Abstract
Collaborative edge intelligence, a distributed computing paradigm, refers to a system where multiple edge devices work together to process data and perform distributed machine learning (DML) tasks locally. Decentralized Internet of Things (IoT) devices share knowledge and resources to improve the quality of service (QoS) of the system with reduced reliance on centralized cloud infrastructure. However, the paradigm is vulnerable to free-riding attacks, where some devices benefit from the collective intelligence without contributing their fair share, potentially disincentivizing collaboration and undermining the system’s effectiveness. Moreover, data collected from heterogeneous IoT devices may contain biased information that decreases the prediction accuracy of DML models. To address these challenges, we propose a novel incentive mechanism that relies on time-dependent blockchain records and multi-access edge computing (MEC). We formulate the QoS problem as an unbounded multiple knapsack problem at the network edge. Furthermore, a decentralized valuation protocol is introduced atop blockchain to incentivize contributors and disincentivize free-riders. To improve model prediction accuracy within latency requirements, a data scheduling algorithm is given based on a curriculum learning framework. Based on our computer simulations using heterogeneous datasets, we identify two critical factors for enhancing the QoS in collaborative edge intelligence systems: (1) mitigating the impact of information loss and free-riders via decentralized data valuation and (2) optimizing the marginal utility of individual data samples by adaptive data scheduling.
1. Introduction
In machine learning (ML), data and the model are two fundamental elements. Traditional model-centric approaches focus on improving the prediction accuracy of artificial intelligence (AI) by using larger and more delicate models. For example, wider and deeper Transformer models perform better than smaller ones in AI training [1]. However, Internet of Things (IoT) devices are predominantly engineered with stringent constraints on physical size and power consumption, prioritizing portability and energy efficiency. Consequently, these resource-constrained devices often lack the computational power and energy capacity necessary for training and inferencing large AI models effectively. Nevertheless, edge intelligence in the future internet [2] requires even more stringent quality of service (QoS).
For years, a fixation on models has led to difficulties with understanding and reproducing ML results [3]. Therefore, the severe challenge of QoS at the network edge raises a fundamental question: Apart from model design, can the QoS of edge intelligence be improved by device collaboration and data conditioning at the network edge?
In this work, we focus on the exploration of an affirmative answer to the above question. We aim to give a simple yet effective framework to motivate collaboration for improved QoS at the network edge. Fortunately, distributed machine learning (DML) provides an opportunity to realize collaborative edge intelligence. DML is a paradigm that enables the training of ML models across multiple decentralized edge devices without exchanging private local data samples directly. Federated learning (FL) [4] is a well-known example of collaborative DML. In the context of FL, private and distributed data are not allowed to be shared for privacy reasons, as the model is trained locally by mini-batch stochastic gradient descent (SGD) on each participant’s private data, and only model weights are communicated to a central server for global model aggregation. FL is especially beneficial for AI to learn private information under data regulations [5]. For instance, smart health applications rely on IoT data: especially private health data [4]. Instead of uploading IoT data, users transmit model weights trained from health data for prediction. Despite its privacy preservation feature, FL suffers from free-riding attacks [6,7,8], wherein malicious participants exploit the system by benefiting from the global model without meaningful contributions, thereby compromising the efficiency and fairness of the collaborative learning process. Moreover, FL requires a centralized parameter server, which may constitute a single point of failure (SPOF). Therefore, a decentralized approach is needed to enhance system security and reliability. As a distributed ledger technology, blockchain is a decentralization approach with consecutive timestamps to solve the above issues.
Additionally, data-centric methods have recently emerged for understanding and conditioning data in the context of centralized ML [9,10,11]. Compared with large datasets containing biased information, a small but unbiased dataset tends to have more useful information [9]. Therefore, data valuation and scheduling are needed before feeding data into an ML model such as a deep neural network (DNN). Intuitively, the more useful information that a DNN can obtain from data, the more accurate prediction results we can achieve. However, IoT data are often heterogeneous at the network edge. User data depend on living habits, preferences and locations. They are often not independent and identically distributed (non-IID). However, DML relies on a training method named mini-batch SGD, which is designed under the assumption that data are IID [4,5]. A mismatch between model and real data decreases a model’s prediction accuracy. In this paper, we consider two factors that violate the IID property of data: label distribution skew (i.e., users produce biased data) and data quantity skew (i.e., users produce different amounts of data). These factors are particularly significant in DML scenarios where, due to beneficial data protection regulations, raw data are not directly accessible during model training. Without knowledge of data valuation, it is difficult to apply data-centric methods at a network edge.
To solve the above challenges, we propose a blockchain-based incentive mechanism to diversify rewards received by different contributors according to decentralized data valuation. Intuitively, an up-to-date model is of greater utility. Therefore, we aim to ensure every participant will leave the system with a global model reflecting its incremental contributions in the form of data valuation. Data valuation can be recorded on the blockchain, which is maintained by a group of entities instead of a centralized server. Therefore, data valuation becomes a consensus among all entities. By replacing one-server decisions with a group consensus, the evaluation of data valuation is decentralized. However, the consensus mechanism in blockchain, e.g., proof-of-work (PoW), is not suitable for data valuation recording because it requires extensive computing resources, which delays the training process of DML [12].
In this paper, we investigate a blockchain based on multi-access edge computing (MEC) servers, where a delegated proof-of-stake (DPoS) [13] is adopted as the blockchain consensus mechanism. We refer to the MEC server simply as a server because there is only one kind of server in this paper. As a server is located closer to users than a cloud computing center, communication latency in DML is further reduced [12]. Instead of uploading local data distributions [14], valuations of decentralized data are based on private validation datasets. As private information is not included in blockchain records, data valuation is evaluated privately.
To the best of our knowledge, this is the first work that explores blockchain’s potential in diversifying model rewards by decentralized data valuation and data scheduling. Our major contributions are summarized as follows:
- A time-dependent incentive mechanism is proposed atop blockchain to diversify model rewards. It improves the QoS of collaborative edge intelligence while preventing free-riders from using the system.
- We propose a decentralized data valuation method combining cross-validation and DPoS consensus to mitigate information loss of DML on heterogeneous data. The valuation function achieves group rationality, fairness and additivity at the network edge.
- To maximize the marginal utility of data samples, a curriculum data scheduling approach is designed. With an adaptive moving window, the efficiency of data scheduling is improved with reduced latency.
The rest of this paper is organized as follows. Related works are summarized in Section 2. The system model and problem formulation are described in Section 3. Our proposed blockchain-based incentive mechanism is given in Section 4 to defend against free-rider attacks. An adaptive curriculum learning method is further proposed in Section 5 to improve the QoS of each user. We further propose our algorithms in Section 6 as an optimized solution to the formulated QoS problem. Performance evaluation results on non-IID datasets are provided in Section 7. Finally, we conclude this paper in Section 8.
2. Related Works
2.1. The Integration of Blockchain and Edge Intelligence
In the next generation of IoT, a massive number of diverse devices will be connected [15]. To enhance locally trained models with knowledge gained at other nodes, participants must securely exchange model parameters on a peer-to-peer basis. Blockchains offer this secure sharing capability without requiring mutual trust between nodes or reliance on a trusted third party [16]. Once local model parameters are recorded in a block, they become traceable, immutable and irrevocable, ensuring data integrity throughout the collaborative process [17]. As edge nodes increasingly support DML and provide AI models for rapid decision-making, their computational resources may become strained and insufficient. To address this challenge, it may be beneficial for neighboring edge nodes to share their computational resources. To encourage such sharing, an incentive mechanism offering rewards can be implemented [18]. Blockchain technology provides an ideal platform for deploying such a mechanism in a distributed manner, ensuring transparency and trust among participating nodes. Specifically, an AI-Chain has been proposed with a proof-of-learning protocol to unlock the sharing of more advanced intelligence among edges [19]. A blockchain-enabled decentralization approach was given in [20] to optimize the QoS of industrial IoT. Furthermore, smart contracts have been designed and applied to FL for personalized edge intelligence service in IoT systems [21]. In this paper, we discuss a novel integration of blockchain and edge intelligence via decentralized data valuation to improve QoS.
2.2. Data Valuation for Collaborative Edge Intelligence
The data valuation problem has been a central topic in the realm of collaborative ML for a long time. Fairness of data valuation has been recognized as the key to trustworthy AI [22]. As a line of research, Shapley values have been extensively investigated as an approach in data valuation [23]. Specifically, the data Shapley value measures the contribution of a single data point to a learning task [24]. The distributional Shapley value extends the concept to arbitrary data distributions and provides stability guarantees [25]. The contribution index extends the data Shapley value to FL by gradient-based model reconstructions [26]. The authors of [26] investigated the profit allocation problem for FL, wherein a diminishing valuation factor was introduced to encourage participants in early rounds. The federated Shapley value is determined from local model updates in each training iteration, avoiding the need for retraining the model [27]. Proof-of-Shapley opens opportunities for Shapley-value-based blockchain consensus without additional need for trust [28]. However, it is often challenging to identify a viable, well-defined and regulated source of financial compensation for data contributors in the public domain. Apart from Shapley value, self-reported valuation requests the data owners to submit their bids, which consist of information about the combination of resources, local accuracy and costs [29]. Additionally, permutation-based data valuation is for identifying the training points (a labeled data sample) that are most responsible for a given prediction [30]. The method depends on computing influence functions of data samples. Furthermore, the reinforcement-learning-based method adaptively learns the contribution of each data point towards the learned predictor model [31]. Unlike the existing literature, we aim to explore blockchain’s potential for improving the QoS of edge intelligence via decentralized, time-dependent and token-independent data valuation.
3. System Model and Problem Formulation
In this section, we describe the network model, task model, training model, threat model and blockchain incentive model.
3.1. Network Model
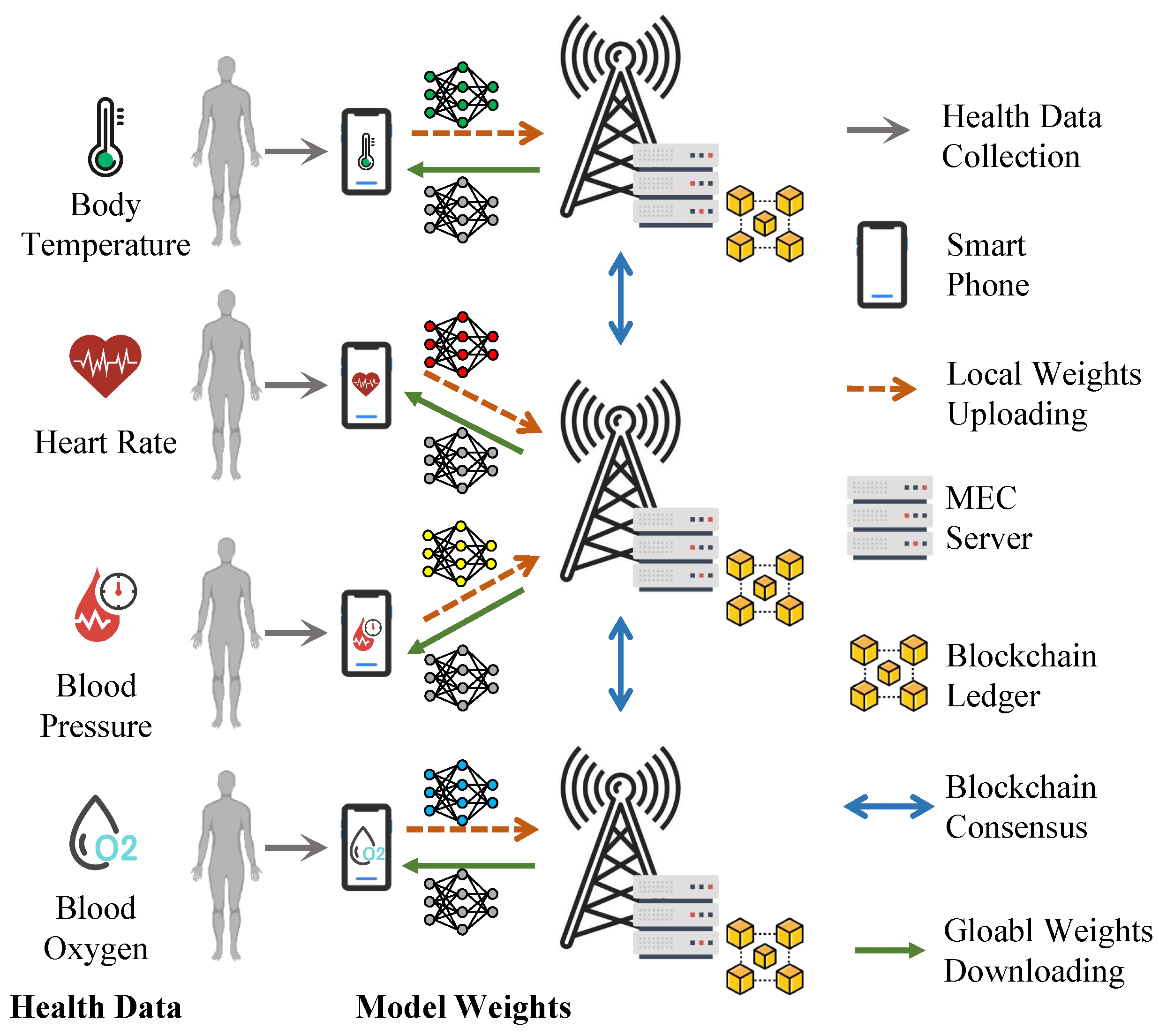
We consider an IoT network as illustrated in Figure 1, where M servers serve N smartphones. Smartphones collect health data with L possible labels and execute DML training for local model weights. We assume each smartphone uploads local weights to its nearest server. As raw IoT data never leave the corresponding smartphones in DML training, privacy leakage is reduced [12].
