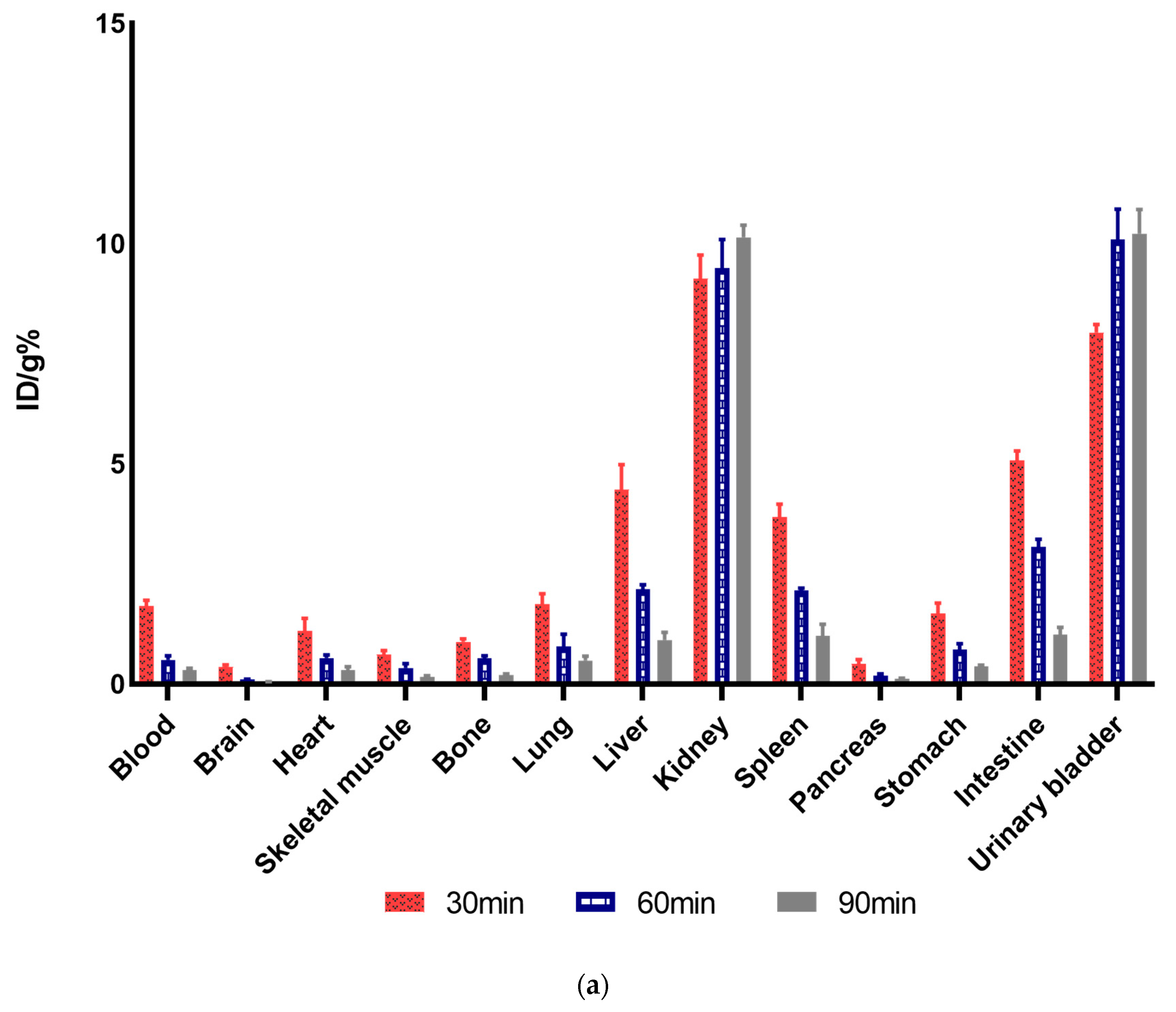
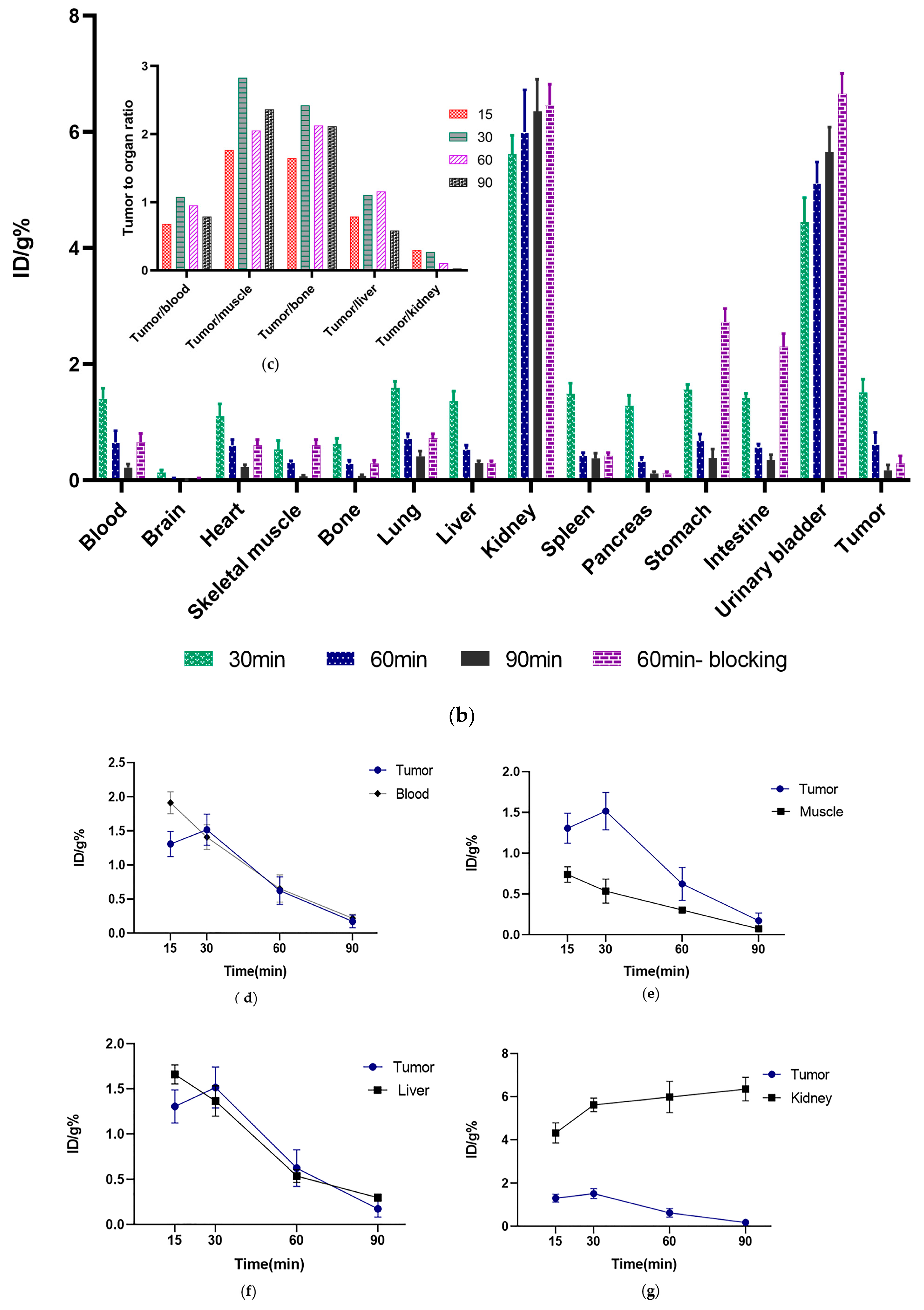
3.7. Ex Vivo Biodistribution Studies
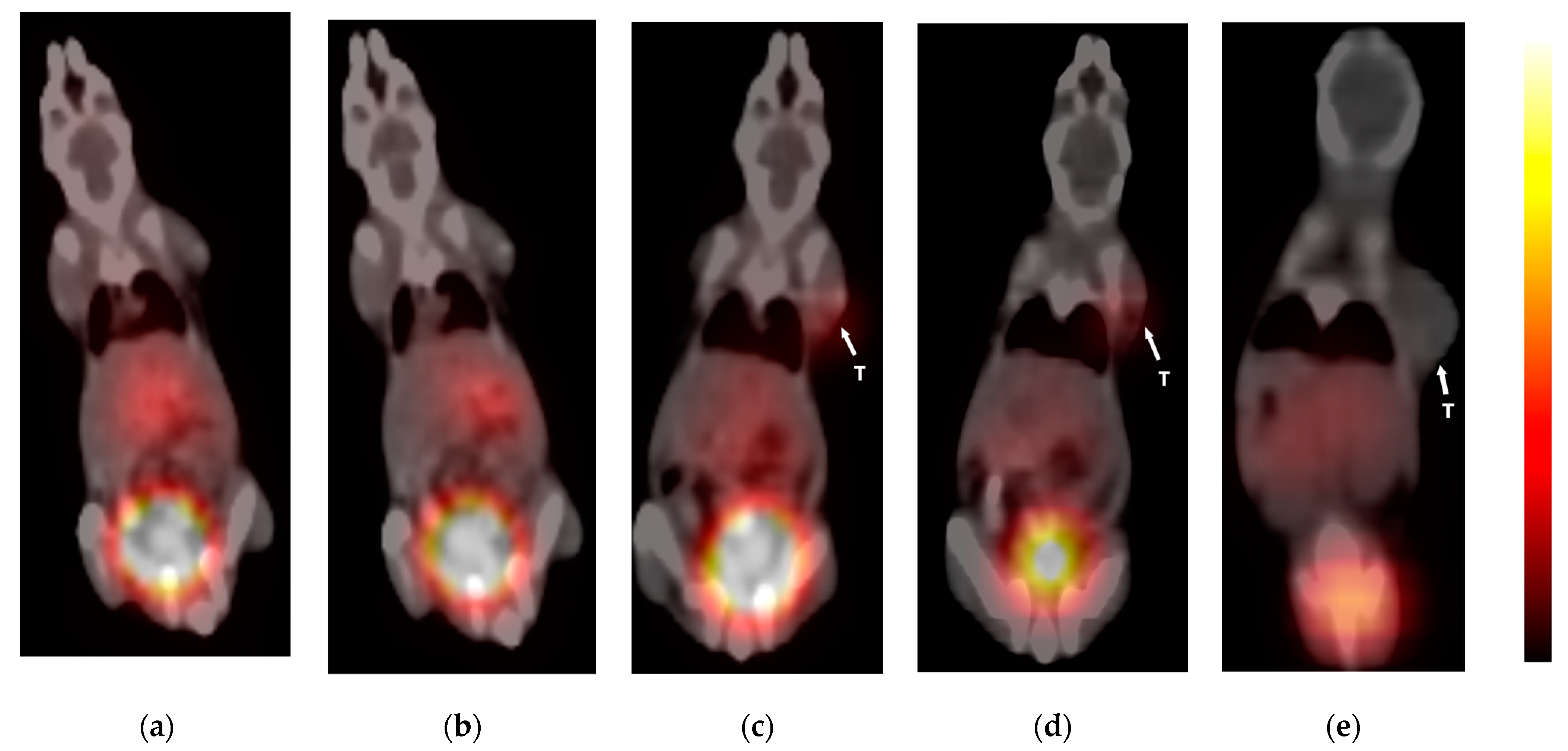
3.8. PET-CT Imaging
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Arnold, M.; Morgan, E.; Rumgay, H.; Mafra, A.; Singh, D.; Laversanne, M.; Vignat, J.; Gralow, J.R.; Cardoso, F.; Siesling, S.; et al. Current and future burden of breast cancer: Global statistics for 2020 and 2040. Breast 2022, 66, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Wagle, N.S.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2023. CA. Cancer J. Clin. 2023, 73, 17–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elebiyo, T.C.; Rotimi, D.; Evbuomwan, I.O.; Maimako, R.F.; Iyobhebhe, M.; Ojo, O.A.; Oluba, O.M.; Adeyemi, O.S. Reassessing vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) in anti-angiogenic cancer therapy. Cancer Treat. Res. Commun. 2022, 32, 100620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shibuya, M. Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF) and Its Receptor (VEGFR) Signaling in Angiogenesis: A Crucial Target for Anti- and Pro-Angiogenic Therapies. Genes Cancer 2011, 2, 1097–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaufman, N.E.M.; Dhingra, S.; Jois, S.D.; Vicente, M.d.G.H. Molecular Targeting of Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR) and Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Receptor (VEGFR). Molecules 2021, 26, 1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weathers, S.-P.; de Groot, J. VEGF Manipulation in Glioblastoma. Oncology 2015, 29, 720–727. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.-D.; McCrudden, C.M.; Kwok, H.F. Prognostic significance of combining VEGFA, FLT1 and KDR mRNA expression in lung cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2015, 10, 1893–1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costache, M.I.; Ioana, M.; Iordache, S.; Ene, D.; Costache, C.A.; Săftoiu, A. VEGF Expression in Pancreatic Cancer and Other Malignancies: A Review of the Literature. Rom. J. Intern. Med. 2015, 53, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bendardaf, R.; Buhmeida, A.; Hilska, M.; Laato, M.; Syrjänen, S.; Syrjänen, K.; Collan, Y.; Pyrhönen, S. VEGF-1 expression in colorectal cancer is associated with disease localization, stage, and long-term disease-specific survival. Anticancer Res. 2008, 28, 3865–3870. [Google Scholar]
