Experimental Setup for Splash Erosion Monitoring—Study of Silty Loam Splash Characteristics
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
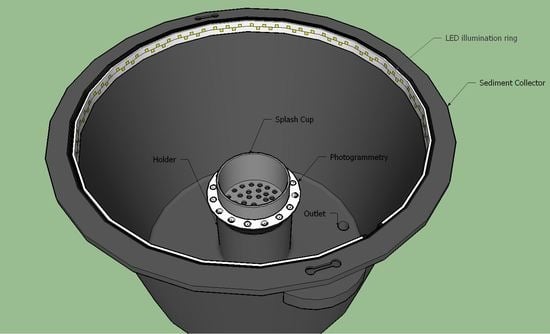
2.1. Splash Erosion Collection Device
2.2. Soil Sample Preparation and Analysis
2.3. Rainfall Simulation
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fernández-Raga, M.; Palencia, C.; Keesstra, S.; Jordán, A.; Fraile, R.; Angulo-Martínez, M.; Cerdà, A. Splash erosion: A review with unanswered questions. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2017, 171, 463–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morgan, R.P.C. Field measurement of splash erosion. Int. Assoc. Sci. Hydrol. Publ. 1981, 133, 373–382. [Google Scholar]
- Poesen, J.; Torri, D. The effect of cup size on splash detachment and transport measurements. Part I. Field measurements. Geomorphic Process. Environ. Strong Seas. Contrasts Vol. I Hillslope Process. Catena Suppl. 1988, 12, 113–126. [Google Scholar]
- Fernández-Raga, M.; Fraile, R.; Keizer, J.J.; Teijeiro, M.E.V.; Castro, A.; Palencia, C.; Calvo, A.I.; Koenders, J.; Marques, R.L.D.C. The kinetic energy of rain measured with an optical disdrometer: An application to splash erosion. Atmos. Res. 2010, 96, 225–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truman, C.C.; Bradford, J.M. Soil Science Society of America journal. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1976, 59, 519–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinnell, P.I.A. Splash Erosion: Some Observations on the Splash-Cup Technique 1. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1974, 38, 657–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholten, T.; Geißler, C.; Goc, J.; Kühn, P.; Wiegand, C. A new splash cup to measure the kinetic energy of rainfall. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 2011, 174, 596–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Wu, X.; Cai, C. Splash erosion of clay–sand mixtures and its relationship with soil physical properties: The effects of particle size distribution on soil structure. Catena 2015, 135, 254–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaledi Darvishan, A.; Sadeghi, S.H.; Homaee, M.; Arabkhedri, M. Measuring sheet erosion using synthetic color-contrast aggregates. Hydrol. Process. 2014, 28, 4463–4471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watung, R.L.; Sutherland, R.A.; El-Swaify, S.A. Influence of rainfall energy flux density and antecedent soil moisture content on splash transport and aggregate enrichment ratios for a Hawaiian Oxisol. Soil Technol. 1996, 9, 251–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legout, C.; Leguedois, S.; Le Bissonnais, Y.; Issa, O.M. Splash distance and size distributions for various soils. Geoderma 2005, 124, 279–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzen, M.; Iserloh, T.; Casper, M.C.; Ries, J.B. Quantification of particle detachment by rain splash and wind-driven rain splash. CATENA 2015, 127, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Li, G.; Wang, D.; Zheng, T.; Yang, M. Raindrop Energy Impact on the Distribution Characteristics of Splash Aggregates of Cultivated Dark Loessial Cores. Water 2019, 11, 1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fu, Y.; Li, G.; Zheng, T.; Li, B.; Zhang, T. Splash detachment and transport of loess aggregate fragments by raindrop action. Catena 2017, 150, 154–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Raga, M.; Campo, J.; Rodrigo-Comino, J.; Keesstra, S.D. Comparative Analysis of Splash Erosion Devices for Rainfall Simulation Experiments: A Laboratory Study. Water 2019, 11, 1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bisal, F. Calibration of splash cup for soil erosion studies. Agric. Eng. 1950, 31, 621–622. [Google Scholar]
- Bisal, F. The effect of raindrop size and impact velocity on sand-splash. Can. J. Soil Sci. 1960, 40, 242–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mazurak, A.P.; Mosher, P.N. Detachment of Soil Particles in Simulated Rainfall 1. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1968, 32, 716–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vigiak, O.; Okoba, B.O.; Sterk, G.; Groenenberg, S. Modelling catchment-scale erosion patterns in the East African Highlands. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2005, 30, 183–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vigiak, O.; Sterk, G.; Romanowicz, R.J.; Beven, K.J. A semi-empirical model to assess uncertainty of spatial patterns of erosion. Catena 2006, 66, 198–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghadam, B.K.; Jabarifar, M.; Bagheri, M.; Shahbazi, E. Effects of land use change on soil splash erosion in the semi-arid region of Iran. Geoderma 2015, 241, 210–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghi, S.H.; Harchegani, M.K.; Asadi, H. Variability of particle size distributions of upward/downward splashed materials in different rainfall intensities and slopes. Geoderma 2017, 290, 100–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angulo-Martinez, M.; Beguería, S.; Navas, A.; Machin, J. Splash erosion under natural rainfall on three soil types in NE Spain. Geomorphology 2012, 175, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dexter, A.R. Effect of rainfall on the surface micro-relief of tilled soil. J. Terramechanics 1977, 14, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assouline, S.; Mualem, Y. Modeling the dynamics of seal formation and its effect on infiltration as related to soil and rainfall characteristics. Water Resour. Res. 1997, 33, 1527–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bretar, F.; Arab-Sedze, M.; Champion, J.; Pierrot-Deseilligny, M.; Heggy, E.; Jacquemoud, S. An advanced photogrammetric method to measure surface roughness: Application to volcanic terrains in the Piton de la Fournaise, Reunion Island. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 135, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oro, L.A.; Buschiazzo, D.E. Degradation of the soil surface roughness by rainfall in two loess soils. Geoderma 2011, 164, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Zheng, Z.; Li, T.; He, S. Spatial heterogeneity of microtopography and its influence on the flow convergence of slopes under different rainfall patterns. J. Hydrol. 2017, 545, 88–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angulo-Martínez, M.; Beguería, S.; Kyselý, J. Use of disdrometer data to evaluate the relationship of rainfall kinetic energy and intensity (KE-I). Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 568, 83–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lobo, G.P.; Bonilla, C.A. Sensitivity analysis of kinetic energy-intensity relationships and maximum rainfall intensities on rainfall erosivity using a long-term precipitation dataset. J. Hydrol. 2015, 527, 788–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meshesha, D.T.; Tsunekawa, A.; Tsubo, M.; Haregeweyn, N.; Tegegne, F. Evaluation of kinetic energy and erosivity potential of simulated rainfall using Laser Precipitation Monitor. CATENA 2016, 137, 237–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, B. Soil splash as an important agent of erosion. Geogr. Pol. 1990, 58, 99–106. [Google Scholar]
- Chesworth, W.; Camps Arbestain, M.; Macías, F.; Spaargaren, O.; Spaargaren, O.; Mualem, Y.; Morel-Seytoux, H.J.; Horwath, W.R.; Almendros, G.; Chesworth, W.; et al. Classification of Soils: World Reference Base (WRB) for Soil Resources; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2008; pp. 120–122. [Google Scholar]
- Kubínová, R. Grain Size Distribution of Eroded Soil. Master’s Thesis, Faculty of Civil Engineering, Czech Techical University in Prague, Prague, Czech Republic, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Kavka, P.; Neumann, M.; Laburda, T.; Zumr, D. Developing of the laboratory rainfall simulator for testing the technical soil surface protection measures and droplets impact. In Proceedings of the XVII ECSMGE-2019 European Conference on Soil Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering, Reykjavik, Iceland, 1–6 September 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Van Dijk, A.I.J.; Bruijnzeel, L.; Rosewell, C. Rainfall intensity–kinetic energy relationships: A critical literature appraisal. J. Hydrol. 2002, 261, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steiner, M.; Smith, J.A.; Steiner, M.; Smith, J.A. Reflectivity, Rain Rate, and Kinetic Energy Flux Relationships Based on Raindrop Spectra. J. Appl. Meteorol. 2000, 39, 1923–1940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wischmeier, W.H.; Smith, D.D. Predicting Rainfall Erosion Losses—A Guide to Conservation Planning; Science and Education Administration United States Department of Agriculture: Hyattsville, MD, USA, 1978; p. 58. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, L.C.; Foster, G.R. Storm Erosivity Using Idealized Intensity Distributions. Trans. ASABE 1987, 30, 0379–0386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrů, J.; Kalibová, J. Measurement and computation of kinetic energy of simulated rainfall in comparison with natural rainfall. Soil Water Res. 2018, 13, 226–233. [Google Scholar]
