Efficient Integration of Heterogeneous Mobility-Pollution Big Data for Joint Analytics at Scale with QoS Guarantees
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Related Literature
3. Overview and Theoretical Foundations
3.1. The Notion of Quality-of-Service in Big Data Management
3.2. Big Spatial Multidimensional Data Analytics
3.2.1. Spatial Data Models
3.2.2. Spatial Joins
3.2.3. Geospatial Dimensionality Reduction: Geohash Encoding
3.2.4. Spatial Query Optimization
3.3. Meteorological and Pollution Data Analytics
Integrating Mobility and Meteorological Data for Joint Analytics
4. Mobility and Environmental Data Integration: System Overview
4.1. Problem Formulation
4.2. System Architecture
4.2.1. Georeferenced Data Collector
4.2.2. Spatial Join Processor
4.2.3. Data Aggregator
5. Results and Discussion
5.1. Baseline System
5.2. Deployment Settings
5.2.1. Datasets
- Meteorological and pollution data
- 2.
- Mobility data
5.2.2. Deployment Settings
5.3. Testing Scenarios
5.3.1. Queries Supported
- Top-N query
- 2.
- Average query
5.3.2. Significance of the Performance Tests
5.4. Testing Procedure
5.4.1. Variation of Data Loads and Query Types
5.4.2. Testing Accuracy
6. Results Discussion
6.1. Running Time
6.2. Accuracy Test Results
6.3. Testing the Ability to Generate Region-Based Aggregate Geo-Maps from the Unified View
7. Challenges and Future Research Perspectives
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bryant, R.E. Data-Intensive Scalable Computing for Scientific Applications. Comput. Sci. Eng. 2011, 13, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorton, I.; Gracio, D.K. Data-Intensive Computing: Architectures, Algorithms, and Applications; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, M.; Chen, W.; Xia, J.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Luo, Y.; Huang, Z.; Liu, L. Location2vec: A Situation-Aware Representation for Visual Exploration of Urban Locations. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2019, 20, 3981–3990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodge, S.; Bohrer, G.; Weinzierl, R.; Davidson, S.C.; Kays, R.; Douglas, D.; Cruz, S.; Han, J.; Brandes, D.; Wikelski, M. The environmental-data automated track annotation (Env-DATA) system: Linking animal tracks with environmental data. Mov. Ecol. 2013, 1, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brum-Bastos, V.S.; Long, J.A.; Demšar, U. Weather effects on human mobility: A study using multi-channel sequence analysis. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2018, 71, 131–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cornacchia, G.; Nanni, M.; Pedreschi, D.; Pappalardo, L. Effects of Route Randomization on Urban Emissions. SUMO Conf. Proc. 2023, 4, 75–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohm, M.; Nanni, M.; Pappalardo, L. Quantifying the Presence of Air Pollutants over a Road Network in High Spatio-Temporal Resolution. In NeurIPS 2020 Workshop on Tackling Climate Change with Machine Learning; 2020; Available online: https://www.climatechange.ai/papers/neurips2020/28 (accessed on 25 July 2023).
