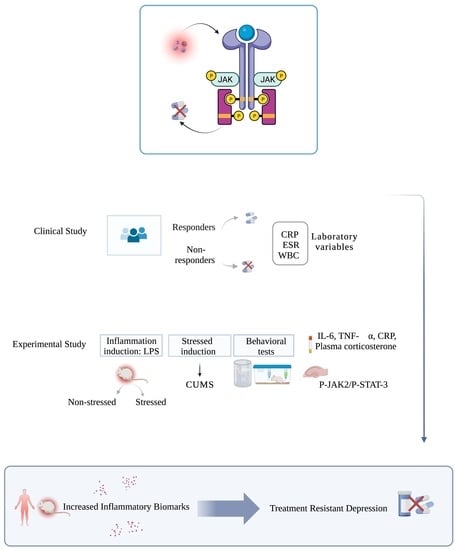
Inflammation and Treatment-Resistant Depression from Clinical to Animal Study: A Possible Link?
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Clinical Study
2.1.1. Study Design and Setting
2.1.2. Participants and Psychiatric Assessment
2.1.3. Data Sources
2.1.4. Measures of Antidepressant Resistance
2.1.5. Inflammatory Biomarkers
2.1.6. Sample Size Calculation
2.1.7. Statistical Analyses
2.2. Experimental Study
2.2.1. Animals
2.2.2. Drugs and Chemicals
2.2.3. Experimental Design
2.2.4. Experimental Procedures
Induction of Inflammation by LPS
Induction of Depression by CUMS
Behavioral Tests
Forced Swimming Test
Sucrose Preference Test
2.2.5. Preparation of the Blood and Brain Samples
2.2.6. Assessment of Inflammatory Biomarkers
2.2.7. Measurement of Plasma Corticosterone
2.2.8. Histological Examination
2.2.9. Immunohistochemistry for Assessment of Expression of JAK2/STAT3
2.2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Clinical Results
3.1.1. Study Population, Demographic Characteristics and Clinical Data
3.1.2. Evaluation of Inflammatory Biomarkers (CRP, ESR, WBC)
Analysis 1: Healthy Group vs. Depressed Group
Analysis 2: Treatment Responders Group vs. Treatment Resistant Group
3.2. Experimental Results
3.2.1. Fluoxetine-resistant Depression Model and Behavior Evaluation
The Sucrose Preference Test (SPT)
The Forced Swimming Test
3.2.2. Fluoxetine-resistant Depression Model and Evaluation of Stress Markers
Corticosterone
3.2.3. Fluoxetine-resistant Depression Model and Evaluation of Inflammatory Markers
C-Reactive Protein Plasma Levels
Inflammatory Cytokines (IL-6, TNF-α)
3.2.4. Fluoxetine-resistant Depression Model and Histological Examination
3.2.5. Immunohistochemical Study of the Role of Phosphorylated Janus Kinase 2 (P-JAK2) and Phosphorylated Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 3 (P-STAT3) Pathway in FLX-resistant Depression Rats
4. Discussion
Study Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schroder, H.S.; Patterson, E.H.; Hirshbein, L. Treatment-Resistant Depression Reconsidered. SSM Ment. Health 2022, 2, 100081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gkesoglou, T.; Bargiota, S.I.; Iordanidou, E.; Vasiliadis, M.; Bozikas, V.P.; Agorastos, A. Prognostic Significance of Blood-Based Baseline Biomarkers in Treatment-Resistant Depression: A Literature Review of Available Studies on Treatment Response. Brain Sci. 2022, 12, 940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alzahrani, A.; Alghamdi, A.; Alqarni, T.; Alshareef, R.; Alzahrani, A. Prevalence and Predictors of Depression, Anxiety, and Stress Symptoms among Patients with Type II Diabetes Attending Primary Healthcare Centers in the Western Region of Saudi Arabia: A Cross-Sectional Study. Int. J. Ment. Health Syst. 2019, 13, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Depression and Other Common Mental Disorders: Global Health Estimates; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 1–24. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, W.; Ning, Y.; Hong, W.; Wang, J.; Liu, Z.; Li, M.D. Crosstalk between Inflammation and Glutamate System in Depression: Signaling Pathway and Molecular Biomarkers for Ketamine’s Antidepressant Effect. Mol. Neurobiol. 2019, 56, 3484–3500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Deng, H.; Cui, H.; Fang, J.; Zuo, Z.; Deng, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhao, L. Inflammatory Responses and Inflammation-Associated Diseases in Organs. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 7204–7218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Haroon, E.; Raison, C.L.; Miller, A.H. Psychoneuroimmunology Meets Neuropsychopharmacology: Translational Implications of the Impact of Inflammation on Behavior. Neuropsychopharmacology 2012, 37, 137–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amodeo, G.; Allegra Trusso, M.; Fagiolini, A. Depression and Inflammation: Disentangling a Clear Yet Complex and Multifaceted Link. Neuropsychiatry 2018, 7, 448–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muscat, S.-A.; Hartelius, G.; Crouch, C.R.; Morin, K.W. Optimized Clinical Strategies for Treatment-Resistant Depression: Integrating Ketamine Protocols with Trauma- and Attachment-Informed Psychotherapy. Psych 2022, 4, 119–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, S.; Rittenbach, K.; Cheung, S.; McKean, G.; MacMaster, F.P.; Clement, F. Current and Common Definitions of Treatment-Resistant Depression: Findings from a Systematic Review and Qualitative Interviews. Can. J. Psychiatry 2019, 64, 380–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ionescu, D.F.; Rosenbaum, J.F.; Alpert, J.E. Pharmacological Approaches to the Challenge of Treatment-Resistant Depression. Dialogues Clin. Neurosci. 2015, 17, 111–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, A.H. Inflammation and Treatment Resistance in Major Depression: The Perfect Storm. Psychiatr. Times 2013, 30, S239–S240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.H.; Chen, M.H.; Tu, P.C.; Bai, Y.M.; Su, T.P.; Yang, B.H.; Liu, R.S.; Li, C.T. Elevated Tumor Necrosis Factor-Alpha Receptor Subtype 1 and the Association with Abnormal Brain Function in Treatment-Resistant Depression. J. Affect. Disord. 2018, 235, 250–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, A.H.; Raison, C.L. Role of Inflammation in Depression. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2017, 16, 22–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Haroon, E.; Daguanno, A.W.; Woolwine, B.J.; Goldsmith, D.R.; Baer, M.; Wommack, E.C.; Felger, J.C.; Miller, A.H. Antidepressant treatment resistance is associated with increased inflammatory markers in patients with major depressive disorder. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2018, 95, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Samhari, M.M.; Al-Rasheed, N.M.; Al-Rejaie, S.; Al-Rasheed, N.M.; Hasan, I.H.; Mahmoud, A.M.; Dzimiri, N. Possible Involvement of the JAK/STAT Signaling Pathway in N-Acetylcysteine-Mediated Antidepressant-like Effects. Exp. Biol. Med. 2016, 241, 509–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shariq, A.S.; Brietzke, E.; Rosenblat, J.D.; Pan, Z.; Rong, C.; Ragguett, R.M.; Park, C.; McIntyre, R.S. Therapeutic Potential of JAK/STAT Pathway Modulation in Mood Disorders. Rev. Neurosci. 2019, 30, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osimo, E.F.; Baxter, L.J.; Lewis, G.; Jones, P.B.; Khandaker, G.M. Prevalence of Low-Grade Inflammation in Depression: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of CRP Levels. Psychol. Med. 2019, 49, 1958–1970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sample Size Calculator—Confidence Level, Confidence Interval, Sample Size, Population Size, Relevant Population—Creative Research Systems. Available online: https://www.surveysystem.com/sscalc.htm (accessed on 11 October 2021).
