Abstract
Despite high expectations for the growth of Fintech, it has not reached the expected growth in the real world. As Fintech is innovative but inherently unpredictable, customers are still hesitant to adopt and use Fintech, which ultimately affects its growth. To achieve the sustainable development and growth of Fintech, an in-depth investigation of Fintech continuance intentions is required. To investigate continuous-use behavior in a Fintech context, this study focuses on two relevant issues: uncertainty and information technology (IT) quality. Uncertainty is more critical in Fintech than in traditional e-banking transactions because Fintech transactions are complicated and less predictable. IT quality is also crucial to Fintech success because IT plays a key role in Fintech transactions. This study mainly explores the relationship between uncertainty and IT quality, both of which significantly affect Fintech continuance intentions. For the purpose, we integrated an IT quality–based perspective with a trust-based model to investigate Fintech continuance intentions. Our results demonstrate that system quality is negatively related to perceived risk, whereas information quality is positively related to trust. Service quality is the most important quality factor for controlling uncertainty and encouraging continued use of Fintech. We found a more extended role of IT in Fintech than in other digital services. This study provides Fintech providers with the practical guidance in the design and implementation of Fintech innovation, thereby achieving the sustainable development of Fintech.
1. Introduction
Fintech is revolutionizing traditional financial transactions. Fintech is fundamentally disruptive because its major innovations of the existing financial systems and other infrastructure lead to diverse, new financial business with their own sustainable ecosystem [1,2]. Fintech is also regarded as an engine for a sustainable economic growth as a new industry having different characteristics from the traditional financial industry. With high expectations for the growth of Fintech, global Fintech investments have increased significantly. KPMG [3] reported that global investment in Fintech has doubled more than six times, from USD 18.9 billion to USD 111.8 billion between 2013 and 2018. Although the acceptance and use of Fintech among financial customers is gradually increasing, in the real world Fintech has not reached the expected growth. As Fintech is innovative but inherently unpredictable like both sides of the same coin, customers are still hesitant to adopt and use Fintech, which ultimately affects its growth. Fintech providers have faced a challenge to retain users and promote post-adoption use. To achieve the sustainable development and growth of Fintech, an in-depth investigation of Fintech continuance intentions is required.
To investigate continuous-use behavior in a Fintech context, this study focuses on two main issues: uncertainty and information technology (IT) quality. Uncertainty is more critical in Fintech than in traditional e-banking transactions because the disruptive nature of Fintech make them less predictable. Much uncertainty exists because Fintech intrinsically involves no supervision of central authorities, the lack of safety nets along with opportunistic behavior of Fintech providers, region-specific financial regulation, financial fraud, criminal usage and hacks, all of which can lead to monetary losses and social damage [4,5,6]. Thus, the uncertainty makes users hesitant to adopt and use Fintech, and eventually affects the speed and scope of the transition toward a sustainable development of Fintech. Uncertainty can be effectively reduced by building high levels of trust and low levels of perceived risks, satisfying customers’ expectations and retaining their loyalty [7,8,9]. In prior studies, the uncertainty in online and mobile transactions has been typically investigated by positioning trust and perceived risk [7,8,9]. Thus, to precisely investigate uncertainty in the Fintech context, both trust and perceived risk of Fintech need to be identified as well as their relationship with Fintech use. Although many studies have explored the effect of trust and risk on various digital services, little attention has been paid to theoretical and empirical validation in a Fintech context.
According to Arner et al. [10], Fintech is a financial sector innovation in which IT is a key element. Shin and Choi [11] pointed out that Fintech refers to IT-enabled financial solutions. Ernst and Young [12] highlighted the growing role of IT in Fintech, which is that of a true innovator, not a facilitator or enabler. They asserted that IT in Fintech transcends existing value chains and transforms services rather than simply improving efficiency. Given the key role of IT in Fintech innovation, customers may perceive IT quality as representative of overall Fintech quality; if users perceive that IT quality in Fintech is high, the likelihood of future use of Fintech may increase. That is, IT quality might be a crucial factor that facilitates the user’s willingness to use Fintech, leading to the long-term sustainability of Fintech. Although many studies have underlined the importance of IT in Fintech, an empirical study of the effect of IT on Fintech use has not yet been explored.
Although uncertainty and IT play critical roles in a sustainable development of Fintech, few studies have explored the relationships among uncertainty, IT, and Fintech continuous use. A deeper understanding of the interrelationships among uncertainty, IT, and Fintech continuous use can help Fintech providers to effectively attract and retain users, thereby accelerating the popularization of Fintech. Therefore, we investigated Fintech continuance intentions by applying an IT quality based perspective to a trust-based model. To evaluate overall perceptions of IT quality in Fintech, this study employed three IT quality dimensions (i.e., system, information, and service qualities) proposed by DeLone and McLean [13]’s information systems success (ISS) model. We then examined how IT quality can improve trust and reduce perceived risk to improve user willingness to continue using Fintech. Given the key role of IT in Fintech, IT quality may directly affect users’ continuance intentions by providing simple and speedy financial transactions, lower transaction costs, and temporal and spatial flexibility using mobile applications [5]. To validate the direct effect of IT on Fintech use, we conducted a mediation test of trust and perceived risk between IT quality and Fintech continuous use. That is, if no mediation effect exists between trust and perceived risk, IT quality should directly affect Fintech continuance intentions, demonstrating that high-quality IT by itself can retain Fintech users and facilitate Fintech use. However, a full mediation effect implies IT quality has only an indirect effect on Fintech continuance intentions, leaving no true innovator role for IT in Fintech innovation. Therefore, this study aimed to (1) investigate the direct effect of user trust and perceived risks on Fintech continuance intentions; (2) examine the direct effect of IT quality on user trust and perceived risk; and (3) determine the direct effect of IT quality on Fintech continuance intentions.
Drawing on data collected from 218 Fintech users in South Korea, we empirically validated the interrelationships among three IT qualities, trust, perceived risk, and subsequent Fintech continuance intentions. To ensure a sustainable development of Fintech in the long term, this study provides timely insight into how trust and perceived risk affect the diffusion of Fintech innovations and how IT quality affects uncertainty and subsequent user intentions of Fintech. Our study can help practitioners and policy makers appropriately incorporate IT into their service development to improve innovation success, thereby achieving the sustainable development of Fintech.
2. Theoretical Background
2.1. Fintech Viewpoint
The pace of technological change is ever increasing and ever more transformative. IT innovation accompanied by process disruption and service transformation has dominated the financial service industry in recent years [14]. The term “Fintech” refers to financial sector innovation, which relies on IT-enabled business models aimed at disintermediation of financial transactions. Disintermediation, an essential characteristic of Fintech, means bypassing or removing traditional financial institutions in finance transactions.
Fintech involves more uncertainty and risks compared with traditional e-banking or e-commerce transactions because the risks in Fintech are not limited to privacy and security, but extend to multidimensional concepts such as performance, transaction processes, and legal, social, financial and time-loss risks [4,5]. For example, peer-to-peer (P2P) lending arrangements can result in bankruptcy during economic recessions because the profitability of P2P lending is highly dependent on the loans they intermediate, putting their balance sheets at risk [15]. For payment services, the anonymity, speed, and global reach of some cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin can facilitate money laundering, tax evasion, and the funding of illegal activities [4]. Fintech providers who offer global remittance services across multiple countries are struggling with region-specific financial regulations [14]. As a result, the unpredictability of Fintech transactions makes some users fearful of Fintech usage. Researchers have pointed out that Fintech is more likely to be complementary to traditional financial institutions than a competitor because of the former’s high levels of uncertainty and risk [4,14]. The key to success in Fintech business is simultaneously improving customer trust and reducing risk.
