Scanning Electron Microscopy Analysis of Biofilm-Encased Bacteria Exposed to Cuprous Oxide-Impregnated Wound Dressings
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
Statistical Analysis
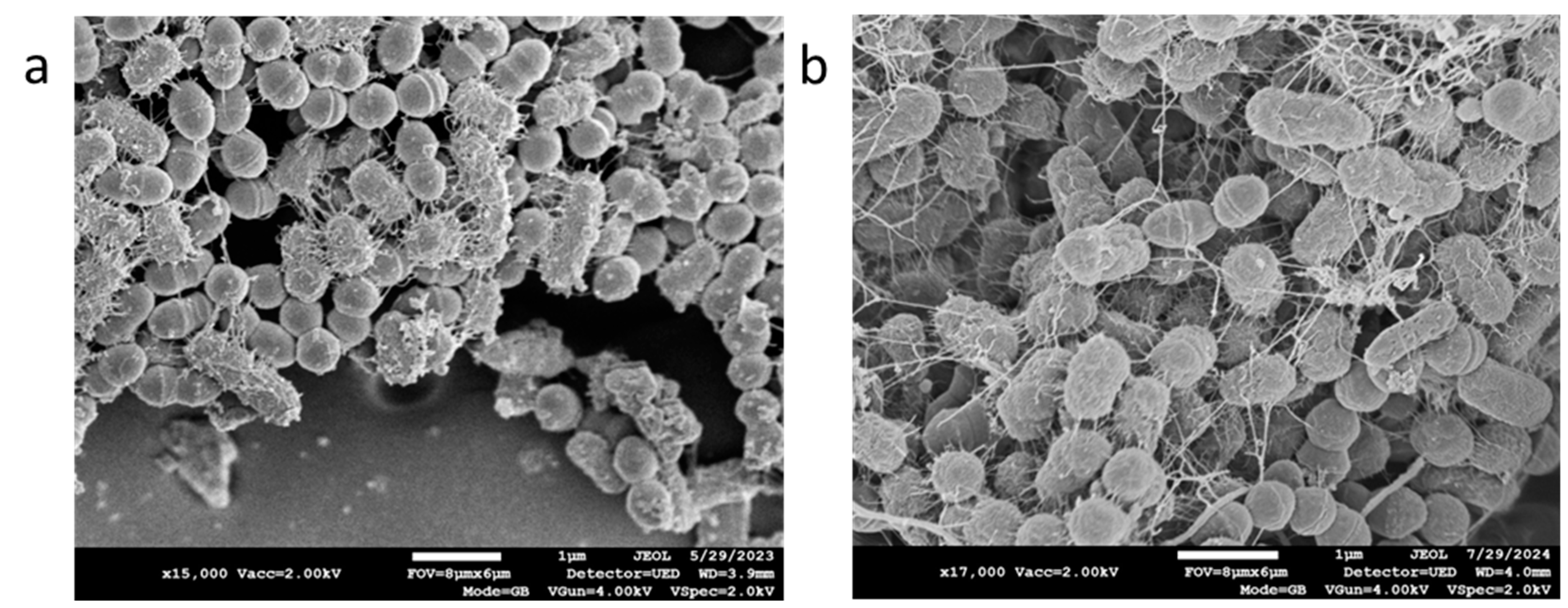
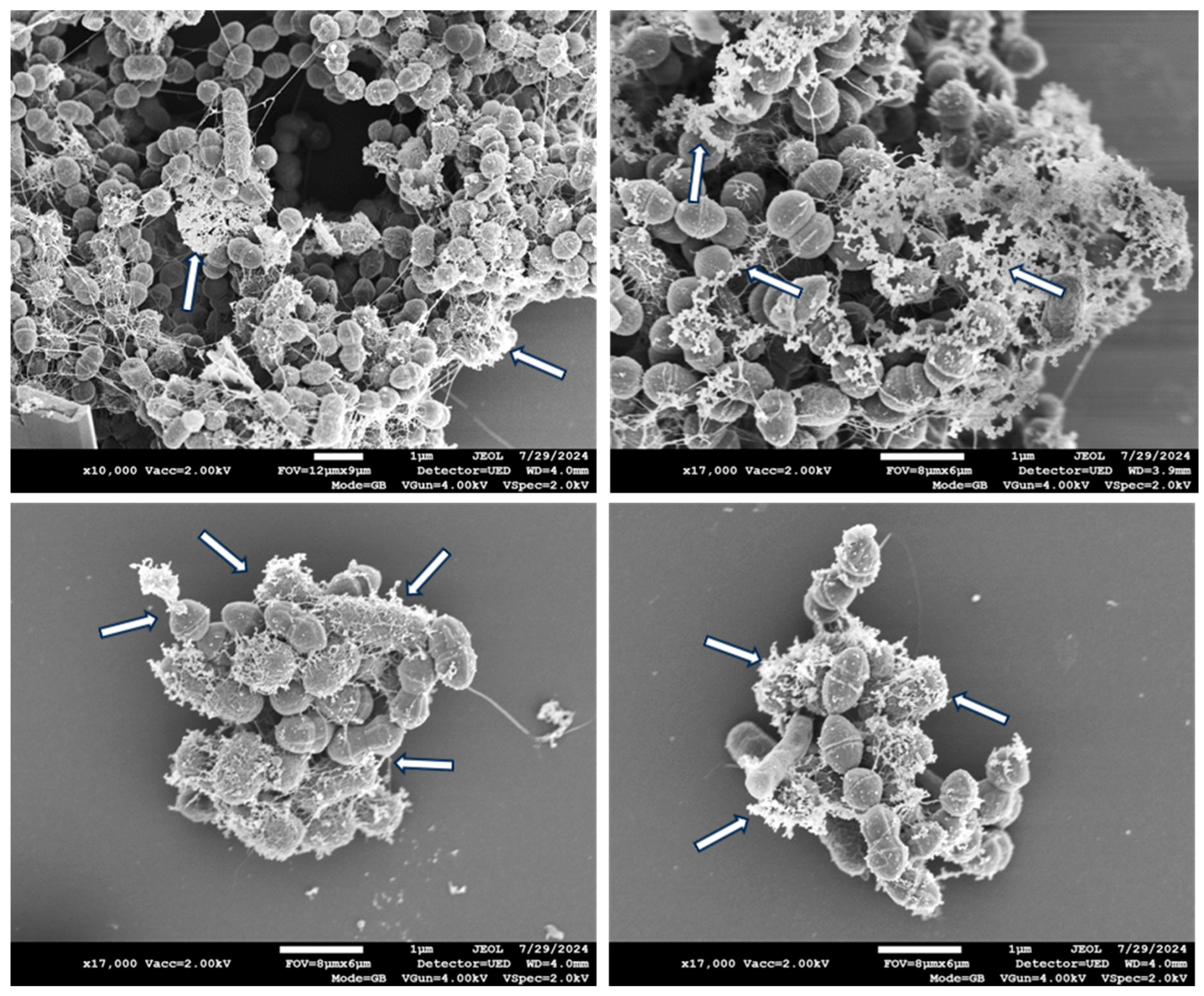
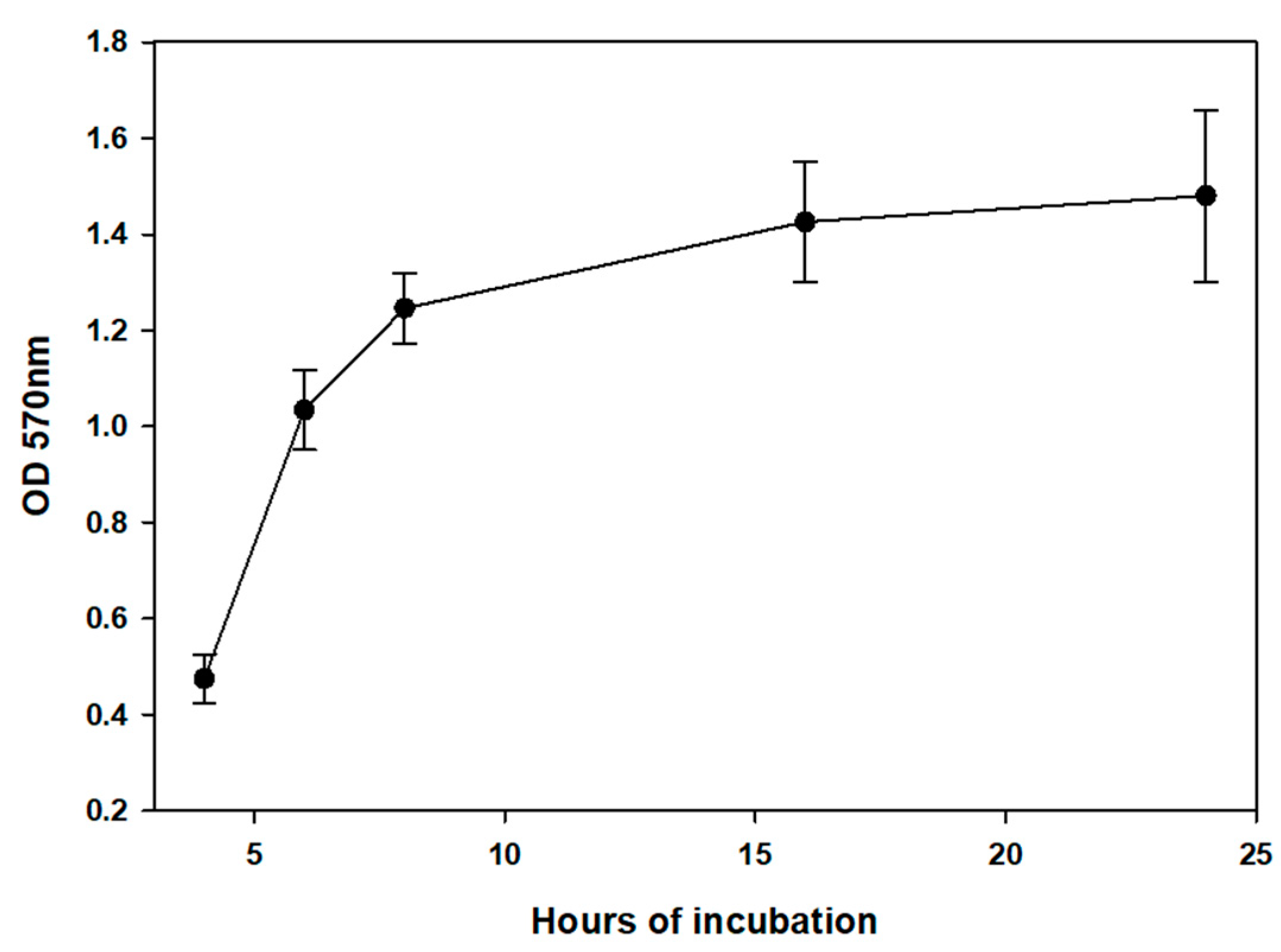
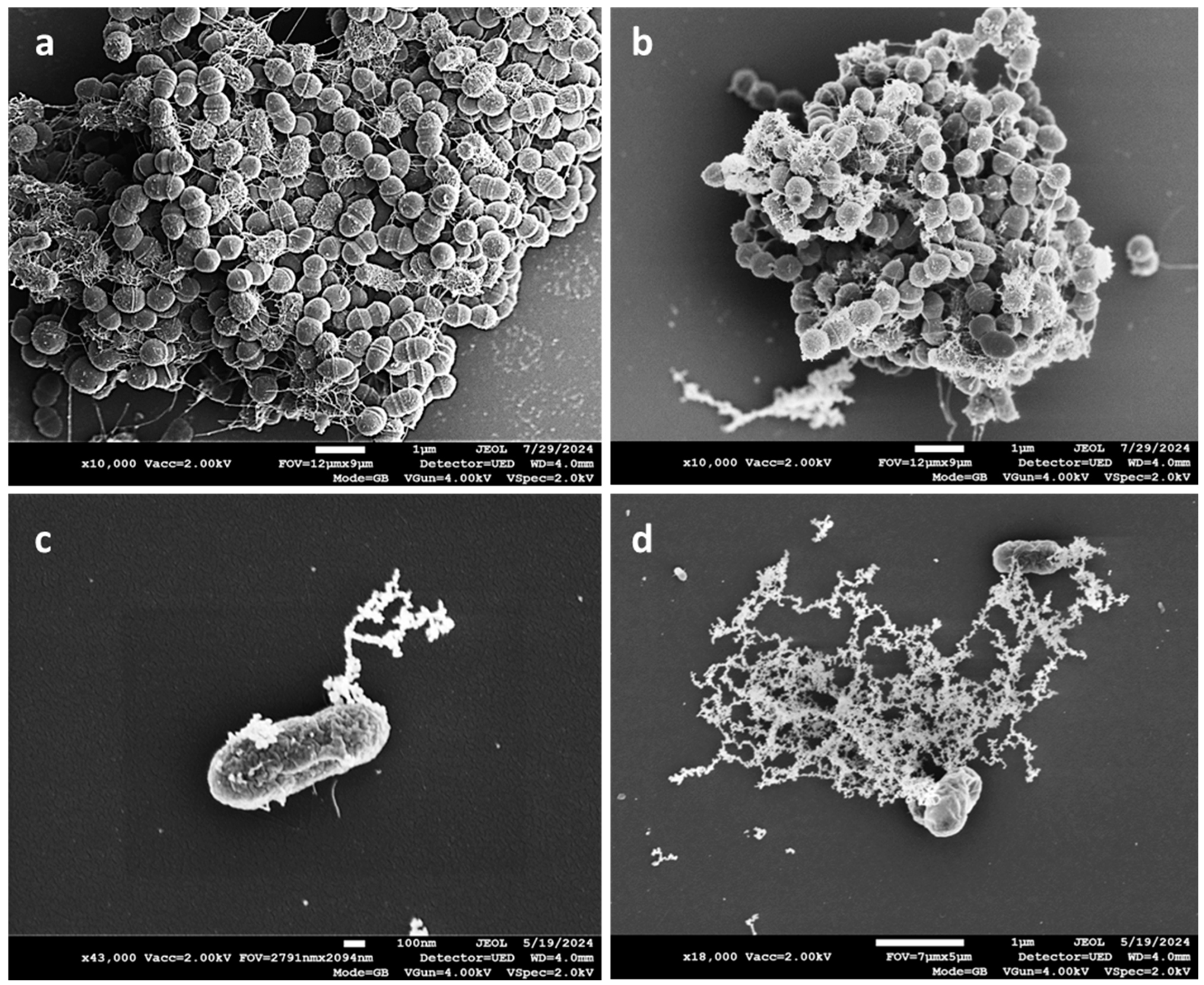
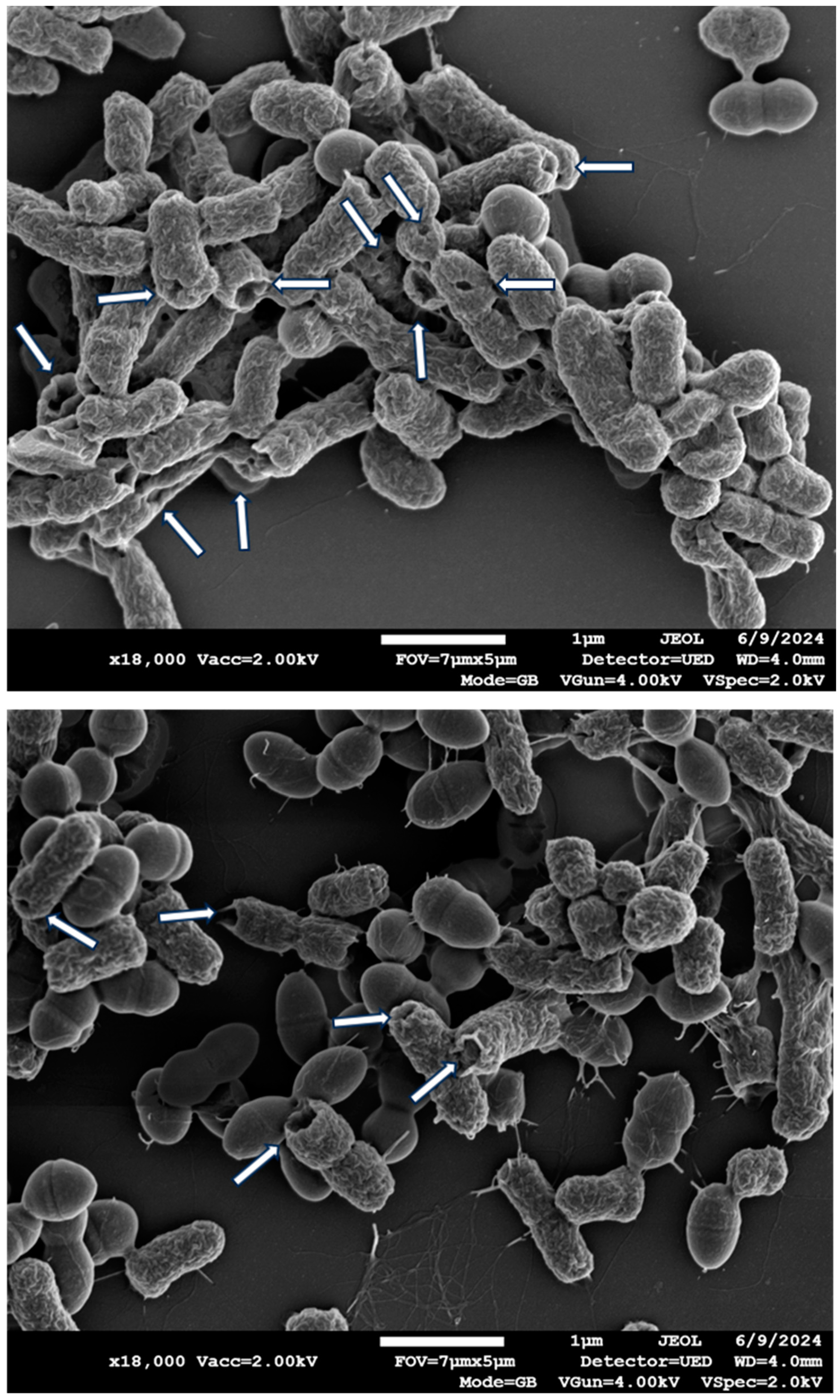
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Uberoi, A.; McCready-Vangi, A.; Grice, E.A. The wound microbiota: Microbial mechanisms of impaired wound healing and infection. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2024, 22, 507–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maheswary, T.; Nurul, A.A.; Fauzi, M.B. The Insights of Microbes’ Roles in Wound Healing: A Comprehensive Review. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahim, K.; Saleha, S.; Zhu, X.; Huo, L.; Basit, A.; Franco, O.L. Bacterial Contribution in Chronicity of Wounds. Microb. Ecol. 2017, 73, 710–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flemming, H.C.; Wingender, J.; Szewzyk, U.; Steinberg, P.; Rice, S.A.; Kjelleberg, S. Biofilms: An emergent form of bacterial life. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2016, 14, 563–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall-Stoodley, L.; Costerton, J.W.; Stoodley, P. Bacterial biofilms: From the natural environment to infectious diseases. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2004, 2, 95–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badia, J.M.; Casey, A.L.; Petrosillo, N.; Hudson, P.M.; Mitchell, S.A.; Crosby, C. Impact of surgical site infection on healthcare costs and patient outcomes: A systematic review in six European countries. J. Hosp. Infect. 2017, 96, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Hsia, H.C. The Impact of Microbial Communities on Wound Healing: A Review. Ann. Plast. Surg. 2018, 81, 113–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anjana, J.; Rajan, V.K.; Biswas, R.; Jayakumar, R. Controlled Delivery of Bioactive Molecules for the Treatment of Chronic Wounds. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2017, 23, 3529–3537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borkow, G. Using copper to fight microorganisms. Curr. Chem. Biol. 2012, 6, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borkow, G.; Salvatori, R.; Kanmukhla, V.K. Drastic Reduction of Bacterial, Fungal and Viral Pathogen Titers by Cuprous Oxide Impregnated Medical Textiles. J. Funct. Biomater. 2021, 12, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borkow, G.; Sidwell, R.W.; Smee, D.F.; Barnard, D.L.; Morrey, J.D.; Lara-Villegas, H.H.; Shemer-Avni, Y.; Gabbay, J. Neutralizing viruses in suspensions by copper oxide based filters. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2007, 51, 2605–2607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borkow, G.; Roth, T.; Kalinkovich, A. Wide spectrum potent antimicrobial efficacy of wound dressings impregnated with cuprous oxide microparticles. Microbiol. Res. 2022, 13, 366–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borkow, G.; Melamed, E. Copper, an abandoned player returning to the wound healing battle. In Recent Advances in Wound Healing, 1st ed.; Shahin, A., Ed.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2021; pp. 165–184. [Google Scholar]
