Revealing Three-Dimensional Printing Technology Advances for Oral Drug Delivery: Application to Central-Nervous-System-Related Diseases
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Context
1.2. Global Market for Personalized Neurological Drugs via 3D Printing
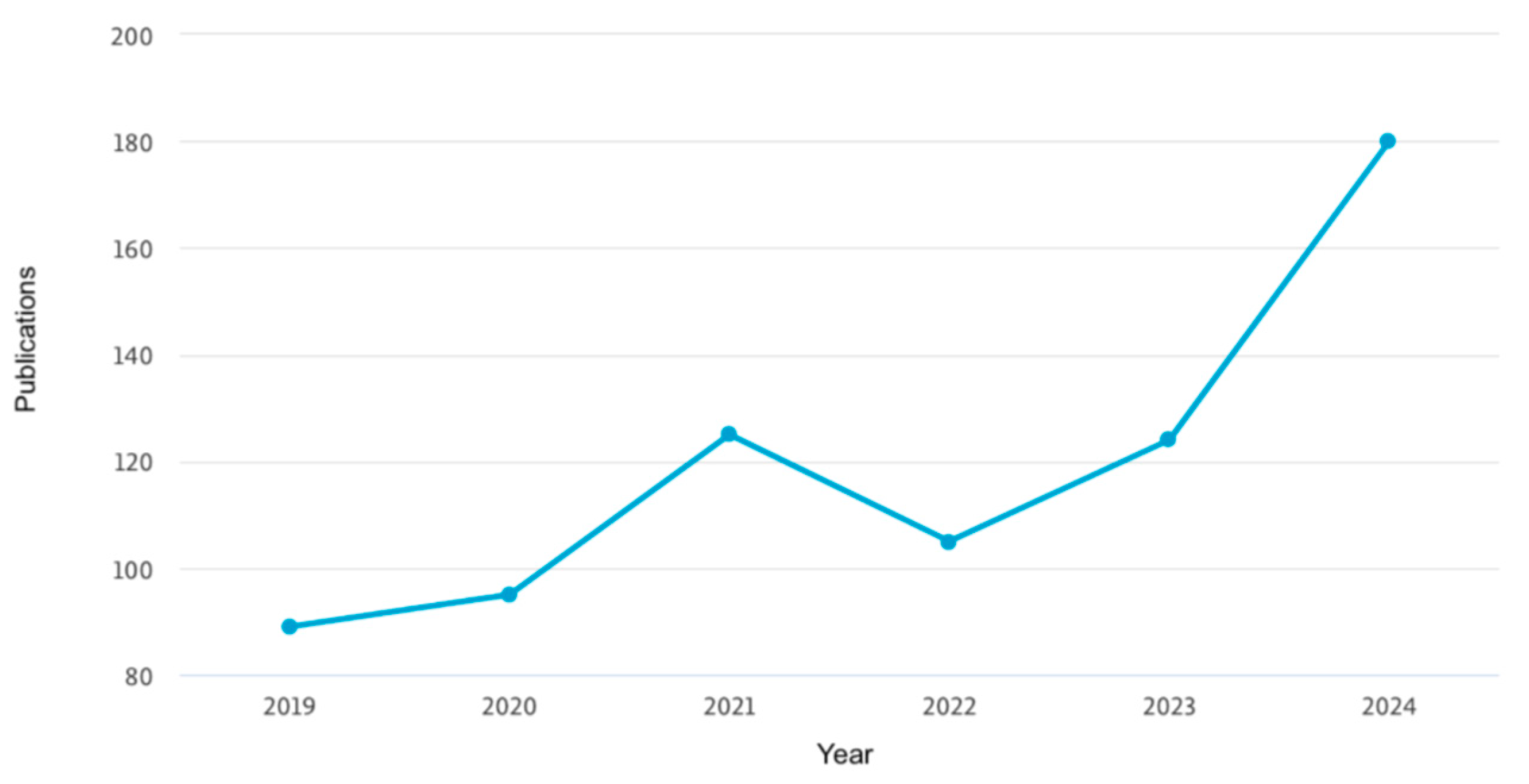
2. Methodology
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Three-Dimensional Printing Techniques for Central Nervous System (CNS) Oral Drugs
3.1.1. Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) Technique
3.1.2. Semi-Solid Extrusion (SSE) Technique
3.1.3. Stereolithography (SLA) and Digital Light Processing (DLP) Techniques
3.1.4. Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) Technique
3.1.5. Binder Jetting (BJ) Technique
3.2. Characteristics and Applications
3.3. Printing Materials
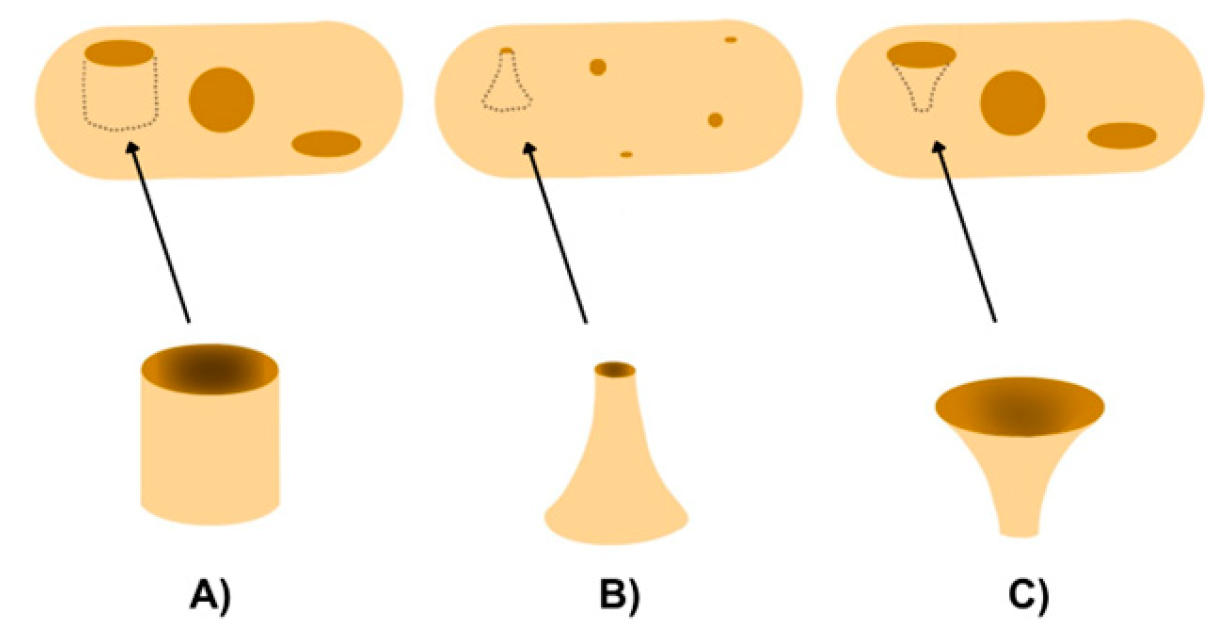
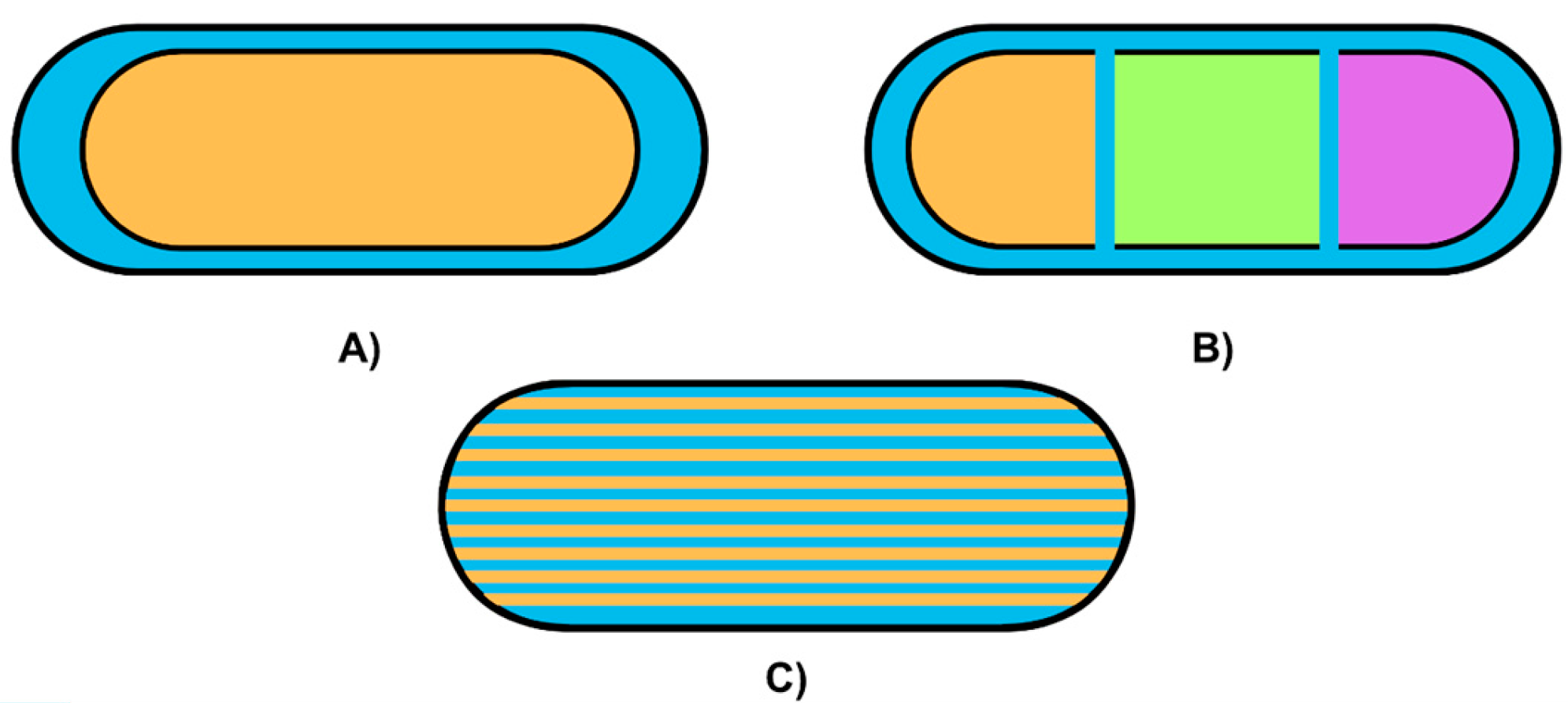
3.4. Design Factors
3.5. User Acceptance
3.6. Quality Processes
3.7. Regulatory Context
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Meaning | Abbreviations | Meaning | Abbreviations |
| Central Nervous System | CNS | World Health Organization | WHO |
| Active Pharmaceutical Ingredient | API | Competitive Technology Intelligence | CTI |
| Fused Deposition Modeling | FDM | Semi-Solid Extrusion | SSE |
| Stereolithography | SLA | Digital Light Processing | DLP |
| Selective Laser Sintering | SLS | Binder Jetting | BJ |
| Neurological Drug Administration Systems | NDDS | Oral Dispersible Films | ODF |
| Web of Science | WoS | Computer-Aided Design | CAD |
| Attention Deficit Hyperactive Disorder | ADHD | Polylactic Acid | PLA |
| Polyvinyl Alcohol | PVA | Polycaprolactone | PCL |
| Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene | ABS | High-Impact Polystyrene | HIPS |
| Pressure-Assisted Micro Syringes | PAM | Ultraviolet | UV |
| Hot Melt Extrusion | HME | Center for Drug Evaluation and Research | CDER |
| Chemistry Manufacturing, and Controls | CMC | Good Manufacturing Practices | GMP |
| International Organization for Standardization | ISO | American National Standards Institute | ANSI |
| European Medicines Agency | EMA | International Council for Harmonization | ICH |
References
- Ghomi, E.R.; Khosravi, F.; Neisiany, R.E.; Singh, S.; Ramakrishna, S. Future of additive manufacturing in healthcare. Curr. Opin. Biomed. Eng. 2021, 17, 100255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinze, A.; Basulto-Martinez, M.; Suárez-Ibarrola, R. Impresión 3D y sus beneficios en el campo de la educación médica, entrenamiento y asesoría del paciente. Rev. Esp. Educ. Médica 2020, 1, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, V.R.; Saha, T.; Giri, B.R.; Lu, A.; Das, S.H.; Maniruzzaman, M. Recent advancements in pharmaceutical 3D printing industry. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2024, 100, 106072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohapatra, S.; Kar, R.K.; Biswal, P.K.; Bindhani, S. Approaches of 3D printing in current drug delivery. Sens. Int. 2022, 3, 100146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huanbutta, K.; Burapapadh, K.; Sriamornsak, P.; Sangnim, T. Practical Application of 3D Printing for Pharmaceuticals in Hospitals and Pharmacies. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 1877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bg, P.K.; Mehrotra, S.; Marques, S.M.; Kumar, L.; Verma, R. 3D Printing in Personalized Medicines: A Focus on Applications of the Technology. Mater. Today Commun. 2023, 35, 105875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goh, O.; Goh, W.J.; Lim, S.H.; Hoo, G.S.; Liew, R.; Ng, T.M. Preferences of Healthcare Professionals on 3D-Printed Tablets: A Pilot Study. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinmetz, J.D.; Seeher, K.M.; Schiess, N.; Nichols, E.; Cao, B.; Servili, C.; Cavallera, V.; Cousin, E.; Hagins, H.; E Moberg, M.; et al. Global, regional, and national burden of disorders affecting the nervous system, 1990–2021: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021. Lancet Neurol 2024, 23, 344–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grisold, W. The expanding burden of neurological disorders. Lancet Neurol. 2024, 23, 326–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Kaur, H.; Kumari, A.; Hooda, G.; Garg, V.; Dureja, H. Drug delivery and testing via 3D printing. Bioprinting 2023, 36, e00298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Müllertz, A.; Rantanen, J. Additive Manufacturing of Solid Products for Oral Drug Delivery Using Binder Jetting Three-Dimensional Printing. AAPS PharmSciTech 2022, 23, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiménez, M.; Romero, L.; Domínguez, I.A.; Espinosa, M.D.M.; Domínguez, M. Additive manufacturing technologies: An overview about 3D printing methods and future prospects. Complexity 2019, 2019, 9656938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, C.V.; Venkatesh, M.P.; Kumar, P. First FDA approved 3D printed drug paved new path for increased precision in patient care. Appl. Clin. Res. Clin. Trials Regul. Aff. 2020, 7, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueiredo, S.; Fernandes, A.I.; Carvalho, F.G.; Pinto, J.F. Performance and paroxetine stability in tablets manufactured by fused deposition modelling-based 3D printing. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2022, 74, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandari, S.; Nyavanandi, D.; Dumpa, N.; Repka, M. Coupling Hot Melt Extrusion and Fused Deposition Modeling: Critical Properties for Successful Performance. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2021, 172, 52–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saviano, M. Design and Production of Personalized Medicines via Innovative 3D Printing Technologies. Ph.D. Thesis, Università Degli Studi di Salerno, Fisciano, Italy, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seoane-Viaño, I.; Trenfield, S.J.; Basit, A.W.; Goyanes, A. Translating 3D printed pharmaceuticals: From hype to real-world clinical applications. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2021, 174, 553–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, M.H.; Honnekeri, A.S.; Samat, D.A.; Shah, P.; Nayak, U.V.; Kini, S.G. Digging deep: Medication adherence in chronic diseases and its association with patient satisfaction and stress in an Indian metropolis. Cureus 2023, 15, e46493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rios-Mata, V.L.; Rodriguez-Salvador, M.; An, J. Uncovering advances in final end- user applications, user acceptability, quality assurance, and digital technologies for 3D-printed oral drug delivery systems. Int. J. Bioprint. 2023, 9, 1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancilla-De-la-Cruz, J.; Rodriguez-Salvador, M.; An, J.; Chua, C.K. Three-dimensional printing technologies for drug delivery applications: Processes, materials, and effects. Int. J. Bioprint. 2022, 8, 622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Salvador, M.; Castillo-Valdez, P.F. Integrating science and technology metrics into a competitive technology intelligence methodology. J. Intell. Stud. Bus. 2021, 11, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, M.; Wahab, A.; Khan, S.U.; Naeem, M.; Rehman, K.; Ali, H. 3D printing technology: A new approach for the fabrication of personalized and customized pharmaceuticals. Eur. Polym. J. 2023, 195, 112240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.; Wang, L. Economic growth effects of public health expenditure in OECD countries: An empirical study using the dynamic panel threshold model. Heliyon 2024, 10, e25684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Englezos, K.; Wang, L.; Tan, E.C.; Kang, L. 3D printing for personalised medicines: Implications for policy and practice. Int. J. Pharm. 2023, 635, 122785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Five Companies Personalizing Treatments with 3D Printed Drugs. Available online: https://www.labiotech.eu/best-biotech/five-companies-personalizing-treatments-with-3d-printed-drugs/ (accessed on 25 March 2024).
