Advances in Modeling Approaches for Oral Drug Delivery: Artificial Intelligence, Physiologically-Based Pharmacokinetics, and First-Principles Models
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Overview of the Physiology and Mechanisms of Human Oral Drug Absorption
3. Approaches for Mathematical Modeling
4. Data-Driven Models
4.1. Conventional Pharmacokinetics Models
4.2. Conventional Quantitative Structure–Activity Relationship (QSAR)
4.3. Artificial Intelligence (AI)
5. Mechanism-Based Models
5.1. Quasi-Equalibrium
5.2. Steady-State
5.3. Dynamic Physiologically-Based Pharmacokinetics (PBPK) Models
5.3.1. Compartmental Models
5.3.2. Continuous Models
6. First Principles Models
6.1. Molecular Modeling
6.2. Continuum Models
7. Discussion
8. Conclusions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Amount of drug in the GIT | |
| ACAT | Advanced CAT |
| ADAM | Advanced Dissolution, Absorption, and Metabolism |
| ADME | Absorption, Distribution, Metabolism, and Elimination |
| An | Absorption Number |
| AP | Absorption Potential |
| BCS | Biopharmaceutics Classification System |
| BDDCS | Biopharmaceutics Drug Disposition Classification System |
| C | Concentration along the SI |
| CAT | Compartmental Absorption and Transit |
| Clearance from the body | |
| Plasma blood concentration | |
| CYP | Cytochrome P450 |
| D | Dose |
| Dissolution number | |
| DL | Deep Learning |
| Dose number | |
| DCS | Developability Classification System |
| Dispersion (mixing) coefficient along the SI | |
| F | Oral bioavailability (fraction absorbed) |
| GIT | Gastrointestinal Tract |
| Fraction of the unionized form at pH 6.5 | |
| IV | Intravenous |
| Absorption coefficient | |
| Rate transfer coefficient | |
| LHS | Left-Hand Side |
| LI | Large Intestine |
| Length of the SI | |
| MD | Molecular Dynamics |
| ML | Machine Learning |
| ODE | Ordinary Differential Equations |
| P | Partition coefficient |
| PBPK | Physiologically-Based Pharmacokinetics |
| PDE | Partial Differential Equations |
| Effective drug permeability | |
| Intrinsic permeability of the SI | |
| PK | Pharmacokinetics |
| Flow flux in the SI | |
| QSAR | Quantitative Structure–Activity Relationship |
| rDCS | Refined Developability Classification System |
| Initial particle radius | |
| RHS | Right-Hand Side |
| Radius of the SI | |
| SAR | Structure–Activity Relationship |
| Surface area factor of the SI | |
| S | Solubility |
| SI | Small Intestine |
| SPP | Similarity–Property Principle |
| u | Velocity along the SI |
| V | Volume of distribution |
| Water content of the SI | |
| Fraction of the drug amount in compartment i | |
| Drug density |
Appendix A. Partial Differential Equations (PDE)
Appendix A.1. Interpratation
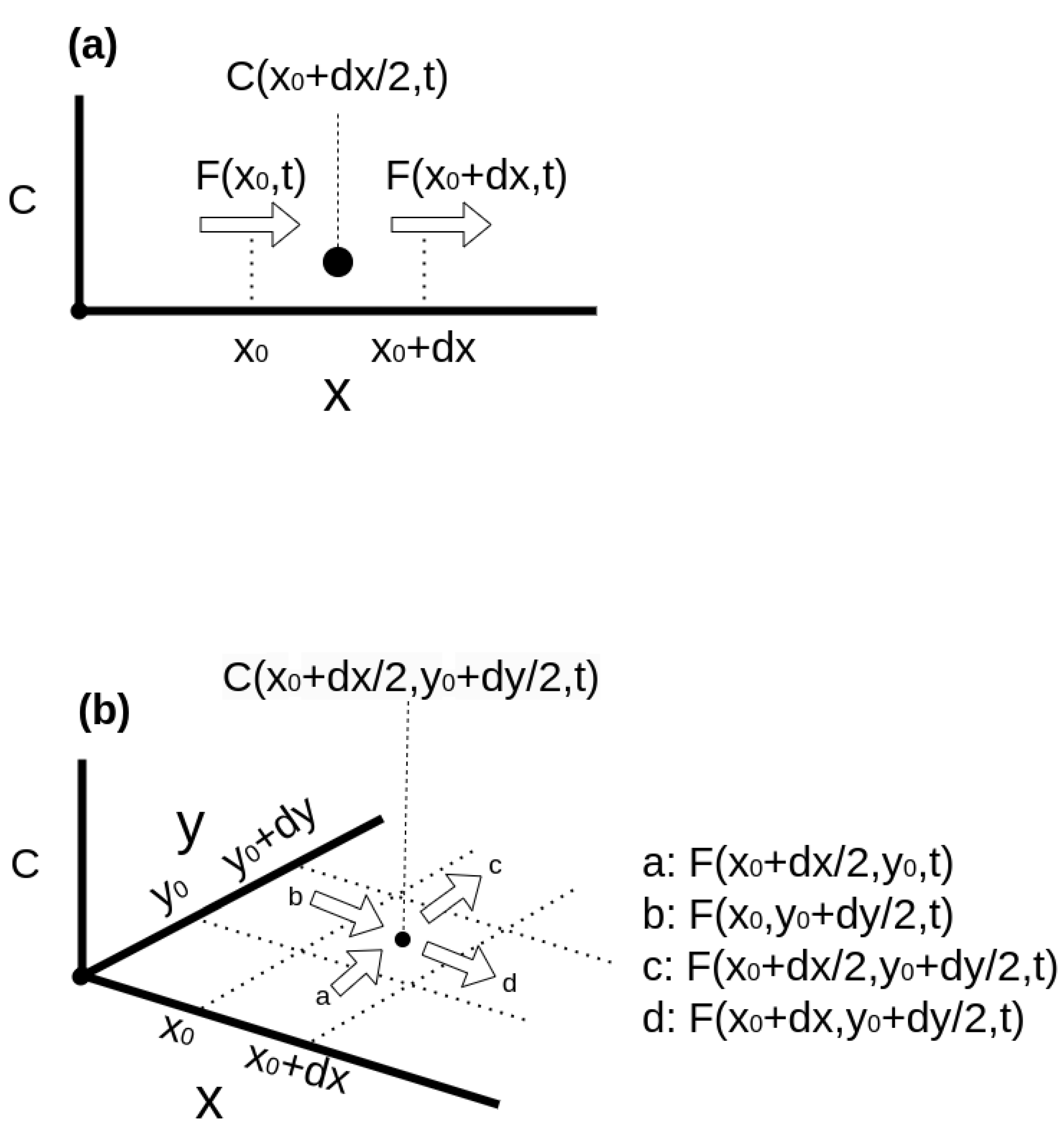
Appendix A.2. Solving PDEs
Appendix B. Dispersion Model with Dissolution

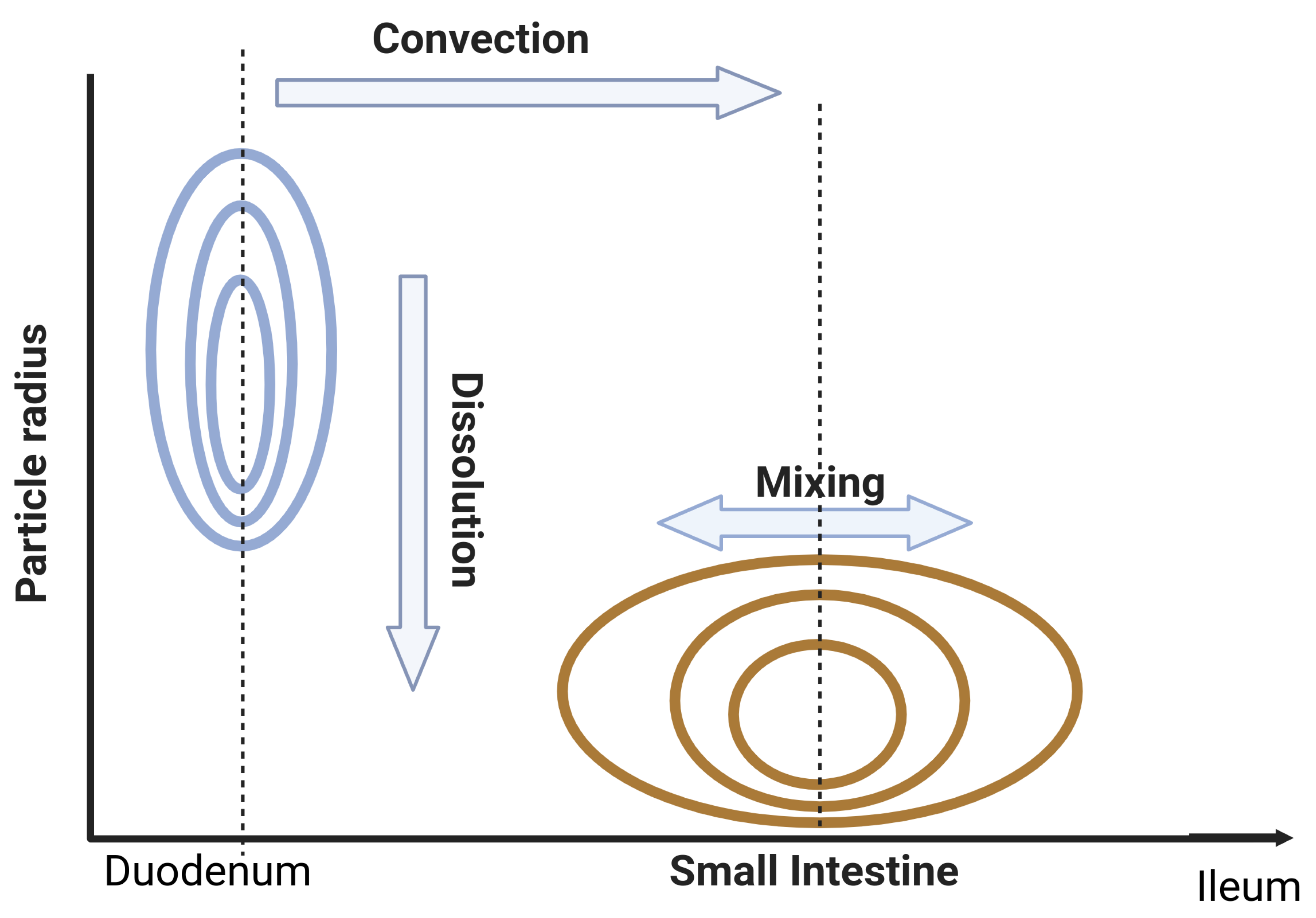
References
- Alqahtani, M.S.; Kazi, M.; Alsenaidy, M.A.; Ahmad, M.Z. Advances in Oral Drug Delivery. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 618411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneckener, S.; Grimbs, S.; Hey, J.; Menz, S.; Osmers, M.; Schaper, S.; Hillisch, A.; Göller, A.H. Prediction of Oral Bioavailability in Rats: Transferring Insights from in Vitro Correlations to (Deep) Machine Learning Models Using in Silico Model Outputs and Chemical Structure Parameters. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2019, 59, 4893–4905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Homayun, B.; Lin, X.; Choi, H.J. Challenges and recent progress in oral drug delivery systems for biopharmaceuticals. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Lee, S.L.; Yu, L.X. Mechanistic approaches to predicting oral drug absorption. AAPS J. 2009, 11, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Wong, H. Predicting oral drug absorption: Mini review on physiologically-based pharmacokinetic models. Pharmaceutics 2017, 9, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.; Gao, W.; Hu, H.; Zhou, S. Why 90% of clinical drug development fails and how to improve it? Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2022, 12, 3049–3062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wienkers, L.C.; Heath, T.G. Predicting in vivo drug interactions from in vitro drug discovery data. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2005, 4, 825–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guengerich, F.P.; Isin, E.M. Mechanisms of Cytochrome P450 Reactions. Acta Chim. Slov. 2008, 55, 7–19. [Google Scholar]
- Mehrer, H.; Stolwijk, N.A. Heroes and Highlights in the History of Diffusion. Open-Access J. Basic Princ. Diffus. Theory Exp. Appl. 2009, 11, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benedetti, M.S.; Whomsley, R.; Poggesi, I.; Cawello, W.; Mathy, F.X.; Delporte, M.L.; Papeleu, P.; Watelet, J.B. Drug metabolism and pharmacokinetics. Drug Metab. Rev. 2009, 41, 344–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Mu, H. Microenvironmental pH Modification in Buccal/Sublingual Dosage Forms for Systemic Drug Delivery. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanade, T.; Gupta, A.; Mahajan, S.; Darwhekar, G. Review on Sublingual Tablets—A Promising Formulation for Instant Action. Int. J. Pharm. Sci 2023, 1, 250–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pather, I.; Rathbone, M.J.; Şenel, S. Current status and the future of buccal drug delivery systems. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2008, 5, 531–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinto, S.; Pintado, M.E.; Sarmento, B. In vivo, ex vivo and in vitro assessment of buccal permeation of drugs from delivery systems. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2020, 17, 33–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wanasathop, A.; Patel, P.B.; Choi, H.A.; Li, S.K. Permeability of buccal mucosa. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fedi, A.; Vitale, C.; Ponschin, G.; Ayehunie, S.; Fato, M.; Scaglione, S. In vitro models replicating the human intestinal epithelium for absorption and metabolism studies: A systematic review. J. Control. Release 2021, 335, 247–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naoki, U.; Yoshiteru, W.; Takahisa, S.; Junko, M.; Yoshiaki, M.; Mitsuo, M. Carrier-Mediated Transport of Monocarboxylic Acids in Primary Cultured Epithelial Cells from Rabbit Oral Mucosa. Pharm. Res. 1997, 14, 320–324. [Google Scholar]