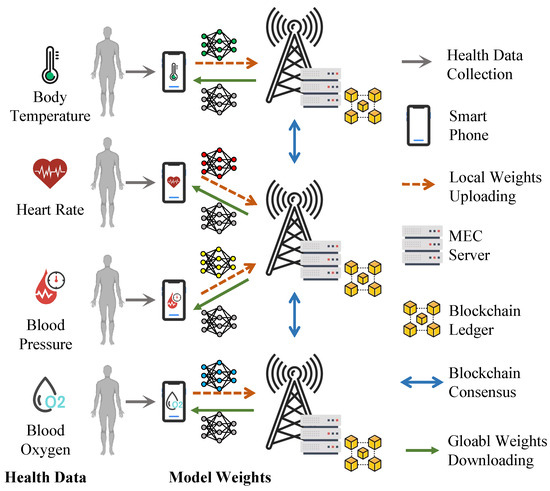
Figure 1.
Blockchain-enabled DML for smart health: an example with 4 smartphones, 3 MEC servers and 4 data labels (N = 4, M = 3, L = 4).
To further secure DML for smart health, a permissioned blockchain is used [32]. Only verified entities can join the proposed DML system. We assume servers are honest and do not launch attacks. Servers store complete records of all blocks, while smartphones only store block headers to verify and download global weights [33]. However, smartphones may become free-riders by contributing very little while still downloading the global model [8]. A detailed threat model is introduced later in this section.
3.2. Task Model
We consider any smartphone n, n∈ = {1, 2, ⋯, N}, which aims to obtain a well-trained model with the maximal utility (i.e., model test accuracy), denoted by , within a latency threshold, denoted by .
A DML model is trained for the detection of potential health risks. Specifically, the goal of DML is to train a model with L possible outputs for health data classification with L data labels through R rounds of collaborations. For example, data label l, l∈ = {1, 2, ⋯, L}, could be “high blood pressure”. In round r∈ = {1, 2, ⋯, R}, let ∈ = {, , ⋯, } denote the observed categorical distribution of N smartphone data labels. Denote q as the constant IID categorical distribution of L labels throughout R rounds. Then, = {, , ⋯, }, and q = {, , ⋯, }.
For example, a model is trained for detecting blood pressure risk. Collected health data have three labels: “high”, “low” and “normal”. In round 3, smartphone 1 owns 10 health data samples, including 2 samples of high blood pressure, 1 low blood pressure sample and 7 samples of normal blood pressure. Then, = {} and q can be a uniform distribution or other constant distribution, e.g., q = {}. However, q can be largely unknown by smartphones and servers during DML. In this paper, we do not assume prior knowledge of q at the network edge.
To achieve the goal of DML, any smartphone n should decide when to participate in DML and how much effort it should contribute to DML. Let , , , be a decision variable such that = 1 indicates that smartphone n participates in round r; otherwise, = 0. That is,
In practice, any smartphone n owns a limited amount of private data. Let and denote the total data size and the training dataset actually used in round r, respectively. Let be the local training dataset owned by smartphone n, , where denotes one instance that includes the raw data and label. Then,
Let be the time consumed for DML training round r, including the time for local training, model aggregation and blockchain consensus. The latency constraint for smartphone n is described as
3.3. Training Model
As there is only one type of round in this paper, we refer to a DML training round simply as a round. In round r, smartphone n produces one set of local weights, denoted by = {, , ⋯, }. N sets of local weights are uploaded to M servers for model aggregation. After receiving N sets of local weights, server m, m∈ = {1, 2, ⋯, M}, executes model aggregation to obtain global weights, represented by .
Let = {, , ⋯, } and = {, , ⋯, } denote the number of data samples and the actual contribution produced by smartphone n in round r, respectively. Define as the local loss function used by smartphone n. Popular loss functions include cross-entropy loss and mean squared error [4]. Let denote the total amount of actual contributions produced by N smartphones. We define the global loss function on all distributed health data as
cannot be directly computed without sharing and among smartphones and servers. Note that FedAvg [5] uses to approximate . However, this approximation may not always accurately reflect the true contribution or value of data samples to global model performance. Let , and denote the learning rate, gradients and total number of data samples used in round r, respectively. For FedAvg, weight aggregation is described as
In DML, the marginal utility of data samples diminishes as the quantity of data (i.e., ) increases [34]. This principle of diminishing returns suggests that each additional data sample contributes less to model improvement than previous data samples with the same quality. However, (5) does not account for the diminishing marginal utility. In Section 4.3 and Section 5.1, we propose and discuss alternative methods to approximate in (4) that incorporate the concept of diminishing marginal utility, aiming to reflect the true value of additional data samples more accurately.
In this paper, the objective of DML is to determine the optimal set of global weights for round r that minimizes the global loss function . The optimization problem is
The above problem is often solved by mini-batch SGD [4] due to its NP-hardness [35].
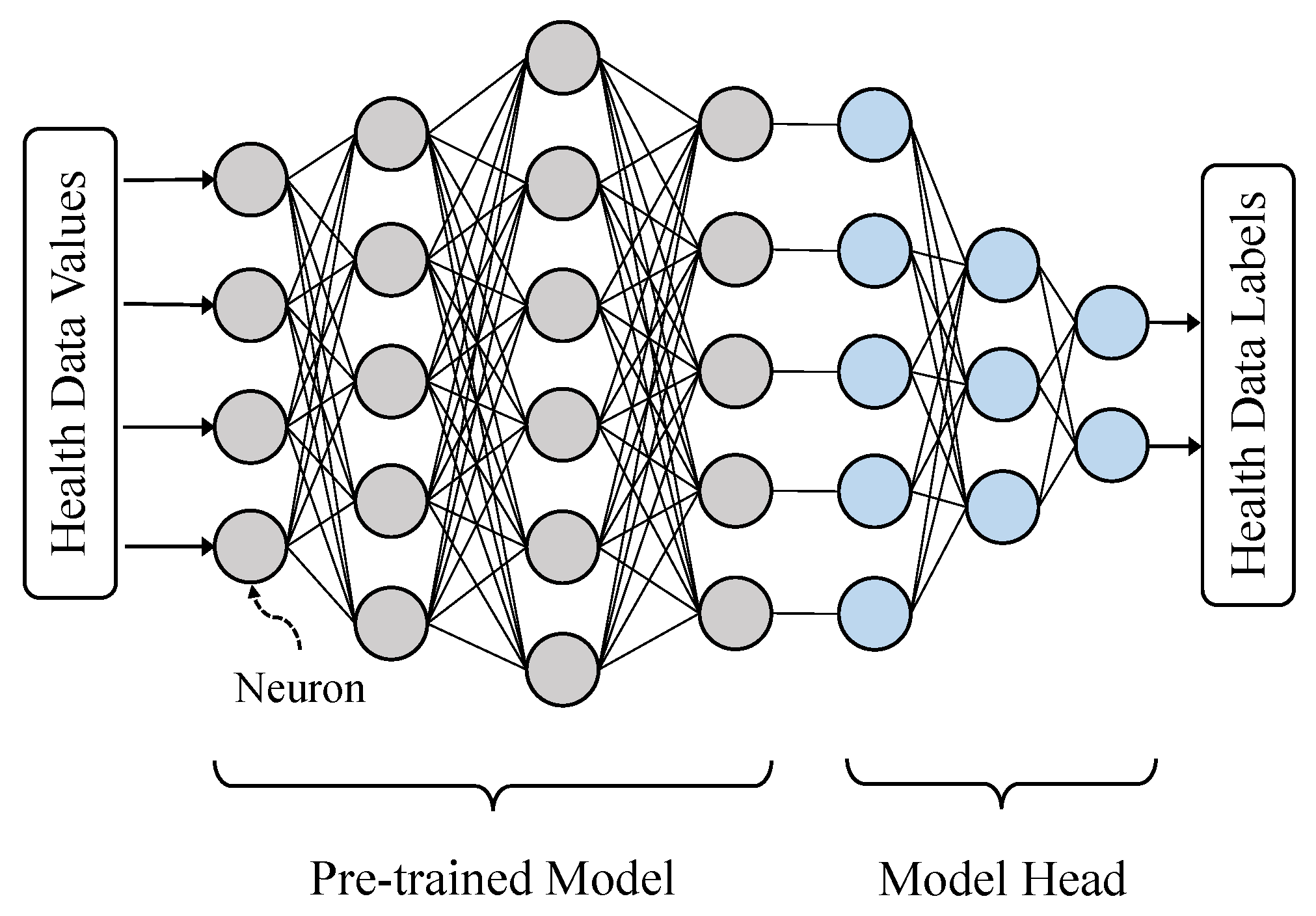
Training a DNN at the network edge is challenging due to resource constraints: IoT devices often lack the computational power required to efficiently perform SGD and backpropagation on large models. To solve this problem, we introduce a pre-trained model framework in Figure 2 for efficient feature extraction [36]. Neurons in gray color are frozen during training and inference. Only the weights of model heads are trainable, i.e., global and local weights in this paper. Instead of training and uploading the whole model, any smartphone n can train and upload the weights of the model head. Utilizing pre-trained models for feature extraction is not novel. As it can significantly reduce computational and communication overheads, we would like to highlight this method for improved QoS at the network edge.
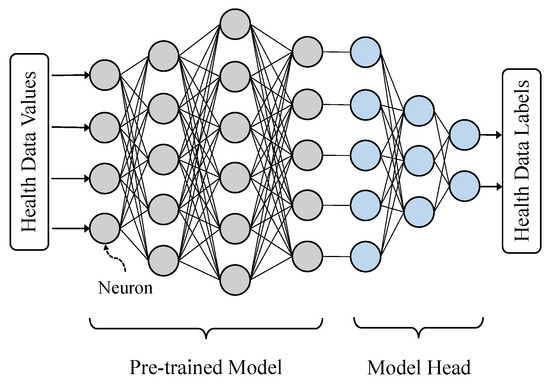
Figure 2.
Pre-trained model for feature extraction: only parameters for the model head are trainable and exchangeable in order to reduce the computational and communication overheads at the network edge.
3.4. Threat Model
Despite the benefits of the collaboration among edge devices, there are critical threats and trust issues. One major problem is how to defend against free-rider attacks. To be specific, we consider two categories of free-riders: (1) Fake contributors: These free-riders typically deceive the system by submitting fabricated local model weights. Fake contributions can include random model parameters, a combination of existing model weights and existing model weights altered with additive noise. (2) Weak contributors: Each free-rider trains a local model based on a private local dataset. However, the submitted local model barely improves the performance of the global model. Weak contributors may use noisy or very small amounts of data during training. Free-riders contribute very little while still reaping the benefit of the aggregated global model in every round.
To better clarify the impact of free-riding attacks, we classify possible consequences into three categories: unfair reward allocation, delay of service and poor performance of the global model. Unfair reward allocation is due to the fact that all honest contributors and free-riders receive the same and up-to-date global model, while their contributions are distinct. Delay of service is obvious since the inclusion of free-riders takes system resources, such as communication bandwidth, consensus overheads, etc. Furthermore, it is catastrophic to aggregate local models submitted by free-riders into the global model. The convergence speed and test accuracy of the global model can be degraded significantly [7]. Therefore, eliminating free-riders is a critical need for a robust and fair DML system.
Existing defensive methods [6,7,8] assume a trusted model aggregator to conduct free-riding detection, which is not applicable to DML. Detecting free-riders in a peer-to-peer network is challenging because each participant has limited information about the true positive contributions of others, which are based solely on their private local dataset. To solve the problem, we aim to use a decentralized approach to defend against free-rider attacks. We aim to develop an incentive mechanism that ensures every participant leaves the system with a global model reflecting their incremental contributions to DML.
