Abstract
The ecotoxic potential of seven Moselle river watershed sediments was assessed with a battery of bioassays comprised of rapid phototrophic [LuminoTox solid phase (L-SPA) and elutriate (L-ELU) assays] and bacterial [Microtox solid phase assay (M-SPA)] exposure tests, as well as with two micro-invertebrate solid phase tests conducted with Hydra attenuata (lethal and sublethal effects solid phase assay, HL-SPA and HSL-SPA) and Chironomus riparius. Measured effects of sediments and their elutriates were varied and reflected responses that were ecotoxicity test-, endpoint- and site-dependent, suggesting some degree of risk toward benthic and water column organisms, respectively, at specific sites. Correlation analysis demonstrated that L-SPA and M-SPA ecotoxicity responses were significantly linked with the Hydra HSL-SPA assay, indicating their ability to predict ecotoxicity towards an invertebrate taxonomic group representing secondary consumers. While the L-SPA and M-SPA assays hold promise as rapid screens for sediment ecotoxicity, correlation analysis with grain size (L-SPA: r=–0.795, P=0.033; M-SPA: r=–0.73, P=0.07) points out that their responses can be influenced by the presence of fines (i.e., sediment particles ≤0.063 mm in size) and that this information is essential to properly interpret ecotoxicity data generated with these assays. Finally, notable differences observed in trophic level sensitivities once again recall the importance of employing a test battery to adequately appraise the ecotoxicity of sediments.
Introduction
In freshwater ecosystems, biota can be impacted by the resuspension of ecotoxic sediments via both natural (e.g., flood scouring) and man-made (e.g., dredging, navigation, open water deposition) activities. Sediment contamination owing to metals and varied pollutants released into surface waters via diverse types of (non) point sources of pollution (urban, industrial, agricultural) thus continues to be an important environmental issue.
While several bioassays have been developed to measure the ecotoxicity of sediment elutriates, pore waters and extracts, fewer are presently available to evaluate that of whole sediment where both readily-soluble and adsorbed toxicants may be present.1 Whole sediment ecotoxicity tests are usually performed with benthic organisms that measure survival and growth after 10 or 14 days of exposure.2,3 Other tests have also been proposed to measure growth and/or reproduction inhibition endpoints of sediment pore waters (with the submerged plant Myriophyllum aquaticum4) or of whole sediment at the water-sediment interface (with the crustacean Gammarus pulex5 and the gastropod Valvata piscinalis6). Time to results for these latter bioassays run from 10 days to four and eight weeks, respectively.
With the intent of permitting more rapid and cost-effective decisions to be taken concerning sediment contamination, alternative research efforts have also been conducted to develop smaller-scale direct contact tests featuring shorter exposure times, as well as increased sample throughput. Increasingly, such micro-scale assays are often used as prescreens to rapidly identify ecotoxic sediment samples that can then be confirmed as such by the more traditional benthic organism tests. Examples include bioassays conducted with bacteria7,8,9 and micro-algae10,11 or by test batteries incorporating biotests of different trophic levels.12,13,14,15 To obtain preliminary insights on the potential ecotoxicity of previously untested Moselle river watershed (Lorraine Province, France) sediments, as well as to compare the testing capabilities and usefulness of small-scale bioassays presently applied in our laboratories for such assessments, sediment was collected at seven sites of interest. Herein, we thus report sediment toxicity results generated with four different test procedures comprising the well-standardized Microtox solid phase bacterial luminescence inhibition assay (MSPA),16 the LuminoTox photosynthetic efficiency inhibition measuring system for liquids17 and solids,18 the Hydra attenuata solid phase ecotoxicity assay (newly developed and described herein), as well as the Chironomus riparius solid phase assay.3
