Mixed Micellar Gel of Poloxamer Mixture for Improved Solubilization of Poorly Water-Soluble Ibuprofen and Use as Thermosensitive In Situ Gel
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Sample Preparation
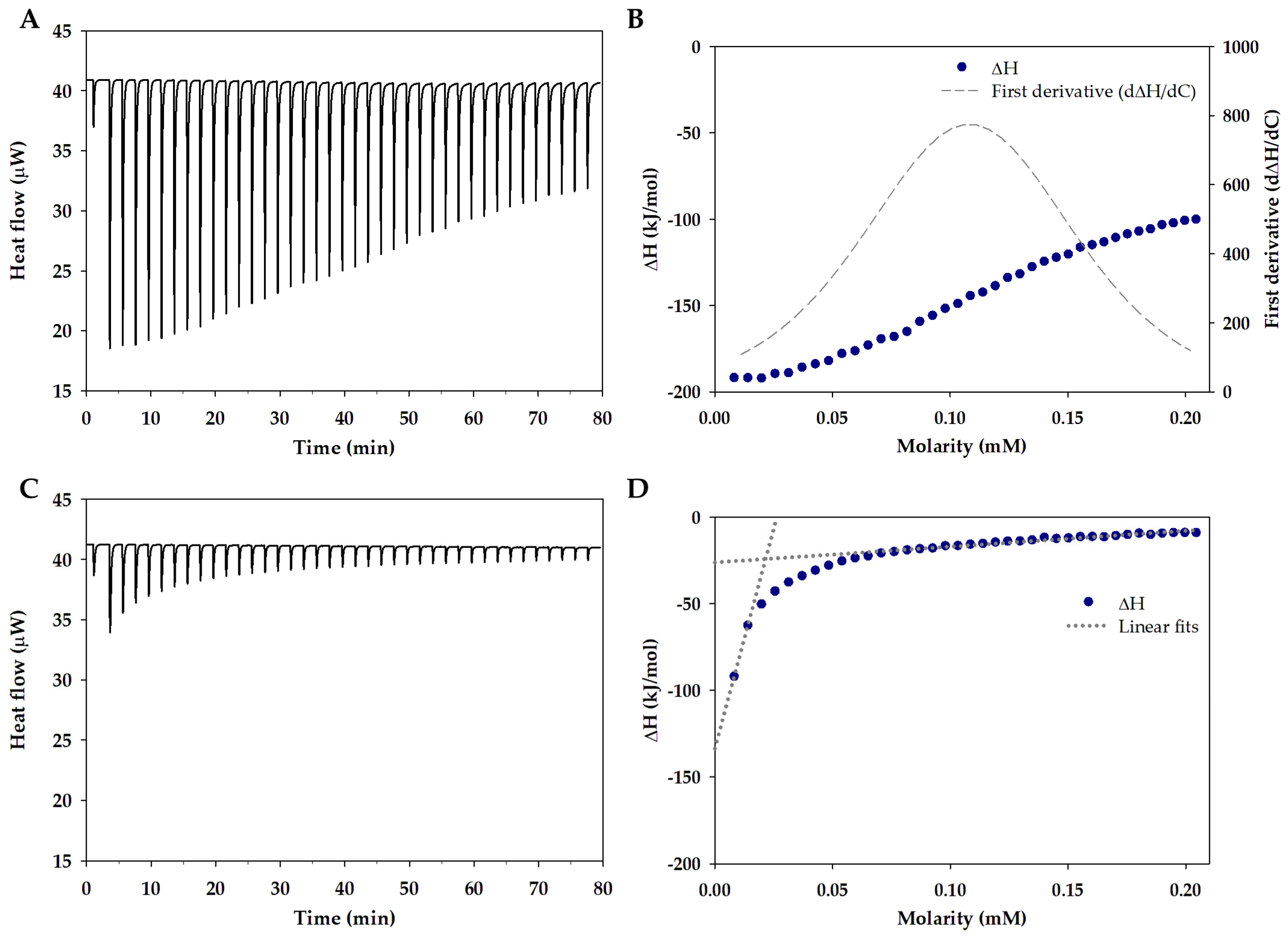
2.3. Isothermal Titration Calorimetry
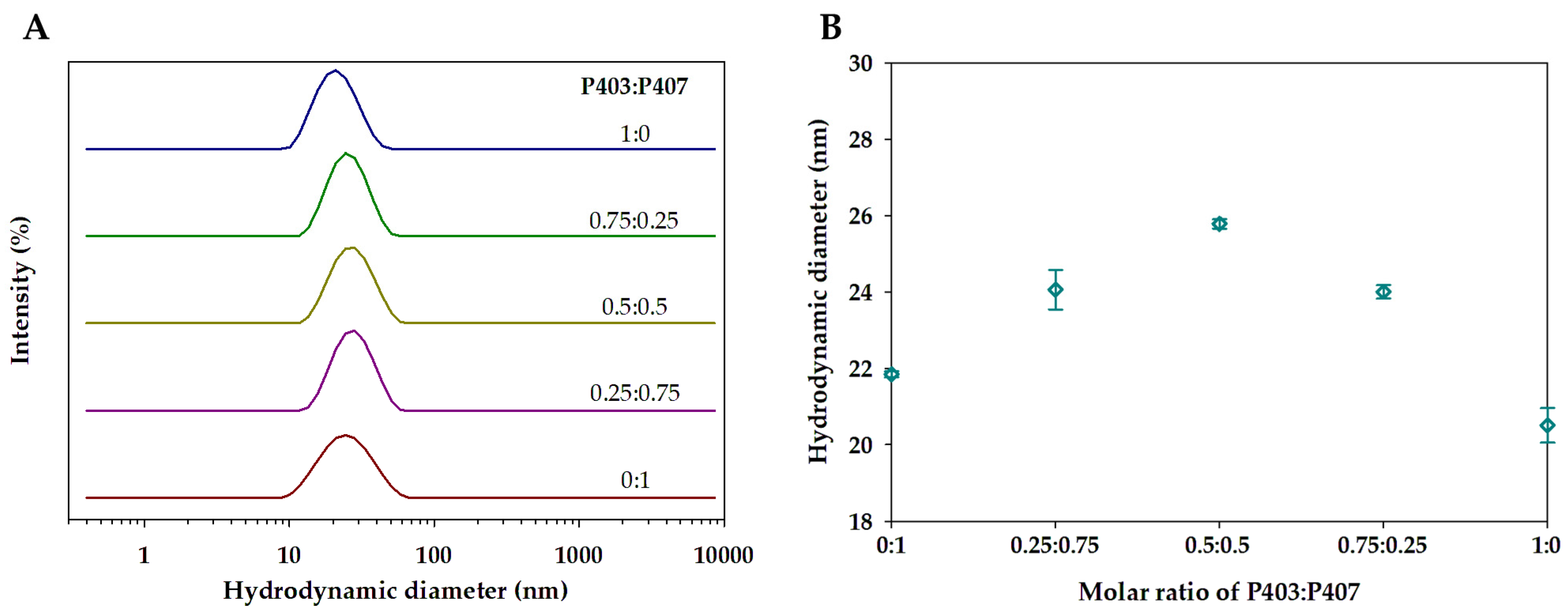
2.4. Dynamic Light Scattering
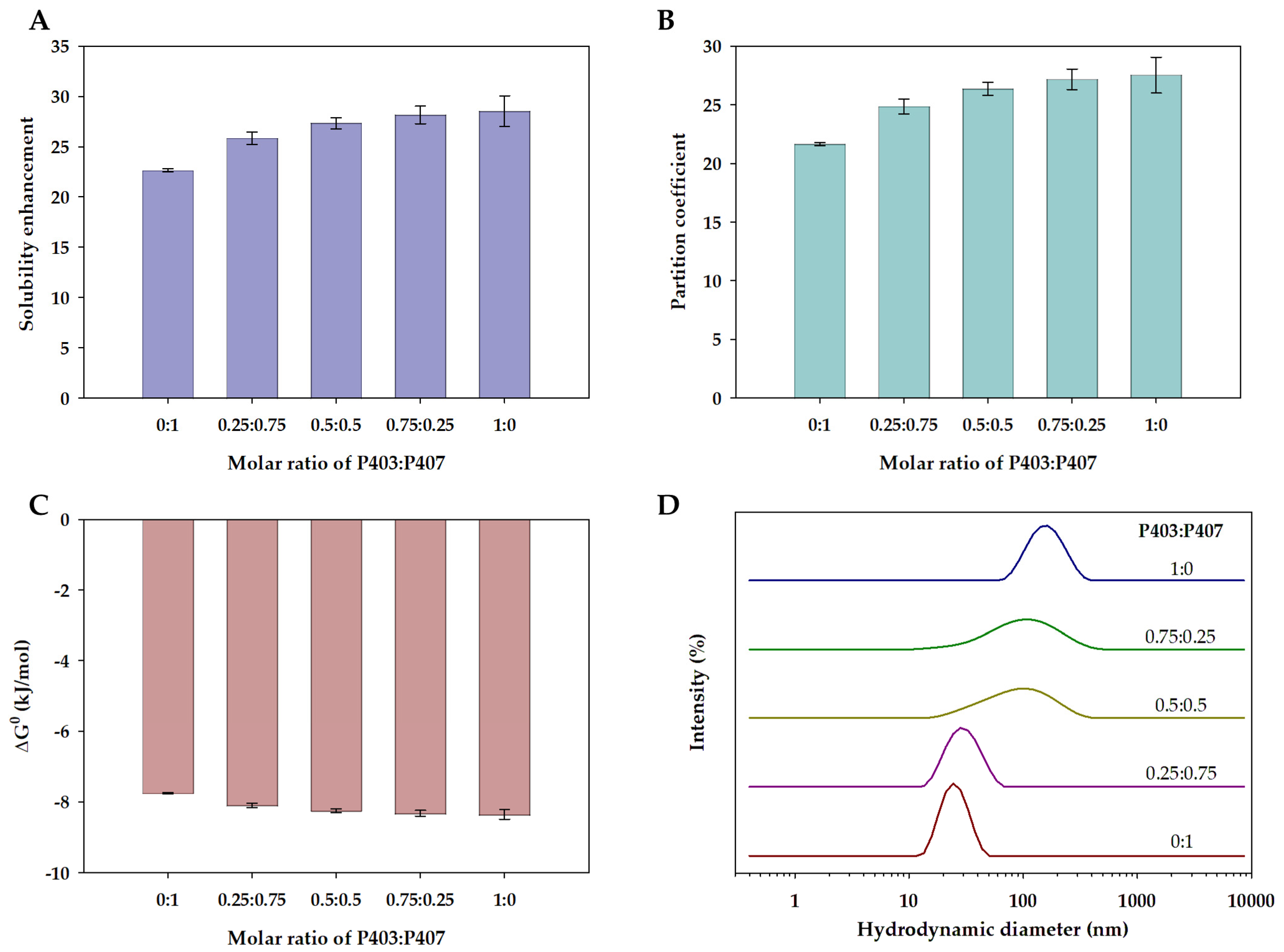
2.5. Solubility Study
2.6. Test Tube Tilting Experiment
2.7. Differential Scanning Calorimetry
2.8. Rheometry
2.9. In Vitro Release Study
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
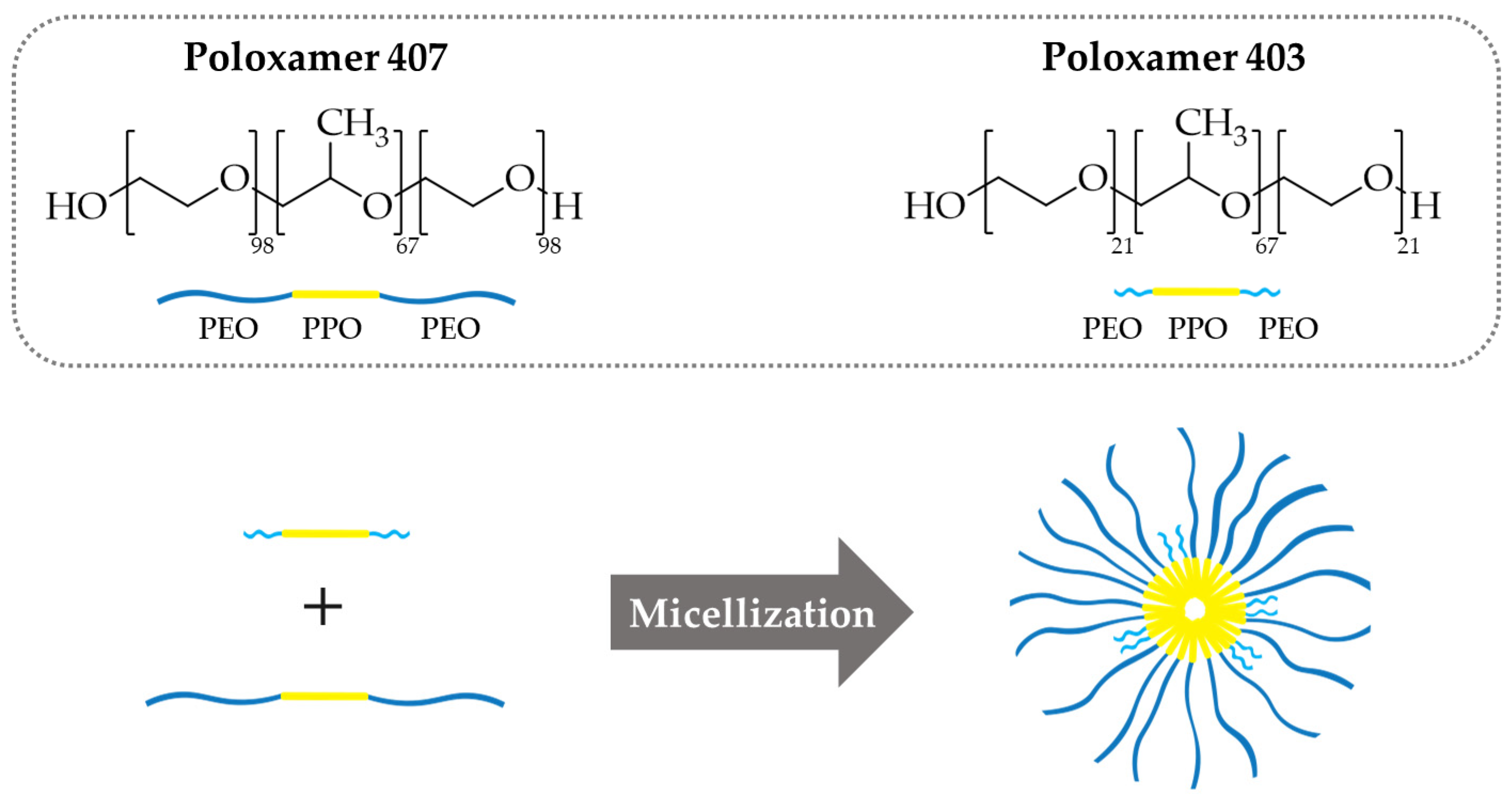
3.1. Single and Mixed Polymeric Micelles
3.2. Solubilization of Ibuprofen in Single and Mixed Polymeric Micelles
3.3. Thermosensitive Micellization and Gel Formation
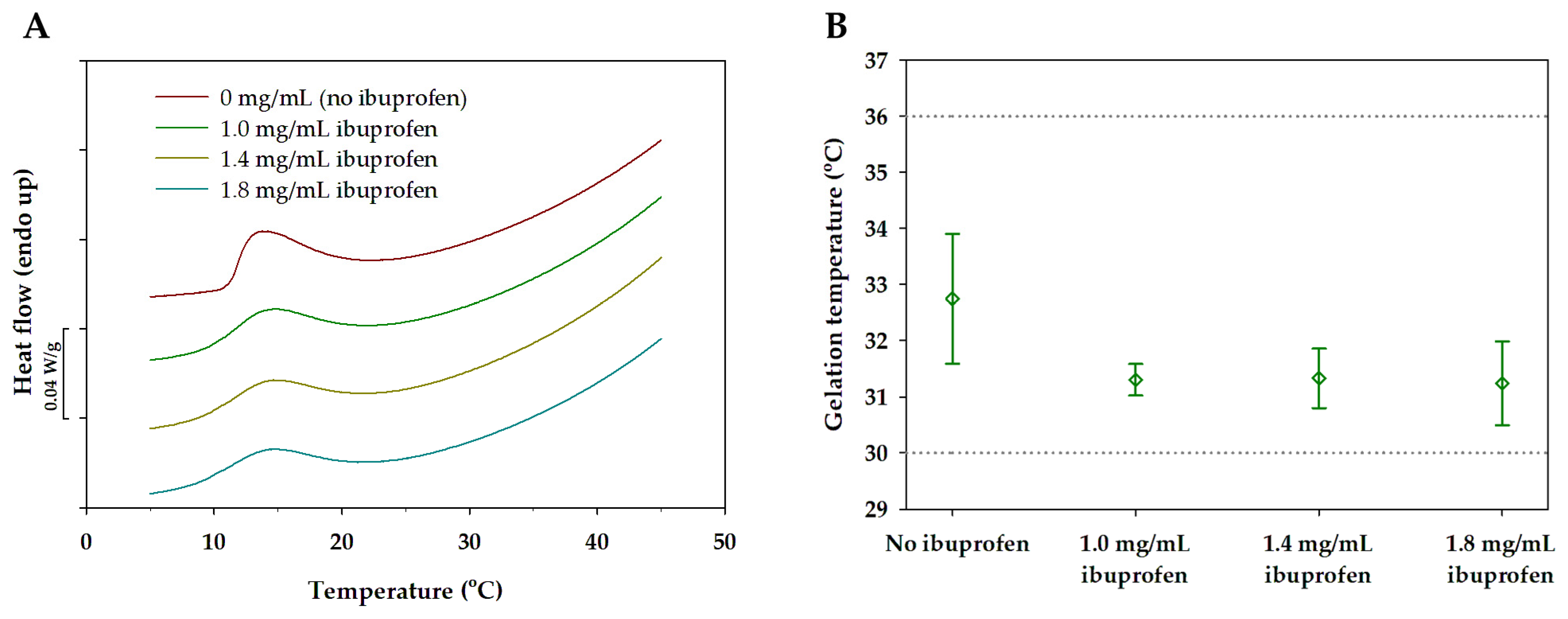
3.4. Mixed Micellar Gels with Incorporated Ibuprofen
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Negut, I.; Bita, B. Polymeric Micellar Systems—A Special Emphasis on “Smart” Drug Delivery. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahajan, D.; Suares, D.; Rachana, R.; Shetty, S. Types of Polymeric Micelles for Controlled Drug Release. In Polymeric Micelles: Principles, Perspectives and Practices; Singh, S.K., Gulati, M., Mutalik, S., Dhanasekaran, M., Dua, K., Eds.; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2023; pp. 69–86. [Google Scholar]
- Rao, M.R.P.; Deshpande, S.; Deshpande, P. Dapsone-Loaded Mixed Micellar Gel for Treatment of Acne Vulgaris. AAPS PharmSciTech 2023, 24, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huysecom, A.S.; Glorieux, C.; Thoen, J.; Thielemans, W.; Fustin, C.A.; Moldenaers, P.; Cardinaels, R. Phase Behavior of Medium-Length Hydrophobically Associating PEO-PPO Multiblock Copolymers in Aqueous Media. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2023, 641, 521–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirun, N.; Tantishaiyakul, V.; Sangfai, T.; Boonlai, W.; Soontaranon, S.; Rugmai, S. The Effect of Poly(Acrylic Acid) on Temperature-Dependent Behaviors and Structural Evolution of Poloxamer 407. Polym. Int. 2021, 70, 1282–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirun, N.; Kraisit, P.; Tantishaiyakul, V. Thermosensitive Polymer Blend Composed of Poloxamer 407, Poloxamer 188 and Polycarbophil for the Use as Mucoadhesive In Situ Gel. Polymers 2022, 14, 1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khimani, M.; Rao, U.; Bahadur, P.; Bahadur, P. Calorimetric and Scattering Studies on Micellization of Pluronics in Aqueous Solutions: Effect of the Size of Hydrophilic PEO End Blocks, Temperature, and Added Salt. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 2014, 35, 1599–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Khateb, K.; Ozhmukhametova, E.K.; Mussin, M.N.; Seilkhanov, S.K.; Rakhypbekov, T.K.; Lau, W.M.; Khutoryanskiy, V.V. In Situ Gelling Systems Based on Pluronic F127/Pluronic F68 Formulations for Ocular Drug Delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2016, 502, 70–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Spirito, N.A.; Grizzuti, N.; Casalegno, M.; Castiglione, F.; Pasquino, R. Phase Transitions of Aqueous Solutions of Pluronic F68 in the Presence of Diclofenac Sodium. Int. J. Pharm. 2023, 644, 123353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Araújo, D.R.; Oshiro, A.; da Silva, D.C.; Akkari, A.C.S.; de Mello, J.C.; Rodrigues, T. Poloxamers as Drug-Delivery Systems: Physicochemical, Pharmaceutical, and Toxicological Aspects. In Nanotoxicology: Materials, Methodologies, and Assessments; Durán, N., Guterres, S.S., Alves, O.L., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 281–298. [Google Scholar]
- Dumortier, G.; Grossiord, J.L.; Agnely, F.; Chaumeil, J.C. A Review of Poloxamer 407 Pharmaceutical and Pharmacological Characteristics. Pharm. Res. 2006, 23, 2709–2728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reeve, L.E. The Poloxamers: Their Chemistry and Medical Applications. In Handbook of Biodegradable Polymers; Domb, A.J., Kost, J., Wiseman, D., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1998; pp. 231–249. [Google Scholar]
- Boonlai, W.; Tantishaiyakul, V.; Hirun, N.; Phaisan, S.; Uma, T. The Effect of the Preservative Methylparaben on the Thermoresponsive Gelation Behavior of Aqueous Solutions of Poloxamer 407. J. Mol. Liq. 2017, 240, 622–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeidi, Z.; Giti, R.; Emami, A.; Rostami, M.; Mohammadi, F. Thermosensitive and Mucoadhesive Gels Containing Solid Lipid Nanoparticles Loaded with Fluconazole and Niosomes Loaded with Clindamycin for the Treatment of Periodontal Diseases: A Laboratory Experiment. BMC Oral Health 2024, 24, 551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonacucina, G.; Spina, M.; Misici-Falzi, M.; Cespi, M.; Pucciarelli, S.; Angeletti, M.; Palmieri, G.F. Effect of Hydroxypropyl β-Cyclodextrin on the Self-Assembling and Thermogelation Properties of Poloxamer 407. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2007, 32, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boonlai, W.; Tantishaiyakul, V.; Hirun, N.; Sangfai, T.; Suknuntha, K. Thermosensitive Poloxamer 407/Poly(Acrylic Acid) Hydrogels with Potential Application as Injectable Drug Delivery System. AAPS PharmSciTech 2018, 19, 2103–2117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ávila-Salas, F.; Durán-Lara, F.E. An Overview of Injectable Thermo-Responsive Hydrogels and Advances in Their Biomedical Applications. Curr. Med. Chem. 2020, 27, 5773–5789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Song, J.; Liu, D.; Liu, Z.; Cheng, J.; Chen, Z.; Yang, Y.; Jiang, W.; Wang, H.; Ye, J.; et al. Simple and Versatile In Situ Thermo-Sensitive Hydrogel for Rectal Administration of SZ-A to Alleviate Inflammation and Repair Mucosal Barrier in Ulcerative Colitis. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2024, 35, 109736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rana, S.; Bhattacharjee, J.; Barick, K.C.; Verma, G.; Hassan, P.A.; Yakhmi, J.V. Interfacial Engineering of Nanoparticles for Cancer Therapeutics. In Nanostructures for Cancer Therapy; Ficai, A., Grumezescu, A.M., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 177–209. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, C.F.; Tseng, H.W.; Bahadur, P.; Chen, L.J. Synergistic Effect of Binary Mixed-Pluronic Systems on Temperature Dependent Self-assembly Process and Drug Solubility. Polymers 2018, 10, 593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Djabourov, M.; Bourgaux, C.; Bouchemal, K. Nanostructured Fluids from Pluronic® Mixtures. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 454, 599–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarisozen, C.; Joshi, U.; Mendes, L.P.; Torchilin, V.P. Stimuli-Responsive Polymeric Micelles for Extracellular and Intracellular Drug Delivery. In Stimuli Responsive Polymeric Nanocarriers for Drug Delivery Applications; Makhlouf, A.S.H., Abu-Thabit, N.Y., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2019; pp. 269–304. [Google Scholar]
- Gaisford, S.; Beezer, A.E.; Mitchell, J.C. Diode-Array UV Spectrometric Evidence for Cooperative Interactions in Binary Mixtures of Pluronics F77, F87, and F127. Langmuir 1997, 13, 2606–2607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.Y.; Zhang, W.M. Recent Progress in Drug Delivery of Pluronic P123: Pharmaceutical Perspectives. J. Drug Target. 2017, 25, 471–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunha-Filho, M.S.S.; Alvarez-Lorenzo, C.; Martínez-Pacheco, R.; Landin, M. Temperature-Sensitive Gels for Intratumoral Delivery of β-Lapachone: Effect of Cyclodextrins and Ethanol. Sci. World J. 2012, 2012, 126723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abioye, A.O.; Kola-Mustapha, A.; Chi, G.T.; Ilya, S. Quantification of In Situ Granulation-Induced Changes in Pre-Compression, Solubility, Dose Distribution and Intrinsic In Vitro Release Characteristics of Ibuprofen–Cationic Dextran Conjugate Crystanules. Int. J. Pharm. 2014, 471, 453–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.; Dash, U.N.; Talukdar, M. Solubility Enhancement and Study of Molecular Interactions of Poorly Soluble Ibuprofen in Presence of Urea, a Hydrotropic Agent. Mater. Today Proc. 2020, 30, 246–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montero-Padilla, S.; Velaga, S.; Morales, J.O. Buccal Dosage Forms: General Considerations for Pediatric Patients. AAPS PharmSciTech 2017, 18, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myburgh, J.; Liebenberg, W.; Willers, C.; Dube, A.; Gerber, M. Investigation and Evaluation of the Transdermal Delivery of Ibuprofen in Various Characterized Nano-Drug Delivery Systems. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 2413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navti, P.D.; Pandey, A.; Nikam, A.N.; Padya, B.S.; Kalthur, G.; Koteshwara, K.B.; Mutalik, S. Ionic Liquids Assisted Topical Drug Delivery for Permeation Enhancement: Formulation Strategies, Biomedical Applications, and Toxicological Perspective. AAPS PharmSciTech 2022, 23, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agossa, K.; Delepierre, A.; Lizambard, M.; Delcourt-Debruyne, E.; Siepmann, J.; Siepmann, F.; Neut, C. In-Situ Forming Implants for Dual Controlled Release of Chlorhexidine and Ibuprofen for Periodontitis Treatment: Microbiological and Mechanical Key Properties. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2020, 60, 101956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irvine, J.; Afrose, A.; Islam, N. Formulation and Delivery Strategies of Ibuprofen: Challenges and Opportunities. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2018, 44, 173–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, X.; Liu, Y.; Di, X. Thermosensitive In Situ Gel Based on Solid Dispersion for Rectal Delivery of Ibuprofen. AAPS PharmSciTech 2018, 19, 338–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamed, R.; Al-Adhami, Y.; Abu-Huwaij, R. Concentration of a Microemulsion Influences the Mechanical Properties of Ibuprofen In Situ Microgels. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 570, 118684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boffito, M.; Laurano, R.; Giasafaki, D.; Steriotis, T.; Papadopoulos, A.; Tonda-Turo, C.; Cassino, C.; Charalambopoulou, G.; Ciardelli, G. Embedding Ordered Mesoporous Carbons into Thermosensitive Hydrogels: A Cutting-Edge Strategy to Vehiculate a Cargo and Control Its Release Profile. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 2165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Alexandridis, P. Micellization Thermodynamics of Pluronic P123 (EO20PO70EO20) Amphiphilic Block Copolymer in Aqueous Ethylammonium Nitrate (EAN) Solutions. Polymers 2018, 10, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juhász, Á.; Seres, L.; Varga, N.; Ungor, D.; Wojnicki, M.; Csapó, E. Detailed Calorimetric Analysis of Mixed Micelle Formation from Aqueous Binary Surfactants for Design of Nanoscale Drug Carriers. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 3288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parmar, A.; Parekh, P.; Bahadur, P. Solubilization and Release of a Model Drug Nimesulide from PEO–PPO–PEO Block Copolymer Core–Shell Micelles: Effect of Size of PEO Blocks. J. Solut. Chem. 2013, 42, 80–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patidar, P.; Pillai, S.A.; Sheth, U.; Bahadur, P.; Bahadur, A. Glucose Triggered Enhanced Solubilisation, Release and Cytotoxicity of Poorly Water Soluble Anti-Cancer Drugs fromT1307 Micelles. J. Biotechnol. 