- Vondracek, M.; Xi, Z.; Larsson, P.; Baker, V.; Mace, K.; Pfeifer, A.; Tjälve, H.; Donato, M.; Gomez-Lechon, M. Cytochrome P450 expression and related metabolism in human buccal mucosa, to significant xenobiotic metabolism in human buccal epithelium. Notably, metabolic activation of AFB 1 was not activity in SVpgC2a under both monolayer and organotypic. Carcinogenesis 2001, 22, 481–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonseca-Santos, B.; Chorilli, M. An overview of polymeric dosage forms in buccal drug delivery: State of art, design of formulations and their in vivo performance evaluation. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2018, 86, 129–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badawy, S.I.F.; Hussain, M.A. Microenvironmental pH modulation in solid dosage forms. J. Pharm. Sci. 2007, 96, 948–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doherty, C.; York, P. Microenvironmental pH control of drug dissolution. Int. J. Pharm. 1989, 50, 223–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taniguchi, C.; Kawabata, Y.; Wada, K.; Yamada, S.; Onoue, S. Microenvironmental pH-modification to improve dissolution behavior and oral absorption for drugs with pH-dependent solubility. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2014, 11, 505–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, M.; He, S.; Fan, Y.; Wang, Y.; Ge, Z.; Shan, L.; Gong, W.; Huang, X.; Tong, Y.; Gao, C. Microenvironmental pH-modified solid dispersions to enhance the dissolution and bioavailability of poorly water-soluble weakly basic GT0918, a developing anti-prostate cancer drug: Preparation, characterization and evaluation in vivo. Int. J. Pharm. 2014, 475, 97–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willmann, S.; Schmitt, W.; Keldenich, J.; Lippert, J.; Dressman, J.B. A physiological model for the estimation of the fraction dose absorbed in humans. J. Med. Chem. 2004, 47, 4022–4031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, L.; Wong, H. Food effects on oral drug absorption: Application of physiologically-based pharmacokinetic modeling as a predictive tool. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oberle, R.L.; Amidon, G.L. The Influence of Variable Gastric Emptying and Intestinal Transit Rates on the Plasma Level Curve of Cimetidine; An Explanation for the Double Peak Phenomenon. J. Pharmacokinet. Biopharm. 1987, 15, 529–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, S.S.; Hardy, J.G.; Fara, J.W. The transit of dosage forms through the small intestine. Gut 1986, 27, 886–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amidon, G.L.; Lennernäs, H.; Shah, V.P.; Crison, J.R. A Theoretical Basis for a Biopharmaceutic Drug Classification: The Correlation of in Vitro Drug Product Dissolution and in Vivo Bioavailability. Pharm. Res. 1995, 12, 413–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeSesso, J.M.; Jacobson, C.F. Anatomical and physiological parameters affecting gastrointestinal absorption in humans and rats. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2001, 39, 209–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arav, Y.; Bercovier, M.; Parnas, H. Selecting the particle size distribution for drugs with low water solubility mathematical model. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2012, 38, 940–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schütt, M. A Digital Twin of the Human Colon for the Design and Optimisation of Colon-Targeted Drug Delivery Systems. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Birmingham, Birmingham, UK, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- den Mooter, G.V. Colon drug delivery. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2006, 3, 111–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, C.G. The transit of dosage forms through the colon. Int. J. Pharm. 2010, 395, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aulton, M.E.; Taylor, K. Aulton’s Pharmaceutics—The Design and Manufacture of Medicines; Aulton, M.E., Taylor, K.M.G., Eds.; Elvesier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, A.T.; Frisella, M.E.; Johnson, K.C. Dissolution modeling: Factors affecting the dissolution rates of polydisperse powders. Pharm. Res. 1993, 10, 1308–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glomme, A.; März, J.; Dressman, J. Predicting the Intestinal Solubility of Poorly Soluble Drugs; Wiley: Weinheim, Germany, 2006; pp. 259–280. [Google Scholar]
