Abstract
This paper introduces an adaptive path-tracking control algorithm for autonomous mobility based on recursive least squares (RLS) with external conditions and covariance self-tuning. The advancement and commercialization of autonomous driving necessitate universal path-tracking control technologies. In this study, we propose a path-tracking control algorithm that does not rely on vehicle parameters and leverages RLS with self-tuning mechanisms for external conditions and covariance. We designed an integrated error for effective path tracking that combines the lateral preview distance and yaw angle errors. The controller design employs a first-order derivative error dynamics model with the coefficients of the error dynamics estimated through the RLS using a forgetting factor. To ensure stability, we applied the Lyapunov direct method with injection terms and finite convergence conditions. Each regression process incorporates external conditions, and the self-tuning of the injection terms utilizes residuals. The performance of the proposed control algorithm was evaluated using MATLAB®/Simulink® and CarMaker under various path-tracking scenarios. The evaluation demonstrated that the algorithm effectively controlled the front steering angle for autonomous path tracking without vehicle-specific parameters. This controller is expected to provide a versatile and robust path-tracking solution in diverse autonomous driving applications.
1. Introduction
Autonomous driving control requires a controller that improves convenience for users and ensures robust performance for path tracking. Therefore, prominent universities and research institutes have developed a variety of parameter-independent adaptive control algorithms. Recent studies have employed a range of methodologies to estimate the parameters of system models. Scholars have estimated vehicle mass, road gradient, longitudinal and lateral velocity, etc., based on nonlinear vehicle dynamics models using the Extended Kalman Filter (EKF) and Unscented Kalman Filter (UKF) [1,2,3]. Both filters can estimate the state even when the system is nonlinear, but the linearization process of a nonlinear system involves mathematical complexity when it comes to calculating the Jacobian or performing stochastic sampling. Alternatively, studies have been conducted to investigate methods to estimate longitudinal and lateral tire forces using artificial neural networks [4,5]. They can achieve high performance in complex nonlinear systems but a large amount of training data are required to train the neural network. If the training data are insufficient, overfitting may occur and the data may not be suitable for real-time estimation. In studies considering linear systems, other scholars have used the recursive least squares (RLS) method to estimate vehicle mass, vehicle center height, and cornering stiffness coefficient [6,7,8,9]. In linear systems, RLS guarantees fast convergence speed and operates relatively accurately and efficiently. Ref. [10] used an adaptive sliding mode observer to estimate the lateral tire force of each wheel. The adaptive sliding mode observer is robust to noise and can handle nonlinear systems. However, due to the nature of the sliding mode, it may cause shaking problems and its design may be more complex than the estimators mentioned above. A review of existing research reveals that various methods, such as Kalman Filters, Extended Kalman Filters, Unscented Kalman Filters, and recursive least squares (RLS), have been employed to estimate the parameters of mathematical models. In this paper, we do not consider nonlinearity because it does not require the mathematical information of the system, and we adopt the recursive least squares method because it has low computational complexity and can estimate real-time parameters. In this case, we utilize an RLS approach with a forgetting factor to account for the individual weights of the estimated parameters.
In addition, various studies are being conducted with regard to control parameters or model independence. Refs. [11,12,13,14] proposed a methodology for self-tuning PID gains. An adaptive learning methodology was proposed based on the particle swarm optimization technique, Lyapunov stability theorem, and a gain self-tuning methodology applying fuzzy logic theory. Ref. [15] proposed a model-free adaptive integral sliding mode control based on a data-driven technique for identifying object models for parking systems of autonomous four-wheel vehicles. In addition, ref. [16] proposed a model-free control method using an artificial neural network-based data-driven approach for tracking output model references for unknown systems. The authors of [17,18] proposed a model-free adaptive control to address the challenge of constructing an accurate mathematical model for nonlinear four-wheel steering vehicles or the strong nonlinearity and uncertainty of six-wheel independent drive and four-wheel independent steering vehicles with variable wheelbases. The authors of [19] proposed a model-free control approach for position control of uncertain modeled DC motors.
A commonly used control algorithm is model predictive control. Self-tuning and model-free control algorithms are being developed for general control of unknown systems, and in this study, a mathematical model that does not require system parameters is designed for path-tracking control without information about the system. The authors of [20,21,22,23,24,25] propose an MPC controller for path following. In the case of the model predictive controller designed in previous studies, dynamic models such as side slips are considered. Since these dynamic models, especially the standard bicycle model, do not accurately describe the vehicles’ behavior, there are problems with inaccurate motion prediction when these models are used for MPC [24]. Another control method is the sliding mode controller [26,27,28,29]. It has the advantage of being robust to internal/external disturbances, but this control methodology also requires a dynamic model of the system.
In this study, we propose an adaptive path-tracking control algorithm for autonomous mobility based on RLS with external conditions and a covariance self-tuning method. The proposed adaptive control algorithm only needs to know some of the parameters, such as the forgetting factor, initial values, constants for finite convergence, and external conditions for path tracking of autonomous mobility. For reasonable performance evaluation, the proposed control algorithm was evaluated using CarMaker software under various driving scenarios. The remainder of this paper is organized as follows. Section 2 describes the adaptive path tracking control algorithm for autonomous mobility using RLS with external conditions and covariance self-tuning. Section 3 discusses evaluation results obtained from the Matlab®/Simulink® and CarMaker co-simulation. Finally, Section 4 presents the conclusions and an analysis of the limitations and future works.
2. Adaptive Path Tracking Control Algorithm
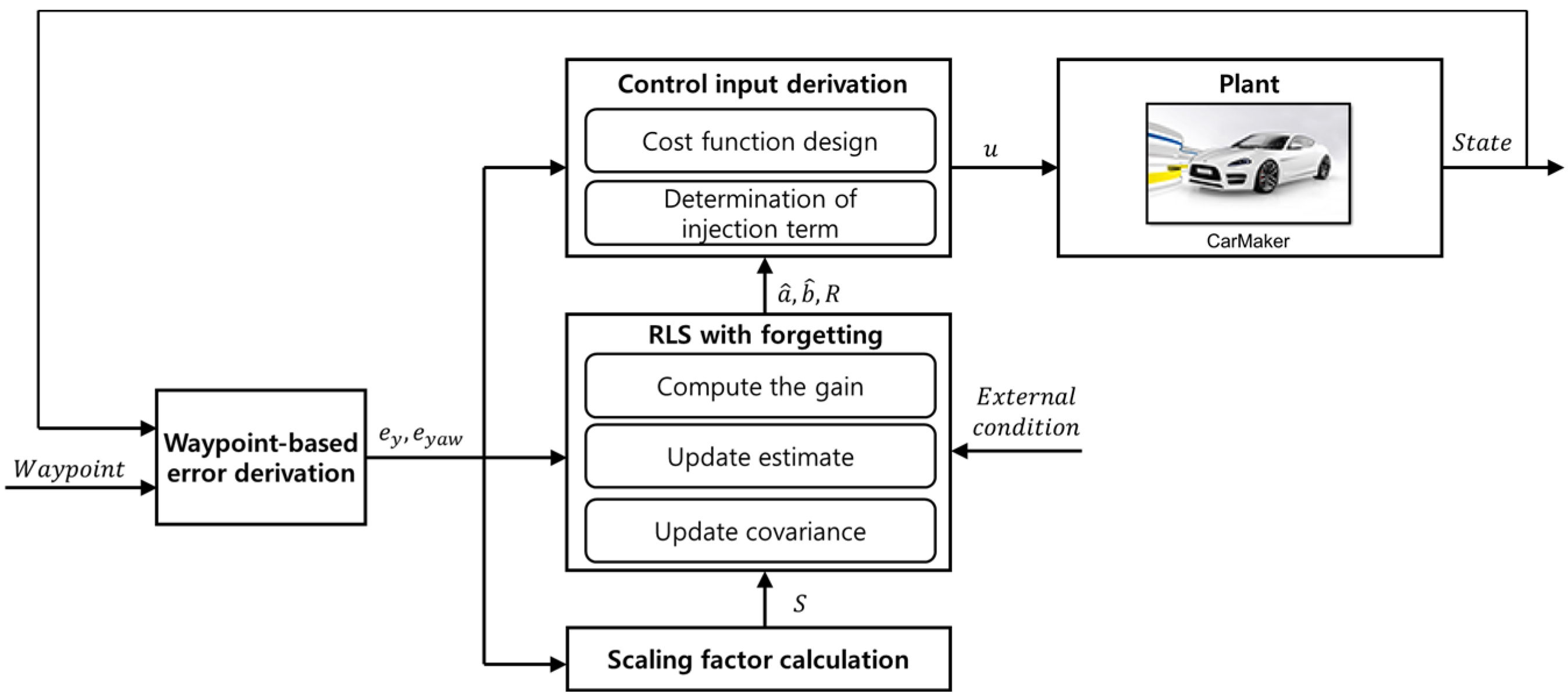
Figure 1 shows a schematic of the proposed path-tracking control algorithm. The controller consists of four blocks: error derivation, scaling factor calculation, recursive least squares (RLS) with forgetting, and control input derivation. In sequence, it receives the vehicle’s position, attitude-related state variables, and current target path data to calculate the error. The calculated error was used in the remaining three blocks, and it was recommended that the first step should be to obtain and verify the scaling factor S to update the covariance of the RLS. Using the derived scaling factor, the RLS estimates the coefficients of the designed first-order error dynamics. The control input is derived using the Lyapunov direct method based on the estimated coefficients. In this process, a sliding mode approach was applied, and the magnitude of the injection term was self-tuned using the residuals of the RLS. The developed method uses adaptive recursive least squares (RLS) filtering. Thus, the proposed algorithm adaptively tracks the target path using the RLS estimated in real time.
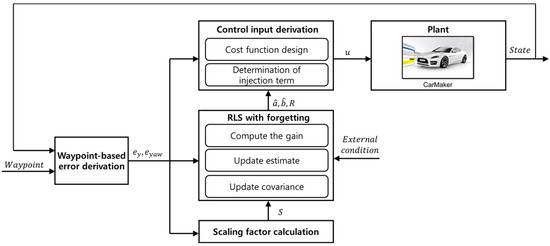
Figure 1.
Schematic of the proposed path-tracking control algorithm.
In Figure 1, and are the lateral and yaw angle errors derived from the waypoints, respectively. Scale factor calculated using the absolute value of the error derivative was used for covariance self-tuning. The coefficients and were estimated using RLS with the forgetting factor. The residual R from the RLS algorithm was used for injection term self-tuning. Finally, control input was derived using errors, estimated coefficients, and the residual. Equation (1) represents the integrated error designed by applying weights to the lateral and yaw angle errors. Weights (, ) were set at 1. Based on the above equation, simplified error dynamics were designed, as shown in Equation (2).
2.1. RLS-Based Coefficient Estimation with External Condition and Covariance Self-Tuning
In this study, coefficients and were estimated using the RLS with forgetting factors. A relational function was designed for parameter estimation, as shown in Equation (3). Equation (4) presents the following RLS equations: in the virtual relational function, , , and represent the output, regressor, and estimated value, respectively.
In this study, the cost function was defined as following Equation (5) to design an RLS algorithm with multiple forgetting factors ranging from zero to one. As the forgetting factor approaches 1, a greater weight is assigned to past data, resulting in more gradual changes in the parameter estimation. In least squares estimation, unknown parameters are chosen in such a way that the sum of the squares of the difference between the actually observed and the computed values is a minimum at each time instance . The RLS method with multiple forgetting factors was designed based on a previous study [30].
The estimated values that minimize the cost function of the recursive least squares method defined in Equation (5) are computed using the regressor described in Equation (4). The calculation process is shown in Equation (6):
In Equation (6), the optimal gain for the estimation and the covariance matrix , which remains positive definite, are updated at each sampling instance using the forgetting and covariance update factors, as described in Equation (7) [30].
The equation of the scaling factor calculation used for covariance self-tuning is as follows. The scaling factor is computed based on the designed function using the absolute value of the time derivative of the error and certain parameters. Equation (8) describes the scaling factor function for covariance self-tuning. The threshold value of the time derivative of error was taken as an appropriate value through evaluation, with the upper threshold being 0.1 and the lower threshold being 0.03. The minimum value of the scale factor was set to 1, and the maximum value was set to 1.1.
In addition, an evaluation was conducted by applying external constraints to analyze the influence of the coefficients estimated by the RLS. External constraints were placed such that the estimated and parameters did not change, and an analysis was conducted to determine whether the control inputs were reasonably derived. The related content is explained in more detail in Section 3.
2.2. Derivation of Control Input Based on the Lyapunov Direct Method
In this study, the direct Lyapunov method was used to ensure the stability of the control algorithm. The Lyapunov function is defined to ensure that the error converges to zero within a finite time, and finite stability conditions are applied, as in Equation (9).
Suppose the rate of change in the Lyapunov candidate function with respect to time is negatively definite. In that case, the equilibrium is guaranteed to be asymptotically stable. Therefore, the Lyapunov candidate function must always be negative, and the defined function must be differentiated with respect to time, as shown in Equation (10).
To derive a control input that can converge the error to zero, the control input of Equation (10) is defined using the estimation coefficients and discussed in Section 2.1. At this time, the injection term based on sliding mode method is applied to ensure control stability with the magnitude of the injection term as follows.
The time derivative of the cost function in Equation (10) can be rewritten as Equation (12) using the control input in Equation (11). This can then be rewritten using the residual between the current and estimated values, as shown in Equation (13).
The disturbance boundary range can be determined using the reachability factor and is expressed as an inequality condition, as shown in Equation (15). Equation (16) describes the substitution of Equation (15) into Equation (13). If convergence condition 1 is applied within finite time, it can be reformulated as Equation (17).
Because the right-hand sides of Equations (16) and (17) can be assumed to be the same because they are the time-varying quantities of the same cost function, the magnitude of the injection term is determined accordingly.
Equation (10) can be expressed as Equation (19) by using the magnitude of the injection term derived in Equation (18). The control input may cause unrealistic chattering when the sign function of the error is applied, similarly to the conventional sliding-mode technique. Therefore, as shown in Equation (20), the sign function is replaced by a sigmoid function with error and sigmoid function gradient . The final adaptive control input is given by Equation (21).
3. Performance Evaluation
The proposed path-tracking control algorithm was evaluated using the MATLAB®/Simulink® (2019a version) and CarMaker (8.1.1 version) software environment. The evaluation was conducted for four scenarios: an S-curved road with a large radius of 100 m and a small radius of 65 m, low-speed driving at 30 km/h, and high-speed driving at 50 km/h.
Table 1 lists the vehicle parameters used for the performance evaluation. Table 2 lists the control parameters used to derive the control inputs. The control parameters of the algorithm were determined through an iterative trial and error method. When the control inputs were excessive relative to the target trajectory, the covariance values were adjusted to reduce their magnitude, and when the inputs were insufficient, the values were increased accordingly. Furthermore, the decay rate of the Lyapunov function was adjusted to prevent excessive chattering at points where curved and straight roads transitioned. The control parameters were determined through trial and error and the same values were applied for all four driving scenarios. The critical parameters that required adjustment to achieve reasonable control performance were, as mentioned, the covariance and the decay rate of the Lyapunov function. Through trial and error, it was confirmed that adjusting these two parameters could potentially enhance transferability, even when the vehicle to which the controller is applied changes. As mentioned in Section 2.1, this study derives the control inputs using the estimated coefficients; therefore, unreasonable control parameters can affect the control performance. Therefore, we assumed a situation in which one of the coefficients, or , could not be reasonably estimated because the control parameters were not set appropriately by applying external constraints to each coefficient. We evaluated whether the other coefficients could compensate for this and estimated reasonable parameters, even when external constraints were applied.

Table 1.
Vehicle parameters for proposed controller.

Table 2.
Design parameters for front-wheel steering vehicle adaptive steering control.