Materials and Methods
Sediment samples
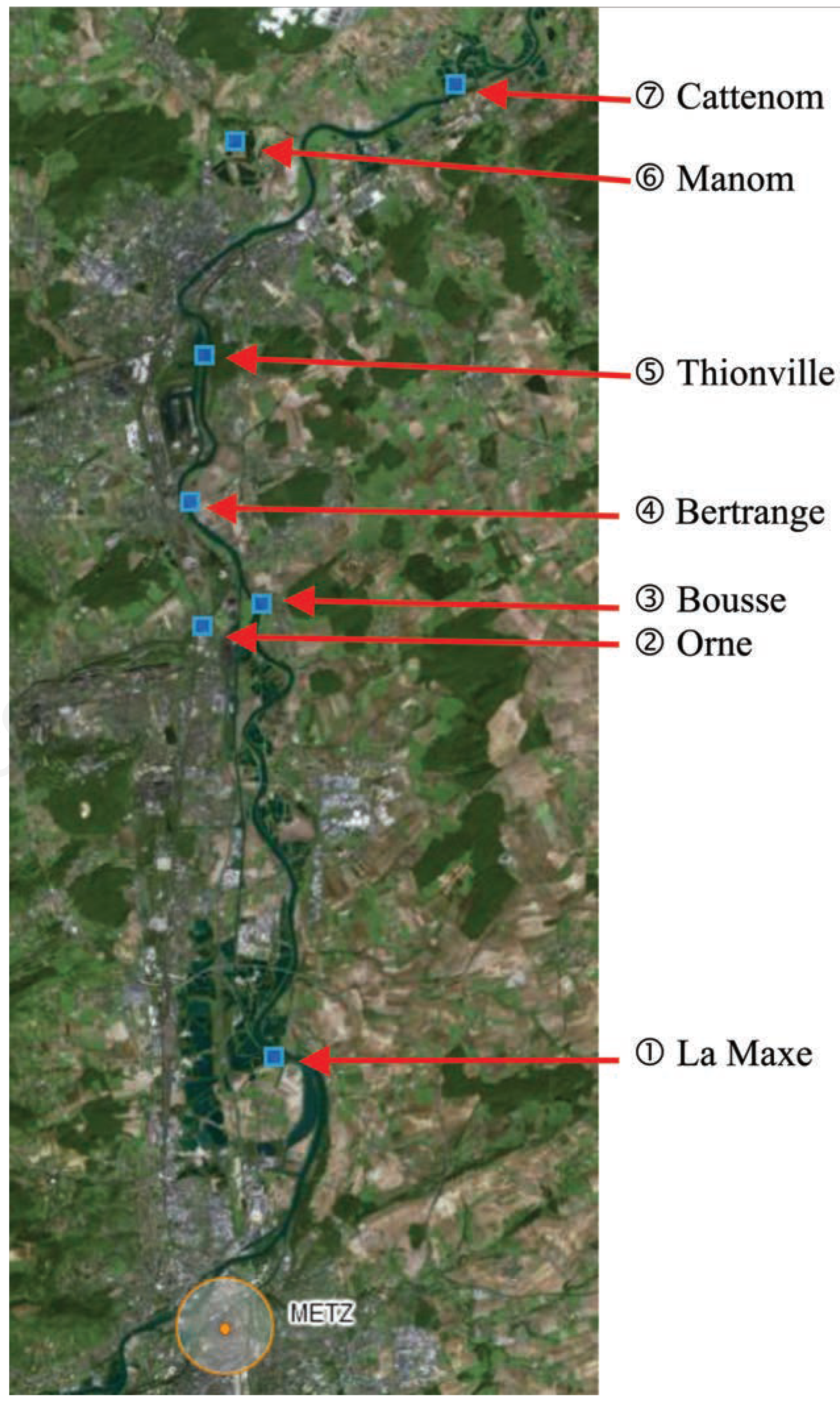
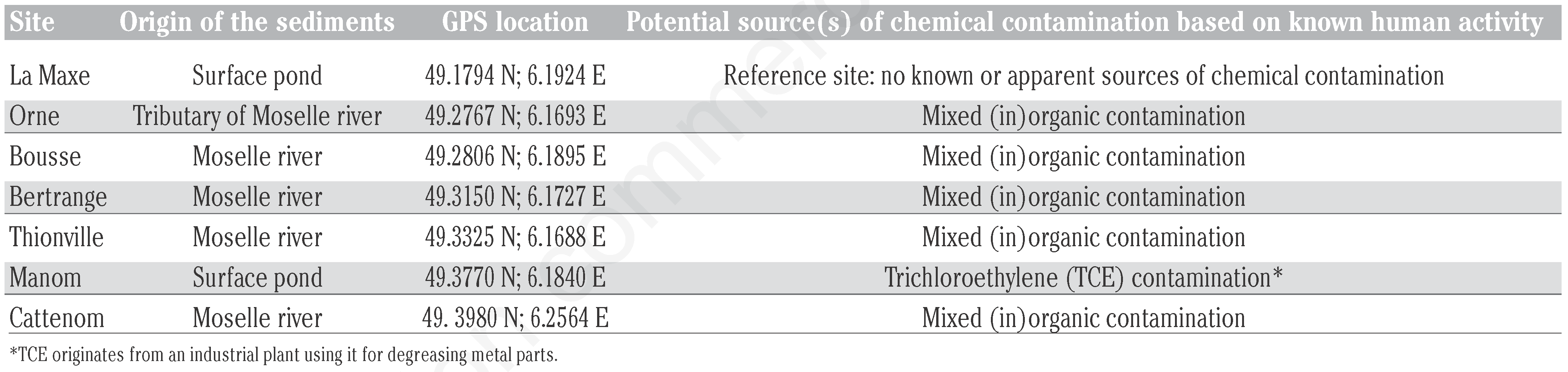
Seven sediment samples were collected in May 2006 to generate ecotoxicity data with the bioassay procedures described below. A handheld dredge, specially-designed by the University of Lorraine (Metz-LIEC) enabled superficial sediments (0-10 cm depth) to be raked from sites by an operator wearing hip waiters at distances varying from 2-7 m off the shoreline. They were extracted from sites (Figure 1) located on the Moselle river itself (Bousse, Bertrange, Thionville, Cattenom), from one of its tributaries (Orne) and from two adjacent surface ponds (La Maxe, Manom). Sites were chosen to reflect mixed and/or varying degrees of contamination based on historical knowledge of human activities linked to (in)organic chemicals (Table 1).
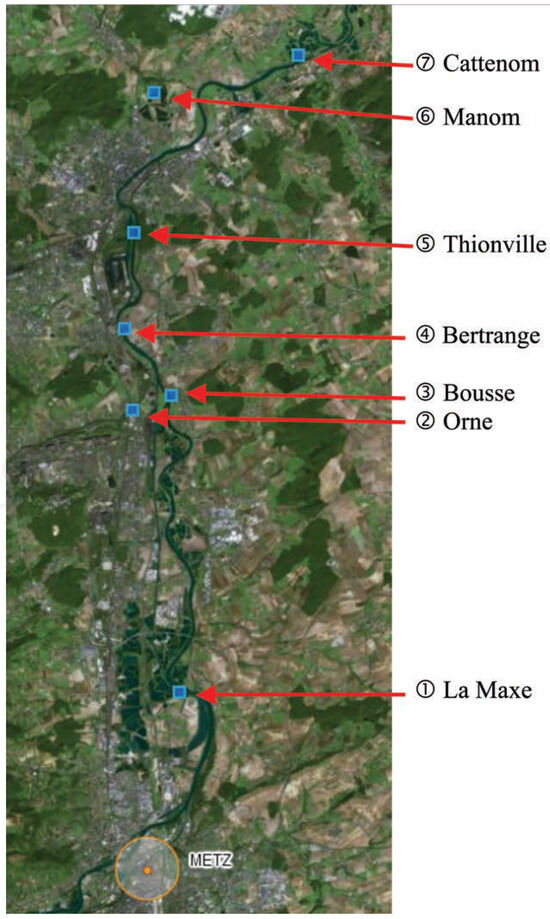
Figure 1.
Moselle river watershed (Lorraine Province, France) sediment sampling sites.

Table 1.
Characteristics of Moselle river watershed sediment sampling sites in terms of their emplacement and potential for contamination.
After sampling, sediments were directly processed on site. They were first passed through a 1 cm2-meshed sieve to remove any observed biological (e.g., mollusk shells, vegetation), mineral (e.g., pebbles) or xenobiotic (e.g., plastics, glass) material. Then, they were manually homogenized in a large (40 L) polypropylene bucket with the help of a plastic spatula and sub-aliquoted in appropriate volumes to either Ziploc plastic bags or 50 mL plastic tubes with caps (Fisher Scientific, # 14-961-33) for later toxicity testing. All sediment sub-samples were kept in coolers with ice-paks during transport back to the laboratory. Because the time lapse for the conduct of the different bioassays in our respective laboratories was expected to vary for up to three months, we elected to freeze (– 20°C) all samples on arrival at the LIEC laboratory. Sub-samples were later shipped frozen to the Environment Canada and IRSTEA-Lyon laboratories for conduct of the H. attenuata solid phase assay and the C. riparius solid phase assay, respectively. Once thawed in view of toxicity testing, all sub-samples were rapidly bioassayed within 24 h.
Sediment characterization
Subsamples from the seven sites were also kept for sediment grain-size determination. This analysis was performed by wet sieving after hydrometric sedimentation employing a method commonly used by Environment Canada laboratories.19 In brief, after drying (40°C; 24 h), any gravel was removed by sieving on 4- and 2-mm mesh screens. Sediment smaller than 2 mm in diameter was deflocculated for 24 h with sodium hexametaphosphate (5%) and placed in a 1 L sedimentation tube. Hydrometric sedimentation measurements were taken after 1/2, 1, 3 and 10 min, and 1, 2, 6 and 24 h with a standard hydrometer (ASTM # 152H hydrometer). The sediment was then sieved with water on a mesh screen corresponding to sand fractions (1, 0.5, 0.25, 0.125 and 0.063 mm). After sieving, the sediment fractions were dried and weighed before being recorded as a percentage of the total.
