Advances in Pure Drug Self-Assembled Nanosystems: A Novel Strategy for Combined Cancer Therapy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Mechanisms of Pure Drug Self-Assembly
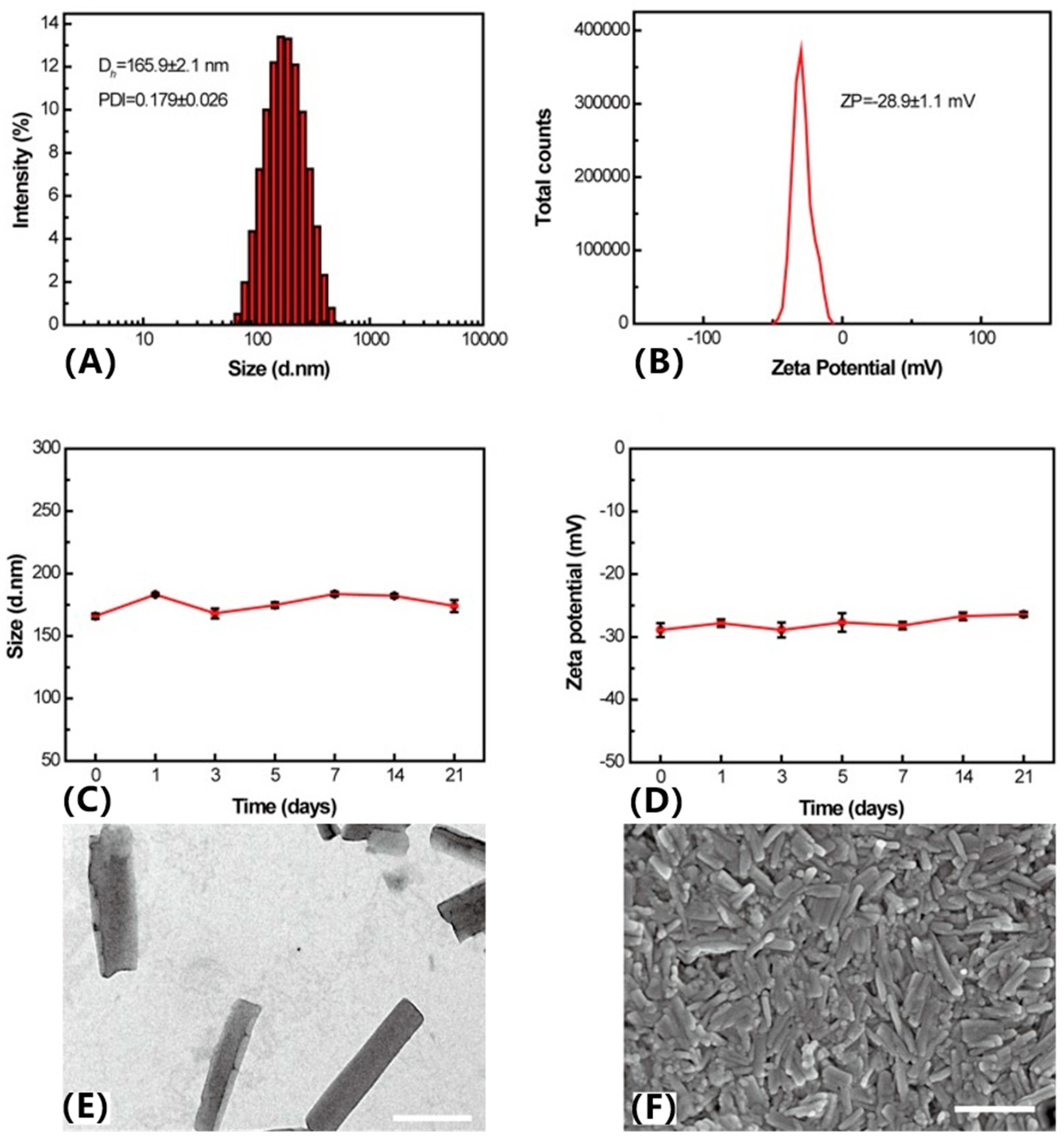
3. Pure Drug Molecule Nano-Assembly
3.1. Single-Drug Self-Assembly
3.2. Co-Assembly of Dual Drugs
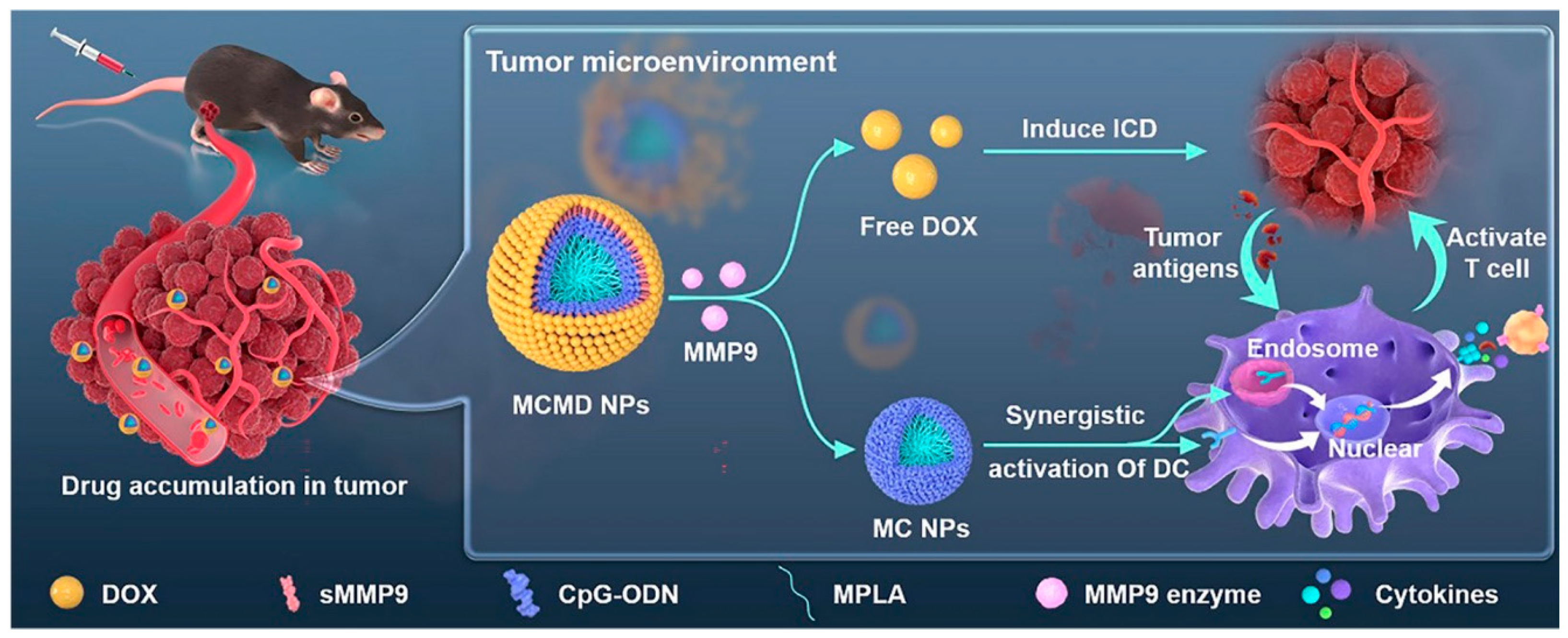
3.3. Multidrug Co-Assembly
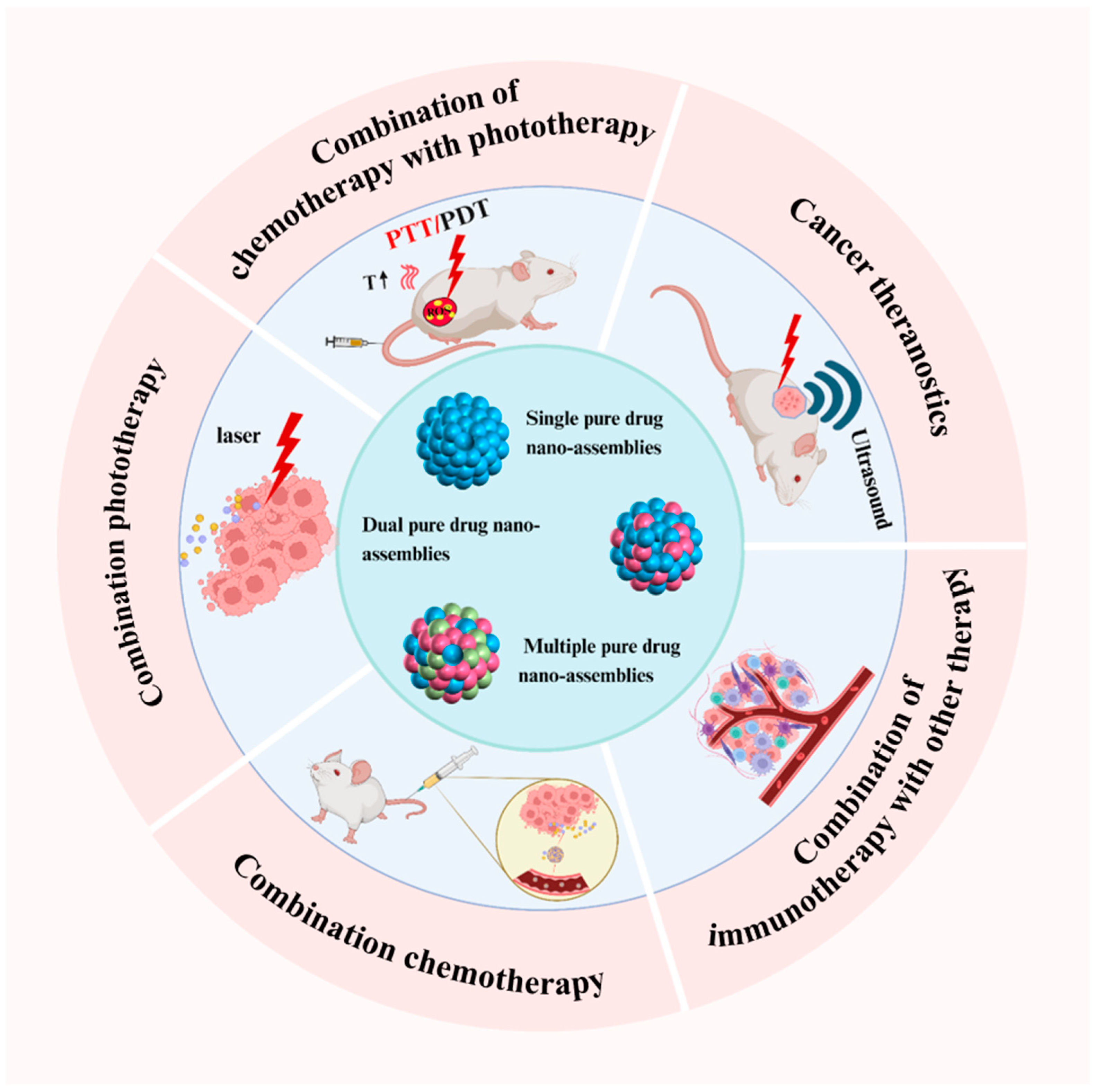
4. Efficient Combination Cancer Therapy Based on Pure Drug Nano-Assemblies
4.1. Cancer Theranostics
4.2. Combined Chemotherapy
4.3. Combination Phototherapy
4.4. Chemotherapy Combined with Phototherapy
4.5. Combination of Immunotherapy with Other Therapies
5. Conclusions
5.1. Challenges
5.2. Outlook
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bray, F.; Laversanne, M.; Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA A Cancer J. Clin. 2024, 74, 229–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Q.; Ke, H.; Dai, Z.; Liu, Z. Nanoscale theranostics for physical stimulus-responsive cancer therapies. Biomaterials 2015, 73, 214–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.Y.; Cheng, R.; Yang, Z.; Tian, Z.M. Nanotechnology for Cancer Therapy Based on Chemotherapy. Molecules 2018, 23, 826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Q.; Yang, Z.; Nie, Y.; Shi, Y.; Fan, D. Multi-drug resistance in cancer chemotherapeutics: Mechanisms and lab approaches. Cancer Lett. 2014, 347, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estanqueiro, M.; Amaral, M.H.; Conceição, J.; Sousa Lobo, J.M. Nanotechnological carriers for cancer chemotherapy: The state of the art. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2015, 126, 631–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dallavalle, S.; Dobričić, V.; Lazzarato, L.; Gazzano, E.; Machuqueiro, M.; Pajeva, I.; Tsakovska, I.; Zidar, N.; Fruttero, R. Improvement of conventional anti-cancer drugs as new tools against multidrug resistant tumors. Drug Resist. Updates Rev. Comment. Antimicrob. Anticancer Chemother. 2020, 50, 100682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, Z.; Dong, S.; Zhao, S.C.; Liu, K.; Tan, Y.; Jiang, X.; Assaraf, Y.G.; Qin, B.; Chen, Z.S.; Zou, C. Novel nanomedicines to overcome cancer multidrug resistance. Drug Resist. Updates Rev. Comment. Antimicrob. Anticancer Chemother. 2021, 58, 100777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, J.; Kantoff, P.W.; Wooster, R.; Farokhzad, O.C. Cancer nanomedicine: Progress, challenges and opportunities. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2017, 17, 20–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, X.; Gong, X.; Li, J.; Wen, J.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Z. Current approaches of nanomedicines in the market and various stage of clinical translation. Acta Pharm. Sinica B 2022, 12, 3028–3048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barenholz, Y. Doxil®–the first FDA-approved nano-drug: Lessons learned. J. Control. Release Off. J. Control. Release Soc. 2012, 160, 117–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barkat, M.A.; Beg, S.; Pottoo, F.H.; Ahmad, F.J. Nanopaclitaxel therapy: An evidence based review on the battle for next-generation formulation challenges. Nanomedicine 2019, 14, 1323–1341. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, L.-H.; Zhang, X.-Z. Carrier-free nanomedicines for cancer treatment. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2022, 125, 100919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, S.Y.; Zhang, A.Q.; Cheng, S.X.; Rong, L.; Zhang, X.Z. Drug self-delivery systems for cancer therapy. Biomaterials 2017, 112, 234–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Li, N.; Zhang, S.; Sun, B.; Chen, Q.; He, Z.; Luo, C.; Sun, J. Emerging carrier-free nanosystems based on molecular self-assembly of pure drugs for cancer therapy. Med. Res. Rev. 2020, 40, 1754–1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Yang, P.; Zhao, X.; Gao, D.; Sun, N.; Tian, Z.; Ma, T.; Yang, Z. Multifunctional Cargo-Free Nanomedicine for Cancer Therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.; Sun, B.; Li, Y.; Luo, C.; He, Z.; Sun, J. Small-Molecule Prodrug Nanoassemblies: An Emerging Nanoplatform for Anticancer Drug Delivery. Small 2021, 17, e2101460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bookstaver, M.L.; Hess, K.L.; Jewell, C.M. Self-Assembly of Immune Signals Improves Codelivery to Antigen Presenting Cells and Accelerates Signal Internalization, Processing Kinetics, and Immune Activation. Small 2018, 14, e1802202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurunathan, S.; Thangaraj, P.; Wang, L.; Cao, Q.; Kim, J.H. Nanovaccines: An effective therapeutic approach for cancer therapy. Biomed. Pharmacother. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2024, 170, 115992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Z.; He, L.; Deng, X.; Wang, H.; Huang, Z.; Xue, Q.; Qing, Z.; Lei, Y.; Yang, R.; Liu, J. Zn(2+) -Coordination-Driven RNA Assembly with Retained Integrity and Biological Functions. Angew. Chem. (Int. Ed. Engl.) 2021, 60, 22970–22976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cong, Y.; Ji, L.; Gao, Y.J.; Liu, F.H.; Cheng, D.B.; Hu, Z.; Qiao, Z.Y.; Wang, H. Microenvironment-Induced In Situ Self-Assembly of Polymer-Peptide Conjugates That Attack Solid Tumors Deeply. Angew. Chem. (Int. Ed. Engl.) 2019, 58, 4632–4637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, P.; Wang, J.; Han, X.; Wang, Y. Hydrophobic drug self-delivery systems as a versatile nanoplatform for cancer therapy: A review. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2019, 180, 202–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patra, J.K.; Das, G.; Fraceto, L.F.; Campos, E.V.R.; Rodriguez-Torres, M.D.P.; Acosta-Torres, L.S.; Diaz-Torres, L.A.; Grillo, R.; Swamy, M.K.; Sharma, S.; et al. Nano based drug delivery systems: Recent developments and future prospects. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2018, 16, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, C.; Sun, B.; Wang, C.; Zhang, X.; Chen, Y.; Chen, Q.; Yu, H.; Zhao, H.; Sun, M.; Li, Z.; et al. Self-facilitated ROS-responsive nanoassembly of heterotypic dimer for synergistic chemo-photodynamic therapy. J. Control. Release Off. J. Control. Release Soc. 2019, 302, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanković, I.M.; Niu, S.; Hall, M.B.; Zarić, S.D. Role of aromatic amino acids in amyloid self-assembly. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 156, 949–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, D.; Jiang, Y.; Ji, L.; Ouyang, G.; Liu, M. Self-Assembly through Coordination and π-Stacking: Controlled Switching of Circularly Polarized Luminescence. Angew. Chem. (Int. Ed. Engl.) 2019, 58, 5946–5950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandler, D. Interfaces and the driving force of hydrophobic assembly. Nature 2005, 437, 640–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cárdenas, M.; Nylander, T.; Jönsson, B.; Lindman, B. The interaction between DNA and cationic lipid films at the air-water interface. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2005, 286, 166–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Z.T.; Huang, F. Multiple hydrogen bonding driven supramolecular architectures and their biomedical applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2024, 53, 1592–1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shan, X.; Zhang, X.; Wang, C.; Zhao, Z.; Zhang, S.; Wang, Y.; Sun, B.; Luo, C.; He, Z. Molecularly engineered carrier-free co-delivery nanoassembly for self-sensitized photothermal cancer therapy. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2021, 19, 282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, R.; Zheng, G.; Fan, L.; Shen, Z.; Jiang, K.; Guo, Y.; Shao, J.W. Carrier-free nanodrug by co-assembly of chemotherapeutic agent and photosensitizer for cancer imaging and chemo-photo combination therapy. Acta Biomater. 2018, 70, 197–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, J.Q.; Yang, F.; Yin, M.D.; Zhao, R.R.; Zhang, B.C.; Li, C.; Lin, J.F.; Fang, Y.F.; Lin, Y.T.; Shao, J.W. Biomimetic polyphenol-coated nanoparticles by Co-assembly of mTOR inhibitor and photosensitizer for synergistic chemo-photothermal therapy. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2022, 209 Pt 2, 112177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Deng, F.; Zheng, R.; Chen, X.; Zhao, L.; Yu, B.; Chen, A.; Jiang, X.; Cheng, H.; Li, S. Self-delivery nanomedicine for vascular disruption-supplemented chemo-photodynamic tumor therapy. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 612, 562–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Yang, F.; Sun, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, H.; Kan, Q.; Sun, J.; He, Z.; et al. Precisely engineering a carrier-free hybrid nanoassembly for multimodal DNA damage-augmented photodynamic therapy. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 426, 130838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Y.; Zhang, W.; Gong, N.; Wang, Y.F.; Guo, H.B.; Guo, W.; Wang, P.C.; Liang, X.J. Carrier-free, self-assembled pure drug nanorods composed of 10-hydroxycamptothecin and chlorin e6 for combinatorial chemo-photodynamic antitumor therapy in vivo. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 14347–14356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, R.; Xing, R.; Jiao, T.; Ma, K.; Chen, C.; Ma, G.; Yan, X. Carrier-Free, Chemophotodynamic Dual Nanodrugs via Self-Assembly for Synergistic Antitumor Therapy. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 13262–13269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Y.; Elkhabaz, A.; Yengej, F.A.; van den Dikkenberg, J.; Hennink, W.E.; van Nostrum, C.F. π-π Stacking induced enhanced molecular solubilization, singlet oxygen production, and retention of a photosensitizer loaded in thermosensitive polymeric micelles. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2014, 3, 2023–2031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamay, Y.; Shah, J.; Işık, M.; Mizrachi, A.; Leibold, J.; Tschaharganeh, D.F.; Roxbury, D.; Budhathoki-Uprety, J.; Nawaly, K.; Sugarman, J.L.; et al. Quantitative self-assembly prediction yields targeted nanomedicines. Nat. Mater. 2018, 17, 361–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, Q.; Wang, Z.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, M.; Deng, W.; Wei, X.; Xiao, J.; Duan, X. Eradication of Large Tumors by Nanoscale Drug Self-Assembly. Adv. Mater. 2024, 36, 2410536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, H.; Wang, W.; Li, X.; Han, X.; Zhang, X.; Wang, J.; Liu, C.; Huang, L.; Gao, W. Natural small molecules enabled efficient immunotherapy through supramolecular self-assembly in P53-mutated colorectal cancer. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 2464–2477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mei, H.; Cai, S.; Huang, D.; Gao, H.; Cao, J.; He, B. Carrier-free nanodrugs with efficient drug delivery and release for cancer therapy: From intrinsic physicochemical properties to external modification. Bioact. Mater. 2022, 8, 220–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Wang, Y.; Kong, Z.; Zhang, X.; Sun, B.; Yu, H.; Chen, Q.; Luo, C.; Sun, J.; He, Z. Pure photosensitizer-driven nanoassembly with core-matched PEGylation for imaging-guided photodynamic therapy. Acta Pharm. Sinica B 2021, 11, 3636–3647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, W.; Shi, N.; Li, W.; Bi, J.; Feng, X.; Shi, N.; Zhu, W.; Xie, Z. Self-assembly and self-delivery of the pure nanodrug dihydroartemisinin for tumor therapy and mechanism analysis. Biomater. Sci. 2023, 11, 2478–2485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, B.; Niu, Z.; Hou, B.; Zhou, L.; Li, Y.; Yu, H. Enhancing Triple Negative Breast Cancer Immunotherapy by ICG-Templated Self-Assembly of Paclitaxel Nanoparticles. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 1906605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Ma, Q.; Sun, B.; Wang, Q.; Ding, Z.; Zhang, H.; Chu, X.; Liu, M.; Wang, Z.; et al. Carrier-Free, Dual-Functional Nanorods Via Self-Assembly Of Pure Drug Molecules For Synergistic Chemo-Photodynamic Therapy. Int. J. Nanomed. 2019, 14, 8665–8683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Li, M.; Sun, X.; Jia, H.; Liu, W. NIR-responsive cancer cytomembrane-cloaked carrier-free nanosystems for highly efficient and self-targeted tumor drug delivery. Biomaterials 2018, 159, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Ji, Y.; Tong, J. Triple stimuli-responsive supramolecular nanoassembly with mitochondrial targetability for chemophotothermal therapy. J. Control. Release Off. J. Control. Release Soc. 2020, 327, 35–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, M.; Zhang, X.; Yang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Tian, B.; Jie, J.; Zhang, X. Carrier-free functionalized multidrug nanorods for synergistic cancer therapy. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 8960–8967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.; Lei, L.; Cai, X.; Wei, H.; Yu, C.Y. Immunomodulatory Peptides for Tumor Treatment. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2024, e2400512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, W.; Liu, Y.; Chen, B.; Fan, L. Target prediction and potential application of dihydroartemisinin on hepatocarcinoma treatment. Naunyn-Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmacol. 2024, 397, 7711–7724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, S.; Li, G.; Zang, W.; Zhou, X.; Shi, K.; Zhai, Y. Pure drug nano-assemblies: A facile carrier-free nanoplatform for efficient cancer therapy. Acta Pharm. Sinica B 2022, 12, 92–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.; Sun, B.; Yeo, Y. Albumin-coated nanocrystals for carrier-free delivery of paclitaxel. J. Control. Release Off. J. Control. Release Soc. 2017, 263, 90–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, H.; Zhang, Q.; Xu, H.; Yan, Z. Effects of nanoparticle size on antitumor activity of 10-hydroxycamptothecin-conjugated gold nanoparticles: In vitro and in vivo studies. Int. J. Nanomed. 2016, 11, 929–940. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, H.Z.; Chen, W.H.; Wang, X.; Lei, Q.; Yin, W.N.; Wang, Y.; Zhuo, R.X.; Feng, J.; Zhang, X.Z. Virus-Surface-Mimicking Surface Clustering of AuNPs onto DNA-Entrapped Polymeric Nanoparticle for Enhanced Cellular Internalization and Nanocluster-Induced NIR Photothermal Therapy. Adv. Sci. 2015, 2, 1500108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marusyk, A.; Almendro, V.; Polyak, K. Intra-tumour heterogeneity: A looking glass for cancer? Nature reviews. Cancer 2012, 12, 323–334. [Google Scholar]
- Dhanyamraju, P.K. Drug resistance mechanisms in cancers: Execution of pro-survival strategies. J. Biomed. Res. 2024, 38, 95–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashyap, B.K.; Singh, V.V.; Solanki, M.K.; Kumar, A.; Ruokolainen, J.; Kesari, K.K. Smart Nanomaterials in Cancer Theranostics: Challenges and Opportunities. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 14290–14320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Chen, Q.; Xu, Q.; Wei, Z.; Shen, Y.; Wang, H.; Cai, H.; Gu, M.; Xiao, Y. Hierarchical Self-Assembly Molecular Building Blocks as Intelligent Nanoplatforms for Ovarian Cancer Theranostics. Adv. Sci. 2024, 11, e2309547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, Z.; Yang, M.; Feng, X.; Liao, H.; Zhang, Z.; Du, Y. Multifunctional Theranostic Nanoparticles for Enhanced Tumor Targeted Imaging and Synergistic FUS/Chemotherapy on Murine 4T1 Breast Cancer Cell. Int. J. Nanomed. 2022, 17, 2165–2187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, X.; Sun, J.; Wang, Y.; He, Z. Recent Advances in Platinum (IV) Complex-Based Delivery Systems to Improve Platinum (II) Anticancer Therapy. Med. Res. Rev. 2015, 35, 1268–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Liu, J.; Guo, M.; Zhou, H.; Jin, J.; Liu, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, C. Synergistic combination chemotherapy using carrier-free celastrol and doxorubicin nanocrystals for overcoming drug resistance. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 12639–12649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, Y.; Jia, C.; Zhang, X.; Liao, X.; Yang, B.; Cong, Y.; Pu, S.; Gao, C. Targeting drug delivery system for platinum(Ⅳ)-Based antitumor complexes. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 194, 112229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
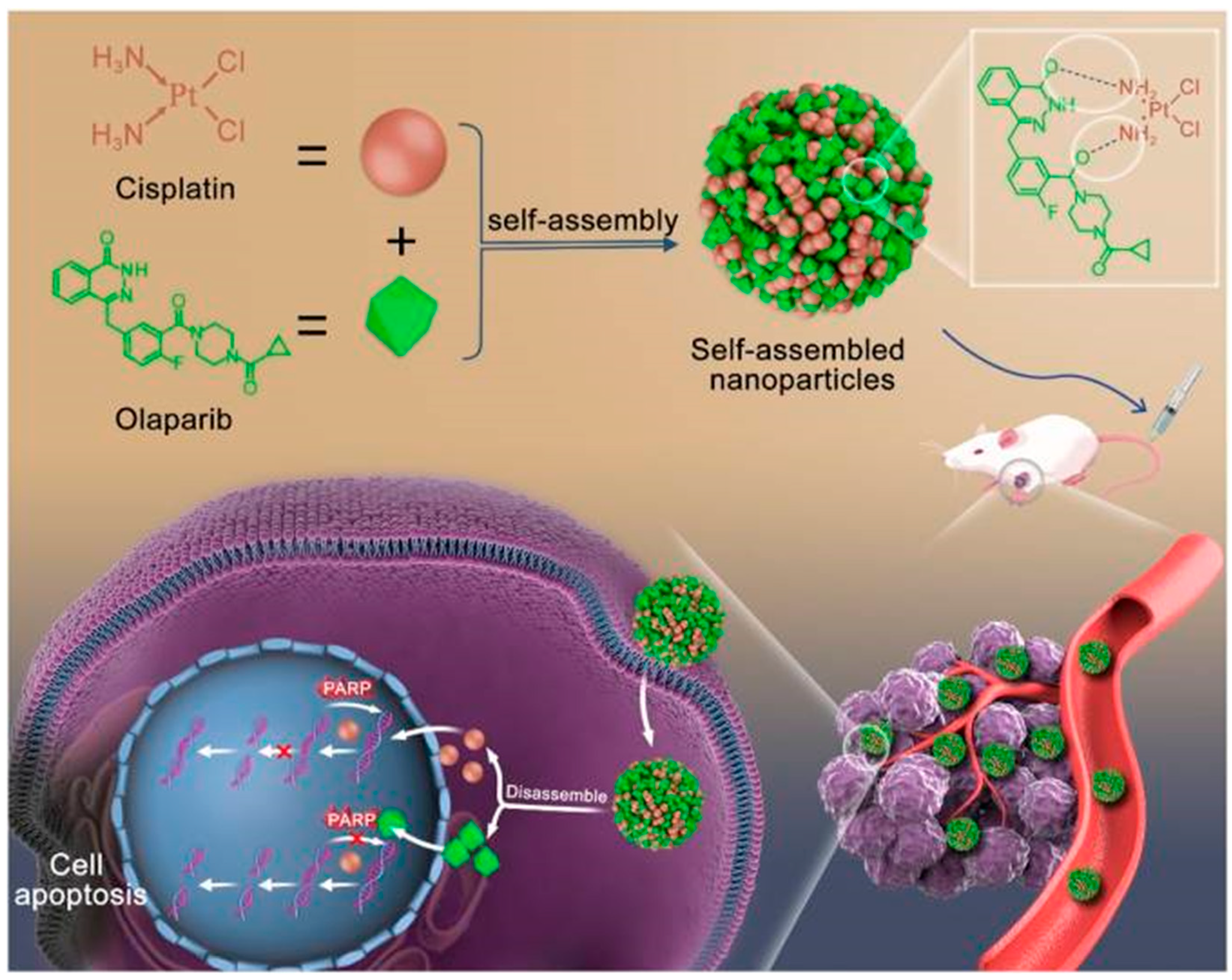
- Zhang, T.; Li, X.; Wu, L.; Su, Y.; Yang, J.; Zhu, X.; Li, G. Enhanced cisplatin chemotherapy sensitivity by self-assembled nanoparticles with Olaparib. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2024, 12, 1364975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Cheng, Y.; Li, D.; An, Q.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Fu, Y. Antitumor Applications of Photothermal Agents and Photothermal Synergistic Therapies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 7909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, Q.; Abbas, M.; Zhao, L.; Li, S.; Shen, G.; Yan, X. Biological Photothermal Nanodots Based on Self-Assembly of Peptide-Porphyrin Conjugates for Antitumor Therapy. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 1921–1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Song, M.; Jiang, G.; Liang, M.; Chen, C.; Yang, Z.; Zou, L. Progress in advanced nanotherapeutics for enhanced photodynamic immunotherapy of tumor. Theranostics 2022, 12, 5272–5298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Gong, Q.; Jiao, L.; Hao, E. Research advances in BODIPY-assembled supramolecular photosensitizers for photodynamic therapy. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2023, 496, 215367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.-K.; Zheng, J.; Wang, H.; Niu, L.-Y.; Yang, Q.-Z. BODIPY-based photosensitizers with simultaneous photodynamic antitumor and antibacterial effects. Mater. Chem. Front. 2023, 7, 5879–5890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, C.; Chen, X. Combined Photodynamic and Photothermal Therapy and Immunotherapy for Cancer Treatment: A Review. Int. J. Nanomed. 2022, 17, 6427–6446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Xiong, J.; Wang, K.; Yu, H.; Sun, B.; Ye, H.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, N.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, S.; et al. Erythrocyte membrane-camouflaged carrier-free nanoassembly of FRET photosensitizer pairs with high therapeutic efficiency and high security for programmed cancer synergistic phototherapy. Bioact. Mater. 2021, 6, 2291–2302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shan, X.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, C.; Sun, J.; He, Z.; Luo, C.; Zhang, S. Emerging Prodrug-Engineered nanomedicines for synergistic Chemo-Phototherapy. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 442, 136383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, B.; Peng, X.; Cheng, J.; Wang, J. Natural gambogic acid-tuned self-assembly of nanodrugs towards synergistic chemophototherapy against breast cancer. J. Mater. Chem. B 2024, 12, 5940–5949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