3.1. Large Radius of Curvature Scenarios
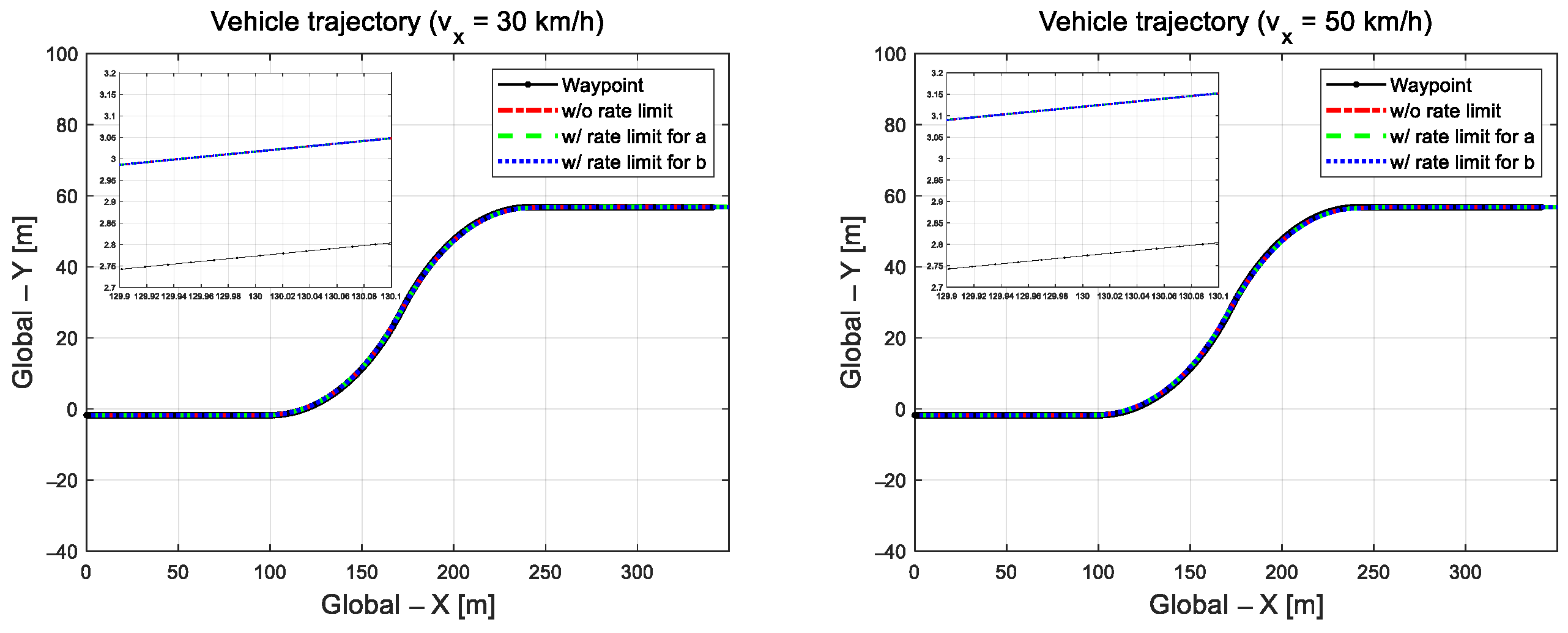
As shown in Figure 2, the path-trajectory tracking performance was evaluated at a relatively low speed of 30 km/h and high speed of 50 km/h on an S-curved road with a relatively large curvature radius of 100 m. In the previous study [31], under these driving conditions with relatively low speed and large curvature, where control is comparatively reasonable, the vehicle was able to track the target path without lane departure. The control input derived for path tracking was applied identically to the front wheels of the CarMaker vehicle model.
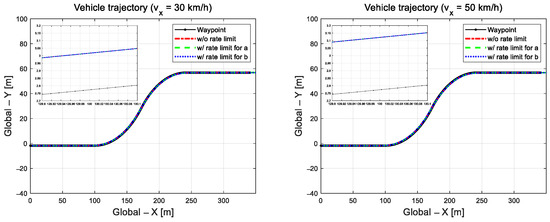
Figure 2.
Driving trajectories at 30 km/h (left) and 50 km/h (right).
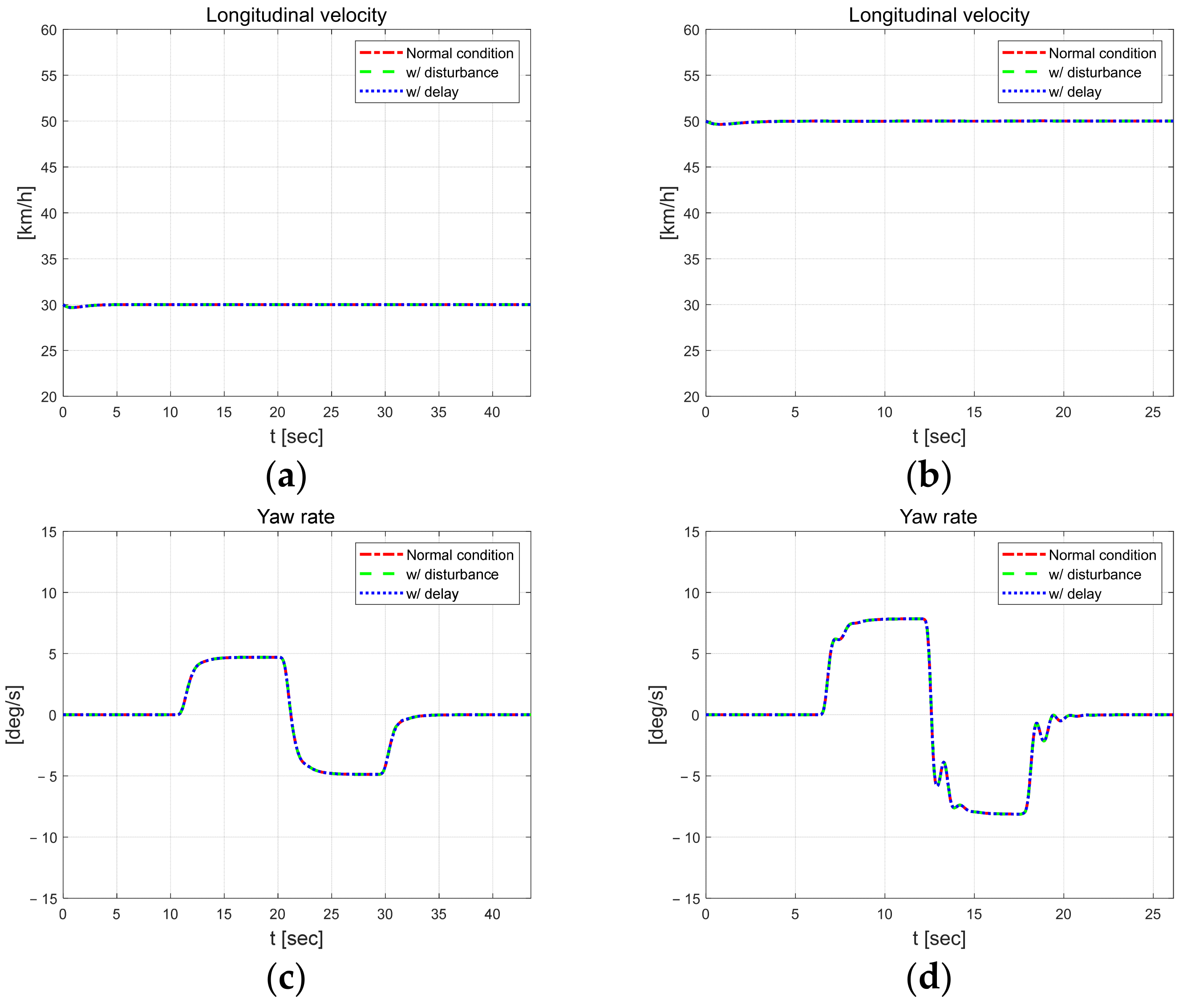
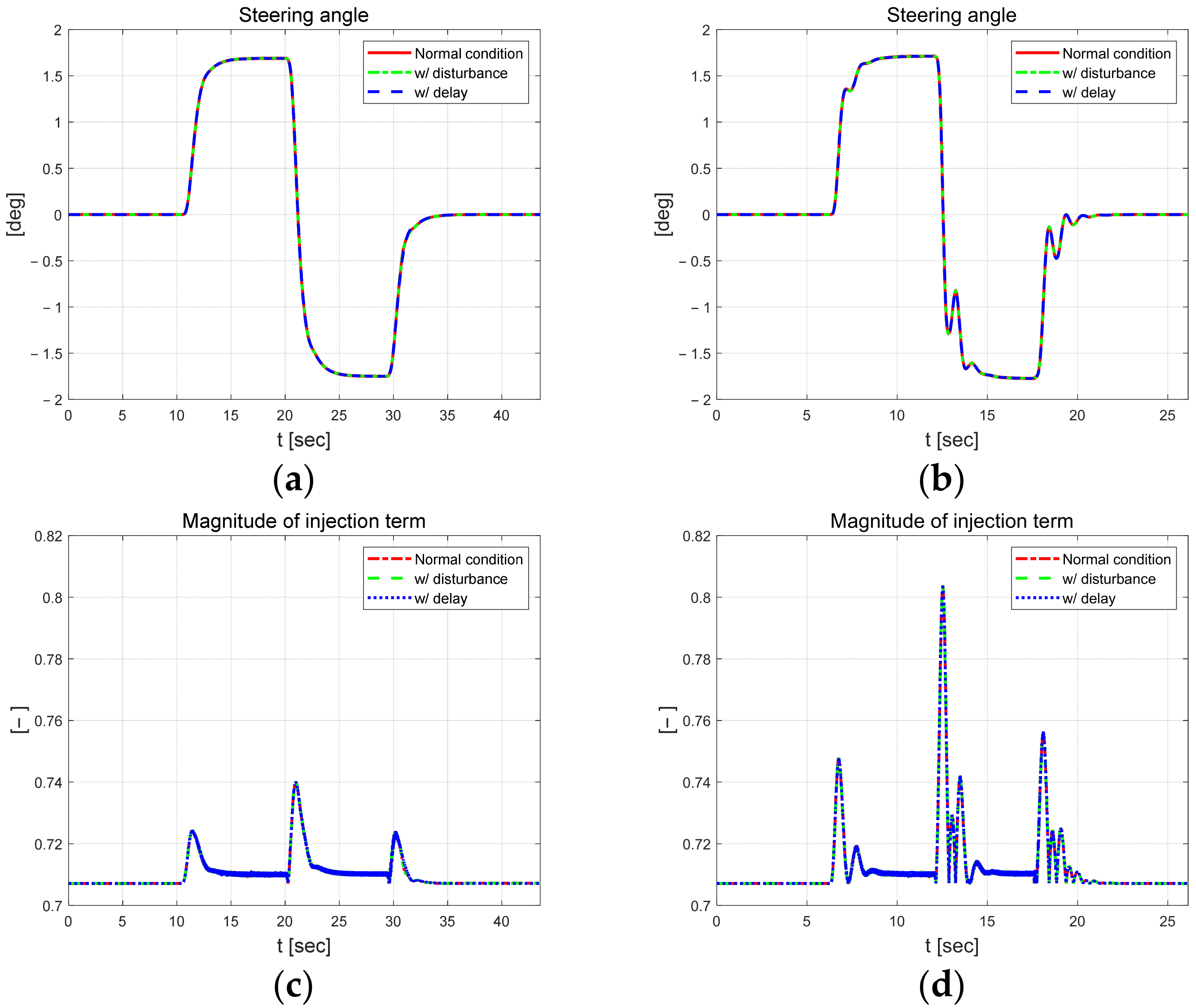
Figure 3 shows the longitudinal velocity and yaw rate of the dynamic behavior of the vehicle. And even when external constraints are applied, the results are not significantly different from those obtained without constraints, indicating that the vehicle can reasonably follow the target path. When comparing driving results according to speed, the yaw rate increases by approximately 3°/s. Figure 4 shows the control input and the magnitude of the injection term. While the absolute value of the steering angle is similar at both speeds, it oscillates more at the higher speed of 50 km/h. And the magnitude of the injection term is greater at higher speeds, with a larger amplitude.
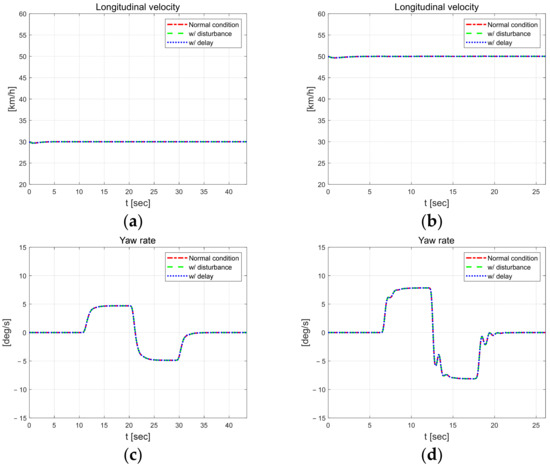
Figure 3.
Vehicle dynamic behavior at 30 km/h (left) and 50 km/h (right). Longitudinal velocity at 30 km/h (a) and km/h (b), yaw rate in at 30 km/h (c) and 50 km/h (d).
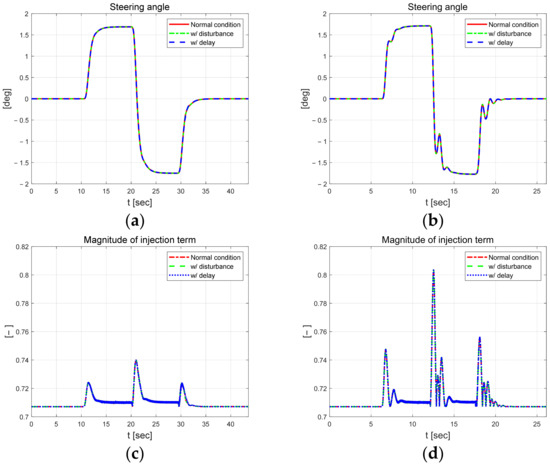
Figure 4.
Control parameters at km/h (left) and 50 km/h (right). Steering angle at 30 km/h (a) and 50 km/h (b). Magnitude of injection term at 30 km/h (c) and 50 km/h (d).
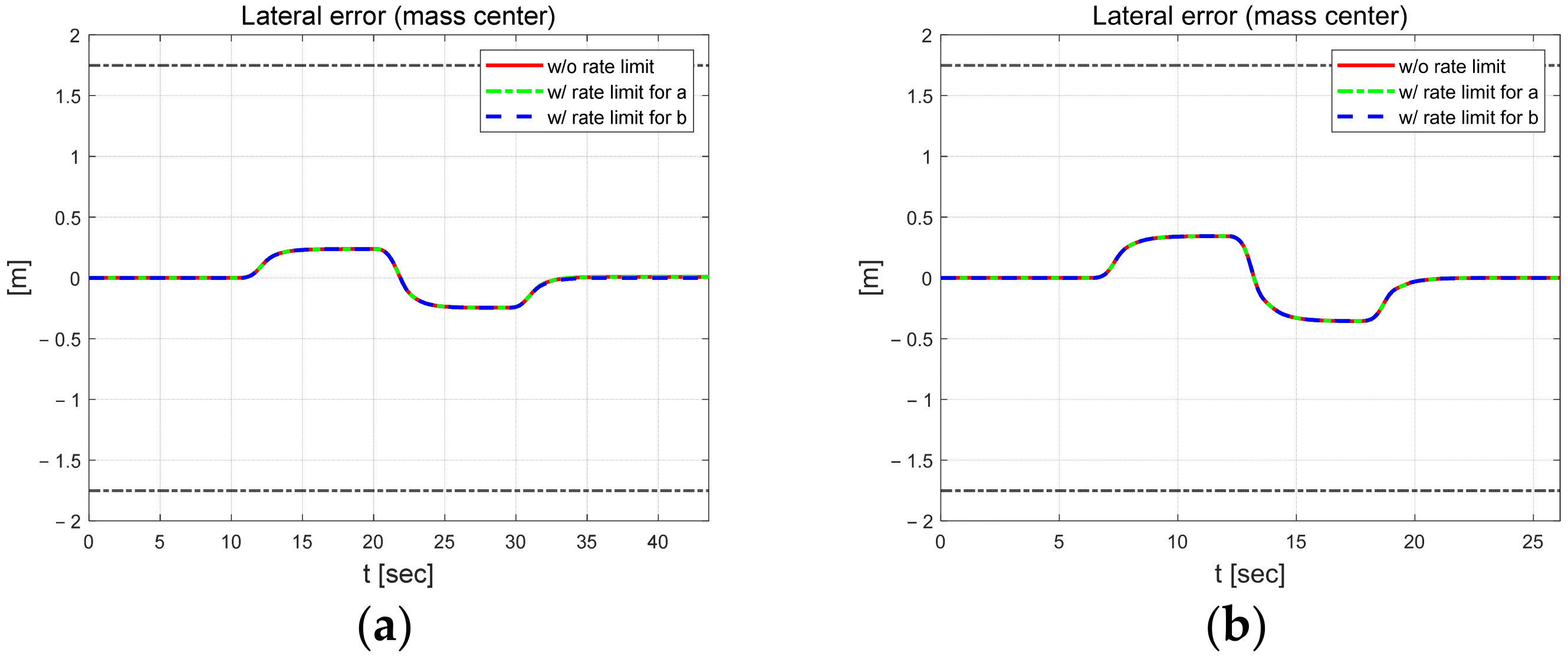
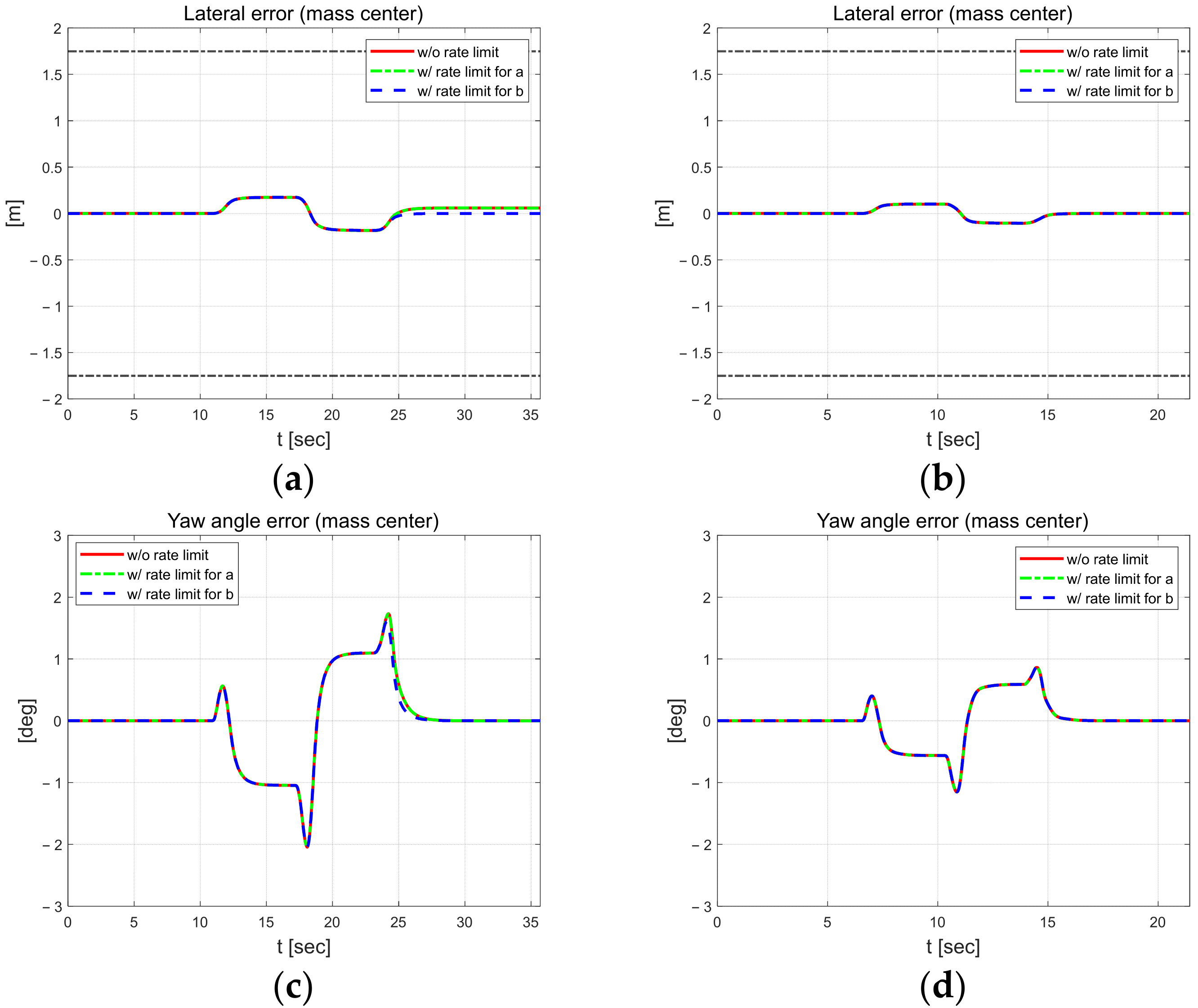
Figure 5 shows the lateral and yaw angle errors. The black dash-dotted line indicates the width of the road. The upper 1.75 m and lower −1.75 m lines are the positions of the lanes. The width of the vehicle is 1.662 m. Therefore, if the error magnitude is greater than about 0.9 m, the vehicle will deviate from the lane. The lateral error shows relatively different results when applying external constraints to parameter b at 30 km/h. At both speeds, it shows a symmetrical shape around the inflection point of the S-curve. The lateral error is within about 0.3 m at 30 km/h. At 50 km/h, it is a little larger, within 0.4 m. The yaw angle error increases in absolute value when changing from a straight to a curved section, from a curve to a straight section, and at the inflection point of the S-curve. In addition, this error is about 0.5 to 1° larger in the high-speed scenario.