Toxicity testing procedures
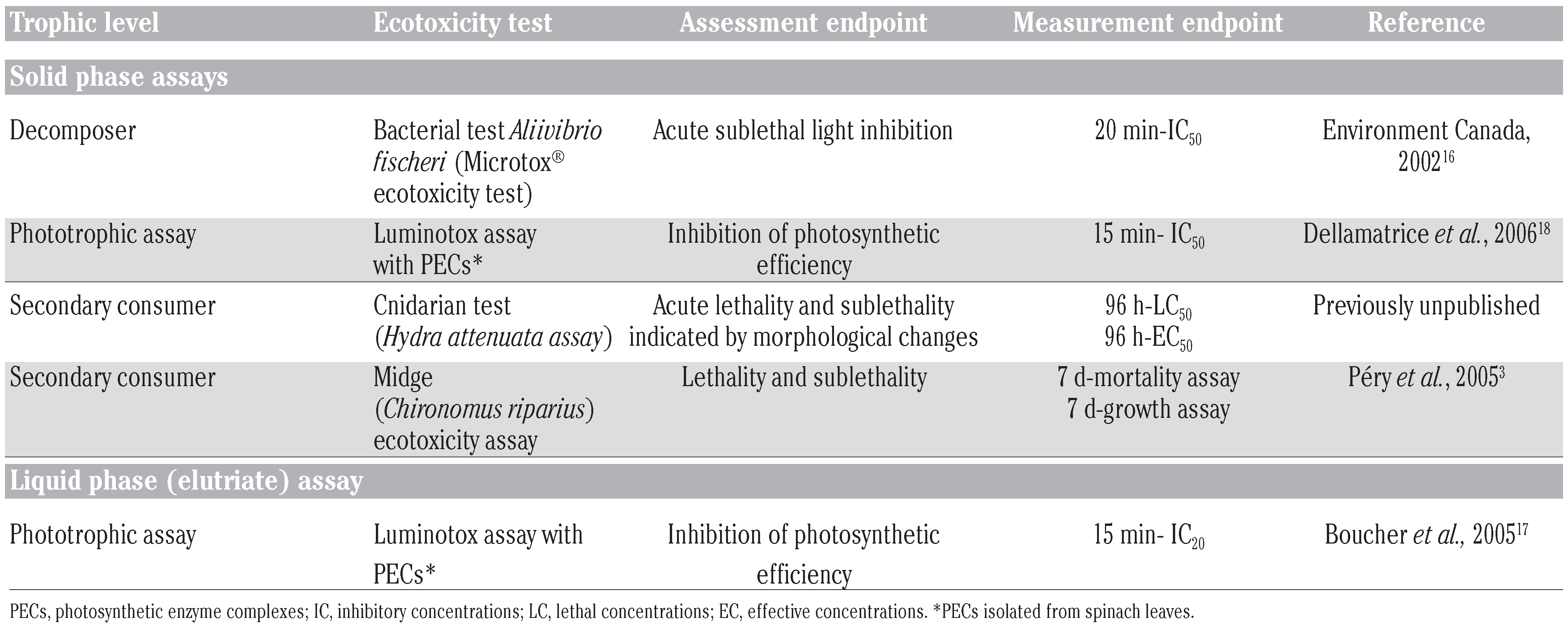
The characteristics of the solid phase and elutriate bioassays conducted to assess sediment ecotoxicity are highlighted in Table 2.3,16,17,18 Only the Hydra solid phase assay (H-SPA), previously unpublished, is more fully described below, while the testing principle and procedures of the other assays are more briefly recalled. References listed in Table 2 can be consulted for more ample details on testing procedures. Measurement endpoints of the bioassays were determined with statistical methods and software recommended for each procedure. Correlation analyses (Pearson’s product moment or Spearman’s rank order tests with significance set at P<0.05) were performed with Statistica software, version 5.5. Measurement endpoints for solid phase tests were invariably reported on a dry-weight basis (see below). For this purpose, sediment moisture content (% humidity) was determined on subsamples according to a well-standardized procedure.16 Validity of test results relating to quality control (i.e., respect of test criteria and performance of biological reagents) were insured by following recommended protocols published for the Microtox solid phase assay,16 the LuminoTox elutriate assay (L-ELU),17 LuminoTox solid phase assay (L-SPA)18 and for the C. riparius solid phase assay.3 Appearance of normal post-exposure control animals in the Hydra solid phase assay insured that test’s validity (see below).

Table 2.
Characteristics of the small-scale bioassays used to determine the ecotoxic potential of the seven sediments.
Microtox (bacteria luminescence) solid phase assay
The principle of the M-SPA is based on the fact that Aliivibrio fischeri, the luminescent marine bacterium employed in this assay, undergoes suppression of light output after short-term exposure to toxicants. In brief, 0.3 g of sediment (wet weight) is combined to 1.5 mL of a 3.5% saline diluent in special Microtox solid phase polystyrene tubes, from which subsequent (two-fold) dilutions are prepared, along with three control tubes (1.5 mL diluent only). Afterwards, 20 µL of re-hydrated bacteria are pipetted into each tube. The highest dilution (primary test concentration) is then 19.7% wet weight per volume [i.e., (0.3 g ÷ 1.520 mL) × 100 = 19.7%]. Bacterial contact with sediment then occurs for 20 min at 15°C. After exposure, bacteria are separated from the sediment fraction by pressing a filter column (pore size between 15-45 µm) into the exposure tube where they are then concentrated in the filtrate and subsequently aliquoted to a reading tube. The light output of all tubes (sediment-exposed and controls) is measured with a photometer, after which inhibition percentages can be calculated. The determined endpoint is a 20-min inhibitory concentration causing 50% light loss (IC50) initially expressed in % wet wt/v (g of wet sediment per 100 mL of dilution water) and afterwards converted to % dry wt/v (g of dry sediment per 100 mL of dilution water), considering % humidity (moisture content) values determined for each sediment.
LuminoTox solid phase and elutriate assays
The LuminoTox toxicity testing procedure reagent employed in our study made use of stabilized photosynthetic enzyme complexes (PECs), isolated from spinach plant extracts.17 When PECs are challenged with contaminants that can interfere with transmission of chlorophyll fluorescence linked to Photosystems I and II reaction sites, a corresponding decrease in fluorescence emission results, as quantified with the LuminoTox Analyzer that measures photosynthetic efficiency (ϕp: expressed in relative fluorescence units) of exposed and unexposed PECs. Percentages of inhibition based on exposure to different sample concentrations can then be calculated as follows:
ì% inhibition = [(ϕblank – ϕsample) / ϕblank] x 100
This rapid (15-min exposure) small-scale test has demonstrated sensitivity to metals as well as to various classes of organic pollutants20 and thus offers a simple and effective means of screening liquid or solid samples for the presence of toxicity.
