Abstract
To save electricity consumption in university buildings, we measured and compared the amount of electricity use with and without motion detection sensors and room management systems in underground parking lots, lecture rooms, and dormitories of a university building. The underground parking lots and lecture rooms were measured as sensors were applied and then removed during the semester. University classes are held weekly, so it can be assumed that the number of cars and people’s entering and using conditions are the same. In the university’s underground parking lots, a daily electricity savings of 39.5 Wh/(m2 day) of lights was achieved, with a savings rate of 77.6%. In the lecture rooms, these values were 25.0 Wh/(m2 day) and 32.4%, respectively. Savings in the use of air conditioning were 55.0 Wh/(m2 day), with a savings rate of 27.9%. Dormitories use electrical energy for lighting, heating, and socket outlets. As a reference group, 120 rooms were selected and the room management system was applied to 10 samples. For dormitories, daily electricity savings of 142.4 Wh/(m2 day) were achieved, with a savings rate of 28.2%. Thus, this study demonstrated that applying motion detection sensors and room management systems saved significant electrical energy in university underground parking lots, lecture rooms, and dormitories.
1. Introduction
1.1. Background
As energy use and greenhouse gas emissions increase worldwide, global warming is speeding up. In South Korea, energy conservation and the development of renewable energy to replace fossil fuels have become important issues, leading to various efforts to reduce energy use [1].
As part of energy conservation, Green IT (Green environment achievement by IT and green technology for IT) aims to achieve continuous added value as the next new growth engine while actively responding to issues such as global warming, tightening environmental regulations, energy depletion, and environmental pollution. Power industries are actively integrating information and communication technologies such as the environmentally-friendly intelligent future smart grid (Smart Grid) with technologies including distributed generation, energy storage, renewable energy, electric vehicles (Plug-in Hybrid Vehicle), Smart Meter, and Demand Response as a national growth engine [2]. Smart grid is an intelligent power grid system that improves efficiency by integrating information and communication technology into the process of generating, transporting, and consuming electricity, and interacting with each other between suppliers and consumers. Smart Meter is a remote power meter reading and management device that notifies both power suppliers and consumers by reading the value of the watt hour meter installed in apartment houses, etc. Demand Response is a technology that controls the loads according to the overall demand fluctuations for infrastructure reliability and optimization.
Thus, given the above trends, South Korea requires solutions to reduce buildings’ energy consumption [3]. According to the 2017 Energy Statistics Handbook of the Korea Energy Agency, university buildings are third (13.6%) among the top 10 industries that report their energy usage, which exceeds the yearly average [4].
Low-carbon green growth has emerged as a new paradigm for the future; thus, it is important to preserve the environment of university campuses [5] and to play a leading role through energy control to ensure consistent energy savings [6]. Energy savings and management in university buildings are continuously required [7,8]. The Green Campus concept emphasizes the importance of sustainability to meet the international standards of energy efficiency in buildings, and it has been perceived globally as an extremely natural value that universities should pursue [9,10]. The International Sustainable Campus Network (ISCN) was formed in 2007 as a cooperative network between universities with the aims of exchanging information and ideas, operating sustainable campuses, and sharing ways to reduce heating and cooling energy use [11].The environmental impact caused by universities via diverse activities, teaching and research operations, and the provision of support services could be considerably reduced by the application of effective organizational and managerial measures [12]. As Figure 1 shows, many countries are conducting studies on the Green Campus concept.

Figure 1.
Works on the sustainability development of university campuses.
1.2. Literature Review
Studies have been conducted on monitoring systems [13,14], design [15], performance improvements [16,17], energy usage analysis [18,19,20] and comparison [21], building operations [22,23], and energy feedback [11,24] based on IOT(Internet of Things) [25] for reducing energy usage in universities. In addition, many universities have installed controls inside buildings—such as occupancy sensors [26]—and room management systems in dormitories to save energy. For instance, the lighting is automatically turned off by the room management system in empty rooms. If a card key is inserted into the door card reader when entering a room, the electricity is turned on. If the key is removed when leaving the room, the electricity is turned off to reduce energy consumption. Abidin et al. [27] revealed that U.S. colleges—Boston University, in particular—were among the 11 universities surveyed that had adopted the installation of occupancy sensors as part of energy efficiency initiatives.
Prior studies on power reduction via control systems can be summarized as follows. Jeong and Seo [28] proposed an energy-saving system using an occupancy sensor with a PIR sensor (passive infrared sensor which detects movement of the human body in a certain section at an acute angle of 9 to 12 degrees through a Fresnel lens) and a smart plug capable of measuring current consumption, resulting in savings of about 34% of electrical energy by cutting off power to unnecessarily operated appliances. Hong et al. [29] proposed an intelligent indoor lighting control system using daylight and detecting occupancy to reduce electrical energy use by up to 65.2%. In order to reduce light energy usage, Nam et al. [30] conducted an experiment where they attached a PIR sensor to a classroom’s lighting fixtures and achieved a 10% reduction rate.
Yoon [31] published a study that derived and typified the influencing factors based on monthly energy consumption data for the energy management of university buildings in Seoul, Korea, concluding that energy management guidelines should be different for each building type.
Wen-Jye Shyr et al. [32] found that an energy management system via the Internet of Things provided significant energy savings by eliminating standby consumption and/or adapting the behavior of appliances to real environmental conditions. Dionysia Kolokotsaa et al. [12] demonstrated that campus buildings can reduce energy consumption by 15 to 30% (depending on the period of the year) through the study’s proposed web-based platform system. This system aims to reduce campus energy consumption through the optimal use of energy systems while simultaneously improving indoor environmental quality. Guo and Wei et al. [33] conducted an energy consumption analysis using BIM(Building Information Modeling) technology and simulated the re-design of a university building in Taiwan. This work introduced a design scheme with high energy savings at a lower cost. Finally, Soares et al. [34] proposed an energy efficiency plan for a Portuguese higher education building. The study conducted an energy audit of electricity, natural gas, and water usage and suggested energy-saving measures through a cost analysis.
1.3. Objectives and Limits of Research
It is generally known that electrical energy can be saved by applying devices that can control the use of energy as mentioned above. Most of the work found in the literature were based on predictions of energy savings through assumptions and simulations, rather than in situ experiments. However, in this work, energy consumption of parking lots, classrooms and dormitories with and without motion detection sensors and room management system during long periods (four weeks) of normal operation has been measured. The data were obtained with occupants living their regular lives and activities. Thus, we consider our work is realistic and can be useful for field application. This work can serve as basic data for estimating the effect of these applications when constructing, expanding or renovating university buildings in the future. Therefore, this study’s objective is to quantify the amount of electrical energy saved through experiments and data analysis so that it can be used as basic data for the implementation of electrical energy-saving systems in university buildings. In this study, we used sensors that respond to the behavior of occupants living in actual buildings, rather than a system that controls buildings’ operation schedules. By adjusting energy consumption according to residents’ behavior, we attempted to achieve maximum energy savings and efficiency.