3.5. Blockchain Incentive Model
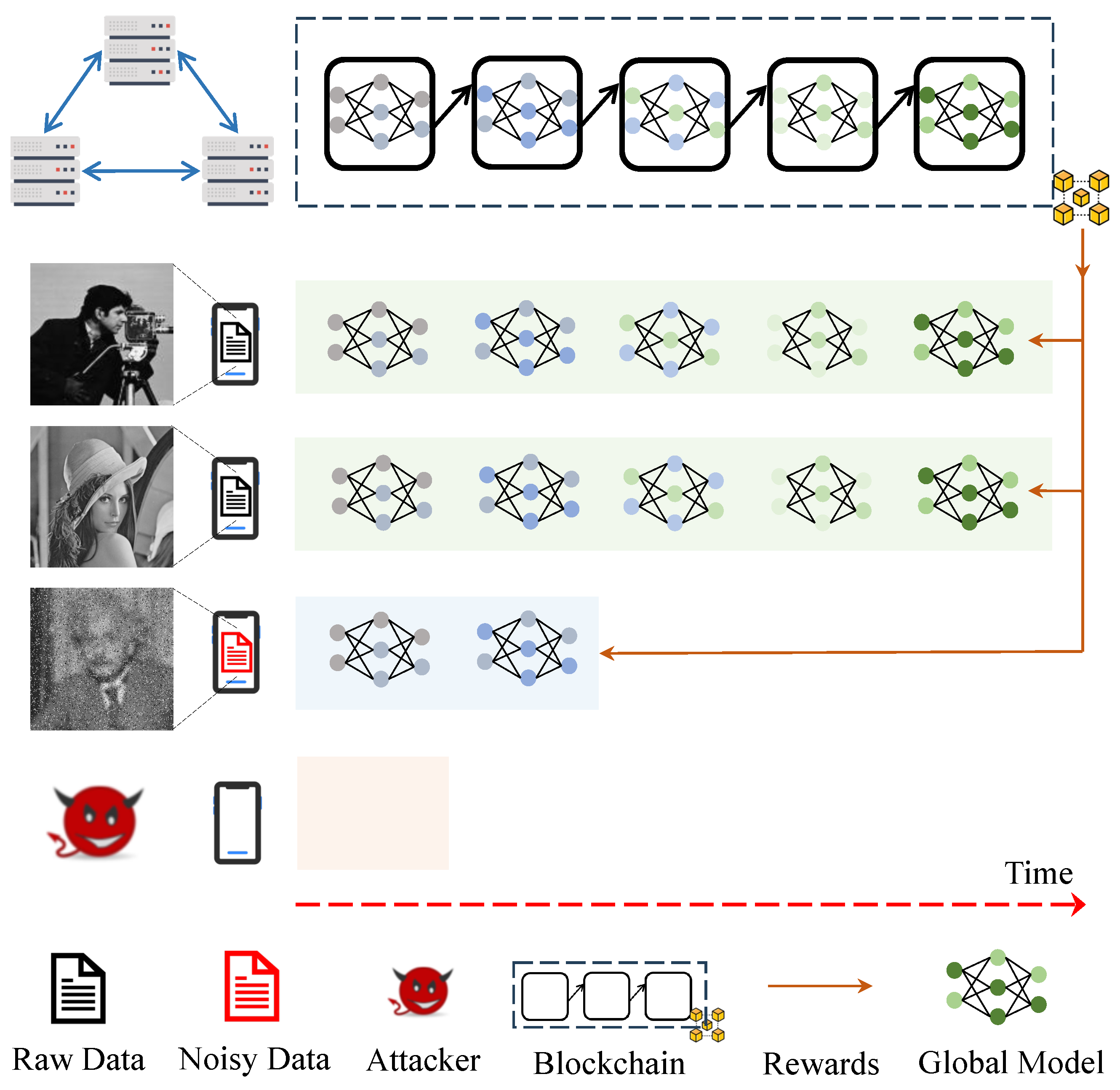
Blockchain is a record list chained with consecutive timestamps. As training continues, the performance of the global model improves. Therefore, it is perfectly suitable to discriminate the value of global models according to timestamped records. Our proposed incentive model is illustrated in Figure 3.
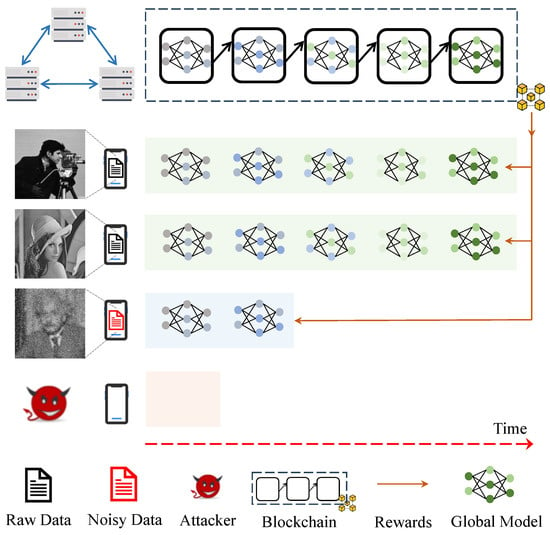
Figure 3.
Proposed time-dependent incentive mechanism atop blockchain: users gain access to varying sets of global models as rewards in each round, depending on their diverse contributions; free-riders have very limited or no access to global models recorded on the blockchain.
In this paper, we consider synchronized communication during DML, as illustrated in Figure 1. However, smartphones may only be allowed to continue synchronized DML until a specific round based on their data valuations. For any smartphone n, it can download the up-to-date global model only when the phone is in the system. At the end of DML, smartphone n leaves the system with a global model reflecting its contribution to DML. All smartphones are required to contribute continually such that they can obtain the up-to-date global model as the model reward. As illustrated in Figure 3, any contributor, including free-riders, may access a set of global models. However, the length of the accessible model chain depends on the individual incremental contribution. Free-riders cannot access specific models that are beyond their access length. For any model recorded on blockchain, the length of the accessible model chain determines whether the access to is denied or permitted. In this context, weak contributors can still access a subset of on-chain models, while fake contributors may not have access to any model on the blockchain. As expected, weak contributors are not penalized at the same level as fake contributors.
Let V and be the valuation function in the system and the exit round of smartphone n, respectively. Let be a system parameter reflecting the valuation rate. For any smartphone n, we formally introduce the model reward constraint as
The above constraint ensures that any model reward will surely be based on data valuations contributed from any smartphone. Let ∈ = {, , ⋯, } denote the valuation of data contributed from smartphone n in round r. Refer to Section 4 for the calculation of . To estimate actual data contributions in round r, the data valuation of N distributed datasets are recorded on the blockchain.
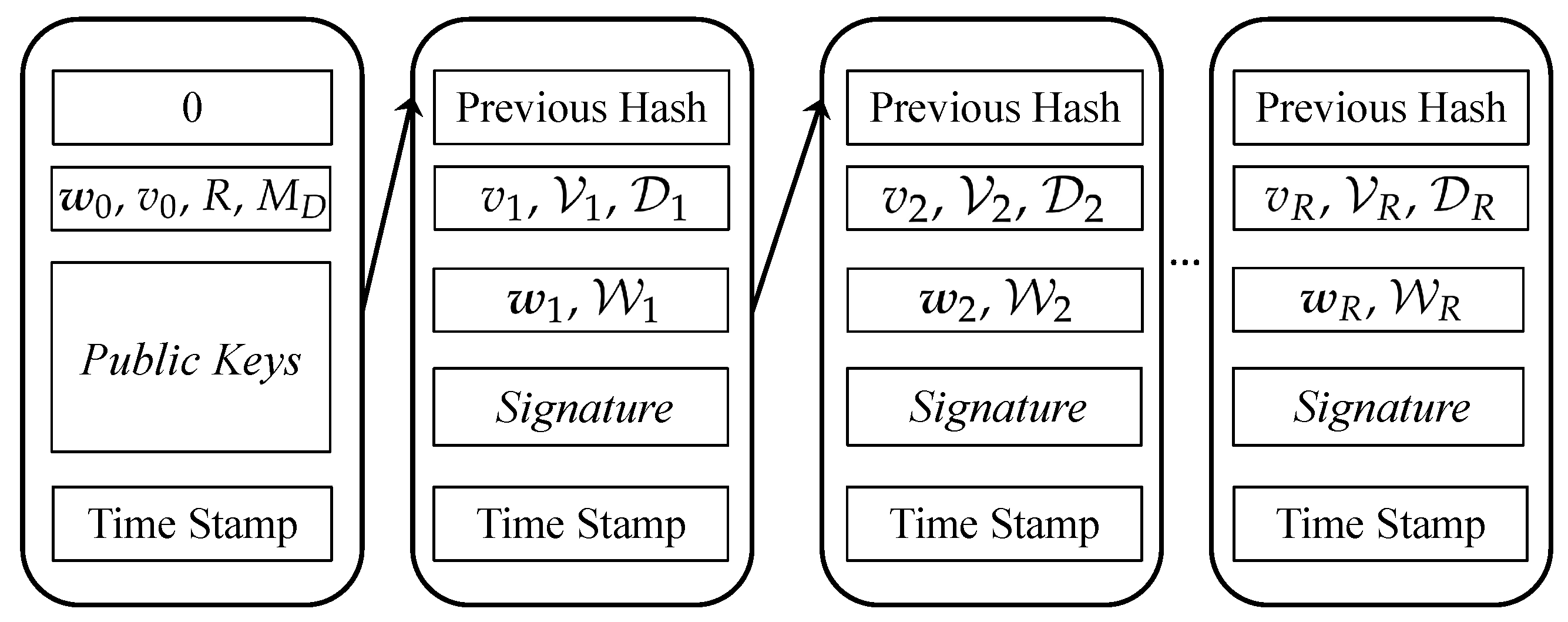
Our proposed blockchain structure is shown in Figure 4. Subscripts represent different rounds in DML. Let denote weights of the initial model for DML. keys are exchanged among verified smartphones and servers. Note that blockchain-enabled DML for smart health needs to follow data regulations for data safety protection. Therefore, a DPoS [13] is used in our system to ensure the security and integrity of data in distributed ledgers. We assume stakeholders stake tokens for votes. Stakeholders (i.e., smartphones) vote for servers with their stakes. Let ∈ = {, , ⋯, } denote votes received by server m in round r. Let denote the number of delegated servers in DML. A detailed block generation workflow is described in Section 4. Note that the recorded data valuation can be verified by evaluating the prediction accuracy of local weights. Further discussions on blockchain-based data valuation are given in Section 4.
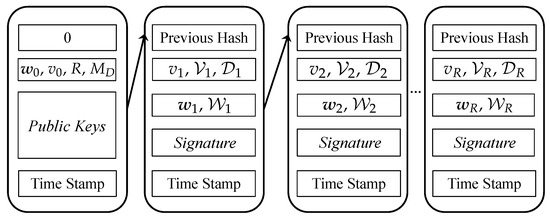
Figure 4.
Proposed blockchain for DML considering data valuation.
3.6. Problem Formulation
In a typical decentralized edge system, each smartphone prioritizes its own QoS without considering the impact on others. To improve the QoS of collaborative edge intelligence, for any user n, we focus on maximizing the utility of the downloaded global model within the latency requirement . Let and . More formally, considering constraints (1)–(3) and (7), we formulate the QoS optimization problem for any user as follows:
Note that (8) is a variant of the unbounded multiple knapsack problem (UMKP), a classic NP-hard combinatorial optimization problem [37], but differs from UMKP due to additional constraints (3) for a QoS guarantee and (7) for fair reward allocation. It is very challenging to achieve the optimal solution to (8) in DML, as true data distributions in heterogeneous edge networks are largely unpredictable. According to inequality (7), (8) can be relaxed to the following data valuation maximization problem:
We propose V based on decentralized calculations in Section 4 and discuss an optimized solution to (8) in Section 5.
4. Decentralized Data Valuation
In this section, we demonstrate a collaborative method to evaluate data value for improving the QoS of every smartphone. We first describe the workflow of block generation for a decentralized assessment of data contribution. We further identify the IID property of data as a criterion in distributed data evaluation. Then, we propose our novel data valuation approach for our decentralized system.
4.1. Block Generation Workflow
In our DPoS blockchain, servers that ascend to the top votes join the consensus group and become delegated servers. Servers with the same number of votes are sorted by ascending hash values of public keys. To attract enough votes, servers need to build strong and positive reputations by following data regulations in DML.
For round r, a leading server , ∈ = {1, 2, ⋯, }, from the delegated servers is selected by
Then, delegated server collects transactions, aggregates local weights and generates a new block. Note that L equals the number of output digits from .
As an additional clarification of Figure 4, we first show genesis block generation at the start of DML: Genesis Block Generation: (round 0): (1) Blockchain stakeholders deploy initial weights with total round number R and number of delegated servers ; (2) verified servers and smartphones register in DML by submitting their keys; (3) smartphones submit votes to select servers; (4) a server is selected by (10) to create a genesis block.
We further clarify the workflow of one round as follows: Regular Block Generation: (round r, ): (1) Any smartphone n, n∈, collects health data to train a set of local weights ; (2) after exchanging in a peer-to-peer network, each smartphone n calculates and broadcasts other smartphones’ data contributions and determines based on received local weights and its local health data, respectively; (3) any smartphone n submits , and to servers by launching a blockchain transaction signed by its key; (4) each server receives and verifies N transactions by the key set recorded on the genesis block, and then, a server is selected by DPoS to aggregate model weights; (5) the selected delegated server signs with its key and generates a new block, and then, the block is propagated to all servers for verification; (6) once is recorded on the blockchain, permitted smartphones can download ; (7) any smartphone can verify by the server’s key.
4.2. KL Divergence in Distributed Data
The Kullback–Leibler (KL) divergence of probability distribution p diverging from the referenced probability distribution q is denoted as [38]. In a general interpretation, KL divergence quantifies the expected information loss because of using distribution q to approximate the actual data distribution p.
In DML, training a deep network relies on the assumption that a stochastic gradient on distributed data is an unbiased estimate of the full gradient on the entire dataset (i.e., distributed health data are assumed to be IID) [5]. However, as introduced in Section 1, real datasets are non-IID. Therefore, a decrease in DML performance is inevitable. We use KL divergence as a metric to evaluate the information loss when applying SGD, which was originally designed for IID training data, in non-IID cases.
For smartphone n in round r, the KL divergence between the real data distribution and IID data distribution q is
where is unknown. Note KL divergence is asymmetric (i.e., ) in most cases [38]. According to (11), we can calculate the information loss of applying SGD on instead of the unknown q.
Let be the data quality of for N smartphones in round r. Suppose the data quantity is the same across N smartphones; is calculated by
can be used to indicate the true quality of distributed data in DML [39]. However, it is very challenging to compute due to the uncertainty of q and data quantity skews. In this paper, we investigate an alternative method to evaluate the valuation of any .