For the L-SPA, seven two-mL serial sediment dilutions (10 to 0.16% slurries) and controls (0%) are prepared in small plastic tubes (identical to those used to perform the M-SPA). A 100 µL volume of PECs is then pipetted into each plastic tube for a 15 min exposure period. Afterwards, PECs are easily separated from the sediment fraction by pressing a filter column (identical to that used to perform the M-SPA) into the exposure tube. The PEC-containing filtrate contents (approximately 2 mL) are next poured into a methyl acrylate (VWR Scientific Products, # 58017-875) reading cuvette. Each cuvette is then placed into the LuminoTox Analyzer to obtain fluorescence readings, from which photosynthetic efficiency (ϕp) and percentages of inhibition values can be determined. The reported endpoint is a 15-min IC50 (inhibitory concentration causing a 50% fluorescence inhibition related to photosynthetic efficiency) initially expressed in % wet wt/v (g of wet sediment per 100 mL of dilution water) and afterwards converted to % dry wt/v (g of dry sediment per 100 mL of dilution water), considering % humidity (moisture content) values determined for each sediment.
The experimental protocol developed for testing sediment elutriate ecotoxicity with the LuminoTox Analyzer (L-ELU) was performed with some variants as compared to the L-SPA assay. Briefly, a 25% sediment slurry (5 g/20 mL) is prepared, in triplicate, in 50 mL plastic tubes (Fisher Scientific, # 14-961-33) with Millipore Super Q water. Each triplicate of these capped 50 mL tubes is placed in a vertical rotator (Caframo™ Reax 2 rotating mixer). Rotating speed was set at 30 rpm at room temperature (22±2°C) for 30 min to optimize transfer of soluble chemicals present in the sediment into the aqueous phase. Afterwards, tubes are centrifuged (3000 rpm, 10 min) and a series of seven serial dilutions of each triplicate supernatant (25 to 0.39%) and controls (0%) are prepared in smaller tubes (any plastic or glass tube of 10-15 mL volume capacity is adequate for this purpose) with Millipore Super Q water as dilution medium. Contents of these tubes comprise the sediment elutriates from which 2 mL of each are then pipetted into other tubes (e.g., M-SPA tubes) to which have just been added 100 µL of (rehydrated and stabilized) PECs. Following a 15-min exposure period, the content of each tube (i.e., elutriate + 100 µL of PECs) is poured into a reading (methyl acrylate) cuvette. Each cuvette is then placed into the LuminoTox Analyzer to obtain fluorescence readings from which photosynthetic efficiency (ϕp) and percentages of inhibition are determined. The reported endpoint is a 15-min IC20 (inhibitory concentration causing a 20% fluorescence inhibition related to photosynthetic efficiency) expressed in % of wet sediment elutriate prepared from a 25% sediment slurry (i.e., 5 g of wet sediment per 20 mL of dilution water). In contrast to the three small-scale solid phase toxicity tests where a 50% effect measurement endpoint was determined (i.e., M-SPA, L-SPA, H-SPA), we elected to measure a 20% effect endpoint (i.e., IC20) in the L-ELU test to enhance its sensitivity.
Hydra solid phase assay
The experimental protocol followed for testing whole sediment ecotoxicity with Hydra attenuata is quite similar to its earlier developed liquid phase counterpart.21 The H-SPA first calls for preparing a 25% (10 g/40 mL) sediment slurry in a 50 mL plastic tube (Fisher Scientific, # 14-961-33) with Hydra medium (Calcium chloride, CaCl2 • 2H2O, 2.94 g; N-tris [hydroxymethyl]methyl 1-2-aminoethanesulfonic acid, TES buffer, 2.2 g; ultrapure water, 20.0 L). For routine maintenance and culture of Hydra in the laboratory, 0.080 g of ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA) is part of the 20 L Hydra medium solution described above.21 For toxicity testing in this work, however, EDTA was excluded from Hydra medium to avoid any possible metal chelation effects on sediment samples. With other 50 mL tubes, seven twenty-mL serial sediment dilutions (25 to 0.39 % slurries) and one control (0%) are prepared from which 3×4 mL of each tube dilution are dispensed into three adjacent (column) wells of a 12-well microplate (Falcon, # 3043). During the sediment dilution preparation, as well as just prior to the dispensing of diluted sediment into the microplate wells, it is essential to vortex tubes immediately before withdrawing sample volumes to ensure proper transfer of sediment slurry percentages. Hydra (circa 0.5 cm in length per animal) are then collected from a laboratory culture and 10-15 are transferred (with a Pasteur pipette) into each of a series of individual Petri dishes (35¥10 mm, Corning, # 25000) containing 4 mL of control and prepared sediment slurry concentrations dispensed from the 50 mL tubes. Then, starting with Hydra in the control Petri dish and progressing toward those placed in Petri dishes of increasing concentrations of sediment slurries, three animals are transferred into each corresponding microplate well with the help of a Pasteur pipette. Placing Hydra in the Petri dishes at all test concentrations prior to dispensing them into the two 12-well microplate wells ensures that no sediment slurry concentration will be altered during their transfer. Placing three animals into each of three wells (as opposed to placing nine animals in one well) is meant to facilitate their observation to check for morphological changes, which relate to (sub)lethal ecotoxic effects.