Furthermore, a link between financial services and IT was originally applied to the back-end of financial transactions in traditional financial institutions. However, Fintech has expanded financial innovations from the back-end to front-end payments, cross-border transfers, retail banking, lending, and cryptocurrencies [14]. Ernst and Young [12] pointed out that IT in emergent Fintech is a true innovator that disrupts and transforms existing services, transaction processes, and delivery channels, leading to fundamental changes. Because IT has a greater impact in Fintech than it does in traditional e-banking, users may perceive IT quality as representative of overall Fintech quality. Although IT plays a key role for the sustainable development of Fintech, little attention has been paid its effect on continuous use and other factors in a Fintech context.
2.2. Trust and Perceived Risk
Trust is more essential in Fintech than in traditional e-commerce and e-banking transactions because of the implicit uncertainty and risk in Fintech transactions. Previous research has identified two roles of trust in financial transactions. First, trust is fundamental for capturing user behavior. Kim et al. [16] reported that trust can provide users with high expectations for their successful transactions, and they will use services with high satisfaction rates. Trust can positively influence customer intentions in various digital service contexts, such as e-commerce [16], internet banking [7], online social networks [17,18], mobile shopping [19,20], mobile banking [21,22], and mobile payments [23,24]. Fintech companies can simultaneously retain existing users and attract potential users if they supply a trustworthy environment in which users feel secure and are convinced their transactions are secure. Second, trust can reduce uncertainty and risk in an uncertain environment. Previous reports indicated that trust can reduce risks in e-commerce [16,25,26], internet banking [7], mobile shopping [19,27], mobile banking [28], and mobile payments [23,29]. Trust in financial transactions in particular can alleviate privacy and security concerns [30,31] as well as the risks associated with the opportunistic behavior of Fintech providers [19]. Trust is critical because trust drives Fintech-use behavior while reducing uncertainty and risk, and it has become a reliable strategy for effectively handling risky and uncertain financial transactions. Previous literature revealed that trust is defined as a user’s belief that a service provider will meet user expectations without introducing risks [32]. Hence, we defined trust as a user’s belief that a Fintech company will fulfill its transactional obligations to meet a user’s expectations.
Perceived risk is an important impediment to use behavior. Perceived risks come from users’ feelings of uncertainty or concerns about the behavior and possible negative outcomes associated with using a product or service [29,33]. Perceived risk is reportedly considered a negative factor in overall behavioral intentions across digital service contexts such as mobile payment and internet banking [7,23]. Security and privacy have been traditionally considered the main issues when it comes to risk [31], but more recent studies embrace a multidimensional concept that includes financial, performance, social, psychological, physical, and time risks [27,28,34,35,36] when consumers make transactions. In this study, perceived risk is defined as a user’s belief about the uncertainty leading to a potential negative outcome from a Fintech transaction. Although many studies have investigated the incorporation of trust and perceived risk during the adoption and use of technology, few have identified the relationships among trust, perceived risk, and Fintech behavioral intentions. Deep understandings of the effects of trust and risk on Fintech continuous use will help Fintech businesses meet their sustainable development goals.
2.3. IT Quality
The ISS model developed by DeLone and McLean [37] has been employed widely to examine user adoption and use in numerous digital services [38]. The ISS model introduced two success factors (i.e., system and information qualities) that are positively correlated with the use of digital services and user satisfaction; each has individual and organizational impacts. More recently, DeLone and McLean [13] extended their original model by incorporating a service quality factor that reflects the effectiveness of the service providers. Consequently, the ISS model consists of three quality dimensions: system, information, and service. System and information qualities are important factors to consider when measuring the success of individual IT system, and service quality is crucial for assessing the overall success of an IS (information systems) department [13].
Substantial studies have been carried out by integrating the ISS model with trust or perceived risk to predict continuance intentions in e-commerce [33,39,40], business-to-business data exchange [8,41], information exchange virtual communities [42], mobile banking [21,22], and mobile payment applications [23,38]. Given that the three quality dimensions of the ISS model were found to significantly influence user trust and perceived risk as well as behavior in online and mobile environments [7,8,23,31,33], the ISS model was a suitable tool for validating our research concept. In our proposed model, we conceptualized the three quality dimensions as potential trust facilitators and risk mitigators that indirectly influence continuance intentions in Fintech.
3. Research Model and Hypotheses
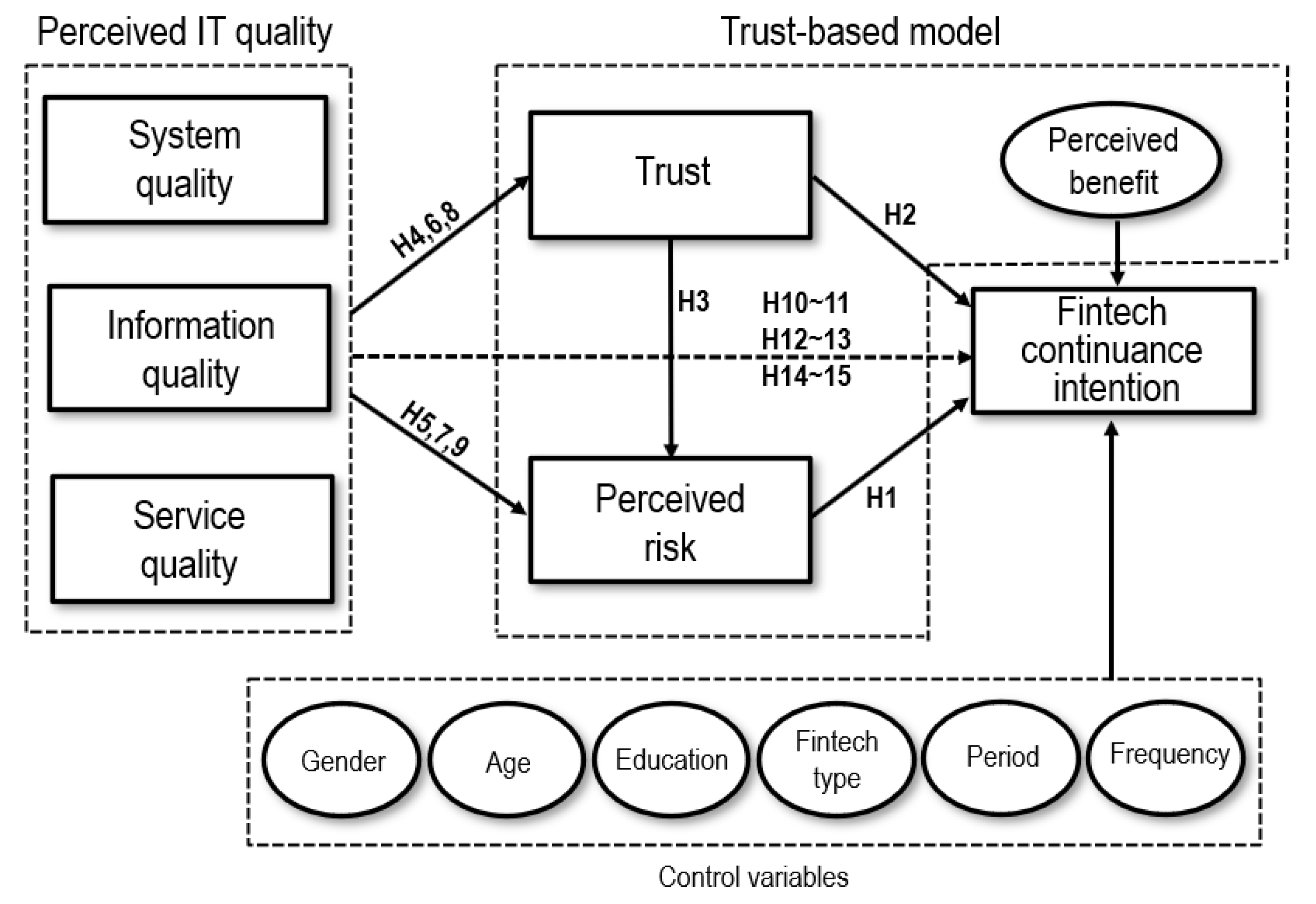
To examine the relationship among uncertainty, IT, and continuance intention in a Fintech context, we applied an IT quality perspective to a trust-based model. We employed the three IT quality dimensions (i.e., system, information, and service qualities) proposed by the ISS model to measure IT quality in Fintech. Our proposed model then attempted to investigate Fintech continuance intentions by adopting the three IT quality dimensions as antecedents of trust and perceived risk based on a Nicolaou and McKnight [8]’s model. To control for the effect of perceived benefits on Fintech continuous use, we added a perceived benefit construct to our model by referring to a trust-based decision-making model proposed by Kim et al. [16]. Finally, the mediation effect of trust and perceived risk between the three IT quality dimensions and Fintech continuance intentions were determined. The overall research model is shown in Figure 1.