4.3. Decentralized Calculation of Data Valuation
One approach to approximate q is via decentralized cross-validation in distributed data networks. We define the utility of a global model as the validation accuracy based on private local data. Let be the validation dataset of smartphone n. The validation accuracy of any model , denoted by , is calculated by the ratio of matching predictions to the total number of validation samples. More formally, for any smartphone n, the utility of the global model in round r is calculated by
Let be the contribution of to smartphone i, . Then, is defined by
Note that because datasets from individual smartphones remain localized and are never transmitted beyond their respective devices. Then, the valuation of data contribution from any smartphone n is determined by all smartphones except n. That is,
Equation (15) describes a cross-validation of contributions. Every smartphone’s data valuation is truly based on its uploaded model weights and is determined by other smartphones. Therefore, the calculation of (i.e., ) is fully decentralized: relying solely on the blockchain records of model weights. To solve (8) and maximize , we argue that decentralized calculation of is a critical step to minimize at the network edge, especially when q is unpredictable.
- (1)
- Group rationality: The valuation of the per-round data contribution is completely distributed among all data contributors, i.e., .
- (2)
- Fairness: Two data contributors with identical data contributions should have the same valuation, i.e., if datasets and are identical; a free-rider n with zero for all other smartphones has zero valuation, i.e., .
- (3)
- Additivity: In any round r, the data valuation of multiple data contributors equals the sum of the data valuations of individual data contributors, i.e., .
Furthermore, we present the following theorem to elucidate how decentralized data valuation benefits collaborative edge intelligence.
Theorem 1.
Cross-validation of data contributions using (15) can prevent free-riders.
Proof of Theorem 1.
We will prove this by contradiction.
Suppose in any round r, , a free-rider j, , has data valuation of . An honest data contributor k, , has as the lowest data contribution among other honest contributors.
Suppose for the sake of contradiction proof, that the free-rider, smartphone j, can mimic the honest data contributor, smartphone k. That is, , and we can obtain
By examining (13) and (14), we can conclude that the free-rider achieves a greater improvement in validation accuracy on other smartphones compared with the honest contributor when the improvement is measured against the previous global model .
Therefore, the free-rider must improve more than the honest contributor. Now we have arrived at a contradiction. Thus, our initial assumption that smartphone i is a free-rider must be false. No free-rider can mimic an honest data contributor without a true contribution to the global model.
Therefore, (15) can make free-riders unable to mimic honest contributors and can block free-riders from our system. This completes the proof. □
5. Curriculum Data Scheduling
In this section, we introduce a novel method for smartphones to schedule their limited private data across multiple rounds for better QoS. We first give the analysis of the marginal utility of data samples. Next, principles of curriculum learning [40] are introduced, with a focus on local data scheduling at the network edge. Finally, a novel data scheduling method is proposed for every smartphone to improve the utility of the downloaded model.
5.1. Marginal Utility of Data Samples
Despite data valuation, the performance of a trained model also relies on the quantity of data used in DML. However, the test accuracy of a trained model does not increase linearly with the number of data samples [34]. In fact, as data quantity grows larger, model test accuracy increases more slowly. In other words, the marginal utility of data samples diminishes with data quantity in terms of test accuracy. Specifically, the term marginal refers to one health data sample in this paper. In round r, the utility of data samples, denoted by U, is used to measure contribution for improving the test accuracy of global model . We define the marginal utility of data samples as
where represents the change of contribution by adding one data sample, and = 1.
To demonstrate the diminishing of the marginal utility in DML, we define the marginal utility of data samples by the reciprocal of multiplied by a system parameter :
Therefore, is calculated by
where , meaning at least two samples are required for the calculation of the marginal utility. For a finite set of data samples , maximizing the marginal utility of each sample results in the highest possible value for . In this paper, we propose a novel solution to maximize data utility by optimizing the marginal value of each sample.
5.2. Principles of Curriculum Learning at the Network Edge
Curriculum, a learning strategy, refers to a structured set of content and learning experiences. In the realm of ML, curriculum learning is a concept inspired by the way humans learn new information progressively, from simpler instances to more complex ones. In the context of DML, we aim to design a training process in a way that starts with easier tasks and gradually moves to more difficult tasks. This learning approach has been proven to be helpful for improving the utility of global models [41].
To apply curriculum learning at the network edge, for any smartphone n, we summarize the following key principles:
- (1)
- Score functions should depend on the global model: Any instance in is mapped to a numerical value by a score function. As (8) aims to maximize the utility of the global model, this score function should solely rely on the global model.
- (2)
- Pacing functions should be monotonically increasing: The number of data samples scheduled per round is determined by a pacing function. Intuitively, it becomes more difficult to improve the performance as the global model converges. Therefore, more data should be scheduled for the later rounds to push the performance of the global model.
- (3)
- The difficulty level should be progressively increased: As model training progresses through successive rounds, the average difficulty level of is expected to increase with the round number r. Furthermore, should be sorted such that the difficulty level of instances is also progressively increasing during local training.
- (4)
- The amount of data learned per round should be optimized: In a typical edge system, latency should be considered a key QoS factor. Therefore, data samples processed per round should be controlled and optimized; otherwise, curriculum learning may not be practical for the network edge.
5.3. Optimized Data Scheduling with an Adaptive Window
Next, we introduce our approach based on the above principles. To begin with, we first define our score function for reflecting the difficulty of any instance. Motivated by [41], we choose a loss-based measure as the score. Let denote the true label indicator of the ith instance in : if the ground-truth class of the instance is l; otherwise, . Let be the probability value predicted from the softmax layer of global model . In any round r, the difficulty score of the ith instance in , denoted by , is defined as
A greater indicates a higher difficulty level.
Once is sorted in ascending order according to , the next step is to use a proper pacing function to balance the trade-off between effectiveness and latency. Let denote the sorted in round r. For any round r and smartphone n, we assume that is a system parameter and that the latency requirement is known before training. By examining (3), the upper bound of the number of rounds, denoted by , that smartphone n can participate in is calculated by
Unlike the pacing functions described in [41], we use a moving window that gradually increases and selects more difficult instances for training. Let , and be the initial number of data samples and start and end index of the sorted in round r, respectively. Considering the marginal utility of data samples, as described in Section 5.1, we propose the following moving window as our pacing function for any round r:
Note that only a subset of private local data is selected per round, i.e., . Our approach is shown to be effective in Section 7 with improved QoS. Then, the optimized dataset consists of instances selected from , which has been sorted based on difficulty. These instances are chosen from within a moving windows defined by Equations (22)–(24).
6. Algorithm Design for Improved QoS
In this section, we propose our solution to solve (8). We first analyze an optimized participation strategy for every smartphone and then summarize the model aggregation algorithm followed by a curriculum data scheduling algorithm.
6.1. An Optimized Participation Strategy at the Network Edge
For any smartphone n that aims to optimize (8), is required to be maximized within a limited number of rounds due to (3). As (8) is equivalent to (9), smartphone n can target maximizing the valuation of its data contribution within .
In DML with synchronized model aggregation, being denied access to the up-to-date global model even once can be catastrophic. Local training starting from a stale model results in a reduced contribution to the overall model utility [42]. Therefore, any smartphone n should make sure that the accumulated valuation is large enough to access the up-to-date global model; otherwise, will be reduced, since local training based on a stale model is inevitable. As time is limited, every participation opportunity is valuable. Therefore, an optimized strategy is to contribute in every round to accumulate valuations for better model rewards: that is,
Private data of any smartphone n are limited. An optimized approach to data usage in DML is to reuse each instance as frequently as possible to maximize its value. However, the reuse of instances might lead to model overfitting on and further reduce the valuation calculated by other smartphones. Therefore, we can use the proposed curriculum data scheduling in Section 5.3 for greater data valuation while not reducing global model utility. More formally, the optimized data scheduling for any smartphone n is described as
Intuitively, the proposed moving window ensures that easier instances are only used in the early rounds to help the global model converge fast. In contrast, more difficult instances are used in later rounds to push the near-converged model to better performance.
6.2. Decentralized Algorithm Design
Based on the above analysis, we propose (1) a data scheduling algorithm that can help maximize model utility within a latency constraint—curriculum learning is used in the algorithm with an adaptive moving window—and (2) an aggregation algorithm that can better reflect the diminishing marginal contribution effect with the data quantity to replace the one proposed by FedAvg. Both the valuation and marginal utility of data samples are considered in order to improve the test accuracy of the aggregated model.
We first describe our curriculum data scheduling algorithm as the pseudo-code in Algorithm 1.
Note that calculating is basically model inference on . The time complexity varies depending on the model structure. The time complexity of sorting operations for smartphone n is .
After local training on curriculum data, model weights are aggregated into a global model. Let and denote weights aggregated by considering marginal utility and information loss, respectively. We provide the pseudo-code for weight aggregation using blockchain-based data valuation in Algorithm 2.
| Algorithm 1 Proposed curriculum data scheduling for any smartphone n in round r. | |
| Input: Global model weights , private local dataset and latency requirement . | |
| Output: Local training dataset for the current round . | |
| 1: | for instance ∈ do // obtain difficulty score. |
| 2: | Calculate by (20); |
| 3: | end for |
| 4: | Sorting in ascending order. |
| 5: | Obtain by sorting accordingly. |
| 6: | Obtain according to (26). |
| Algorithm 2 Proposed aggregation algorithm for round r. | |
| Input: Model weights , and data quantity . | |
| Output: Global weights . | |
| 1: | for smartphone n∈ do // decentralized data valuation. |
| 2: | for i∈, do |
| 3: | Calculate by (14); |
| 4: | end for |
| 5: | end for |
| 6: | for server m∈ do // delegated servers conduct model aggregation. |
| 7: | if then // a round-robin leader conducts aggregation. |
| 8: | for n∈ do |
| 9: | Calculate by (15); |
| 10: | Calculate by (19); |
| 11: | end for |
| 12: | ←; |
| 13: | ←; |
| 14: | ←; // aggregation by valuation of data samples. |
| 15: | ←; // aggregation by data marginal utility. |
| 16: | if results in greater validation accuracy then |
| 17: | ←; |
| 18: | else |
| 19: | ←. |
| 20: | end if |
| 21: | end if |
| 22: | end for |
We choose to apply two aggregation protocols separately in every round. Global weights are obtained by comparing the utilities of aggregated weights and , i.e., and . Our scheme is shown to be effective in Section 7.
7. Performance Evaluations
In this section, we evaluate the proposed incentive mechanism against free-riders. Additionally, curriculum data scheduling is tested on two datasets: (1) CIFAR-10 images with 10 classes and (2) CIFAR-100 images with 100 classes [43]. We also show the information loss when training DNN on non-IID human activity recognition (HAR) signals [44]. We aim to show that data valuation and scheduling will work on datasets with different scales and distributions.
7.1. Experiment Settings and Benchmarks
To simulate real-world data distributions, two kinds of data distribution skews are applied to local datasets. Detailed settings are described as follows:
- (1)
- Label distribution skew: For the HAR dataset, we assume each smartphone owns the same number of samples. Six human activities are labeled: sitting, lying down, walking, going upstairs, going downstairs and standing. A total of 34,440 data samples are assigned to smartphones according to a Dirichlet distribution [45]. To match real-world data distributions, we set concentration parameter at 0.5 [46].
- (2)
- Label and data quantity skew: For the CIFAR-10 and CIFAR-100 datasets, we consider that each smartphone owns at most 4 out of 10 labels for CIFAR-10 and at most 8 out of 100 labels for CIFAR-100. Note that we do not consider simple cases wherein labels or the quantity of training data are uniformly distributed. We process CIFAR-10 data samples (10 classes, with 6000 images per class) and CIFAR-100 data samples (100 classes, with 600 images per class) to form our synthetic non-IID datasets based on [46]. To be specific, we simulate label skew by assigning a random subset of classes to each smartphone. The number of classes per phone is generated using the function random.randint( ). Then, we create quantity skew by using a Dirichlet distribution to allocate different amounts of data for each class to different smartphones. The use of the function numpy.random.dirichlet( ) results in non-uniform data quantities across smartphones (https://github.com/IBM/probabilistic-federated-neural-matching/blob/master/experiment.py accessed on 30 June 2024). To simulate different degrees of skews, we set = 10 and = 0.5 for CIFAR-10 and CIFAR-100, respectively.
We consider a fixed for smartphones (i.e., ) and in experiments. For each smartphone, data samples are shuffled according to a discrete uniform distribution. Then, 70% of 60,000 samples are used for training and 15% of 60,000 samples are used for validating and testing, respectively. For benchmarks and model training, we follow similar parameter settings as the open-source code base (https://github.com/CharlieDinh/pFedMe accessed on 30 June 2024). To be specific, we set the local learning rate to 0.005 for mini-batch SGD. The batch size and local iterations are set to 64 and 10, respectively.
In our experiments, we use a DNN for classification. To be specific, a DNN is defined in [47] for HAR datasets. For CIFAR datasets, we use Swin transformer v2 [48] trained on Imagenet as the pre-trained model. Model heads are three-layer DNNs with input size 768, middle dimensions 500 and 100, and output size 10 for CIFAR-10 and 100 for CIFAR-100. We perform DML using PyTorch [49] version 2.3.0+computecanada. To run the simulation, an NVIDIA V100L GPU is used, and 24 CPU cores and 180 gigabytes of RAM are allocated.
To assess our approaches on heterogeneous datasets, seven benchmarks are considered in our experiments: namely, FedProx [50], pFedMe [51], PerAvg [52], Curricula [41], Anti-Curricula, Random Weights and Addictive Noise [7,8]. FedProx uses a regulation term between local and global models to mitigate deviations. Similarly, pFedMe uses Moreau envelopes as regularized loss functions. PerAvg is a meta-learning approach to handle the data heterogeneity problem. The superiority of our data scheduling is shown by comparing it with the state-of-the-art (SOTA) Curricula, for which our proposed adaptive window is missing. Curricula uses 20% of in round 1, linearly increases to 100% at round , and maintains the quantity thereafter. Additionally, we use Anti-Curricula as a benchmark, wherein instances are learned from difficult ones to easier ones. To ensure consistency across experiments, FedAvg [53] is employed as the standard aggregation protocol for both the proposed data scheduling method and the benchmark scheduling algorithms.