The experiments were done on a weekly basis. Since there were differences of class operation, outdoor weather conditions, and number of people, it was impossible to impose exactly the same condition each week. However, the schedule repeats the same each week in university and outdoor weather conditions did not change much during the experiment period. Thus, it was concluded that other uncontrollable factors did not significantly affect the main results of our experimental study.
2. Materials and Methods
To study the effect of a motion detection sensor and room management system on electricity consumption, sensors were installed in underground parking lots, lecture rooms, and dormitories of a university building. Sensors were turned on and off on a weekly basis based on the assumption that the class schedule and operation pattern were repeated similarly every week. Electrical energy consumption of lighting, cooling, heating and others with and without sensor operation was measured and compared.
2.1. University Campus
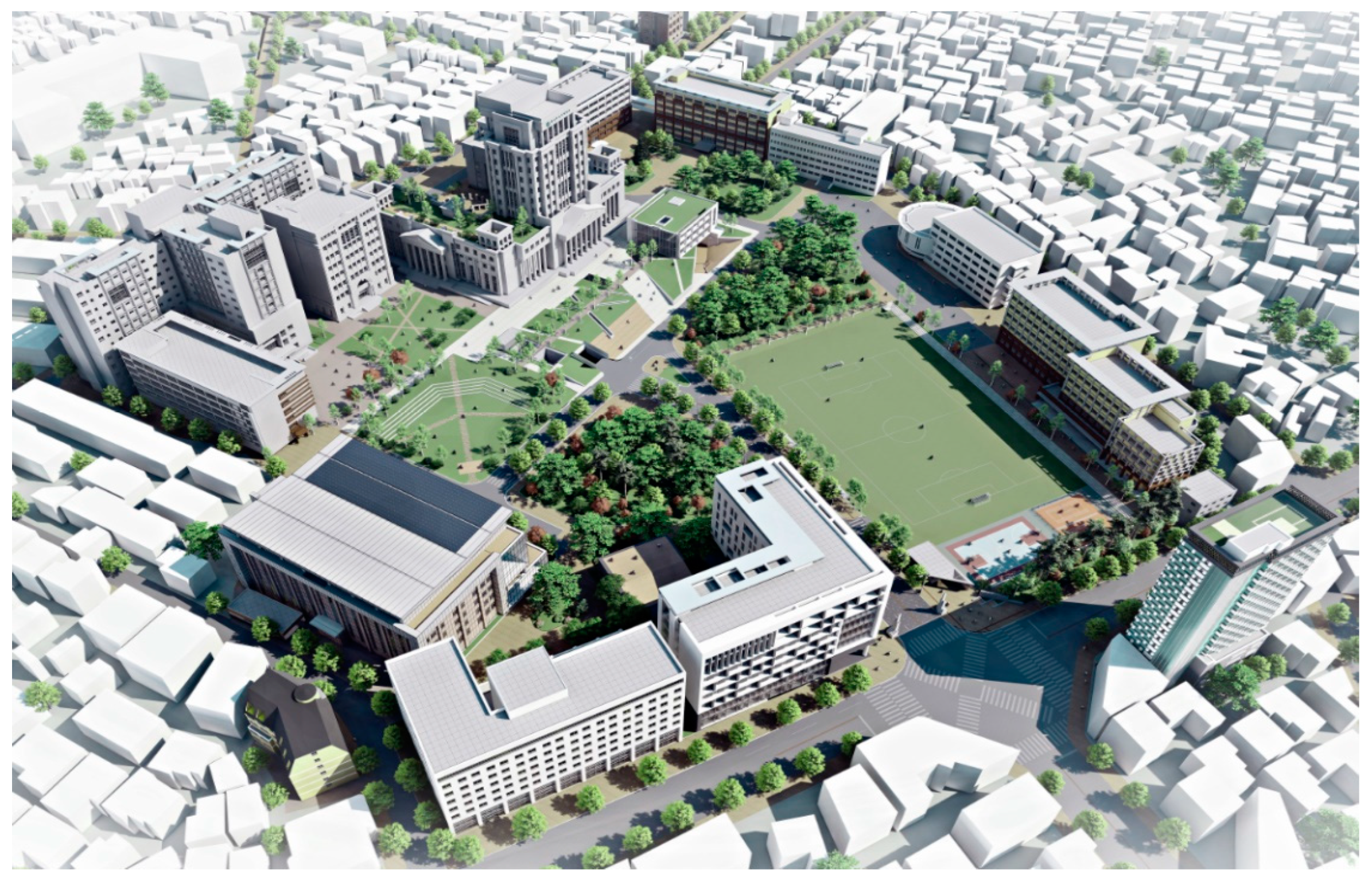
We measured energy savings in university buildings at the campus of H University located in Seoul City. Table 1 and Figure 2 present an overview of the university.

Table 1.
General information of H University’s Seoul campus.

Figure 2.
Overview of H University’s Seoul campus.
Figure 3 shows the buildings and dormitory selected for this study. Table 2 lists basic information regarding the building and dormitory.

Figure 3.
(a) University building with underground parking lot and lecture room; (b) Dormitory.

Table 2.
Summary of university building and dormitory characteristics.
2.2. Experimental Conditions
Table 3 presents a summary of the study’s experiment. Experiments 1 and 2 were conducted in a lecture hall (Cyber Building) located within H University’s Seoul campus. The experiments focused on saving lighting and cooling energy using the occupancy sensors. We measured the amount of electrical power used by applying the occupancy sensors for one week and then disabling them for one week for four consecutive weeks from May to June.

Table 3.
Summary of experiment.
The experiment focused on lighting in the underground parking lots and lighting and cooling energy usage in lecture rooms—two campus settings in which the greatest amount of energy is used.
Experiment 3 was conducted in a dormitory inhabited by students 24 h per day and where relatively more electrical energy was used than in other buildings. We created two groups: the first featured a room management system while the second did not. The reference group, which had the system always turned on, was used to calculate the amount of electricity saved by the room management system.
2.3. Control Method
2.3.1. Motion Detection Sensor—RF Sensor
Automatic detection sensors save energy by automatically turning off lights when no people are detected in the target space. This is one of the most efficient energy-saving systems.
Typical movement-detecting sensors include infrared, ultrasonic, and Doppler sensors. Infrared sensors output voltage signals when they detect differences from the ambient temperature, and they are widely used in automatic doors, apartment entrances, and unmanned security systems. They operate by detecting differences from the ambient temperature; therefore, they are the most sensitive when objects with temperatures vastly different from the ambient temperature move. Once objects get closer to the sensor and the ambient temperature rises, the sensors’ sensitivity drops sharply [35].
Ultrasonic sensors can detect relatively long distances and can even adjust detecting distances. These sensors can do this regardless of material and color. However, they operate slowly and are heavily influenced by the surrounding environment, including factors such as temperature and dust [36]. To compensate for this problem, RF sensors operate by reflecting a microwave signal onto a moving object. The frequency of the signal changes proportionally to the speed of the object due to the Doppler effect [37,38]. Therefore, this type of sensor is not greatly affected by the surrounding environment.