- Morse, M.A.; Sun, W.; Kim, R.; He, A.R.; Abada, P.B.; Mynderse, M.; Finn, R.S. The Role of Angiogenesis in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 912–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, G.; Li, Y.; Jiang, G. Role of VEGF/VEGFR in the pathogenesis of leukemias and as treatment targets (Review). Oncol. Rep. 2012, 28, 1935–1944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Tamimi, R.M.; Collins, L.C.; Schnitt, S.J.; Gilmore, H.L.; Connolly, J.L.; Colditz, G.A. The association between vascular endothelial growth factor expression in invasive breast cancer and survival varies with intrinsic subtypes and use of adjuvant systemic therapy: Results from the Nurses’ Health Study. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2011, 129, 175–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, S.; Sullivan, C.; Zerkowski, M.; Molinaro, A.; Rimm, D.; Camp, R.; Chung, G. High levels of vascular endothelial growth factor and its receptors (VEGFR-1, VEGFR-2, neuropilin-1) are associated with worse outcome in breast cancer. Hum. Pathol. 2008, 39, 1835–1843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srabovic, N.; Mujagic, Z.; Mujanovic-Mustedanagic, J.; Softic, A.; Muminovic, Z.; Rifatbegovic, A.; Begic, L. Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Receptor-1 Expression in Breast Cancer and Its Correlation to Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor A. Int. J. Breast Cancer 2013, 2013, 746749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhukova, L.G.; Zhukov, N.V.; Lichinitser, M.R. Expression of Flt-1 and Flk-1 receptors for vascular endothelial growth factor on tumor cells as a new prognostic criterion for locally advanced breast cancer. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 2003, 135, 478–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toi, M.; Inada, K.; Suzuki, H.; Tominaga, T. Tumor angiogenesis in breast cancer: Its importance as a prognostic indicator and the association with vascular endothelial growth factor expression. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 1995, 36, 193–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrara, N.; Hillan, K.J.; Gerber, H.-P.; Novotny, W. Discovery and development of bevacizumab, an anti-VEGF antibody for treating cancer. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2004, 3, 391–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rüegg, C.; Hasmim, M.; Lejeune, F.J.; Alghisi, G.C. Antiangiogenic peptides and proteins: From experimental tools to clinical drugs. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Rev. Cancer 2006, 1765, 155–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tortora, G.; Melisi, D.; Ciardiello, F. Angiogenesis: A target for cancer therapy. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2004, 10, 11–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Backer, M.V.; Backer, J.M. Imaging Key Biomarkers of Tumor Angiogenesis. Theranostics 2012, 2, 502–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Stasi, R.; De Rosa, L.; D’Andrea, L.D. Structure-Based Design of Peptides Targeting VEGF/VEGFRs. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masłowska, K.; Halik, P.K.; Tymecka, D.; Misicka, A.; Gniazdowska, E. The Role of VEGF Receptors as Molecular Target in Nuclear Medicine for Cancer Diagnosis and Combination Therapy. Cancers 2021, 13, 1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.; Xie, J.; Chen, X. Peptide-based probes for targeted molecular imaging. Biochemistry 2010, 49, 1364–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berillo, D.; Yeskendir, A.; Zharkinbekov, Z.; Raziyeva, K.; Saparov, A. Peptide-Based Drug Delivery Systems. Medicina 2021, 57, 1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackson, J.A.; Hungnes, I.N.; Ma, M.T.; Rivas, C. Bioconjugates of Chelators with Peptides and Proteins in Nuclear Medicine: Historical Importance, Current Innovations, and Future Challenges. Bioconjug. Chem. 2020, 31, 483–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDermott, S.; Kilcoyne, A. Molecular imaging—Its current role in cancer. QJM Int. J. Med. 2016, 109, 295–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galli, F.; Artico, M.; Taurone, S.; Manni, I.; Bianchi, E.; Piaggio, G.; Weintraub, B.D.; Szkudlinski, M.W.; Agostinelli, E.; Dierckx, R.A.J.O.; et al. Radiolabeling of VEGF165 with 99mTc to evaluate VEGFR expression in tumor angiogenesis. Int. J. Oncol. 2017, 50, 2171–2179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Feng, S.; Liu, J.; Li, Q.; Zheng, L.; Xie, L.; Li, H.; Huang, D. Novel small peptides derived from VEGF125-136: Potential drugs for radioactive diagnosis and therapy in A549 tumor-bearing nude mice. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 4278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Z.; Li, Q.; Liu, G.; Luo, C.; Xie, G.; Zheng, L.; Huang, D. Imaging targeted at tumor with 188Re-labeled VEGF189 exon 6-encoded peptide and effects of the transfecting truncated KDR gene in tumor-bearing nude mice. Nucl. Med. Biol. 2009, 36, 535–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, K.; Shang, J.; Xie, L.; Hanyu, M.