Under conditions of intoxication, Hydra characteristically show gradual changes in shape going from normal (slender body with well-extended tentacles), to clubbed (slender body with clubbed tentacles in their extremities), to shortened (shortened body with markedly reduced and thickened tentacles), to tulip (where the protracted body essentially takes the shape of a tulip bulb), and finally to disintegrated. Lethal effects occur rapidly once Hydra reach the tulip stage, following which the animal’s body disintegrates. After a 96 h exposure, animals are examined in each well of the two 12-well microplates (stereoscope with a 6-10X magnification) and scored morphologically. A test is considered valid if a maximum of one Hydra out of nine fails to display a normal appearance in controls. In comparison with controls exhibiting a normal shape, observing the number of animals in sediment test concentrations displaying either the clubbed or shortened stage and those displaying the tulip or disintegrated stage allows recording sublethal (effective concentrations, EC) and lethal (lethal concentrations, LC) effects, respectively.21 The sediment concentration affecting 50% of organisms (96 h-EC50 or 96 h-LC50), and its 95% confidence limits, was estimated by using a previously published method based on quantal data.22
Chironomus riparius solid phase assay
Organisms from the species Chironomus riparius originated from an IRSTEA laboratory culture of the fourth co-author. They were exposed in 0.6 L beakers, filled with 0.1 L sediment and 0.4 L water (half demineralized water and half from an uncontaminated spring near the IRSTEA laboratory; pH was 8.1 and conductivity 400 µS/cm). Beakers were set in a water bath at 21°C with a 16:8 h light:dark photoperiod. Conductivity, temperature, pH, amount of dissolved oxygen were measured daily. We used an aeration system (air introduced through a Pasteur pipette in each beaker) to maintain oxygen level. The control sediment was a silica artificial sediment (Sable de Fontainebleau, Elvetec, Genas, France) with the following particle size distribution: 90% between 50 and 200 µm, 10% under 50 µm. Sediments were transferred in beakers three days before starting tests. There were five beakers per tested sediment. The experiment was initiated with two-day-old larvae (end of first instar). Ten larvae were introduced into each beaker. Length at the beginning of the test, measured on 20 organisms, was 1.7 +/- 0.1 mm. Organisms were fed daily with 0.6 mg per larva Tetramin® fish food. At day 7, survival and growth were monitored. Individuals were counted, killed using formaldehyde, and length was measured using a binocular microscope.
Results and Discussion
Sediment processing and freezing
Unquestionably, manipulation (sieving, mixing and sub-sampling) and subsequent freezing of the sediment samples may have altered their chemistry (e.g., via oxidation, loss of volatiles and/or release of metals owing to lysing of bacteria possibly modifying partitioning between pore waters and solid phase). Moreover, these operations may have affected sediment unionized ammonia (NH3) levels and/or its speciation via changes in pH, temperature and oxygen concentration, all of which can infuence toxicity responses (Canadian Council of Ministers of the Environment).23 However, logistics associated with the chronologically-different conduct of biological testing in three different laboratories (two in France and one in Canada) imposed this modus operandi. Again, we emphasize that objectives of our study sought to gain initial information on the ecotoxicity of unstudied sediments (processed as indicated above) determined by comparing results of the practical micro-scale assays described herein.
Sediment ecotoxicity results
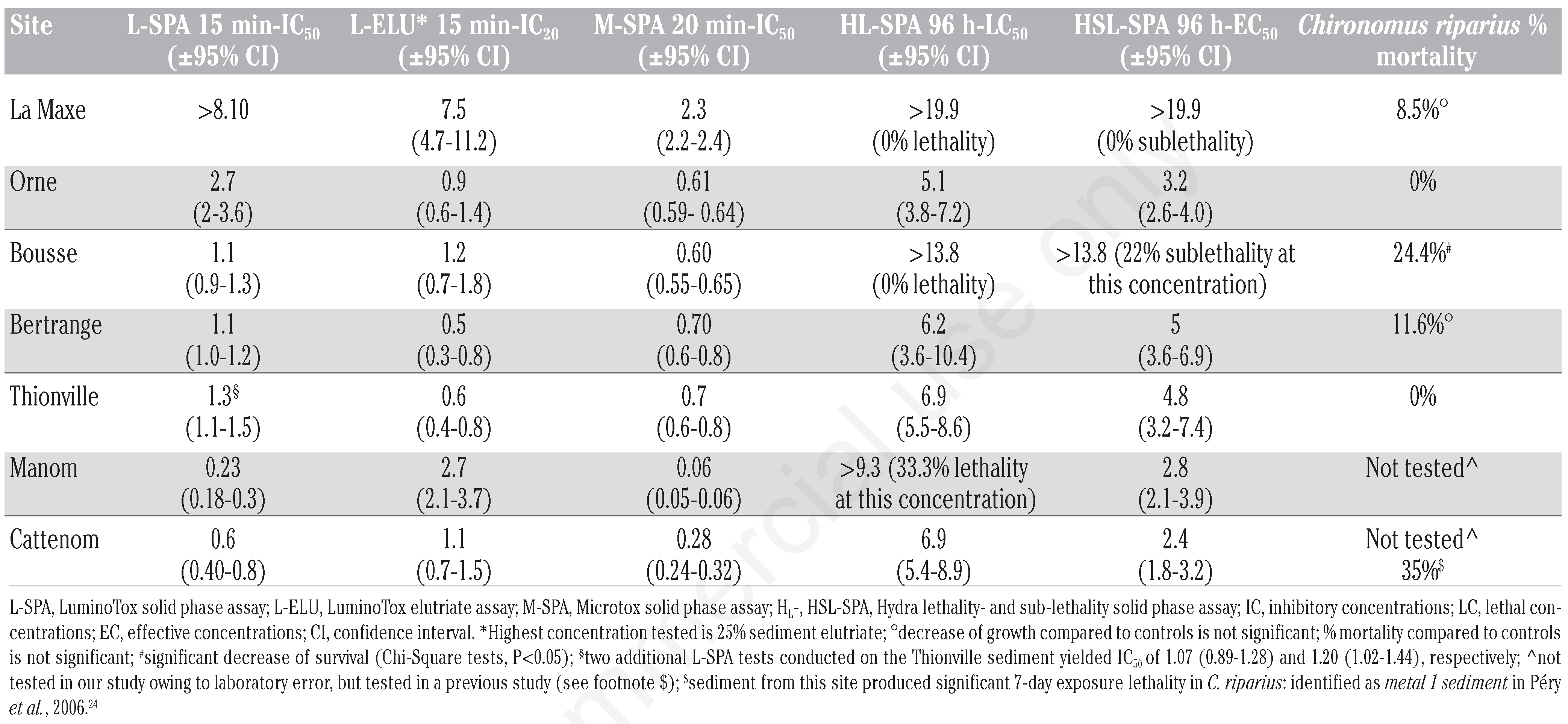
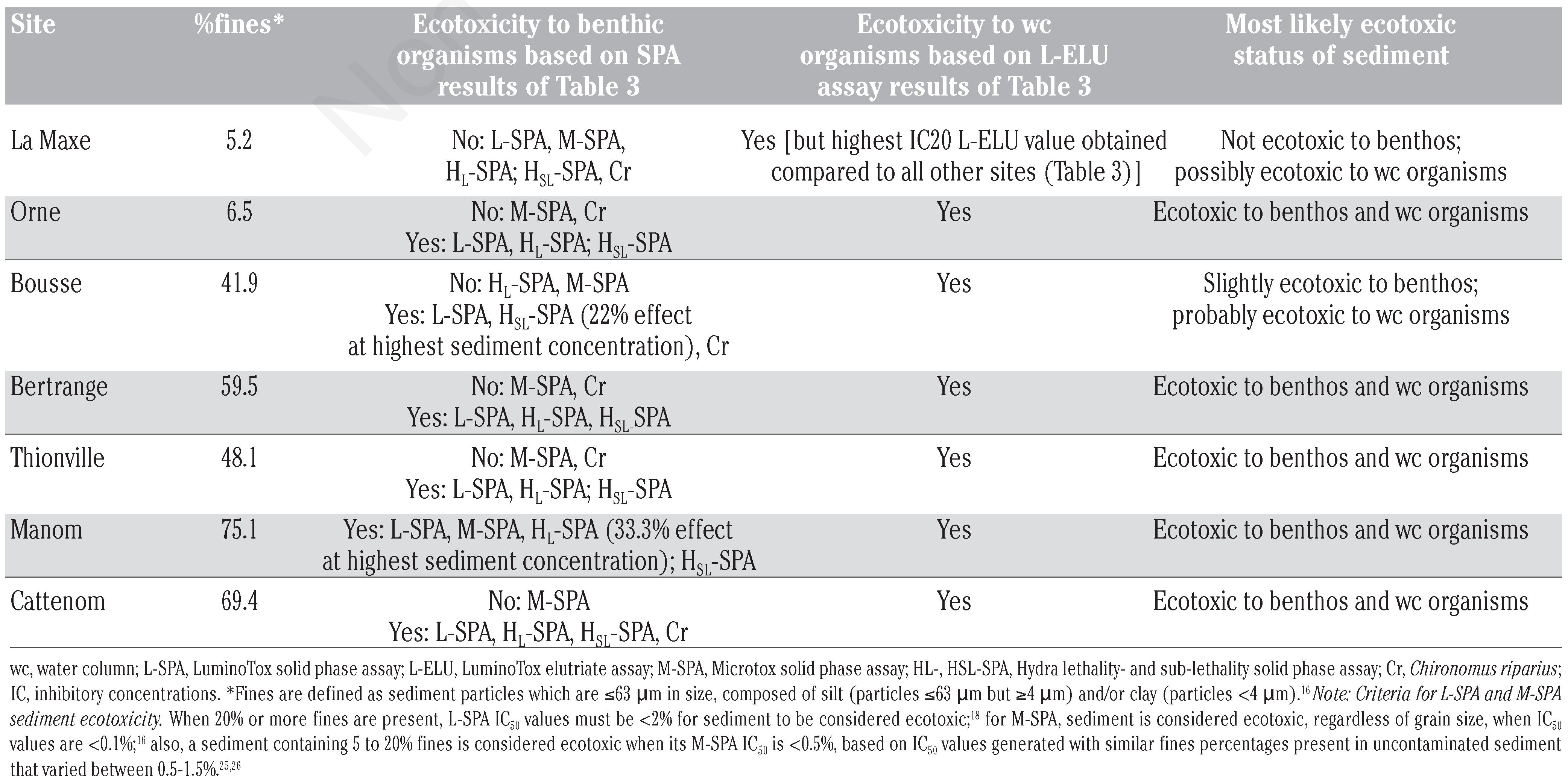
Solid phase and elutriate assay results obtained for the seven sediments are reported in Table 3.24 In general, bioassay results indicate varying degrees of ecotoxicity that are ecotoxicity test- and site-dependent. Because of our intended future use of the L-SPA for rapid sediment ecotoxicity screening, the Thionville sediment sample was bioassayed twice more to appraise its reproducibility. These additional results confirm its reliability (Table 3, footnote §). The Hydra (lethal and sublethal) solid phase assays (HL-SPA and HSL-SPA), for the five sites exhibiting ecotoxicity (with the exception of La Maxe and Bousse), display very narrow LC50/EC50 ratios that span from 1.24 (Bertrange) to >3.27 (Manom). A similar ratio ranging from 1.1 to 2.6 separating lethal from sublethal effects was also reported when H. attenuata were exposed in liquid phase to industrial effluents.20 The quantal (all or none) responses of this organism thus appear to occur in a limited sediment concentration range with initial sublethal effects rapidly leading to lethal effects following small increments in sample concentration.