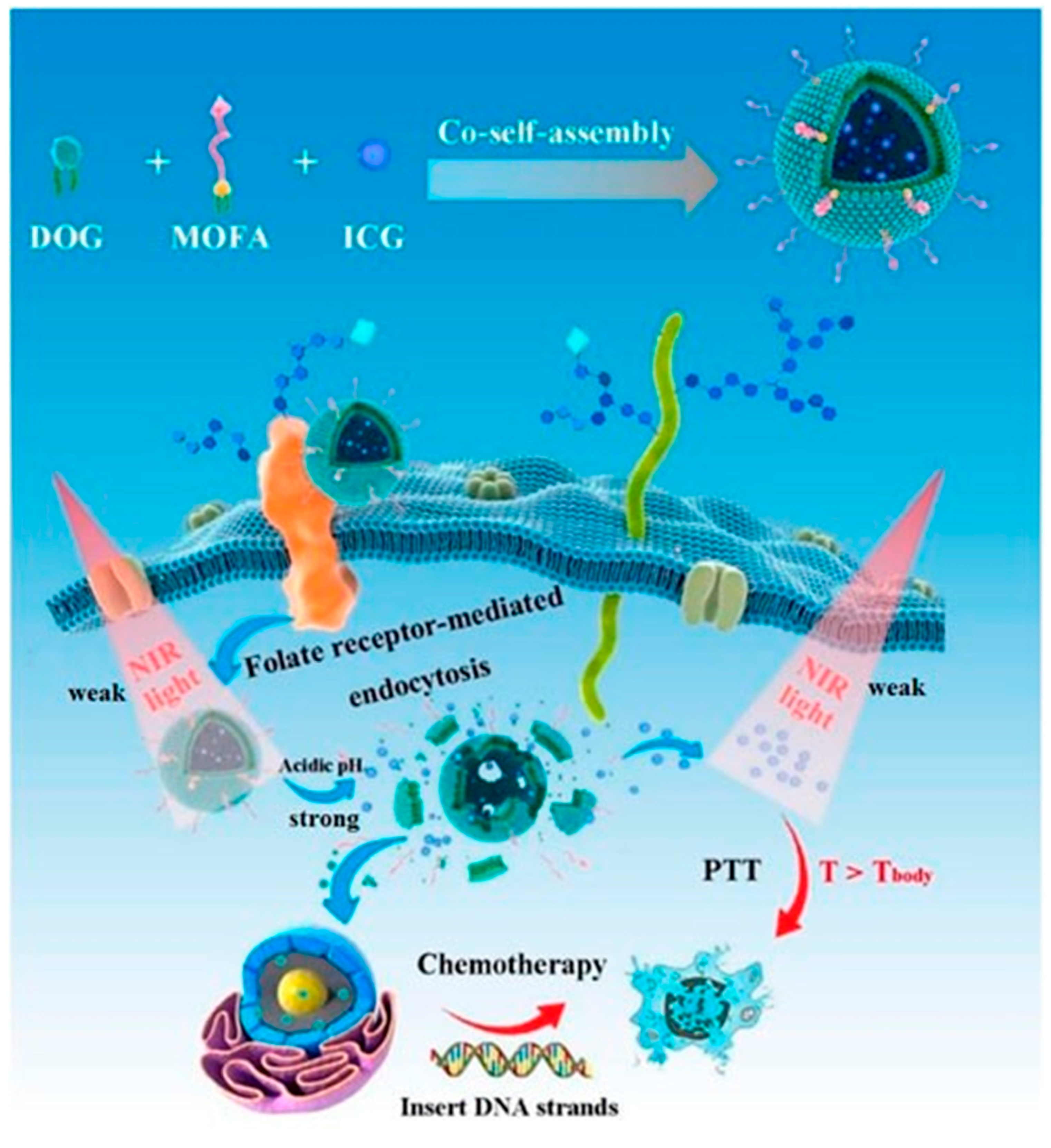
- Kuang, S.; Liu, S.; Wang, S.; Yang, L.; Zeng, Y.; Ming, X. Folate-receptor-targeted co-self-assembly carrier-free gemcitabine nanoparticles loading indocyanine green for chemo-photothermal therapy. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2023, 11, 1266652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Jiao, D.; Feng, D.; Liu, Q.; Huang, Y.; Hou, J.; Ding, D.; Zhang, W. Transformable Supramolecular Self-Assembled Peptides for Cascade Self-Enhanced Ferroptosis Primed Cancer Immunotherapy. Adv. Mater. 2024, 36, 2311733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vincent, M.P.; Navidzadeh, J.O.; Bobbala, S.; Scott, E.A. Leveraging self-assembled nanobiomaterials for improved cancer immunotherapy. Cancer Cell 2022, 40, 255–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valerio, T.I.; Furrer, C.L.; Sadeghipour, N.; Patrock, S.-J.X.; Tillery, S.A.; Hoover, A.R.; Liu, K.; Chen, W.R. Immune modulations of the tumor microenvironment in response to phototherapy. J. Innov. Opt. Health Sci. 2023, 16, 2330007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mai, Z.; Zhong, J.; Zhang, J.; Chen, G.; Tang, Y.; Ma, W.; Li, G.; Feng, Z.; Li, F.; Liang, X.-J. Carrier-free immunotherapeutic nano-booster with dual synergistic effects based on glutaminase inhibition combined with photodynamic therapy. ACS Nano 2023, 17, 1583–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Xie, L.; Li, X.; Wang, L.; Yang, Z. Chemo-immunotherapy by dual-enzyme responsive peptide self-assembling abolish melanoma. Bioact. Mater. 2024, 31, 549–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Gong, Z.; Liu, X.; Meng, F.; Sun, X.; Yuan, X.; Li, A.; Huang, H.; Wang, Y.; Lu, C. Stepwise targeting and tandem responsive peptide nanoparticles enhance immunotherapy through prolonged drug retention. ACS Mater. Lett. 2023, 5, 2604–2613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Tan, M.; Wang, Y.; Liu, X.; Lin, A. Advances in modification and delivery of nucleic acid drugs. Zhejiang Da Xue Xue Bao. Yi Xue Ban=J. Zhejiang Univ. Med. Sci. 2023, 52, 417–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, B.; Ma, Y.; Deng, B.; Xiao, P.; Huang, P.; Wang, D.; Liu, L. Tumor microenvironment-responsive spherical nucleic acid nanoparticles for enhanced chemo-immunotherapy. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2023, 21, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zang, W.; Mi, Z.; Li, J.; Wang, L.; Xie, D.; Zhao, L.; Wang, D. Tailoring carrier-free nanocombo of small-molecule prodrug for combinational cancer therapy. J. Control. Release Off. J. Control. Release Soc. 2022, 352, 256–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]








| Advantages | Disadvantages | |
|---|---|---|
| Nanocarrier delivery system |
|
|
| PDANS |
|
|
| Types | Drug 1 | Drug 2 | Drug 3 | Drug Loading | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Single pure drug nano-assemblies | Pyropheophorbide a | - | - | 74.8% | [41] |
| Dihydroartemisinin | - | - | >92% | [42] | |
| Dual pure drug nano-assemblies | Indocyanine green | Paclitaxel | - | ≈100% | [43] |
| 10-Hydroxycamptothecin | Chlorin e6 | - | - | [44] | |