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, Z.; Xu, H.; Wang, L.; Zhang, M.-R. PET Imaging of VEGFR with a Novel 64Cu-Labeled Peptide. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 8508–8514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masłowska, K.; Witkowska, E.; Tymecka, D.; Halik, P.K.; Misicka, A.; Gniazdowska, E. Synthesis, Physicochemical and Biological Study of Gallium-68- and Lutetium-177-Labeled VEGF-A165/NRP-1 Complex Inhibitors Based on Peptide A7R and Branched Peptidomimetic. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dénes, N.; Kis, A.; Szabó, J.P.; Jószai, I.; Hajdu, I.; Arató, V.; Enyedi, K.N.; Mező, G.; Hunyadi, J.; Trencsényi, G.; et al. In vivo preclinical assessment of novel 68Ga-labelled peptides for imaging of tumor associated angiogenesis using positron emission tomography imaging. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 2021, 174, 109778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barta, P.; Kamaraj, R.; Kucharova, M.; Novy, Z.; Petrik, M.; Bendova, K.; Hajduch, M.; Pavek, P.; Trejtnar, F. Preparation, In Vitro Affinity, and In Vivo Biodistribution of Receptor-Specific 68Ga-Labeled Peptides Targeting Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Receptors. Bioconjug. Chem. 2022, 33, 1825–1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelson, B.J.B.; Andersson, J.D.; Wuest, F.; Spreckelmeyer, S. Good practices for 68Ga radiopharmaceutical production. EJNMMI Radiopharm. Chem. 2022, 7, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davey, P.R.W.J.; Paterson, B.M. Modern Developments in Bifunctional Chelator Design for Gallium Radiopharmaceuticals. Molecules 2023, 28, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadremomtaz, A.; Ali, A.M.; Jouyandeh, F.; Balalaie, S.; Navari, R.; Broussy, S.; Mansouri, K.; Groves, M.R.; Asghari, S.M. Molecular docking, synthesis and biological evaluation of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF) B based peptide as antiangiogenic agent targeting the second domain of the Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Receptor 1 (VEGFR1D2) for anticancer applicat. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2020, 5, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Namjoo, M.; Ghafouri, H.; Assareh, E.; Aref, A.R.; Mostafavi, E.; Hamrahi Mohsen, A.; Balalaie, S.; Broussy, S.; Asghari, S.M. A VEGFB-Based Peptidomimetic Inhibits VEGFR2-Mediated PI3K/Akt/mTOR and PLCγ/ERK Signaling and Elicits Apoptotic, Antiangiogenic, and Antitumor Activities. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tornesello, A.L.; Buonaguro, L.; Tornesello, M.L.; Buonaguro, F.M. New Insights in the Design of Bioactive Peptides and Chelating Agents for Imaging and Therapy in Oncology. Molecules 2017, 22, 1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Hathaway, H.; Royce, M.E.; Prossnitz, E.R.; Miao, Y. Influences of hydrocarbon linkers on the receptor binding affinities of gonadotropin-releasing hormone peptides. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2013, 23, 5484–5487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parry, J.J.; Andrews, R.; Rogers, B.E. MicroPET imaging of breast cancer using radiolabeled bombesin analogs targeting the gastrin-releasing peptide receptor. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2007, 101, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hennrich, U.; Eder, M. [68Ga]Ga-PSMA-11: The First FDA-Approved 68Ga-Radiopharmaceutical for PET Imaging of Prostate Cancer. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markowska, A.; Markowski, A.R.; Jarocka-Karpowicz, I. The Importance of 6-Aminohexanoic Acid as a Hydrophobic, Flexible Structural Element. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merrifield, R.B. Solid Phase Peptide Synthesis. I. The Synthesis of a Tetrapeptide. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1963, 85, 2149–2154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coin, I.; Beyermann, M.; Bienert, M. Solid-phase peptide synthesis: From standard procedures to the synthesis of difficult sequences. Nat. Protoc. 2007, 2, 3247–3256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, M.; Wang, R.; Li, M.; Cai, H.; Tian, R. Peptide-Based [68Ga]Ga Labeled PET Tracer for Tumor Imaging by Targeting Tumor-Associated Macrophages. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 2511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serdons, K.; Verbruggen, A.; Bormans, G. The Presence of Ethanol in Radiopharmaceutical Injections. J. Nucl. Med. 2008, 49, 2071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meisenheimer, M.; Kürpig, S.; Essler, M.; Eppard, E. Ethanol effects on 68Ga-radiolabelling efficacy and radiolysis in automated synthesis utilizing NaCl post-processing. EJNMMI Radiopharm. Chem. 2019, 4, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirooznia, N.; Abdi, K.; Beiki, D.; Emami, F.; Arab, S.S.; Sabzevari, O.; Pakdin-Parizi, Z.; Geramifar, P. Radiosynthesis, Biological Evaluation, and Preclinical Study of a 68Ga-Labeled Cyclic RGD Peptide as an Early Diagnostic Agent for Overexpressed αvβ3 Integrin Receptors in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. Contrast Media Mol. Imaging 2020, 2020, 8421657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Zeng, C.