- Jan, T.; Azami, P.; Iranmanesh, S.; Sianaki, O.A.; Hajiebrahimi, S. Determining the Optimal Restricted Driving Zone Using Genetic Algorithm in a Smart City. Sensors 2020, 20, 2276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cornacchia, G.; Böhm, M.; Mauro, G.; Nanni, M.; Pedreschi, D.; Pappalardo, L. How routing strategies impact urban emissions. In Proceedings of the 30th International Conference on Advances in Geographic Information Systems, Seattle, WA, USA, 1–4 November 2022; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Böhm, M.; Nanni, M.; Pappalardo, L. Gross polluters and vehicle emissions reduction. Nat. Sustain. 2022, 5, 699–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böhm, M.; Nanni, M.; Pappalardo, L. Improving vehicles’ emissions reduction policies by targeting gross polluters. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2107.03282v1. [Google Scholar]
- Al Jawarneh, I.M.; Bellavista, P.; Corradi, A.; Foschini, L.; Montanari, R. Efficient QoS-Aware Spatial Join Processing for Scalable NoSQL Storage Frameworks. IEEE Trans. Netw. Serv. Manag. 2020, 18, 2437–2449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolokolov, Y.; Monovskaya, A.; Volkov, V.; Frolov, A. Intelligent integration of open-access weather-climate data on local urban areas. In Proceedings of the 2017 9th IEEE International Conference on Intelligent Data Acquisition and Advanced Computing Systems: Technology and Applications (IDAACS), Bucharest, Romania, 21–23 September 2017; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2017; Volume 1, pp. 465–470. [Google Scholar]
- Poryazov, S.A.; Saranova, E.T.; Andonov, V.S. Overall Model Normalization towards Adequate Prediction and Presentation of QoE in Overall Telecommunication Systems. In Proceedings of the 2019 14th International Conference on Advanced Technologies, Systems and Services in Telecommunications (TELSIKS), Nis, Serbia, 23–25 October 2019; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2019; pp. 360–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batterman, S.; Chambliss, S.; Isakov, V. Spatial resolution requirements for traffic-related air pollutant exposure evaluations. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 94, 518–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fameli, K.M.; Kotrikla, A.M.; Psanis, C.; Biskos, G.; Polydoropoulou, A. Estimation of the emissions by transport in two port cities of the northeastern Mediterranean, Greece. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 257, 113598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, J.; Macedo, E.; Fernandes, P.; Bandeira, J.; Rouphail, N.; Coelho, M.C. Assessing traffic-related environmental impacts based on different traffic monitoring applications. Transp. Res. Procedia 2019, 37, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Liu, F.; Hsieh, H.-P. U-air: When urban air quality inference meets big data. In Proceedings of the 19th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, Chicago, IL, USA, 11–14 August 2013; pp. 1436–1444. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Z.-Y.; Cao, Y.; Kang, Y.; Xu, Z.-Y. Prediction of Spatiotemporal Evolution of Urban Traffic Emissions Based on Taxi Trajectories. Int. J. Autom. Comput. 