- Gorel, O.; Hamuda, M.; Feldman, I.; Kucyn-Gabovich, I. Enhanced healing of wounds that responded poorly to silver dressing by copper wound dressings: Prospective single arm treatment study. Health Sci. Rep. 2024, 7, e1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melamed, E.; Borkow, G. Continuum of care in hard-to-heal wounds by copper dressings: A case series. J. Wound Care 2023, 32, 788–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melamed, E.; Kiambi, P.; Okoth, D.; Honigber, I.; Tamir, E.; Borkow, G. Healing of Chronic Wounds by Copper Oxide-Impregnated Wound Dressings-Case Series. Medicina 2021, 57, 296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melamed, E.; Rovitsky, A.; Roth, T.; Assa, L.; Borkow, G. Stimulation of Healing of Non-Infected Stagnated Diabetic Wounds by Copper Oxide-Impregnated Wound Dressings. Medicina 2021, 57, 1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melamed, E.; Rovitsky, A.; Roth, T.; Borkow, G. Anterior ankle full thickness skin necrosis treated with copper oxide dressings without debridment and skin graft a case report. Arch. Clin. Med. Case Rep. 1980, 6, 501–510. [Google Scholar]
- Weitman, C.C.; Roth, T.; Borkow, G. Copper dressings to the wound rescue after everything else failed: Case report. Arch. Clin. Med. Case Rep. 2022, 6, 466–473. [Google Scholar]