2.3.2. Room Management System
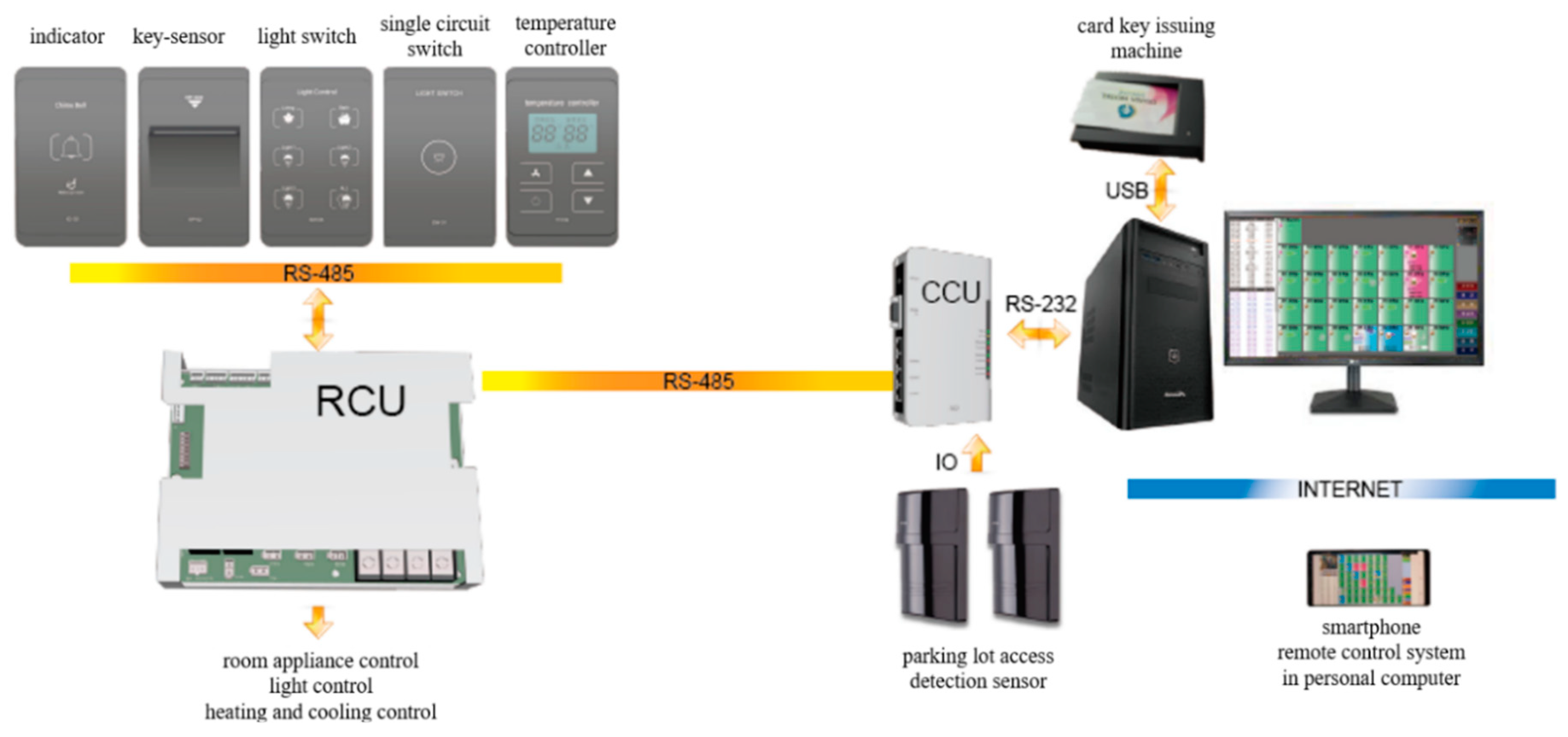
In order to operate dormitories efficiently, a range of operating systems and functions are needed. Room management systems aim to manage rooms efficiently and are programmed to ensure electrical safety, to prevent unnecessary energy use in empty rooms, and to maintain a pleasant room environment. The composition of this study’s room management system is shown in Figure 4.
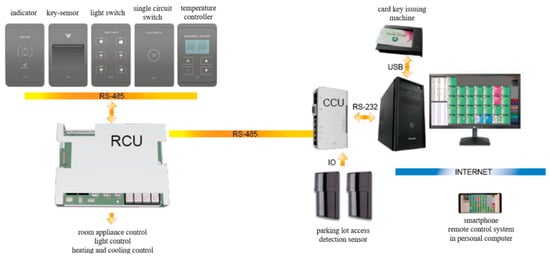
Figure 4.
Room management system.
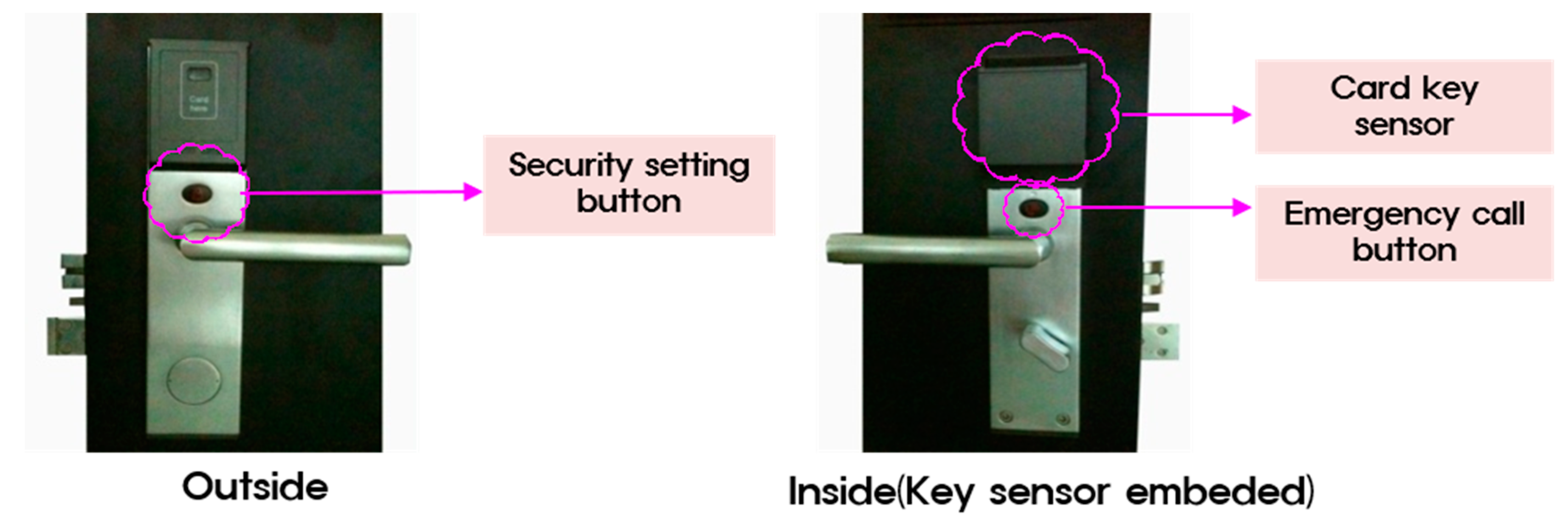
The room management system was applied to the experimental group in the dormitory selected for this study. Students were issued card keys, which signaled the electricity to turn on automatically when inserted into the card reader when entering a room. When a key was removed, the lighting and heating would be automatically cut off to save electrical energy (with the exception of refrigerators).