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, X.; Li, Z.; Chen, Y. Comparative evaluation of 68Ga-labelled TATEs: The impact of chelators on imaging. EJNMMI Res. 2020, 10, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekinci, M.; Çalışkan, E.E.; Çakar, B.; İlem-Özdemir, D.; Uyanıkgil, Y.; Çetin Uyanıkgil, E.Ö. [99mTc]Technetium-Labeled Niosomes: Radiolabeling, Quality Control, and In Vitro Evaluation. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 6279–6288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sammartano, A.; Migliari, S.; Scarlattei, M.; Baldari, G.; Ruffini, L. Synthesis, validation and quality controls of [68Ga]-DOTA-Pentixafor for PET imaging of chemokine receptor CXCR4 expression. Acta Biomed. 2020, 91, e2020097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, J.; Vatsa, R.; Garg, N.; Bhusari, P.; Watts, A.; Mittal, B.R. Quality control of positron emission tomography radiopharmaceuticals: An institutional experience. Indian J. Nucl. Med. IJNM Off. J. Soc. Nucl. Med. India 2013, 28, 200–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajaratinam, H.; Rasudin, N.S.; Safuan, S.; Abdullah, N.A.; Mokhtar, N.F.; Mohd Fuad, W.E. Passage Number of 4T1 Cells Influences the Development of Tumour and the Progression of Metastasis in 4T1 Orthotopic Mice. Malays. J. Med. Sci. 2022, 29, 30–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Workman, P.; Aboagye, E.O.; Balkwill, F.; Balmain, A.; Bruder, G.; Chaplin, D.J.; Double, J.A.; Everitt, J.; Farningham, D.A.H.; Glennie, M.J.; et al. Guidelines for the welfare and use of animals in cancer research. Br. J. Cancer 2010, 102, 1555–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mansi, R.; Abid, K.; Nicolas, G.P.; Del Pozzo, L.; Grouzmann, E.; Fani, M. A new 68Ga-labeled somatostatin analog containing two iodo-amino acids for dual somatostatin receptor subtype 2 and 5 targeting. EJNMMI Res. 2020, 10, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schottelius, M.; Šimeček, J.; Hoffmann, F.; Willibald, M.; Schwaiger, M.; Wester, H.