- Stepanovic, S.; Vukovic, D.; Dakic, I.; Savic, B.; Svabic-Vlahovic, M. A modified microtiter-plate test for quantification of staphylococcal biofilm formation. J. Microbiol. Methods 2000, 40, 175–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, S.Y.; Manikam, R.; Muniandy, S. Prevalence and antibiotic susceptibility of bacteria from acute and chronic wounds in Malaysian subjects. J. Infect. Dev. Ctries. 2015, 9, 936–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavallo, I.; Sivori, F.; Mastrofrancesco, A.; Abril, E.; Pontone, M.; Di Domenico, E.G.; Pimpinelli, F. Bacterial Biofilm in Chronic Wounds and Possible Therapeutic Approaches. Biology 2024, 13, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elmehrath, S.; Ahsan, K.; Munawar, N.; Alzamly, A.; Nguyen, H.L.; Greish, Y. Antibacterial efficacy of copper-based metal-organic frameworks against Escherichia coli and Lactobacillus. RSC Adv. 2024, 14, 15821–15831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Bai, J.; Chen, X.; Wang, L.; Peng, W.; Zhao, Y.; Weng, J.; Zhi, W.; Wang, J.; Zhang, K.; et al. Constructing a highly efficient multifunctional carbon quantum dot platform for the treatment of infectious wounds. Regen. Biomater. 