Investigating the Effect of Enzymatically-Derived Blackcurrant Extract on Skin Staphylococci Using an In Vitro Human Stratum Corneum Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Preparation of Blackcurrant Extract
2.2.2. Polyphenol Profiling
2.2.3. Culturing Bacteria
2.2.4. Preparation of the Callus-Based Stratum Corneum Model
2.2.5. Microbial Growth Monitoring
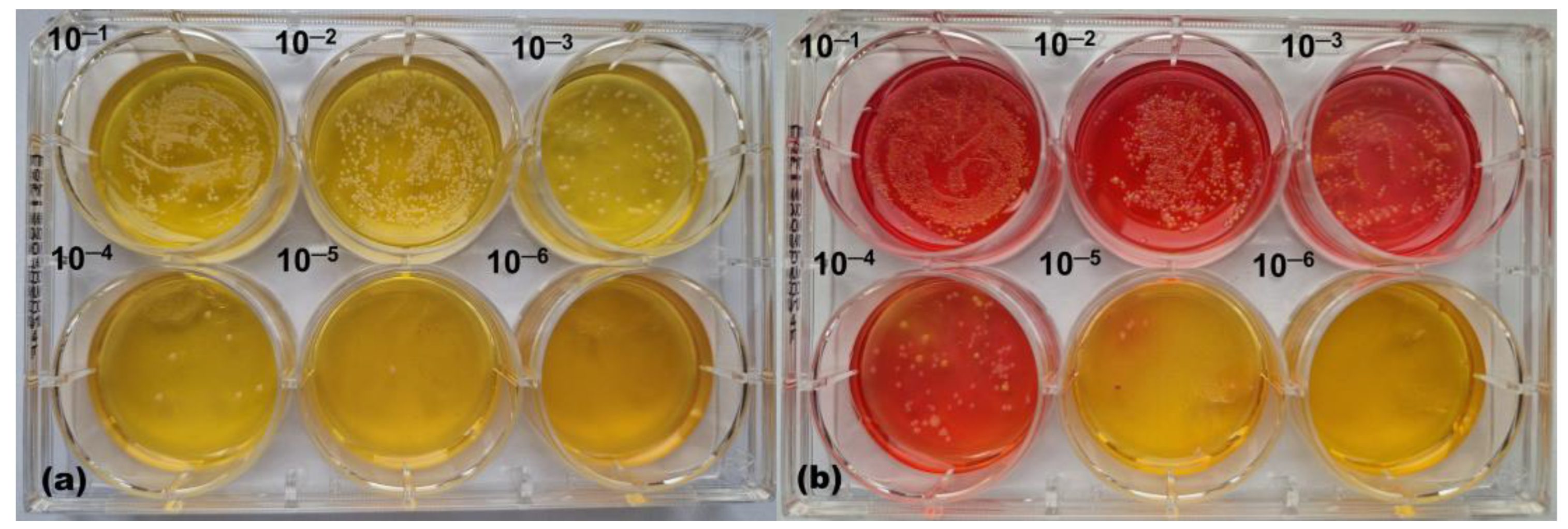
2.2.6. Collection of Microbiome Samples
2.2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Determination of the Polyphenolic Profile of Enzymatically Derived Blackcurrant Extract
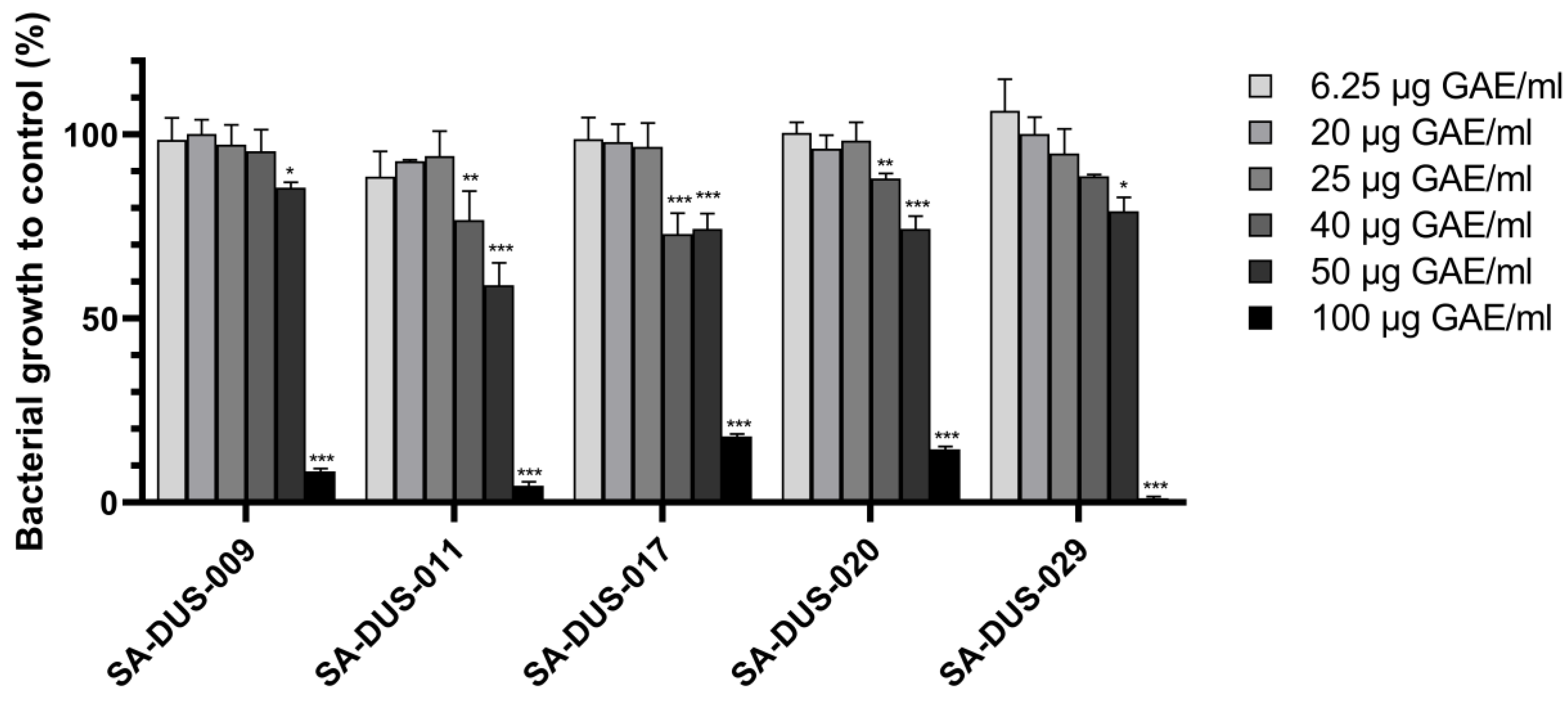
3.2. Effect of Enzymatic Blackcurrant Extract on Clinical S. aureus Strains
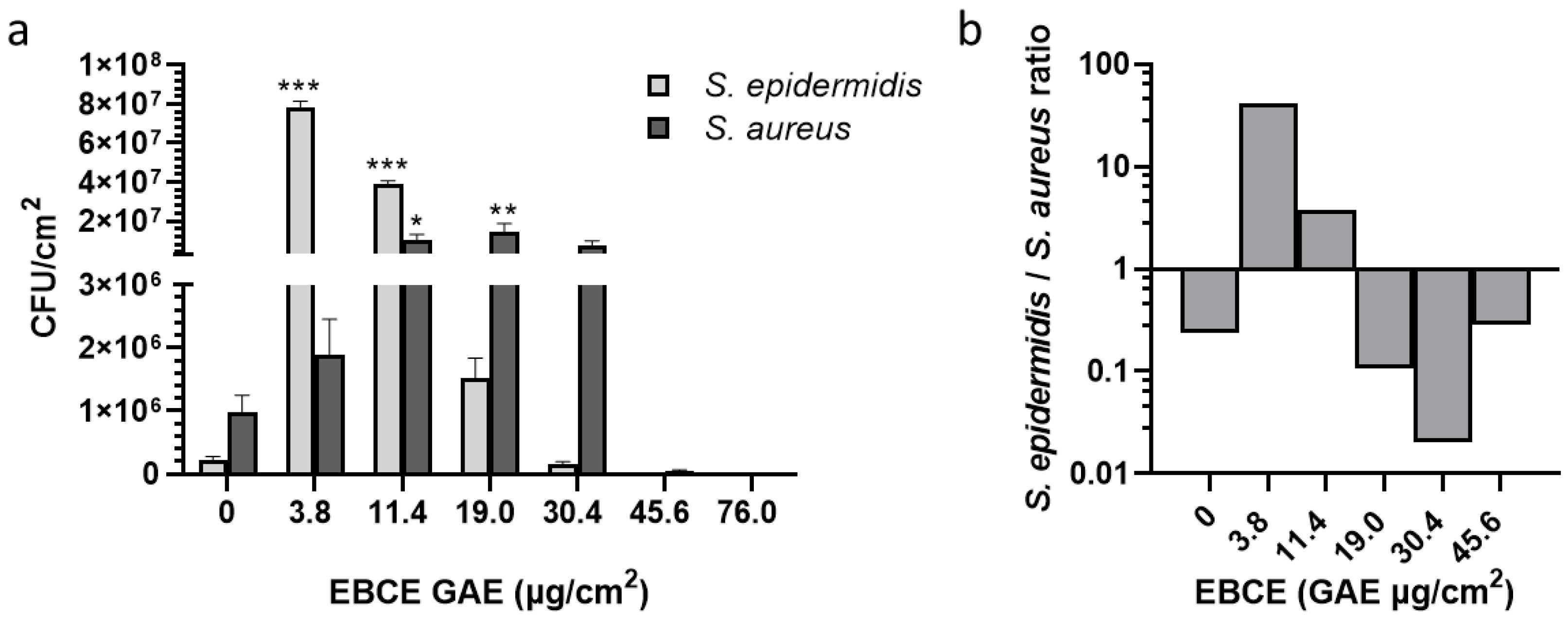
3.3. Effect of Enzymatic Blackcurrant Extract on the Growth of S. aureus SA-DUS-017 and S. epidermidis DSM 20044 Co-Cultured on the Stratum Corneum Model
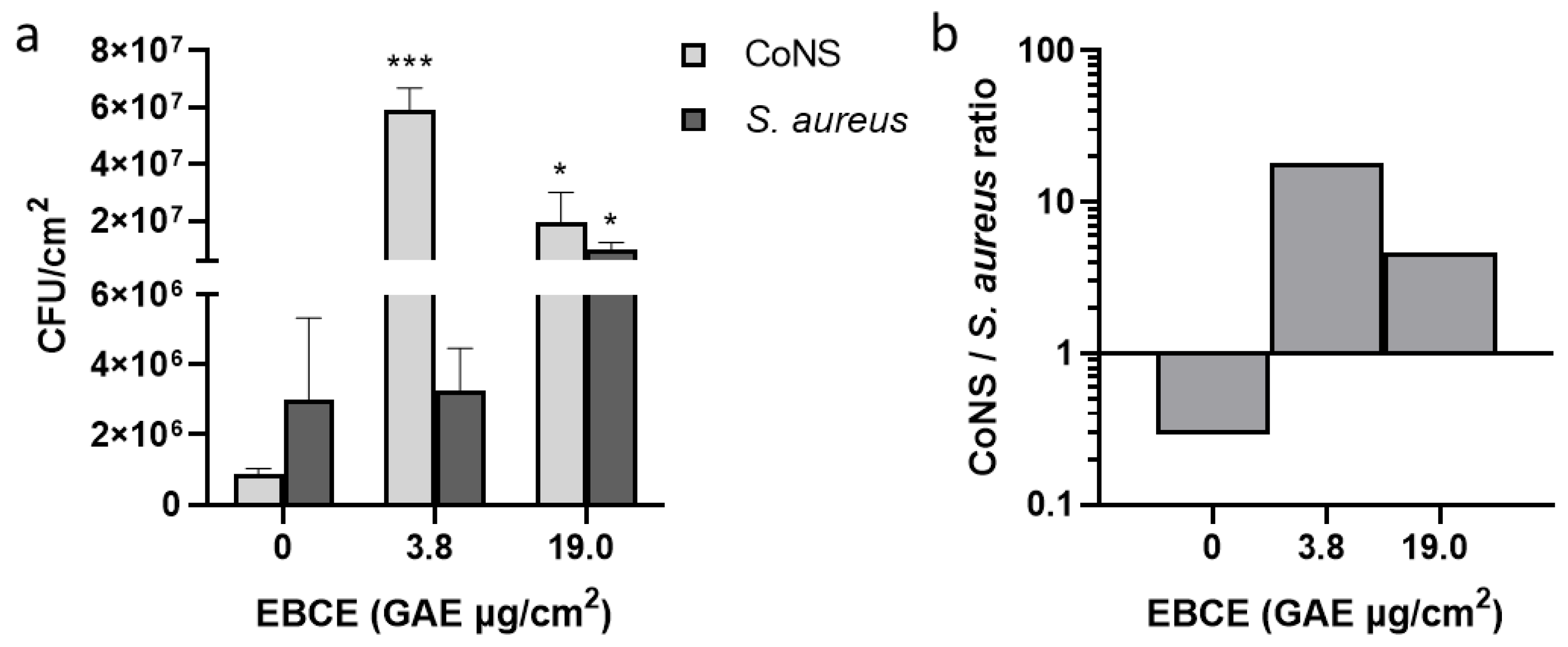
3.4. Effect of Enzymatic Blackcurrant Extract on the Growth of S. aureus SA-DUS-017 and Skin Microbiome Samples Co-Cultured on the Stratum Corneum Model
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Grice, E.A.; Segre, J.A. The skin microbiome. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2011, 9, 244–253. [Google Scholar]
- Parlet, C.P.; Brown, M.M.; Horswill, A.R. Commensal staphylococci influence Staphylococcus aureus skin colonization and disease. Trends Microbiol. 2019, 27, 497–507. [Google Scholar]
- Bier, K.; Schittek, B. Beneficial effects of coagulase-negative Staphylococci on Staphylococcus aureus skin colonization. Exp. Dermatol. 2021, 30, 1442–1452. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.; Kim, B.E.; Ahn, K.; Leung, D.Y. Interactions between atopic dermatitis and Staphylococcus aureus infection: Clinical implications. Allergy Asthma Immunol. Res. 2019, 11, 593–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Yu, X.; Cheng, G. Human skin bacterial microbiota homeostasis: A delicate balance between health and disease. mLife 2023, 2, 107–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cogen, A.; Nizet, V.; Gallo, R. Skin microbiota: A source of disease or defence? Br. J. Dermatol. 2008, 158, 442–455. [Google Scholar]
- van der Krieken, D.A.; Rikken, G.; Ederveen, T.H.; Jansen, P.A.; Rodijk-Olthuis, D.; Meesters, L.D.; van Vlijmen-Willems, I.M.; van Cranenbroek, B.; van der Molen, R.G.; Schalkwijk, J.; et al. Gram-positive anaerobic cocci guard skin homeostasis by regulating host-defense mechanisms. iScience 2023, 26, 106483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakatsuji, T.; Brinton, S.L.; Cavagnero, K.J.; O’Neill, A.M.; Chen, Y.; Dokoshi, T.; Butcher, A.M.; Osuoji, O.C.; Shafiq, F.; Espinoza, J.L.; et al. Competition between skin antimicrobial peptides and commensal bacteria in type 2 inflammation enables survival of S. aureus. Cell Rep. 2023, 42, 112494. [Google Scholar]
- Byrd, A.L.; Belkaid, Y.; Segre, J.A. The human skin microbiome. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2018, 16, 143–155. [Google Scholar]
- Nakatsuji, T.; Chen, T.H.; Narala, S.; Chun, K.A.; Two, A.M.; Yun, T.; Shafiq, F.; Kotol, P.F.; Bouslimani, A.; Melnik, A.V.; et al. Antimicrobials from human skin commensal bacteria protect against Staphylococcus aureus and are deficient in atopic dermatitis. Sci. Transl. Med. 2017, 9, eaah4680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwase, T.; Uehara, Y.; Shinji, H.; Tajima, A.; Seo, H.; Takada, K.; Agata, T.; Mizunoe, Y. Staphylococcus epidermidis Esp inhibits Staphylococcus aureus biofilm formation and nasal colonization. Nature 2010, 465, 346–349. [Google Scholar]