Finally, to show the effectiveness of our incentive mechanism as a defense against free-riding attacks, we use random weights and local weights from other models with additive Gaussian noise to simulate attackers. A total of 10% of the smartphones are considered as free-riders in our system. Specifically, the Random Weights attack generates a new model with weights sampled from a normal distribution based on the statistics of the current global model weights. The mean of each new weight is set to the mean of the corresponding global weights, while the standard deviation is scaled to 1% of the original standard deviation. The Additive Noise attack adds Gaussian noise to the aggregated model of the local models submitted from others in the current round, where the noise is drawn from a normal distribution with mean 0 and a standard deviation set to 10% of the parameter’s current standard deviation. Both attacks aim to simulate different strategies that malicious participants might employ to free-ride in the DML system without meaningful contributions.
7.2. Results and Discussion
We evaluate our blockchain-based approaches from different perspectives, with a focus on heterogeneous data environments at the network edge.
7.2.1. QoS Improvement with Heterogeneous Data
In an edge intelligence system utilizing DML, QoS is primarily determined by two factors: training latency and model test accuracy. An improvement in QoS is achieved either by reducing the time required to produce a deployable global model or by attaining a global model with higher test accuracy within the specified latency constraints.
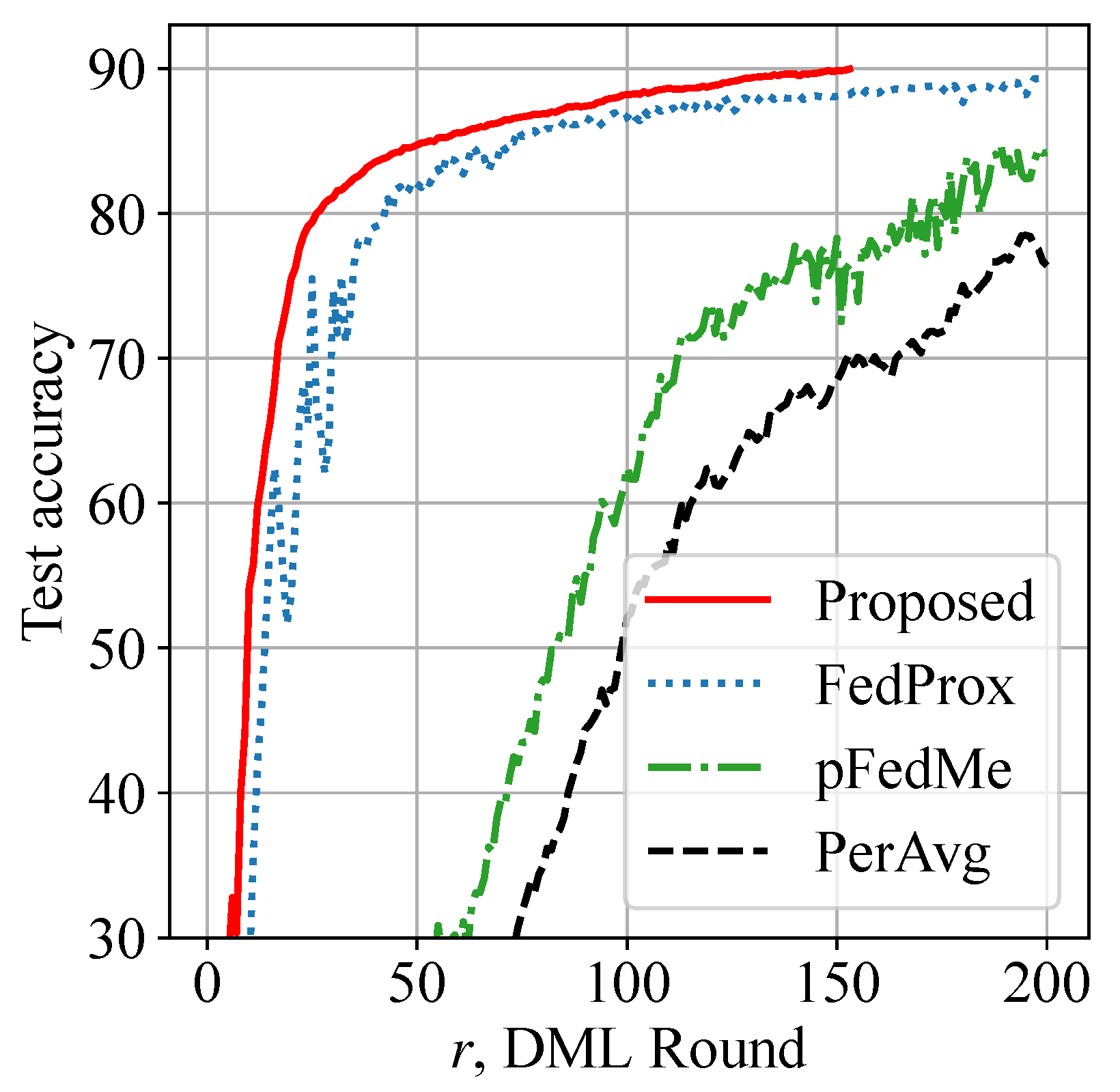
Figure 5 shows a training latency reduction by the proposed Algorithms 1 and 2. The test accuracy is calculated by averaging global model test accuracy values across 20 smartphones. An observation related to the CIFAR-10 dataset is that the global model converges smoothly and quickly to 90% accuracy using our approach. Latency is reduced by more than 25% compared with benchmarks. However, an additional observation is that the test accuracy of our proposed protocol and FedProx is relatively close when = 10. Therefore, our solution may not boost test accuracy significantly when local data distributions are more homogeneous.
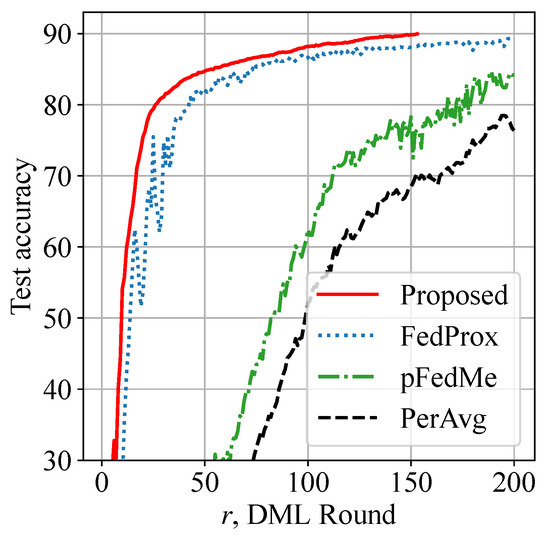
Figure 5.
Training latency reduction: proposed approach shows more than 25% faster convergence speed to reach 90% test accuracy on CIFAR-10 dataset.
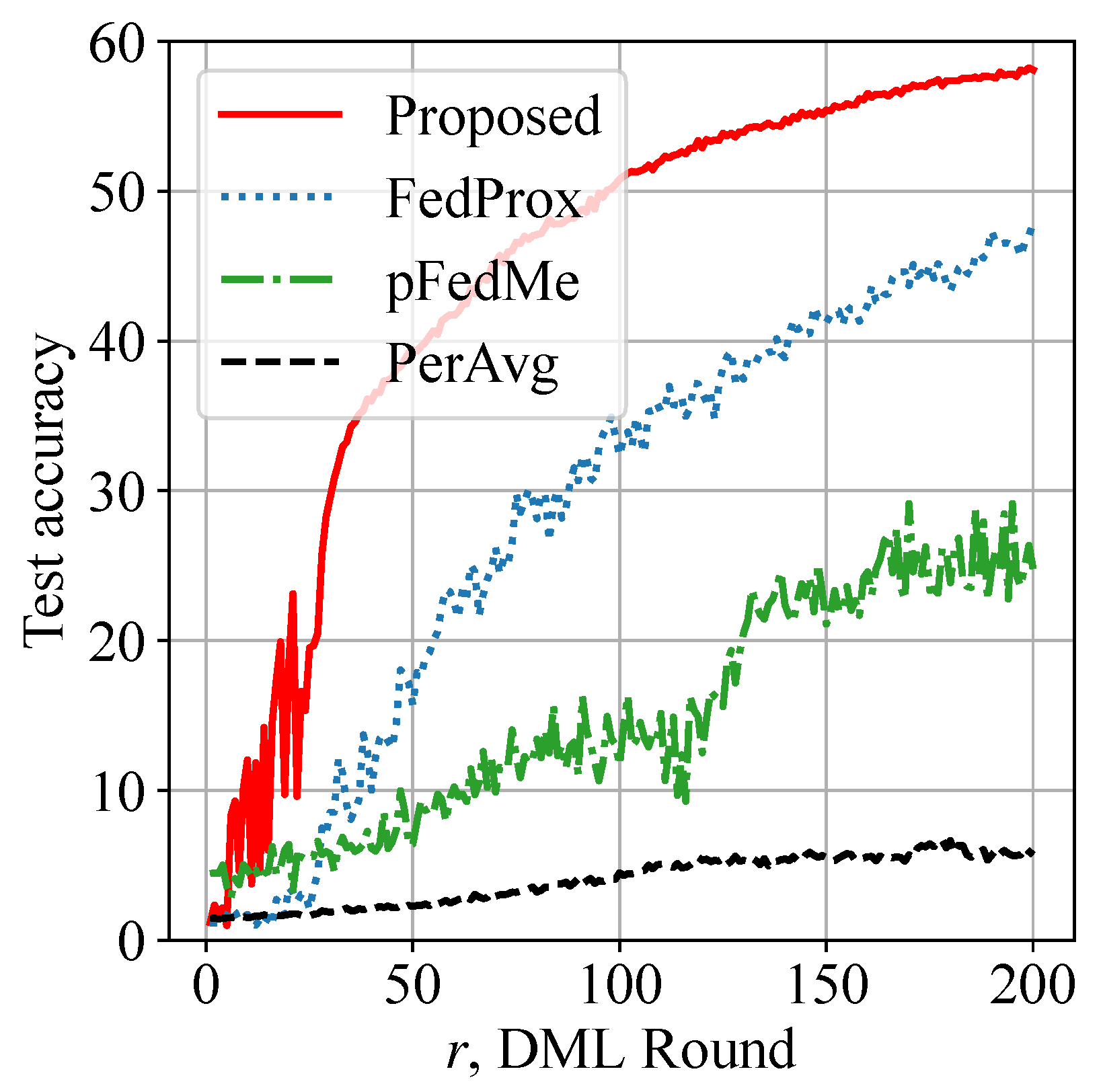
Figure 6 demonstrates a more challenging scenario using the CIFAR-100 dataset, where the global model is trained within a time constraint to classify testing instances into 100 distinct categories. A notable improvement in test accuracy is achieved by our approach, while the benchmarks are below 50% accuracy and are thus not usable. Therefore, the model utility is shown to be enhanced. We also remind the reader that it is very challenging to reach a test accuracy close to 100% on CIFAR-100 in heterogeneous networks where = 0.5. Although model design is not the focus of this paper, an advanced model structure can be considered atop our solution for improved model utility.
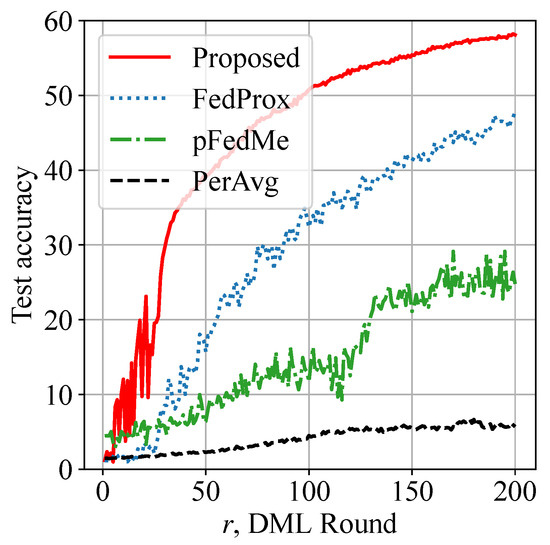
Figure 6.
Model utility enhancement: proposed approach shows more than 10% improvement in test accuracy on CIFAR-100 dataset.
Compared with the benchmarks, our proposed Algorithm 2 utilizes decentralized data valuation to assess actual contributions. Therefore, local weights trained from a dataset that closely resembles an IID dataset have larger summation weights in aggregation. As mini-batch SGD is designed for training on IID data, our proposed scheme can make mini-batch SGD function well under non-IID data settings.