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Experiment 1: Underground Parking Lot
3.1.1. Experimental Procedure
Underground parking lots are often preferred over ground parking lots to enhance space utilization; however, this places a great demand on lighting energy. Thus, Experiment 1 focused on an underground parking lot that typically uses a vast amount of lighting energy on campus and installed an RF (Doppler) detection sensor to confirm the reduction of lighting.
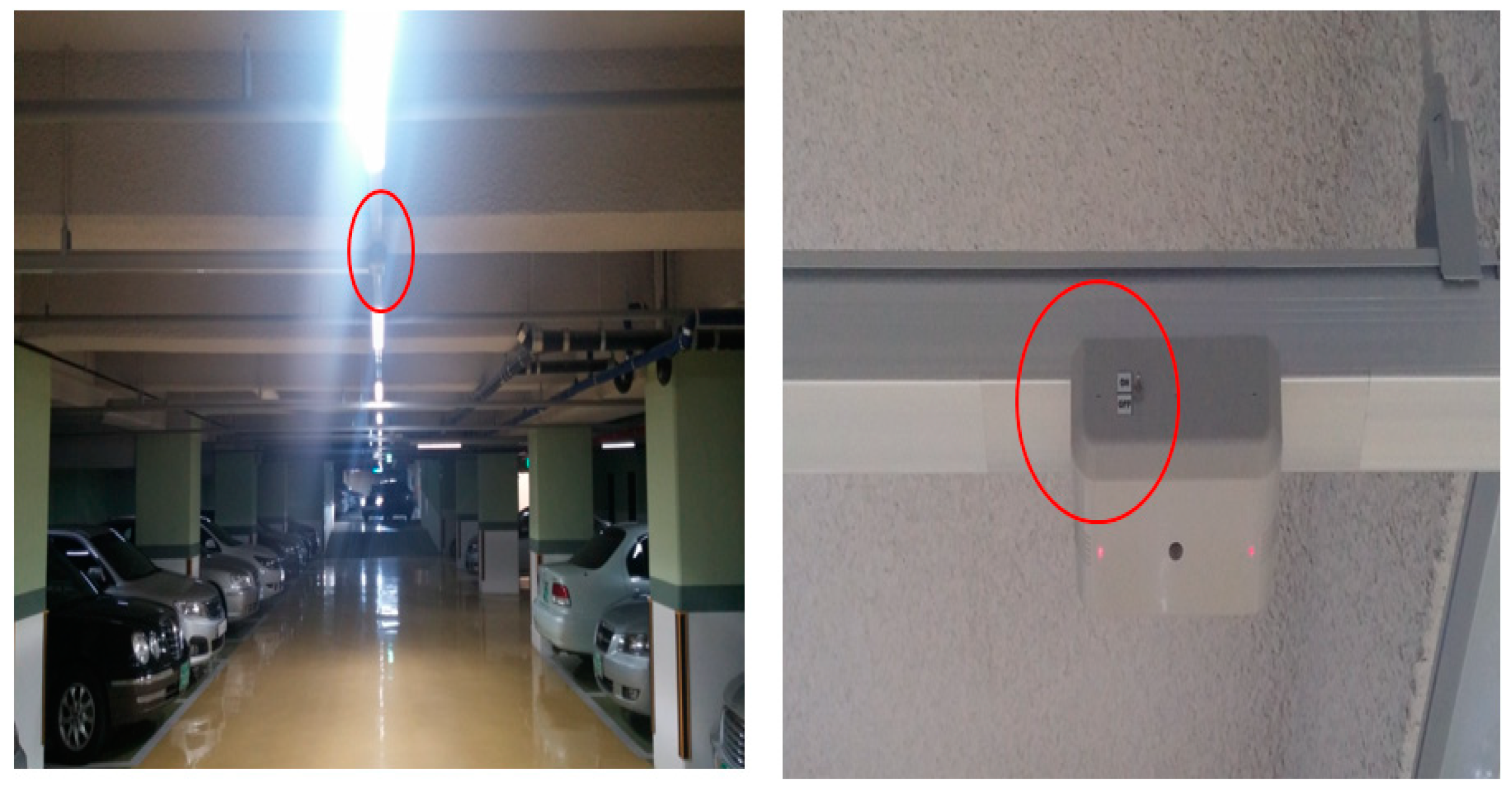
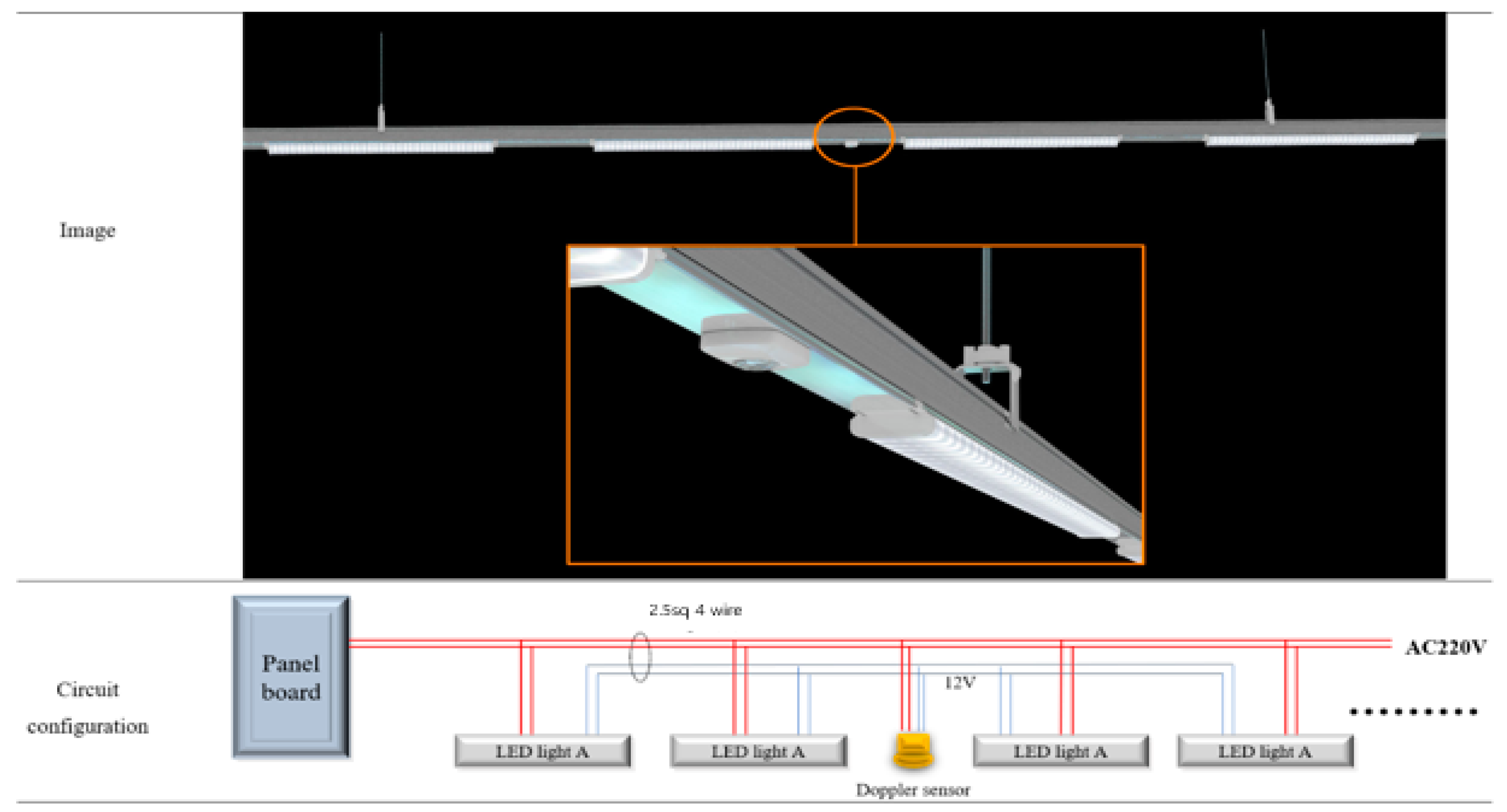
The device for Experiment 1, an RF sensor, is mainly used to control light fixtures in underground parking lots. The installed lighting fixture with a wattage capacity of 40 W per unit is dimmable; when a vehicle is recognized, it raises its light level to 100% and then remains at 20% when the vehicle is no longer detected. This device reduces electrical energy by adjusting the brightness