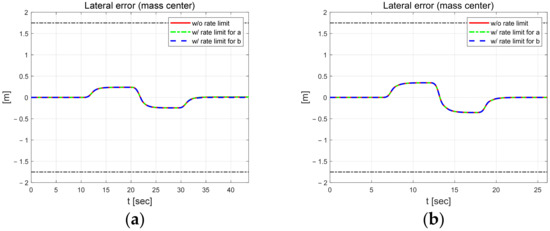
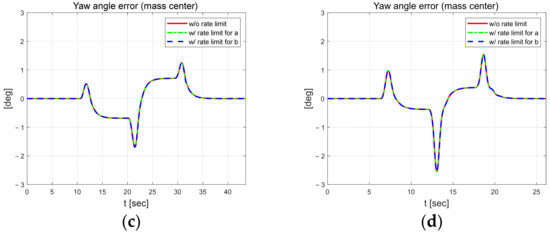
Figure 5.
Control errors at 30 km/h (left) and 50 km/h (right). Lateral error at 30 km/h (a) and 50 km/h (b). Yaw angle error at 30 km/h (c) and 50 km/h (d).
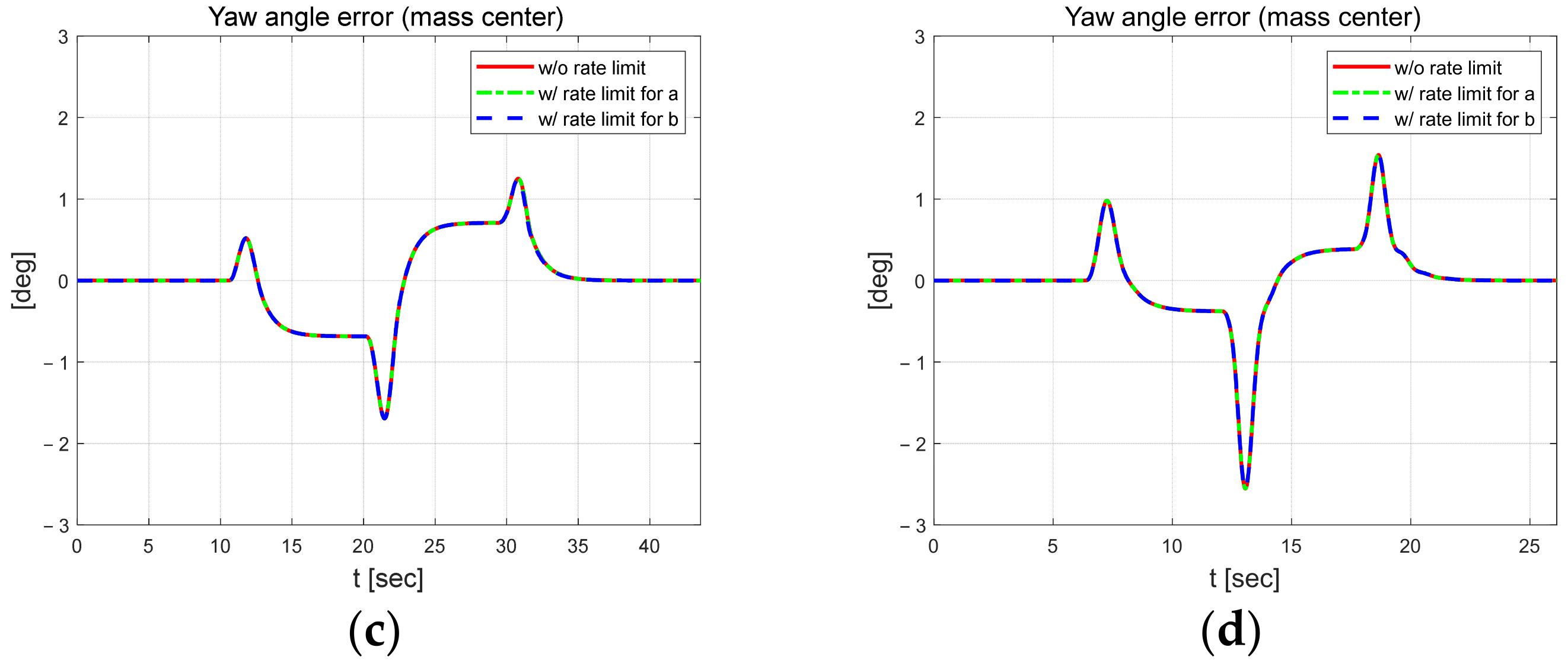
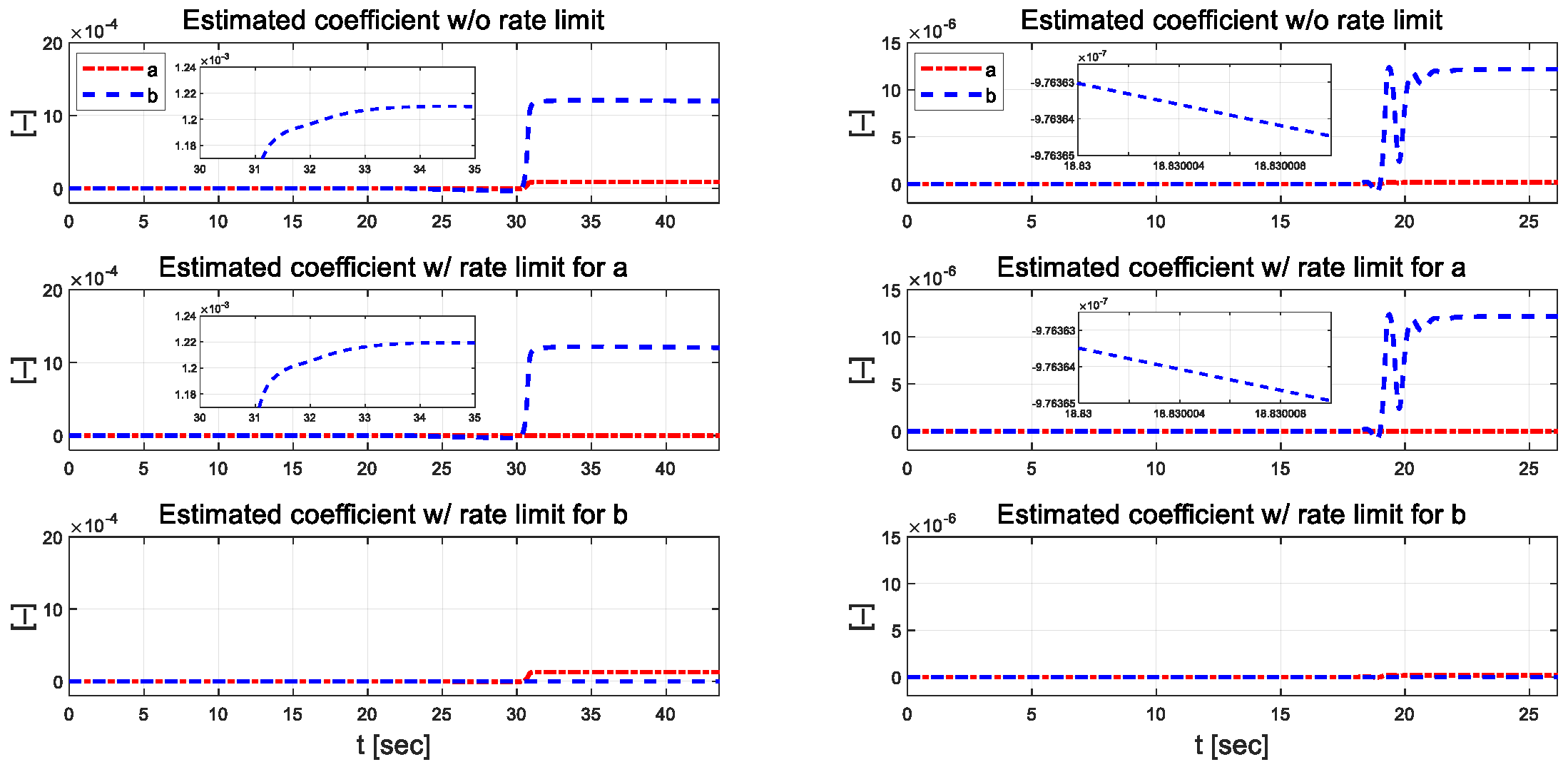
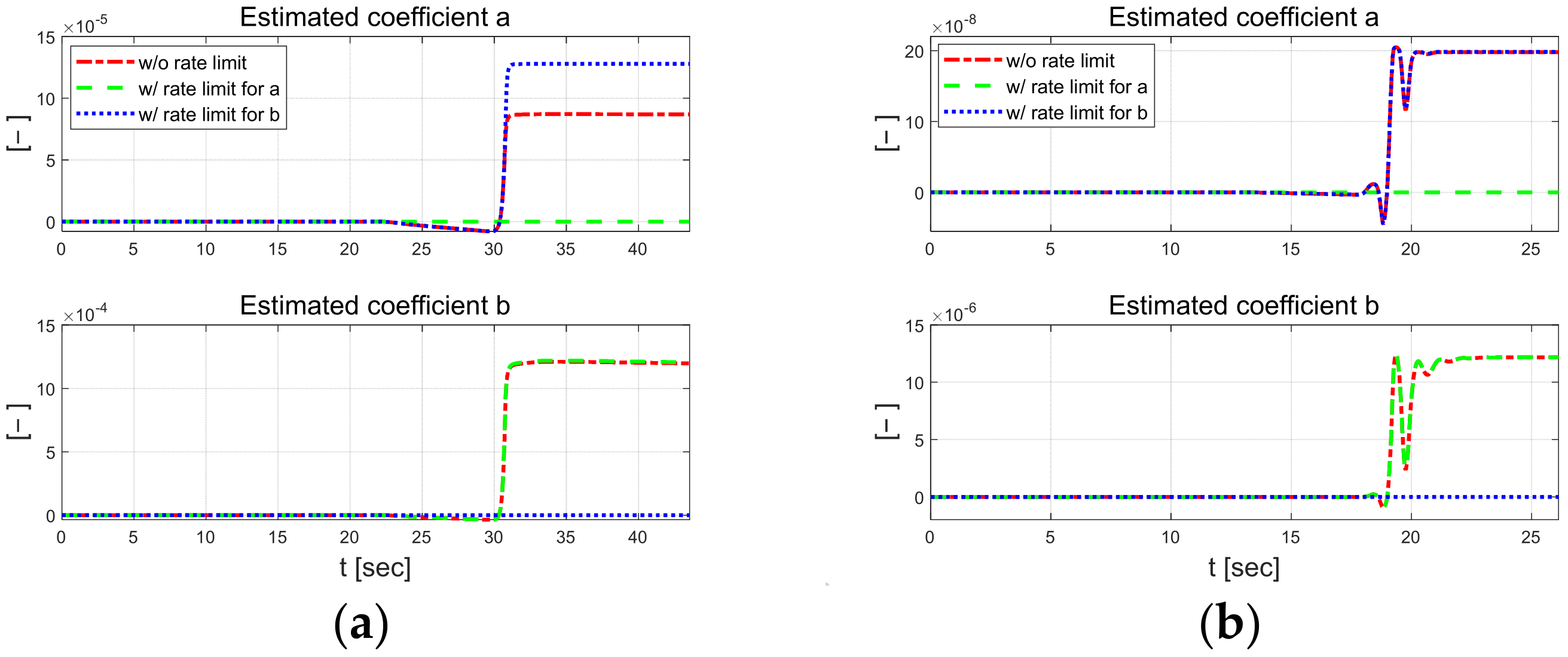
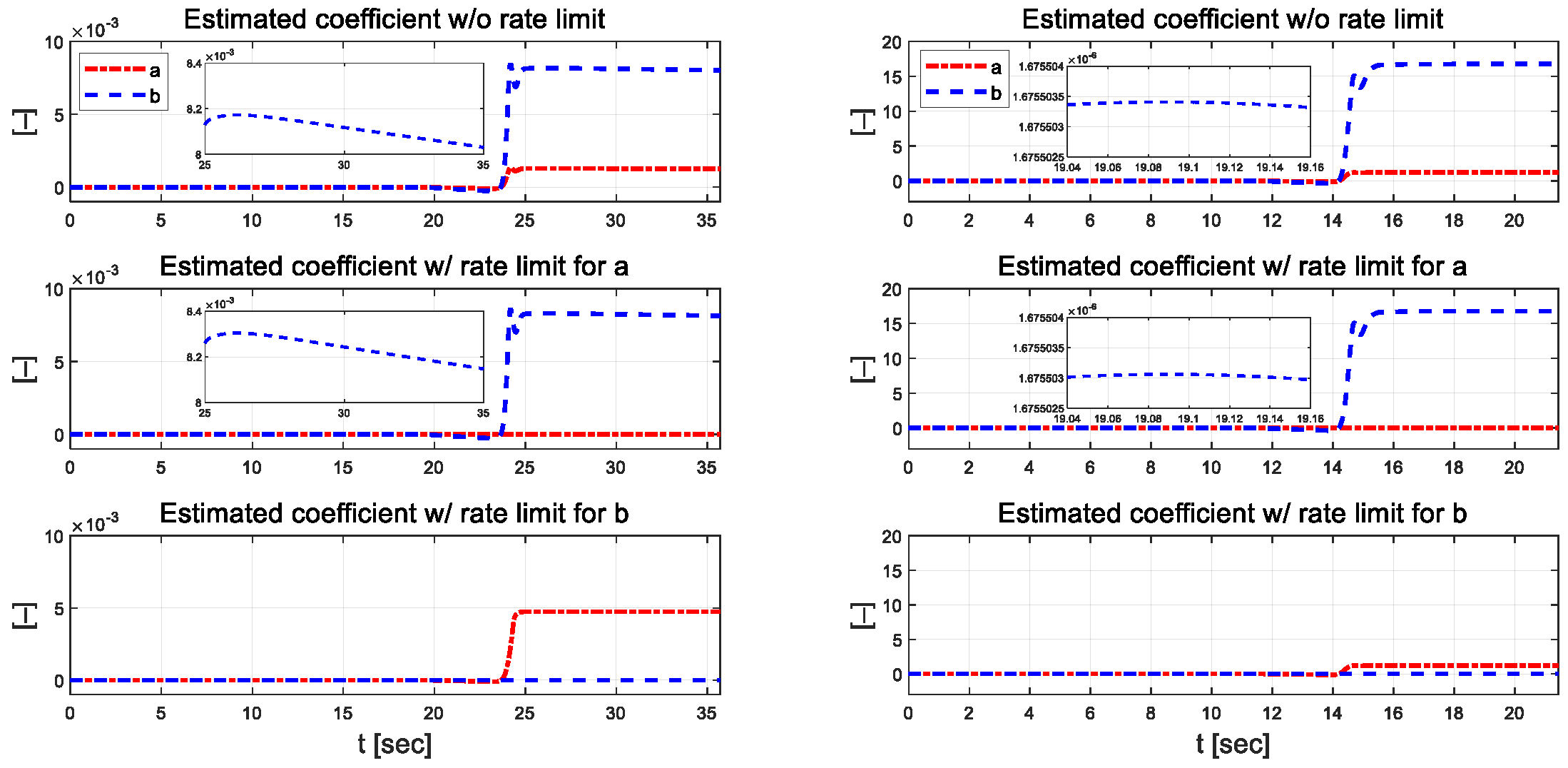
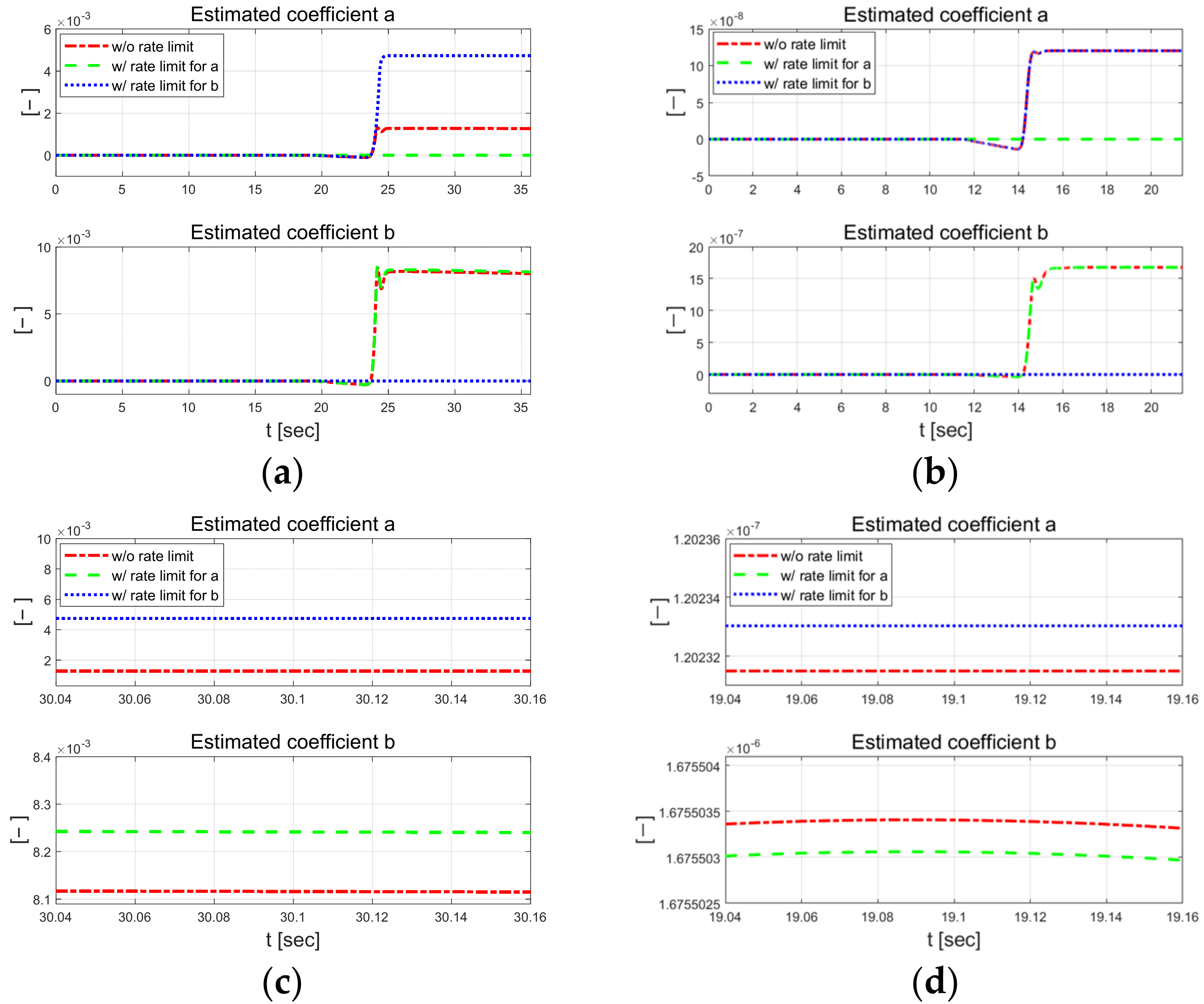
Figure 6 and Figure 7 present the coefficients estimated using the designed RLS. External constraints were applied to each regression process, in which coefficients and were estimated using the rate-limit condition. Compared to the case without the rate limit constraint, when the rate limit constraint is applied to a, it can be seen that b changes significantly, and when the constraint is applied to b, it also changes significantly. When rate constraints were applied to each individual parameter, it was observed that the other parameter was adjusted to maintain control performance. This result suggests that even if one parameter is inaccurately estimated due to external disturbance during the control algorithm’s operation, the other parameter can adapt and be estimated in such a method that allows the vehicle to complete the driving task reasonably. In the low-speed scenario, parameter has a relatively large difference when external constraints are applied, and the absolute magnitude of the estimated parameter is also large.