Figure 1.
Research model.
The theory of perceived risk suggests that perceived risk has a negative effect on users’ behavioral decisions with respect to various digital services [8,27,28]. Customers face risks when they use an emerging digital service such as Fintech, because their transactions may not go as expected. For example, with respect to P2P lending and crowdfunding, there are no guarantees that Fintech providers will not act immorally and opportunistically. Fintech providers may misappropriate personal and financial data, including names, social security numbers, phone numbers, addresses, and even bank account and credit card information [5]. Moreover, Fintech users may suffer from financial losses because their financial transactions may not perform as anticipated or may be associated with tax evasion, money laundering, and the funding of illegal activities [4]. Fintech users therefore pay attention to the risks that might result in potential negative outcomes and such risks may weaken their willingness to continuously use Fintech. We therefore formulated the following hypothesis:
Hypothesis 1 (H1).
Perceived risk negatively affects Fintech continuance intention.
Recent IS research has described trust as a primary predictor of technology adoption and usage rates. Because Fintech is not a face-to-face financial service, the concerns of users about their financial transactions extend beyond the privacy and security issues of traditional financial services. In Fintech, trust becomes an important element in controlling uncertain and unpredictable situations. Trust occurs when users believe that Fintech providers provide high-quality services [43] that benefit their customers. For example, if Fintech providers offer users security and stability; updated, accurate, and comprehensive information; and high-quality services that meet users’ expectations, they can reduce user fears and build trust in their products.
In addition, trust can help reduce perceived risk because users can overcome uncertainty or anxiety regarding provider behavior and possible outcomes [44]. As more users trust mobile transactions, less risk is perceived [29,45]. Trust reduces the possibility that a Fintech company will engage in opportunistic behavior. Trusted Fintech providers can also reduce environmental uncertainties and risks related to financial infrastructure. That is, if users perceive that Fintech transactions are unpredictable and providers are opportunistic, their willingness to use Fintech can decline. Trust strengthens user confidence in a technology and attenuates perceived risks regarding Fintech transactions, the associated Fintech infrastructure, and Fintech providers. We therefore made the following hypotheses:
Hypothesis 2 (H2).
Trust positively affects Fintech continuance intention.
Hypothesis 3 (H3).
Trust negatively affects perceived risk.
System quality refers to perceptions derived from the overall performance of IT systems [13,21,46]. System quality reflects a system’s technical characteristics, including accessibility, ease of use, response time, reliability, and stability. Lee and Chung [47] claimed that users first impressions are based on their experience with IT systems. Poor system quality and challenging user interfaces can cause Fintech users to doubt the overall competence of a Fintech provider, leading to a decrease in trust and an increase in perceived risks. In contrast, users of high-performing Fintech systems are likely to trust Fintech, leading to continued use and a willingness to pay for the service [44]. The effect of system quality on user trust has been identified in e-commerce, internet banking, mobile banking and mobile payments [9,38,40]. Users’ perceptions of risk are also linked to technical support [36]. If a Fintech system is slow, difficult to use, unreliable, and unstable, Fintech users are more likely to worry about the release of their personal and financial information, malfunctions in Fintech systems, and non-performance caused by system failure [5]. With low-quality IT systems, users may conclude that Fintech providers lack the ability to provide high-quality services in general, which leads to lower trust and higher perceived risk in Fintech. We therefore developed the following hypotheses:
Hypothesis 4 (H4).
System quality positively affects trust.
Hypothesis 5 (H5).
System quality negatively affects perceived risk.
Information quality refers to an individual’s perception of service providers’ abilities to meet the user’s needs [13,21,46]. High information quality is relevant, accurate, helpful, and comprehensive [31]. Nicolaou and McKnight [8] stressed the importance of information quality in building trust in online interactions because users tend to depend on service providers for current, relevant, timely, and insightful information. When service providers provide higher-quality information, user trust increases. For example, although customers expect to pay for products or services and receive payment information through mobile applications anytime and anywhere, insufficient, inaccurate, or outdated information can lead customers to doubt the information management abilities of Fintech providers [42,47]. Prior studies have indicated a significant and positive relationship between information quality and trust in online and mobile environments [8,23,38,41]. Moreover, information quality can help reduce uncertainty because shared, accurate, current, and relevant information can mitigate unpredictable outcomes. As high-quality information meets users’ needs, confidence in information quality can weaken perceived risks. We therefore proposed:
Hypothesis 6 (H6).
Information quality positively affects trust.
Hypothesis 7 (H7).
Information quality negatively affects perceived risk.
Service quality is defined as an individual’s perception of the level of support received from an IS department and its IT support system [13,40,46]. Service quality generally represents service providers’ abilities and benevolence, reflecting reliability, responsiveness, assurance capacity, and personalization [23,31]. A positive effect on user trust has been linked to service quality in previous IS studies [7,22,23,31]. Trust in Fintech is driven by users’ confidence that providers can carry out financial transactions, keep their promises, and are sensitive to users’ interests, not just their own [26]. For example, when providers offer quick responses and proficient service, users come to believe that a provider can satisfy their expectations. Moreover, personalized and professional services that use mobile applications can reduce the time and effort involved in financial transactions and provide users with enjoyable experiences, leading to increased user trust [23]. Service quality can be a distinguishing characteristic for Fintech providers and improve users’ trust. It also has a negative relationship with perceived risk in digital services [7,33,48]. For example, if a Fintech provider offers slow, unreliable, and unprofessional service, users may greatly increase the perceived risk associated with the provider. We therefore hypothesized that:
Hypothesis 8 (H8).