of the light fixture via the Doppler sensor’s operation. Figure 5 and Figure 6 illustrate the product’s installed figure and control configurations.

Figure 5.
Underground parking space with motion detection sensor installed in ceiling.
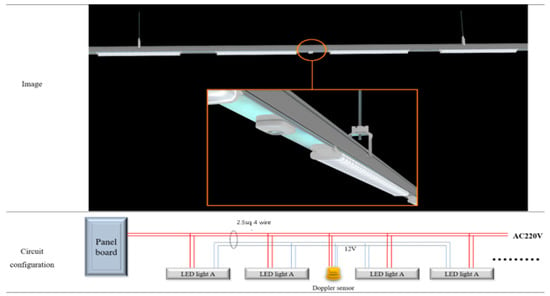
Figure 6.
RF sensor and light control circuit configuration.
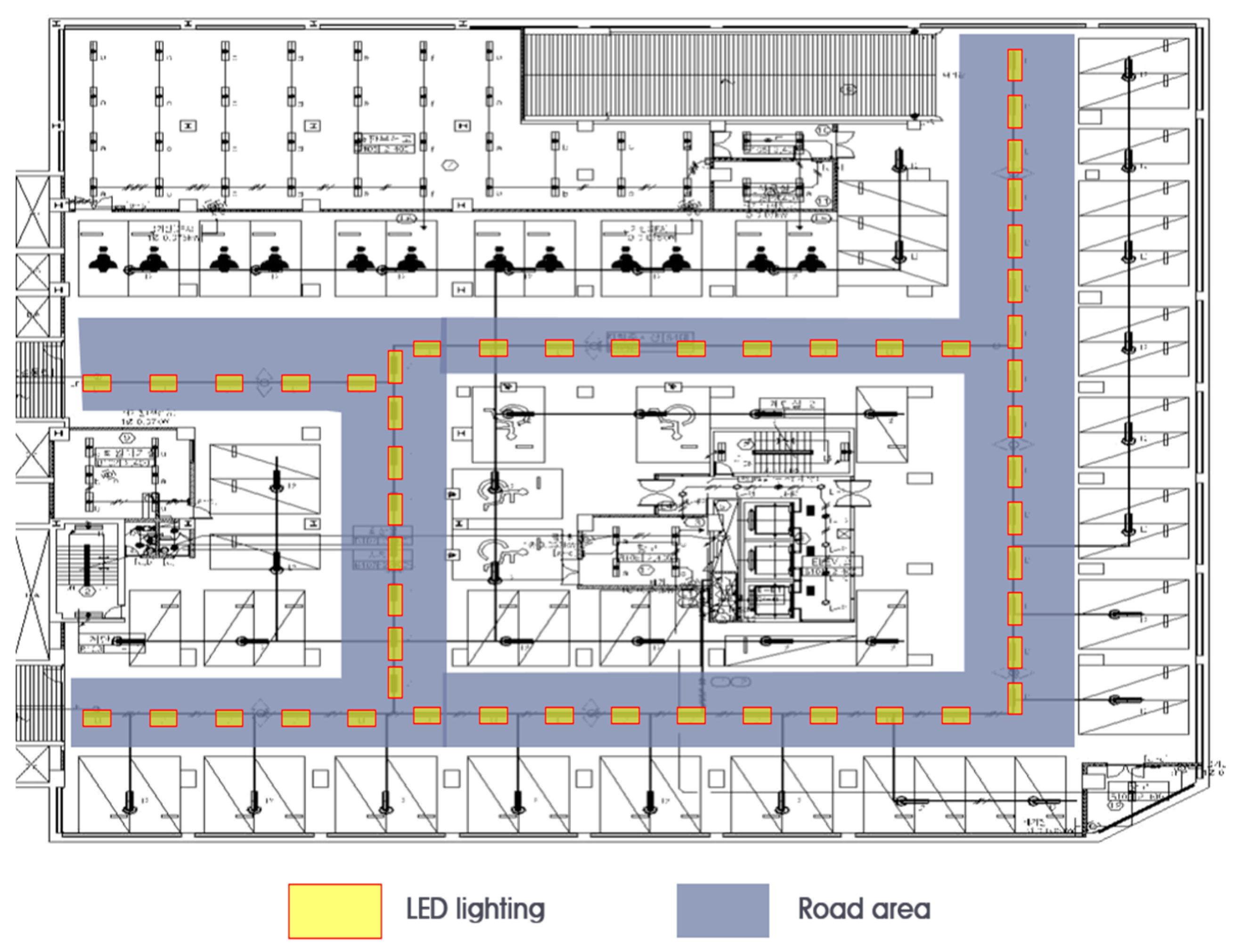
The experiment was conducted on floor B1 of the underground parking lot of the Cyber Building. Table 4 presents the specifications of the installed lighting fixture control sensor. Meanwhile, Figure 7 presents the plan and installation status chart of the target space in Experiment 1. The experiment was conducted around the passageway where vehicles would move in the underground parking lot. There were 51 total lights and the passageway area was 918.66 m2, with a light density of 2.22 W/m2. This area’s total power usage was measured for 24 h and then analyzed.