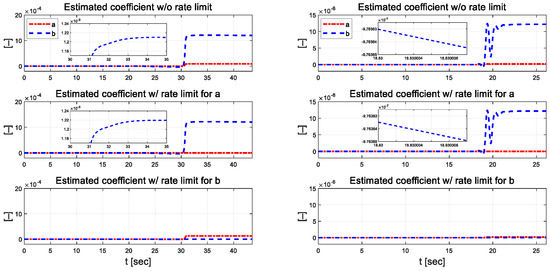
Figure 6.
Estimated coefficients for each scenario at 30 km/h (left) and 50 km/h (right).
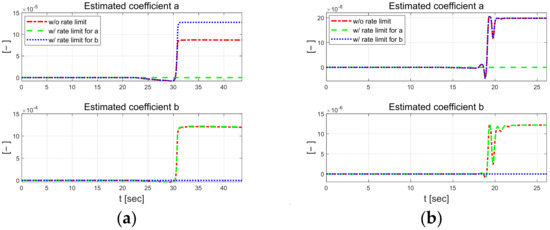
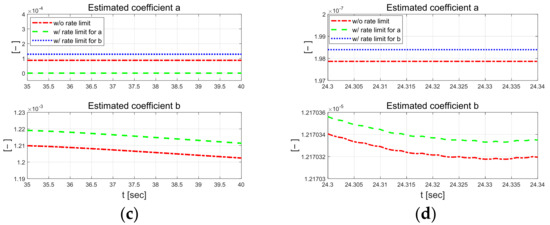
Figure 7.
Comparison of estimated coefficients at 30 km/h (left) and 50 km/h (right). Full at 30 km/h (a) and 50 km/h (b). Zoomed in at 30 km/h (c) and 50 km/h (d).
3.2. Comparison of APTA and LQR-Based Path-Tracking Performance
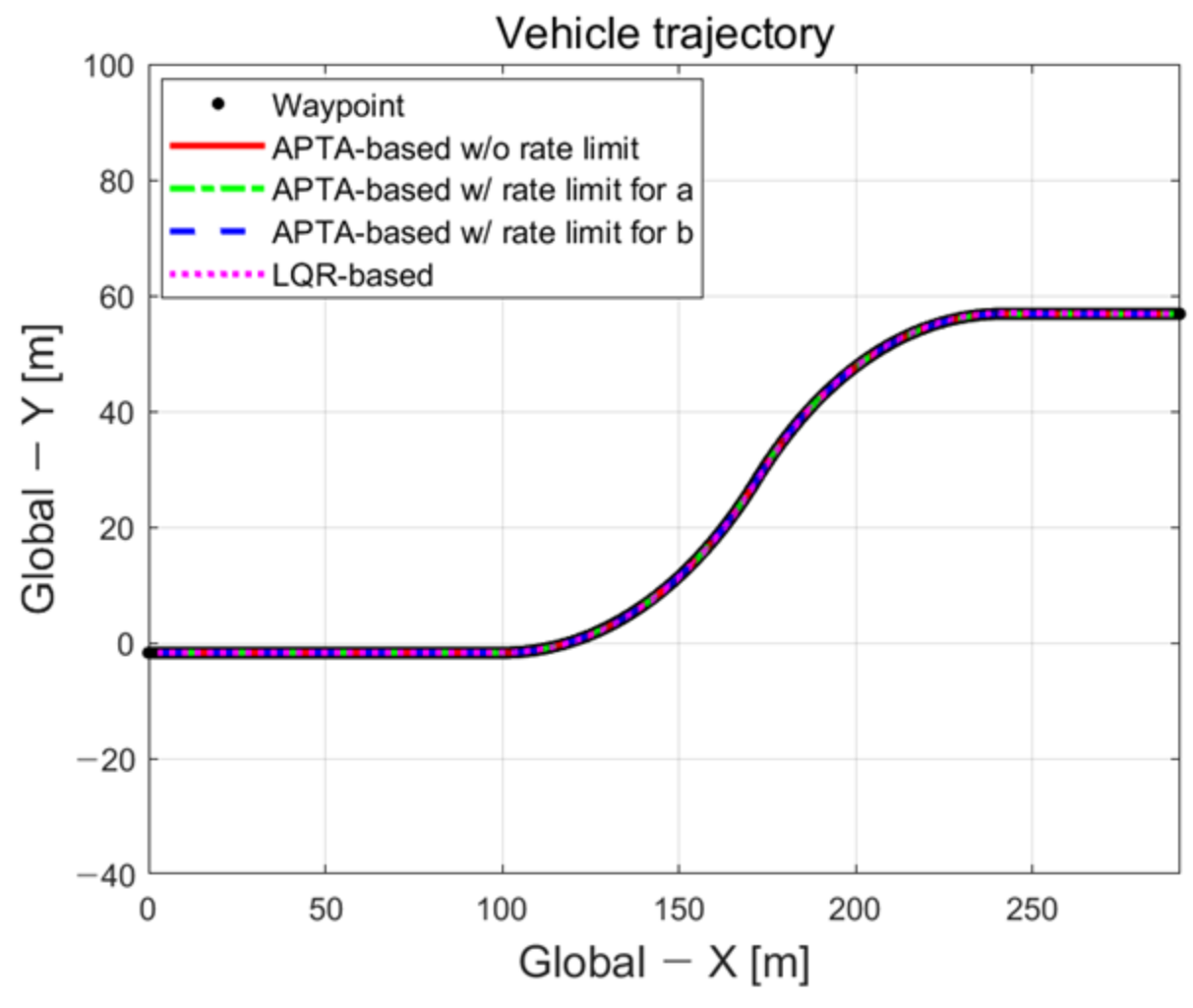
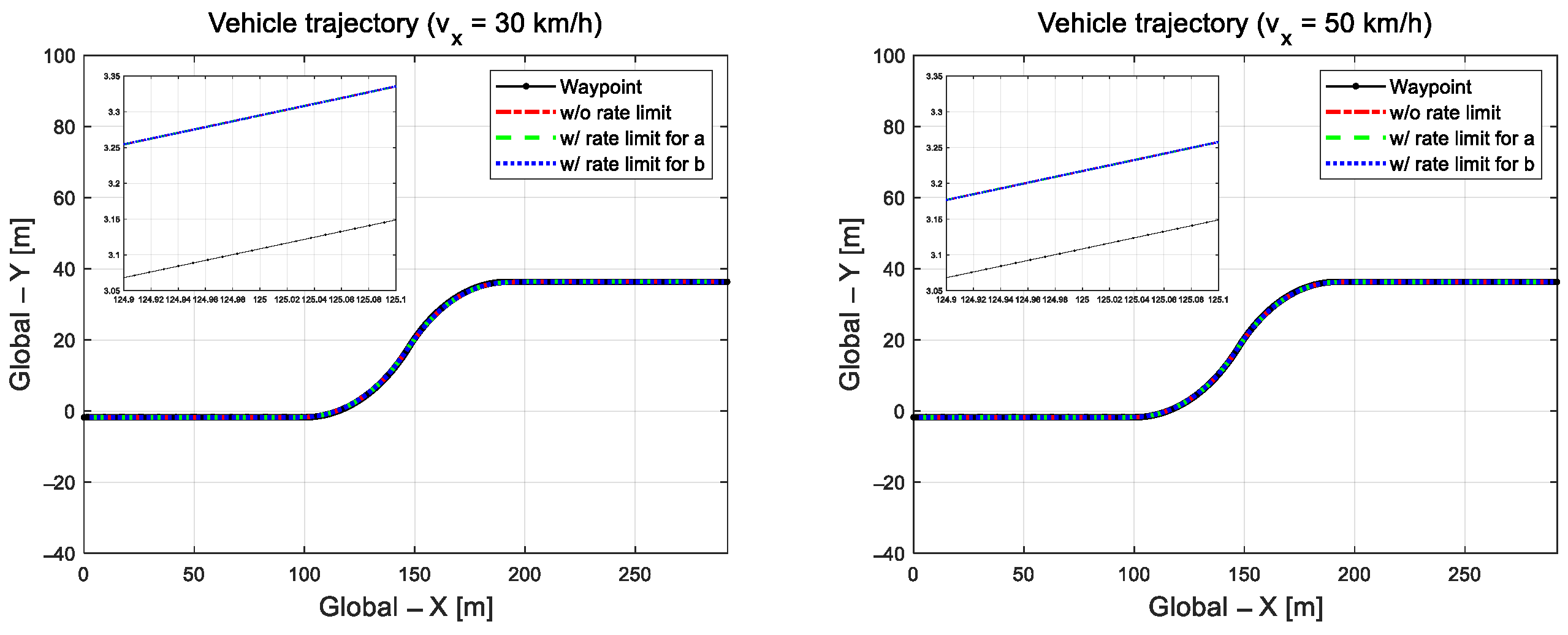
To compare the model-free method-based path-tracking control performance proposed Adaptive Path-Tracking Algorithm (APTA) in this study with another controller, a conventional linear quadratic regulator (LQR) was used to conduct performance evaluation under the extra-high-speed path-tracking scenario with a large-curvature-radius road. The mathematical model of LQR used the bicycle dynamic model in terms of error. As shown in Figure 8, the path tracking performance of the LQR algorithm for comparison with the proposed algorithm was evaluated at a road curvature radius of 100 m.
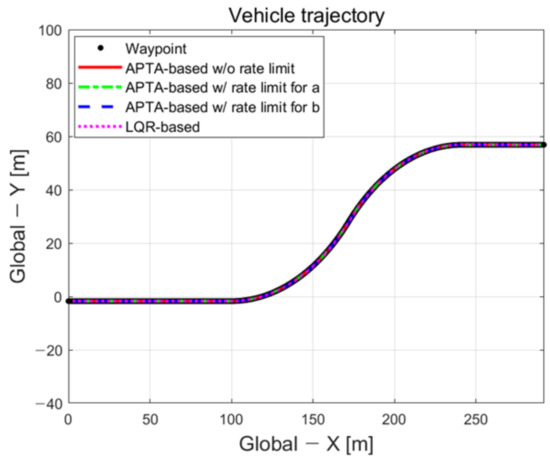
Figure 8.
Driving trajectory.
