The Effect of Students’ Experience with the Transition from Primary to Secondary School on Self-Regulated Learning and Motivation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Theoretical Framework
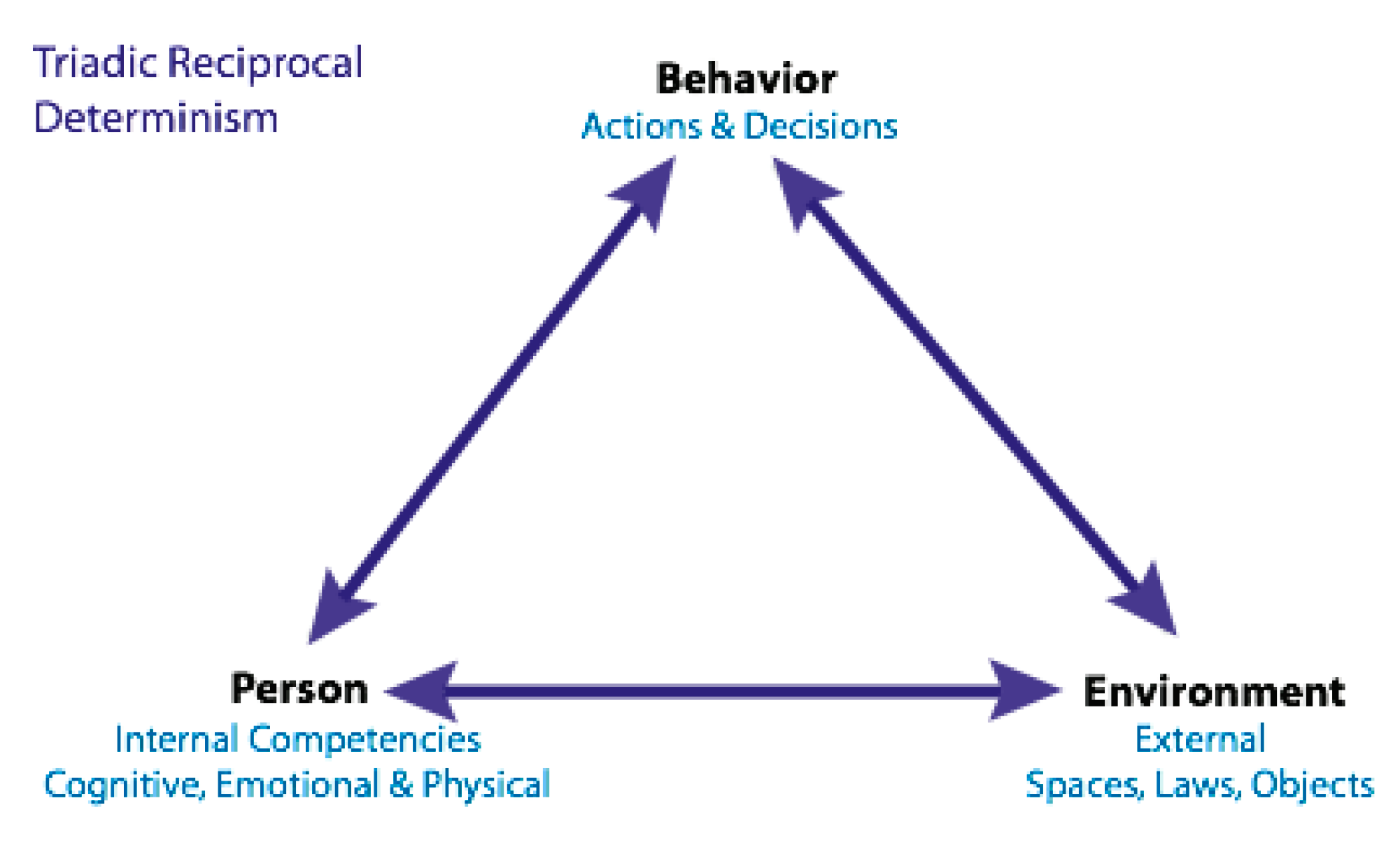
2.1. Students’ Transition from Primary to Secondary School and SRL
2.2. Students’ Transition from Primary to Secondary School and Motivation
2.3. Effect of Gender on Students’ Transition from Primary to Secondary School, SRL, and Motivation
3. Method
3.1. Participants, Sampling, and Procedure
3.2. Measurement Tool
3.3. Measures
3.4. Data Analysis
4. Results
5. Discussion and Conclusions
6. Limitations and Implications for Future Research
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Maghnouj, S.; Fordham, E.; Guthrie, C.; Henderson, K.; Trujillo, D. OECD Reviews of Evaluation and Assessment in Education: Albania; OECD Reviews of Evaluation and Assessment in Education; OECD: Paris, France, 2020; ISBN 9789264764804. [Google Scholar]
- Wort, M.; Pupovci, D.; Ikonomi, E. Appraisal of the Pre-University Education Strategy 2014–2020; UNICEF Albania: Tirana, Albania, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Achoka, J. In search of remedy to secondary school dropout pandemic in Kenya: Role of the principal. Educ. Res. Rev. 2007, 2, 236–244. [Google Scholar]
- Basilaia, G.; Kvavadze, D. Transition to Online Education in Schools during a SARS-CoV-2 Coronavirus (COVID-19) Pandemic in Georgia. Pedagog. Res. 2020, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniel, S.J. Education and the COVID-19 pandemic. Prospects 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brammer, S.; Clark, T. COVID-19 and Management Education: Reflections on Challenges, Opportunities, and Potential Futures. Br. J. Manag. 2020, 31, 453–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.; Tlili, A.; Chang, T.-W.; Zhang, X.; Nascimbeni, F.; Burgos, D. Disrupted classes, undisrupted learning during COVID-19 outbreak in China: Application of open educational practices and resources. Smart Learn. Environ. 