2017, 254, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dugar, R.P.; Gajera, B.Y.; Dave, R.H. Fusion Method for Solubility and Dissolution Rate Enhancement of Ibuprofen Using Block Copolymer Poloxamer 407. AAPS PharmSciTech 2016, 17, 1428–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, H.; Pan, P.; Shan, G.; Bao, Y. In Situ Formation and Gelation Mechanism of Thermoresponsive Stereocomplexed Hydrogels upon Mixing Diblock and Triblock Poly(Lactic Acid)/Poly(Ethylene Glycol) Copolymers. J. Phys. Chem. B 2015, 119, 6471–6480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- da Silva, J.B.; Cook, M.T.; Bruschi, M.L. Thermoresponsive Systems Composed of Poloxamer 407 and HPMC or NaCMC: Mechanical, Rheological and Sol-Gel Transition Analysis. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 240, 116268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haroun, A.A.; El-Halawany, N.R.; Loira-Pastoriza, C.; Maincent, P. Synthesis and In Vitro Release Study of Ibuprofen-Loaded Gelatin Graft Copolymer Nanoparticles. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2014, 40, 61–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostróżka-Cieślik, A.; Maciążek-Jurczyk, M.; Pożycka, J.; Dolińska, B. Pre-Formulation Studies: Physicochemical Characteristics and In Vitro Release Kinetics of Insulin from Selected Hydrogels. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witika, B.A.; Stander, J.C.; Smith, V.J.; Walker, R.B. Nano Co-Crystal Embedded Stimuli-Responsive Hydrogels: A Potential Approach to Treat HIV/AIDS. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artyukhov, A.A.; Nechaeva, A.M.; Shtilman, M.I.; Chistyakov, E.M.; Svistunova, A.Y.; Bagrov, D.V.; Kuskov, A.N.; Docea, A.O.; Tsatsakis, A.M.; Gurevich, L.; et al. Nanoaggregates of Biphilic Carboxyl-Containing Copolymers as Carriers for Ionically Bound Doxorubicin. Materials 2022, 15, 7136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Huo, M.; Zhou, J.; Zou, A.; Li, W.; Yao, C.; Xie, S. DDSolver: An Add-In Program for Modeling and Comparison of Drug Dissolution Profiles. AAPS J. 2010, 12, 263–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nasir, F.; Iqbal, Z.; Khan, J.A.; Khan, A.; Khuda, F.; Ahmad, L.; Khan, A.; Khan, A.; Dayoo, A.; Roohullah. Development and Evaluation of Diclofenac Sodium Thermorevesible Subcutaneous Drug Delivery System. Int. J. Pharm. 2012, 439, 120–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prasanthan, P.; Kishore, N. Self-Essemblies of Pluronic Micelles in Partitioning of Anticancer Drugs and Effectiveness of This System Towards Target Protein. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 22057–22069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouchemal, K.; Agnely, F.; Koffi, A.; Ponchel, G. A Concise Analysis of the Effect of Temperature and Propanediol-1, 2 on Pluronic F127 Micellization Using Isothermal Titration Microcalorimetry. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2009, 338, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagh, S.S.; Sarolia, J.; Patil, Y.K.; Aswal, V.K.; Bahadur, P.; Tiwari, S. Cooperative Interaction of a Highly Hydrophilic Pluronic with Bile Salts of Different Hydrophobicity. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2023, 672, 131709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clint, J.H. Micellization of Mixed Nonionic Surface Active Agents. J. Chem. Soc. Faraday Trans. 1 1975, 71, 1327–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.S. Molecular Self-Assembly in Solution I: Micelles. In Self-Assembly and Nanotechnology: A Force Balance Approach; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2008; pp. 47–73. [Google Scholar]
- Piazzini, V.; D’Ambrosio, M.; Luceri, C.; Cinci, L.; Landucci, E.; Bilia, A.R.; Bergonzi, M.C. Formulation of Nanomicelles to Improve the Solubility and the Oral Absorption of Silymarin. Molecules 2019, 24, 1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scamehorn, J.F. An Overview of Phenomena Involving Surfactant Mixtures. In Phenomena in Mixed Surfactant Systems; American Chemical Society: Washington, DC, USA, 1986; pp. 1–27. [Google Scholar]
- Zhai, Y.; Guo, S.; Liu, C.; Yang, C.; Dou, J.; Li, L.; Zhai, G. Preparation and In Vitro Evaluation of Apigenin-Loaded Polymeric Micelles. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2013, 429, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, M.; Hassan, P.A. Influence of Temperature and Organic Acid on Self-Assembly Behavior of Pluronic F127. J. Mol. Liq. 2023, 378, 121630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafari-Chashmi, P.; Bagheri, A. The Strong Synergistic Interaction between Surface Active Ionic Liquid and Anionic Surfactant in the Mixed Micelle Using the Spectrophotometric Method. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 269, 816–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tănase, M.A.; Raducan, A.; Oancea, P.; Diţu, L.M.; Stan, M.; Petcu, C.; Scomoroşcenco, C.; Ninciuleanu, C.M.; Nistor, C.L.; Cinteza, L.O. Mixed Pluronic—Cremophor Polymeric Micelles as Nanocarriers for Poorly Soluble Antibiotics—The Influence on the Antibacterial Activity. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tampucci, S.; Monti, D.; Burgalassi, S.; Terreni, E.; Paganini, V.; Di Gangi, M.; Chetoni, P. Binary Polymeric Surfactant Mixtures for the Development of Novel Loteprednol Etabonate Nanomicellar Eyedrops. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Tan, Y.B. Preparation and Properties of Mixed Micelles Made of Pluronic Polymer and PEG-PE. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2008, 317, 326–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Shi, Y.; Chen, Y.; Hao, J.; Sha, X.; Fang, X. The Potential of Pluronic Polymeric Micelles Encapsulated with Paclitaxel for the Treatment of Melanoma Using Subcutaneous and Pulmonary Metastatic Mice Models. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 5934–5944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamenova, K.; Trzebicka, B.; Momekova, D.; Petrov, P. Double Stimuli Responsive Mixed Aggregates from Poly(Acrylic Acid)-Block-Poly(ε-Caprolactone)-Block-Poly(Acrylic Acid) and Poly(Ethylene Oxide)-Block-Poly(Propylene Oxide)-Block-Poly(Ethylene Oxide) Triblock Copolymers. Polym. Bull. 2017, 74, 707–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soni, S.S.; Vekariya, R.L.; Aswal, V.K. Ionic Liquid Induced Sphere-to-Ribbon Transition in the Block Copolymer Mediated Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 8398–8406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhang, X.; Lu, W.; Zhang, Q. A Novel Mixed Micelle Gel with Thermo-Sensitive Property for the Local Delivery of Docetaxel. J. Control. Release 2009, 135, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newby, G.E.; Hamley, I.W.; King, S.M.; Martin, C.M.; Terrill, N.J. Structure, Rheology and Shear Alignment of Pluronic Block Copolymer Mixtures. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2009, 329, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shokri, J.; Nokhodchi, A.; Dashbolaghi, A.; Hassan-Zadeh, D.; Ghafourian, T.; Barzegar Jalali, M. The Effect of Surfactants on the Skin Penetration of Diazepam. Int. J. Pharm. 2001, 228, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pooja, D.; Kulhari, H.; Singh, M.K.; Mukherjee, S.; Rachamalla, S.S.; Sistla, R. Dendrimer–TPGS Mixed Micelles for Enhanced Solubility and Cellular Toxicity of Taxanes. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2014, 121, 461–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinarov, Z.; Katev, V.; Burdzhiev, N.; Tcholakova, S.; Denkov, N. Effect of Surfactant–Bile Interactions on the Solubility of Hydrophobic Drugs in Biorelevant Dissolution Media. Mol. Pharm. 2018, 15, 5741–5753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singla, P.; Chabba, S.; Mahajan, R.K. A Systematic Physicochemical Investigation on Solubilization and In Vitro Release of Poorly Water Soluble Oxcarbazepine Drug in Pluronic Micelles. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2016, 504, 479–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senthilkumar, M.; Sheelarani, B.; Joshi, R.G.; Dash, S. Solubilization and Interaction of Ciprofloxacin with Pluronics and Their Mixed Micelles. New J. Chem. 2019, 43, 16530–16537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, S.; Peeters, M.; Mahajan, R.K.; Singla, P. Loading of Hydrophobic Drug Silymarin in Pluronic and Reverse Pluronic Mixed Micelles. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2022, 75, 103699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Huang, W.; Rongcai, L.; Sun, K.; Zhang, F.; Liu, W.; Li, Y. Improvement of In Vivo Efficacy of Recombinant Human Erythropoietin by Encapsulation in PEG–PLA Micelle. Int. J. Nanomedicine 2012, 8, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kazemi, M.; Emami, J.; Hasanzadeh, F.; Minaiyan, M.; Mirian, M.; Lavasanifar, A. Pegylated Multifunctional pH-Responsive Targeted Polymeric Micelles for Ovarian Cancer Therapy: Synthesis, Characterization and Pharmacokinetic Study. Int. J. Polym. Mater. 