-J. Twins in spirit—Episode I: Comparative preclinical evaluation of [68Ga]DOTATATE and [68Ga]HA-DOTATATE. EJNMMI Res. 2015, 5, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, R.; Shokri, B.; Shamshirian, D.; Zarghi, A.; Shahhosseini, S. Synthesis and biological evaluation of RGD conjugated with Ketoprofen/Naproxen and radiolabeled with [99mTc] via N4(GGAG) for αVβ3 integrin-targeted drug delivery. DARU J. Pharm. Sci. 2020, 28, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Liu, W.; Li, K.; Chen, K.; He, S.; Zhang, J.; Gu, B.; Xu, X.; Song, S. PET imaging of PARP expression using 68Ga-labelled inhibitors. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2023, 50, 2606–2620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biabani Ardakani, J.; Akhlaghi, M.; Nikkholgh, B.; Hosseinimehr, S.J. Targeting and imaging of HER2 overexpression tumor with a new peptide-based 68Ga-PET radiotracer. Bioorg. Chem. 2021, 106, 104474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray Banerjee, S.; Chen, Z.; Pullambhatla, M.; Lisok, A.; Chen, J.; Mease, R.C.; Pomper, M.G. Preclinical Comparative Study of 68Ga-Labeled DOTA, NOTA, and HBED-CC Chelated Radiotracers for Targeting PSMA. Bioconjug. Chem. 2016, 27, 1447–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Lin, C.; Zhang, D.; Chen, J.; Ouyang, L.; Wu, F.; Zhang, J.; Chen, L. Recent progress on vascular endothelial growth factor receptor inhibitors with dual targeting capabilities for tumor therapy. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2022, 15, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rapisarda, A.; Melillo, G. Role of the VEGF/VEGFR axis in cancer biology and therapy. Adv. Cancer Res. 2012, 114, 237–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.-L.; Zhao, H.; Ren, X.-B. Relationship of VEGF/VEGFR with immune and cancer cells: Staggering or forward? Cancer Biol. Med. 2016, 13, 206–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okikawa, S.; Morine, Y.; Saito, Y.; Yamada, S.; Tokuda, K.; Teraoku, H.; Miyazaki, K.; Yamashita, S.; Ikemoto, T.; Imura, S.; et al. Inhibition of the VEGF signaling pathway attenuates tumor-associated macrophage activity in liver cancer. Oncol. Rep. 2022, 47, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadremomtaz, A.; Mansouri, K.; Alemzadeh, G.; Safa, M.; Rastaghi, A.E.; Asghari, S.M. Dual blockade of VEGFR1 and VEGFR2 by a novel peptide abrogates VEGF-driven angiogenesis, tumor growth, and metastasis through PI3K/AKT and MAPK/ERK1/2 pathway. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Gen. Subj. 2018, 1862, 2688–2700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, I.; Paeng, J.C.; Lee, S.J.; Shin, C.S.; Jang, J.