- Paharik, A.E.; Parlet, C.P.; Chung, N.; Todd, D.A.; Rodriguez, E.I.; Van Dyke, M.J.; Cech, N.B.; Horswill, A.R. Coagulase-negative staphylococcal strain prevents Staphylococcus aureus colonization and skin infection by blocking quorum sensing. Cell Host Microbe 2017, 22, 746–756.e745. [Google Scholar]
- Chin, D.; Goncheva, M.I.; Flannagan, R.S.; Deecker, S.R.; Guariglia-Oropeza, V.; Ensminger, A.W.; Heinrichs, D.E. Coagulase-negative staphylococci release a purine analog that inhibits Staphylococcus aureus virulence. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1887. [Google Scholar]
- Petrov Ivanković, A.; Milivojević, A.; Ćorović, M.; Simović, M.; Banjanac, K.; Jansen, P.; Vukoičić, A.; Van den Bogaard, E.; Bezbradica, D. In vitro evaluation of enzymatically derived blackcurrant extract as prebiotic cosmetic ingredient: Extraction conditions optimization and effect on cutaneous microbiota representatives. Chem. Biol. Technol. Agric. 2023, 10, 125. [Google Scholar]
- D’Arcangelo, S.; Di Fermo, P.; Diban, F.; Ferrone, V.; D’Ercole, S.; Di Giulio, M.; Di Lodovico, S. Staphylococcus aureus/Staphylococcus epidermidis from skin microbiota are balanced by Pomegranate peel extract: An eco-sustainable approach. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0308211. [Google Scholar]
- Petrov Ivanković, A.; Ćorović, M.; Milivojević, A.; Simović, M.; Banjanac, K.; Veljković, M.; Bezbradica, D. Berries pomace valorization: From waste to potent antioxidants and emerging skin prebiotics. Int. J. Fruit Sci. 2024, 24, 85–101. [Google Scholar]
- Ivanovska, A.; Gajić, I.S.; Mravik, Ž.; Reljić, M.; Ilić-Tomić, T.; Savić, I.; Luxbacher, T.; Lađarević, J. Transforming discarded walnut green husk into a resource of valuable compounds for colored bioactive textiles with a focus on circular economy concept. Dyes Pigm. 2024, 231, 112406. [Google Scholar]