- Mohammed, A.A.; Algahtani, M.S.; Ahmad, M.Z.; Ahmad, J.; Kotta, S. 3D Printing in medicine: Technology overview and drug delivery applications. Ann. 3D Print. Med. 2021, 4, 100037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, J.; Garg, A.; Mustafa, G.; Mohammed, A.A.; Ahmad, M.Z. 3D printing technology as a promising tool to design nanomedicine-based solid dosage forms: Contemporary research and future scope. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bordianu Bolganschi, D.A. La Impresión 3D Como Nuevo Modelo de Producción. Bachelor Thesis, Universidad de Valladolid, Valladolid, Spain, 2023. Available online: https://uvadoc.uva.es/handle/10324/61465 (accessed on 17 March 2024).
- Chakit, M. Scopus Sources Title List July 2024; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Windolf, H.; Chamberlain, R.; Breitkreutz, J.; Quodbach, J. 3D printed mini-floating-Polypill for Parkinson’s disease: Combination of levodopa, benserazide, and pramipexole in various dosing for personalized therapy. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ElEleftheriadis, G.K.; Kantarelis, E.; Monou, P.K.; Andriotis, E.G.; Bouropoulos, N.; Tzimtzimis, E.K.; Tzetzis, D.; Rantanen, J.; Fatouros, D.G. Automated digital design for 3D-printed individualized therapies. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 599, 120437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uziel, A.; Shpigel, T.; Goldin, N.; Lewitus, D.Y. Three-Dimensional Printing for Drug Delivery Devices: A State-of-the-Art Survey. J. 3D Print. Med. 2019, 3, 95–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, H.; Lin, Q.; Wang, D.; Sun, X.; Quan, B.; Chen, X.; Chen, Z. 3D Printed Integrated Multi-Layer Microfluidic Chips for Ultra-High Volumetric Throughput Nanoliposome Preparation. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2021, 9, 773705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saydam, M.; Takka, S. Improving the dissolution of a water-insoluble orphan drug through a fused deposition modelling 3-dimensional printing technology approach. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2020, 152, 105426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-H.; Park, C.; Song, I.-O.; Lee, B.-J.; Kang, C.-Y.; Park, J.-B. Investigation of patient-centric 3D-Printed orodispersible films containing amorphous aripiprazole. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, B.-C.; Jin, G.; Park, C.; Park, J.-B.; Lee, B.-J. Preparation and evaluation of identifiable quick response (QR)-coded orodispersible films using 3D printer with directly feeding nozzle. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 584, 119405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Łyszczarz, E.; Brniak, W.; Szafraniec-Szczęsny, J.; Majka, T.M.; Majda, D.; Zych, M.; Pielichowski, K.; Jachowicz, R. The impact of the preparation method on the properties of orodispersible films with Aripiprazole: Electrospinning vs. Casting and 3D printing methods. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatt, U.; Malakar, T.K.; Murty, U.S.; Banerjee, S. 3D printing of immediate-release tablets containing olanzapine by filaments extrusion. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2021, 47, 1200–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabriz, A.G.; Mithu, S.; Antonijevic, M.D.; Vilain, L.; Derrar, Y.; Grau, C.; Morales, A.; Katsamenis, O.L.; Douroumis, D. 3D printing of LEGO® like designs with tailored release profiles for treatment of sleep disorder. Int. J. Pharm. 2023, 632, 122574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Wei, W.; Niu, R.; Li, Q.; Hu, C.; Jiang, S. 3D printed intragastric floating and sustained-release tablets with air chambers. J. Pharm. Sci. 2022, 111, 116–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaiwarit, T.; Aodsab, N.; Promyos, P.; Panraksa, P.; Udomsom, S.; Jantrawut, P. Fabrication of Hydroxypropyl methylcellulose orodispersible film loaded mirtazapine using a syringe extrusion 3D printer. Sci. Pharm. 2022, 90, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gkaragkounis, A.; Fatouros, D.G. Semi-solid Extrusion 3D Printing for the Development of Dosage Forms for Special Patient Groups. Nano-Microfab. Tech. Drug Deliv. 2023, 1, 125–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, M.; Pan, H.; Fang, D.; Qiao, S.; Wang, S.; Pan, W. Fabrication of high drug loading levetiracetam tablets using semi-solid extrusion 3D printing. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Tech. 2020, 57, 101683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conceição, J.; Farto-Vaamonde, X.; Goyanes, A.; Adeoye, O.; Concheiro, A.; Cabral-Marques, H.; Lobo, J.M.S.; Alvarez-Lorenzo, C. Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin-based fast dissolving carbamazepine printlets prepared by semisolid extrusion 3D printing. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 221, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Fitaihi, R.; Abukhamees, S.; Abdelhakim, H.E. Formulation and characterisation of carbamazepine orodispersible 3D-Printed mini-tablets for paediatric use. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, X.; Han, X.; Li, X.; Li, J.; Wang, Z.; Zheng, A. Binder jet 3D printing of compound LEV-PN dispersible tablets: An innovative approach for Fabricating drug systems with multicompartmental structures. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamichhane, S.; Park, J.-B.; Sohn, D.H.; Lee, S. Customized novel design of 3D printed Pregabalin tablets for intra-gastric floating and controlled release using fused deposition modeling. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henry, S.; De Vadder, L.; Decorte, M.; Francia, S.; Van Steenkiste, M.; Saevels, J.; Vanhoorne, V.; Vervaet, C. Development of a 3D-Printed dosing platform to aid in zolpidem withdrawal therapy. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamov, I.; Stanojević, G.; Medarević, D.; Ivković, B.; Kočović, D.; Mirković, D.; Ibrić, S. Formulation and characterization of immediate-release oral dosage forms with zolpidem tartrate fabricated by digital light processing (DLP) 3D printing technique. Int. J. Pharm. 2022, 624, 122046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, H.-W.; Baek, S.-H.; Lee, B.-J.; Jin, H.-E. Orodispersible polymer films with the poorly water-soluble drug, olanzapine: Hot-melt pneumatic extrusion for single-process 3D printing. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Windolf, H.; Chamberlain, R.; Quodbach, J. Dose-independent drug release from 3D printed oral medicines for patient-specific dosing to improve therapy safety. Int. J. Pharm. 2022, 616, 121555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, D.M.; Della Rocca, J. Clinical Applications of 3D Printed Drug Products. Emerg. Technol. Funct. Polym. Excip. Drug Prod. Dev. 2023, 1, 29–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Xu, P.J.; Bandari, S.; Repka, M.A. Development of controlled release oral dosages by density gradient modification via three-dimensional (3D) printing and hot-melt extrusion (HME) technology. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Tech. 2022, 71, 103355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, M.; Choudhury, H.; Fern, J.L.C.; Kee, A.T.K.; Kou, J.; Jing, J.L.J.; Her, H.C.; Yong, H.S.; Ming, H.C.; Bhattamisra, S.K.; et al. 3D printing for oral drug delivery: A new tool to customize drug delivery. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2020, 10, 986–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomczak, D.; Wichniarek, R.; Kuczko, W. Caffeine–Acrylic Resin DLP-Manufactured Composite as a Modern Biomaterial. Designs 2023, 7, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robles-Martinez, P.; Xu, X.; Trenfield, S.J.; Awad, A.; Goyanes, A.; Telford, R.; Basit, A.W.; Gaisford, S. 3D printing of a multi-layered polypill containing six drugs using a novel stereolithographic method. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wojtyłko, M.; Lamprou, D.A.; Froelich, A.; Kuczko, W.; Wichniarek, R.; Osmałek, T. 3D-printed solid oral dosage forms for mental and neurological disorders: Recent advances and future perspectives. Expert. Opin. Drug Deliv. 2023, 21, 1523–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, G.; Kushwaha, A.; Sharma, M. Ultra-trace detection of caffeine and theophylline with high sensitivity and selectivity using Gd2 (MoO4) 3 nanosheets. Mater. Today Commun. 2022, 31, 103390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Đuranović, M.; Obeid, S.; Madžarević, M.; Cvijić, S.; Ibrić, S. Paracetamol extended release FDM 3D printlets: Evaluation of formulation variables on printability and drug release. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 592, 120053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SShuklinova, O.; Wyszogrodzka-Gaweł, G.; Baran, E.; Lisowski, B.; Wiśniowska, B.; Dorożyński, P.; Kulinowski, P.; Polak, S. Can 3D Printed Tablets Be Bioequivalent and How to Test It: A PBPK Model Based Virtual Bioequivalence Study for Ropinirole Modified Release Tablets. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suhail, M.; Chiu, I.H.; Lai, Y.R.; Khan, A.; Al-Sowayan, N.S.; Ullah, H.; Wu, P.C. Xanthan-Gum/Pluronic-F-127-based-drug-loaded polymeric hydrogels synthesized by free radical polymerization technique for management of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Gels 2023, 9, 640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awad, A.; Fina, F.; Goyanes, A.; Gaisford, S.; Basit, A.W. 3D printing: Principles and pharmaceutical applications of selective laser sintering. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 586, 119594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Thakkar, R.; Zhang, J.; Lu, A.; Duggal, I.; Pillai, A.; Wang, J.; Aghda, N.H.; Maniruzzaman, M. Investigating the use of magnetic nanoparticles as alternative sintering agents in selective laser sintering (SLS) 3D printing of oral tablets. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2023, 9, 2924–2936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulinowski, P.; Malczewski, P.; Pesta, E.; Łaszcz, M.; Mendyk, A.; Polak, S.; Dorożyńsk, P. Selective laser sintering (SLS) technique for pharmaceutical applications—Development of high dose controlled release printlets. Addit. Manuf. 2021, 38, 101761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakkar, R.; Jara, M.O.; Swinnea, S.; Pillai, A.R.; Maniruzzaman, M. Impact of laser speed and drug particle size on selective laser sintering 3D printing of amorphous solid dispersions. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trenfield, S.J.; Xu, X.; Goyanes, A.; Rowland, M.; Wilsdon, D.; Gaisford, S.; Basit, A. Releasing fast and slow: Non-destructive prediction of density and drug release from SLS 3D printed tablets using NIR spectroscopy. Int. J. Pharm. 2023, 5, 100148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seoane-Viaño, I.; Pérez-Ramos, T.; Liu, J.; Januskaite, P.; Guerra-Baamonde, E.; González-Ramírez, J.; Vázquez-Caruncho, M.; Basit, A.W.; Goyanes, A. Visualizing disintegration of 3D printed tablets in humans using MRI and comparison with in vitro data. J. Controll. Rel 2024, 365, 348–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tabriz, A.G.; Nandi, U.; Scoutaris, N.; Sanfo, K.; Alexander, B.; Gong, Y.; Hui, H.-W.; Kumar, S.; Douroumis, D. Personalised paediatric chewable Ibuprofen tablets fabricated using 3D micro-extrusion printing technology. Int. J. Pharm. 2022, 626, 122135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, M.; Lopes, C.M.; Gonçalves, H.; Pinto, J.F.; Catita, J. Personalised Esomeprazole and Ondansetron 3D Printing Formulations in Hospital Paediatric Environment: I-Pre-Formulation Studies. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 10585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aprecia Pahrmaceuticals. Spritam. Available online: https://www.aprecia.com/ (accessed on 9 April 2024).