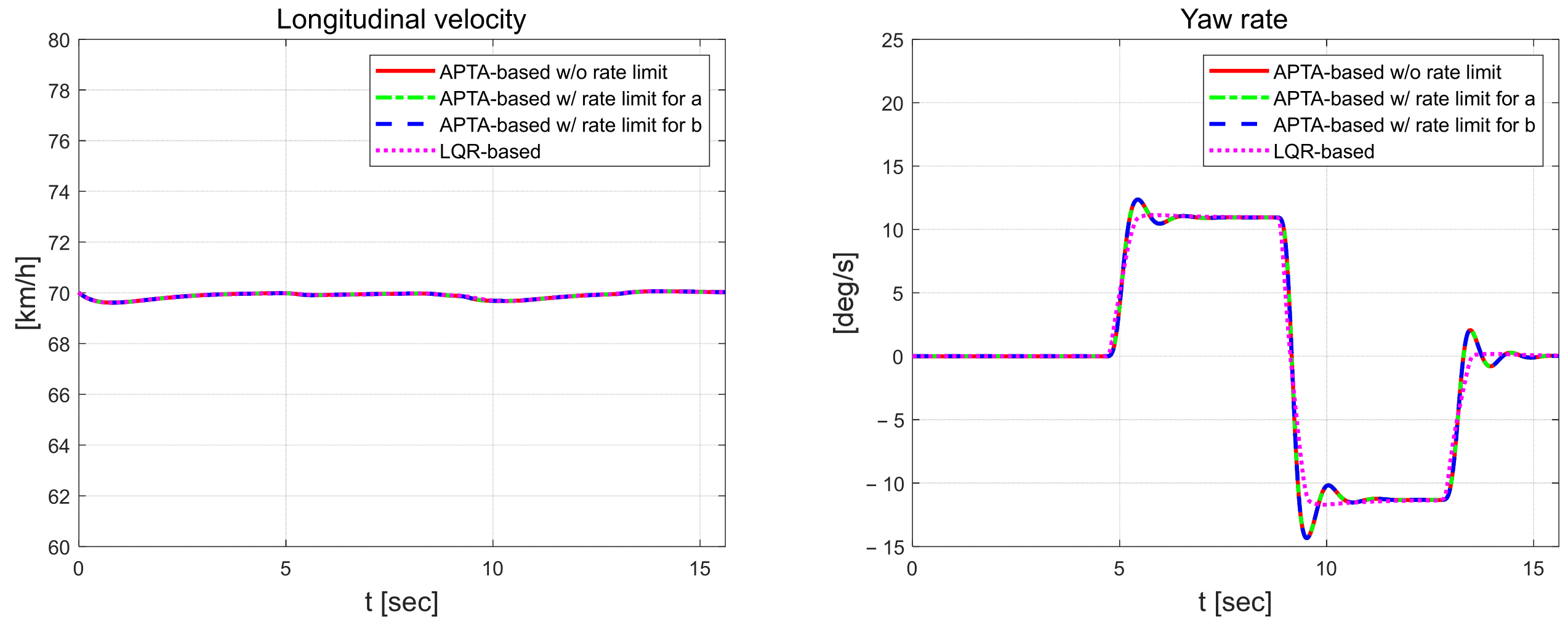
The longitudinal velocity was set to 70 km/h, which is faster than 50 km/h, which was previously set as a high speed. In Figure 9, the velocity was set to 70 km/h, but it decreased to approximately 69.6 km/h around the 10 s inflection point of the curve. The proposed model-free adaptive control results in the yaw rate tended to oscillate around the 5 s, 9 sand 13 s regardless of whether external constraints were applied. Compared to the yaw rate in the previous high-speed scenario, the amplitude increased by a maximum of about 2°/s. However, there was little oscillation in the yaw rate behavior for the LQR control.
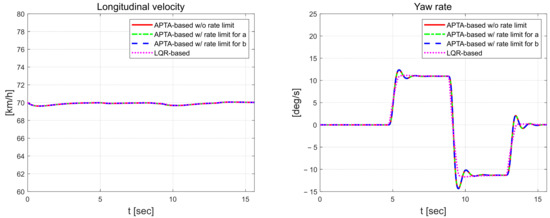
Figure 9.
Longitudinal velocity (left) and yaw rate (right).
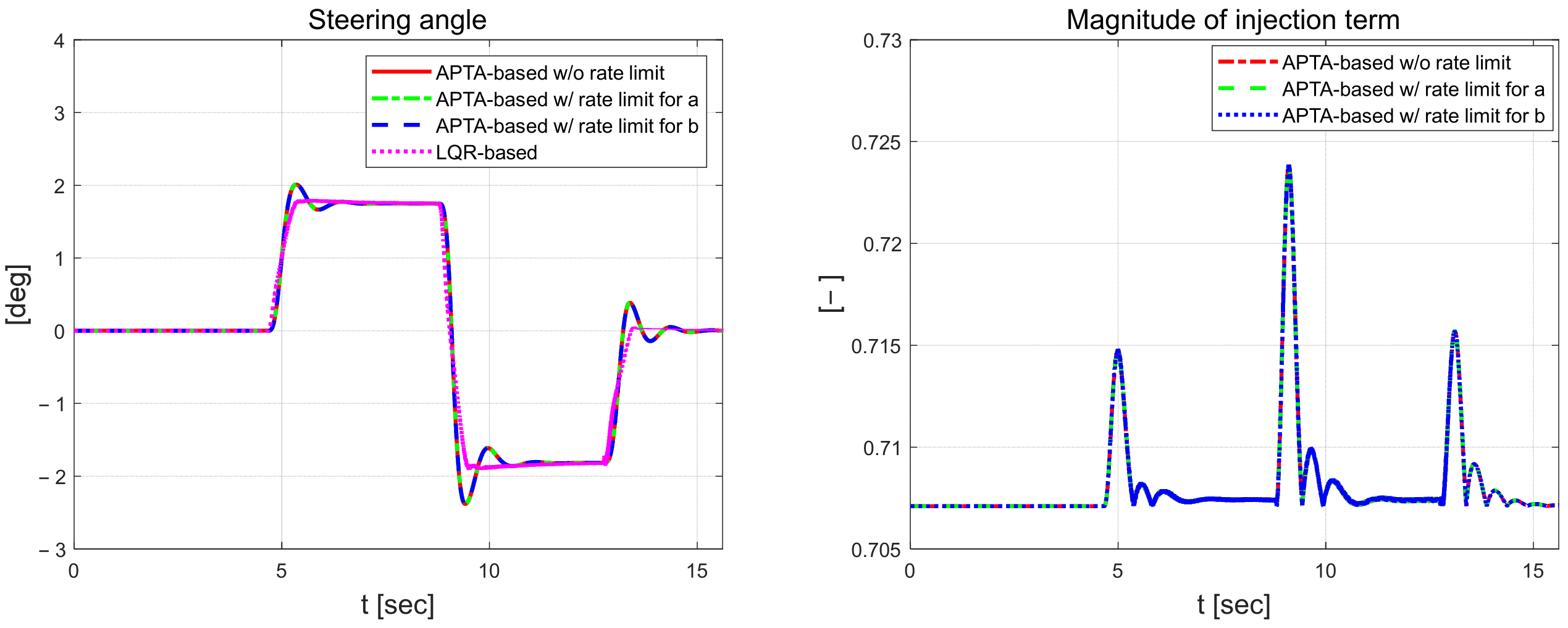
Figure 10 shows the steering angle of the vehicle, which is the control input, and the magnitude of the injection term, which is a component of the control input. The magnitude of the injection term is calculated using the residual of RLS and oscillates in the section where the road environment changes. The control input affected by the magnitude of the injection term also oscillates in a similar section. The steering angle, which is the control input of the LQR controller, does not have oscillations like the proposed algorithm, but shows the chattering in the S-curve road.
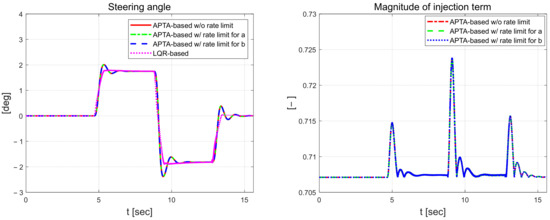
Figure 10.
Front-wheel angle (left) and magnitude of injection term (right).
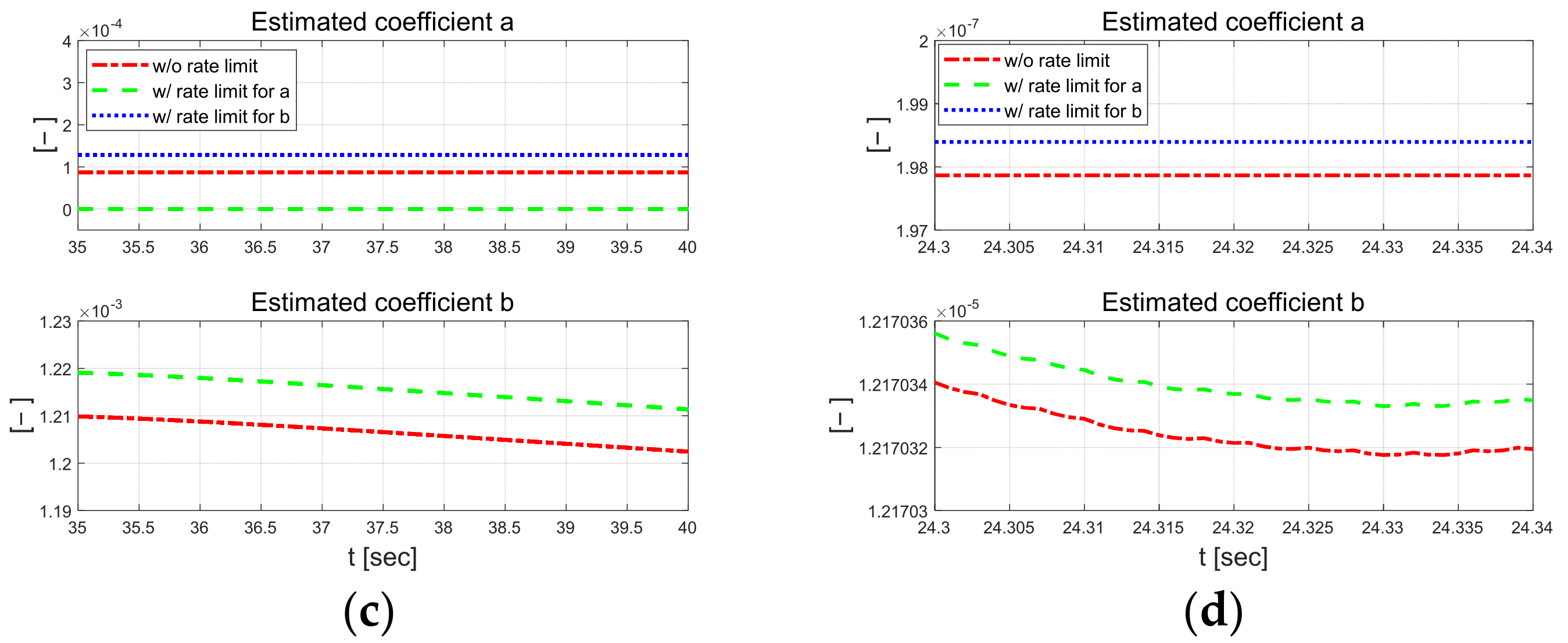
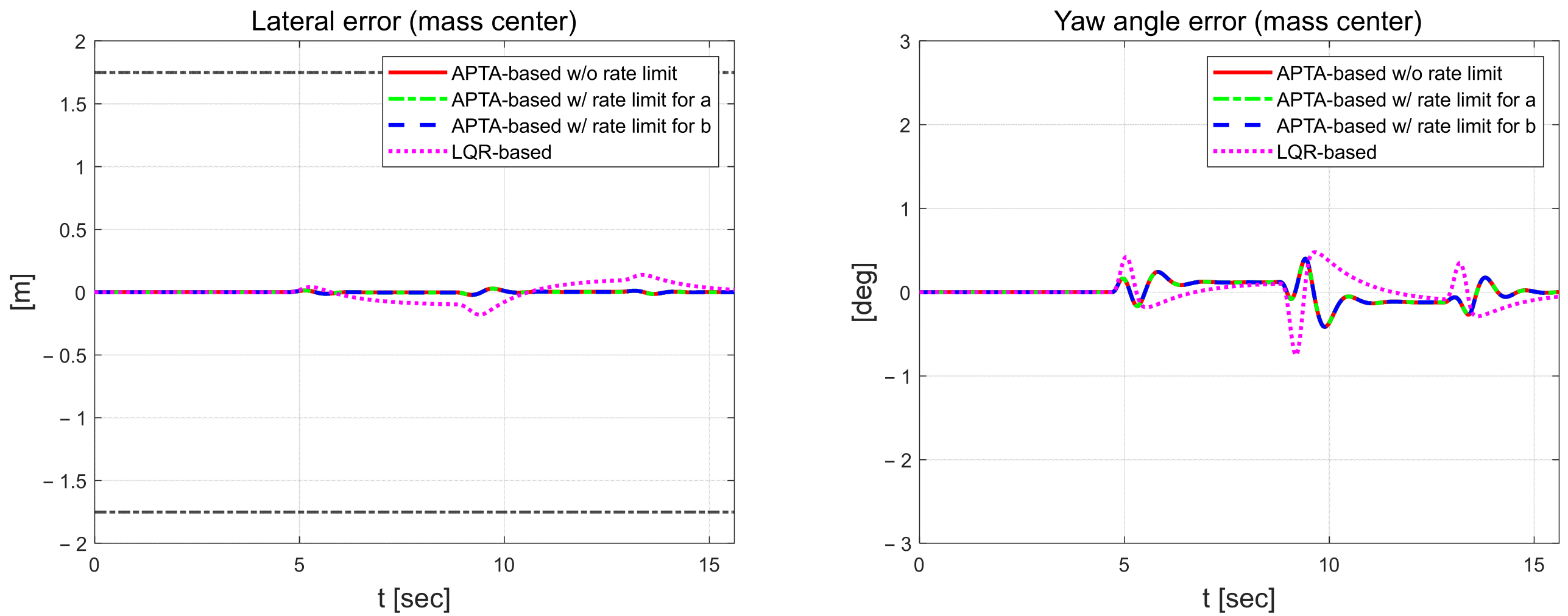
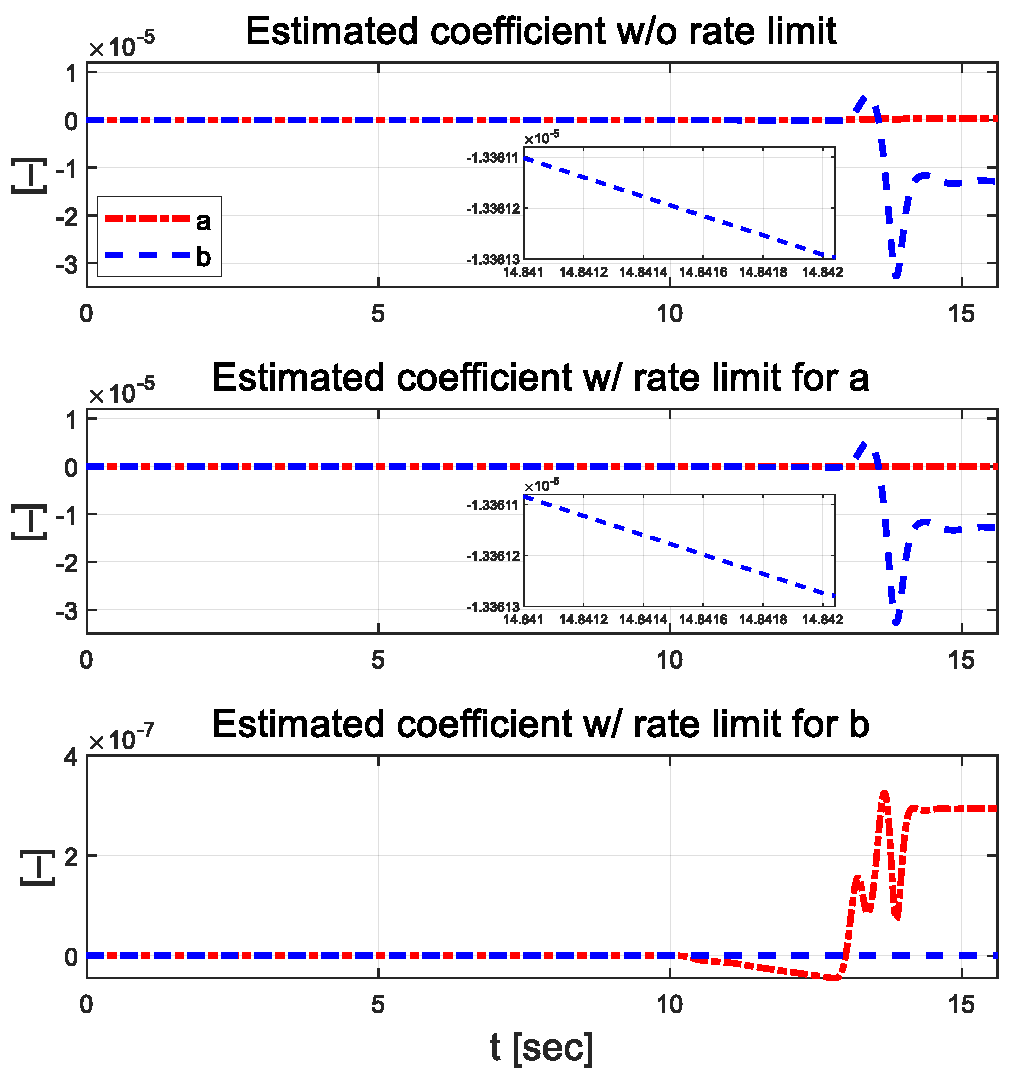
In Figure 11, the lateral error for the proposed algorithm remains below approximately 0.03 m, regardless of the application of external constraints during driving, whereas the LQR control exhibits an error of around 0.3 m. The magnitude of the lateral error, which can be analyzed as lane departure, is smaller than 0.9 m. For the yaw angle error, the proposed algorithm shows a maximum value of about 0.4°, while the LQR used as a comparative controller has a maximum error of approximately 1.7°. This difference was because the cornering stiffness coefficient and vertical axis rotational inertia were treated as constants in the bicycle model, which is a system model, but in actual driving, they change due to dynamic factors such as curved driving, which causes differences from the mathematical model. Figure 12 shows the estimated parameters using RLS for each scenario.
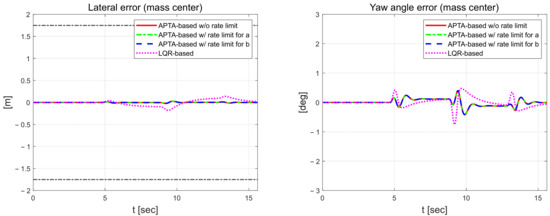
Figure 11.
Lateral error (left) and yaw angle error (right).