2020, 7, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferdig, R.E.; Baumgartner, E.; Hartshorne, R.; Kaplan-Rakowski, R.; Mouza, C. Teaching, Technology, and Teacher Education during the Covid-19 Pandemic: Stories from the Field; Association for the Advancement of Computing in Education (AACE): Waynesville, NC, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Galton, M.; Gray, J.; Ruddock, J. The Impact of School Transitions and Transfers on Pupil Progress and Attainment. In Transitions and Transfers: A Review; DfEE Research Report No. 131; HMSO: Norwich, UK, 1999; ISBN 1841850500. [Google Scholar]
- Griebel, W.; Berwanger, D. Transition from primary school to secondary school in Germany. Int. J. Transit. Child. 2006, 2, 32–39. [Google Scholar]
- Zanobini, M.; Usai, M.C. Domain-specific Self-concept and Achievement Motivation in the Transition from Primary to Low Middle School. Educ. Psychol. 2002, 22, 203–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masonbrink, A.R.; Hurley, E. Advocating for Children during the COVID-19 School Closures. Pediatrics 2020, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Copland, F.; Garton, S.; Burns, A. Challenges in Teaching English to Young Learners: Global Perspectives and Local Realities. TESOL Q. 2014, 48, 738–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pufahl, I.; Rhodes, N.C. Foreign Language Instruction in U.S. Schools: Results of a National Survey of Elementary and Secondary Schools. Foreign Lang. Ann. 2011, 44, 258–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alivernini, F.; Lucidi, F.; Manganelli, S. Assessment of academic motivation: A mixed methods study. Int. J. Mult. Res. Approaches 2008, 2, 71–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, T.; Pintrich, P.R. Regulating motivation and cognition in the classroom: The role of self-schemas and self-regulatory strategies. Self Regul. Learn. Perform. Issues Educ. Appl. 1994, 127–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, T.; Pintrich, P.R. Student Motivation and Self-Regulated Learning: A LISREL Model. Available online: https://eric.ed.gov/?id=ED333006 (accessed on 15 October 2020).