- Milliken, R.L.; Quinten, T.; Andersen, S.K.; Lamprou, D.A. Application of 3D printing in early phase development of pharmaceutical solid dosage forms. Int. J. Pharm. 2024, 21, 123902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gueche, Y.; Sanchez-Ballester, N.; Cailleaux, S.; Bataille, B.; Soulairol, I. Selective Laser Sintering (SLS), a New Chapter in the Production of Solid Oral Forms (SOFs) by 3D Printing. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, K.; West, T.G.; Chaudhuri, B. History and Present Scenario of Additive Manufacturing in Pharmaceuticals. In Additive Manufacturing in Pharmaceuticals; Springer: Singapore, 2023; pp. 1–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karami, T.; Ghobadi, E.; Akrami, M.; Haririan, I. Fabrication of a Controlled-Release Core-Shell Floating Tablet of Ketamine Hydrochloride Using a 3D Printing Technique for Management of Refractory Depressions and Chronic Pain. Polymers 2024, 16, 746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menditto, E.; Orlando, V.; De Rosa, G.; Minghetti, P.; Musazzi, U.M.; Cahir, C.; Kurczewska-Michalak, M.; Kardas, P.; Costa, E.; Lobo, J.M.S.; et al. Patient centric pharmaceutical drug product design—The impact on medication adherence. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulkhaleq, N.M.; Ghareeb, M.M. Combination of FDM 3D Printing and Compressed Tablet for Preparation of Baclofen as Gastro-Floating Drug Delivery System. J. Pharm. Sci. 2022, 1, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, C.; Kabra, A.; Thakur, N.; Kaur, B. 3D printing in drug delivery: Current trends and future prospects. AIP Conf Proc. 2023, 2535, 050004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Jangra, N.; Dheer, D.; Jha, S.K.; Gupta, G.; Puri, V.; Kesharwani, P. Understanding the journey of biopolymeric nanoformulations for oral drug delivery: Conventional to advanced treatment approaches. Eur. Polym. J. 2024, 218, 113338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hines, R.M.; Khumnark, M.; Macphail, B.; Hines, D.J. Administration of micronized caffeine using a novel oral delivery film results in rapid absorption and electroencephalogram suppression. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillay, V.; Adeyemi, S.A.; Kumar, P.; du Toit, L.C.; Choonara, Y.E. Three-Dimensional Printing (3DP) for Space Pharmaceuticals. In Handbook of Space Pharmaceuticals; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; Volume 1, pp. 221–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.J.N.; Yong, W.P.; Kochhar, J.S.; Khanolkar, J.; Yao, X.; Sun, Y.; Ao, C.K.; Soh, S. On-demand fully customizable drug tablets via 3D printing technology for personalized medicine. J. Control. Release 2020, 322, 42–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajput, A.; Pingale, P.; Telange, D.; Musale, S.; Chalikwar, S. A current era in pulsatile drug delivery system: Drug journey based on chronobiology. Heliyon 2024, 10, e29064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allahham, N.; Fina, F.; Marcuta, C.; Kraschew, L.; Mohr, W.; Gaisford, S.; Basit, A.W.; Goyanes, A. Selective laser sintering 3D printing of orally disintegrating printlets containing ondansetron. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, N.R.; Subburaj, K.; Sandhu, K.; Sharma, V. Applications of 3D printing in Biomedical Engineering; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salahuddin, B.; Wang, S.; Sangian, D.; Aziz, S.; Gu, Q. Hybrid gelatin hydrogels in nanomedicine applications. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2021, 4, 2886–2906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malekmohammadi, S.; Aminabad, N.S.; Sabzi, A.; Zarebkohan, A.; Razavi, M.; Vosough, M.; Bodaghi, M.; Maleki, H. Smart and biomimetic 3D and 4D printed composite hydrogels: Opportunities for different biomedical applications. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okafor-Muo, O.L.; Hassanin, H.; Kayyali, R.; ElShaer, A. 3D Printing of Solid Oral Dosage Forms: Numerous Challenges with Unique Opportunities. J. Pharm. Sci. 2020, 109, 3535–3550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Karp, J.M.; Langer, R.; Joshi, N. The future of drug delivery. Chem. Mater. 2023, 35, 359–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krueger, L.; Miles, J.A.; Popat, A. 3D Printing for Novel Dosage Form Design. In 3D & 4D Printing Methods for Pharmaceutical Manufacturing and Personalised Drug Delivery; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; Volume 11, pp. 25–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homaee Borujeni, S.; Mirdamadian, S.Z.; Varshosaz, J.; Taheri, A. Three-dimensional (3D) printed tablets using ethyl cellulose and hydroxypropyl cellulose to achieve zero order sustained release profile. Cellulose 2020, 27, 1573–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tagami, T.; Morimura, C.; Ozeki, T. Effective and simple prediction model of drug release from “ghost tablets” fabricated using a digital light projection-type 3D printer. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 604, 120721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Funk, N.L.; Fantaus, S.; Beck, R.C.R. Immediate release 3D printed oral dosage forms: How different polymers have been explored to reach suitable drug release behaviour. Int. J. Pharm. 2022, 625, 122066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panraksa, P.; Zhang, B.; Rachtanapun, P.; Jantanasakulwong, K.; Qi, S.; Jantrawut, P. ‘Tablet-in-syringe’: A novel dosing mechanism for dysphagic patients containing fast-disintegrating tablets fabricated using semisolid extrusion 3D printing. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Funk, N.L.; Leão, J.; de Oliveira, T.V.; Beck, R.C.R. Semi-Solid Extrusion (SSE) in Pharmaceuticals. In Additive Manufacturing in Pharmaceuticals; Springer: Singapore, 2023; pp. 171–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nizam, M.; Purohit, R.; Taufik, M. Extrusion based additive manufacturing of medicines. AIP Conf. Proc. 2024, 3007, 100046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enke, M.; Schwarz, N.; Gruschwitz, F.; Winkler, D.; Hanf, F.; Jescheck, L.; Seyferth, S.; Fischer, D.; Schneeberger, A. 3D screen printing technology enables fabrication of oral drug dosage forms with freely tailorable release profiles. Int. J. Pharm. 