- Caldarone, B.J.; Zachariou, V.; King, S.L. Rodent Models of Treatment-Resistant Depression. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2016, 753, 51–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Cui, X.L.; Liu, Y.F.; Gao, F.; Wei, D.; Li, X.W.; Wang, H.N.; Tan, Q.R.; Jiang, W. LPS Inhibits the Effects of Fluoxetine on Depression-like Behavior and Hippocampal Neurogenesis in Rats. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2011, 35, 1831–1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardo, J.V.; Sheikh, S.A.; Schwindt, G.; Lee, J.T.; Adson, D.E.; Rittberg, B.; Abuzzahab, F.S. A Preliminary Study of Resting Brain Metabolism in Treatment-Resistant Depression before and after Treatment with Olanzapine-Fluoxetine Combination. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0226486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willner, P.; Towell, A.; Sampson, D.; Sophokleous, S.; Muscat, R. Reduction of Sucrose Preference by Chronic Unpredictable Mild Stress, and Its Restoration by a Tricyclic Antidepressant. Psychopharmacology 1987, 93, 358–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Yang, F.; Liu, Y.F.; Gao, F.; Jiang, W. Acetylsalicylic Acid as an Augmentation Agent in Fluoxetine Treatment Resistant Depressive Rats. Neurosci. Lett. 2011, 499, 74–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yankelevitch-Yahav, R.; Franko, M.; Huly, A.; Doron, R. The Forced Swim Test as a Model of Depressive-like Behavior. J. Vis. Exp. 2015, e52587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Porsolt, R.D.; Anton, G.; Blavet, N.; Jalfre, M. Behavioural Despair in Rats: A New Model Sensitive to Antidepressant Treatments. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1978, 47, 379–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilkowska, A.; Cubała, W.J. The Downstaging Concept in Treatment-Resistant Depression: Spotlight on Ketamine. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 4605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergström, A.; Jayatissa, M.N.; Thykjær, T.; Wiborg, O. Molecular Pathways Associated with Stress Resilience and Drug Resistance in the Chronic Mild Stress Rat Model of Depression—A Gene Expression Study. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2007, 33, 201–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, A.J.; Foley, B.M.; Sutor, S.L.; McGillivray, J.A.; Frye, M.A.; Tye, S.J. Peripheral Proinflammatory Markers Associated with Ketamine Response in a Preclinical Model of Antidepressant-Resistance. Behav. Brain Res. 2015, 293, 198–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekhbat, M.; Glasper, E.R.; Rowson, S.A.; Kelly, S.D.; Neigh, G.N. Measuring Corticosterone Concentrations over a Physiological Dynamic Range in Female Rats. Physiol. Behav. 2018, 194, 73–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buoli, M.; Capuzzi, E.; Caldiroli, A.; Ceresa, A.; Esposito, C.M.; Posio, C.; Auxilia, A.M.; Capellazzi, M.; Tagliabue, I.; Surace, T.; et al. Clinical and Biological Factors Are Associated with Treatment-Resistant Depression. Behav. Sci. 2022, 12, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carney, R.M.; Freedland, K.E. Treatment-Resistant Depression and Mortality after Acute Coronary Syndrome. Am. J. Psychiatry 2009, 166, 410–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.H.; Giuliani, F. The Role of Inflammation in Depression and Fatigue. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, J.; Luo, Y.; Ma, Y.; Guo, C.; Du, Z.; Gao, S.; Chen, L.; Wang, Z.; Li, X.; Xu, K. Brain Sciences Sex Differences of the Functional Brain Activity in Magnetic Resonance Study. Brain Sci. 2022, 12, 1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sluzewska, A.; Sobieska, M.; Rybakowski, A.K. Changes in Acute-Phase Proteins during Lithium Potentiation of Antidepressants in Refractory Depression. Neuropsychobiology 1997, 35, 123–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nothdurfter, C.; Milenkovic, V.M.; Sarubin, N.; Hilbert, S.; Manook, A.; Weigl, J.; Almeqbaali, K.; Wetzel, C.H.; Rupprecht, R.; Baghai, T.C. The Cytokine IL-17A as a Marker of Treatment Resistance in Major Depressive Disorder? Eur. J. Neurosci. 