7.2.2. Effectiveness of Data Scheduling at the Network Edge
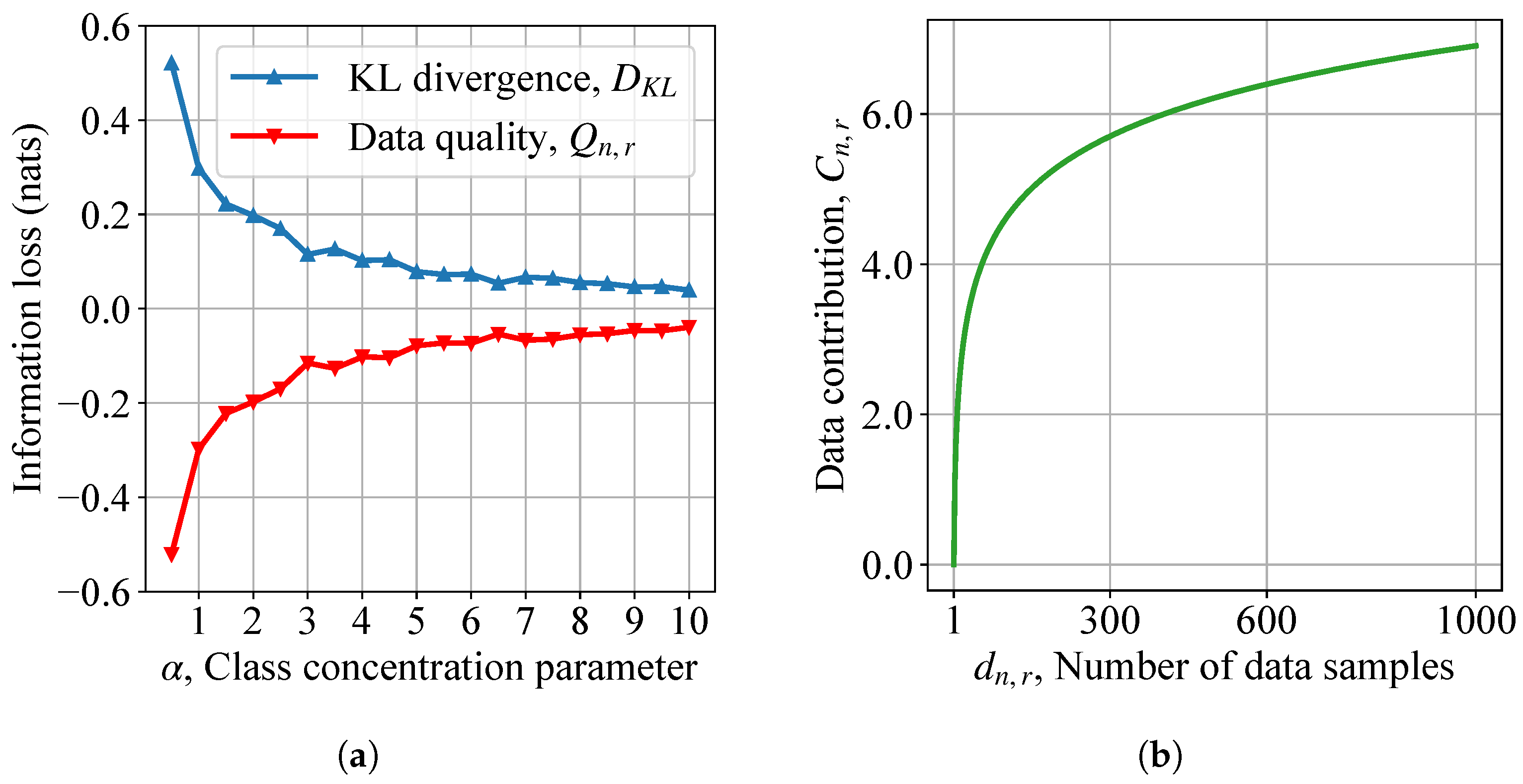
To evaluate data scheduling at the network edge, we first illustrate the information loss and marginal utility of non-IID HAR data samples in Figure 7.
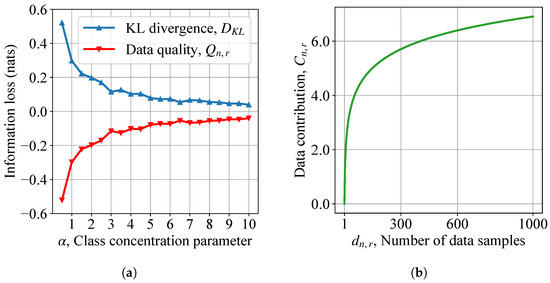
Figure 7.
Information loss and marginal utility of heterogeneous HAR datasets: (a) information loss of label skews; (b) marginal utility as a function of data quantity.
As class concentration parameter increases, local data distributions become more homogeneous. As mini-batch SGD performs well on IID datasets, data quality increases in Figure 7a. Furthermore, the diminishing effect of data marginal utility is shown in Figure 7b. An interesting observation is that the prediction accuracy curves in Section 7.2.1 reflect the marginal utility. Therefore, (19) as derived can approximate the real diminishing formula of the data marginal utility effectively.
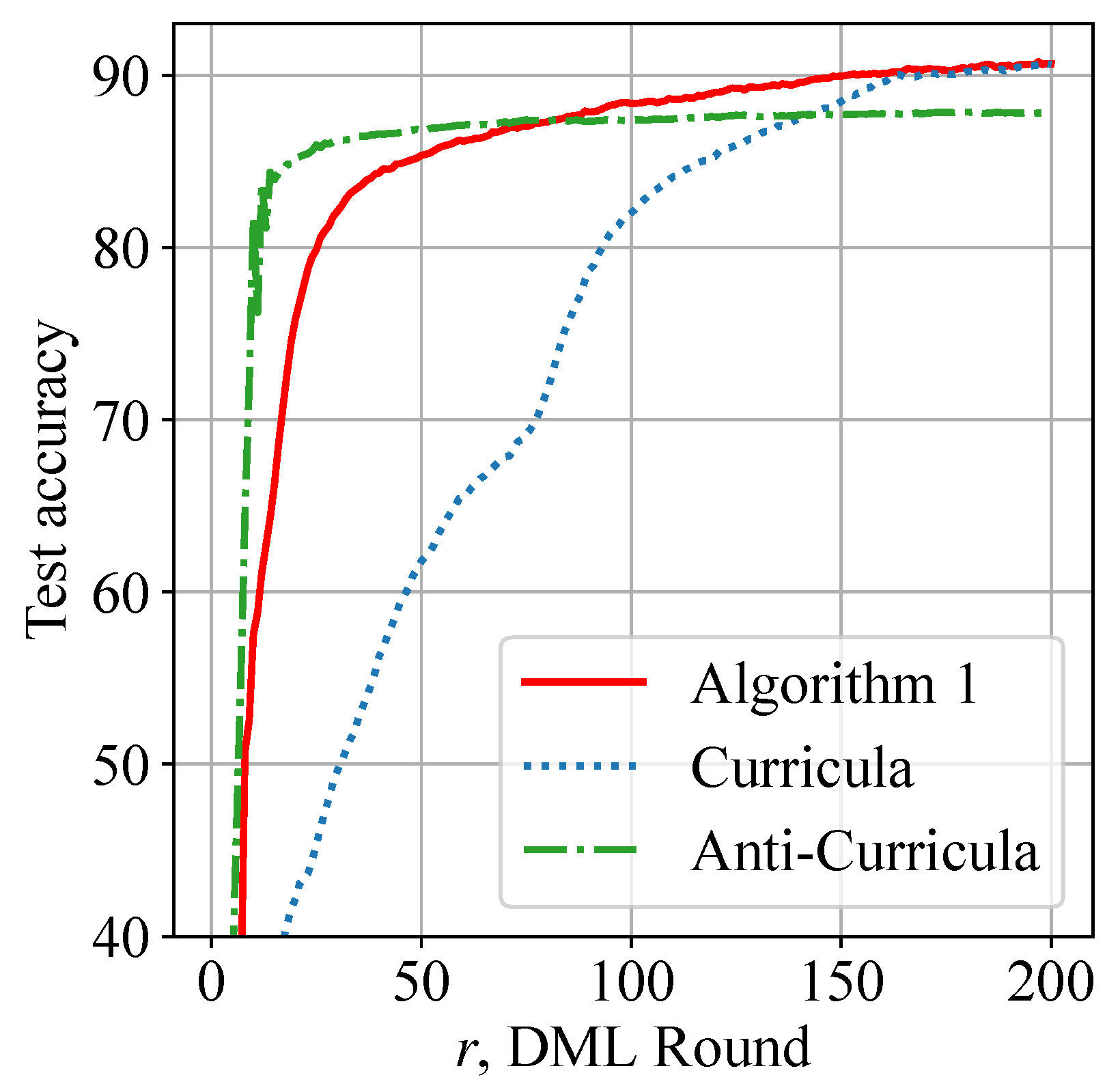
Figure 8 shows that our proposed data scheduling can achieve slightly better performance than SOTA Curricula when all three methods use FedAvg as the model aggregation protocol. Algorithm 1 and Curricula achieve 90% test accuracy on CIFAR-10 images with similar times, while Anti-Curricula fails to reach the desired 90% accuracy threshold.
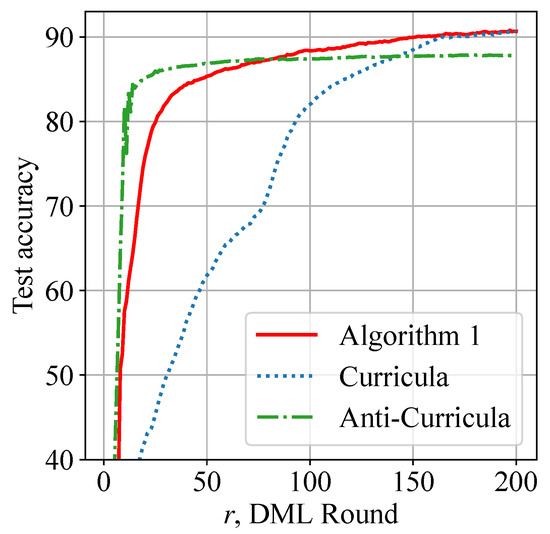
Figure 8.
Similar performance with SOTA Curricula: Algorithm 1 and Curricula reach 90% test accuracy faster than Anti-Curricula.
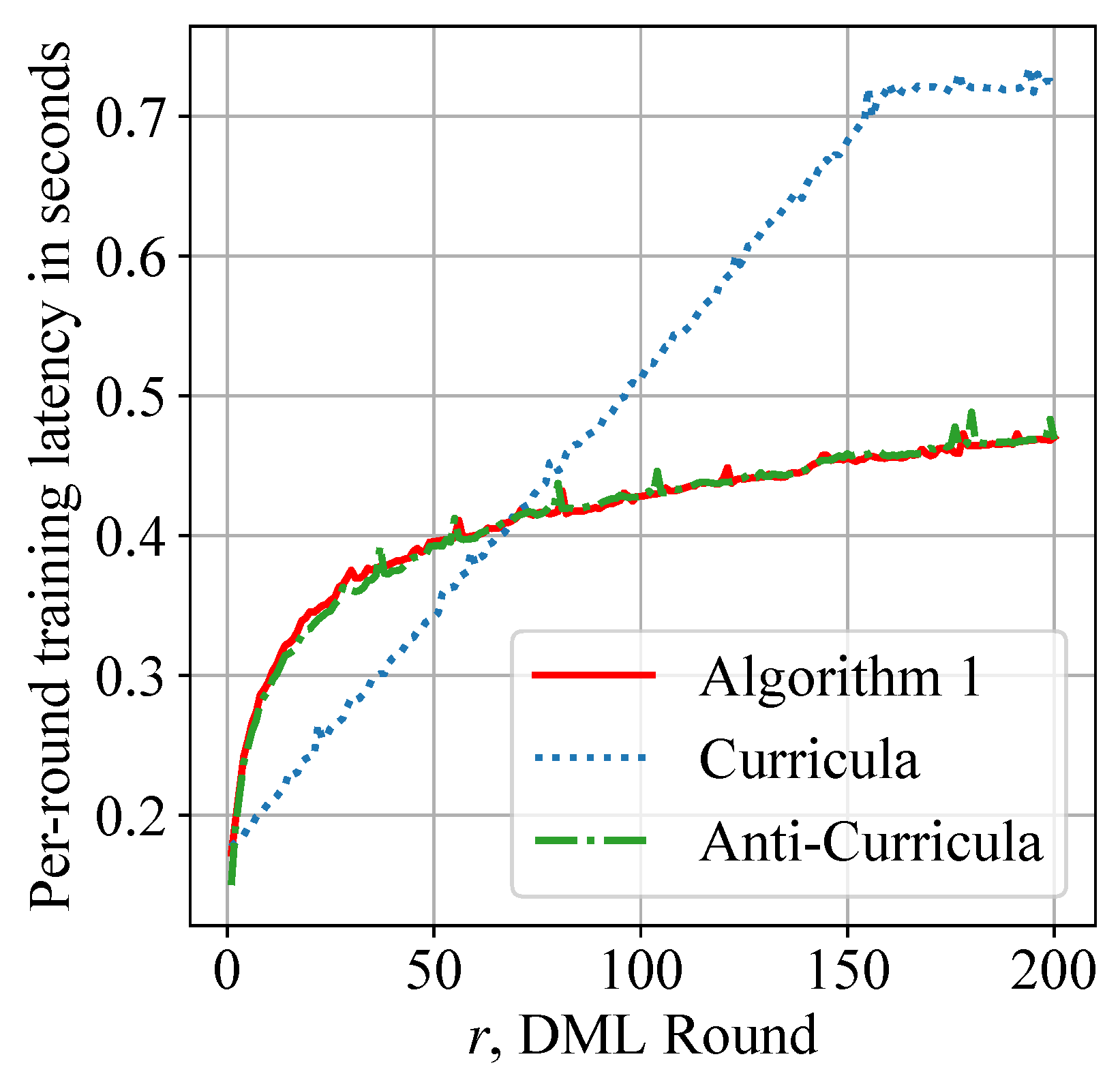
Although Curricula achieves similar performance to our design, it uses a significantly greater amount of data samples per round; thereby, training latency is increased. Figure 9 shows the average training latency of each smartphone during DML. Algorithm 1 is observed to reduce the overall training latency by 30% and achieve approximately 50% latency reduction in later rounds. Figure 8 and Figure 9 jointly show the superiority of our data scheduling algorithm.