- Geißler, C.; Kühn, P.; Böhnke, M.; Bruelheide, H.; Shi, X.; Scholten, T. Splash erosion potential under tree canopies in subtropical SE China. CATENA 2012, 91, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angulo-Martínez, M.; Beguería, S.; Latorre, B.; Fernández-Raga, M. Comparison of precipitation measurements by OTT Parsivel2 and Thies LPM optical disdrometers. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2018, 22, 2811–2837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boroghani, M.; Hayavi, F.; Noor, H. Affectability of splash erosion by polyacrylamide application and rainfall intensity. Soil Water Res. 2012, 7, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, B.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Shen, N.; Liu, J. Evaluating and modelling splash detachment capacity based on laboratory experiments. CATENA 2019, 176, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farres, P.J. The dynamics of rainsplash erosion and the role of soil aggregate stability. CATENA 1987, 14, 119–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekwue, E.I. The effects of soil organic matter content, rainfall duration and aggregate size on soil detachment. Soil Technol. 1991, 4, 197–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, R.-M.; Li, Z.-X.; Cai, C.-F.; Wang, J.-G. The dynamic response of splash erosion to aggregate mechanical breakdown through rainfall simulation events in Ultisols (subtropical China). CATENA 2014, 121, 279–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei Arshad, R.; Mahmoodabadi, M.; Farpoor, M.H.; Fekri, M. Experimental investigation of rain-induced splash and wash processes under wind-driven rain. Geoderma 2019, 337, 1164–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Zheng, Z.; Li, T.; He, S. Assessing the impacts of microtopography on soil erosion under simulated rainfall, using a multifractal approach. Hydrol. Process. 2018, 32, 2543–2556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helming, K.; Roth, C.H.; Wolf, R.; Diestel, H. Characterization of rainfall-microrelief interactions with runoff using parameters derived from digital elevation models (DEMs). Soil Technol. 1993, 6, 273–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Reference | Soil | Sample Preparation, Experiment Specifications | Rainfall Intensity (mm h−1) | Rainfall Kinetic Energy (J m−2 mm−1) | Splash–Rainfall Relationship |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bisal 1960 [17,18] | Sand | Leveled with the rim | 76–152 | - | No significant relationship (R2 = 0.31) |
| Angulo-Martinez et al. 2012 [23] | Silty soil | Leveled 25 mm below the rim, under natural rainfall | 12–93 | 2–12 | Linear function |
| Geissler et al., 2012 [41] | Fine sand | Leveled with the rim; measured under forest vegetation where the throughfall’s KE is reported as 2.53 times higher | 1–45 | - | Linear function (R2 = 0.74) |
| Boroghani et al., 2012 [43] | Silt-clay-loam | Not known, only three datapoints measured | 69–120 | - | Linear function (R2 = 0.91) |
| Wu et al., 2019 [44] | Silty loam, seedbed conditions | Leveled with the rim | 48–150 | 4–7 | Polynomial function |
| Fernández-Raga et al., 2019 [15] | Fine sand | Leveled to the rim | 38–160 | 26–29 | Linear function (R2 = 0.18) |
| This study | Silty loam, seed bed conditions (Cambisol) | Leveled 10 mm below the rim | 19–78 | 11 | Linear function (R2 = 0.70) |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zumr, D.; Mützenberg, D.V.; Neumann, M.; Jeřábek, J.; Laburda, T.; Kavka, P.; Johannsen, L.L.; Zambon, N.; Klik, A.; Strauss, P.; et al. Experimental Setup for Splash Erosion Monitoring—Study of Silty Loam Splash Characteristics. Sustainability 2020, 12, 157. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12010157
Zumr D, Mützenberg DV, Neumann M, Jeřábek J, Laburda T, Kavka P, Johannsen LL, Zambon N, Klik A, Strauss P, et al. Experimental Setup for Splash Erosion Monitoring—Study of Silty Loam Splash Characteristics. Sustainability. 2020; 12(1):157. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12010157
Chicago/Turabian StyleZumr, David, Danilo Vítor Mützenberg, Martin Neumann, Jakub Jeřábek, Tomáš Laburda, Petr Kavka, Lisbeth Lolk Johannsen, Nives Zambon, Andreas Klik, Peter Strauss, and et al. 2020. "Experimental Setup for Splash Erosion Monitoring—Study of Silty Loam Splash Characteristics" Sustainability 12, no. 1: 157. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12010157
APA StyleZumr, D., Mützenberg, D. V., Neumann, M., Jeřábek, J., Laburda, T., Kavka, P., Johannsen, L. L., Zambon, N., Klik, A., Strauss, P., & Dostál, T. (2020). Experimental Setup for Splash Erosion Monitoring—Study of Silty Loam Splash Characteristics. Sustainability, 12(1), 157. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12010157