2021, 18, 219–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Cao, Y.; Kang, Y. Deep spatiotemporal residual early-late fusion network for city region vehicle emission pollution prediction. Neurocomputing 2019, 355, 183–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iskandaryan, D.; Ramos, F.; Trilles, S. Air Quality Prediction in Smart Cities Using Machine Learning Technologies Based on Sensor Data: A Review. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 2401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nyhan, M.; Sobolevsky, S.; Kang, C.; Robinson, P.; Corti, A.; Szell, M.; Streets, D.; Lu, Z.; Britter, R.; Barrett, S.R.; et al. Predicting vehicular emissions in high spatial resolution using pervasively measured transportation data and microscopic emissions model. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 140, 352–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, K.; Lu, J.; Li, J.; Xu, Z. A Hybrid Autoformer Network for Air Pollution Forecasting Based on External Factor Optimization. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Cao, Y.; Xu, Z.; Kang, Y. Traffic emission estimation under incomplete information with spatiotemporal convolutional GAN. Neural Comput. Appl. 2023, 35, 15821–15835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Kang, Y.; Cao, Y.; Li, Z. Spatiotemporal Graph Convolution Multifusion Network for Urban Vehicle Emission Prediction. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2020, 32, 3342–3354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ordonez-Ante, L.; Van Seghbroeck, G.; Wauters, T.; Volckaert, B.; De Turck, F. EXPLORA: Interactive Querying of Multidimensional Data in the Context of Smart Cities. Sensors 2020, 20, 2737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lundblad, P.; Eurenius, O.; Heldring, T. Interactive visualization of weather and ship data. In Proceedings of the 2009 13th International Conference Information Visualisation, Barcelona, Spain, 15–17 July 2009; IEEE: New York, NY, USA; pp. 379–386. [Google Scholar]
- Desimoni, F.; Ilarri, S.; Po, L.; Rollo, F.; Trillo-Lado, R. Semantic Traffic Sensor Data: The TRAFAIR Experience. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 5882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Po, L.; Rollo, F.; Bachechi, C.; Corni, A. From sensors data to urban traffic flow analysis. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Smart Cities Conference (ISC2), Casablanca, Morocco, 14–17 October 2019; IEEE: New York, NY, USA; pp. 478–485. [Google Scholar]
- Zaldei, A.; Camilli, F.; De Filippis, T.; Di Gennaro, F.; Di Lonardo, S.; Dini, F.; Gioli, B.; Gualtieri, G.; Matese, A.; Nunziati, W.; et al. An integrated low-cost road traffic and air pollution monitoring platform for next citizen observatories. Transp. Res. Procedia 2017, 24, 531–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilarri, S.; Trillo-Lado, R.; Marrodán, L. Traffic and Pollution Modelling for Air Quality Awareness: An Experience in the City of Zaragoza. SN Comput. Sci. 2022, 3, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinnachodteeranun, R.; Honda, K. Sensor Observation Service API for Providing Gridded Climate Data to Agricultural Applications. Future Internet 2016, 8, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Silva, M.; Signoretti, G.; Oliveira, J.; Silva, I.; Costa, D.G. A Crowdsensing Platform for Monitoring of Vehicular Emissions: A Smart City Perspective. Future Internet 2019, 11, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Obaid, M.; Torok, A.; Ortega, J. A Comprehensive Emissions Model Combining Autonomous Vehicles with Park and Ride and Electric Vehicle Transportation Policies. Sustainability 2021, 13, 4653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; He, X.; Zhou, Z.; Thiele, L. MapTransfer: Urban air quality map generation for downscaled sensor deployments. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/ACM Fifth International Conference on Internet-of-Things Design and Implementation (IoTDI), Sydney, Australia, 21–24 April 2020; IEEE: New York, NY, USA; pp. 14–26. [Google Scholar]
- Leung, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Lam, K.-Y.; Fung, T.; Cheung, K.-Y.; Kim, T.; Jung, H. Integration of air pollution data collected by mobile sensors and ground-based stations to derive a spatiotemporal air pollution profile of a city. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2019, 33, 2218–2240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Jawarneh, I.M.; Bellavista, P.; Corradi, A.; Foschini, L.; Montanari, R. QoS-Aware Approximate Query Processing for Smart Cities Spatial Data Streams. Sensors 2021, 21, 4160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacox, E.H.; Samet, H. Spatial join techniques. ACM Trans. Database Syst. 2007, 32, 7-es. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brinkhoff, T.; Kriegel, H.-P.; Schneider, R.; Seeger, B. Multi-step processing of spatial joins. ACM Sigmod Rec. 1994, 23, 197–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Raaschou-Nielsen, O.; Andersen, Z.J.; Beelen, R.; Samoli, E.; Stafoggia, M.; Weinmayr, G.; Hoffmann, B.; Fischer, P.; Nieuwenhuijsen, M.J.; Brunekreef, B.; et al. Air pollution and lung cancer incidence in 17 European cohorts: Prospective analyses from the European Study of Cohorts for Air Pollution Effects (ESCAPE). Lancet Oncol. 2013, 14, 813–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berman, J.D.; Ebisu, K. Changes in U.S. air pollution during the COVID-19 pandemic. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 739, 139864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Quéré, C.; Jackson, R.B.; Jones, M.W.; Smith, A.J.P.; Abernethy, S.; Andrew, R.M.; De-Gol, A.J.; Willis, D.R.; Shan, Y.; Canadell, J.G.; et al. Temporary reduction in daily global CO2 emissions during the COVID-19 forced confinement. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2020, 10, 647–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putaud, J.-P.; Pisoni, E.; Mangold, A.; Hueglin, C.; Sciare, J.; Pikridas, M.; Savvides, C.; Mbengue, S.; Wiedensohler, A.; Weinhold, K.; et al. Impact of 2020 COVID-19 lockdowns on particulate air pollution across Europe. EGUsphere 2023, 2023, 1–21. [Google Scholar]