2024, 11, rbae105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopinath, V.; Priyadarshini, S.; Loke, M.F.; Jagadheesan, A.; Marsili, E.; MubarakAli, D.; Velusamy, P.; Vadivelu, J. Biogenic synthesis, characterization of antibacterial silver nanoparticles and its cell cytotoxicity. Arab. J. Chem. 2017, 10, 1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahire, J.J.; Hattingh, M.; Neveling, D.P.; Dicks, L.M. Copper-Containing Anti-Biofilm Nanofiber Scaffolds as a Wound Dressing Material. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0152755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shehabeldine, A.M.; Amin, B.H.; Hagras, F.A.; Ramadan, A.A.; Kamel, M.R.; Ahmed, M.A.; Atia, K.H.; Salem, S.S. Potential Antimicrobial and Antibiofilm Properties of Copper Oxide Nanoparticles: Time-Kill Kinetic Essay and Ultrastructure of Pathogenic Bacterial Cells. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2023, 195, 467–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.; Rao, A.; Oropallo, A.; Gawlik, S.; Haight, J. Use of Copper Nanoparticles to Reduce Bioburden in the Treatment of Diabetic Foot Ulcers. Eplasty 2022, 22, QA4. [Google Scholar]
- Nowak, M.; Baranska-Rybak, W. Nanomaterials as a Successor of Antibiotics in Antibiotic-Resistant, Biofilm Infected Wounds? Antibiotics 2021, 10, 941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




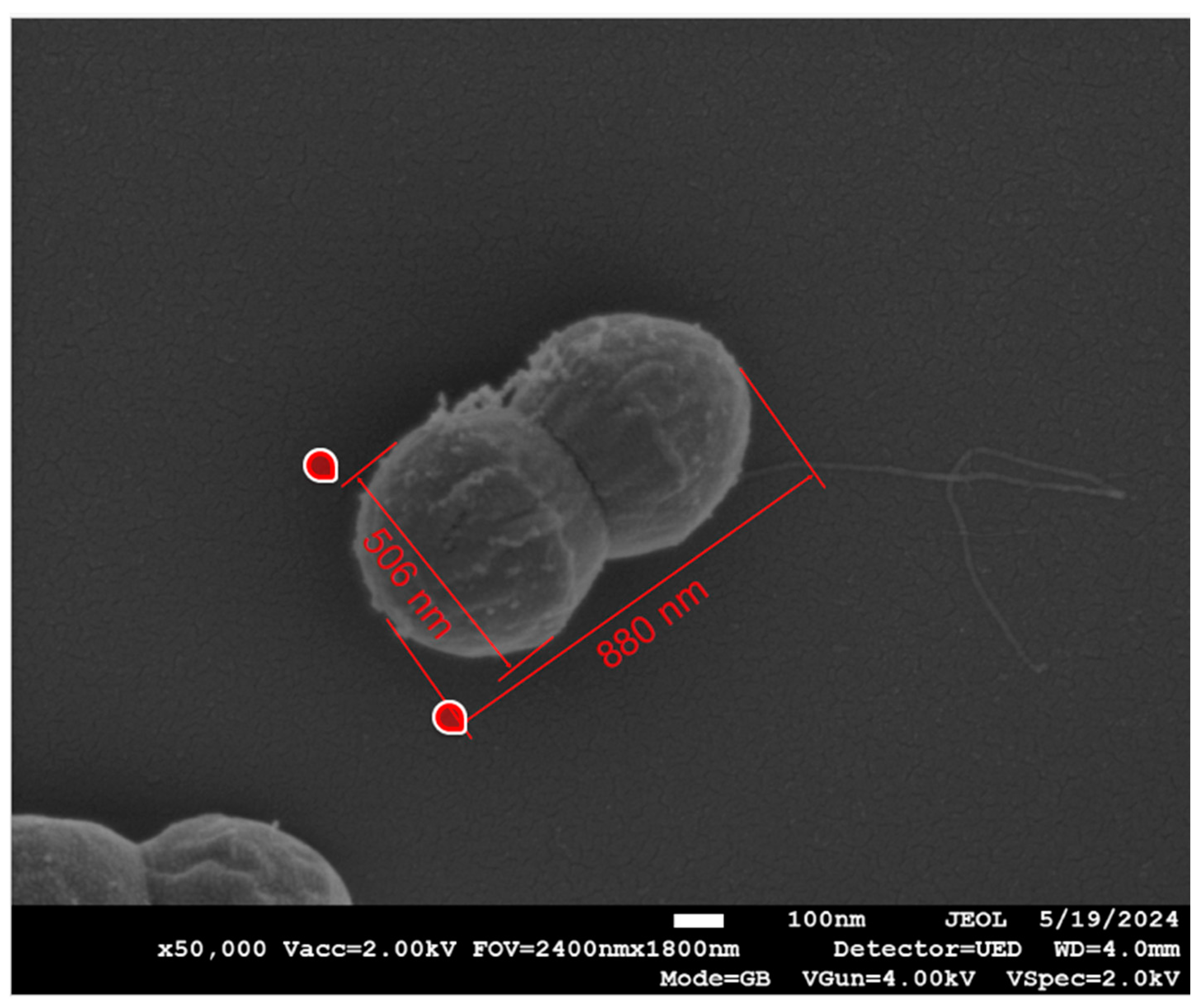
| Measurement | Bacteria | Dressing | n | Mean (nm) | Standard Deviation | Lower 95% | Upper 95% | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Width | Gram-positive | COD | 108 | 530.75 | 37.55 | 523.58 | 537.91 | <0.0001 |
| Control | 96 | 463.83 | 73.8 | 448.87 | 478.80 | |||
| Gram-negative | COD | 54 | 440.64 | 57.20 | 425.02 | 456.25 | 0.885 | |
| Control | 42 | 438.65 | 73.26 | 415.82 | 461.48 | |||
| Length | Gram-positive | COD | 41 | 673.2 | 131.4 | 631.8 | 714.7 | 0.49 |
| Control | 51 | 690.3 | 99.2 | 662.5 | 718.2 | |||
| Gram-negative | COD | 30 | 1076.2 | 217.9 | 994.8 | 1157.5 | 0.32 | |