Table 3.
Ecotoxicity data generated with the Moselle river watershed sediments: solid phase assay results are expressed in % dry weight (g/100 mL) and the elutriate assay in % w/v of sediment elutriate.
Correlation among toxicity tests
Correlation analysis demonstrated that L-SPA and M-SPA ecotoxicity responses were significantly correlated (r=0.96, P= 0.01 calculated from Table 3 data), suggesting that both tests answer to (at least some of) the same types of bio-available contaminants likely present in these sediments. This redundancy in ecotoxic information also suggests that the two tests could be interchangeable within a test battery and that selecting one or the other would suffice to capture the ecotoxic potential of similar freshwater sediments in future studies. Other notable linkages stemming from correlation analysis of Table 3 ecotoxicity responses indicate that the two rapid exposure L-SPA and M-SPA test results are also significantly correlated with the Hydra sublethal solid phase assay (HSL-SPA) 96 h-EC50 data: L-SPA versus HSL-SPA, r=0.784, P=0.037; M-SPA versus HSL-SPA, r=0.841, P=0.02. Unsurprisingly, both Hydra solid phase assays were found to be significantly correlated: HL-SPA (96 h-LC50) versus HSL-SPA (96 h-EC50), r=0.907, P=0.005. Finally, barring the C. riparius test, the results of all solid phase assays, L-SPA (r=0.876, P=0.01, M-SPA (r=0.813, P=0.03), HL-SPA (r=0.85, P=0.02) and HSL-SPA (r=0.76, P=0.049) were significantly correlated with the L-ELU. This can suggest that at least some of the bioavailable contaminants that are producing ecotoxic responses in the whole sediment solid phase tests are extractible from the sediments and also active in the L-ELU elutriate assay.
Influence of grain size on toxicity results
While a clear spread of IC50 values have been generated with both the L-SPA and M-SPA assays (barring the La Maxe site for L-SPA showing an indeterminate IC50>8.05%) in Table 3, concluding that these sediments are actually ecotoxic is not readily evident. This is owing to the fact that test sediment grain size has been shown to be an important confounding factor interfering with ecotoxicity responses in solid phase assays conducted with luminescent bacteria16 and with LuminoTox PECs.18
With the M-SPA assay, decreasing grain size causes a pronounced decrease in IC50 (increased ecotoxicity) when fines, defined as sediment particles ≤0.063 mm in size, increase within the sediment matrix.23,24 Indeed, M-SPA assays undertaken with 100% (uncontaminated) kaolin clay, where sediment particles are <0.004 mm in size, have been found to produce IC50 ranging from 0.14 to 0.245%.25,26 These studies have prompted the establishment of guidelines to confirm the ecotoxicity of sediment samples assessed by M-SPA assays, one of which is to consider ecotoxic any sediment with an IC50<0.1%, regardless of grain size.16 Again, sediments with 5~20% fines are considered ecotoxic when their IC50≤0.5%, based on IC50 values generated with similar fines percentages present in uncontaminated sediment that varied between 0.5-1.5%.25,26
In a manner similar to that of the M-SPA assay, L-SPA IC50 have been shown to display a sharp drop when the percentage of fines in uncontaminated kaolin clay sediment increases to 20% or more. At such concentrations of fines (i.e., 20-100% fines), IC50 ranged from 2.17 to 4.72%.18 These results intimate that sediment samples appraised with the L-SPA protocol should only be considered ecotoxic when their IC50 are less than 2%, especially if sediment grain size has not been determined. For percentages in uncontaminated kaolin clay sediment ranging between 0-20% fines, L-SPA IC50 varied from 4.7-20.5%.18 In fact, correlation analysis revealed that Table 3 L-SPA IC50 are inversely and significantly linked with Table 416,18,25,26 fines percentage values (r=–0.795, P=0.033). Similarly, M-SPA IC50 also show an inverse relationship with fines percentage values that is close to significance (r=–0.73, P=0.07).