Table 4.
Specifications of RF sensor for light control.
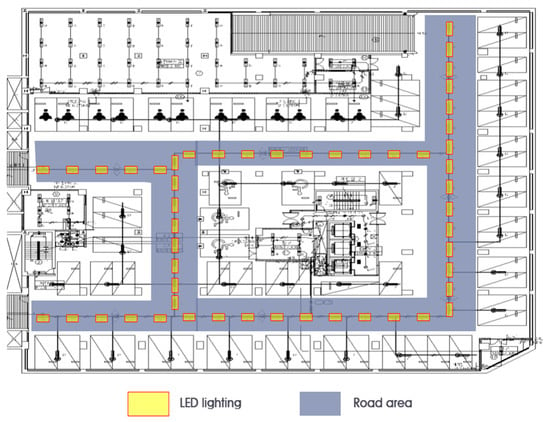
Figure 7.
Plane figure of Experiment 1 in underground parking area.
3.1.2. Experimental Results
We measured the cumulative amount of electricity used by installing electric power meters that measured the lighting energy of the parking lot passageway on B1F for six weeks from May to June. The test was conducted to study the effect of the RF sensors with dimming control. The RF sensors were operated for one whole week on a biweekly basis. Table 5 presents the test results.

Table 5.
Electricity consumption of underground 1st-level parking area.
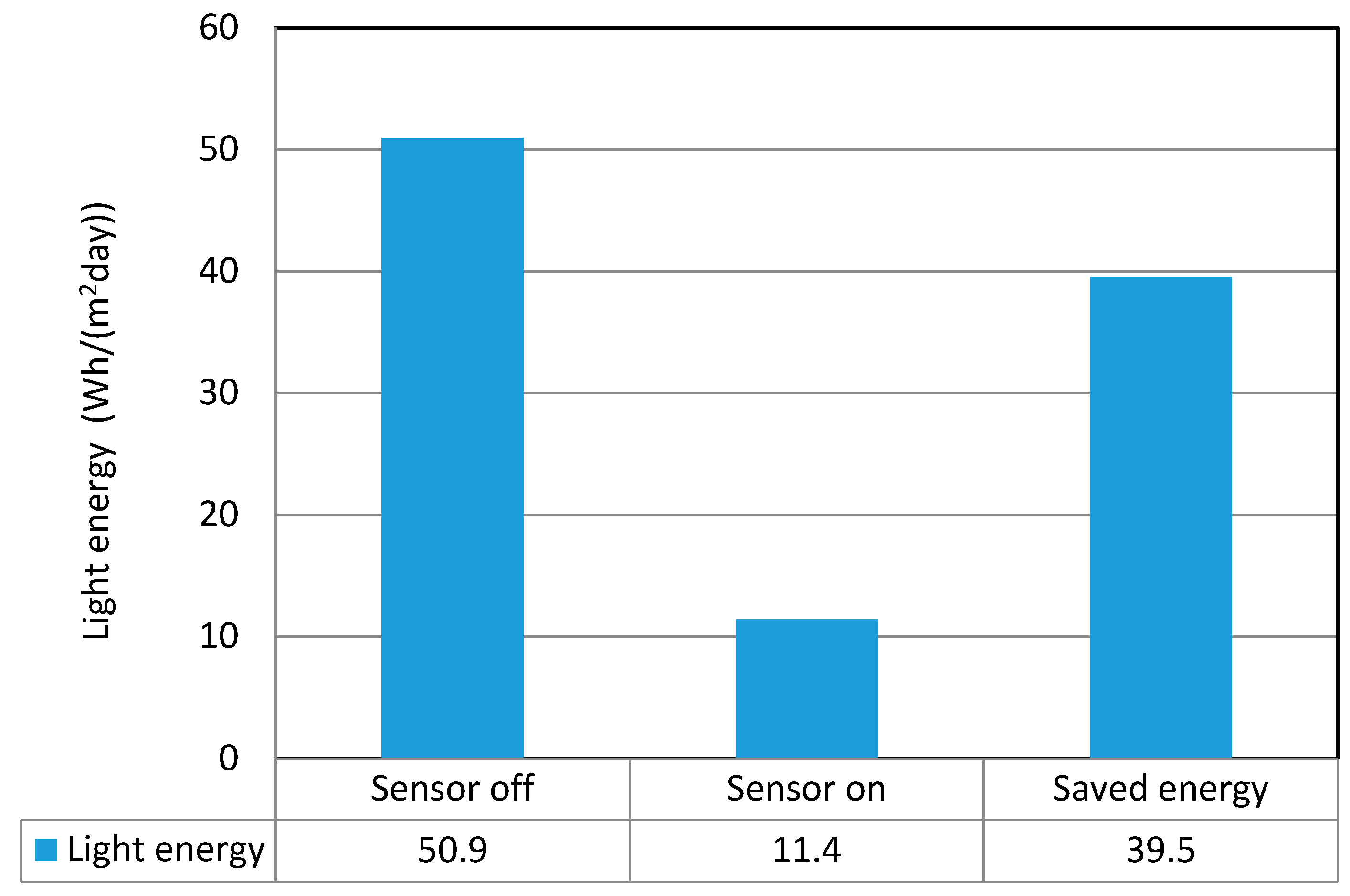
The average daily savings of light electricity in this underground parking lot using RF sensors were 39.5 Wh/m2, as shown in Table 6. The average energy savings were 77.6%.

Table 6.
Average daily electricity consumption of underground 1st-level parking area.
3.2. Experiment 2: Classroom
3.2.1. Experimental Procedure
Lecture rooms occupy the majority of space on university campuses. Thus, in order to save energy on campus, lecture rooms’ energy usage must be evaluated. In this study, lighting and cooling energy usage were measured by applying the RF sensors in lecture rooms.