- van der Krieken, D.A.; Ederveen, T.H.; Van Hijum, S.A.; Jansen, P.A.; Melchers, W.J.; Scheepers, P.T.; Schalkwijk, J.; Zeeuwen, P.L. An in vitro model for bacterial growth on human stratum corneum. Acta Derm. Venereol. 2016, 96, 873–879. [Google Scholar]
- Fyhrquist, N.; Muirhead, G.; Prast-Nielsen, S.; Jeanmougin, M.; Olah, P.; Skoog, T.; Jules-Clement, G.; Feld, M.; Barrientos-Somarribas, M.; Sinkko, H.; et al. Microbe-host interplay in atopic dermatitis and psoriasis. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 4703. [Google Scholar]
- Zeeuwen, P.L.; Boekhorst, J.; van den Bogaard, E.H.; de Koning, H.D.; van de Kerkhof, P.M.; Saulnier, D.M.; van Swam, I.I.; van Hijum, S.A.; Kleerebezem, M.; Schalkwijk, J.; et al. Microbiome dynamics of human epidermis following skin barrier disruption. Genome Biol. 2012, 13, R101. [Google Scholar]
- Petrov Ivanković, A.; Ćorović, M.; Milivojević, A.; Blagojević, S.; Radulović, A.; Pjanović, R.; Bezbradica, D. Assessment of enzymatically derived blackcurrant extract as cosmetic ingredient—Antioxidant properties determination and in vitro diffusion study. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ejaz, A.; Waliat, S.; Afzaal, M.; Saeed, F.; Ahmad, A.; Din, A.; Ateeq, H.; Asghar, A.; Shah, Y.A.; Rafi, A.; et al. Biological activities, therapeutic potential, and pharmacological aspects of blackcurrants (Ribes nigrum L.): A comprehensive review. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 11, 5799–5817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uehara, Y.; Shimamura, Y.; Takemura, C.; Suzuki, S.; Masuda, S. Effects of cosmetic ingredients on growth and virulence factor expression in Staphylococcus aureus: A comparison between culture medium and in vitro skin model medium. AIMS Microbiol. 