Most likely ecotoxic status of investigated sediments
Keeping in mind grain size ecotoxicity criteria for L-SPA and M-SPA tests, the ecotoxic status of the Moselle river watershed sediments can then be established based on the overall bioassay results shown in Table 3. In this assessment, we assume that positive responses of solid phase assays performed on whole sediment indicate hazard toward benthic organisms and that positive responses of the L-ELU assay performed on sediment elutriates reflect hazard toward water column organisms (Table 4). The latter assay, unlike the L-SPA and M-SPA assays, is totally independent of sediment grain size as far as interpreting its ecotoxicity responses are concerned.

Table 4.
Ecotoxic status of Moselle river watershed sediments according to solid phase and LuminoTox elutriate test results of Table 3, as well as on sediment ecotoxicity criteria based on grain size considerations.
Whole sediment of the La Maxe site is clearly not ecotoxic to benthic organisms based on all solid phase tests conducted (Table 4). Here, L-SPA and M-SPA yield IC50values that are well above those reflecting adverse effects based on ecotoxicity criteria discussed above, no lethal and sublethal effects are observed with the H-SPA, and mortality observed with C. riparius is not significant (Table 3). Exceptionally, the IC20 value of 7.51% obtained for the L-ELU assay at this site, the highest in comparison to all other sites, suggests that some degree of ecotoxicity to water column organisms is possible.
The C. riparius test, conducted on six of the seven sediments (Table 3), displayed significant ecotoxic responses for two sites (Bousse, Cattenom), likely explainable by the specific (in)organic contaminant make-up of these sediments, which thus incurred lethal effects on chironomids.
The Bousse site sediment has a marked percentage of fines (Table 4), which places the M-SPA IC50 of 0.60% (Table 3) into the non ecotoxic category based on grain size criteria (Table 4, see Note). There are no lethal effects in the HL-SPA assay, but all other solid phase test results display ecotoxic effects. Again, by virtue of its IC50=1.09% which is below the 2% cut-off concentration taking into account sediment grain size content, the L-SPA assay confirms ecotoxicity for this sediment and the L-ELU assay indicates the presence of bio-available toxicants in its elutriate.
Sediments of the remaining five sites all clearly demonstrate ecotoxicity to both benthic and water column organisms. As for the Bousse site, M-SPA IC50s are not low enough to indicate ecotoxicity to Bertrange, Orne, Thionville and Cattenom sediments because of percentage fines ecotoxicity criteria imposed on this solid phase assay. The Manom site sediment elicited the most pronounced ecotoxic effects based on IC50 generated with the L-SPA (0.23%) and M-SPA (0.06%) assays, and by considering as well its HSL-SPA IC50 value response, as intense as those of the Cattenom and Orne site sediments. Interestingly, Manom sediment elutriate ecotoxicity is less pronounced than that at all other sites, barring La Maxe, which suggests that its sediments are likely more contaminated with organic contaminants that are not easily extractible in aqueous medium.
Conclusions
The battery of bioassays applied to assess the ecotoxic potential of seven Moselle river watershed sediments demonstrated varying degrees of effects on whole sediments and their elutriates that suggest some hazard toward benthic and water column organisms, respectively. The two rapid exposure bacterial (M-SPA) and phototrophic (L-SPA) solid phase assays were significantly correlated with the Hydra solid phase assay, indicating that they were able to predict ecotoxicity to an invertebrate taxonomic group. Our investigation also points out the importance of having grain size information when conducting sediment ecotoxicity testing with the L-SPA and M-SPA assays since fines contents will influence their ecotoxic responses. Moreover, our study recalls the usefulness of employing a representative test battery to assess sediment ecotoxicity owing to differences in trophic level sensitivities. Lastly, while the micro-scale tests employed here have been shown purportedly capable of providing beneficial information on sediment toxicity, their adequacy for this purpose will have to be confirmed by conducting future studies on freshly collected sediments accompanied by chemical analysis and, ideally, ecological assessment of sites in order to demonstrate their relevance for aquatic environmental appraisal.15,27
Research highlights
The ecotoxic potential of seven Moselle river (Lorraine province, France) watershed sediments was assessed with a battery of small-scale bioassays at the phototrophic, bacterial and micro-invertebrate levels.
Measured effects of sediments and their elutriates were varied and reflected responses that were ecotoxicity test-, endpoint- and site-dependent, suggesting some degree of risk toward benthic and water column organisms, respectively, at specific sites.
Notable differences observed in trophic level sensitivities once again emphasize the importance of employing a test battery to adequately appraise the ecotoxicity of sediments.
Funding
the third and last authors acknowledge funding obtained under the Saint-Lawrence River Action Plan, Environment Canada, to advance knowledge on sediment toxicity testing assessment.
Contributions
equal contribution by all authors in conception and design for this work. The first four authors contributed to laboratory and field work. The third author wrote the draft of the manuscript after all authors had provided significant input in data analysis/interpretation. All authors offered critical remarks, which produced the final version, submitted for publication.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank their respective managements for supporting this research initiative. We are also grateful to Frederic Mayer (Institut National Polytechnique de Lorraine, Nancy, France), as well as to Environment Canada staff (Manon Harwood, Sylvain Trottier and Sophie Trépanier) for their respective help in conducting some of the bioassays. Finally, we acknowledge Magella Pelletier, Geo-chemist at Environment Canada in Montreal, for undertaking the sediment granulometric analyses.
Conflicts of Interest
the authors declare no potential conflict of interests.