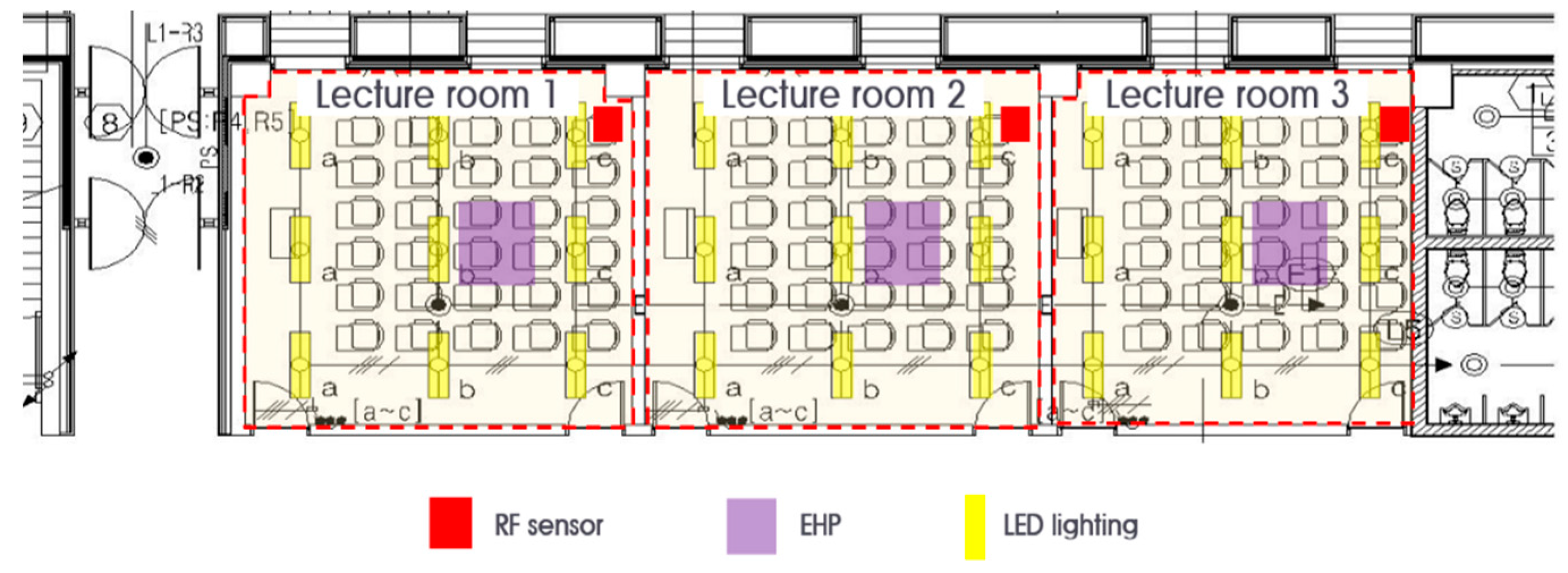
In this experiment, the RF sensor was switched on/off on a weekly basis to compare and analyze lighting and cooling energy usage. Lecture rooms were selected based on the criteria of little variation in class schedule for about six weeks, with lectures held on a weekly basis. In the case of individual classrooms, it was difficult to objectify the schedule of use, so three rooms’ energy use was averaged. Figure 8 presents the experiment’s layout.
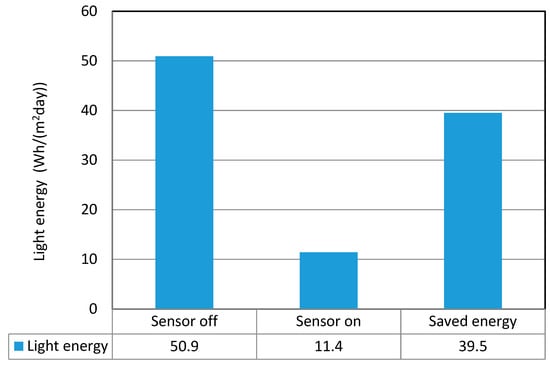
Figure 8.
Average daily electricity consumption of underground 1st-level parking area.
This experiment was divided into heating and cooling EHP (Electric Heat Pump) in addition to light energy. Figure 9 illustrates the location of the room sensor used in this experiment. Table 7 outlines the detailed specifications of the radio frequency motion detection sensor.
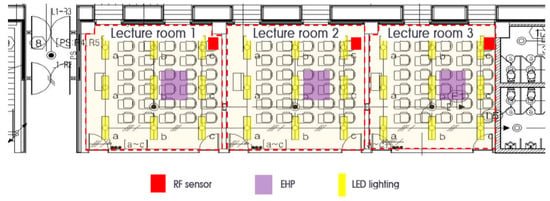
Figure 9.
Plane figure of Experiment 2: Classroom.

Table 7.
Specifications of motion detection sensor.
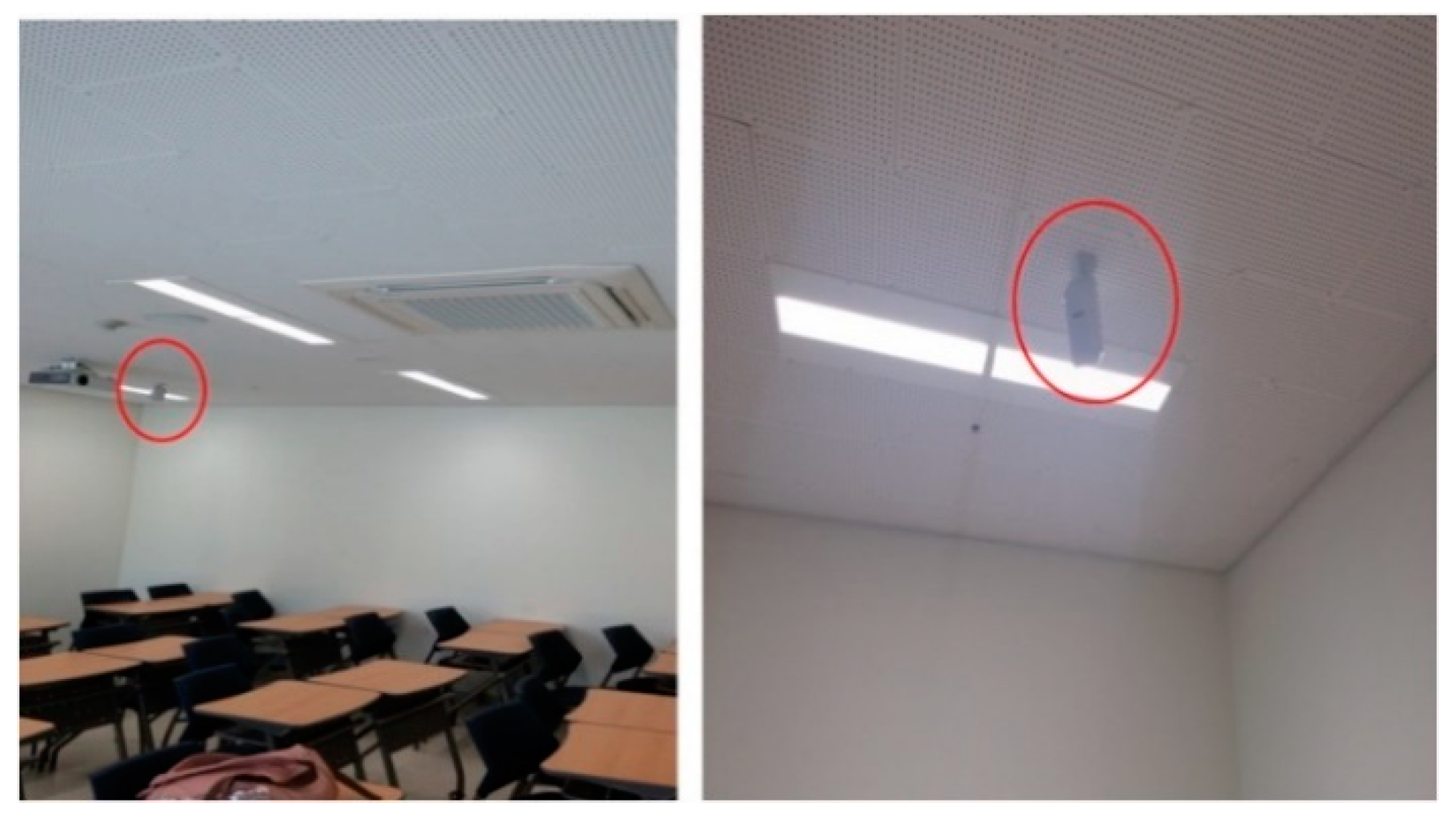
In these three classrooms, 27 units of 42 W LED and 3 units of EHP were installed. The rated capacity of the EHP is 11 kW for cooling and 12.4 kW for heating. The experiment was conducted between May and June when the university’s classrooms began to use more cooling energy. Figure 10 illustrates the EHP and lighting control plots for each classroom.