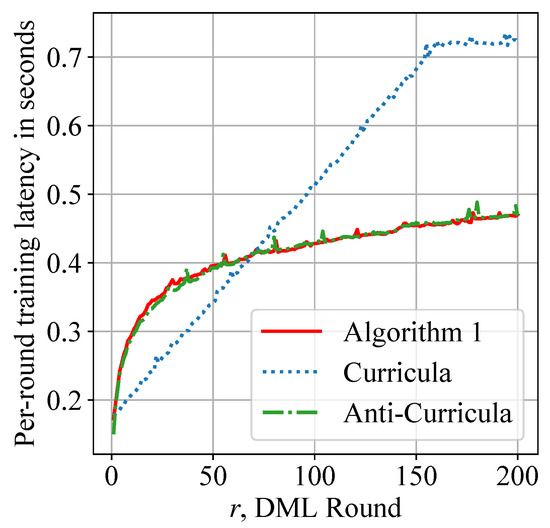
Figure 9.
Reduced per-round training latency: our adaptive moving window is applied to both Algorithm 1 and Anti-Curricula to reduce overall training latency by about 30% during DML.
7.2.3. Robustness against Free-Riding Attacks
Our proposed time-dependent incentive mechanism aims to track the incremental contribution of each smartphone. Note that Algorithm 2 takes data valuation as the factor in model aggregation. With our design, contributors with low or zero data valuations will have minimal impact on the aggregated global model. We further illustrate the incremental valuation of honest contributors and attackers to show the superiority of our decentralized data valuation.
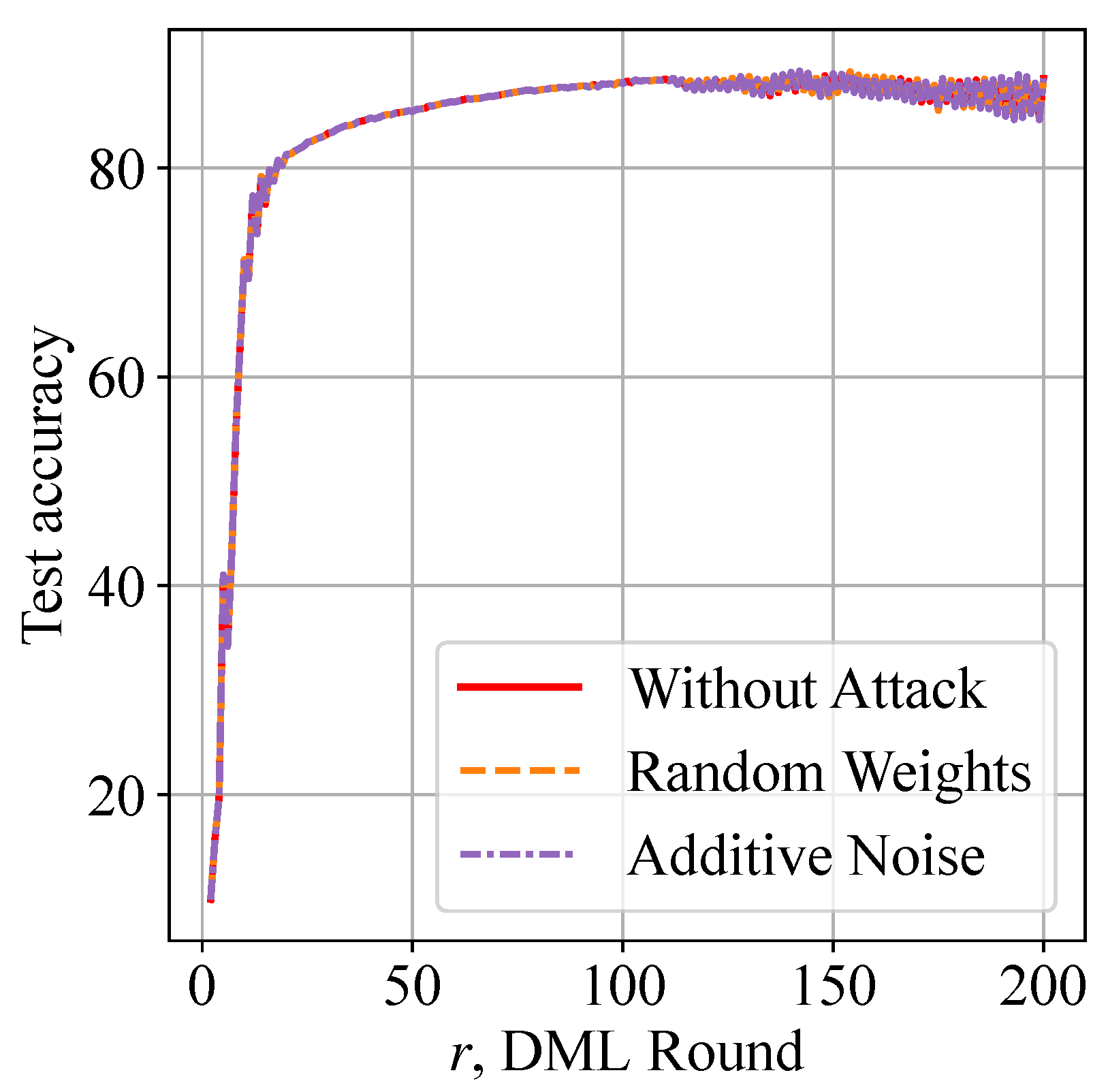
Figure 10 shows that the QoS of classifying CIFAR-10 images is not changed with or without free-riding attacks. The resilience against free-riders is a desired security feature in collaborative edge intelligence, where fairness must be guaranteed.
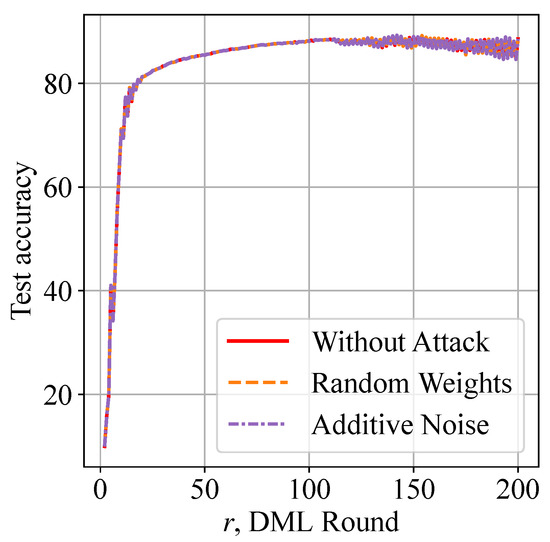
Figure 10.
Superior resilience against free-riding attacks: free-riders that conduct random weights and additive noise attacks do not harm the QoS of collaborative edge intelligence.
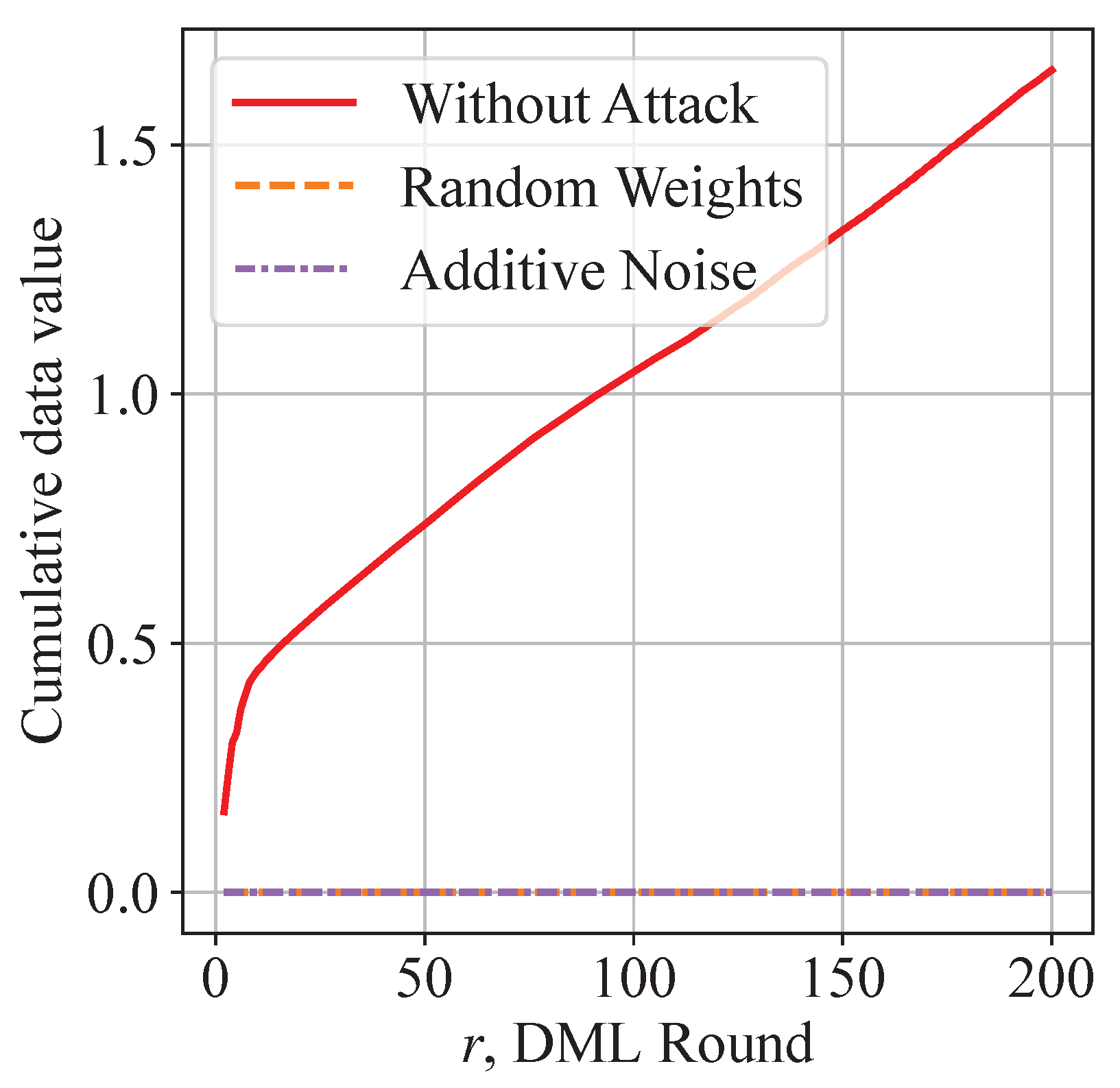
Furthermore, Figure 11 shows the cumulative data valuation of honest contributors without an attack and with free-riders conducting an attack. As attackers do not contribute to the validation accuracy of honest contributors, the data valuation of attackers remains zero. In Figure 11, free-riders try to attack in every round. As the cumulative data valuation of honest contributors increases, it becomes increasingly difficult to mimic an honest contributor and achieve a successful attack. The observation and analysis jointly explain why the QoS of our system does not change under free-riding attacks.
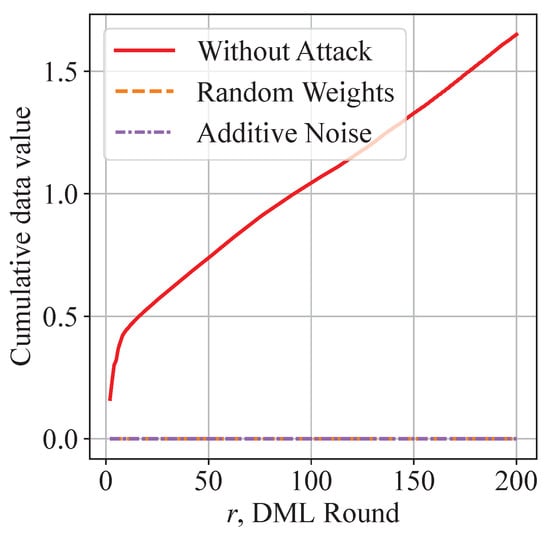
Figure 11.
Distinct data valuation helps discriminate attackers: decentralized valuation of data contribution shows superior discriminative performance.
8. Conclusions
In this paper, a time-dependent and decentralized data valuation approach has been proposed to improve the QoS of collaborative edge intelligence and defend against free-riding attacks. By considering information loss and diminishing marginal utility of data, a robust aggregation algorithm has been proposed for improving DML on non-IID data. Based on experimental results, we have shown that the QoS of edge intelligence can be improved by decentralized device collaboration and curriculum data scheduling at the network edge. We have improved DML by evaluating and understanding data rather than designing finely tuned models. Our blockchain-enabled data-centric method has been shown to be simple yet effective at improving the fairness and performance of DML. Based on experiments and observations, we conclude that decentralization of data valuation with scheduling is a promising approach towards collaborative edge intelligence.
