VSI Nonlinearity Compensation of a PMSM Drive System Using Deadbeat Prediction Based Current Zero-Crossing Detection
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- (1)
- Harmonic analysis methods. A low pass filter is used to separate high-frequency harmonic components of the control system. Then, the distortion voltage is estimated by minimizing the harmonics. Finally, the disturbance voltage due to the VSI nonlinearity is suppressed by performing feedback compensation [4,15,16,17,18,19];
- (2)
- (3)
- Model predictive control. The relationship between the voltage sector and current polarity are modeled and the error of the voltage vector can be obtained by the polarity of the current and real-time switching state. Finally, the synthesized voltage vectors can be applied to PWM-VSI to enhance the system’s performance [25,26,27].
- (4)
- Repetitive controller. It is assumed in Refs. [28,29] that the disturbance signal of the previous fundamental period is repeated at the same instant of the next period. On this basis, the controller generates an appropriate output according to the difference between the given and feedback signals, which can reduce the voltage distortion and improve the robustness of the system.
2. Mathematical Model of PMSM System Considering the VSI Nonlinearity
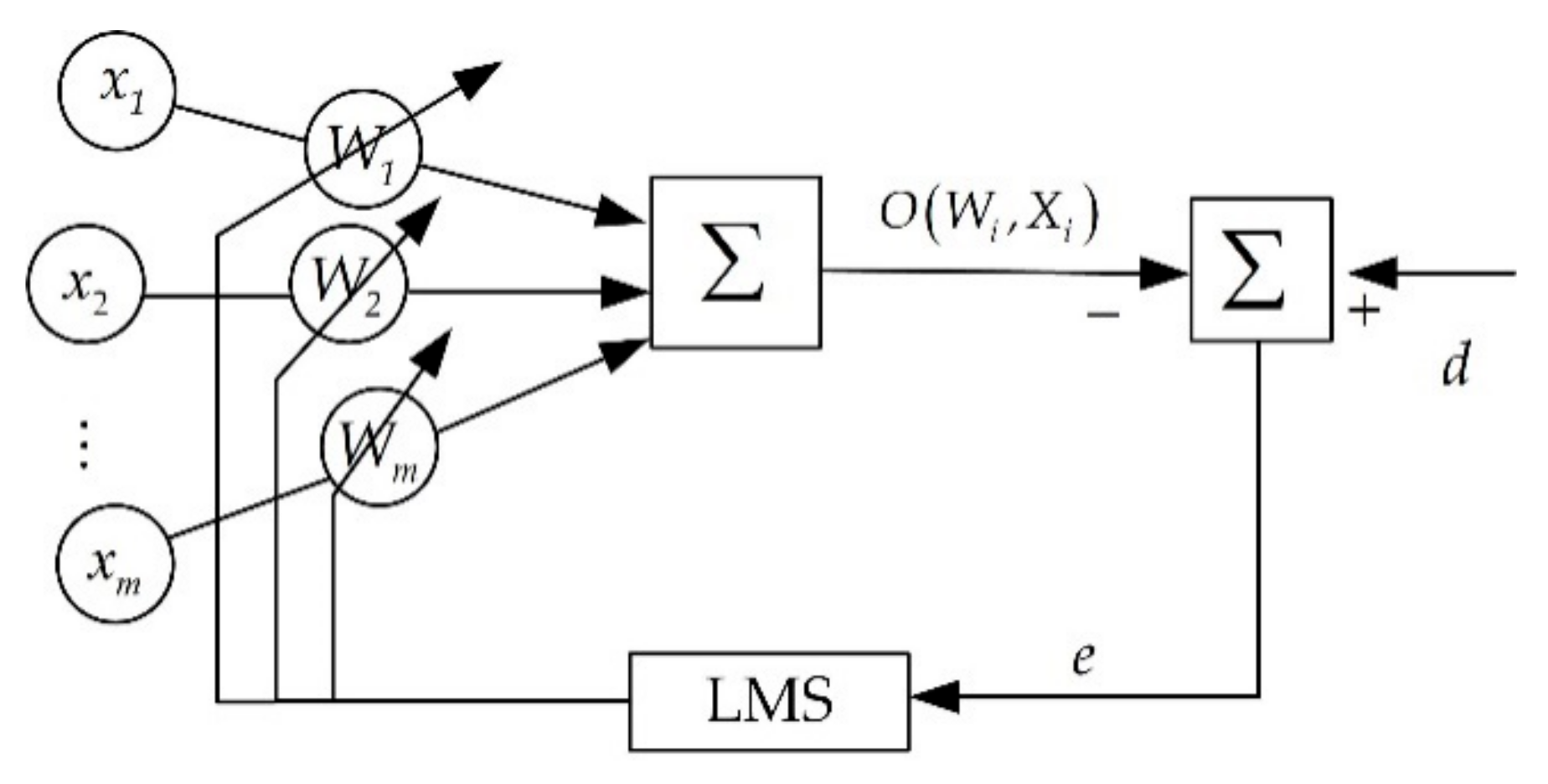
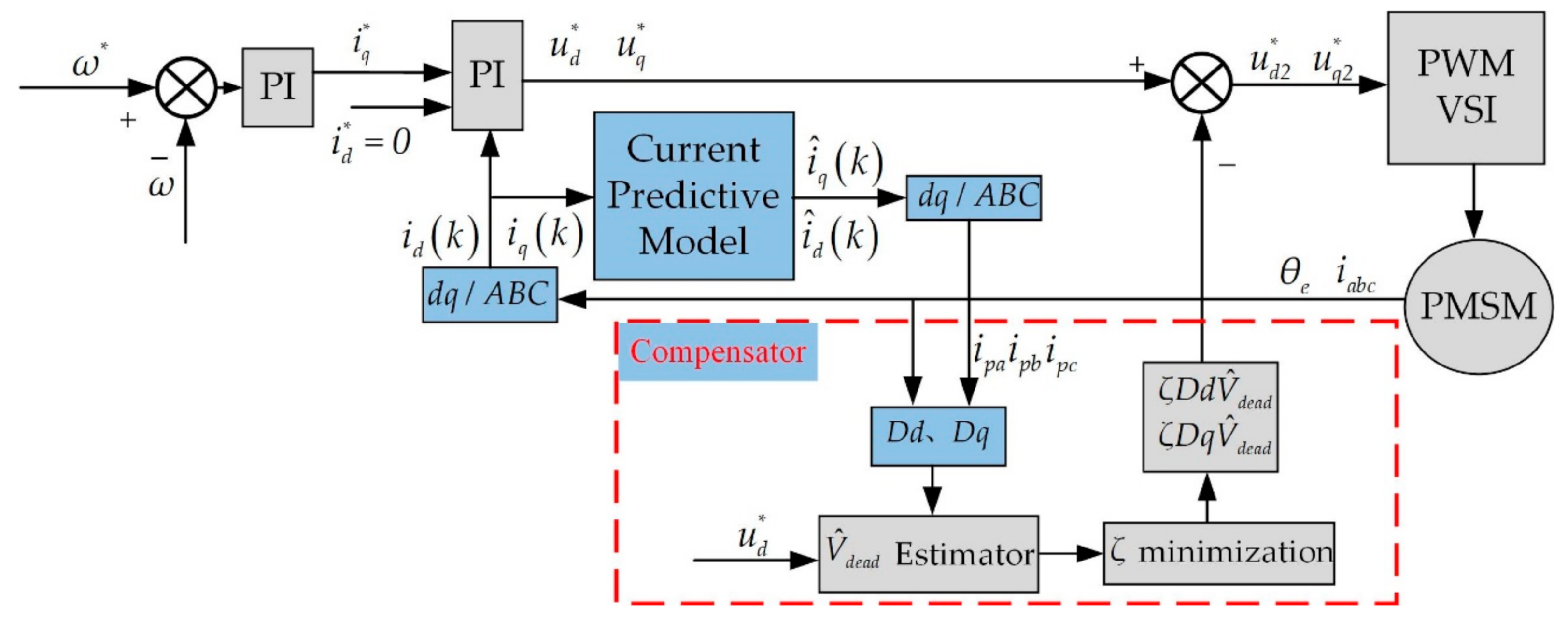
3. Conventional Compensation Scheme of VSI Nonlinearity Using DM-CZD
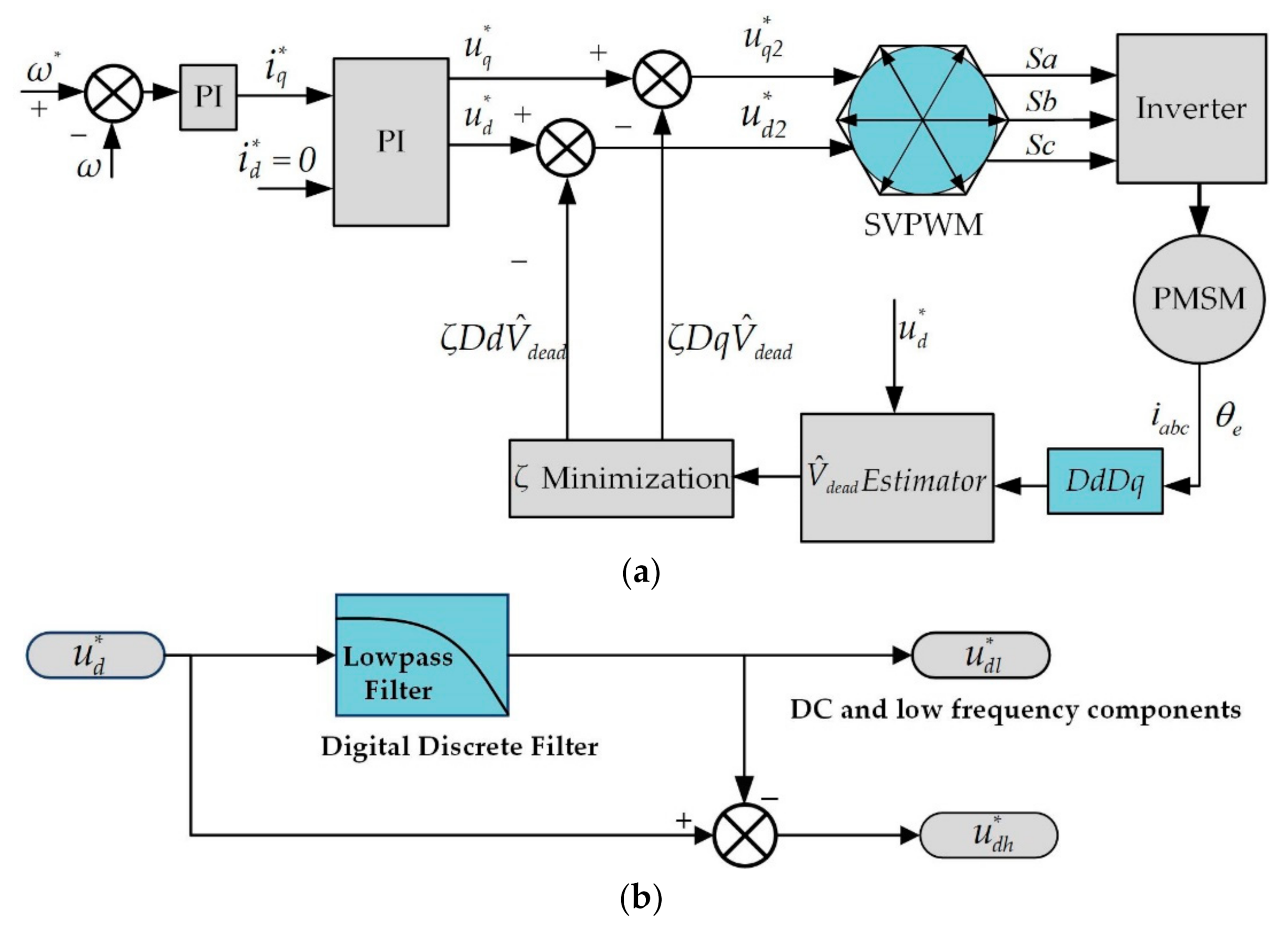
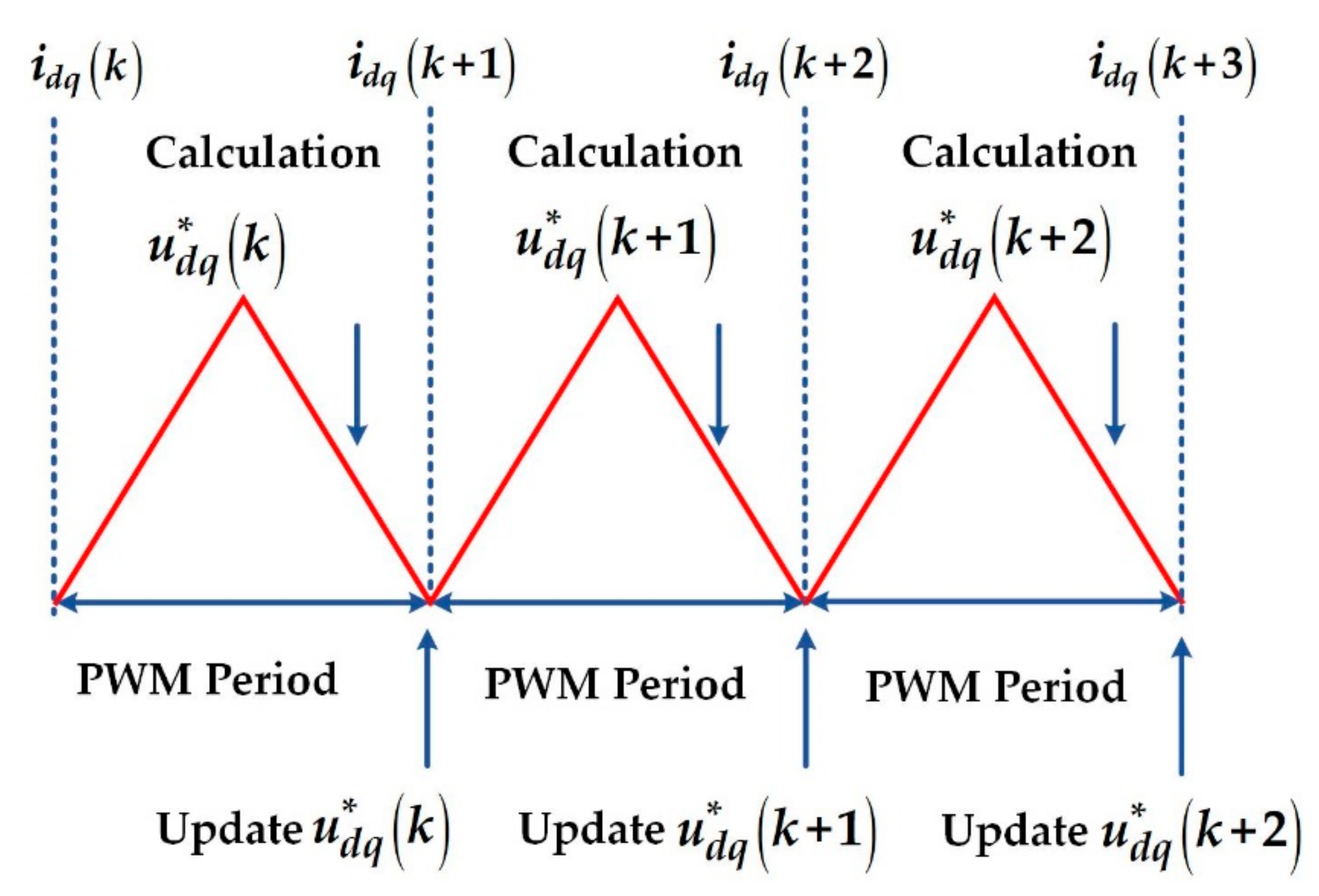
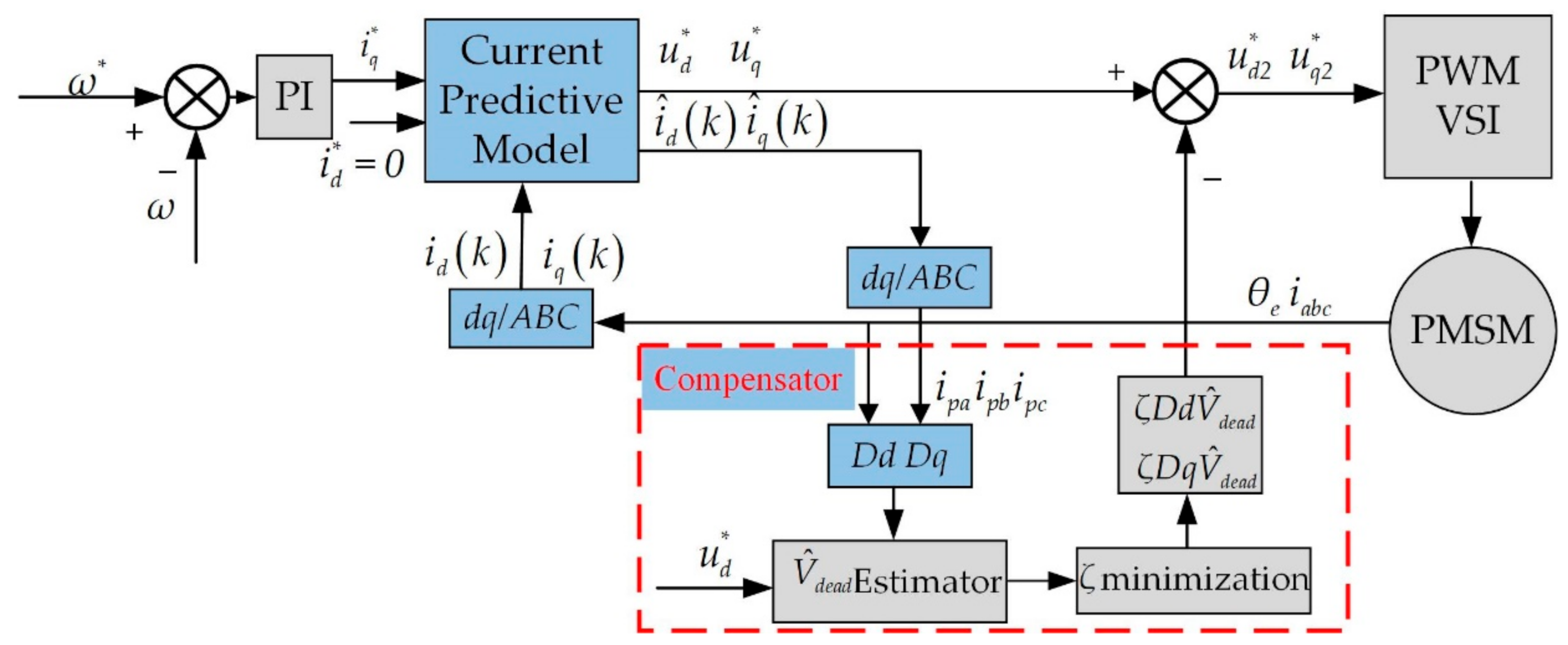
4. The Proposed Compensation Scheme of VSI Nonlinearity Using DP-CZD
4.1. DP-CZD and Compensation of VSI Nonlinearity
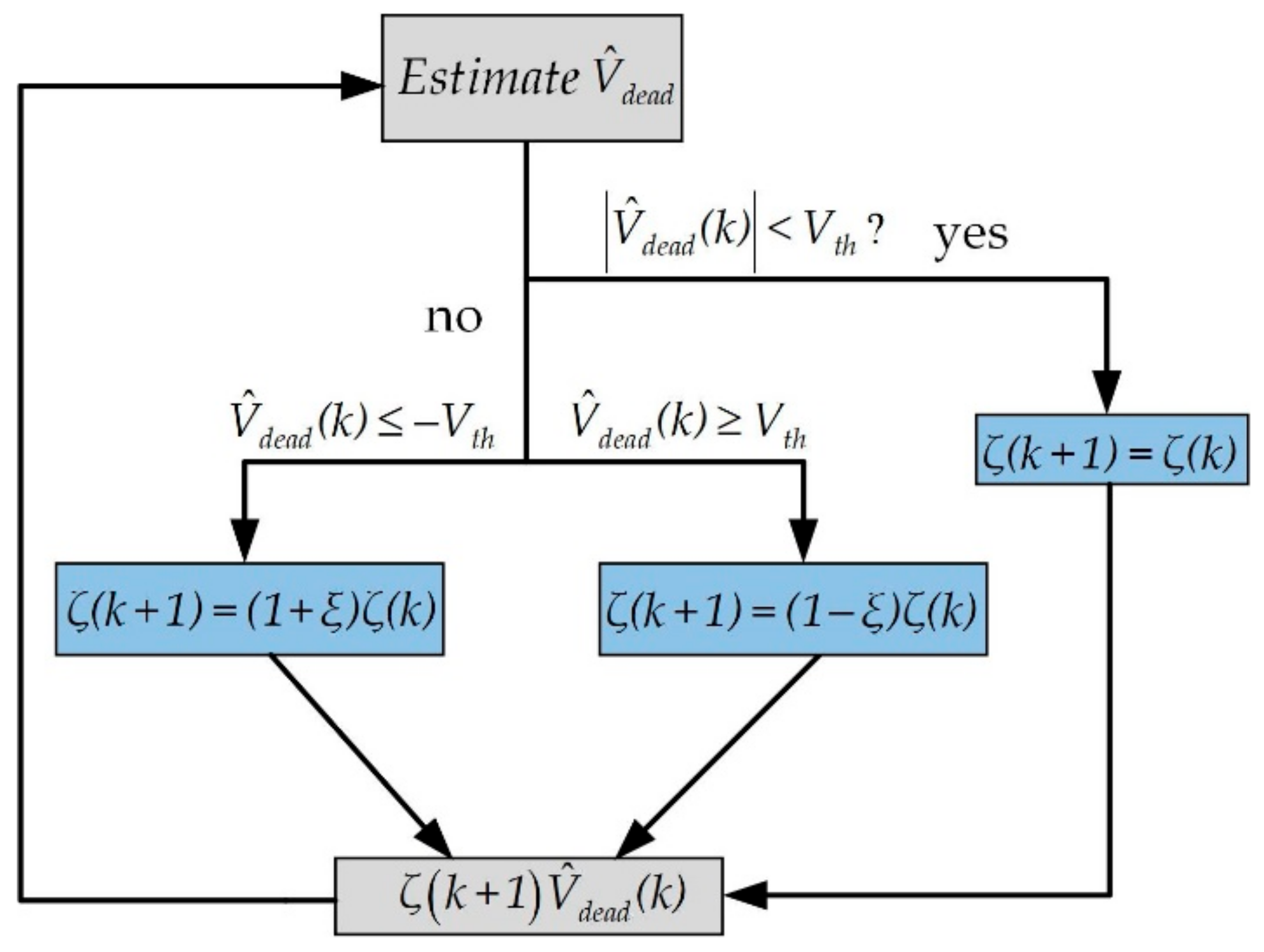
4.2. DP-CZD with Parameter Uncertainty
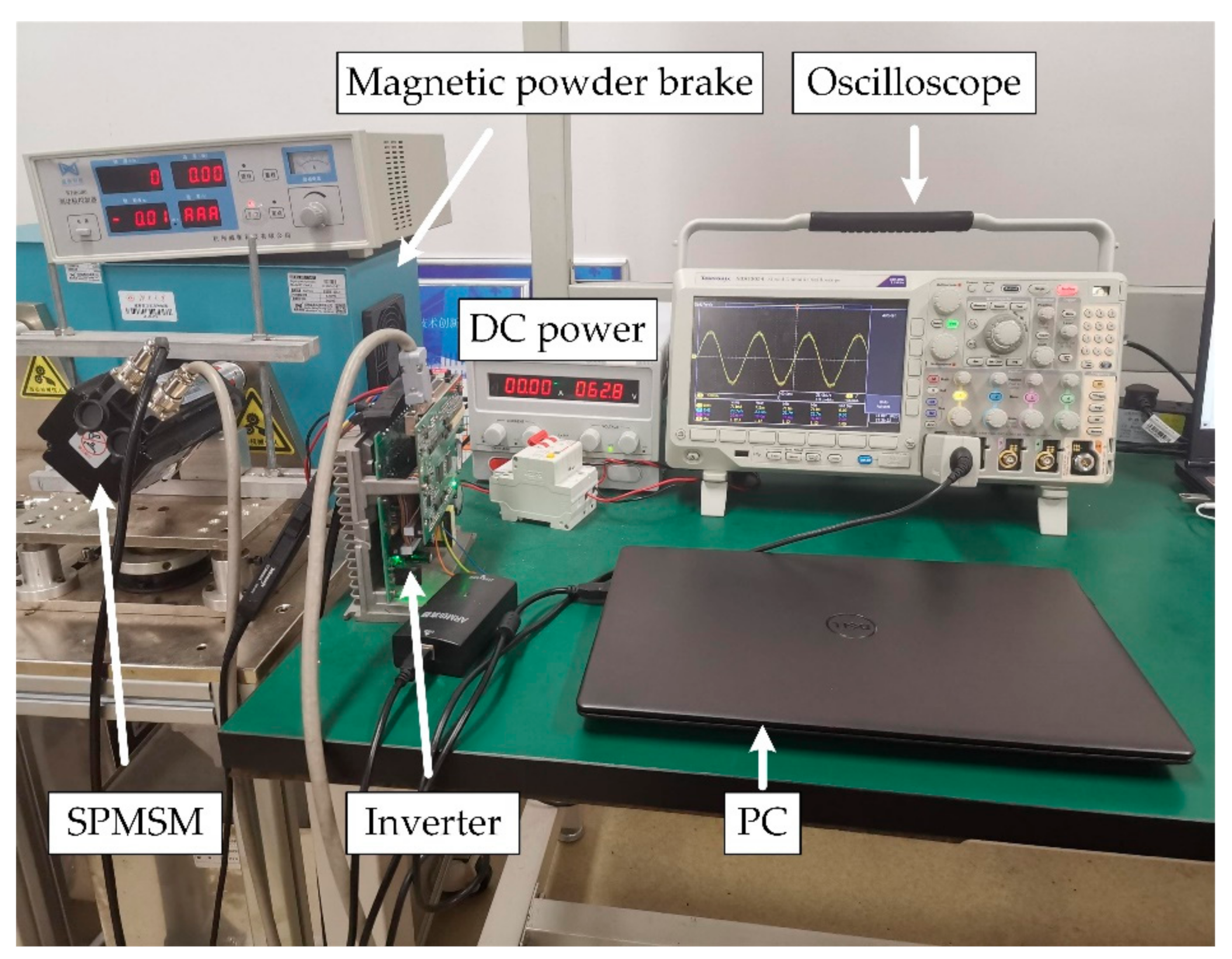
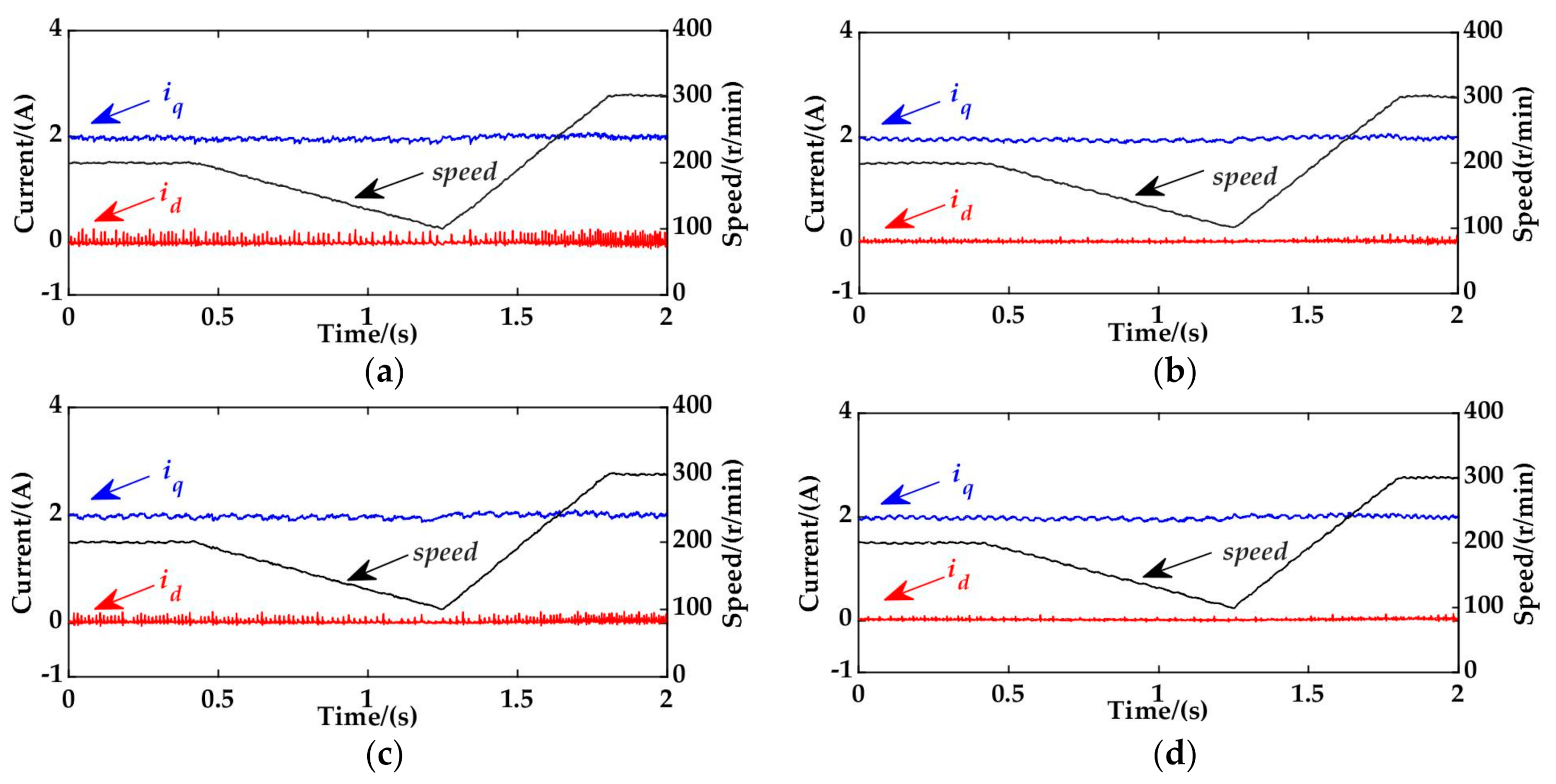
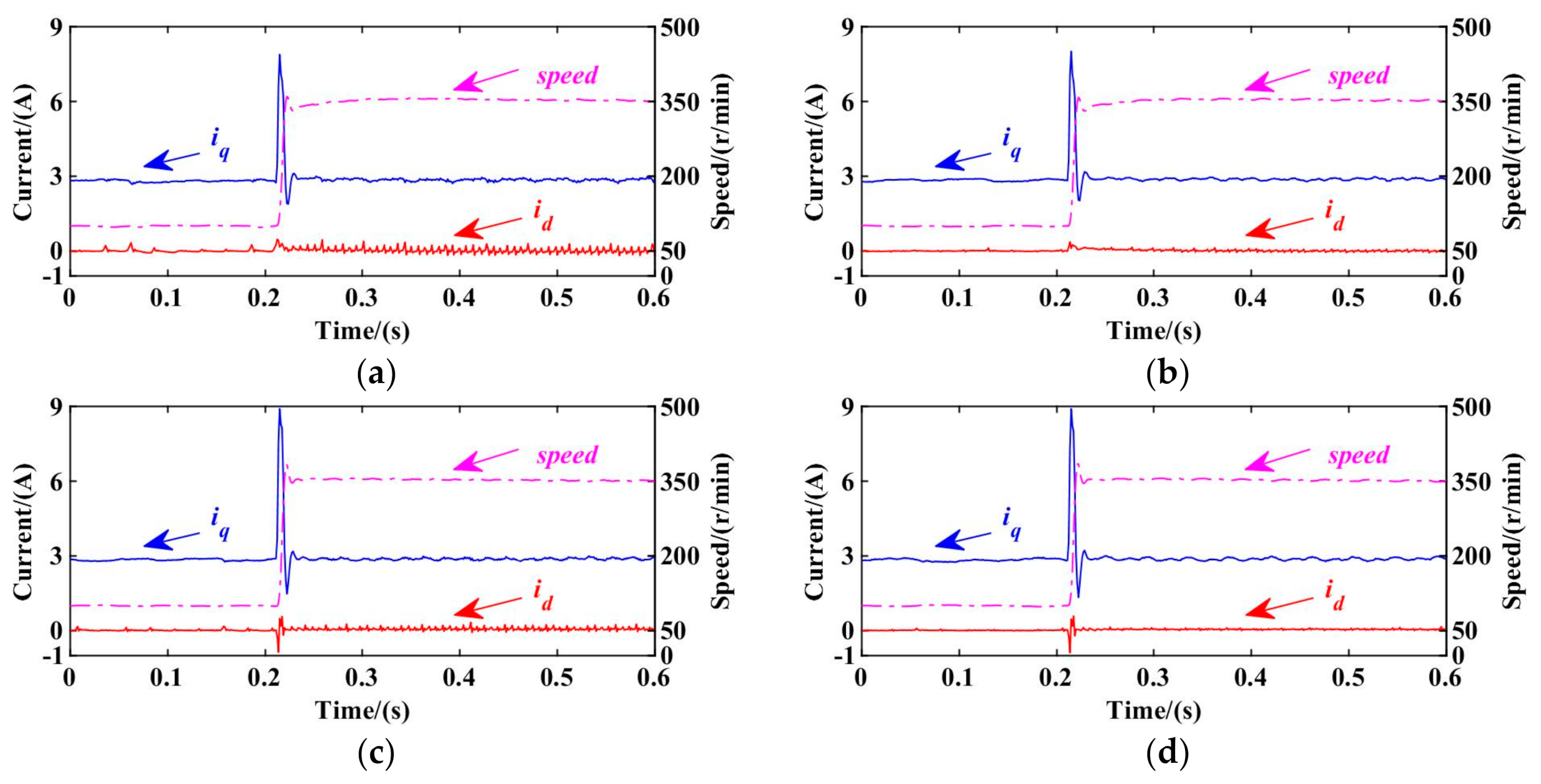
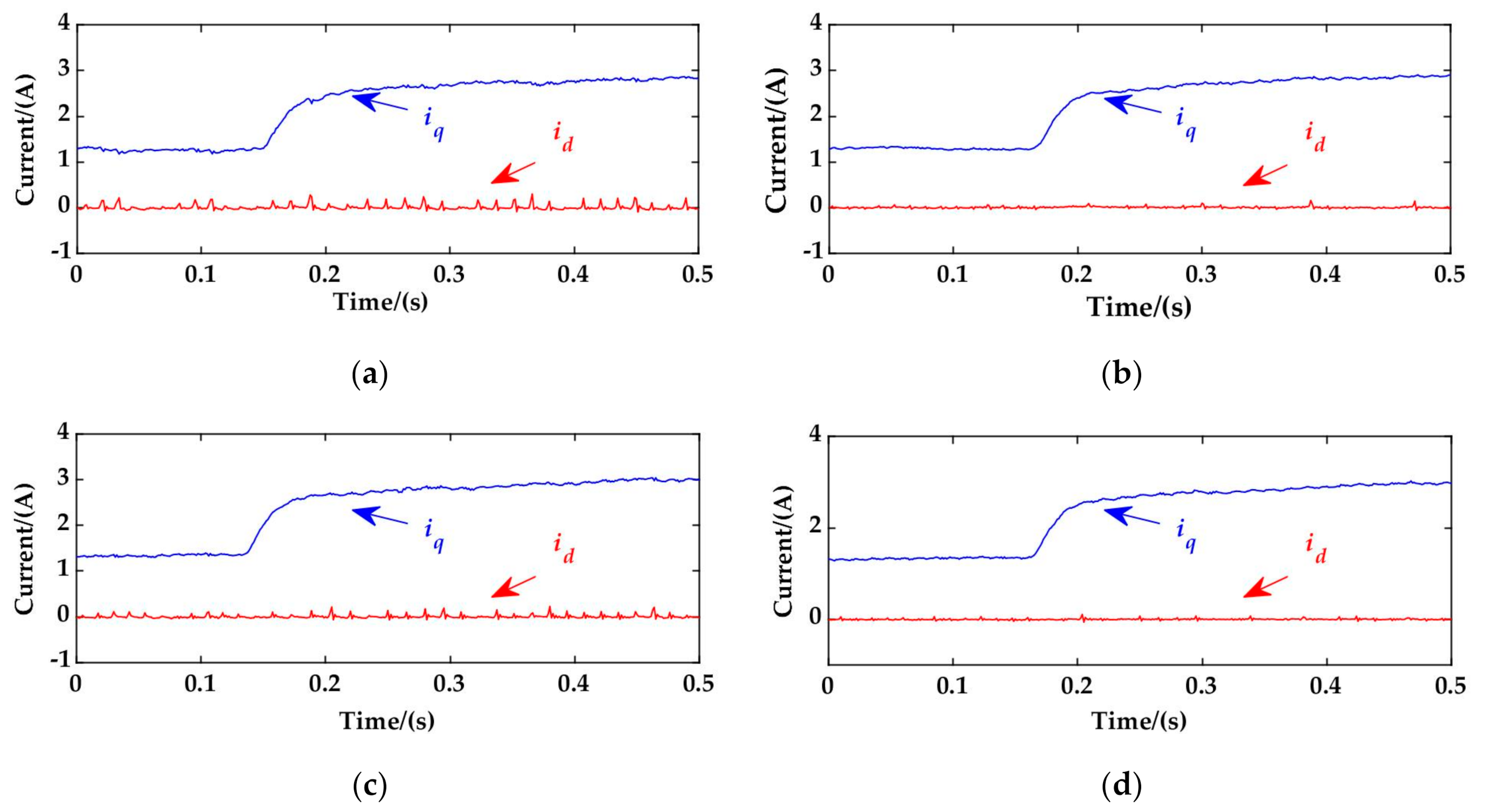