2021, 53, 172–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keers, R.; Aitchison, K.J. Gender Differences in Antidepressant Drug Response. Int. Rev. Psychiatry 2010, 22, 485–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moderie, C.; Nuñez, N.; Fielding, A.; Comai, S.; Gobbi, G. Sex Differences in Responses to Antidepressant Augmentations in Treatment-Resistant Depression. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2022, 25, 479–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenblat, J.D.; McIntyre, R.S.; Alves, G.S.; Fountoulakis, K.N.; Carvalho, A.F. Beyond Monoamines-Novel Targets for Treatment-Resistant Depression: A Comprehensive Review. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2015, 13, 636–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Janssen, D.G.A.; Caniato, R.N.; Verster, J.C.; Baune, B.T. A Psychoneuroimmunological Review on Cytokines Involved in Antidepressant Treatment Response. Hum. Psychopharmacol. Clin. Exp. 2010, 25, 201–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, M.K.; Minhajuddin, A.; Gadad, B.S.; Greer, T.; Grannemann, B.; Soyombo, A.; Mayes, T.L.; Rush, A.J.; Trivedi, M.H. Can C-Reactive Protein Inform Antidepressant Medication Selection in Depressed Outpatients? Findings from the CO-MED Trial. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2017, 78, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caldiroli, A.; Capuzzi, E.; Tagliabue, I.; Capellazzi, M.; Marcatili, M.; Mucci, F.; Colmegna, F.; Clerici, M.; Buoli, M.; Dakanalis, A. Augmentative Pharmacological Strategies in Treatment-resistant Major Depression: A Comprehensive Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 3070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galvão, A.C.d.M.; de Almeida, R.N.; Silva, E.A.d.S.; Freire, F.A.M.; Palhano-Fontes, F.; Onias, H.; Arcoverde, E.; Maia-de-Oliveira, J.P.; de Araújo, D.B.; Lobão-Soares, B.; et al. Cortisol Modulation by Ayahuasca in Patients with Treatment Resistant Depression and Healthy Controls. Front. Psychiatry 2018, 9, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kubera, M.; Curzytek, K.; Duda, W.; Leskiewicz, M.; Basta-Kaim, A.; Budziszewska, B.; Roman, A.; Zajicova, A.; Holan, V.; Szczesny, E.; et al. A New Animal Model of (Chronic) Depression Induced by Repeated and Intermittent Lipopolysaccharide Administration for 4 months. Brain. Behav. Immun. 2013, 31, 96–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, D.J.; Samuels, B.A.; Rainer, Q.; Wang, J.W.; Marsteller, D.; Mendez, I.; Drew, M.; Craig, D.A.; Guiard, B.P.; Guilloux, J.P.; et al. Neurogenesis-Dependent and -Independent Effects of Fluoxetine in an Animal Model of Anxiety/Depression. Neuron 2009, 62, 479–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Farhan, M.; Haleem, D.J. Anxiolytic Profile of Fluoxetine as Monitored Following Repeated Administration in Animal Rat Model of Chronic Mild Stress. Saudi Pharm. J. 2016, 24, 571–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Peselow, E.D.; Tobia, G.; Karamians, R.; Pizano, D.; IsHak, W.W. Prophylactic Efficacy of Fluoxetine, Escitalopram, Sertraline, Paroxetine, and Concomitant Psychotherapy in Major Depressive Disorder: Outcome after Long-Term Follow-Up. Psychiatry Res. 2015, 225, 680–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nava Catorce, M.; Gevorkian, G. LPS-Induced Murine Neuroinflammation Model: Main Features and Suitability for Pre-Clinical Assessment of Nutraceuticals. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2016, 14, 155–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yücel, G.; Zhao, Z.; El-Battrawy, I.; Lan, H.; Lang, S.; Li, X.; Buljubasic, F.; Zimmermann, W.H.; Cyganek, L.; Utikal, J.; et al. Lipopolysaccharides Induced Inflammatory Responses and Electrophysiological Dysfunctions in Human-Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell Derived Cardiomyocytes. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 2935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bras, J.P.; Pinto, S.; Almeida, M.I.; Prata, J.; von Doellinger, O.; Coelho, R.; Barbosa, M.A.; Santos, S.G. Peripheral Biomarkers of Inflammation in Depression: Evidence from Animal Models and Clinical Studies. In Psychiatric Disorders; Humana Press: New York, NY, USA, 2019; pp. 467–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frisbee, J.C.; Brooks, S.D.; Stanley, S.C.; D’Audiffret, A.C. An Unpredictable Chronic Mild Stress Protocol for Instigating Depressive Symptoms, Behavioral Changes and Negative Health Outcomes in Rodents. J. Vis. Exp. 2015, e53109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Willner, P. Validity, Reliability and Utility of the Chronic Mild Stress Model of Depression: A 10-Year Review and Evaluation. Psychopharmacology 1997, 134, 319–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdul Shukkoor, M.S.; Baharuldin, M.T.H.B.; Mat Jais, A.M.; Mohamad Moklas, M.A.; Fakurazi, S.; Basir, R. Antidepressant-like Effect of Lipid Extract of Channa Striatus in Postpartum Model of Depression in Rats. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2017, 2017, 2986090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Commons, K.G.; Cholanians, A.B.; Babb, J.A.; Ehlinger, D.G. The Rodent Forced Swim Test Measures Stress-Coping Strategy, Not Depression-like Behavior. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2017, 8, 955–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Powell, T.R.; Fernandes, C.; Schalkwyk, L.C. Depression-Related Behavioral Tests. Curr. Protoc. Mouse Biol. 2012, 2, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolas, C.S.; Peineau, S.; Amici, M.; Csaba, Z.; Fafouri, A.; Javalet, C.; Collett, V.J.; Hildebrandt, L.; Seaton, G.; Choi, S.L.; et al. The JAK/STAT Pathway Is Involved in Synaptic Plasticity the JAK Inhibitor AG490 Specifically Blocks the Induction of NMDAR-LTD. Neurons 2008, 73, 347–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Girotti, M.; Donegan, J.J.; Morilak, D.A. Chronic Intermittent Cold Stress Sensitizes Neuro-Immune Reactivity in the Rat Brain. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2011, 36, 1164–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]










| Associated Factors | Group | p-Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Healthy | Depression | |||
| Gender | Female | 62 | 71 | 0.190 |
| 60.2% | 68.9% | |||
| Male | 41 | 32 | ||
| 39.8% | 31.1% | |||
| Education | No | 7 | 70 | <0.001 |
| 24.1% | 76.9% | |||
| Yes | 22 | 21 | ||
| 75.9% | 23.1% | |||
| Smoking | No | 95 | 95 | 0.498 |
| 96.9% | 94.1% | |||
| Yes | 3 | 6 | ||
| 3.1% | 5.9% | |||
| Chronic Disease | No | 42 | 33 | 0.193 |
| 40.8% | 32.0% | |||
| Yes | 61 | 70 | ||
| 59.2% | 68.0% | |||
| Age Mean (SD) | 51.9(18.7) | 52.6(16.6) | 0.777 | |
| BMI Mean (SD) | 29.9(7.2) | 30.8(7.8) | 0.378 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Almutabagani, L.F.; Almanqour, R.A.; Alsabhan, J.F.; Alhossan, A.M.; Alamin, M.A.; Alrajeh, H.M.; Alonazi, A.S.; El-Malky, A.M.; Alrasheed, N.M. Inflammation and Treatment-Resistant Depression from Clinical to Animal Study: A Possible Link? Neurol. Int. 2023, 15, 100-120. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurolint15010009
Almutabagani LF, Almanqour RA, Alsabhan JF, Alhossan AM, Alamin MA, Alrajeh HM, Alonazi AS, El-Malky AM, Alrasheed NM. Inflammation and Treatment-Resistant Depression from Clinical to Animal Study: A Possible Link? Neurology International. 2023; 15(1):100-120. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurolint15010009
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlmutabagani, Lara F., Raghad A. Almanqour, Jawza F. Alsabhan, Abdulaziz M. Alhossan, Maha A. Alamin, Haya M. Alrajeh, Asma S. Alonazi, Ahmed M. El-Malky, and Nouf M. Alrasheed. 2023. "Inflammation and Treatment-Resistant Depression from Clinical to Animal Study: A Possible Link?" Neurology International 15, no. 1: 100-120. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurolint15010009
APA StyleAlmutabagani, L. F., Almanqour, R. A., Alsabhan, J. F., Alhossan, A. M., Alamin, M. A., Alrajeh, H. M., Alonazi, A. S., El-Malky, A. M., & Alrasheed, N. M. (2023). Inflammation and Treatment-Resistant Depression from Clinical to Animal Study: A Possible Link? Neurology International, 15(1), 100-120. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurolint15010009