| Indocyanine green | Doxorubicin | - | 89.8% | [45] | |
| Multi-pure drug nano-assemblies | Indocyanine green | Berberine | Camptothecin | - | [46] |
| 10-Hydroxycamptothecin | Methotrexate | Paclitaxel | 100% | [47] |
| Trade Name | Nanotechnology Platform | Cancer Type | First Approval |
|---|---|---|---|
| Doxil | PEGylated Doxorubicin Liposomes | Ovarian Cancer, Kaposi’s Sarcoma, Breast Cancer, Multiple Myeloma | USA |
| DaunoXome | Doxorubicin Liposome | Kaposi’s Sarcoma | USA |
| Marqibo | Vincristine Liposomal | Leukemia | USA |
| Myocet | Doxorubicin Liposome | Breast Cancer | Europe |
| MEPACT | Muramyl Tripeptide Phosphatidylethanolamine Liposomes | Osteosarcoma | Europe |
| SMANCS | Polymer-based Novel Anticancer Drug Conjugates | Hepatocellular Carcinoma, Renal cell Carcinoma | Japan |
| Genexol-PM | Paclitaxel Micelles | Breast Cancer, Small-Cell Lung Cancer | Korea |
| Lipusu | Paclitaxel Liposome | Breast Cancer, Lung Cancer, Ovarian Cancer | China |
| DepoCyt | Cytarabine Liposome | Lymphoma Meningitis | USA |
| Abraxane | Albumin-bound Paclitaxel Nanoparticles | Multiple Cancers, Metastatic Pancreatic Cancer | USA |
| Oncaspar | Polymer–Protein Conjugate | Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia | USA |
| Eligard | Leuprorelin Acetate Polymer | Prostate Cancer | USA |
| Ontak | Leuprorelin Acetate Polymer | Cutaneous T-Cell Lymphoma | USA |
| Vyxeos | Cytarabine and Daunorubicin Liposomes | Acute Myeloid Leukemia | USA |
| Nano-therm | Iron Oxide Nanoparticles | Glioblastoma | USA |
| Onivyde | Irinotecan Liposome | Pancreatic Cancer | USA |
| Nanoxel | Paclitaxel Polymeric Micelles | Multiple Cancers | India |
| Paclical | Paclitaxel Micelles | Ovarian Cancer, Fallopian Tube Carcinoma, Peritoneal Cancer | Russia |
| Hensify | Hafnium Oxide Nanoparticles | Soft-Tissue Sarcoma | Europe |
| Liporaxel | Paclitaxel Liposome | Gastric Cancer | Korea |
| PICN | PICN | Breast Cancer | India |
| Duoenda | Mitoxantrone Liposome | Peripheral T-Cell Lymphoma | China |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Niu, R.; Liu, X.; Yang, X.; Du, X.; Wang, S.; Ma, X.; Yin, S.; Shao, L.; Zhang, J. Advances in Pure Drug Self-Assembled Nanosystems: A Novel Strategy for Combined Cancer Therapy. Pharmaceutics 2025, 17, 68. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17010068
Niu R, Liu X, Yang X, Du X, Wang S, Ma X, Yin S, Shao L, Zhang J. Advances in Pure Drug Self-Assembled Nanosystems: A Novel Strategy for Combined Cancer Therapy. Pharmaceutics. 2025; 17(1):68. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17010068
Chicago/Turabian StyleNiu, Runyan, Xuexue Liu, Xian Yang, Xiao Du, Siliang Wang, Xiaolong Ma, Shaoping Yin, Lihua Shao, and Jinping Zhang. 2025. "Advances in Pure Drug Self-Assembled Nanosystems: A Novel Strategy for Combined Cancer Therapy" Pharmaceutics 17, no. 1: 68. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17010068
APA StyleNiu, R., Liu, X., Yang, X., Du, X., Wang, S., Ma, X., Yin, S., Shao, L., & Zhang, J. (2025). Advances in Pure Drug Self-Assembled Nanosystems: A Novel Strategy for Combined Cancer Therapy. Pharmaceutics, 17(1), 68. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17010068