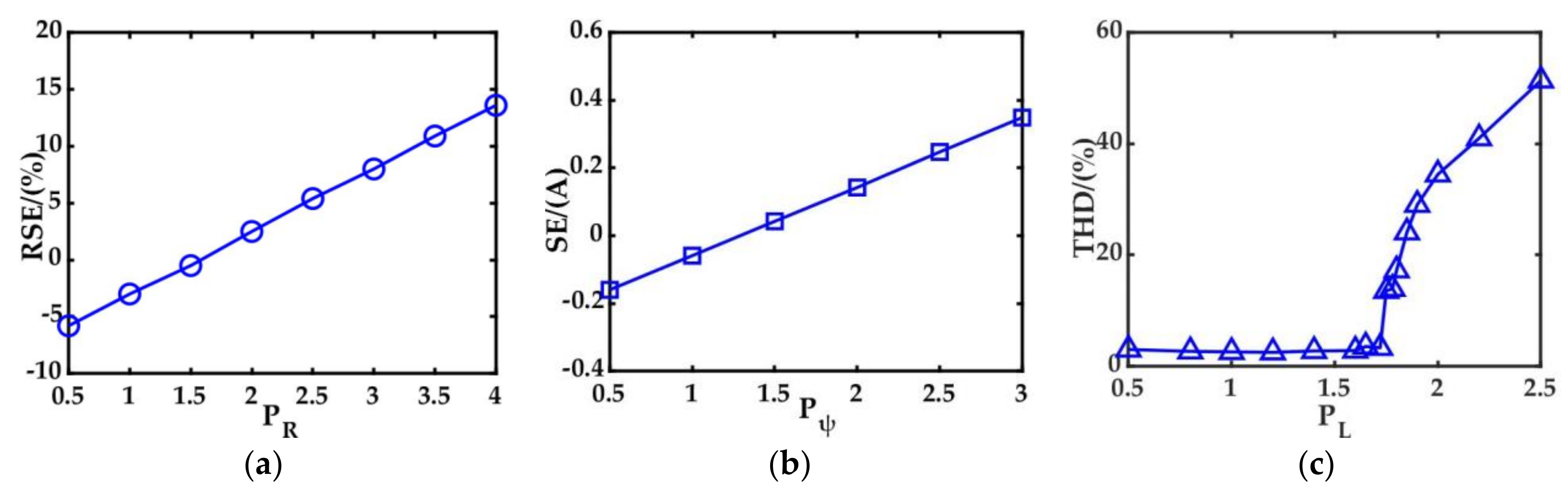
5. Experimental Results
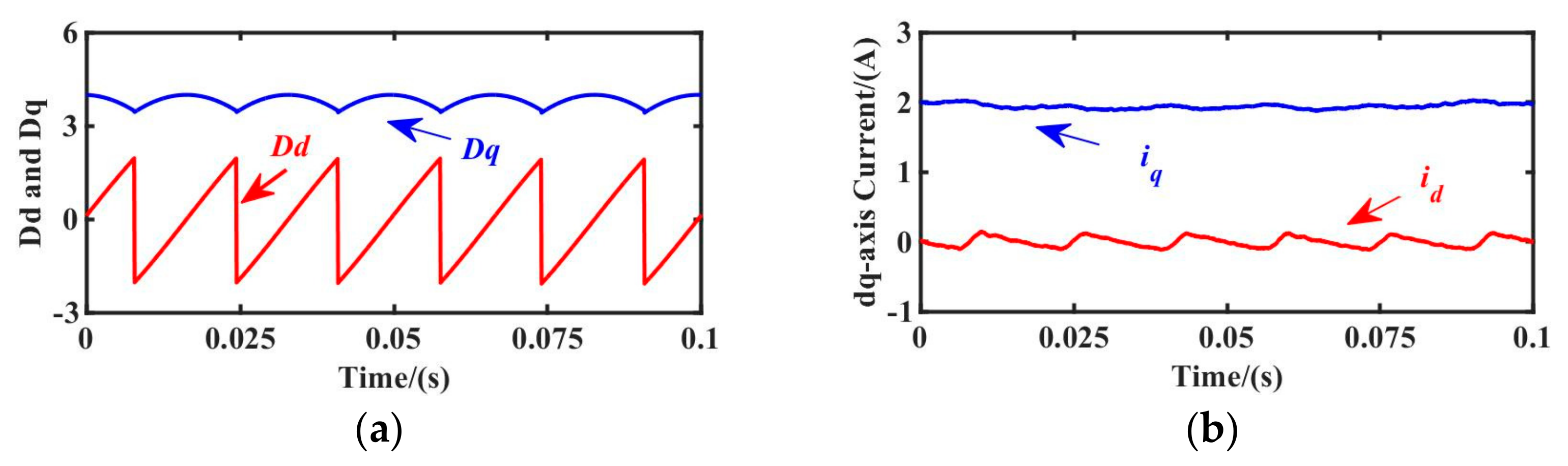
5.1. Evaluation of Steady State Performance
5.2. Evaluation of Dynamic Performance
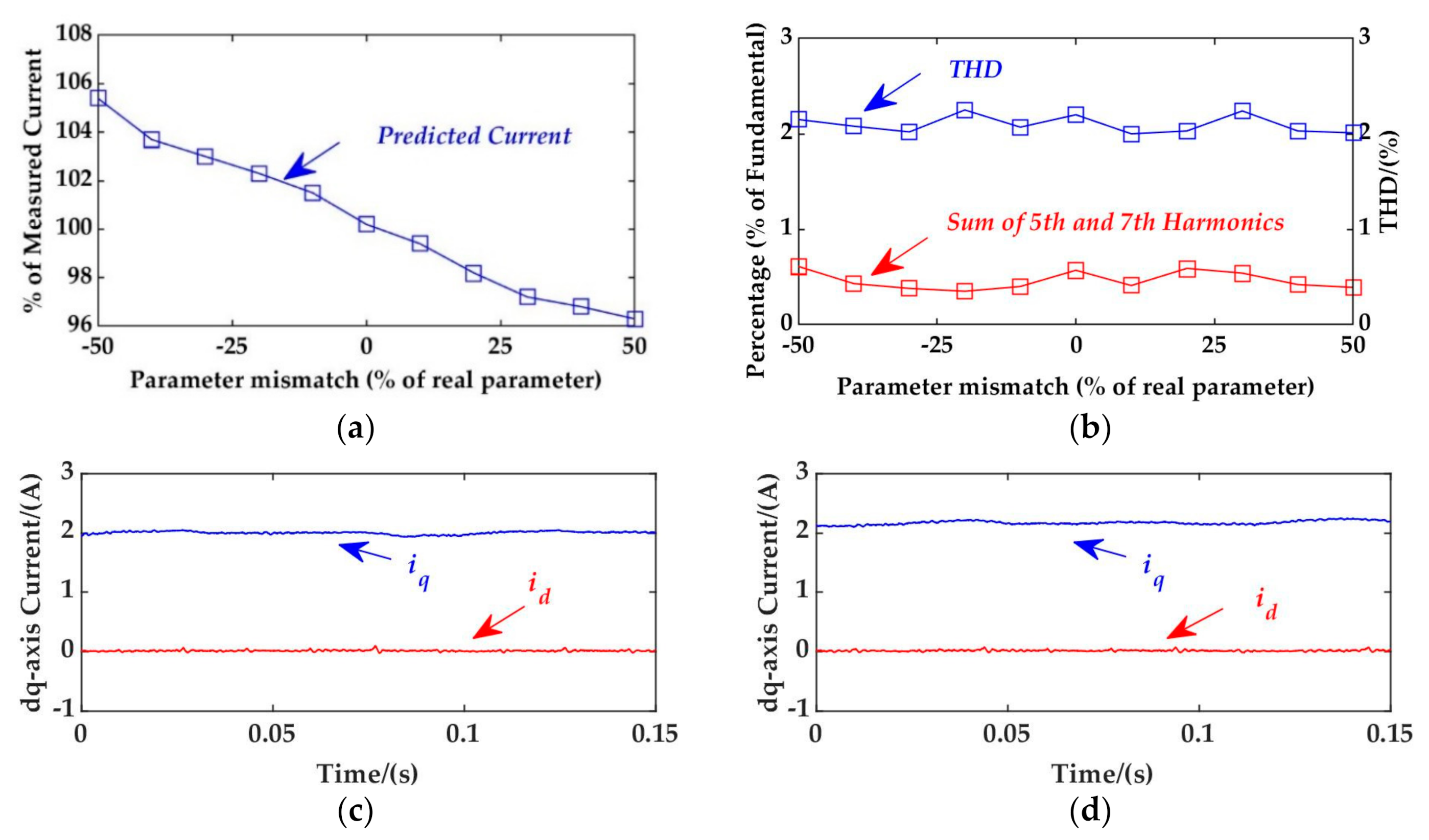
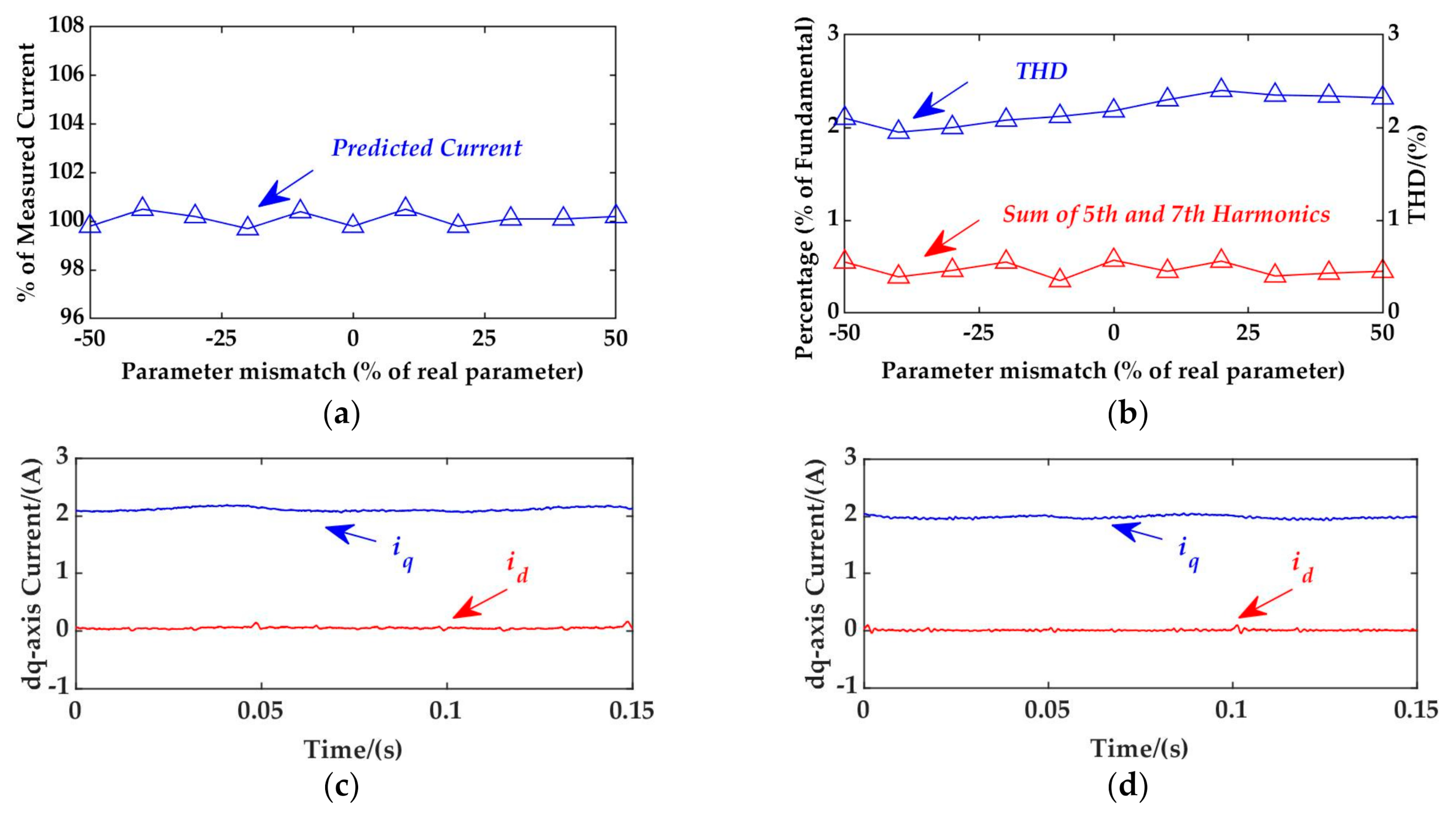
5.3. Evaluation of Robustness against Parameter Mismatches
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Ls | dq-axis inductance (mH) |
| R | Stator winding resistance (Ω) |
| ψf | Permanent magnet flux linkage (Wb) |
| θe | Electrical angle (rad) |
| ωe | Electrical angular velocity (rad/s) |
| ω | Mechanical angular velocity (r/min) |
| * | Denotes a reference variable |
| ^ | Denotes a predicted value |
| , | Actual dq -axis current (A) |
| , | Reference dq-axis current (A) |
| Three-phase currents (A) | |
| , | Actual dq-axis voltages (V) |
| , | Reference d-axis voltage (V), Reference q-axis voltage (V) |
| Dd, Dq | Functions of θe and the directions of three-phase currents |
| Vdead | Distorted voltage due to inverter nonlinearity in dq-axis reference system (V) |
| Vdc, Vsat, Vd | DC bus voltage (V), voltage drops of switching tubes and freewheeling diodes (V) |
| rce, rd | On-resistance of switching tubes and freewheeling diodes (Ω) |
Appendix A
References
- Li, L.; Xiao, J.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, K.; Peng, X.; Luan, H.; Li, K. Robust Position Anti-Interference Control for PMSM Servo System with Uncertain Disturbance. China Electrotech. Soc. Trans. Electr. Mach. Syst. 2020, 4, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Zhu, Z.Q.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, J. Influence of Nonideal Voltage Measurement on Parameter Estimation in Permanent-Magnet Synchronous Machines. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2011, 59, 2438–2447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Zhu, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, J.; Shen, A. Influence of Inverter Nonlinearity on Parameter Estimation in Permanent Magnet Synchronous Machines. In Proceedings of the XIX International Conference on Electrical Machines—ICEM 2010, Rome, Italy, 6–8 September 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, G.; Lai, C.; Mukherjee, K.; Kar, N.C. Current Injection-Based Online Parameter and VSI Nonlinearity Estimation for PMSM Drives Using Current and Voltage DC Components. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2016, 2, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, G.; Yao, W.; Chen, B.; Wang, K.; Lee, K.; Lu, Z. Automeasurement of the Inverter Output Voltage Delay Curve to Compensate for Inverter Nonlinearity in Sensorless Motor Drives. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2013, 29, 5542–5553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, D.I.; Rubio, J.D.J.; Vargas, T.M.; Garcia, V.; Ochoa, G.; Balcazar, R.; Cruz, D.R.; Aguilar, A.; Novoa, J.F.; Aguilar-Ibanez, C. Stabilization of Robots with a Regulator Containing the Sigmoid Mapping. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 89479–89488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubio, J.D.J.; Novoa, J.F.; Ochoa, G.; Mujica-Vargas, D.; Garcia, E.; Balcazar, R.; Elias, I.; Cruz, D.R.; Juarez, C.F.; Aguilar, A. Structure Regulator for the Perturbations Attenuation in a Quadrotor. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 138244–138252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escobedo-Alva, J.O.; Garcia-Estrada, E.C.; Paramo-Carranza, L.A.; Meda-Campana, J.A.; Tapia-Herrera, R. Theoretical Application of a Hybrid Observer on Altitude Tracking of Quadrotor Losing GPS Signal. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 76900–76908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubio, J.D.J.; Martinez, D.I.; Garcia, V.; Gutierrez, G.J.; Vargas, T.M.; Ochoa, G.; Balcazar, R.; Pacheco, J.; Meda-Campana, J.A.; Mujica-Vargas, D. The Perturbations Estimation in Two Gas Plants. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 83081–83091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar-Ibanez, C.; Suarez-Castanon, M.S. A Trajectory Planning Based Controller to Regulate an Uncertain 3D Overhead Crane System. Int. J. Appl. Math. Comput. Sci. 2019, 29, 693–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- García-Sánchez, J.R.; Tavera-Mosqueda, S.; Silva-Ortigoza, R.; Hernández-Guzmán, V.M.; Gutiérrez, J.S.; Marcelino-Aranda, M.; Taud, H.; Marciano-Melchor, M. Robust Switched Tracking Control for Wheeled Mobile Robots Considering the Actuators and Drivers. Sensors 2018, 18, 4316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Urasaki, N.; Senjyu, T.; Kinjo, T.; Funabashi, T.; Sekine, H. Dead-Time Compensation Strategy for Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor Drive Taking Zero-Current Clamp and Parasitic Capacitance Effects into Account. IEE Proc. Electr. Power Appl. 2005, 152, 845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Peng, F.Z. Dead-Time Elimination for Voltage Source Inverters. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2008, 23, 574–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.-K.; Lai, Y.-S. Dead-Time Elimination of PWM-Controlled Inverter/Converter without Separate Power Sources for Current Polarity Detection Circuit. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2009, 56, 2121–2127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.-W.; Youn, M.-J.; Cho, K.-Y.; Kim, H.-S. Nonlinearity Estimation and Compensation of PWM VSI for PMSM under Resistance and Flux Linkage Uncertainty. IEEE Trans. Control. Syst. Technol. 2006, 14, 589–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, D.; Li, J.; Qu, R.; Kong, W. Adaptive Second-Order Sliding-Mode Observer for PMSM Sensorless Control Considering VSI Nonlinearity. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2018, 33, 8994–9004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Zhu, Z.-Q. Online Estimation of the Rotor Flux Linkage and Voltage-Source Inverter Nonlinearity in Permanent Magnet Synchronous Machine Drives. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2014, 29, 418–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, T.; Li, Q.; Tong, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, K. An Adaptive Strategy to Compensate Nonlinear Effects of Voltage Source Inverters Based on Artificial Neural Networks. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 129992–130002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Wu, Q.M.J.; Kawamura, A. An Accurate Approach of Nonlinearity Compensation for VSI Inverter Output Voltage. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2004, 19, 1029–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolognani, S.; Ceschia, M.; Mattavelli, P.; Paccagnella, A. Improved FPGA-Based Dead Time Compensation for SVM Inverters. In Proceedings of the Second International Conference on Power Electronics, Machines and Drives (PEMD), Edinburgh, UK, 31 March–2 April 2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.-S.; Kim, K.-H.; Youn, M.-J. On-Line Dead-Time Compensation Method Based on Time Delay Control. IEEE Trans. Control. Syst. Technol. 2003, 11, 279–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Huang, W.; Yan, Y. A Simple Inverter Nonlinearity Compensation Method Using On-Line Voltage Error Observer. In Proceedings of the 2019 22nd International Conference on Electrical Machines and Systems (ICEMS), Harbin, China, 11–14 August 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Wang, D.; Jin, Y.; Wang, M.; Zhang, P. Current-Detection-Independent Dead-Time Compensation Method Based on Terminal Voltage A/D Conversion for PWM VSI. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2017, 64, 7689–7699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.-Y.; Lee, W.; Rho, M.-S.; Park, S.-Y. Effective Dead-Time Compensation Using a Simple Vectorial Disturbance Estimator in PMSM Drives. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2009, 57, 1609–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attaianese, C.; Tomasso, G. Predictive Compensation of Dead-Time Effects in VSI Feeding Induction Motors. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2001, 37, 856–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abronzini, U.; Attaianese, C.; D’Arpino, M.; Di Monaco, M.; Tomasso, G. Steady-State Dead-Time Compensation in VSI. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2016, 63, 5858–5866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Li, K.; Zhang, P.; Gao, F. Predictive Current Control for Voltage Source Inverters Considering Dead-Time Effect. China Electrotech. Soc. Trans. Electr. Mach. Syst. 2020, 4, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Brahim, L. On the Compensation of Dead Time and Zero-Current Crossing for a PWM-Inverter-Controlled AC Servo Drive. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2004, 51, 1113–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.; Akin, B. Compensation of Dead-Time Effects Based on Revised Repetitive Controller for PMSM Drives. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Applied Power Electronics Conference and Exposition (APEC), Tampa, FL, USA, 26–30 March 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Huang, Y.; Peng, F.; Dong, J.; Zhang, H. An Improved Deadbeat Predictive Current Control with Online Parameter Identification for Surface-Mounted PMSMs. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2019, 67, 10145–10155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, K.; Zhang, J. Adaline Neural Network Based Online Parameter Estimation for Surface-Mounted Permanent Magnet Synchronous Machines. Proc. CSEE 2010, 30, 68–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Yu, A.; Li, X.; Zhang, G.; Xia, C. A Novel Current Predictive Control Based on Fuzzy Algorithm for PMSM. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2019, 7, 990–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Hou, B.; Mei, Y. Deadbeat Predictive Current Control of Permanent-Magnet Synchronous Motors with Stator Current and Disturbance Observer. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2017, 32, 3818–3834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, Q. Robust Predictive Current Control with Parallel Compensation Terms against Multi-Parameter Mismatches for PMSMs. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2020, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Zaikun, H.; Shuai, L. Deadbeat Predictive Current Control for Permanent Magnet Synchronous Machines with Closed-Form Error Compensation. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2020, 35, 5018–5030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widrow, B.; Lehr, M. 30 Years of Adaptive Neural Networks: Perceptron, Madaline, and Backpropagation. Proc. IEEE 1990, 78, 1415–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



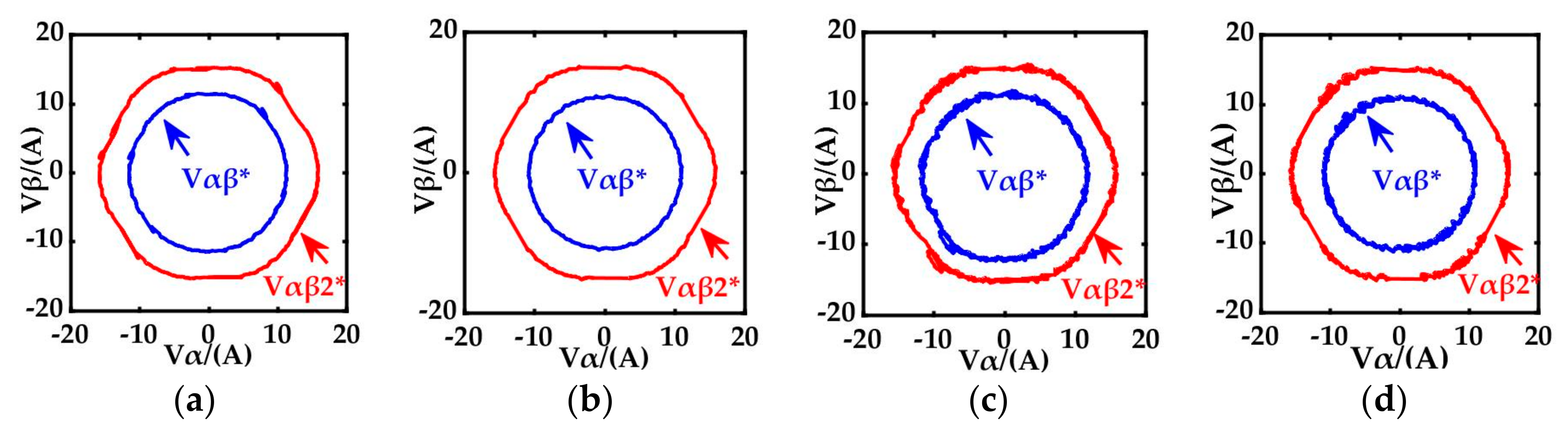
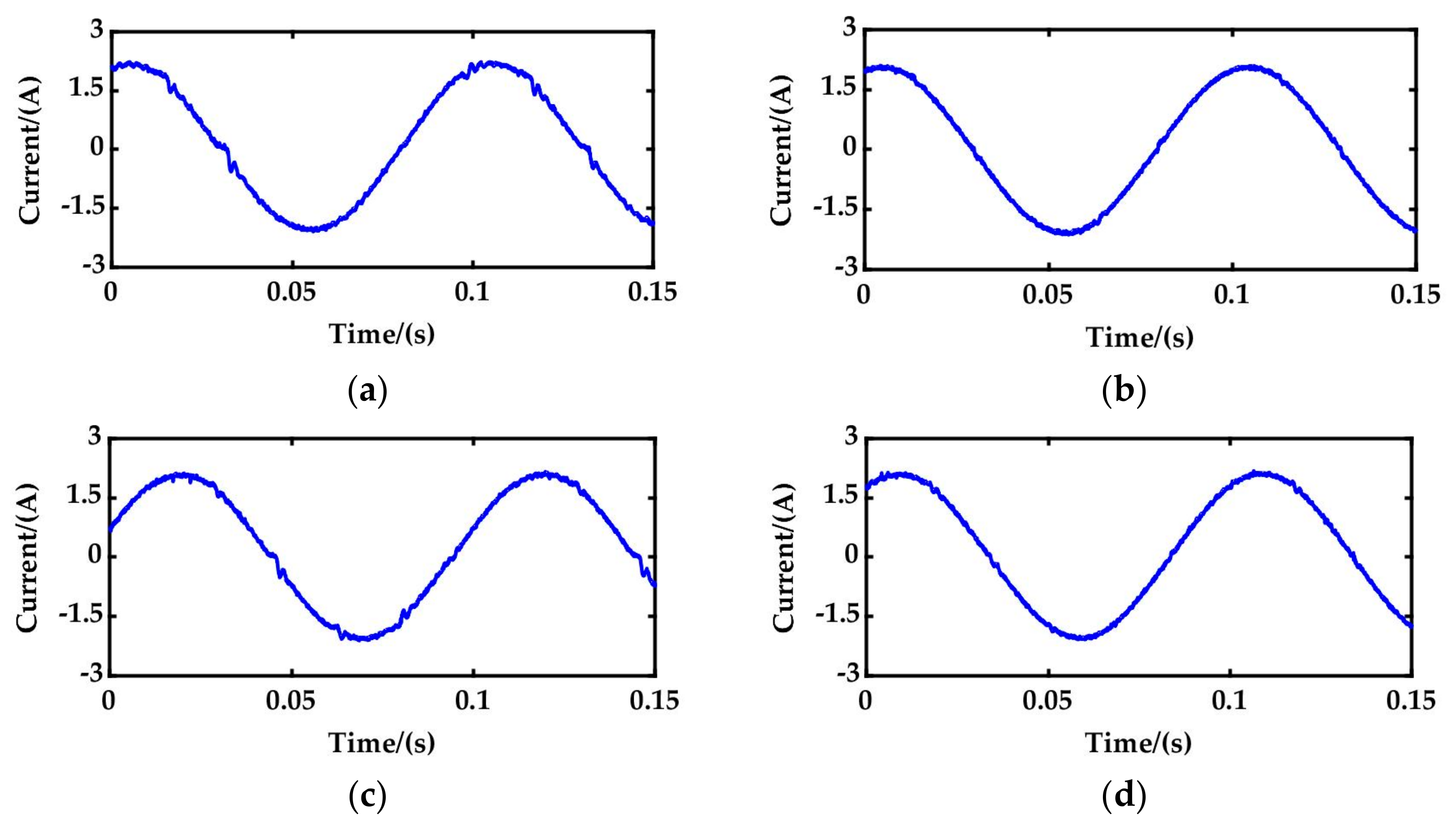
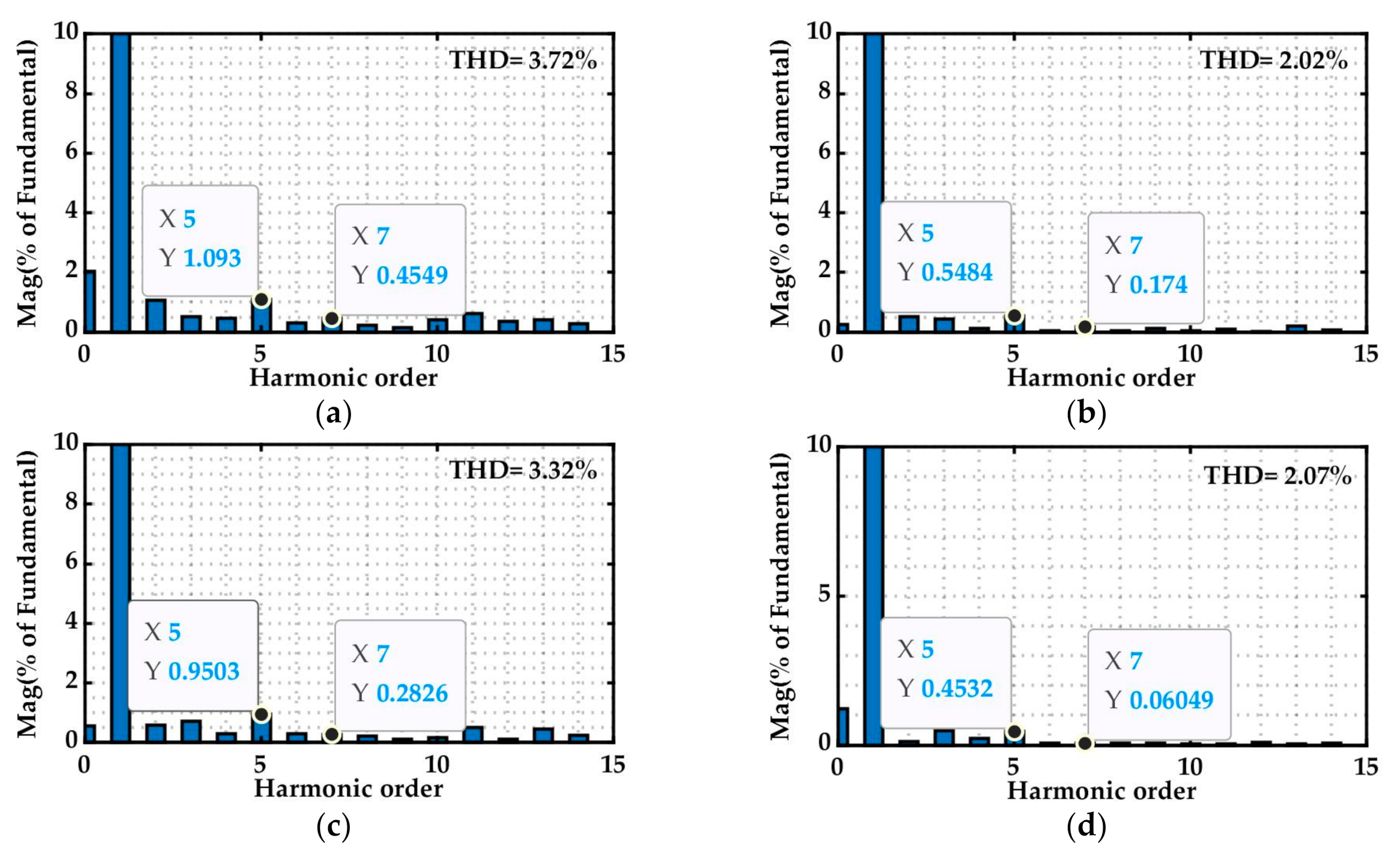
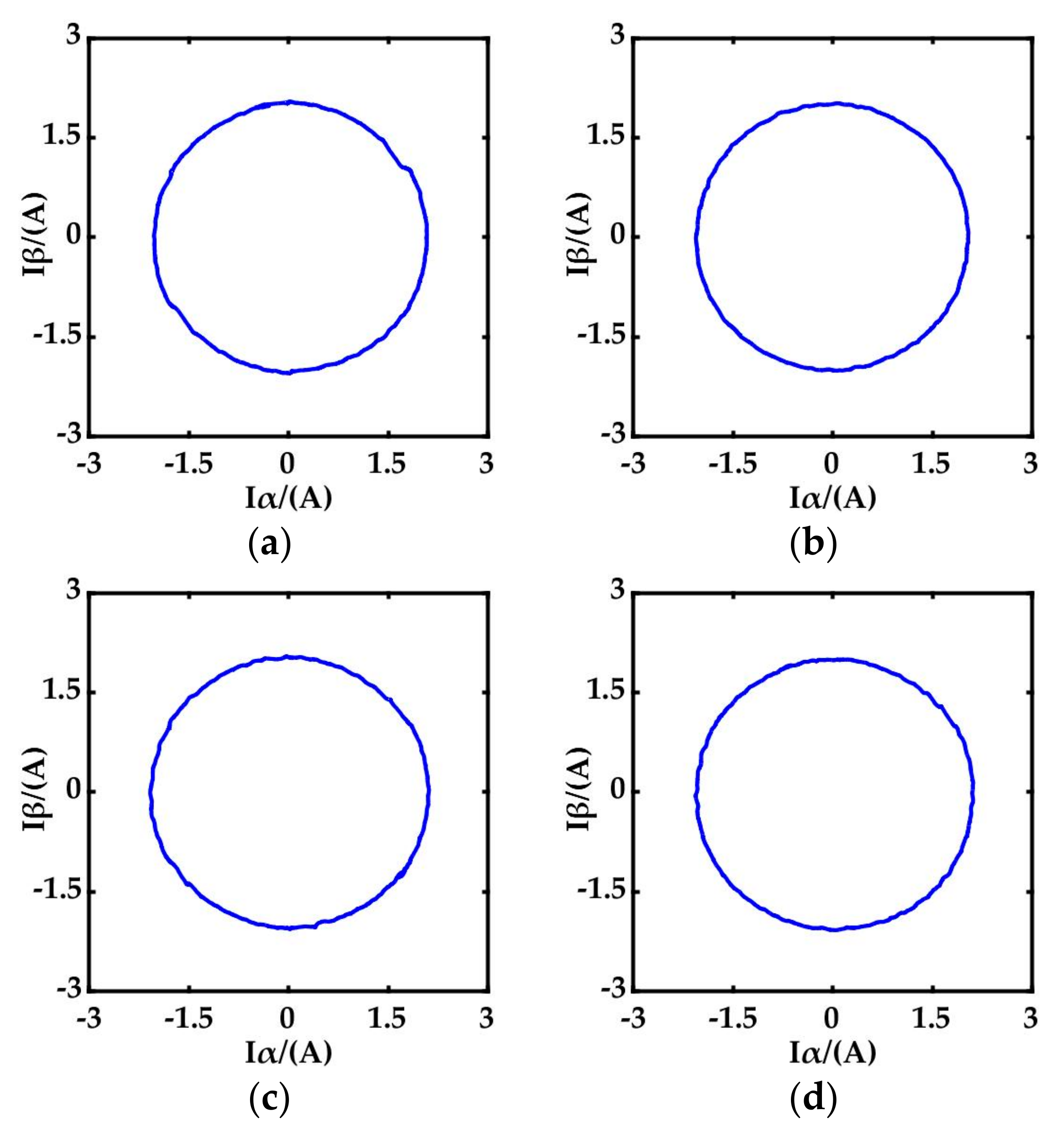


| Case | θe | Sign(i) | VdeadDd | VdeadDq | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ia | ib | ic | ||||
| 1 | −π/6 – λ ~ π/6 − λ | 1 | −1 | −1 | 4Vdeadsin(θe) | 4Vdeadcos(θe) |
| 2 | π/6 − λ ~ π/2 − λ | 1 | 1 | −1 | 4Vdeadsin(θe − π/3) | 4Vdeadcos(θe − π/3) |
| 3 | π/2 – λ ~ 5π/6 − λ | −1 | 1 | −1 | 4Vdeadsin(θe − 2π/3) | 4Vdeadcos(θe − 2π/3) |
| 4 | 5π/6 − λ ~ 7π/6 − λ | −1 | 1 | 1 | 4Vdeadsin(θe − π) | 4Vdeadcos(θe − π) |