Service quality positively affects trust.
Hypothesis 9 (H9).
Service quality negatively affects perceived risk.
The three quality factors in the ISS model (i.e., system, information, and service qualities) were found to be fully mediated by trust and perceived risk in various digital services [7,31,33,41]. However, in the real world, and given the expanding role of IT in Fintech, the three dimensions of the ISS model may directly affect Fintech continuance intentions by lowering transaction costs, providing simple and speedy processes, and adding economic benefits [8]. Previous studies provided no empirical evidence for the mediating effects of trust and perceived risk among the three types of IT quality and intentions to use Fintech. That is, while it is likely that trust and perceived risk have significant mediating effects, they may not fully mediate the effects of the three dimensions of IT quality in every setting. For example, high-quality Fintech systems by themselves may attract and retain Fintech users and there may be a partial mediation effect of trust and perceived risk between system quality and Fintech continuance intention. We therefore developed the following hypotheses:
Hypothesis 10 (H10).
The effect of system quality on Fintech continuance intention is partially mediated by trust.
Hypothesis 11 (H11).
The effect of system quality on Fintech continuance intention is partially mediated by perceived risk.
Hypothesis 12 (H12).
The effect of information quality on Fintech continuance intention is partially mediated by trust.
Hypothesis 13 (H13).
The effect of information quality on Fintech continuance intention is partially mediated by perceived risk.
Hypothesis 14 (H14).
The effect of service quality on Fintech continuance intention is partially mediated by trust.
Hypothesis 15 (H15).
The effect of service quality on Fintech continuance intention is partially mediated by perceived risk.
4. Research Methodologies
4.1. Measurement Development
Survey items were developed from an intensive literature review to ensure content validity. Multiple item measures of seven constructs were developed from a review of previous innovations and IS reports. We measured three items of both trust and perceived risk from Featherman and Pavlou [49] and Kim et al. [16]. The three IT quality dimensions in the ISS model, namely system quality, information quality, and service quality, were each measured by four items drawn primarily from Bharati and Chaudhury [50]. Measurement of Fintech continuance intentions as a dependent variable was based on four items from Chen [48] and Lee [51]. All measures were based on a seven-point Likert scale that ranged from “extremely low (1)” to “extremely high (7).” The structure of all survey items is shown in Appendix A.
Based on the trust-based model proposed by Kim et al. [16], perceived benefit was controlled in our proposed model because perceived benefit is an important factor in determining behavioral intentions regarding digital services [5,52,53]. Perceived benefit is defined as an individual’s perception of the possible positive outcomes resulting from using a product or service. Previous studies have pointed out that perceived benefit is particularly crucial to Fintech continuance intentions because real-world Fintech users may engage in risky behavior, despite a low level of trust, if the expected benefits are sufficiently attractive. For example, Bitcoin users engage in speculation because of expectations of high rates of return, although they recognize that Bitcoin speculation is inherently risky. In this study, the perceived benefit was measured by three items from Kim et al. [16] and Ryu [5]: (1) using Fintech is beneficial to me; (2) using Fintech is useful for me; (3) using Fintech yields a more superior outcome quality than traditional financial services.
Gender, age, education, Fintech type, period of use, and frequency of use were also employed as control variables in our research model. Dapp et al. [54] indicated that Fintech adoption and its use differ by gender, age, education, income, and the personal propensities of the users because gender, age, and education are considered important demographic variables in technology acceptance research [55,56]. Gender was measured by the respondents answering that they were either male or female. Age and education were measured with ordinal scales (five categories for age, six categories for education, respectively). Fintech type was controlled using a dummy variable consisting of four Fintech services (i.e., mobile payment, mobile remittance, P2P lending, and crowdfunding). As recent studies have identified period and frequency of actual use as important factors affecting Fintech-use intentions [57,58], we also controlled for the period and frequency of Fintech use using ordinal scales (six categories for period, seven categories for frequency, respectively).
4.2. Data Collection
A pre-test was conducted to determine the reliability and validity of all variables by focusing on 30 respondents who had experience using Fintech. The pre-test resulted in a significant refining and restructuring of the questionnaire as well as establishing the initial face and internal validity of the measures. After the pre-test, questionnaires of a main survey were distributed to 1000 participants as a panel pool for three weeks in April 2017. The survey targeted users who had actively used Fintech for more than three months. If inconsistency was detected during a response in the panel, the data were discarded, and the respondent was excluded from the panel pool. With this initial screening question, we confirmed that respondents fully understood the survey context and whether they were current Fintech users. Among the 1000 participants, 262 responses were collected, and 218 responses were found to be useful for this study, corresponding to a response rate of 21.8%. Table 1 summarizes the respondent characteristics. As shown in Table 1, many responses came from mobile payment (28.9%), mobile remittance (26.6%), crowdfunding (24.3%) and P2P lending (20.2%) uses. Our sample consisted predominantly of those who used Fintech monthly (35.8%) or within one year (76.7%). The sample also showed a large proportion of respondents aged 40–49 years (30.3%) with a bachelor’s degree (59.2%).

Table 1.
Sample characteristics.
5. Analysis and Results
We examined the proposed model and its hypotheses using the partial least squares (PLS) tool. Considering the small sample size (n = 218) and an initial stage to develop a theoretical model for the effect of IT quality on trust, perceived risk, and Fintech continuance intentions, the fit of PLS to the exploratory study appeared to be favorable [59]. Based on Gefen et al. [60], this study employed a two-step approach to conduct data analysis. The first step analyzed the measurement model and the second step involved a structural model test. Smart PLS version 3.20 was employed to analyze the measurements and structural models.
5.1. Measurement Model
Following a two-step approach developed by Gefen et al. [60], the measurement model tested the content, convergent, and discriminant validities. To validate content, several pre-tests and pilot tests were performed [61]. For the responsibility test, we evaluated Cronbach’s alpha, the composite reliability (CR) and average variance extracted (AVE) for each construct.
As seen in Table 2, all Cronbach’s alpha and CR values exceeded the recommended threshold of 0.7 and all AVE values exceeded the 0.5 acceptance level [62], supporting convergent validity. The square root of AVE (SAVE) was used to determine discriminant validity [62]. As shown in Table 3, SAVE values of all constructs exceeded the correlation with the other constructs. We found variance inflation factor (VIF) values ranged from 1.458 to 1.884, a low level of multicollinearity [46]. Finally, to control for common method variance (CMV) [63], we applied Harman’s single-factor test; no excessive CMV was found. These results indicated that the measurement model was appropriate for further analysis.

Table 2.
Results of reliability and validity test.

Table 3.
Results of correlations test with square root of AVE.