2021, 70, 1012–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binkhathlan, Z.; Alomrani, A.H.; Hoxha, O.; Ali, R.; Kalam, M.A.; Alshamsan, A. Development and Characterization of PEGylated Fatty Acid-Block-Poly(ε-caprolactone) Novel Block Copolymers and Their Self-Assembled Nanostructures for Ocular Delivery of Cyclosporine A. Polymers 2022, 14, 1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limón, D.; Amirthalingam, E.; Rodrigues, M.; Halbaut, L.; Andrade, B.; Garduño-Ramírez, M.L.; Amabilino, D.B.; Pérez-García, L.; Calpena, A.C. Novel Nanostructured Supramolecular Hydrogels for the Topical Delivery of Anionic Drugs. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2015, 96, 421–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meissner, S.; Akepogu, J.H.; Arnet, S.M.; Dean, M.Z.; Ji, J.; Wright, G.; Harland, B.; Raos, B.; Svirskis, D.; Thakur, S.S. Investigating the Influence of Ultrasound Parameters on Ibuprofen Drug Release from Hydrogels. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2023, 13, 1390–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Chen, X.; Nguyen, T.X.; Tang, H.; Zhang, L.; Yang, G. Nano-Cellulose 3D-Networks as Controlled-Release Drug Carriers. J. Mater. Chem. B 2013, 1, 2976–2984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





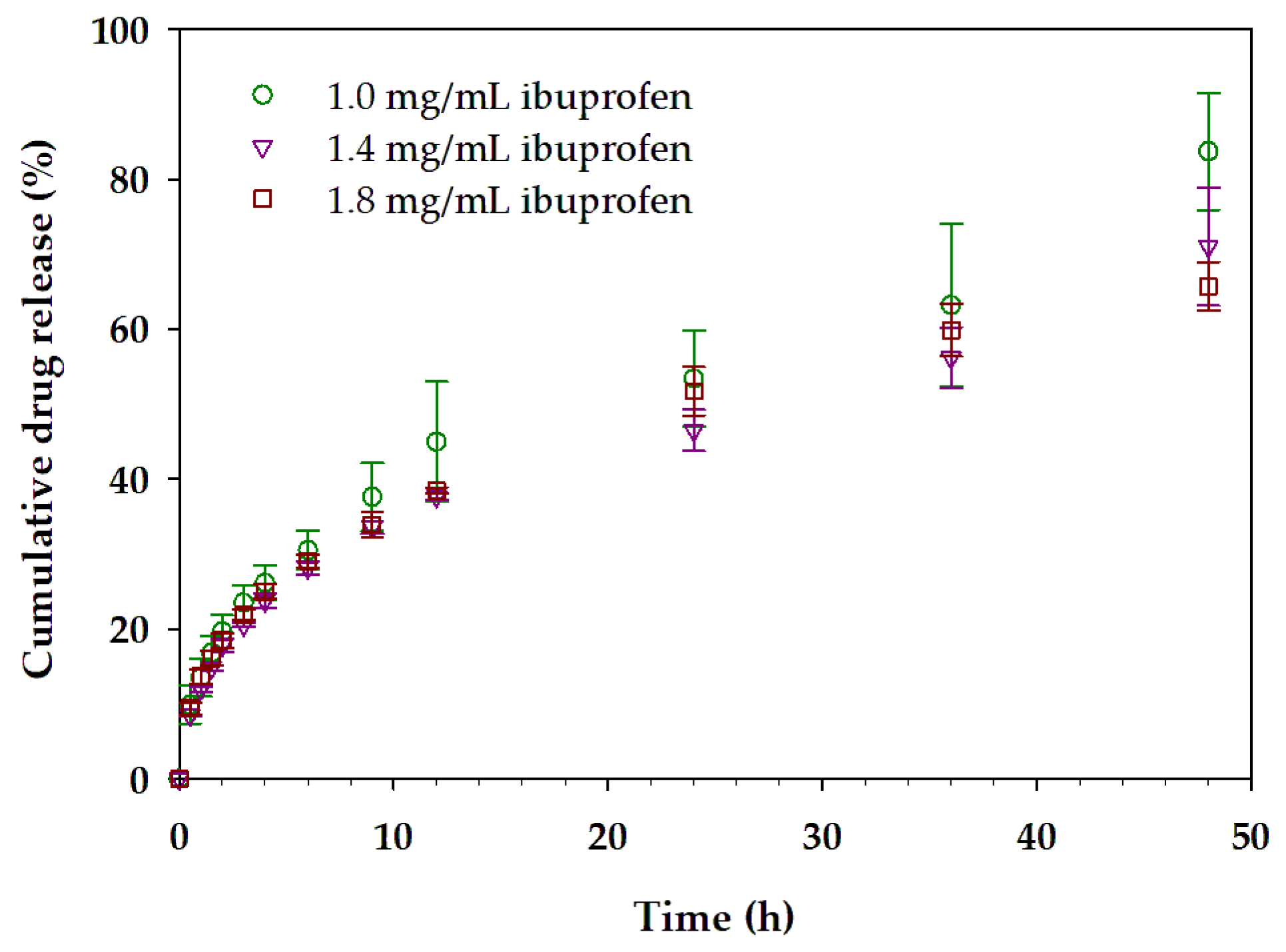
| Concentration of Loaded Ibuprofen (mg/mL) | Korsmeyer–Peppas Model | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| n | KKP | R2 | |
| 1.0 mg/mL | 0.469 | 13.715 | 0.9960 |
| 1.4 mg/mL | 0.409 | 13.148 | 0.9916 |
| 1.8 mg/mL | 0.419 | 13.634 | 0.9991 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hirun, N.; Kraisit, P.; Santhan, S. Mixed Micellar Gel of Poloxamer Mixture for Improved Solubilization of Poorly Water-Soluble Ibuprofen and Use as Thermosensitive In Situ Gel. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 1055. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16081055
Hirun N, Kraisit P, Santhan S. Mixed Micellar Gel of Poloxamer Mixture for Improved Solubilization of Poorly Water-Soluble Ibuprofen and Use as Thermosensitive In Situ Gel. Pharmaceutics. 2024; 16(8):1055. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16081055
Chicago/Turabian StyleHirun, Namon, Pakorn Kraisit, and Supaporn Santhan. 2024. "Mixed Micellar Gel of Poloxamer Mixture for Improved Solubilization of Poorly Water-Soluble Ibuprofen and Use as Thermosensitive In Situ Gel" Pharmaceutics 16, no. 8: 1055. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16081055
APA StyleHirun, N., Kraisit, P., & Santhan, S. (2024). Mixed Micellar Gel of Poloxamer Mixture for Improved Solubilization of Poorly Water-Soluble Ibuprofen and Use as Thermosensitive In Situ Gel. Pharmaceutics, 16(8), 1055. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16081055