- Murakami, T.; Takano, M. Intestinal effl ux transporters and drug absorption. Expert Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol 2008, 4, 923–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watkins, P.B. The barrier function of CYP3A4 and P-glycoprotein in the small bowel. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 1997, 27, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, S.D.; Thummel, K.E.; Watkins, P.B.; Lown, K.S.; Benet, L.Z.; Paine, M.F.; Mayo, R.R.; Turgeon, D.K.; Bailey, D.G.; Fontana, R.J.; et al. Molecular and physical mechanisms of first-pass extraction. Drug Metab. Dispos. 1999, 27, 161–166. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rowland, M.; Tozer, T.N.; Derendorf, H.; Hochhaus, G. Clinical Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Agoram, B.; Woltosz, W.S.; Bolger, M.B. Predicting the impact of physiological and biochemical processes on oral drug bioavailability. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2001, 50, 41–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fagerholm, U.; Hellberg, S.; Spjuth, O. Article advances in predictions of oral bioavailability of candidate drugs in man with new machine learning methodology. Molecules 2021, 26, 2572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmada, N.; Cater, J.E.; Cheng, L.K.; Suresh, V. Modelling Flow and Mixing in the Proximal Small Intestine. In Proceedings of the 2020 42nd Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine & Biology Society (EMBC), Montreal, QC, Canada, 20–24 July 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Sager, J.E.; Yu, J.; Ragueneau-Majlessi, I.; Isoherranen, N. Physiologically Based Pharmacokinetic (PBPK) Modeling and Simulation Approaches: A Systematic Review of Published Models, Applications, and Model Verification. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2015, 43, 1823–1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.; Chen, Y.; Unadkat, J.D.; Zhang, X.; Wu, D.; Heimbach, T. Applications, Challenges, and Outlook for PBPK Modeling and Simulation: A Regulatory, Industrial and Academic Perspective. Pharm. Res. 2022, 39, 1701–1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tropsha, A.; Isayev, O.; Varnek, A.; Schneider, G.; Cherkasov, A. Integrating QSAR modelling and deep learning in drug discovery: The emergence of deep QSAR. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2024, 23, 141–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, H.; Banerjee, P.; Leung, S.S.Y.; Yan, X. Application of Pharmacokinetic-Pharmacodynamic Modeling in Drug Delivery: Development and Challenges. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muratov, E.N.; Bajorath, J.; Sheridan, R.P.; Tetko, I.V.; Filimonov, D.; Poroikov, V.; Oprea, T.I.; Baskin, I.I.; Varnek, A.; Roitberg, A.; et al. QSAR without borders. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2020, 49, 3525–3564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komura, H.; Watanabe, R.; Mizuguchi, K. The Trends and Future Prospective of In Silico Models from the Viewpoint of ADME Evaluation in Drug Discovery. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 2619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vora, L.K.; Gholap, A.D.; Jetha, K.; Thakur, R.R.S.; Solanki, H.K.; Chavda, V.P. Artificial Intelligence in Pharmaceutical Technology and Drug Delivery Design. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De, P.; Kar, S.; Ambure, P.; Roy, K. Prediction reliability of QSAR models: An overview of various validation tools. Arch. Toxicol. 2022, 96, 1279–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stenberg, P.; Bergström, C.A.S.; Luthman, K.; Artursson, P. Theoretical Predictions of Drug Absorption in Drug Discovery and Development. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2002, 41, 877–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lombardo, F.; Gifford, E.; Shalaeva, M.Y. In Silico ADME Prediction: Data, Models, Facts and Myths. Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 2003, 3, 861–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linnankoski, J. Mathematical Modelling of Intestinal Drug Absorption. Ph.D. Thesis, Itä-Suomen yliopisto, Kuopio, Finland, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Lawless, M.; Dibella, J.; Bolger, M.B.; Clark, R.D.; Huehn, E.; Waldman, M.; Zhang, J.; Lukacova, V. In silico prediction of oral bioavailability. In Comprehensive Medicinal Chemistry II ADME Tox Approaches; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, J.; Siramshetty, V.; Nguyen, D.T.; Padilha, E.C.; Kabir, M.; Yu, K.R.; Wang, A.Q.; Zhao, T.; Itkin, M.; Shinn, P.; et al. Using in vitro ADME data for lead compound selection: An emphasis on PAMPA pH 5 permeability and oral bioavailability. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2022, 56, 116588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linnankoski, J.; Ranta, V.P.; Yliperttula, M.; Urtti, A. Passive oral drug absorption can be predicted more reliably by experimental than computational models-Fact or myth. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2008, 34, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Waterbeemd, H.V.; Smith, D.A.; Beaumont, K.; Walker, D.K. Property-based design: Optimization of drug absorption and pharmacokinetics. J. Med. Chem. 2001, 44, 1313–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falcón-Cano, G.; Ángel Cabrera-Pérez, M.; Molina, C. ADME prediction with KNIME: In silico aqueous solubility consensus model based on supervised recursive random forest approaches. ADMET DMPK 2020, 8, 251–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshida, F.; Topliss, J.G. QSAR model for drug human oral bioavailability. J. Med. Chem. 2000, 43, 2575–2585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.H.; Abraham, M.H.; Le, J.; Hersey, A.; Luscombe, C.N.; Beck, G.; Sherborne, B.; Cooper, I. Rate-Limited Steps of Human Oral Absorption and QSAR Studies. Pharm. Res. 2002, 19, 1446–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moda, T.L.; Montanari, C.A.; Andricopulo, A.D. Hologram QSAR model for the prediction of human oral bioavailability. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2007, 15, 7738–7745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, M.; Zhang, X.; Pan, X.; Wang, B.; Ji, C.; Qi, Y.; Zhang, J.Z. HobPre: Accurate prediction of human oral bioavailability for small molecules. J. Cheminform. 2022, 14, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Price, E.; Kalvass, J.C.; Degoey, D.; Hosmane, B.; Doktor, S.; Desino, K. Global Analysis of Models for Predicting Human Absorption: QSAR, in Vitro, and Preclinical Models. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 64, 9389–9403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donovan, D.H.O.; Fusco, C.D.; Kuhnke, L.; Reichel, A. Trends in Molecular Properties, Bioavailability, and Permeability across the Bayer Compound Collection. J. Med. Chem. 2023, 66, 2347–2360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desai, P.V.; Sawada, G.A.; Watson, I.A.; Raub, T.J. Integration of in silico and in vitro tools for scaffold optimization during drug discovery: Predicting P-glycoprotein efflux. Mol. Pharm. 2013, 10, 1249–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berellini, G.; Springer, C.; Waters, N.J.; Lombardo, F. In silico prediction of volume of distribution in human using linear and nonlinear models on a 669 compound data set. J. Med. Chem. 2009, 52, 4488–4495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.W.; Sedykh, A.; Zhu, H.; Liu, S.S.; Tropsha, A. The use of pseudo-equilibrium constant affords improved QSAR models of human plasma protein binding. Pharm. Res. 2013, 30, 1790–1798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Votano, J.R.; Parham, M.; Hall, L.M.; Hall, L.H.; Kier, L.B.; Oloff, S.; Tropsha, A. QSAR modeling of human serum protein binding with several modeling techniques utilizing structure-information representation. J. Med. Chem. 2006, 49, 7169–7181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.; Yang, H.; Li, J.; Wang, T.; Li, W.; Liu, G.; Tang, Y. In Silico Prediction of Compounds Binding to Human Plasma Proteins by QSAR Models. ChemMedChem 2018, 13, 572–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pirovano, A.; Brandmaier, S.; Huijbregts, M.A.; Ragas, A.M.; Veltman, K.; Hendriks, A.J. QSARs for estimating intrinsic hepatic clearance of organic chemicals in humans. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2016, 42, 190–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gombar, V.K.; Hall, S.D. Quantitative structure-activity relationship models of clinical pharmacokinetics: Clearance and volume of distribution. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2013, 53, 948–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simeon, S.; Montanari, D.; Gleeson, M.P. Investigation of Factors Affecting the Performance of in silico Volume Distribution QSAR Models for Human, Rat, Mouse, Dog & Monkey. Mol. Inform. 2019, 38, 1900059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokate, A.; Li, X.; Williams, P.J.; Singh, P.; Jasti, B.R. In silico prediction of drug permeability across buccal mucosa. Pharm. Res. 2009, 26, 1130–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scherrer, R.A. Multi-pH QSAR: II. Regression Analysis Sensitive Enough to Determine the Transition-State pKa of Human Buccal Absorption. Mol. Inform. 2011, 30, 251–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, C.H.; Narayan, R.; Nayak, U.Y. Computational modeling for formulation design. Drug Discov. Today 2019, 24, 781–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaikwad, V.L.; Bhatia, N.M.; Singhvi, I.; Mahadik, K.R.; Bhatia, M.S. Computational Modeling of Polymeric Physicochemical Properties for Formulation Development of a Drug Containing Basic Functionality. J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 106, 3337–3345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeBoyace, K.; Wildfong, P.L. The Application of Modeling and Prediction to the Formation and Stability of Amorphous Solid Dispersions. J. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 107, 57–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landín, M.; Rowe, R.C.; York, P. Advantages of neurofuzzy logic against conventional experimental design and statistical analysis in studying and developing direct compression formulations. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2009, 38, 325–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, A.S.; Kasabe, A.J.; Bhatia, M.S.; Bhatia, N.M.; Gaikwad, V.L. Quantitative Structure–Property Relationship Approach in Formulation Development: An Overview. AAPS PharmSciTech 2019, 20, 268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aguilar, J.E. (Ed.) Formulation Tools for Pharmaceutical Development; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Obrezanova, O.; Segall, M.D. Gaussian processes for classification: QSAR modeling of ADMET and target activity. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2010, 50, 1053–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarker, S.; Jamal, L.; Ahmed, S.F.; Irtisam, N. Robotics and artificial intelligence in healthcare during COVID-19 pandemic: A systematic review. Robot. Auton. Syst. 2021, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fluetsch, A.; Lascio, E.D.; Gerebtzoff, G.; Rodríguez-Pérez, R. Adapting Deep Learning QSPR Models to Specific Drug Discovery Projects. Mol. Pharm. 2024, 21, 1817–1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Ye, Z.; Su, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Li, X.; Ouyang, D. Deep learning for in vitro prediction of pharmaceutical formulations. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2019, 9, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paixão, P.J.P.A. In Silico Prediction of Human Oral Bioavailability. Artificial Neural Networks and Physiologically Based Models. Ph.D. Thesis, Universidade de Lisboa, Lisbon, Portugal, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Kong, X.; Lin, K.; Wu, G.; Tao, X.; Zhai, X.; Lv, L.; Dong, D.; Zhu, Y.; Yang, S. Machine Learning Techniques Applied to the Study of Drug Transporters. Molecules 2023, 28, 5936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Deepika, D.; Kumar, V. Pharmacophore Modeling Using Machine Learning for Screening the Blood–Brain Barrier Permeation of Xenobiotics. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 13471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plonka, W.; Stork, C.; Šícho, M.; Kirchmair, J. CYPlebrity: Machine learning models for the prediction of inhibitors of cytochrome P450 enzymes. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2021, 46, 116388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, K.; Ghosh, J.; Sil, P.C. Machine Learning in Drug Metabolism Study. Curr. Drug Metab. 2022, 23, 1012–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ai, D.; Cai, H.; Wei, J.; Zhao, D.; Chen, Y.; Wang, L. DEEPCYPs: A deep learning platform for enhanced cytochrome P450 activity prediction. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1099093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmer, M.; de Bruyn Kops, C.; Stork, C.; Kirchmair, J. Cypstrate: A set of machine learning models for the accurate classification of cytochrome p450 enzyme substratesand non-substrates. Molecules 2021, 26, 4678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett-Lenane, H.; Griffin, B.T.; O’Shea, J.P. Machine learning methods for prediction of food effects on bioavailability: A comparison of support vector machines and artificial neural networks. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2022, 168, 106018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maltarollo, V.G.; Gertrudes, J.C.; Oliveira, P.R.; Honorio, K.M. Applying machine learning techniques for ADME-Tox prediction: A review. Expert Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 2015, 11, 259–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butina, D. Unsupervised data base clustering based on daylight’s fingerprint and Tanimoto similarity: A fast and automated way to cluster small and large data sets. J. Chem. Inf. Comput. Sci. 1999, 39, 747–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korolev, D.; Balakin, K.V.; Nikolsky, Y.; Kirillov, E.; Ivanenkov, Y.A.; Savchuk, N.P.; Ivashchenko, A.A.; Nikolskaya, T. Modeling of human cytochrome P450-mediated drug metabolism using unsupervised machine learning approach. J. Med. Chem. 2003, 46, 3631–3643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vamathevan, J.; Clark, D.; Czodrowski, P.; Dunham, I.; Ferran, E.; Lee, G.; Li, B.; Madabhushi, A.; Shah, P.; Spitzer, M.; et al. Applications of machine learning in drug discovery and development. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2019, 18, 463–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.X.; Lipka, E.; Crison, J.R.; Amidon, G.L. Transport approaches to the biopharmaceutical design of oral drug delivery systems: Prediction of intestinal absorption. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 1996, 19, 359–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, M.H. Some aspects of cell permeability to weak electrolytes. Symp. Quant. Biol. 1940, 8, 30–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schanker, L.S.; Shore, P.A.; Brodie, B.B.; Hogben, C.A.M. Absorption of drugs from the stomach I. the rat. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1957, 120, 528–539. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hogben, C.A.M.; Schanker, L.S.; Tocco, D.J.; Brodie, B.B. Absorption of drugs from the stomach. II. the human. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1957, 120, 540–545. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Schanker, L.S.; Tocco, D.J.; Brodie, B.B.; Hogben, C.A.M. Absorption of drugs from the rat small intestine. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1958, 123, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dressman, J.B.; Amidon, G.L.; Fleisher, D. Absorption potential: Estimating the fraction absorbed for orally administered compounds. J. Pharm. Sci. 1985, 74, 588–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macheras, P.E.; Symillides, M.Y. Toward a quantitative approach for the prediction of the fraction of dose absorbed using the absorption potential concept. Biopharm. Drug Dispos. 1989, 10, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amidon, G.L.; Sinko, P.J.; Fleisher, D. Estimating Human Oral Fraction Dose Absorbed: A Correlation Using Rat Intestinal Membrane Permeability for Passive and Carrier-Mediated Compounds. Pharm. Res. 1988, 5, 651–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinko, P.J.; Leesman, G.D.; Amidon, G.L. Predicting Fraction Dose Absorbed in Humans Using a Macroscopic Mass Balance Approach. Pharm. Res. 1991, 8, 979–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinko, P.J.; Leesman, G.D.; Amidon, G.L. Mass Balance Approaches for Estimating the Intestinal Absorption and Metabolism of Peptides and Analogues: Theoretical Development and Applications. Pharm. Res. 1993, 10, 271–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.X.; Crison, J.R.; Amidon, G.L. Compartmental transit and dispersion model analysis of small intestinal transit flow in humans. Int. J. Pharm. 