5.2. Structural Model
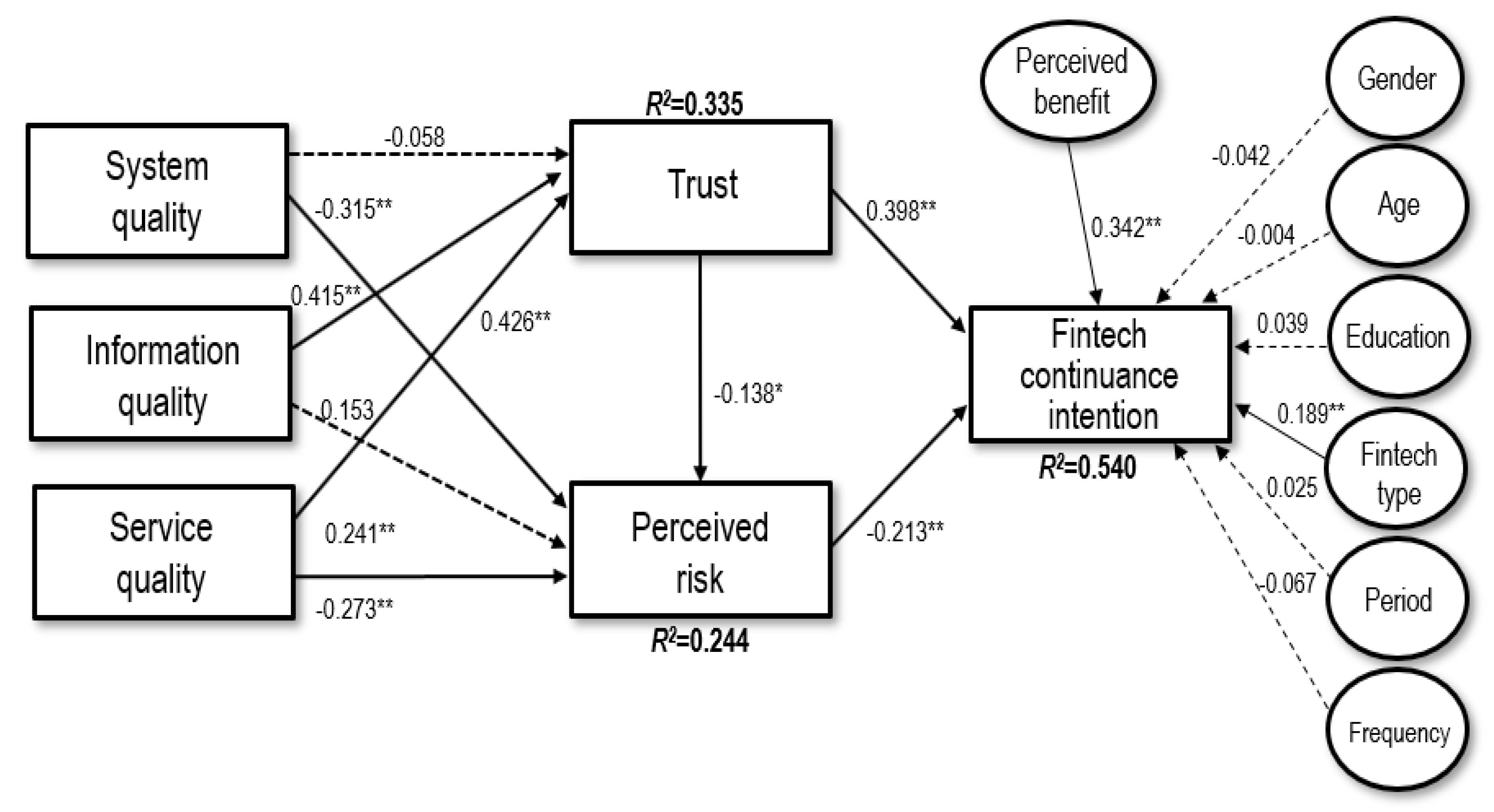
In the second step, the structural model was estimated using PLS. Figure 2 depicts the results of PLS in the proposed model, including path loading and significant levels of the paths. As a control variable, the perceived benefit positively influenced Fintech continuance intentions (β = 0.342, p < 0.01), which was consistent with previous studies [5,16,52,64]. Of the other six control variables, only Fintech type showed a significant and positive relationship with continuance intention (β = 0.189, p < 0.01). The research model accounted for 33.5% of the variance in trust, 24.4% of the perceived risk, and 54.0% of the Fintech continuous-use intentions.
Figure 2.
Results of the proposed research model. Note: *p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01.
Figure 2 shows that the perceived risk negatively influenced respondents’ willingness to continuously use Fintech (β = −0.213, p < 0.01), supporting H1. Trust was positively related with Fintech continuance intentions (β = 0.398, p < 0.01), supporting H2. These results indicated that trust had a significant and positive effect, but perceived risk had a significant and negative effect, on the Fintech continuance intentions. The effect of trust was stronger than that of perceived risk, indicating that users were willing to continue using Fintech. Moreover, trust had a significant negative effect on perceived risk (β = −0.138, p < 0.05). Therefore, H3 was supported. This result showed that building trust helped significantly mitigate the effects of perceived risk.
The results also demonstrated that system quality had no significant effect on trust, whereas system quality had significant and negative effects on perceived risk (β = −0.315, p < 0.01). Therefore, H4 was not supported but H5 was. Information quality positively affected trust (β = 0.415, p < 0.01), but exerted no significant effect on perceived risk. Contrary to system quality, it provided support for H6 but not H7. Service quality positively affected trust (β = 0.241, p < 0.01) but negatively influenced perceived risk (β = −0.273, p < 0.01). The results therefore supported H8 and H9. This finding showed that service quality was associated with both trust and perceived risk while system quality was more related to perceived risk than to trust, and information quality was more related to trust than to perceived risk.
Because we assumed that user IT quality perceptions directly and indirectly affected Fintech continuance intentions through trust and perceived risk, we validated six mediated paths (i.e., H10–11, H12–13 and H14–15) in two different ways. First, a Sobel test was conducted to validate the mediation effects of trust and perceived risk in the proposed model [65]. As described in Table 4, four out of all six mediation paths via trust and perceived risk were significant at p values of <0.01, <0.05, and <0.10. The results suggested that trust statistically mediated the links between the two quality dimensions (i.e., information and service) and Fintech continuance intention (z = 2.896, p = 0.002; z = 2.107, p = 0.035) as shown in rows 3 and 5 of Table 4. Perceived risk also significantly mediated the relationships between two IT qualities (i.e., system and service) and Fintech continuance intention (z = −2.132, p = 0.033; z = 1.828, p = 0.068) (rows 2 and 6).

Table 4.
Results of Sobel test of mediated paths from quality to Fintech continuance intention.
Second, we identified direct, indirect, and total effects of all paths in the research model, as shown in Table 5. Consistent with the results of a Sobel test, four out of all six indirect effects of mediation paths were significant at a 0.05 level. The results also showed that system quality was mediated by perceived risk (β = −0.315, p < 0.01) but not by trust (rows 5 and 6), whereas information quality was mediated by trust (β = 0.415, p < 0.01) but not by perceived risk (rows 7 and 8). Moreover, service quality was mediated by both trust and perceived risk (β = 241, p < 0.05; β = −0.273, p < 0.01) (rows 10 and 11). However, we also found direct effects between quality dimensions and Fintech continuance intention. Information quality and service quality had significant direct effects on Fintech continuance intention (β = 0.144, p = 0.020; β = 0.161, p = 0.003) (rows 9 and 12), whereas system quality had no direct effect on Fintech continuance intention (rows 6). It meant that system quality was fully mediated by perceived risk, information quality was partially mediated by trust, and service quality was partially mediated by both trust and perceived risk.

Table 5.