- Wolters, C.A. Regulation of Motivation: Evaluating an Underemphasized Aspect of Self-Regulated Learning. Educ. Psychol. 2003, 38, 189–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, R.; Wang, Q.; Xu, J.; Zhou, L. Effectiveness of Students’ Self-Regulated Learning during the COVID-19 Pandemic. Sci Insigt 2020, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, J.L.; Dickson-Deane, C.; Galyen, K. e-Learning, online learning, and distance learning environments: Are they the same? Internet High. Educ. 2011, 14, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taşçı, G.; Titrek, O. Evaluation of Lifelong Learning Centers in Higher Education: A Sustainable Leadership Perspective. Sustainability 2019, 12, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Titrek, O.; Gunes, D.Z.; Sezen, G. Higher education and lifelong learning (llp): A model proposal. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Quality in Higher Education; ICQH 2013 Proceedings Book. Sakarya University: Sakarya, Turkey, 2013; pp. 1117–1130. [Google Scholar]
- Sanchez-Gordon, S.; Luján-Mora, S. How could MOOCs become accessible? The case of edX and the future of inclusive online learning. J. Univers. Comp. Sci. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bates, T. What’s Right and What’s Wrong about Coursera-Style MOOCs. Available online: https://www.tonybates.ca/2012/08/05/whats-right-and-whats-wrong-about-coursera-style-moocs/ (accessed on 15 October 2020).
- Chen, K.-C.; Jang, S.-J. Motivation in online learning: Testing a model of self-determination theory. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2010, 26, 741–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnard-Brak, L.; Paton, V.O.; Lan, W.Y. Profiles in self-regulated learning in the online learning environment. Int. Rev. Res. Open Distrib. Learn. 2010, 11, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Halem, N.; van Klaveren, C.; Drachsler, H.; Schmitz, M.; Cornelisz, I. Tracking Patterns in Self-Regulated Learning Using Students’ Self-Reports and Online Trace Data. Front. Learn. Res. 2020, 8, 140–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boekaerts, M.; Corno, L. Self-Regulation in the Classroom: A Perspective on Assessment and Intervention. Appl. Psychol. 2005, 54, 199–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rheinberg, F.; Vollmeyer, R.; Rollett, W. Motivation and Action in Self-Regulated Learning. In Handbook of Self-Regulation; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2000; pp. 503–529. [Google Scholar]
- Puustinen, M.; Pulkkinen, L. Models of Self-regulated Learning: A review. Scand. J. Educ. Res. 2001, 45, 269–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corno, L.; Mandinach, E.B. The role of cognitive engagement in classroom learning and motivation. Educ. Psychol. 1983, 18, 88–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyer, S.L.; Edmondson, D.R.; Artis, A.B.; Fleming, D. Self-Directed Learning. J. Mark. Educ. 2014, 36, 20–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doyle, H.; Parrish, M. Investigating Students’ Ways to Learn English Outside of Class: A Researchers’ Narrative. Stud. Self Access Learn. J. 2012, 3, 196–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicol, D.J.; Macfarlane-Dick, D. Formative assessment and self-regulated learning: A model and seven principles of good feedback practice. Stud. High. Educ. 2006, 31, 199–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boekaerts, M. The Interface between Intelligence and Personality as Determinants of Classroom Learning. In International Handbook of Personality and Intelligence; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1995; pp. 161–183. [Google Scholar]
- Boekaerts, M. Personality and the psychology of learning. Eur. J. Pers. 1996, 10, 377–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boekaerts, M. Teaching students self-regulated learning: A major success in applied research. In Contemporary Psychology in Europe; Georgas, J., Manthouli, M., Besevegis, E., Kokkevi, A., Eds.; Hogrefe: Göttingen, Germany; Huber: Seattle, WA, USA, 1995; pp. 245–259. [Google Scholar]