2025, 11, 22–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves-Santos, A.M.; Sugizaki, C.S.A.; Lima, G.C.; Naves, M.M.V. Prebiotic effect of dietary polyphenols: A systematic review. J. Funct. Foods 2020, 74, 104169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manso, T.; Lores, M.; de Miguel, T. Antimicrobial activity of polyphenols and natural polyphenolic extracts on clinical isolates. Antibiotics 2021, 11, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; Deng, Y.; Cao, X.; Xiao, L.; Ding, Q.; Luo, F.; Huang, P.; Gao, Y.; Liu, M.; Zhao, H. Effects of natural polyphenols on skin and hair health: A review. Molecules 2022, 27, 7832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negari, I.P.; Keshari, S.; Huang, C.-M. Probiotic activity of Staphylococcus epidermidis induces collagen type I production through FFaR2/p-ERK signaling. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Hunt, R.L.; Villaruz, A.E.; Fisher, E.L.; Liu, R.; Liu, Q.; Cheung, G.Y.; Li, M.; Otto, M. Commensal Staphylococcus epidermidis contributes to skin barrier homeostasis by generating protective ceramides. Cell Host Microbe 2022, 30, 301–313.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swaney, M.H.; Kalan, L.R. Two-for-one: Dual host-microbe functions of S. epidermidis Sph. Cell Host Microbe 2022, 30, 279–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stacy, A.; Belkaid, Y. Microbial guardians of skin health. Science 2019, 363, 227–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandecandelaere, I.; Depuydt, P.; Nelis, H.J.; Coenye, T. Protease production by Staphylococcus epidermidis and its effect on Staphylococcus aureus biofilms. Pathog. Dis. 2014, 70, 321–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volz, T.; Kaesler, S.; Draing, C.; Hartung, T.; Röcken, M.; Skabytska, Y.; Biedermann, T. Induction of IL-10-balanced immune profiles following exposure to LTA from Staphylococcus epidermidis. Exp. Dermatol. 