Direct, indirect, and total effect of all paths.
Consequently, as shown in Table 6, the results of these two mediation tests revealed that system quality was fully mediated only by perceived risk, providing no support for H10 and H11. The findings also indicated that trust partially mediated the effect of information quality on continuance intentions. H12 was therefore supported but H13 was not. Both trust and perceived risk partially mediated the effect of service quality on continuance intention, supporting H14 and H15.

Table 6.
Test results of six mediated paths.
6. Discussions and Implications
6.1. Key Findings
As the disruptive nature of Fintech results in uncertainties as well as new innovations, Fintech has faced critical problems in achieving sustainable development. Therefore, this study attempted to understand the relationship between uncertainty, innovation (IT), and subsequent Fintech behavioral intention. Given that IT plays a key role in Fintech innovation, we assumed that IT quality directly and indirectly influences Fintech continuance intentions through uncertainty. For this purpose, we developed the proposed model by integrating an ISS model with a trust-based model. Ten out of fifteen hypotheses were supported.
First, our findings suggested that system quality is negatively related to perceived risk, whereas information quality is positively related to trust, which is consistent with previous research [8,22,23,38,40]. The results indicated that system quality primarily mitigates perceived risk, leading to improved Fintech continuance intentions, but has no direct effect on trust. Poor system quality makes Fintech users anxious about transaction security and therefore reluctant to continue using Fintech. However, user trust does not rely on high system quality itself, as users often believe that high system quality is integral to Fintech providers. Information quality is the most consequential positive factor for building trust in Fintech use. Zhou [22] indicated that information quality represents service providers’ trustworthiness. If information quality is low, users may assume Fintech providers lack the ability to provide quality service, leading to a decline in trust. Our findings indicated that users depend primarily on information quality to develop trust and rely largely on system quality to mitigate perceived risk, which ultimately affects Fintech continuous use.
Second, we found that high levels of service quality simultaneously improve trust and reduce perceived risk, which had the strongest effect on Fintech continuance intentions among the three quality dimensions. Previous studies showed that service quality is critical to facilitate behavioral intentions in many e-banking and e-commerce services [7,23,33,66]. Consistent with extant studies, our results indicated that service quality significantly affects both trust and perceived risk, although service quality is slightly more effective at mitigating perceived risk (β = −0.273, p < 0.01) than improving trust (β = 0.241, p < 0.01). For example, high service quality, such as immediate responsiveness and a willingness to help, breeds confidence among users that Fintech transactions are trustworthy, resulting in a willingness to continue using Fintech. Fintech that offer high service quality can therefore reduce concerns and doubts of Fintech users about providers’ abilities, replacing those fears with confidence. Given that the effect of service quality on both trust and perceived risk is greater than that of other two quality factors, service quality is the most important quality factor among the three dimensions for controlling uncertainty and encouraging continued use of Fintech.
Third, we discovered that each quality dimension plays a different role in Fintech continuance intentions. Previous IS studies have indicated that the three quality dimensions had indirect effects on technology adoption and use through trust or perceived risk [7,8,23,38]. However, we found that two out of the three quality dimensions (i.e., information and service qualities) directly and indirectly affect Fintech continuance intentions via trust and perceived risk, indicating the enhanced role of IT in Fintech. The results meant that the effects of IT on attracting and retaining Fintech users were extended. However, system quality had only an indirect effect on Fintech continuance intention via perceived risk, indicating IT systems themselves have a limited ability to drive the behavioral intention of users. Overall, our findings confirmed the more extended role of IT in Fintech than that in other digital services, revealing the importance of IT for sustainable development of Fintech.
Finally, trust directly and indirectly improves Fintech continuance intentions, which is also consistent with previous studies. Trust is the strongest predictor of Fintech continuance intentions as well as the largest negative factor in perceived risk. Multiple studies have reported that Fintech is inherently risky and unpredictable, and users need the opportunity to acquire confidence before engaging in such financial transactions. This study also showed that trust reduces perceived risk, indicating that when Fintech users feel the risk reduced, the likelihood of using Fintech will increase. trust-building strategies and risk-mitigation strategies are required for Fintech providers to enhance continuous use of Fintech and meet sustainable development.
6.2. Managerial Implications
From a managerial perspective, this study presents several important implications. First, it provides useful insight into methods of effectively developing Fintech innovation strategies to realize the sustainable development of Fintech. Our study identified the causal relationship between IT, trust, perceived risk, and Fintech continuance intention. For example, we found that users develop trust and continue to use Fintech when they believe information provided by Fintech providers is of high quality and trustworthy because information quality is a strong facilitator of trust. Given that system and service quality can effectively reduce perceived risks, Fintech managers should recognize that user anxiety about the inherent and unpredictable risks of Fintech transactions can be alleviated when Fintech providers provide high-quality IT systems and service. Our findings can provide guidance to Fintech managers regarding innovation by combining IT development with trust-building and risk-mitigating strategies to meet a sustainable development of Fintech.
Second, Fintech managers should recognize the extended role of IT as an important antecedent of trust, perceived risk, and continuance intentions. Previous studies on digital services have identified an indirect effect of IT quality on behavioral use patterns and have regarded trust and perceived risk as full mediators. However, we found that information and service quality directly and indirectly affect Fintech continuance intention, whereas system quality only indirectly influences them. In other words, high-quality information and service can directly enhance trust, directly and indirectly mitigate perceived risk, and directly facilitate continuance intentions at the same time. Our findings imply that information and service quality in Fintech systems are major elements of user-retention strategies. Fintech managers should therefore focus on enhancing the IT quality of Fintech to attract and retain Fintech users, promoting Fintech innovation as beneficial in the long term.
Last, this study confirms that Fintech managers should establish trust to nurture continued Fintech use. Given uncertainty issues from the disruptive nature of Fintech, a trust-building strategy is essential to mitigating uncertainty and improving use behavioral patterns in Fintech. Our results show that high system and service quality can mitigate perceived risk, leading consequently to improved levels of trust. Information quality is the strongest and most direct trust facilitator and exerts the greatest impact on trust among the three quality dimensions. To gain a sustainable development of Fintech, Fintech providers should focus their Fintech innovation on how to build trust by adopting and utilizing new information technologies.
6.3. Limitations and Future Research Directions
Several limitations are associated with this study, some of which suggest directions for future research. First, although we measured unidimensional constructs of trust and perceived risks in a Fintech context, multifaceted, multidimensional trust and risk were not examined. As the effects of unidimensional trust and perceived risk can be biased, subsequent research should provide insights into multifaceted trust (e.g., competence, integrity, and benevolence) and perceived risk (e.g., financial, legal, security-related, privacy, performance, and time risks) to capture post-adoption phenomena in a Fintech context. Second, although our research was based on a trust-oriented model integrated with an ISS model, there may be alternative models which can explain the different relationships among IT quality, trust, perceived risk, and Fintech continuance intentions. For example, trust can be regarded as a moderator between perceived risk and continuance intentions [32]. In this view, trust affects behavior intentions only when transactions are perceived as risky. From another perspective, the relationship between trust and perceived risk can be non-recursive [67]. Given the early stage of Fintech research, future studies should consider how these alternative models may complement explanations of Fintech-use phenomena and how these models can be integrated. Third, this study is a snapshot that focuses on post-adoption behavior of Fintech; it does not consider the changing and dynamic nature of Fintech-use phenomena. Ideally, longitudinal studies that track Fintech adoption behaviors over time are needed. This study suggests that future efforts can provide valuable insights into the dynamic features of Fintech adoption behavior over time by comparing pre-adoption and post-adoption behaviors. Finally, the cultural factors embedded in the empirical context of our study, i.e., Korea, limit our ability to generalize our conclusions to broader contexts, such as those of Singapore, Hong Kong, the UK, USA, and China. Future research that includes different cultural settings would enhance generalizability and external validity.