- Borkowski, J.G.; Chan, L.K.S.; Muthukrishna, N. A process-oriented model of metacognition: Links between motivation and executive functioning of metacognition. In Issues in the Measurement of Metacognition; University of Nebraska-Lincoln: Lincoln, NE, USA, 2000; pp. 1–41. [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerman, B.J. Self-regulating academic learning and achievement: The emergence of a social cognitive perspective. Educ. Psychol. Rev. 1990, 2, 173–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmerman, B.J. Self-Regulated Learning and Academic Achievement: An Overview. Educ. Psychol. 1990, 25, 3–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmerman, B.J. Academic studing and the development of personal skill: A self-regulatory perspective. Educ. Psychol. 1998, 33, 73–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmerman, B.J. Attaining Self-Regulation. In Handbook of Self-Regulation; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2000; pp. 13–39. [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerman, B.J. A social cognitive view of self-regulated academic learning. J. Educ. Psychol. 1989, 81, 329–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, P.E.; Hellman, C.M. Differences in Self-Regulation for Online Learning between First- and Second-Generation College Students. Res. High. Educ. 2004, 45, 71–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crosnoe, R.; Johnson, M.K.; Elder, G.H. Intergenerational Bonding in School: The Behavioral and Contextual Correlates of Student-Teacher Relationships. Sociol. Educ. 2004, 77, 60–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniels, D.H.; Meece, J.L. Child & Adolescent Development for Educators; McGraw Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Cain, K.; Oakhill, J.V.; Barnes, M.A.; Bryant, P.E. Comprehension skill, inference-making ability, and their relation to knowledge. Mem. Cogn. 2001, 29, 850–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van den Broek, P.; Kendeou, P.; Lousberg, S.; Visser, G. Preparing for reading comprehension: Fostering text comprehension skills in preschool and early elementary school children. Int. Electron. J. Elem. Educ. 2011, 4, 259–268. [Google Scholar]
- Coffey, A.; Berlach, R.G.; O’Neill, M. Transitioning Year 7 Primary Students to Secondary Settings in Western Australian Catholic Schools: How Successful Was the Move? RMLE Online 2013, 36, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kift, S.; Nelson, K.; Clarke, J. Transition pedagogy: A third generation approach to FYE—A case study of policy and practice for the higher education sector. Int. J. First Year High. Educ. 2010, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paechter, M.; Maier, B. Online or face-to-face? Students’ experiences and preferences in e-learning. Internet High. Educ. 2010, 13, 292–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderman, L.H. Academic and social perceptions as predictors of change in middle school students’ sense of school belonging. J. Exp. Educ. 2003, 72, 5–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldstein, S.E.; Boxer, P.; Rudolph, E. Middle School Transition Stress: Links with Academic Performance, Motivation, and School Experiences. Contemp. Sch. Psychol. 2015, 19, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eccles, J.S.; Roeser, R.W. Schools as Developmental Contexts during Adolescence. In Handbook of Psychology, 2nd ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Eccles, J.S.; Midgley, C.; Wigfield, A.; Buchanan, C.M.; Reuman, D.; Flanagan, C.; Mac Iver, D. Development during adolescence: The impact of stage–environment fit on young adolescents’ experiences in schools and in families. In The Evolution of Psychology: Fifty Years of the American Psychologist; American Psychological Association: Washington, DC, USA, 1993; pp. 475–501. [Google Scholar]
- Deci, E.L.; Ryan, R.M. A motivational approach to self: Integration in personality. In Current Theory and Research in Motivation; Dienstbier, R.A., Ed.; University of Nebraska Press: Lincoln, NE, USA, 1991; Volume 38, pp. 237–288. [Google Scholar]
- Deci, E.L.; Ryan, R.M. Human Autonomy. In Efficacy, Agency, and Self-Esteem; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1995; pp. 31–49. [Google Scholar]
- Ntoumanis, N.; Edmunds, J.; Duda, J.L. Understanding the coping process from a self-determination theory perspective. Br. J. Health Psychol. 2009, 14, 249–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pintrich, P.R.; de Groot, E.V. Motivational and self-regulated learning components of classroom academic performance. J. Educ. Psychol. 1990, 82, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ennis, C.D. Educating Students for a Lifetime of Physical Activity: Enhancing Mindfulness, Motivation, and Meaning. Res. Q. Exerc. Sport 2017, 88, 241–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliot, A.J.; Harackiewicz, J.M. Approach and avoidance achievement goals and intrinsic motivation: A mediational analysis. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 1996, 70, 461–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoeber, J.; Stoll, O.; Pescheck, E.; Otto, K. Perfectionism and achievement goals in athletes: Relations with approach and avoidance orientations in mastery and performance goals. Psychol. Sport Exerc. 2008, 9, 102–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ames, C.; Archer, J. Achievement Goals in the Classroom: Students’ Learning Strategies and Motivation Processes. J. Educ. Psychol. 