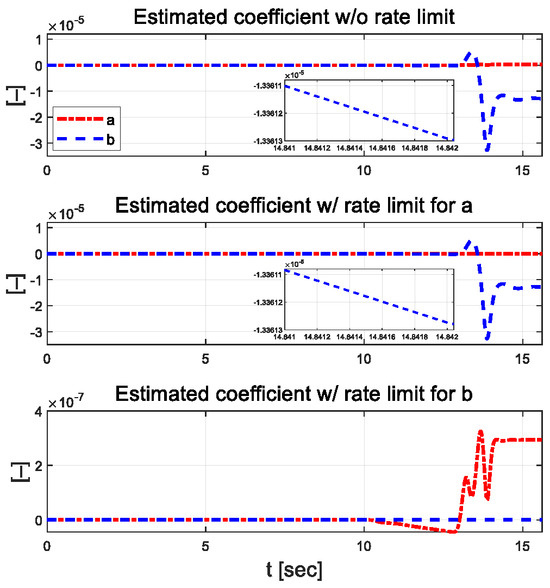
Figure 12.
Estimated coefficients for each scenario.
3.3. Small Radius of Curvature Scenarios
This section examines the results of driving on an S-curved road with a relatively small curvature radius of 65 m at a low speed of 30 km/h and a high speed of 50 km/h. Even if we assume an unreasonable application of the control parameters and impose external constraints on the RLS estimation coefficients, the vehicle can explore the target path without lane departure, as the vehicle trajectory can be seen in Figure 13. Even in the most challenging scenarios with a curvature radius of 65 m and relatively high speed, the target path was reasonably tracked in all cases, where external constraints were imposed on the RLS estimation coefficients.
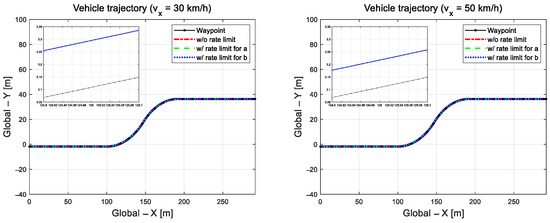
Figure 13.
Driving trajectories at 30 km/h (left) and 50 km/h (right).
Figure 14 shows the longitudinal velocities and yaw rate at 30 kph and 50 kph. The longitudinal velocities for all scenarios were observed, and there was no relatively large variation without an accompanying decrease or oscillations. This indicates that the steering input produced by the controller does not have a significant influence on the vehicle’s longitudinal behavior, and even in the high speed and small radius scenario. The yaw rate is the highest among all the scenarios, reaching approximately 12°/s.
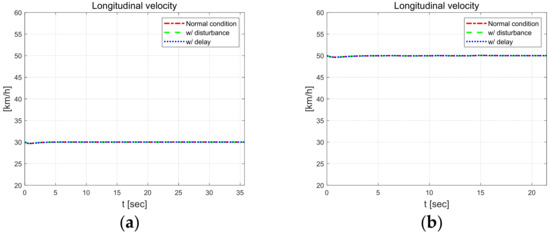
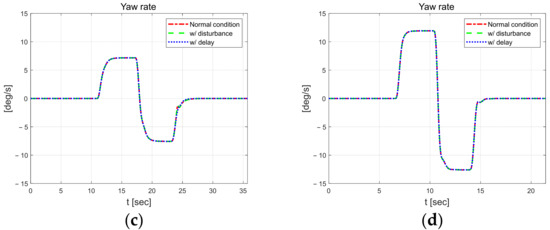
Figure 14.
Vehicle dynamic behavior at 30 km/h (left) and 50 km/h (right). Longitudinal velocity at 30 km/h (a) and 50 km/h (b), yaw rate in at 30 km/h (c) and 50 km/h (d).
The driving results for the steering angle of 50 km/h Figure 15b are not significantly different from those at 30 km/h. The steering angle is approximately 2.5°, which is 0.8° greater than the approximately 1.7 angle mentioned in Section 3.1, owing to the reduced radius of curvature. The magnitude of the injection term is reduced compared to that described in Section 3.1.
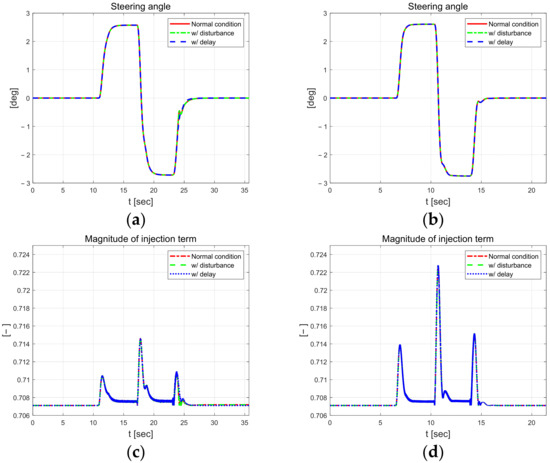
Figure 15.
Control parameters at 30 km/h (left) and 50 km/h (right). Steering angle at 30 km/h (a) and 50 km/h (b). Magnitude of injection term at 30 km/h (c) and 50 km/h (d).
In Figure 16, the lateral error in (a), which is the result of driving at 30 km/h, slightly increases to about 0.2 m on the curve, and the yaw error is about 2°. In particular, when no external constraints are applied (red dash-dotted line) and when an external constraint is applied to the estimated coefficient a (green dotted line), the vehicle drives while maintaining an error of about 0.02 m at the exit point of the S-curve. Furthermore, the yaw angle error (c) is approximately 2°. In the results obtained for high-speed 50 km/h driving, the lateral error is about 0.1 m, which is smaller than that of 30 km/h driving. The yaw angle error is also small and is not greatly affected by the application of external constraints.
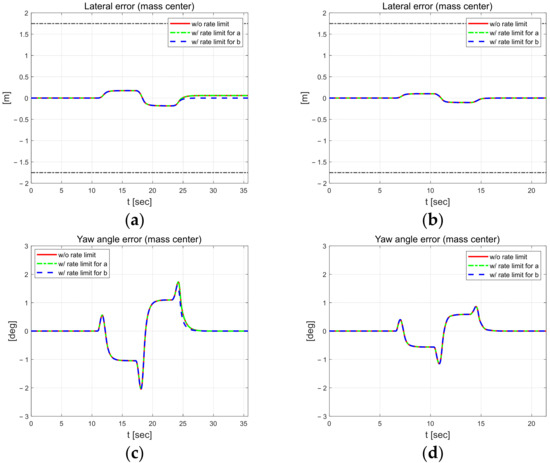
Figure 16.
Control errors at 30 km/h (left) and 50 km/h (right). Lateral error at 30 km/h (a) and 50 km/h (b). Yaw angle error at 30 km/h (c) and 50 km/h (d).
As shown in Figure 17(left), which depicts the results of driving at 30 km/h, the estimated coefficient magnitude increased compared with the previous driving scenarios. There are relatively large changes in the estimated coefficients around 24 s into the simulation time. When external constraints are applied to parameters and , the other parameters are estimated to be larger than when no constraints are applied. The estimated coefficients in Figure 17(right) are smaller than those estimated when driving at 30 km/h. They changed at the exit point in an S-curve for approximately 14 s and converged to a constant value in the straight section. When comparing the results for relatively low velocity (30 km/h) with the same curvature radius for the relatively high-velocity (50 km/h) scenario, as shown in Figure 18, the vehicle can track the target path reasonably well, although there are individual rate limit constraints on parameters and .
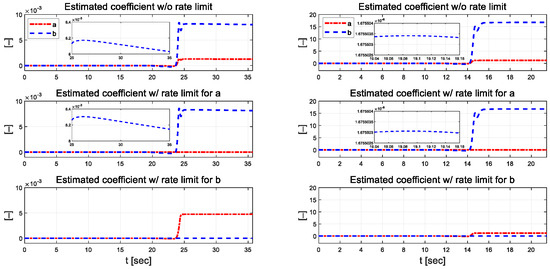
Figure 17.
Estimated coefficients for each scenario at 30 km/h (left) and 50 km/h (right).
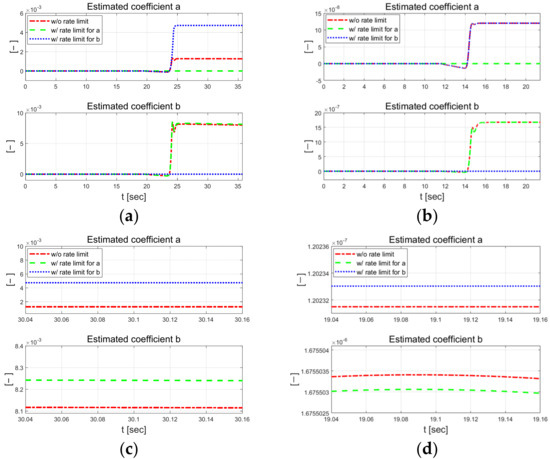
Figure 18.
Comparison of estimated coefficients at 30 km/h (left) and 50 km/h (right). Full at 30 km/h (a) and 50 km/h (b). Zoomed in at 30 km/h (c) and 50 km/h (d).
3.4. System Disturbance and Measurement Delay Scenario
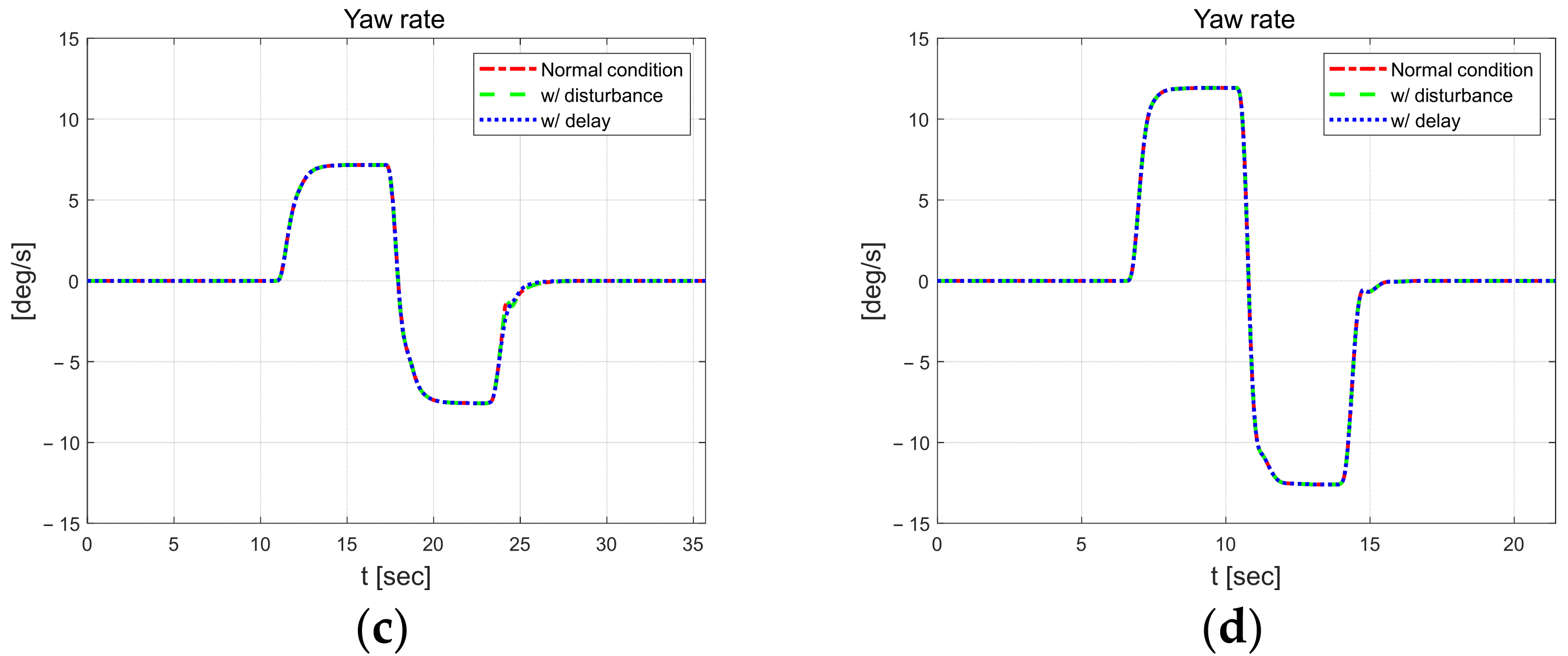
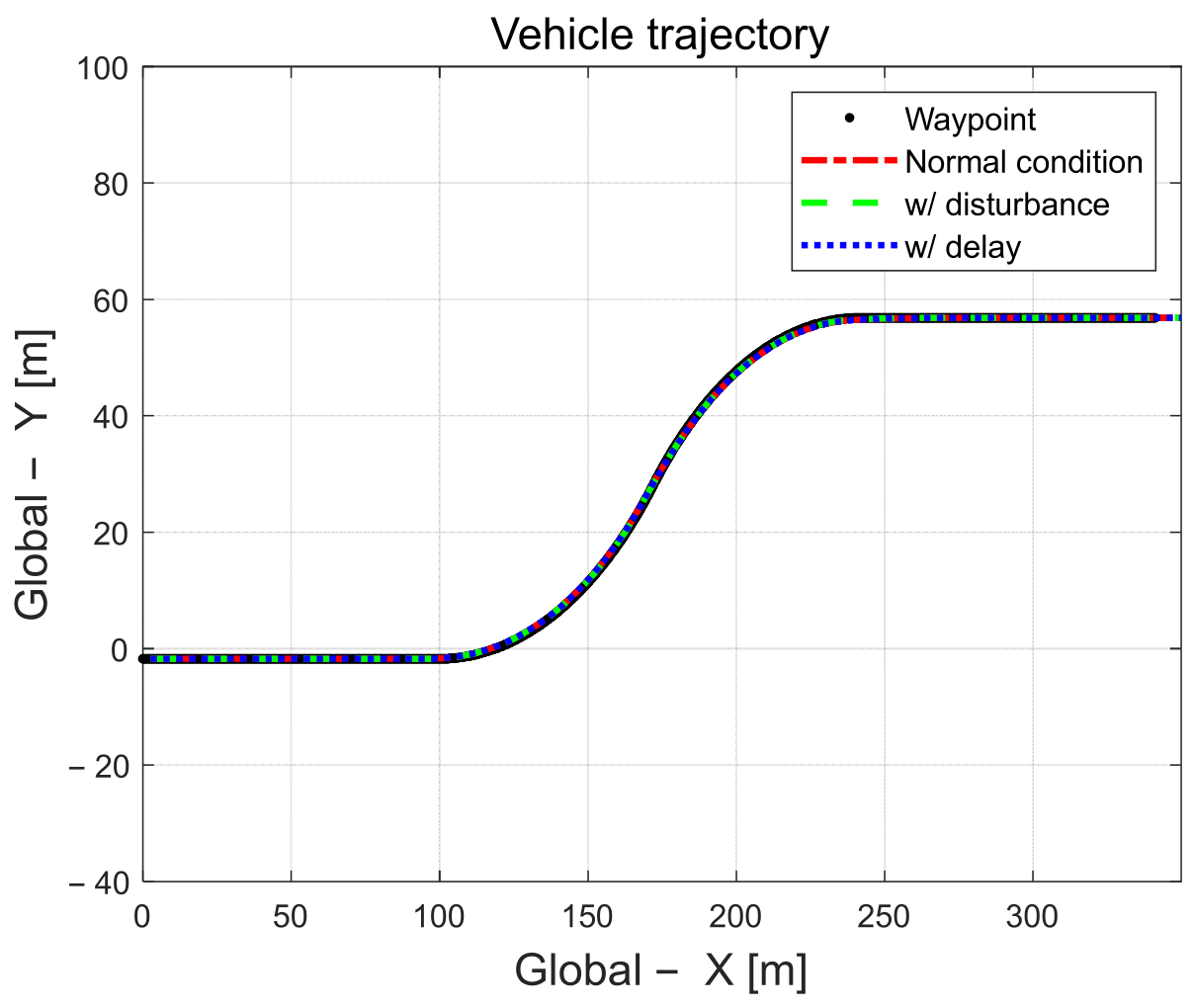
This section describes the results of applying disturbances or delayed input signals during driving. The performance was evaluated in a driving scenario on a 100 m road with a large curvature radius. The disturbance during driving was applied to a situation where a mass load of 500 kg was applied to the vehicle at 10 s, and the delay of the input signal was applied by applying a time delay constant of 0.5 s to the input signal error in order to calculate the control input. As shown in Figure 19, the proposed control algorithm can guarantee a certain level of reasonable control performance even when system disturbances or measurement signal delays occur.
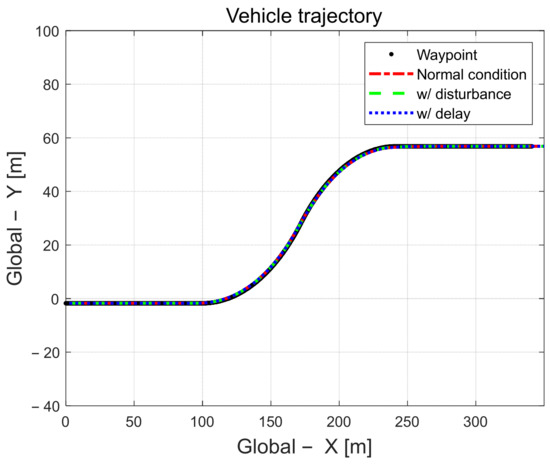
Figure 19.
Driving trajectory.