Author Contributions
H.-S.R. conceived and designed the research, collected and analyzed data, and wrote the original draft; K.S.K. contributed to the progress of the research idea, and the overall review and editing. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Appendix A

Table A1.
Structure of the survey instrument.
Table A1.
Structure of the survey instrument.
| Constructs | ID | Questionnaire | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Perceived risk (PR) | PR1 | Using Fintech has many unexpected problems. | [16,30] |
| PR2 | Using Fintech has high uncertainty in respect of legal issues | ||
| PR3 | Overall, there is a higher potential for loss in using Fintech than using traditional financial services. | ||
| Trust (TR) | TR1 | Fintech is secure in conducting its transaction. | [49,51] |
| TR2 | Fintech is reliable in conducting its transactions. | ||
| TR3 | Overall, Fintech is trustworthy. | ||
| System quality (STQ) | STQ 1 | Fintech systems are easy to use. | [13,43] |
| STQ 2 | Fintech systems can be accessed immediately. | ||
| STQ 3 | Fintech systems enable me to accomplish my financial transactions. | ||
| SYQ 4 | Fintech systems provide helpful functions for my financial transactions. | ||
| Information quality (IFQ) | IFQ 1 | Information provided by Fintech systems is accurate. | [13,43] |
| IFQ 2 | Information provided by Fintech systems is up to date. | ||
| IFQ 3 | Information provided by Fintech systems is easy to understand. | ||
| IFQ 4 | Information provided by Fintech systems meets my needs. | ||
| Service quality (SVQ) | SVQ 1 | Fintech service quickly responds to my needs. | [13,43] |
| SVQ 2 | Fintech service has the knowledge to answer my questions. | ||
| SVQ 3 | Fintech service understands my specific needs. | ||
| SVQ 4 | Fintech service is always willing to help me. | ||
| Continuance intention (CI) | CI1 | I would positively consider Fintech in my choice set. | [48,51] |
| CI2 | I would prefer Fintech. | ||
| CI3 | I would intend to continue to use Fintech. | ||
| CI4 | I will use Fintech in the future. |
References
- Deng, X.; Cheng, X. Can ESG indices improve the enterprises’ stock market performance? An empirical study from China. Sustainability 2019, 11, 4765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zavolokina, L.; Dolata, M.; Schwabe, G. Fintech-What’s in a Name? In Proceedings of the 37th International Conference on Information Systems (ICIS 2016), Dublin, Ireland, 11–14 December 2016; pp. 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- KPMG 2019. The Pulse of Fintech 2018. KPMG. Available online: https://assets.kpmg/content/dam/kpmg/xx/pdf/2018/07/h1–2018-pulse-of-fintech.pdf (accessed on 1 November 2019).
- Cortina, J.J.; Schmukler, S.L. The Fintech Revolution: A Threat to Global Banking; World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Ryu, H.S. What makes users willing or hesitant to use Fintech?: The moderating effect of user type. Ind. Manag. Data Syst. 2018, 118, 541–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobehart, J.R. The FinTech revolution: Quantifying earnings uncertainty and credit risk in competitive business environments with disruptive technologies. J. Risk Manag. Financ. Inst. 2016, 9, 163–174. [Google Scholar]
- Namahoot, K.S.; Laohavichien, T. Assessing the intentions to use internet banking: The role of perceived risk and trust as mediating factors. Int. J. Bank Mark. 2018, 36, 256–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolaou, A.I.; McKnight, D.H. Perceived information quality in data exchanges: Effects on risk, trust, and intention to use. Inf. Syst. Res. 2006, 17, 332–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.-L. Customer adoption of Internet banking: An integration of TAM with trust, perceived risk, and quality. In Proceedings of the 2010 International Conference on Multimedia Information Networking and Security, Nanjing, Jiangsu, China, 4–6 November 2010; pp. 264–268. [Google Scholar]
- Arner, D.W.; Barberis, J.N.; Buckley, R.P. The Evolution of Fintech: A New Post-Crisis Paradigm; University of Hong Kong: Hong Kong, China, 2015; pp. 1–46. [Google Scholar]
- Shin, J.S.; Choi, Y. Feasibility of the Fintech Industry as an Innovation Platform for sustainable economic growth in Korea. Sustainability 2019, 11, 5351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ernst and Young. Landscaping UK Fintech. UK Trade & Investment. 2015, 1, 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- Delone, W.H.; McLean, E.R. The DeLone and McLean model of information systems success: A ten-year update. J. Manag. Inf. Syst. 2003, 19, 9–30. [Google Scholar]
- Gomber, P.; Kauffman, R.J.; Parker, C.; Weber, B.W. On the fintech revolution: Interpreting the forces of innovation, disruption, and transformation in financial services. J. Manag. Inf. Syst. 2018, 35, 220–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirgüç-Kunt, A.; Kane, E.; Laeven, L. Deposit insurance around the world: A comprehensive analysis and database. J. Financ. Stab. 2015, 20, 155–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.J.; Ferrin, D.L.; Rao, H.R. A trust-based consumer decision-making model in electronic commerce: The role of trust, perceived risk, and their antecedents. Dec. Supp. Syst. 2008, 44, 544–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratono, A.H. From social network to firm performance: The mediating effect of trust, selling capability and pricing capability. Manag. Res. Rev. 2018, 41, 680–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.-C.; Huang, Y.; Hsu, C.-L. Benevolence trust: A key determinant of user continuance use of online social networks. Inf. Syst. e-Bus. Manag. 2014, 12, 189–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marriott, H.R.; Williams, M.D. Exploring consumers perceived risk and trust for mobile shopping: A theoretical framework and empirical study. J. Retail. Consum. Serv. 2018, 42, 133–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S. Role of transfer-based and performance-based cues on initial trust in mobile shopping services: A cross-environment perspective. Inf. Syst. e-Bus. Manag. 2016, 14, 47–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.K.; Sharma, M. Examining the role of trust and quality dimensions in the actual usage of mobile banking services: An empirical investigation. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2019, 44, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T. Understanding users’ initial trust in mobile banking: An elaboration likelihood perspective. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2012, 28, 1518–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Waechter, K.A. Examining the role of initial trust in user adoption of mobile payment services: An empirical investigation. Inf. Syst. Front. 2017, 19, 525–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Yang, Z. Examining mobile payment user adoption from the perspective of trust. Int. J. u-and e-Serv. Sci. Tech. 2015, 8, 117–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlou, P.A. Consumer acceptance of electronic commerce: Integrating trust and risk with the technology acceptance model. Int. J. Electron. Commer. 2003, 7, 101–134. [Google Scholar]