References
- Côté, C; Blaise, C; Michaud, JR; Ménard, L; Trottier, S; Gagné, F; et al. Comparisons between microscale and whole-sediment assays for freshwater sediment toxicity assessment. Environ Toxicol Water Qual 1998, 13, 93–110. [Google Scholar]
- Borgmann, U; Grapentine, L; Norwood, WP; Bird, G; Dixon, DG; Lindeman, D. Sediment toxicity testing with the freshwater amphipod Hyalella azteca: Relevance and application. Chemosphere 2005, 61, 1740–3. [Google Scholar]
- Péry, AR; Mons, R; Garric, J. Chironomus riparius solid-phase assay. In Small-scale freshwater toxicity investigations, vol. 1; Blaise, C, Férard, JF, Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, 2005; pp. 437–51. [Google Scholar]
- Feiler, U; Kirchesch, I; Heininger, P. A new plant bioassay for aquatic sediments. J Soils Sediments 2004, 4, 261–6. [Google Scholar]
- McLoughlin, N; Yin, D; Maltby, L; Wood, RM; Yu, H. Evaluation of sensitivity and specificity of two crustacean biochemical markers. Environ Toxicol Chem 2000, 19, 2085–92. [Google Scholar]
- Ducrot, V; Cognat, C; Mons, R; Mouthon, J; Garric, J. Development of rearing and testing protocols for a new freshwater sediment test species: the gastropod Valvata piscinalis. Chemosphere 2006, 62, 1272–81. [Google Scholar]
- Kwan, KK; Dutka, BJ. Comparative assessment of two solid-phase toxicity bioassays: the direct sediment toxicity testing procedure (DSTTP) and the MicrotoxR solid phase test (SPT). Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 1995, 55, 338–46. [Google Scholar]
- Bitton, G; Garland, E; Kong, IC; Morel, JL; Koopman, B. A direct solid phase assay for heavy metal toxicity. I. Methodology. J Soil Contamin 1996, 5, 385–94. [Google Scholar]
- Doe, K; Jackman, P; Scroggins, R; McLeay, D; Wohlgeschaffen, G. Solid-phase test for sediment toxicity using the luminescent bacterium, Vibrio fischeri. In Small-scale freshwater toxicity investigations, vol. 1; Blaise, C, Férard, JF, Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, 2005; pp. 107–36. [Google Scholar]
- Blaise, C; Ménard, L. A micro-algal solid-phase test to assess the toxic potential of freshwater sediments. Water Qual Res Canada 1998, 33, 133–55. [Google Scholar]
- Adams, MS; Stauber, JL. Development of a whole-sediment toxicity test using a benthic marine microalga. Environ Toxicol Chem 2004, 23, 1957–68. [Google Scholar]
- Sahli, L; Afri-Mehennaoui, FZ; El Hadef El Okki, M; Férard, JF; Mehennaoui, S. Assessment of sediment quality and pore water ecotoxicity in Kebir Rhumel basin (NE-Algeria): a combined approach. Water Sci Technol 2012, 65, 393–401. [Google Scholar]
- Manzo, S; Schiavo, S; Aleksi, P; Tabaku, A. Application of a toxicity test battery integrated index for a first screening of the ecotoxicological threat posed by ports and harbors in the southern Adriatic Sea (Italy). Environ Monit Assess 2014, 186, 7127–39. [Google Scholar]
- Palma, P; Ledo, L; Soares, S; Barbosa, IR; Alvarenga, P. Integrated environmental assessment of freshwater sediments: a chemical and ecotoxicological approach at the Alqueva reservoir. Environ Geochem Health 2014, 36, 209–23. [Google Scholar]
- Roig, N; Sierra, J; Nadal, M; Moreno-Garrido, I; Nieto, E; Hampel, M; et al. Assessment of sediment ecotoxicological status as a complementary tool for the evaluation of surface water quality: the Ebro river basin case study. Sci Total Environ 2015, 503-504, 269–78. [Google Scholar]
- Environment Canada. Biological test method: solid-phase reference method for determining the toxicity of sediment using luminescent bacteria (Vibrio fischeri), Environmental Protection Series, Report EPS 1/RM/42; Ottawa, ON; Environment Canada, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Boucher, N; Lorrain, L; Rouette, ME; Perron, E; Déziel, N; Tessier, L; et al. Rapid testing of toxic chemicals. Am Lab 2005, 37, 34–7. [Google Scholar]
- Dellamatrice, P; Monteiro, R; Blaise, C; Slabbert, JL; Gagné, F; Alleau, S. Toxicity assessment of reference and natural freshwater sediments with the Luminotox assay. Environ Toxicol 2006, 21, 395–402. [Google Scholar]
- Pelletier, M. Évolution spatiale et temporelle de la dynamique et de la géochimie des sédiments du lac Saint-Pierre. Rapport scientifique et technique ST-240: Environnement Canada, Direction des sciences et de la technologie. Monitoring et surveillance de la qualité de l’eau, Région du Québec. 2007; [in French]. [Google Scholar]
- Environment Canada, LuminoTox: a tool for rapid toxicity testing. Technological Innovation data sheet; Environment Canada: Montreal, QC, 2005.
- Blaise, C; Kusui, T. Acute toxicity assessment of industrial effluents with a microplate-based Hydra attenuata assay. Environ Toxicol Water Qual 1997, 12, 53–60. [Google Scholar]
- Stephan, CE. Methods for calculating an LC50. In Aquatic toxicology and hazard evaluation, ASTM STP 634; Mayer, FL, Hamelink, JL, Eds.; ASTM: Philadelphia, PA, 1977; pp. 65–84. [Google Scholar]
- CCME (Canadian Council of Ministers of the Environment), Canadian water quality guidelines for the protection of aquatic life: Ammonia. In Canadian environmental quality guidelines; Excerpt from Publication No. 1299; Winnipeg; Canadian Council of Ministers of the Environment; 2010; pp. 1–8.
- Péry, AR; Babut, MP; Mons, RL; Garric, J. Deriving effects on Chironomus population carrying capacity from standard toxicity tests. Environ Toxicol Chem 2006, 25, 144–8. [Google Scholar]
- Ringwood, AH; Delorenzo, ME; Ross, PE; Holland, AF. Interpretation of Microtox solid phase toxicity tests: the effects of sediment composition. Environ Toxicol Chem 1997, 16, 1135–40. [Google Scholar]
- Tay, KL; Doe, KG; MacDonald, AJ; Lee, K. The influence of particle size, ammonia, and sulfide on toxicity of dredged materials for ocean disposal. In Microscale testing in aquatic toxicology - Advances, techniques, and practice; Wells, PG, Lee, K, Blaise, C, Eds.; CRC Press: New York, 1998; pp. 559–74. [Google Scholar]
- Burton, A. Sediment ecotoxicity. In:; Férard, JF, Blaise, C, Eds.; In Encyclopedia of aquatic ecotoxicology, vol. 1 and 2; Springer: Dordrecht, 2013; pp. 1003–14. [Google Scholar]
©Copyright J.F. Férard et al., 2015 Licensee PAGEPress, Italy. This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial 3.0 License (CC BY-NC 3.0).