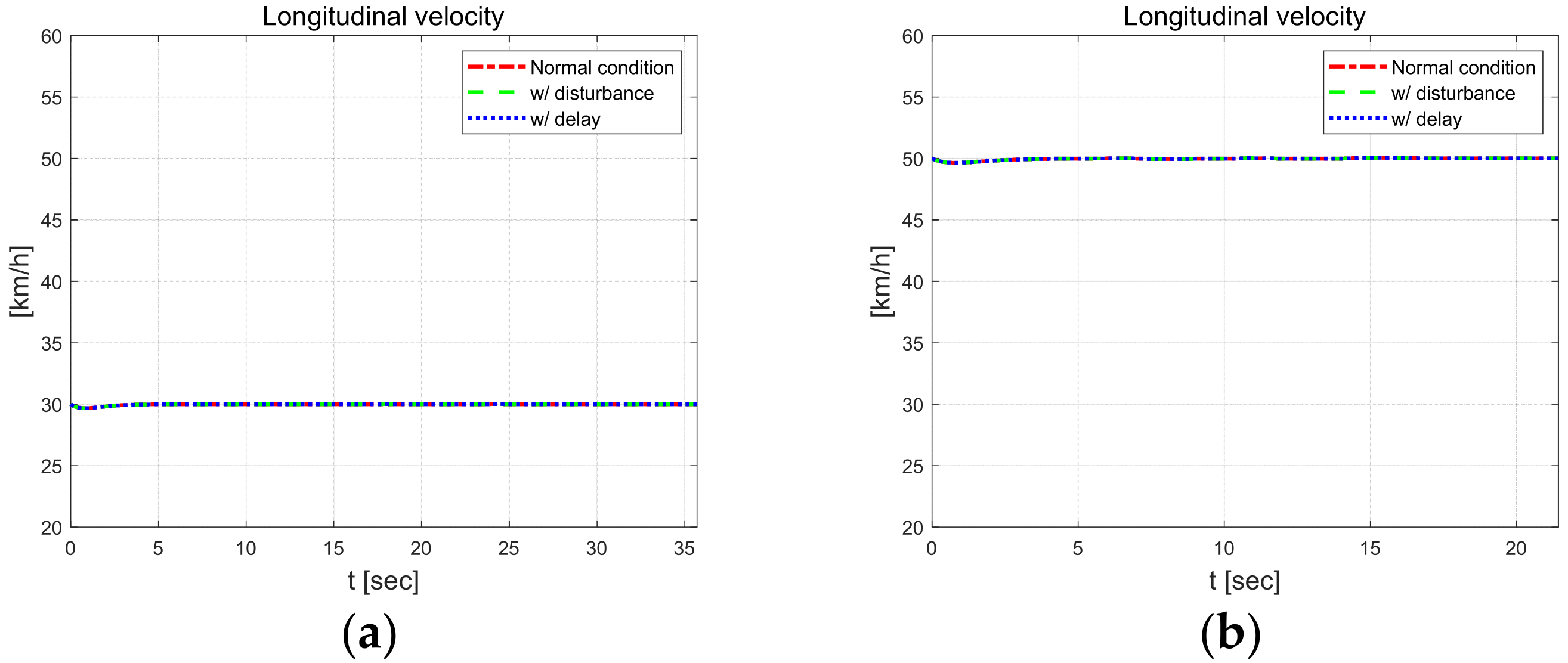
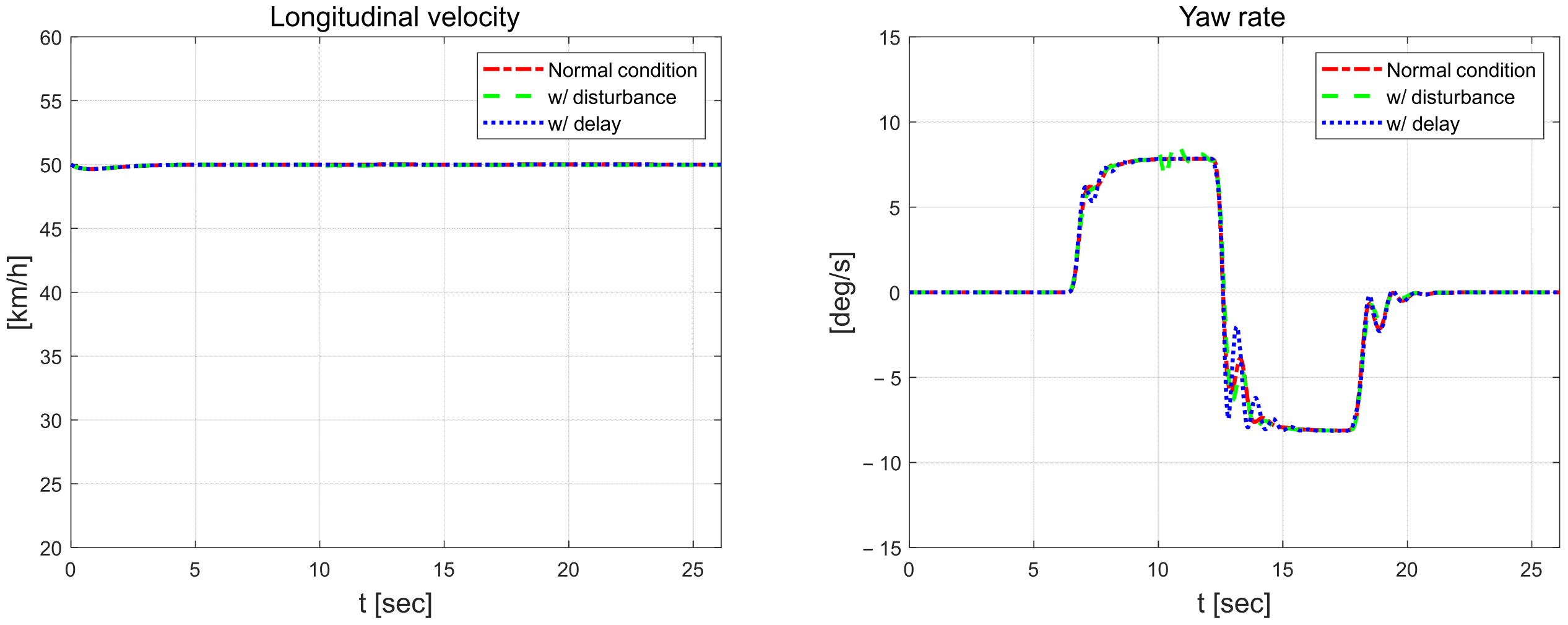
Figure 20 shows the longitudinal velocity and yaw rate. At 10 s, the mass load is applied and the yaw rate oscillates, and the results for all scenarios oscillate at the inflection point of the curve.
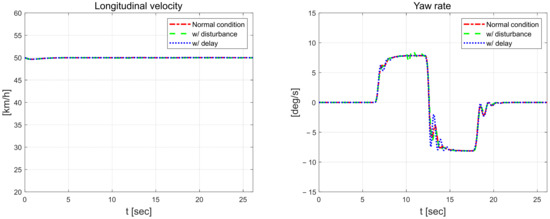
Figure 20.
Longitudinal velocity (left) and yaw rate (right).
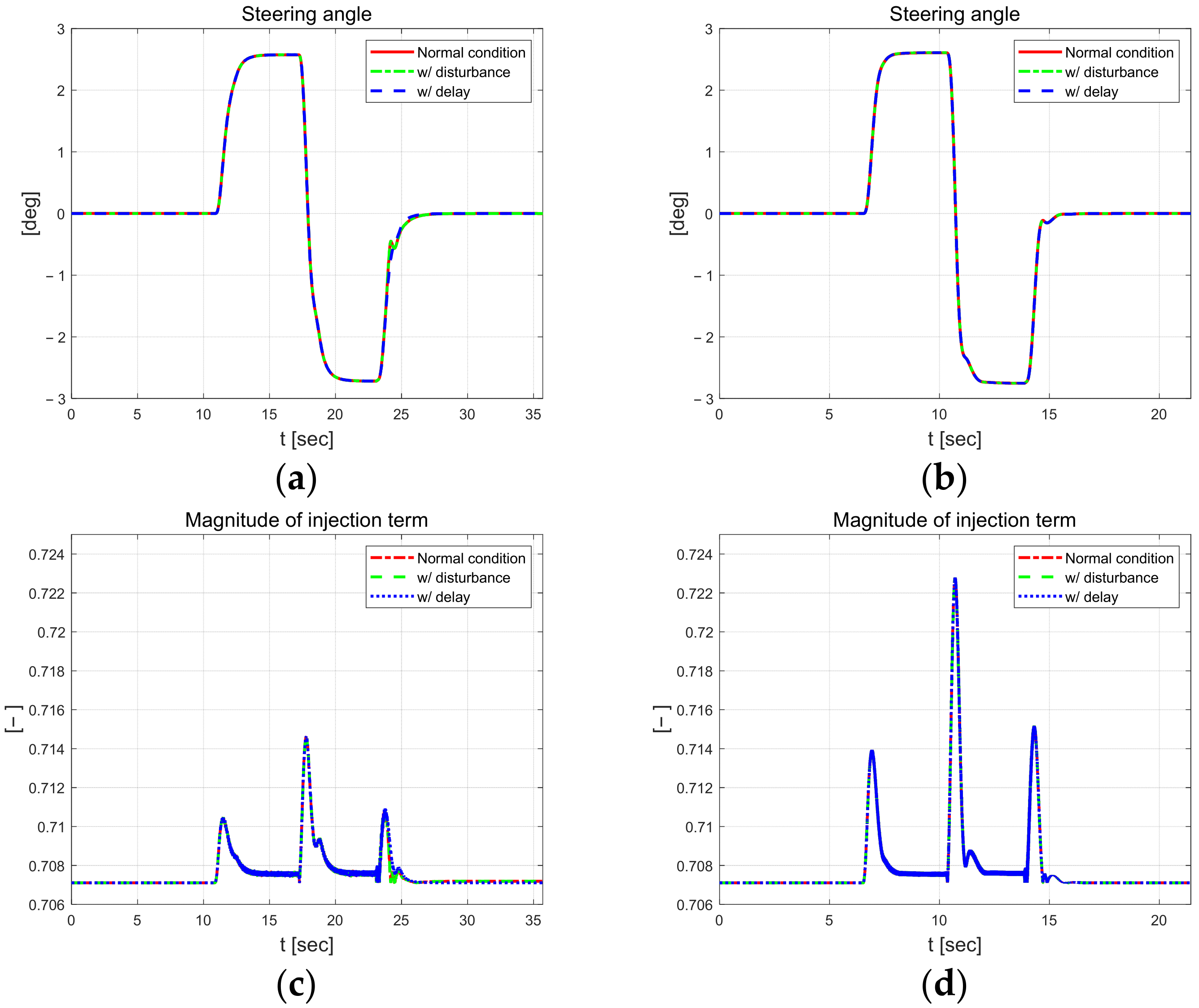
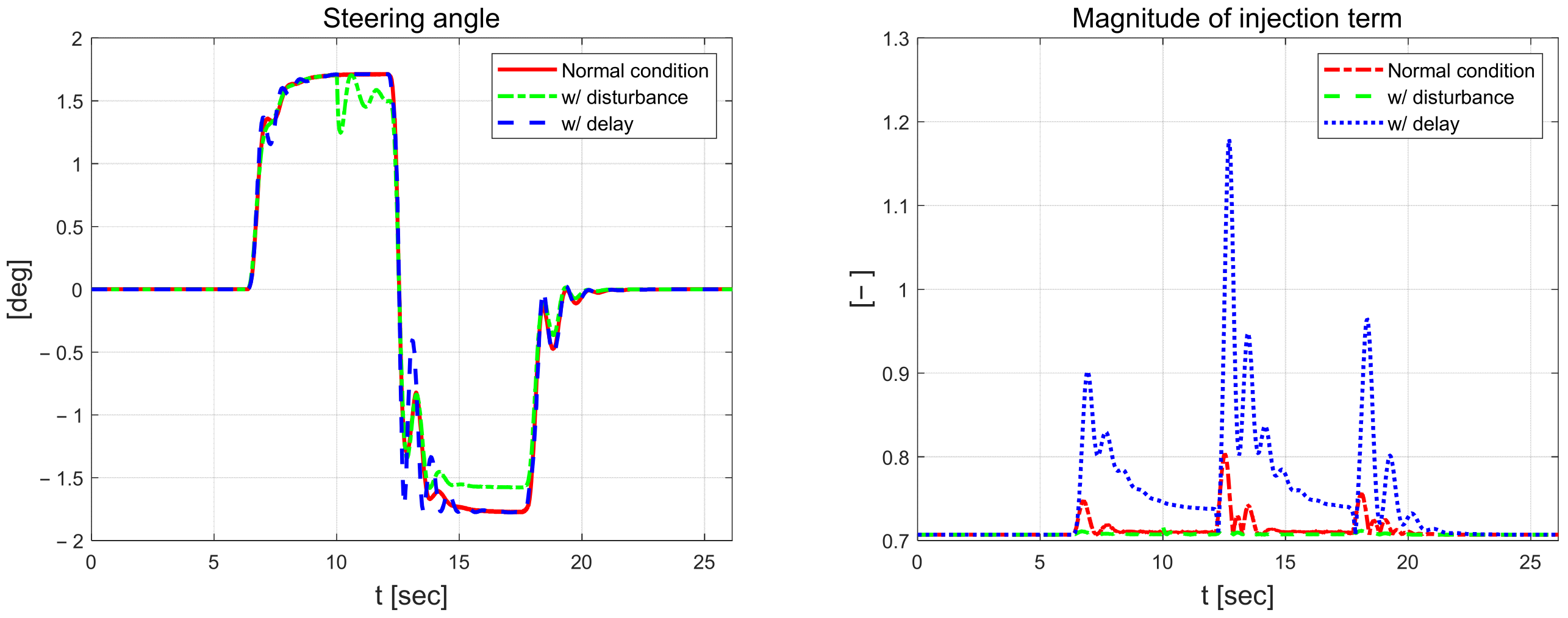
Figure 21 shows the steering angle and the magnitude of the injection term. The steering angle exhibits the most vibration when a mass load disturbance is applied compared to the normal driving results. It is a control input for driving a vehicle that shakes when a large mass load of 500 kg is applied in stages. The magnitude of the injection term is the largest at approximately 1.2 when the input signal is delayed.
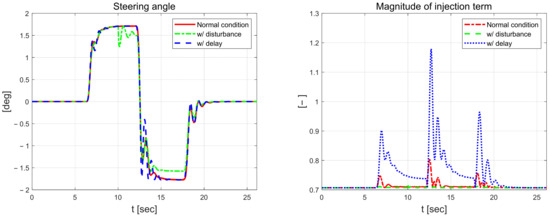
Figure 21.
Front-wheel angle (left) and magnitude of injection term (right).