1996, 140, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, D.M.; Curl, R.L.; Amidon, G.L. Estimating the Fraction Dose Absorbed from Suspensions of Poorly Soluble Compounds in Humans: A Mathematical Model. Pharm. Res. 1993, 10, 264–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beran, K.; Hermans, E.; Holm, R.; Sepassi, K.; Dressman, J. Projection of Target Drug Particle Size in Oral Formulations Using the Refined Developability Classification System (rDCS). Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 1909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.Y.; Benet, L.Z. Predicting drug disposition via application of BCS: Transport/absorption/ elimination interplay and development of a biopharmaceutics drug disposition classification system. Pharm. Res. 2005, 22, 11–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodacre, B.C.; Murray, P.J. A mathematical model of drug absorption. J. Clin. Pharm. Ther. 1981, 6, 117–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, S.K.; Peng, H.B.; Noh, K. The segregated intestinal flow model (SFM) for drug absorption and drug metabolism: Implications on intestinal and liver metabolism and drug–drug interactions. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dressman, J.B.; Fleisher, D. Mixing-Tank Model for Predicting Dissolution Rate Control of Oral Absorption. J. Pharm. Sci. 1986, 75, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hintz, R.J.; Johnson, K.C. The effect of particle size distribution on dissolution rate and oral absorption. Int. J. Pharm. 1989, 51, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dressman, J.B.; Fleisher, D.; Amidon, G.L. Physicochemical Model for Dose-Dependent DrugAbsorption. J. Pharm. Sci. 1984, 73, 1274–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luner, P.E.; Amidon, G.L. Description and simulation of a multiple mixing tank model to predict the effect of bile sequestrants on bile salt excretion. J. Pharm. Sci. 1993, 82, 311–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grass, G.M. Simulation models to predict oral drug absorption from in vitro data. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 1997, 23, 199–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.X.; Amidon, G.L. A compartmental absorption and transit model for estimating oral drug absorption. Int. J. Pharm. 1999, 186, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamei, M.; Yang, J.; Turner, D.; Yeo, K.R.; Tucker, G.T.; Hodjegan, A.R.H. A Novel Physiologically-Based Mechanistic Model for Predicting Oral Drug Absorption: The Advanced Dissolution, Absorption, and Metabolism (ADAM) Model. In Proceedings of the 4th World Conference on Drug Absorption, Transport and Delivery, Edinburgh, UK, 14–16 November 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Dokoumetzidis, A.; Kalantzi, L.; Fotaki, N. Predictive models for oral drug absorption: From in silico methods to integrated dynamical models. Expert Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 2007, 3, 491–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hörter, D.; Dressman, J.B. Influence of physicochemical properties on dissolution of drugs in the gastrointestinal tract. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2001, 46, 75–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Flanagan, D.R. General solution for diffusion-controlled dissolution of spherical particles. 1. Theory. J. Pharm. Sci. 1999, 88, 731–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tubic-Grozdanis, M.; Bolger, M.B.; Langguth, P. Application of Gastrointestinal Simulation for Extensions for Biowaivers of Highly Permeable Compounds. AAPS J. 2008, 10, 213–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.; Wells, E. A Review of Current Methods for Food Effect Prediction During Drug Development. Curr. Pharmacol. Rep. 2020, 6, 267–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dannenfelser, R.M.; He, H.; Joshi, Y.; Bateman, S.; Serajuddin, A.T. Development of clinical dosage forms for a poorly water soluble drug I: Application of polyethylene glycol–polysorbate 80 solid dispersion carrier system. J. Pharm. Sci. 2004, 93, 1165–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuentz, M.; Nick, S.; Parrott, N.; Röthlisberger, D. A strategy for preclinical formulation development using GastroPlus™ as pharmacokinetic simulation tool and a statistical screening design applied to a dog study. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2006, 27, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.; Dalton, C.; Maso, M.D.; Kanfer, I.; Löbenberg, R. Physicochemical characterization of five glyburide powders: A BCS based approach to predict oral absorption. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2008, 69, 1046–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arafat, M.; Sarfraz, M.; Aburuz, S. Development and In Vitro Evaluation of Controlled Release Viagra® Containing Poloxamer-188 Using Gastroplus™ PBPK Modeling Software for In Vivo Predictions and Pharmacokinetic Assessments. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalia, S.H.; Basim Mohsin Mohamed, M. Formulation of metoclopramide HCl gastroretentive film and in vitro- in silico prediction using Gastroplus® PBPK software. Saudi Pharm. J. 2022, 30, 1816–1824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajewska, M.; Blumenstein, L.; Kourentas, A.; Mueller-Zsigmondy, M.; Lorenzo, S.; Sinn, A.; Velinova, M.; Heimbach, T. Physiologically Based Pharmacokinetic Modeling of Oral Absorption, pH, and Food Effect in Healthy Volunteers to Drive Alpelisib Formulation Selection. AAPS J. 2020, 22, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghoneim, A.M.; Mansour, S.M. The effect of liver and kidney disease on the pharmacokinetics of clozapine and sildenafil: A physiologically based pharmacokinetic modeling. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2020, 14, 1469–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, G.J.; Ahire, D.; Taskar, K.S. Physiologically-based pharmacokinetic modeling of prominent oral contraceptive agents and applications in drug–drug interactions. CPT Pharmacometrics Syst. Pharmacol. 2024, 13, 563–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiney, M.S.; Ng, J.; Gibbs, J.P.; Shebley, M. Quantitative Assessment of Elagolix Enzyme-Transporter Interplay and Drug–Drug Interactions Using Physiologically Based Pharmacokinetic Modeling. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2020, 59, 617–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, W.; Shen, C.; Wang, W.; Sun, H.; Wang, X.; Geng, K.; Wang, X.; Xie, H. Development and Validation of Physiologically Based Pharmacokinetic Model of Levetiracetam to Predict Exposure and Dose Optimization in Pediatrics. J. Pharm. Sci. 2023, 112, 2667–2675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Correia, M.G.S. Developing In Vitro and In Silico Approaches to Predict Clinical Outcomes: Focus on Paediatrics. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Bath, Bath, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Cohen-Rabbie, S.; Zhou, L.; Vishwanathan, K.; Wild, M.; Xu, S.; Freshwater, T.; Jain, L.; Schalkwijk, S.; Tomkinson, H.; Zhou, D. Physiologically Based Pharmacokinetic Modeling for Selumetinib to Evaluate Drug-Drug Interactions and Pediatric Dose Regimens. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2021, 61, 1493–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, N.F.H.; Merkle, H.P.; Higuchi, I. Quantitative, mechanistic and physiologically realistic approach to the biopharmaceutical design of oral drug delivery systems. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 1983, 9, 1111–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willmann, S.; Schmitt, W.; Keldenich, J.; Dressman, J.B. A Physiologic Model for Simulating Gastrointestinal Flow and Drug Absorption in Rats. Pharm. Res. 2003, 20, 1766–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arav, Y.; Zohar, A. Model-based optimization of controlled release formulation of levodopa for Parkinson’s disease. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 15869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, J.T.J.T. Turbulence Phenomena; An Introduction to the Eddy Transfer of Momentum, Mass, and Heat, Particularly at Interfaces; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1972; p. 412. [Google Scholar]
- Urso, D.; Chaudhuri, K.R.; Qamar, M.A.; Jenner, P. Improving the Delivery of Levodopa in Parkinson’s Disease: A Review of Approved and Emerging Therapies. CNS Drugs 2020, 34, 1149–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Kuhar, S.; Seo, J.H.; Pasricha, P.J.; Mittal, R. Computational modeling of drug dissolution in the human stomach: Effects of posture and gastroparesis on drug bioavailability. Phys. Fluids 2022, 34, 081904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karplus, M.; McCammon, J.A. Molecular dynamics simulations of biomolecules. Nat. Struct. Biol. 2002, 9, 646–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salo-Ahen, O.M.; Alanko, I.; Bhadane, R.; Alexandre, A.M.; Honorato, R.V.; Hossain, S.; Juffer, A.H.; Kabedev, A.; Lahtela-Kakkonen, M.; Larsen, A.S.; et al. Molecular dynamics simulations in drug discovery and pharmaceutical development. Processes 2021, 9, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adelusi, T.I.; Oyedele, A.Q.K.; Boyenle, I.D.; Ogunlana, A.T.; Adeyemi, R.O.; Ukachi, C.D.; Idris, M.O.; Olaoba, O.T.; Adedotun, I.O.; Kolawole, O.E.; et al. Molecular modeling in drug discovery. Inform. Med. Unlocked 2022, 29, 100880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunker, A.; Róg, T. Mechanistic Understanding From Molecular Dynamics Simulation in Pharmaceutical Research 1: Drug Delivery. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2020, 7, 604770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vivo, M.D.; Masetti, M.; Bottegoni, G.; Cavalli, A. Role of Molecular Dynamics and Related Methods in Drug Discovery. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 59, 4035–4061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollingsworth, S.A.; Dror, R.O. Molecular Dynamics Simulation for All. Neuron 2018, 99, 1129–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Shi, D.; Zhou, S.; Liu, H.; Liu, H.; Yao, X. Molecular dynamics simulations and novel drug discovery. Expert Opin. Drug Discov. 2018, 13, 23–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bera, I.; Payghan, P.V. Use of Molecular Dynamics Simulations in Structure-Based Drug Discovery. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2019, 25, 3339–3349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Rosell, G.; Giorgino, T.; Harvey, M.J.; de Fabritiis, G. Drug Discovery and Molecular Dynamics: Methods, Applications and Perspective Beyond the Second Timescale. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2017, 17, 2617–2625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganesan, A.; Coote, M.L.; Barakat, K. Molecular dynamics-driven drug discovery: Leaping forward with confidence. Drug Discov. Today 2017, 22, 249–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fox, S.J.; Li, J.; Tan, Y.S.; Nguyen, M.N.; Pal, A.; Ouaray, Z.; Yadahalli, S.; Kannan, S. The Multifaceted Roles of Molecular Dynamics Simulations in Drug Discovery. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2016, 23, 3585–3600. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, H. Molecular Simulations of PEGylated Biomolecules, Liposomes, and Nanoparticles for Drug Delivery Applications. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Qattan, M.N.; Deb, P.K.; Tekade, R.K. Molecular dynamics simulation strategies for designing carbon-nanotube-based targeted drug delivery. Drug Discov. Today 2018, 23, 235–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rocco, P.; Cilurzo, F.; Minghetti, P.; Vistoli, G.; Pedretti, A. Molecular Dynamics as a tool for in silico screening of skin permeability. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 106, 328–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fullard, L.A.; Lammers, W.J.; Ferrua, M.J. Advective mixing due to longitudinal and segmental contractions in the ileum of the rabbit. J. Food Eng. 2015, 160, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubinski, A.M.; Shivkumar, G.; Georgi, R.A.; George, S.; Reynolds, J.; Sosa, R.D.; Ju, T.R. Predictive Drug Release Modeling Across Dissolution Apparatuses I and II using Computational Fluid Dynamics. J. Pharm. Sci. 2023, 112, 808–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valibeknejad, M.; Abdoli, S.M.; Alizadeh, R.; Mihăilă, S.M.; Raoof, A. Insights into transport in mucus barrier: Exploring particle penetration through the intestinal mucus layer. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2023, 86, 104752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, J.P.; Ghadiri, M.; Shirazian, S. CFD approach for simulation of API release from solid dosage formulations. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 317, 113899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Ye, Z.; Gao, H.; Ouyang, D. Computational pharmaceutics—A new paradigm of drug delivery. J. Control. Release 2021, 338, 119–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 2024. Available online: https://chatgpt.com/ (accessed on 21 July 2024).
- LeVeque, R.J. Finite Volume Methods for Hyperbolic Problems (Cambridge Texts in Applied Mathematics); Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2002; p. 578. [Google Scholar]
- Ames, W.F. Numerical Methods for Partial Differential Equations; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1977; p. 365. [Google Scholar]
- Gockenbach, M.S. Partial Differential Equations: Analytical and Numerical Methods; Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, H.; Liu, C. A buffered fourier spectral method for non-periodic PDE. Artic. Int. J. Numer. Anal. Model. 2011, 9, 460–478. [Google Scholar]
- COMSOL Multiphysics. Introduction to COMSOL Multiphysics®; Accessed February 1998; COMSOL Multiphysics: Burlington, MA, USA, 2018; Volume 9. [Google Scholar]
- ANSYS Inc. ANSYS Fluent User’s Guide. 2024. Available online: https://www.ansys.com/products/fluids/ansys-fluent (accessed on 26 May 2024).
- Balay, S.; Abhyankar, S.; Adams, M.F.; Brown, J.; Brune, P.; Buschelman, K.; Dalcin, L.; Dener, A.; Eijkhout, V.; Gropp, W.D.; et al. PETSc/TAO Users Manual. 2024. ANL-21/39—Revision 3.21. Available online: https://www.mcs.anl.gov/petsc (accessed on 21 July 2024).
- Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory. HYPRE: High Performance Preconditioners. 2024. Available online: https://computing.llnl.gov/projects/hypre-scalable-linear-solvers-multigrid-methods (accessed on 26 May 2024).
- Trilinos Developers. Trilinos Project Website. 2024. Available online: https://trilinos.github.io (accessed on 26 May 2024).
- OpenFOAM Foundation. OpenFOAM: The Open Source CFD Toolbox User Guide. 2024. Available online: https://www.openfoam.com/documentation/user-guide (accessed on 26 May 2024).
- Ozturk, S.S.; Palsson, B.O.; Dressman, J.B. Dissolution of lonizable Drugs in Buffered and Unbuffered Solutions. Pharm. Res. 1988, 5, 272–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Modeling Approach | Usage/Properties | Limitations |
|---|---|---|
| Data-Driven | • High throughput screening • Extract patterns from large datasets | • Requires large datasets • Harder to provide a physical interpretation |
| Mechanism-based | • Focuses on physiological processes • Misprediction enhances comprehension. | • Requires physiological understanding • Results depend on the simplification methodology |
| First-Principles | • Focuses on physical-chemical processes. • Misprediction enhances comprehension | • High complexity limits spatial and temporal scales • Complex mathematics • Intensive computational resources |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Arav, Y. Advances in Modeling Approaches for Oral Drug Delivery: Artificial Intelligence, Physiologically-Based Pharmacokinetics, and First-Principles Models. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 978. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16080978
Arav Y. Advances in Modeling Approaches for Oral Drug Delivery: Artificial Intelligence, Physiologically-Based Pharmacokinetics, and First-Principles Models. Pharmaceutics. 2024; 16(8):978. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16080978
Chicago/Turabian StyleArav, Yehuda. 2024. "Advances in Modeling Approaches for Oral Drug Delivery: Artificial Intelligence, Physiologically-Based Pharmacokinetics, and First-Principles Models" Pharmaceutics 16, no. 8: 978. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16080978
APA StyleArav, Y. (2024). Advances in Modeling Approaches for Oral Drug Delivery: Artificial Intelligence, Physiologically-Based Pharmacokinetics, and First-Principles Models. Pharmaceutics, 16(8), 978. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16080978