- Gidhagen, L.; Olsson, J.; Amorim, J.H.; Asker, C.; Belušić, D.; Carvalho, A.C.; Engardt, M.; Hundecha, Y.; Körnich, H.; Lind, P.; et al. Towards climate services for European cities: Lessons learnt from the Copernicus project Urban SIS. Urban Clim. 2020, 31, 100549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aljawarneh, I.M.; Bellavista, P.; De Rolt, C.R.; Foschini, L. Dynamic Identification of Participatory Mobile Health Communities. In Cloud Infrastructures, Services, and IoT Systems for Smart Cities: Second EAI International Conference, IISSC 2017 and CN4IoT 2017, Brindisi, Italy, April 20–21, 2017, Proceedings 2; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; pp. 208–217. [Google Scholar]
- Cardone, G.; Corradi, A.; Foschini, L.; Ianniello, R. Participact: A large-scale crowdsensing platform. IEEE Trans. Emerg. Top. Comput. 2015, 4, 21–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardone, G.; Cirri, A.; Corradi, A.; Foschini, L. The participact mobile crowd sensing living lab: The testbed for smart cities. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2014, 52, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehman, A.; O’Rourke, N.; Hatcher, L.; Stepanski, E. JMP for Basic Univariate and Multivariate Statistics: Methods for Researchers and Social Scientists; Sas Institute: Cary, NC, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Rachev, S.T. The Monge–Kantorovich Mass Transference Problem and Its Stochastic Applications. Theory Probab. Its Appl. 1985, 29, 647–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pappalardo, L.; Simini, F.; Barlacchi, G.; Pellungrini, R. Scikit-mobility: A Python library for the analysis, generation and risk assessment of mobility data. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1907.07062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poom, A.; Helle, J.; Toivonen, T. Journey Planners Can Promote Active, Healthy and Sustainable Urban Travel; Helsingin Yliopisto, Kaupunkitutkimusinstituutti Urbaria: Helsinki, Finland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
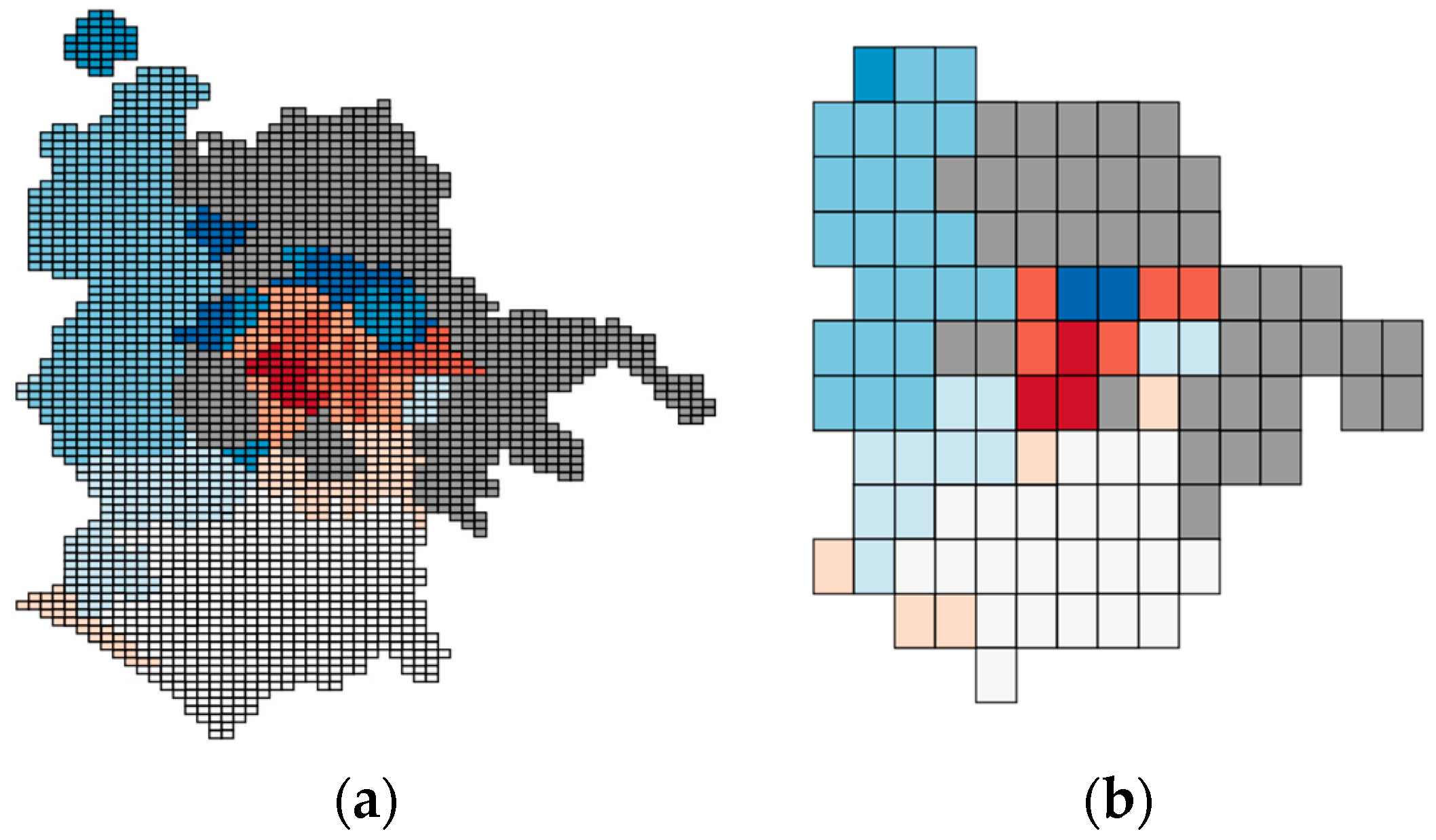




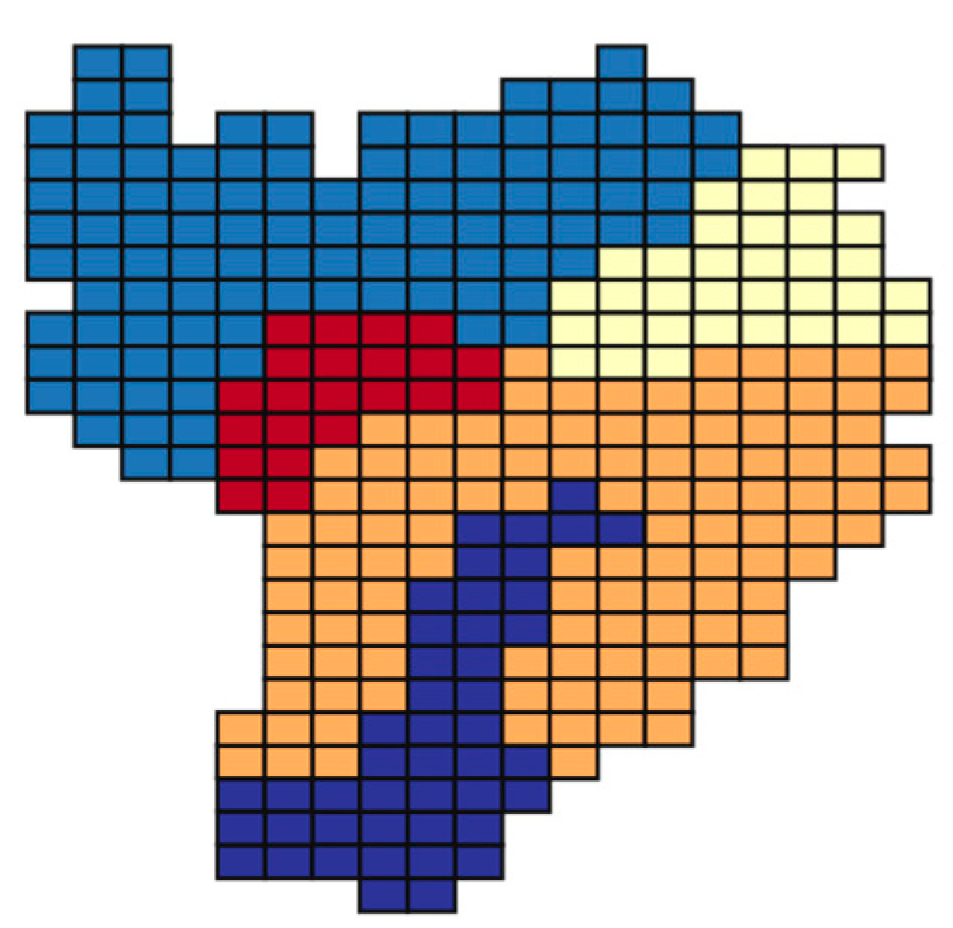











| Datasets | Size (Tuples) | Attributes |
|---|---|---|
| Mobility (Bologna) | 500k | lat, lon, timestamp, trip_value |
| Meteorological (Bologna) | 66k | lat, lon, pm10_value, timestamp |
| Neighborhoods (Bologna) | 9 | Polygon, city, region, province |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Al Jawarneh, I.M.; Foschini, L.; Bellavista, P. Efficient Integration of Heterogeneous Mobility-Pollution Big Data for Joint Analytics at Scale with QoS Guarantees. Future Internet 2023, 15, 263. https://doi.org/10.3390/fi15080263
Al Jawarneh IM, Foschini L, Bellavista P. Efficient Integration of Heterogeneous Mobility-Pollution Big Data for Joint Analytics at Scale with QoS Guarantees. Future Internet. 2023; 15(8):263. https://doi.org/10.3390/fi15080263
Chicago/Turabian StyleAl Jawarneh, Isam Mashhour, Luca Foschini, and Paolo Bellavista. 2023. "Efficient Integration of Heterogeneous Mobility-Pollution Big Data for Joint Analytics at Scale with QoS Guarantees" Future Internet 15, no. 8: 263. https://doi.org/10.3390/fi15080263
APA StyleAl Jawarneh, I. M., Foschini, L., & Bellavista, P. (2023). Efficient Integration of Heterogeneous Mobility-Pollution Big Data for Joint Analytics at Scale with QoS Guarantees. Future Internet, 15(8), 263. https://doi.org/10.3390/fi15080263