2018, 27, 318–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, Y.; Cogen, A.L.; Radek, K.A.; Park, H.J.; MacLeod, D.T.; Leichtle, A.; Ryan, A.F.; Di Nardo, A.; Gallo, R.L. Activation of TLR2 by a small molecule produced by Staphylococcus epidermidis increases antimicrobial defense against bacterial skin infections. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2010, 130, 2211–2221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Compound | Retention Time (min) | Ionisation Mode | Transition | FV (V) | CE (V) | Concentration in EBCE (µg/mL) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gallic acid | 1.65 | Negative | 169 ⟶ 125 | 100 | 10 | 2.22 ± 0.02 |
| Protocatechuic acid | 3.38 | Negative | 153 ⟶ 109 | 100 | 9 | 1.58 ± 0.03 |
| p-Hydroxybenzoic acid | 4.80 | Negative | 137 ⟶ 93 | 100 | 10 | 1.17 ± 0.02 |
| Catechin | 5.05 | Negative | 289 ⟶ 245 | 100 | 10 | 0.32 ± 0.02 |
| Caffeic acid | 5.32 | Negative | 179 ⟶ 135 | 100 | 10 | 1.71 ± 0.05 |
| Vanillic acid | 5.50 | Negative | 167 ⟶ 108 | 100 | 15 | 0.11 ± 0.06 |
| Syringic acid | 5.92 | Negative | 197 ⟶ 182 | 100 | 12 | <0.01 |
| Epicatechin | 6.00 | Negative | 289 ⟶ 245 | 104 | 10 | 0.10 ± 0.02 |
| Malvidin-3-glucoside | 6.20 | Positive | 493.1 ⟶ 331.1 | 116 | 24 | 1.62 ± 0.46 |
| p-Coumaric acid | 6.60 | Negative | 163 ⟶ 119 | 100 | 9 | 7.27 ± 0.51 |
| Taxifolin | 6.82 | Negative | 302.7 ⟶ 284.8 | 100 | 14 | 0.26 ± 0.03 |
| t-Ferulic acid | 6.90 | Negative | 193 ⟶ 134 | 100 | 11 | 0.59 ± 0.06 |
| Salicylic acid | 7.40 | Negative | 137 ⟶ 93 | 100 | 10 | 0.11± 0.08 |
| Resveratrol | 7.41 | Negative | 227 ⟶ 185 | 100 | 20 | 0.05 ± 0.03 |
| Rutin | 7.70 | Negative | 609 ⟶ 300 | 100 | 42 | 12.42 ± 0.28 |
| Ellagic acid | 7.90 | Negative | 301 ⟶ 257 | 100 | 35 | 0.07 ± 0.03 |
| Myricetin | 8.10 | Negative | 316.7 ⟶ 150.9 | 100 | 26 | 8.74 ± 1.69 |