Despite the advantages of our approach, we remind the reader that maintaining local validation data on every smartphone is still required for cross-validation. For future work, we will study a data-free valuation framework. Additionally, the privacy issue of uploading model weights is not the focus of this paper. Therefore, we will also study how to improve the differential privacy of honest contributors in a blockchain network.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization and methodology, Y.D., Z.W. and C.L.; resources, V.C.M.L.; data curation, Y.D.; writing—original draft preparation, Y.D.; writing—review and editing, C.L., Z.W. and V.C.M.L.; visualization, Y.D.; supervision, C.L., Z.W. and V.C.M.L.; project administration, Z.W.; funding acquisition, V.C.M.L., Z.W. and C.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported in part by Blockchain@UBC, by the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council (NSERC) of Canada (CREATE grant 528125 and grants RGPIN-2019-06348, RGPIN-2020-05410, RGPIN-2021-02970 and DGECR-2021-00187), by Public Safety Canada (NS-5001-22170), by the Guangdong Pearl River Talent Recruitment Program (grant 2019ZT08X603), by Guangdong Pearl River Talent (grant 2019JC01X235), by the Shenzhen Science and Technology Innovation Commission (grant R2020A045) and by the UBC PMC-Sierra Professorship in Networking and Communications.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets used in this study are derived from public domain resources. The CIFAR-10 and CIFAR-100 datasets are available from the Canadian Institute for Advanced Research (CIFAR) at: https://www.cs.toronto.edu/~kriz/cifar.html accessed on 30 June 2024. The Human Activity Recognition (HAR) dataset is available from the UCI Machine Learning Repository at: https://archive.ics.uci.edu/ml/datasets/Human+Activity+Recognition+Using+Smartphones accessed on 30 June 2024. These datasets are widely used benchmarks in the machine learning community and are freely accessible for research purposes.
Acknowledgments
Simulations were enabled by support from the Cedar Cluster at the Digital Research Alliance of Canada.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| ML | Machine learning |
| AI | Artificial intelligence |
| IoT | Internet of Things |
| QoS | Quality of service |
| DML | Distributed machine learning |
| FL | Federated learning |
| SGD | Stochastic gradient descent |
| SPOF | Single point of failure |
| DNN | Deep neural network |
| non-IID | Not independent and identically distributed |
| PoW | Proof-of-work |
| MEC | Multi-access computing |
| DPoS | Delegated proof-of-stake |
| UMKP | Unbounded multiple knapsack problem |
| KL | Kullback–Leibler |
| HAR | Human activity recognition |
| CIFAR | Canadian Institute for Advanced Research |
| SOTA | State-of-the-art |
References
- Li, Z.; Wallace, E.; Shen, S.; Lin, K.; Keutzer, K.; Klein, D.; Gonzalez, J. Train big, then compress: Rethinking model size for efficient training and inference of transformers. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, Virtual, 13–18 July 2020; pp. 5958–5968. [Google Scholar]
- Letaief, K.B.; Shi, Y.; Lu, J.; Lu, J. Edge artificial intelligence for 6G: Vision, enabling technologies, and applications. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 2021, 40, 5–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yarkoni, T.; Westfall, J. Choosing prediction over explanation in psychology: Lessons from machine learning. Perspect. Psychol. Sci. 2017, 12, 1100–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, W.Y.B.; Luong, N.C.; Hoang, D.T.; Jiao, Y.; Liang, Y.C.; Yang, Q.; Niyato, D.; Miao, C. Federated Learning in Mobile Edge Networks: A Comprehensive Survey. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutorials 2020, 22, 2031–2063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Sahu, A.K.; Talwalkar, A.; Smith, V. Federated Learning: Challenges, Methods, and Future Directions. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2020, 37, 50–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Li, H.; Liu, X.; Guo, Y. Frad: Free-rider attacks detection mechanism for federated learning in AIoT. IEEE Internet Things J. 2023, 11, 4377–4388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Du, M.; Liu, J. Free-riders in Federated Learning: Attacks and Defenses. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1911.12560. [Google Scholar]
- Fraboni, Y.; Vidal, R.; Lorenzi, M. Free-rider attacks on model aggregation in federated learning. In Proceedings of the Artificial Intelligence and Statistics, Virtual, 13–15 April 2021; pp. 1846–1854. [Google Scholar]
- Strickland, E. Andrew Ng, AI Minimalist: The Machine-Learning Pioneer Says Small is the New Big. IEEE Spectr. 2022, 59, 22–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abarbanel, H.D.; Rozdeba, P.J.; Shirman, S. Machine learning: Deepest learning as statistical data assimilation problems. Neural Comput. 2018, 30, 2025–2055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rausch, O.; Ben-Nun, T.; Dryden, N.; Ivanov, A.; Li, S.; Hoefler, T. A data-centric optimization framework for machine learning. In Proceedings of the ACM International Conference on Supercomputing, Virtual, 28–30 June 2022; pp. 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, D.C.; Ding, M.; Pham, Q.V.; Pathirana, P.N.; Le, L.B.; Seneviratne, A.; Li, J.; Niyato, D.; Poor, H.V. Federated Learning Meets Blockchain in Edge Computing: Opportunities and Challenges. IEEE Internet Things J. 2021, 8, 12806–12825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Zhang, N.; Lou, W.; Hou, Y.T. A Survey of Distributed Consensus Protocols for Blockchain Networks. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2020, 22, 1432–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Li, Y.; Li, W.; Guo, K.; Shao, Y. Personalized federated learning via variational bayesian inference. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, Baltimore, MD, USA, 17–23 July 2022; pp. 26293–26310. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Ren, X.; Qiu, C.; Xiong, Z.; Yao, H.; Leung, V.C. Integrating edge intelligence and blockchain: What, why, and how. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutorials 2022, 24, 2193–2229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Zhu, Y.; Maharjan, S.; Zhang, Y. Edge intelligence and blockchain empowered 5G beyond for the industrial Internet of Things. IEEE Netw. 2019, 33, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Wang, Z.; Leung, C.; Leung, V.C. Accelerating and Securing Blockchain-enabled Distributed Machine Learning. IEEE Trans. Mob. Comput. 2023, 23, 6712–6730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Li, M.; He, Y.; Li, H.; Xiao, K.; Wang, C. A blockchain based privacy-preserving incentive mechanism in crowdsensing applications. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 17545–17556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, C.; Yao, H.; Wang, X.; Zhang, N.; Yu, F.R.; Niyato, D. AI-chain: Blockchain energized edge intelligence for beyond 5G networks. IEEE Netw. 2020, 34, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Shankar, A.; Li, K.; Parameshachari, B.; Lv, J. Blockchain-Enabled Decentralized Edge Intelligence for Trustworthy 6G Consumer Electronics. IEEE Trans. Consum. Electron. 2024, 70, 1214–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Ge, J.; Li, Y.; Deng, Y.; Gao, L.; Zhang, M.; Xiang, Y.; Zheng, X. Scei: A smart-contract driven edge intelligence framework for IoT systems. IEEE Trans. Mob. Comput. 2023, 23, 4453–4466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, W.; Tadesse, G.A.; Ho, D.; Fei-Fei, L.; Zaharia, M.; Zhang, C.; Zou, J. Advances, challenges and opportunities in creating data for trustworthy AI. Nat. Mach. Intell. 2022, 4, 669–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, R.; Dao, D.; Wang, B.; Hubis, F.A.; Hynes, N.; Gürel, N.M.; Li, B.; Zhang, C.; Song, D.; Spanos, C.J. Towards efficient data valuation based on the shapley value. In Proceedings of the Artificial Intelligence and Statistics, Naha, Japan, 16–18 April 2019; pp. 1167–1176. [Google Scholar]
- Ghorbani, A.; Zou, J. Data shapley: Equitable valuation of data for machine learning. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, Long Beach, CA, USA, 9–15 June 2019; pp. 2242–2251. [Google Scholar]
- Ghorbani, A.; Kim, M.; Zou, J. A distributional framework for data valuation. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, Virtual, 13–18 July 2020; pp. 3535–3544. [Google Scholar]
- Song, T.; Tong, Y.; Wei, S. Profit allocation for federated learning. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Big Data, Los Angeles, CA, USA, 9–12 December 2019; pp. 2577–2586. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, T.; Rausch, J.; Zhang, C.; Jia, R.; Song, D. A principled approach to data valuation for federated learning. In Federated Learning: Privacy and Incentive; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 153–167. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Ai, Z.; Sun, S.; Zhang, S.; Liu, Z.; Yu, H. Fedcoin: A peer-to-peer payment system for federated learning. In Federated Learning: Privacy and Incentive; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 125–138. [Google Scholar]
- Le, T.H.T.; Tran, N.H.; Tun, Y.K.; Nguyen, M.N.; Pandey, S.R.; Han, Z.; Hong, C.S. An incentive mechanism for federated learning in wireless cellular networks: An auction approach. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2021, 20, 4874–4887. [Google Scholar]
- Koh, P.W.; Liang, P. Understanding black-box predictions via influence functions. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, Sydney, Australia, 6–11 August 2017; pp. 1885–1894. [Google Scholar]
- Yoon, J.; Arik, S.; Pfister, T. Data valuation using reinforcement learning. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, Virtual, 13–18 July 2020; pp. 10842–10851. [Google Scholar]
- Warnat-Herresthal, S.; Schultze, H.; Shastry, K.L.; Manamohan, S.; Mukherjee, S.; Garg, V.; Sarveswara, R.; Händler, K.; Pickkers, P.; Aziz, N.A.; et al. Swarm, Learning, for, decentralized, a nd confidential clinical machine learning. Nature 2021, 594, 265–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Su, Z.; Zhang, N.; Benslimane, A. Learning in the Air: Secure Federated Learning for UAV-Assisted Crowdsensing. IEEE Trans. Netw. Sci. Eng. 2021, 8, 1055–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, Y.; Li, P.; Qu, Z.; Zeng, D.; Guo, S. A Learning-Based Incentive Mechanism for Federated Learning. IEEE Internet Things J. 2020, 7, 6360–6368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blum, A.L.; Rivest, R.L. Training a 3-node neural network is NP-complete. Neural Netw. 1992, 5, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, U.; Valiati, J.F. Pre-trained convolutional neural networks as feature extractors for tuberculosis detection. Comput. Biol. Med. 2017, 89, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martello, S.; Toth, P. Knapsack Problems: Algorithms and Computer Implementations; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- van Erven, T.; Harremos, P. Rényi Divergence and Kullback-Leibler Divergence. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 2014, 60, 3797–3820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Wang, Z.; Leung, C.; Leung, V. Blockchain-based Data Quality Assessment to Improve Distributed Machine Learning. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Computing, Networking and Communications, Honolulu, HI, USA, 20–22 February 2023; pp. 170–175. [Google Scholar]
- Soviany, P.; Ionescu, R.T.; Rota, P.; Sebe, N. Curriculum learning: A survey. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2022, 130, 1526–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vahidian, S.; Kadaveru, S.; Baek, W.; Wang, W.; Kungurtsev, V.; Chen, C.; Shah, M.; Lin, B. When do curricula work in federated learning? In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Vancouver, BC, CA, 17–24 June 2023; pp. 5084–5094. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, W.; He, L.; Lin, W.; Mao, R.; Maple, C.; Jarvis, S. SAFA: A semi-asynchronous protocol for fast federated learning with low overhead. IEEE Trans. Comput. 2020, 70, 655–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krizhevsky, A. Learning Multiple Layers of Features from Tiny Images. Master’s Thesis, University of Toronto, Toronto, ON, Canada, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Anguita, D.; Ghio, A.; Oneto, L.; Parra Perez, X.; Reyes Ortiz, J.L. A public domain dataset for human activity recognition using smartphones. In Proceedings of the European Symposium on Artificial Neural Networks, Computational Intelligence and Machine Learning, Bruges, Belgium, 24–26 April 2013; pp. 437–442. [Google Scholar]
- Hsu, T.M.H.; Qi, H.; Brown, M. Measuring the Effects of Non-Identical Data Distribution for Federated Visual Classification. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1909.06335. [Google Scholar]
- Yurochkin, M.; Agarwal, M.; Ghosh, S.; Greenewald, K.; Hoang, N.; Khazaeni, Y. Bayesian nonparametric federated learning of neural networks. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, Long Beach, CA, USA, 9–15 June 2019; pp. 7252–7261. [Google Scholar]
- Wong, E.; Schmidt, F.; Metzen, J.H.; Kolter, J.Z. Scaling provable adversarial defenses. In Proceedings of the Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Montréal, QC, Canada, 3–8 December 2018; pp. 8410–8419. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Hu, H.; Lin, Y.; Yao, Z.; Xie, Z.; Wei, Y.; Ning, J.; Cao, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Dong, L.; et al. Swin transformer v2: Scaling up capacity and resolution. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 12009–12019. [Google Scholar]
- Paszke, A.; Gross, S.; Massa, F.; Lerer, A.; Bradbury, J.; Chanan, G.; Killeen, T.; Lin, Z.; Gimelshein, N.; Antiga, L.; et al. Pytorch: An imperative style, high-performance deep learning library. In Proceedings of the Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 8–14 December 2019; pp. 8026–8037. [Google Scholar]
- Li, T.; Sahu, A.K.; Zaheer, M.; Sanjabi, M.; Talwalkar, A.; Smith, V. Federated optimization in heterogeneous networks. Proc. Mach. Learn. Syst. 2020, 2, 429–450. [Google Scholar]
- Dinh, C.T.; Tran, N.; Nguyen, J. Personalized federated learning with Moreau envelopes. In Proceedings of the Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 6–12 December 2020; pp. 21394–21405. [Google Scholar]
- Fallah, A.; Mokhtari, A.; Ozdaglar, A. Personalized federated learning: A meta-learning approach. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2002.07948. Available online: https://arxiv.org/abs/2002.07948 (accessed on 20 July 2024).
- McMahan, B.; Moore, E.; Ramage, D.; Hampson, S.; y Arcas, B.A. Communication-efficient learning of deep networks from decentralized data. In Proceedings of the Artificial Intelligence and Statistics, Ft. Lauderdale, FL, USA, 20–22 April 2017; pp. 1273–1282. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).