| Control | 57 | 1130 | 279.5 | 1055.9 | 1204 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Roth, T.; Zelinger, E.; Kossovsky, T.; Borkow, G. Scanning Electron Microscopy Analysis of Biofilm-Encased Bacteria Exposed to Cuprous Oxide-Impregnated Wound Dressings. Microbiol. Res. 2024, 15, 2358-2368. https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres15040158
Roth T, Zelinger E, Kossovsky T, Borkow G. Scanning Electron Microscopy Analysis of Biofilm-Encased Bacteria Exposed to Cuprous Oxide-Impregnated Wound Dressings. Microbiology Research. 2024; 15(4):2358-2368. https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres15040158
Chicago/Turabian StyleRoth, Tohar, Einat Zelinger, Tally Kossovsky, and Gadi Borkow. 2024. "Scanning Electron Microscopy Analysis of Biofilm-Encased Bacteria Exposed to Cuprous Oxide-Impregnated Wound Dressings" Microbiology Research 15, no. 4: 2358-2368. https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres15040158
APA StyleRoth, T., Zelinger, E., Kossovsky, T., & Borkow, G. (2024). Scanning Electron Microscopy Analysis of Biofilm-Encased Bacteria Exposed to Cuprous Oxide-Impregnated Wound Dressings. Microbiology Research, 15(4), 2358-2368. https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres15040158