1988, 80, 260–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dweck, C.S. Motivational processes affecting learning. Am. Psychol. 1986, 41, 1040–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dweck, C.S.; Leggett, E.L. A social-cognitive approach to motivation and personality. Psychol. Rev. 1988, 95, 256–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meece, J.L.; Blumenfeld, P.C.; Hoyle, R.H. Students’ goal orientations and cognitive engagement in classroom activities. J. Educ. Psychol. 1988, 80, 514–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barber, B.K.; Olsen, J.A. Assessing the Transitions to Middle and High School. J. Adolesc. Res. 2004, 19, 3–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudolph, K.D.; Lambert, S.F.; Clark, A.G.; Kurlakowsky, K.D. Negotiating the Transition to Middle School: The Role of Self-Regulatory Processes. Child. Dev. 2001, 72, 929–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hines, M.T. Adolescent Adjustment to the Middle School Transition: The Intersection of Divorce and Gender in Review. RMLE Online 2007, 31, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toytok, E.; Gürel, S. Does Project Children’s University Increase Academic Self-Efficacy in 6th Graders? A Weak Experimental Design. Sustainability 2019, 11, 778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Titrek, O.; Çetin, C.; Kaymak, E.; Kaşikçi, M.M. Academic Motivation and Academic Self-Efficacy of Prospective Teachers. J. Educ. Train. Stud. 2018, 6, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavas, P. Factors Affecting the Motivation of Turkish Primary Students for Science Learning. Sci. Educ. Int. 2011, 22, 31–42. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.C.K.; Yin, H.; Zhang, Z. Exploring the influence of the classroom environment on students’ motivation and self-regulated learning in Hong Kong. Asia Pacific Educ. Res. 2009, 18, 219–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanrahan, M. The effect of learning environment factors on students’ motivation and learning. Int. J. Sci. Educ. 1998, 20, 737–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassandra, M.; Goudas, M.; Chroni, S. Examining factors associated with intrinsic motivation in physical education: A qualitative approach. Psychol. Sport Exerc. 2003, 4, 211–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sichivitsa, V.O. The influences of parents, teachers, peers and other factors on students’ motivation in music. Res. Stud. Music Educ. 2007, 29, 55–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, S.; Courtney, L.; Tonkyn, A.; Marinis, T. Motivational trajectories for early language learning across the primary-secondary school transition. Br. Educ. Res. J. 2016, 42, 682–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spinath, B.; Steinmayr, R. Longitudinal Analysis of Intrinsic Motivation and Competence Beliefs: Is There a Relation Over Time? Child. Dev. 2008, 79, 1555–1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harter, S.; Whitesell, N.R.; Kowalski, P. Individual Differences in the Effects of Educational Transitions on Young Adolescent’s Perceptions of Competence and Motivational Orientation. Am. Educ. Res. J. 1992, 29, 777–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bru, E.; Stornes, T.; Munthe, E.; Thuen, E. Students’ Perceptions of Teacher Support Across the Transition from Primary to Secondary School. Scand. J. Educ. Res. 2010, 54, 519–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, J.N.; Cao, Q. Trajectories of teacher-student warmth and conflict at the transition to middle school: Effects on academic engagement and achievement. J. Sch. Psychol. 2018, 67, 148–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thévenon, O. Family policies in Europe: Available databases and initial comparisons. Vienna Yearb. Popul. Res. 2008, 6, 165–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norris, P. Women’s legislative participation in Western Europe. West. Eur. Polit. 1985, 8, 90–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinnicombe, S. The position of women in management in Europe. Women Manag. Curr. Res. Issues 2000, 2, 9–25. [Google Scholar]
- Trauth, E.M.; Quesenberry, J.L.; Huang, H. Retaining women in the U.S. IT workforce: Theorizing the influence of organizational factors. Eur. J. Inf. Syst. 2009, 18, 476–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, S. Women in Workforce: Work and Family Conflict. Manag. Labour Stud. 2007, 32, 411–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Örs, M. The Self-Directed Learning Readiness Level of the Undergraduate Students of Midwife and Nurse in Terms of Sustainability in Nursing and Midwifery Education. Sustainability 2018, 10, 3574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smedley, A. The self-directed learning readiness of first year bachelor of nursing students. J. Res. Nurs. 2007, 12, 373–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyde, J.S.; Linn, M.C. Gender differences in verbal ability: A meta-analysis. Psychol. Bull. 1988, 104, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pintrich, P.R.; Zusho, A. Student Motivation and Self-Regulated Learning in the College Classroom. In Higher Education: Handbook of Theory and Research; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2002; pp. 55–128. [Google Scholar]