| Naringenin | 8.74 | Negative | 271 ⟶ 151 | 100 | 16 | 0.06 ± 0.01 |
| Quercetin | 8.80 | Negative | 301 ⟶ 179 | 100 | 15 | 1.84 ± 0.08 |
| Kaempferol | 9.40 | Negative | 285 ⟶ 93.4 | 100 | 52 | 0.35 ± 0.07 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ćorović, M.; Petrov Ivanković, A.; Milivojević, A.; Pfeffer, K.; Homey, B.; Jansen, P.A.M.; Zeeuwen, P.L.J.M.; van den Bogaard, E.H.; Bezbradica, D. Investigating the Effect of Enzymatically-Derived Blackcurrant Extract on Skin Staphylococci Using an In Vitro Human Stratum Corneum Model. Pharmaceutics 2025, 17, 487. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17040487
Ćorović M, Petrov Ivanković A, Milivojević A, Pfeffer K, Homey B, Jansen PAM, Zeeuwen PLJM, van den Bogaard EH, Bezbradica D. Investigating the Effect of Enzymatically-Derived Blackcurrant Extract on Skin Staphylococci Using an In Vitro Human Stratum Corneum Model. Pharmaceutics. 2025; 17(4):487. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17040487
Chicago/Turabian StyleĆorović, Marija, Anja Petrov Ivanković, Ana Milivojević, Klaus Pfeffer, Bernhard Homey, Patrick A. M. Jansen, Patrick L. J. M. Zeeuwen, Ellen H. van den Bogaard, and Dejan Bezbradica. 2025. "Investigating the Effect of Enzymatically-Derived Blackcurrant Extract on Skin Staphylococci Using an In Vitro Human Stratum Corneum Model" Pharmaceutics 17, no. 4: 487. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17040487
APA StyleĆorović, M., Petrov Ivanković, A., Milivojević, A., Pfeffer, K., Homey, B., Jansen, P. A. M., Zeeuwen, P. L. J. M., van den Bogaard, E. H., & Bezbradica, D. (2025). Investigating the Effect of Enzymatically-Derived Blackcurrant Extract on Skin Staphylococci Using an In Vitro Human Stratum Corneum Model. Pharmaceutics, 17(4), 487. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17040487