- Pavlou, P.A.; Gefen, D. Building effective online marketplaces with institution-based trust. Inf. Syst. Res. 2004, 15, 37–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groß, M. Impediments to mobile shopping continued usage intention: A trust-risk-relationship. J. Retail. Consum. Serv. 2016, 33, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Li, H.; Zhang, J.; Shim, J.P. Examining multi-dimensional trust and multi-faceted risk in initial acceptance of emerging technologies: An empirical study of mobile banking services. Dec. Supp. Syst. 2010, 49, 222–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slade, E.L.; Dwivedi, Y.K.; Piercy, N.C.; Williams, M.D. Modeling consumers’ adoption intentions of remote mobile payments in the United Kingdom: Extending UTAUT with innovativeness, risk, and trust. Psy. Mark. 2015, 32, 860–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, H.; Jürjens, J. Data security and consumer trust in FinTech innovation in Germany. Inf. Comput. Secur. 2018, 26, 109–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, E.S.-T.; Lin, R.-L. Perceived quality factors of location-based apps on trust, perceived privacy risk, and continuous usage intention. Behav. Inf. Tech. 2017, 36, 2–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, R.C.; Davis, J.H.; Schoorman, F.D. An integrative model of organizational trust. Acad. Manag. Rev. 1995, 20, 709–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, M.-T.; Tsao, W.-C. Reducing perceived online shopping risk to enhance loyalty: A website quality perspective. J. Risk Res. 2014, 17, 241–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forsythe, S.; Liu, C.; Shannon, D.; Gardner, L.C. Development of a scale to measure the perceived benefits and risks of online shopping. J. Inter. Mark. 2006, 20, 55–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forsythe, S.M.; Shi, B. Consumer patronage and risk perceptions in Internet shopping. J. Bus. Res. 2003, 56, 867–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, N. Consumers’ perceived risk: Sources versus consequences. Electron. Commer. Res. Appl. 2003, 2, 216–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeLone, W.H.; McLean, E.R. Information systems success: The quest for the dependent variable. Inf. Syst. Res. 1992, 3, 60–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T. An empirical examination of continuance intention of mobile payment services. Dec. Supp. Syst. 2013, 54, 1085–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, M.-H.; Chang, C.-M.; Chu, K.-K.; Lee, Y.-J. Determinants of repurchase intention in online group-buying: The perspectives of DeLone & McLean IS success model and trust. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2014, 36, 234–245. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.-T.; Wang, Y.-S.; Liu, E.-R. The stickiness intention of group-buying websites: The integration of the commitment–trust theory and e-commerce success model. Inf. Manag. 2016, 53, 625–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKnight, D.H.; Lankton, N.K.; Nicolaou, A.; Price, J. Distinguishing the effects of B2B information quality, system quality, and service outcome quality on trust and distrust. J. Strateg. Info. Syst. 2017, 26, 118–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Zhao, K.; Stylianou, A. The impacts of information quality and system quality on users’ continuance intention in information-exchange virtual communities: An empirical investigation. Dec. Supp. Syst. 2013, 56, 513–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.S. Assessing e-commerce systems success: A respecification and validation of the DeLone and McLean model of IS success. Inf. Syst. J. 2008, 18, 529–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKnight, D.H.; Choudhury, V.; Kacmar, C. The impact of initial consumer trust on intentions to transact with a web site: A trust building model. J. Strateg. Inf. Syst. 2002, 11, 297–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, T.; Faria, M.; Thomas, M.A.; Popovič, A. Extending the understanding of mobile banking adoption: When UTAUT meets TTF and ITM. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2014, 34, 689–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petter, S.; DeLone, W.; McLean, E. Measuring information systems success: Models, dimensions, measures, and interrelationships. Eur. J. Inf. Syst. 2008, 17, 236–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.C.; Chung, N. Understanding factors affecting trust in and satisfaction with mobile banking in Korea: A modified DeLone and McLean’s model perspective. Interact. Comput. 2009, 21, 385–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C. Perceived risk, usage frequency of mobile banking services. Int. J. Manag. Serv. Qual. 2013, 23, 410–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Featherman, M.S.; Pavlou, P.A. Predicting e-services adoption: A perceived risk facets perspective. Int. J. Hum. Comput. Stud. 2003, 59, 451–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharati, P.; Chaudhury, A. An empirical investigation of decision-making satisfaction in web-based decision support systems. Dec. Supp. Syst. 2004, 37, 187–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.C. Factors influencing the adoption of internet banking: An integration of TAM and TPB with perceived risk and perceived benefit. Electron. Commer. Res. Appl. 2009, 8, 130–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abramova, S.; Böhme, R. Perceived benefit and risk as multidimensional determinants of Bitcoin use: A quantitative exploratory study. In Proceedings of the 37th International Conference on Information Systems (ICIS 2016), Dublin, Ireland, 11–14 December 2016; pp. 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.-G.; Chae, S.H.; Cho, K.M. Drivers and inhibitors of SaaS adoption in Korea. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2013, 33, 429–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dapp, T.F.; Slomka, L.; AG, D.B.; Hoffmann, R. Fintech–The digital (r) evolution in the financial sector. Deutsche Bank Res. 2014, 11, 1–37. [Google Scholar]
- Gefen, D.; Straub, D.W. Gender differences in the perception and use of e-mail: An extension to the technology acceptance model. MISQ 1997, 21, 389–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatesh, V.; Morris, M.G.; Davis, G.B.; Davis, F.D. User acceptance of information technology: Toward a unified view. MISQ. 2003, 27, 425–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo Chuen, D.L.; Teo, E.G. Emergence of FinTech and the LASIC principles. J. Financ. Perspect. 2015, 3, 24–36. [Google Scholar]
- Gulamhuseinwala, I.; Bull, T.; Lewis, S. FinTech is gaining traction and young, high-income users are the early adopters. J. Financ. Perspec. 2015, 3, 1–21. [Google Scholar]
- Chin, W.W. Commentary: Issues and opinion on structural equation modeling. MISQ 1998, 22, vii–xvi. [Google Scholar]
- Gefen, D.; Straub, D.; Boudreau, M.-C. Structural equation modeling and regression: Guidelines for research practice. Commun. Assoc. Inf. Syst. 2000, 4, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Straub, D.; Boudreau, M.-C.; Gefen, D. Validation guidelines for IS positivist research. Commun. Assoc. Inf. Syst. 2004, 13, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fornell, C.; Larcker, D.F. Evaluating structural equation models with unobservable variables and measurement error. J. Mark. Res. 1981, 18, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podsakoff, P.M.; MacKenzie, S.B.; Lee, J.-Y.; Podsakoff, N.P. Common method biases in behavioral research: A critical review of the literature and recommended remedies. J. Appl. Psy. 2003, 88, 879–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melewar, T.; Alwi, S.; Tingchi Liu, M.; Brock, J.L.; Cheng Shi, G.; Chu, R.; Tseng, T.-H. Perceived benefits, perceived risk, and trust: Influences on consumers’ group buying behaviour. Asia Pacific J. Mark. Logis. 2013, 25, 225–248. [Google Scholar]
- Sobel, M.E. Asymptotic confidence intervals for indirect effects in structural equation models. Soc. Method. 1982, 13, 290–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Benbasat, I.; Cenfetelli, R.T. Integrating service quality with system and information quality: An empirical test in the e-service context. MIS Q. 2013, 37, 777–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, V.-W. Consumer perceived risk: Conceptualisations and models. Eur. J. Mark. 1999, 33, 163–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).