- Voyer, D.; Voyer, S.D. Gender differences in scholastic achievement: A meta-analysis. Psychol. Bull. 2014, 140, 1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lietz, P. A meta-analysis of gender differences in reading achievement at the secondary school level. Stud. Educ. Eval. 2006, 32, 317–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pintrich, P.R.; Garcia, T. Self-regulated learning in college students: Knowledge, strategies, and motivation. In Student Motivation, Cognition, and Learning: Essays in Honor of Wilbert J. Mckeachie; Taylor & Francis Group: London, UK, 1994; pp. 113–133. [Google Scholar]
- West, P.; Sweeting, H.; Young, R. Transition matters: Pupils’ experiences of the primary–secondary school transition in the West of Scotland and consequences for well-being and attainment. Res. Pap. Educ. 2010, 25, 21–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snape, M.D.; Viner, R.M. COVID-19 in children and young people. Science 2020, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eccles, J.S.; Roeser, R.W. School and community influences on human development. In Developmental Science: An Advanced Textbook; Bornstein, M.H., Lamb, M.E., Eds.; Psychology Press: Hove, East Sussex, UK, 2011; pp. 571–643. [Google Scholar]
- Grolnick, W.S. The role of parents in facilitating autonomous self-regulation for education. Theory Res. Educ. 2009, 7, 164–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Rens, M.; Haelermans, C.; Groot, W.; Maassen van den Brink, H. Facilitating a Successful Transition to Secondary School: (How) Does it Work? A Systematic Literature Review. Adolesc. Res. Rev. 2018, 3, 43–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wampler, R.S.; Munsch, J.; Adams, M. Ethnic Differences in Grade Trajectories during the Transition to Junior High. J. Sch. Psychol. 2002, 40, 213–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huon, G.; Spehar, B.; Adam, P.; Rifkin, W. Resource use and academic performance among first year psychology students. High. Educ. 2007, 53, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Variable | M (sd) | Range | Skewness | Kurtosis | Frequency | Percentage |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Students’ experience with transition | 3.61 (0.71) | 1–5 | −0.24 | 0.25 | ||
| 2. Students’ self-regulated learning | 3.67 (0.59) | 1–5 | −0.44 | 0.59 | ||
| 3. Students’ motivation | 3.70 (0.64) | 1–5 | −0.65 | 0.12 | ||
| 4. Gender | ||||||
| Male | 33 | 41.2 | ||||
| Female | 47 | 58.8 |
| Variable | M (sd) | t | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Experience with transition | 0.29 | 0.78 | ||
| Males | 3.64 (0.79) | |||
| Females | 3.59 (0.65) | |||
| Self-regulated learning | −0.75 | 0.46 | ||
| Males | 3.61 (0.65) | |||
| Females | 3.71 (0.54) | |||
| Motivation | −0.24 | 0.81 | ||
| Males | 3.68 (0.66) | |||
| Females | 3.72 (0.64) | |||
| Variable | 1 | 2 |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Experience with transition | .. | 0.45 * |
| 2. Self-regulated learning | .. | .. |
| Variable | 1 | 2 |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Experience with transition | .. | 0.45 * |
| 2. Students’ motivation | .. | .. |
| Variable | 1 | 2 |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Self-regulated learning | .. | 0.59 * |
| 2. Students’ motivation | .. | .. |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Uka, A.; Uka, A. The Effect of Students’ Experience with the Transition from Primary to Secondary School on Self-Regulated Learning and Motivation. Sustainability 2020, 12, 8519. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12208519
Uka A, Uka A. The Effect of Students’ Experience with the Transition from Primary to Secondary School on Self-Regulated Learning and Motivation. Sustainability. 2020; 12(20):8519. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12208519
Chicago/Turabian StyleUka, Ana, and Arban Uka. 2020. "The Effect of Students’ Experience with the Transition from Primary to Secondary School on Self-Regulated Learning and Motivation" Sustainability 12, no. 20: 8519. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12208519
APA StyleUka, A., & Uka, A. (2020). The Effect of Students’ Experience with the Transition from Primary to Secondary School on Self-Regulated Learning and Motivation. Sustainability, 12(20), 8519. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12208519