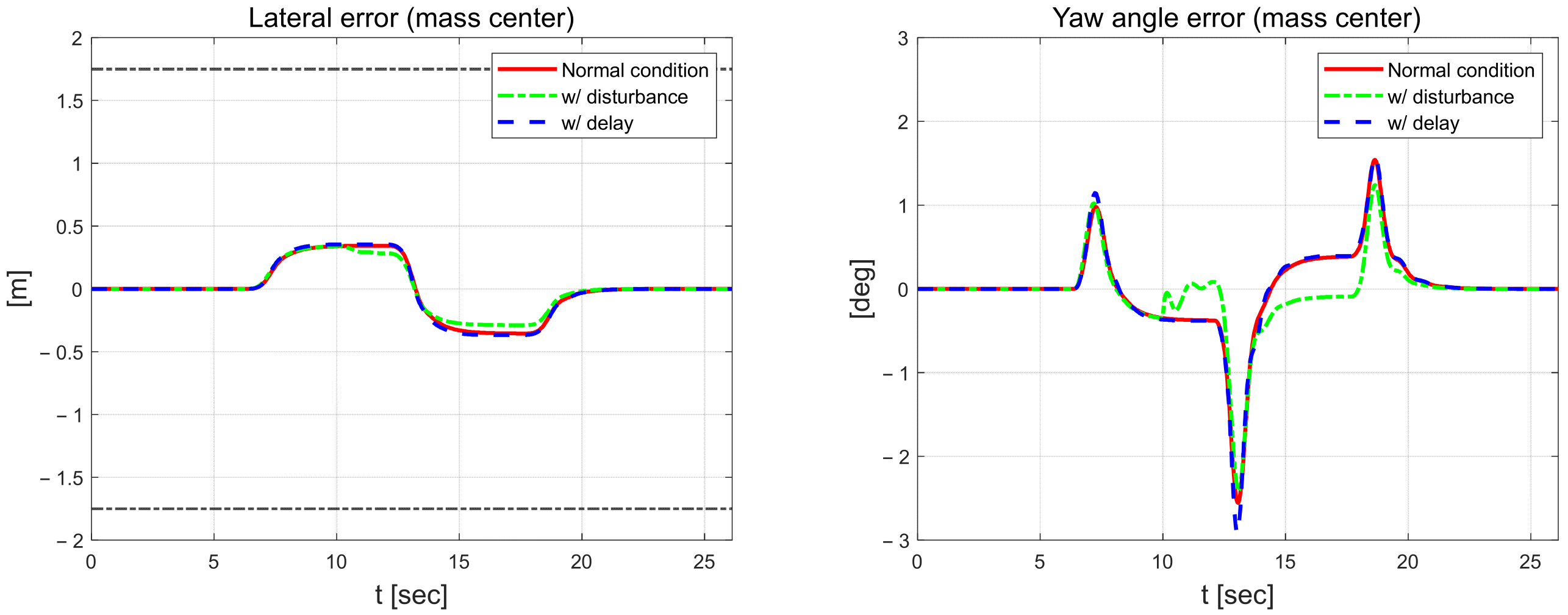
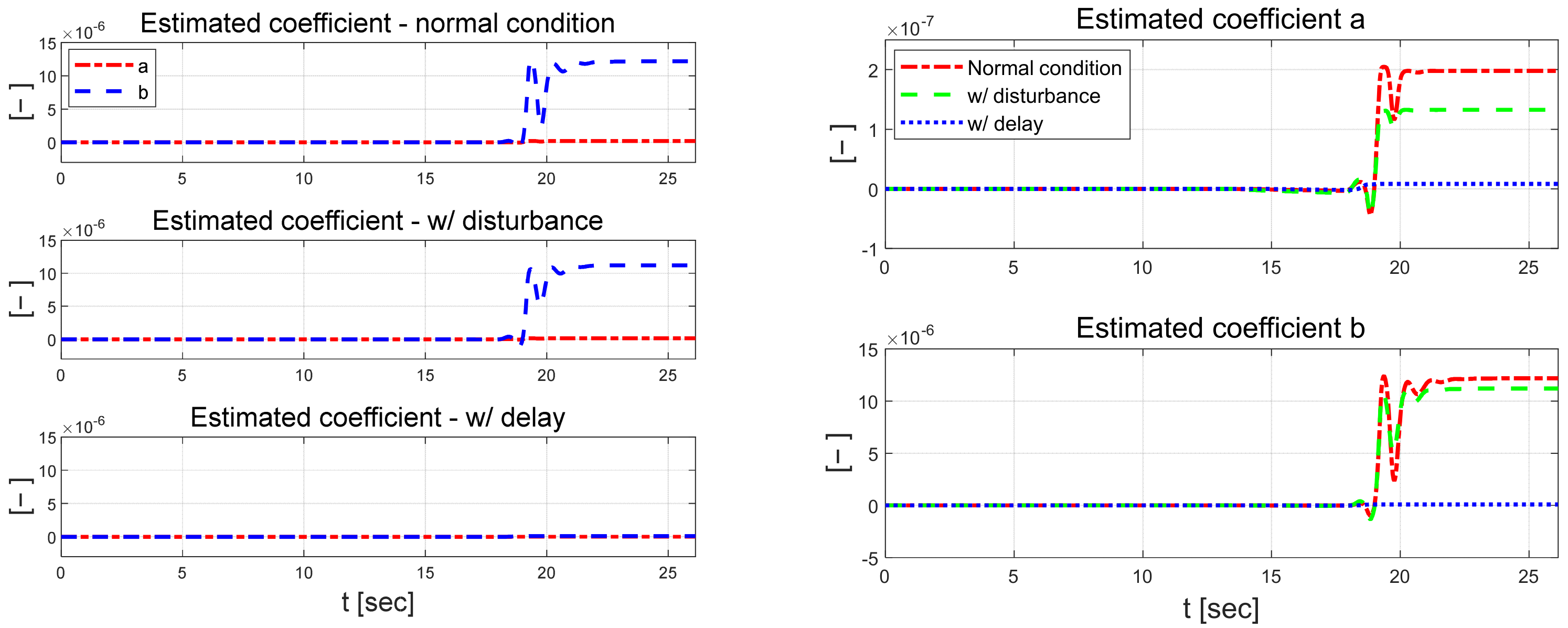
Figure 22 shows the control error. The control error is about 0.01 m larger in the lateral direction and about 0.2° larger for the yaw angle when there is a delay in the measurement signal compared to the normal state. When the disturbance is applied, the result is the smallest in terms of error, although there is some fluctuation. However, the disturbance case has the largest error among all the scenarios performed, and the proposed algorithm does not achieve a reasonable performance when disturbance and delay are applied. Figure 23 shows the estimated coefficients of each scenario from RLS. The estimated coefficients and are largest in the normal state and smallest in the scenario in which a delay is applied to the measurement signal.
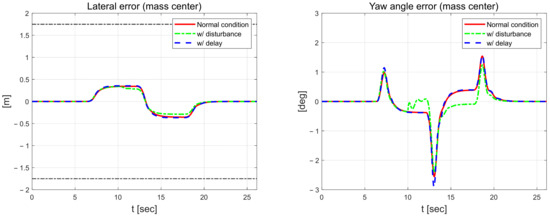
Figure 22.
Lateral error (left) and yaw angle error (right).
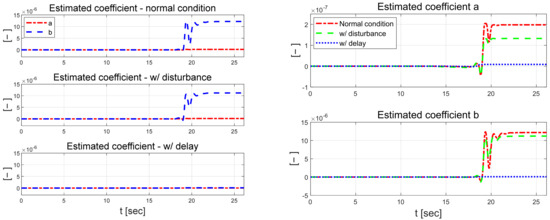
Figure 23.
Estimated coefficients for each scenario (left) and comparison (right).
Table 3 lists the RMSE of APTA- and LQR-based derived integrated error in Equation (1). In driving scenarios with the same curvature radius and driving speed, the RMSE value of APTA is similar even when external constraints are applied. However, there is an exception; when driving at 30 km/h with a curvature radius of 65 m, the results of applying external constraints to parameter are approximately 0.33 smaller than those achieved by applying or not applying said constraints to parameter a. As shown in the tables, when calculating the RMSE value, it was confirmed that the integrated error of LQR compared to APTA was approximately 24% larger for the same scenario. The error did not increase even when disturbance and delays were applied. In the scenario with high speed and a small curvature radius, the error increased. In the scenario with a small curvature radius and high speed, the error is the largest among the cases where the proposed methodology is applied. However, it is smaller than the error in the scenario with model-based LQR control.

Table 3.
RMSE error for each scenario.
When applying disturbance and delay at a curvature radius 100 m and a longitudinal velocity 50 km/h, it was observed that the RMSE value is decreased. The RMSE value is influenced by the initial RLS values, covariance, and estimates in the control input derivation process using the RLS. The control input can have an impact on the path tracking performance. Therefore, analysis of relationship between RLS values and control input is considered as a future work to improve the proposed control algorithm.
4. Discussion with Future Work
The performance of the adaptive path-tracking control algorithm for RLS-based autonomous driving under external conditions and covariance self-tuning was evaluated using MATLAB®/Simulink® and CarMaker. The evaluations performed for the four scenarios based on the curvature radius and driving speed simulated a universally applicable environment for user convenience. Target-value tracking does not require system information. Only a few control parameters, such as initial values and forgetting factors, are required for the RLS-based coefficient estimation and control input derivation. The injection terms were self-tuned in the control input using RLS estimation residuals. The evaluation results confirmed that the adaptive control input using the RLS-based real-time estimated coefficients could reasonably track the target path. The RLS-based coefficient estimation is sensitive to the initial parameter setting.
In this study, the same parameters were applied to all scenarios. Therefore, it can be concluded that the estimation performance did not react sensitively to the initial values. However, unreasonable control parameters or an unstable estimation performance can have a negative impact on coefficient estimation performance, and the control performance may deteriorate. This can be addressed by applying external constraints to each estimated coefficient, and in our study, the control input for tracking the target path was reasonably derived by compensating and adapting other parameters, even when constraints were applied to each parameter. However, vibrations were confirmed in the control input, and the oscillation in the road section was aggravated when driving at high speeds. The vibration that appears as a vehicle state quantity has a relatively small value; however, it can affect the target value tracking when driving at higher speeds. In the future, an enhancement of the proposed control and estimation algorithms using a stabilization approach with the improved external constraint method will be considered to address the aforementioned issue.
5. Conclusions
In this study, we estimated the coefficients of a first-order differential error equation using RLS with multiple forgetting factors for path tracking. The error is designed as an integrated error using the lateral error and yaw angle error of the target path and current vehicle. The control input was derived by applying the Lyapunov direct method with injection terms and finite-time convergence conditions. The sizes of the injection terms were self-tuned using the residual of the RLS. Therefore, the proposed adaptive control algorithm only needs to know constants, such as forgetting factors, initial conditions, and external and finite convergence conditions. Because it does not require information about the system parameters, it can be applied as a general-purpose control algorithm. The control input was calculated using the coefficients of the error dynamics estimated from the RLS. In the case of the RLS, if the control parameters are unreasonable, they can affect the estimated coefficients. Therefore, when the control parameters are assumed to be set incorrectly, and external constraints are applied to each estimated coefficient, we evaluate whether the other parameters compensate and adapt reasonably. A scaling factor is applied to the RLS covariance update process to adjust the adaptability of the coefficient estimation according to the amount of error change. In the MATLAB®/Simulink® and CarMaker environments, the performance was evaluated in four scenarios according to the curvature radius of the S-curved road and driving speed. The performance evaluation results showed a reasonable path-tracking performance for the autonomous vehicle. Even when external constraints were applied, the proposed algorithm drove the target path without lane departure in all situations. The current control algorithm has limitations in single-input and single-output systems, and the results indicate small vibrations under high-speed conditions. In future studies, we plan to investigate the application methodology in an extended system considering a multi-input/output system. We plan to improve the algorithm by developing the self-tuning of the initial value of covariance based on rules through sensitivity analysis of control parameters. In this study, the proposed algorithm achieved path-tracking control without requiring system parameters, relying only on a few control parameters. However, initial control parameter settings were determined through a trial-and-error approach. In future work, we plan to develop a learning-based controller that automatically determines initial control values, allowing these control parameters to operate freely. In addition, along with performance evaluations in various driving scenarios, improving the control algorithm to generate the desired yaw rate stably even under high-speed conditions is being considered as a future research subject.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, K.O.; methodology, H.L. and K.O.; software, H.L.; validation, H.L.; formal analysis, H.L. and K.O.; investigation, H.L.; resources, H.L.; data curation, H.L.; writing—original draft preparation, H.L.; writing—review and editing, H.L. and K.O.; visualization, H.L.; supervision, K.O.; project administration, K.O.; funding acquisition, K.O. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF-2022R1F1A1075167) and the government (Ministry of Science and ICT) in 2022.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Wang, F.; Peng, Q.; Zang, X.; Xue, Q. Adaptive Cruise Control for Intelligent City Bus Based on Vehicle Mass and Road Slope Estimation. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 12137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bersani, M.; Vignati, M.; Mentasti, S.; Arrigoni, S.; Cheli, F. Vehicle State Estimation Based on Kalman Filters. In Proceedings of the 2019 AEIT International Conference of Electrical and Electronic Technologies for Automotive (AEIT AUTOMOTIVE), Turin, Italy, 2–4 July 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, X.; Xiong, L.; Liu, W.; Yu, Z. Automated Vehicle Attitude and Lateral Velocity Estimation Using a 6-D IMU Aided by Vehicle Dynamics. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium (IV), Changshu, China, 26–30 June 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, X.; Cai, Y.; Wang, S.; Xu, X.; Chen, L. Piecewise Affine Identification of Tire Longitudinal Properties for Autonomous Driving Control Based on Data-Driven. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 47424–47432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, B.H.G.; Xu, N.; Askari, H.; Khajepour, A. Lateral Force Prediction Using Gaussian Process Regression for Intelligent Tire Systems. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. 2022, 52, 5332–5343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Škugor, B.; Deur, J. City Bus Mass Estimation Based on GPS and CAN-Collected Tracking Data. In Proceedings of the 2020 International Conference on Smart Systems and Technologies (SST), Osijek, Croatia, 14–16 October 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, M.; Gao, W.; Zeng, Y.; Li, H.; Yu, Z. Vehicle Mass and Road Grade Estimation Based on Adaptive Forgetting Factor RLS and EKF Algorithm. In Proceedings of the 2020 5th International Conference on Power and Renewable Energy (ICPRE), Shanghai, China, 12–14 September 2020; pp. 342–346. [Google Scholar]
- Park, G.; Choi, S. An Integrated Observer for Real-Time Estimation of Vehicle Center of Gravity Height. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2021, 22, 5660–5671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Yao, Q. Adaptive Coordinated Path Tracking Control Strategy for Autonomous Vehicles with Direct Yaw Moment Control. Chin. J. Mech. Eng. 2022, 35, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.; Li, L.; Yan, B.; Liu, C.; Wang, X.; Fang, J. Simultaneous Estimation of Tire Side-Slip Angle and Lateral Tire Force for Vehicle Lateral Stability Control. Mech. Syst. Signal Process 2019, 132, 168–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van, M.; Do, X.P.; Mavrovouniotis, M. Self-Tuning Fuzzy PID-Nonsingular Fast Terminal Sliding Mode Control for Robust Fault Tolerant Control of Robot Manipulator. ISA Trans. 2020, 96, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baz, R.; Majdoub, K.; Giri, F.; Taouni, A. Self-Tuning Fuzzy PID Speed Controller for Quarter Electric Vehicle Driven by In-Wheel BLDC Motor and Pacejka’s Tire Model. IFAC-PapersOnLine 2022, 55, 598–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Abreo, O.; Rodríguez-Reséndiz, J.; Fuentes-Silva, C.; Hernández-Alvarado, R.; Falcón, M.D.C.P.T.; Silva, C. Self-Tuning Neural Network PID with Dynamic Response Control. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 65206–65215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Jiang, D.; Yun, J.; Sun, Y.; Li, C.; Jiang, G.; Fang, Z. Self-Tuning Control of Manipulator Positioning Based on Fuzzy PID and PSO Algorithm. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 9, 817723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Shi, Y.; Ji, Z. Model-Free Adaptive Discrete-Time Integral Sliding-Mode-Constrained-Control for Autonomous 4WMV Parking Systems. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2017, 65, 834–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radac, M.B.; Precup, R.E. Data-Driven Model-Free Tracking Reinforcement Learning Control with VRFT-Based Adaptive Actor-Critic. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Tan, G.; Sun, C. Research on Vehicle Four-Wheel Steering Based on Model-Free Adaptive Control. In Proceedings of the 2020 5th International Conference on Electromechanical Control Technology and Transportation (ICECTT), Nanchang, China, 15–17 May 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Y.; Xu, X.; Zhang, L. Heading Tracking of 6WID/4WIS Unmanned Ground Vehicles with Variable Wheelbase Based on Model-Free Adaptive Control. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2021, 159, 107715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laid, S.; Boubekeur, B. Model-Free and Adaptive Control of a DC Motor: A Comparative Study. In Proceedings of the 2020 International Conference on Electrical Engineering (ICEE), Istanbul, Turkey, 25–27 September 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Fnadi, M.; Plumet, F.; Benamar, F. Model Predictive Control Based Dynamic Path Tracking of a Four-Wheel Steering Mobile Robot. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, Macau, China, 3–8 November 2019; pp. 4518–4523. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, G.; Liu, L.; Meng, Y.; Luo, W.; Gu, Q.; Wang, J. Path Tracking of Wheeled Mobile Robots Based on Dynamic Prediction Model. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 39690–39701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hang, P.; Xia, X.; Chen, G.; Chen, X. Active Safety Control of Automated Electric Vehicles at Driving Limits: A Tube-Based MPC Approach. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrific. 2021, 8, 1338–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Liu, B.; Ping, X.; An, Q. Path Tracking Control for Autonomous Vehicles Based on an Improved MPC. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 161064–161073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, G.C.; Lima, P.F.; Wahlberg, B.; Pettersson, H.; Mårtensson, J. Nonlinear Curvature Modeling for MPC of Autonomous Vehicles. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE 23rd International Conference on Intelligent Transportation Systems, Rhodes, Greece, 20–23 September 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Wang, W.; Li, X.; Liu, F.; He, Z.; Yao, Y.; Zhang, T. MPC-Based High-Speed Trajectory Tracking for 4WIS Robot. ISA Trans. 2022, 123, 413–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xizheng, Z.; Xiaolin, Z. Autonomous Path Tracking Control of Intelligent Electric Vehicles Based on Lane Detection and Optimal Preview Method. Expert Syst. Appl. 2019, 121, 38–48. [Google Scholar]
- Matraji, I.; Al-Wahedi, K.; Al-Durra, A. Higher-Order Super-Twisting Control for Trajectory Tracking Control of Skid-Steered Mobile Robot. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 124712–124721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moudoud, B.; Aissaoui, H.; Diany, M. Robust Trajectory Tracking Control Based on Sliding Mode of Differential Driving Four Wheeled Mobile Robot. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE 6th International Conference on Optimization and Applications, Beni Mellal, Morocco, 20–21 April 2020; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, F.; Xiao, H.; Zhang, Y.; Gong, G. Distributed Drive Electric Bus Handling Stability Control Based on Lyapunov Theory and Sliding Mode Control. Actuators 2022, 11, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vahidi, A.; Stefanopoulou, A.; Peng, H. Recursive Least Squares with Forgetting for Online Estimation of Vehicle Mass and Road Grade: Theory and Experiments. Veh. Syst. Dyn. 2011, 43, 31–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanbyeol, L.; Kwangseok, O. Development of a RLS-based Path Tracking Control Algorithm for Autonomous Mobility with External Condition and Covariance Self-Tuning. In Proceedings of the EVS37 International Electric Vehicle Symposium and Exhibition, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 23–26 April 2024. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Published by MDPI on behalf of the World Electric Vehicle Association. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).