-Y.; Cheon, G.J.; Lee, D.S.; Chung, J.-K.; Kang, K.W. Comparison of Diagnostic Sensitivity and Quantitative Indices Between 68Ga-DOTATOC PET/CT and 111In-Pentetreotide SPECT/CT in Neuroendocrine Tumors: A Preliminary Report. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2015, 49, 284–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fani, M.; Maecke, H.R.; Okarvi, S.M. Radiolabeled peptides: Valuable tools for the detection and treatment of cancer. Theranostics 2012, 2, 481–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezazadeh, F.; Sadeghzadeh, N.; Abedi, S.M.; Abediankenari, S. 99mTc labeled D(LPR): A novel retro-inverso peptide for VEGF receptor-1 targeted tumor imaging. Nucl. Med. Biol. 2018, 62–63, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ebrahimi, F.; Zargari, N.R.; Akhlaghi, M.; Asghari, S.M.; Abdi, K.; Balalaie, S.; Asadi, M.; Beiki, D. Synthesis, Radiolabeling, and Biodistribution Study of a Novel DOTA-Peptide for Targeting Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Receptors in the Molecular Imaging of Breast Cancer. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 899. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16070899
Ebrahimi F, Zargari NR, Akhlaghi M, Asghari SM, Abdi K, Balalaie S, Asadi M, Beiki D. Synthesis, Radiolabeling, and Biodistribution Study of a Novel DOTA-Peptide for Targeting Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Receptors in the Molecular Imaging of Breast Cancer. Pharmaceutics. 2024; 16(7):899. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16070899
Chicago/Turabian StyleEbrahimi, Fatemeh, Nooshin Reisi Zargari, Mehdi Akhlaghi, S. Mohsen Asghari, Khosrou Abdi, Saeed Balalaie, Mahboobeh Asadi, and Davood Beiki. 2024. "Synthesis, Radiolabeling, and Biodistribution Study of a Novel DOTA-Peptide for Targeting Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Receptors in the Molecular Imaging of Breast Cancer" Pharmaceutics 16, no. 7: 899. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16070899
APA StyleEbrahimi, F., Zargari, N. R., Akhlaghi, M., Asghari, S. M., Abdi, K., Balalaie, S., Asadi, M., & Beiki, D. (2024). Synthesis, Radiolabeling, and Biodistribution Study of a Novel DOTA-Peptide for Targeting Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Receptors in the Molecular Imaging of Breast Cancer. Pharmaceutics, 16(7), 899. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16070899