| 5 | 7π/6 – λ ~ 3π/2 − λ | −1 | −1 | 1 | 4Vdeadsin(θe − 4π/3) | 4Vdeadcos(θe − 4π/3) |
| 6 | 3π/2 − λ ~ 11π/6 − λ | 1 | −1 | 1 | 4Vdeadsin(θe − 5π/3) | 4Vdeadcos(θe − 5π/3) |
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| DC-link voltage | 60 V |
| Rated speed | 600 rpm |
| Rated current | 3 A |
| Number of pole pairs | 4 |
| Nominal d-axis inductance | 2.8 mH |
| Nominal q-axis inductance | 2.8 mH |
| Permanent magnet flux linkage | 109.1 mWb |
| Stator winding resistance | 1.86 Ω |
| Parameter | Typical Value |
|---|---|
| Turn-on delay (Ton) | 0.49 μs |
| Turn-off delay (Toff) | 0.86 μs |
| Dead time (Tdead) | 4 μs |
| Switching period (Ts) | 83.3 μs |
| Voltage drop of the switching tube (Vsat) | 2.75 V(max) |
| Voltage drop of the freewheeling diode (Vd) | 2.4 V(max) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, J.; Liu, K.; Li, J.; Li, L.; Hu, W.; Ding, R. VSI Nonlinearity Compensation of a PMSM Drive System Using Deadbeat Prediction Based Current Zero-Crossing Detection. World Electr. Veh. J. 2021, 12, 17. https://doi.org/10.3390/wevj12010017
Zhou J, Liu K, Li J, Li L, Hu W, Ding R. VSI Nonlinearity Compensation of a PMSM Drive System Using Deadbeat Prediction Based Current Zero-Crossing Detection. World Electric Vehicle Journal. 2021; 12(1):17. https://doi.org/10.3390/wevj12010017
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Jing, Kan Liu, Juan Li, Longfei Li, Wei Hu, and Rongjun Ding. 2021. "VSI Nonlinearity Compensation of a PMSM Drive System Using Deadbeat Prediction Based Current Zero-Crossing Detection" World Electric Vehicle Journal 12, no. 1: 17. https://doi.org/10.3390/wevj12010017
APA StyleZhou, J., Liu, K., Li, J., Li, L., Hu, W., & Ding, R. (2021). VSI Nonlinearity Compensation of a PMSM Drive System Using Deadbeat Prediction Based Current Zero-Crossing Detection. World Electric Vehicle Journal, 12(1), 17. https://doi.org/10.3390/wevj12010017