2023, 642, 123101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nashed, N.; Lam, M.; Ghafourian, T.; Pausas, L.; Jiri, M.; Majumder, M.; Nokhodchi, A. An insight into the impact of thermal process on dissolution profile and physical characteristics of theophylline tablets made through 3D printing compared to conventional methods. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rautamo, M.; Kvarnström, K.; Sivén, M.; Airaksinen, M.; Lahdenne, P.; Sandler, N. Benefits and prerequisites associated with the adoption of oral 3D-printed medicines for pediatric patients: A focus group study among healthcare professionals. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madžarević, M.; Ibrić, S. Evaluation of exposure time and visible light irradiation in LCD 3D printing of ibuprofen extended release tablets. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2021, 158, 105688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giri, B.R.; Maniruzzaman, M. Fabrication of sustained-release dosages using powder-based three-dimensional (3D) printing technology. AAPS PharmSciTech 2022, 24, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitzanti, G.; Mathew, E.; Andrews, G.P.; Jones, D.S.; Lamprou, D.A. 3D Printing: An appealing technology for the manufacturing of solid oral dosage forms. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2022, 74, 1427–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Windolf, H.; Chamberlain, R.; Quodbach, J. Predicting drug release from 3D printed oral medicines based on the surface area to volume ratio of tablet geometry. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goh, W.J.; Tan, S.X.; Pastorin, G.; Ho, P.C.L.; Hu, J.; Lim, S.H. 3D printing of four-in-one oral polypill with multiple release profiles for personalized delivery of caffeine and vitamin B analogues. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 598, 120360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, F.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, J. Synthetic Polymers for HME-Based 3D Printing. Tech. Func. Polym. 2023, 44, 79–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishnoi, M.; Mody, N.; Jain, A. Additive manufacturing strategies for personalized drug delivery systems and medical devices. Med. Addit. Manuf. 2024, 27, 619–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cailleaux, S.; Sanchez-Ballester, N.M.; Gueche, Y.A.; Bataille, B.; Soulairol, I. Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM), the new asset for the production of tailored medicines. J. Control. Release 2021, 330, 821–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ianno, V.; Vurpillot, S.; Prillieux, S.; Espeau, P. Pediatric Formulations Developed by Extrusion-Based 3D Printing: From Past Discoveries to Future Prospects. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gültekin, H.E.; Tuğcu Demiröz, F.; Tort, S.; Acartürk, F. Three-dimensional printed dosage forms based on disease-focussed perspectives. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2022, 74, 1406–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awad, A.; Januskaite, P.; Alkahtani, M.; Orlu, M.; Basit, A.W. 3D Printing: Advancements in the Development of Personalised Pharmaceuticals for Older Adults. Pharm. Formul. Older Patients 2023, 1, 157–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cervantes, J.; Espinosa, G.; Serrano, V. Design and 3D printing of signs with Braille system. In Proceedings of the 2023 VI Congreso Internacional en Inteligencia Ambiental, Ingeniería de Software y Salud Electrónica y Móvil, Cali, Colombia, 25–27 October 2023; Volume 1, pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Kumar, M.; Choudhary, D.; Chopra, S.; Bhatia, A. 3D printing technology in drug delivery: Polymer properties and applications. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 2023, 46, 361–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosley-Kellum, K.; Bagde, A.; Spencer, S.; Dev, S.; Singh, M. Development of 3D DLP Printed Sustained Release Ibuprofen Tablets and Their Pharmacokinetic Evaluation in Rats. AAPS PharmSciTech 2023, 24, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Triyono, J.; Sukanto, H.; Saputra, R.M.; Smaradhana, D.F. The effect of nozzle hole diameter of 3D printing on porosity and tensile strength parts using polylactic acid material. Open Eng. 2020, 10, 762–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matulyte, I.; Mataraite, A.; Velziene, S.; Bernatoniene, J. The Effect of Myristica fragrans on Texture Properties and Shelf-Life of Innovative Chewable Gel Tablets. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, L.; Breitkreutz, J.; Quodbach, J. Investigation of the degradation and in-situ amorphization of the enantiomeric drug escitalopram oxalate during Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) 3D printing. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2023, 185, 106423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eleftheriadis, G.K.; Fatouros, D.G. Haptic evaluation of 3D-printed braille-encoded intraoral films. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2021, 157, 105605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazur, H.; Erbrich, L.; Quodbach, J. Investigations into the use of machine learning to predict drug dosage form design to obtain desired release profiles for 3D printed oral medicines. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2023, 28, 219–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karavasili, C.; Gkaragkounis, A.; Moschakis, T.; Ritzoulis, C.; Fatouros, D.G. Pediatric-friendly chocolate-based dosage forms for the oral administration of both hydrophilic and lipophilic drugs fabricated with extrusion-based 3D printing. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2020, 147, 105291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roche, A.; Sanchez-Ballester, N.M.; Aubert, A.; Rossi, J.C.; Begu, S.; Soulairol, I. Preliminary Study on the Development of Caffeine Oral Solid Form 3D Printed by Semi-Solid Extrusion for Application in Neonates. AAPS PharmSciTech 2023, 24, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.; Tian, Y.; Zhang, E.; Gao, X.; Zhang, H.; Liu, N.; Han, X.; Sun, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zheng, A. Semisolid Extrusion 3D Printing of Propranolol Hydrochloride Gummy Chewable Tablets: An Innovative Approach to Prepare Personalized Medicine for Pediatrics. AAPS PharmSciTech 2022, 23, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Januskaite, P.; Xu, X.; Ranmal, S.R.; Gaisford, S.; Basit, A.W.; Tuleu, C.; Goyanes, A. I spy with my little eye: A paediatric visual preferences survey of 3D printed tablets. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yekeler, H.B.; Guler, E.; Beato, P.S.; Priya, S.; Abobakr, F.K.M.; Dogan, M.; Uner, B.; Kalaskar, D.M.; Cam, M.E. Design and in vitro evaluation of curcumin-loaded PLGA nanoparticle-embedded sodium alginate/gelatin 3D printed scaffolds for Alzheimer’s disease. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 268, 131841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayasil, M.P.; del Carmen, M.T.M.; Nuvia, P.C.; Ivette, D.M.; Anayda, A.H. Intoxicación por barbitúricos, una mirada toxicológica. Horiz. Sanit. 2020, 18, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Kumar, M.; Kumar, D.; Kumar, S.; Chopra, S.; Bhatia, A. Therapeutic Precision: Unveiling the Potential of 3D Printing in Drug Delivery, Tissue Engineering, and Regenerative Medicine. Print. Addi Manuf. 2024, 12, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, K.R.; Jami, M.M.; Shyeed, A.; Khatun, K.; Hasan, K.; Cobra, K.; Ahmed, F. Application of 3D printing in medicine: Technologies and challenges. Al-Bahir J. Eng. Pure Sci. 2023, 3, 7–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaity, S.; Sah, S.K.; Karanwad, T.; Banerjee, S. Bootstrap statistics and its application in disintegration and dissolution data analysis. Mol. Pharm. 2023, 20, 3791–3803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, S.; Joshi, U.; Singh, A.; Saharan, V.A. Lipids for Taste masking and Taste assessment in pharmaceutical formulations. Chem. Phys. Lipids 2021, 235, 105031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, A.M.; Bradley, A.M.; Taylor, K.L.; Kennedy, Z.C.; Omberg, K.M. The promise of emergent nanobiotechnologies for in vivo applications and implications for safety and security. Health Secur. 2022, 20, 408–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyousoufi, M.; Lafeber, I.; Kweekel, D.; de Winter, B.C.M.; Swen, J.J.; Le Brun, P.P.H.; Bijleveld-Olierook, E.C.M.; van Gelder, T.; Guchelaar, H.; Moes, D.J.A.R.; et al. Development and Bioequivalence of 3D-Printed Medication at the Point-of-Care: Bridging the Gap Toward Personalized Medicine. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2023, 113, 1125–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnan, A.V.; Lakshman, S.A.; Bhargav, A. 3D Printing and Regulatory Considerations. In 3D & 4D Printing Methods for Pharmaceutical Manufacturing and Personalised Drug Delivery: Opportunities and Challenges; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; Volume 11, pp. 45–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatami, M.; Doniavi, A.; Allahyari, S.; Feizollahi, M.; Abazari, A.M.; Fotouhi, M. Application of 3D printing in pharmaceutical sciences, and evaluation of administration routes for drug-loaded composites. Pharm. Sci. 2023, 29, 283–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]











| Category | Topic |
|---|---|
| 3D Printing Techniques | Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM). |
| Semi-Solid Extrusion (SSE). | |
| Stereolithography (SLA). | |
| Digital Light Processing (DLP). | |
| Selective Laser Sintering (SLS). | |
| Binder Jetting (BJ). | |
| Applications | Pills. |
| Polypills. | |
| Caplets. | |
| Gel Caps. | |
| Multitablets. | |
| Orodispersible Films. | |
| Tablets with one or more API(s). | |
| Materials | Polylactic Acid (PLA). |
| Polyvinyl Alcohol (PVA). | |
| Polycaprolactone (PCL). | |
| Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS). | |
| High-Impact Polystyrene (HIPS). | |
| Design Factors | Geometric Pattern for Drug Release Control. |
| Multi-Compartment Designs. | |
| Release Profiles. | |
| User Acceptance | Personalized Drug Dosages. |
| Customized Shapes and Textures. | |
| Improved Adherence. | |
| Quality Processes | Precision in API Dosage. |
| Biosafety and Regulations. | |
| FDA Approval for 3D-Printed Drugs. |
| 3D Printing Technique | API | Release Profile | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| FDM | Levodopa | Extended Release | [30] |
| Aripiprazole | Immediate Release | [35] | |
| Olanzapine | Immediate Release | [38] | |
| Pregabalin | Immediate Release | [47] | |
| Carbamazepine | Extended Release | [90] | |
| Levetiracetam | Immediate Release | [91] | |
| Theophylline | Immediate Release | [92] | |
| SSE | Levetiracetam | Immediate Release | [43] |
| Phenytoin | Immediate Release | [93] | |
| Gabapentin | Extended Release | [94] | |
| Mirtazapine | Immediate Release | [95] | |
| SLA | Paracetamol | Extended Release | [96] |
| Theophylline | Extended Release | [97] | |
| Methylphenidate | Extended Release | [98] | |
| Ibuprofen | Extended Release | [99] | |
| SLS | Levetiracetam | Immediate Release | [22] |
| Ondansetron | Immediate Release | [83] | |
| Paracetamol | Immediate Release | [100] | |
| BJ | Diclofenac | Immediate Release | [100] |
| Acetaminophen | Immediate Release | [101] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Paipa-Jabre-Cantu, S.I.; Rodriguez-Salvador, M.; Castillo-Valdez, P.F. Revealing Three-Dimensional Printing Technology Advances for Oral Drug Delivery: Application to Central-Nervous-System-Related Diseases. Pharmaceutics 2025, 17, 445. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17040445
Paipa-Jabre-Cantu SI, Rodriguez-Salvador M, Castillo-Valdez PF. Revealing Three-Dimensional Printing Technology Advances for Oral Drug Delivery: Application to Central-Nervous-System-Related Diseases. Pharmaceutics. 2025; 17(4):445. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17040445
Chicago/Turabian StylePaipa-Jabre-Cantu, Samir I., Marisela Rodriguez-Salvador, and Pedro F. Castillo-Valdez. 2025. "Revealing Three-Dimensional Printing Technology Advances for Oral Drug Delivery: Application to Central-Nervous-System-Related Diseases" Pharmaceutics 17, no. 4: 445. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17040445
APA StylePaipa-Jabre-Cantu, S. I., Rodriguez-Salvador, M., & Castillo-Valdez, P. F. (2025). Revealing Three-Dimensional Printing Technology Advances for Oral Drug Delivery: Application to Central-Nervous-System-Related Diseases. Pharmaceutics, 17(4), 445. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17040445