Figure 10.
Classroom with human detection sensor installed in ceiling.
3.2.2. Experimental Results
In general, university classrooms are not used during the July–August vacation period. Thus, classrooms begin to use air conditioning in late May to June. For this reason, the experiment was conducted between May and June (four weeks). The three lecture rooms’ energy consumption was evaluated by measuring the use of lighting and cooling energy. Table 8 presents the amount of electricity used when the RF sensors were operational. Outside temperature, which is a significant factor that often affects the operation of air conditioners, showed little difference during the experimental period.

Table 8.
Classrooms’ electricity consumption in relation to motion detection sensor operations.
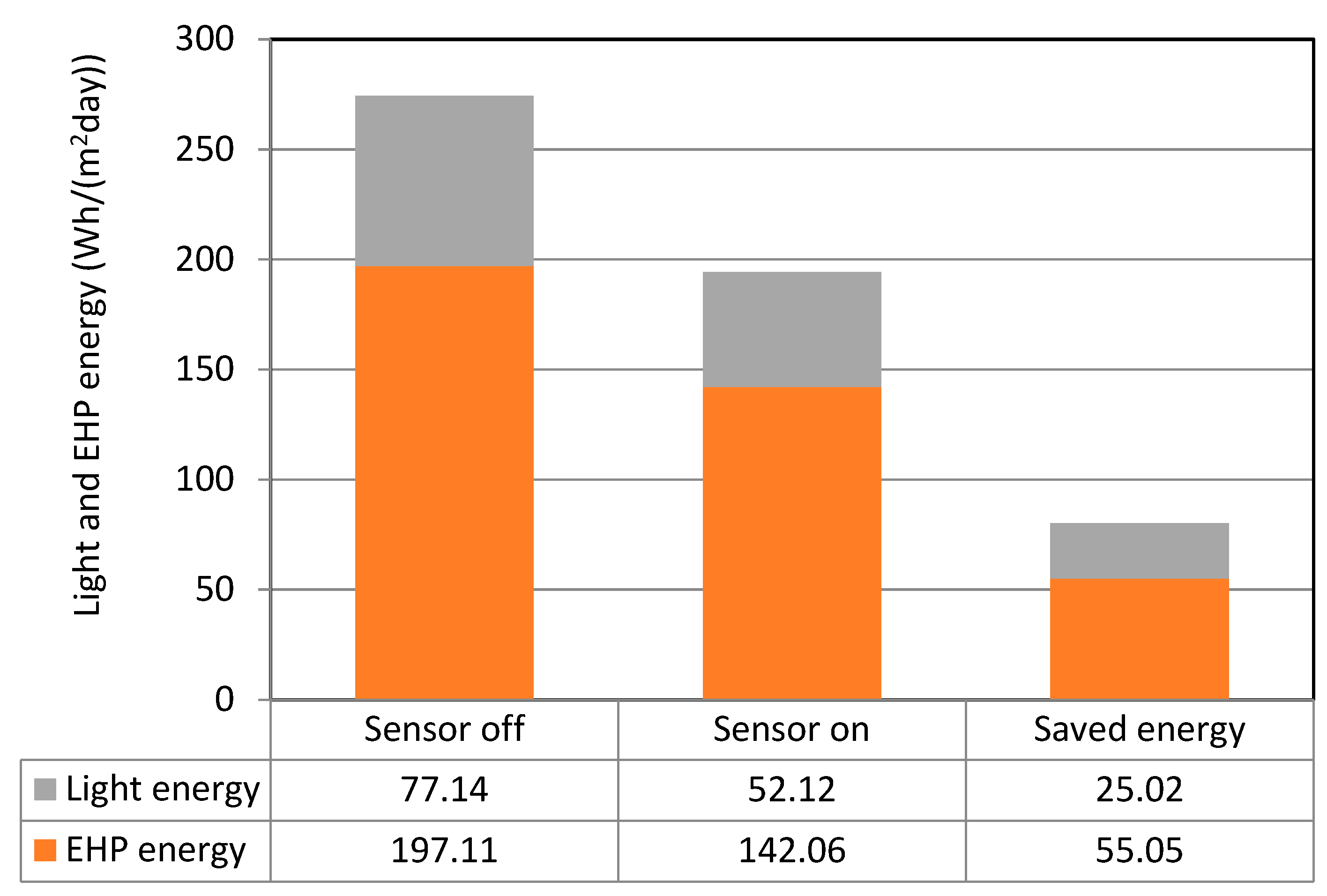
As shown in Table 9, if the RF sensor was turned off, the daily average light energy usage per unit area was 77.14 Wh/(m2 day); this was reduced by 32.4% to 52.12 Wh/(m2day) when the sensor was turned on. In terms of cooling energy, 197.11 Wh/(m2day) was used when the sensor was not operational, and this value was reduced by 27.9% to 142.06 Wh/(m2day) when the sensor was in operation.

Table 9.
Classrooms’ average daily electricity consumption.
3.3. Experiment 3: Dormitory
3.3.1. Experimental Procedure
University dormitories may be used for 24 h per day depending on students’ schedules and the number of people in each room. Therefore, dormitories use significant cooling, heating, and lighting energy. Different ways to save energy in such buildings have been explored and proposed in prior research.
Previous studies on university dormitories have often applied room management systems used in hotels to save energy. In addition, a remote monitoring system was recently applied to monitor energy use in real time. In the present study, two groups were created: one to acquire the basic data and another to study the effects of the room management system.
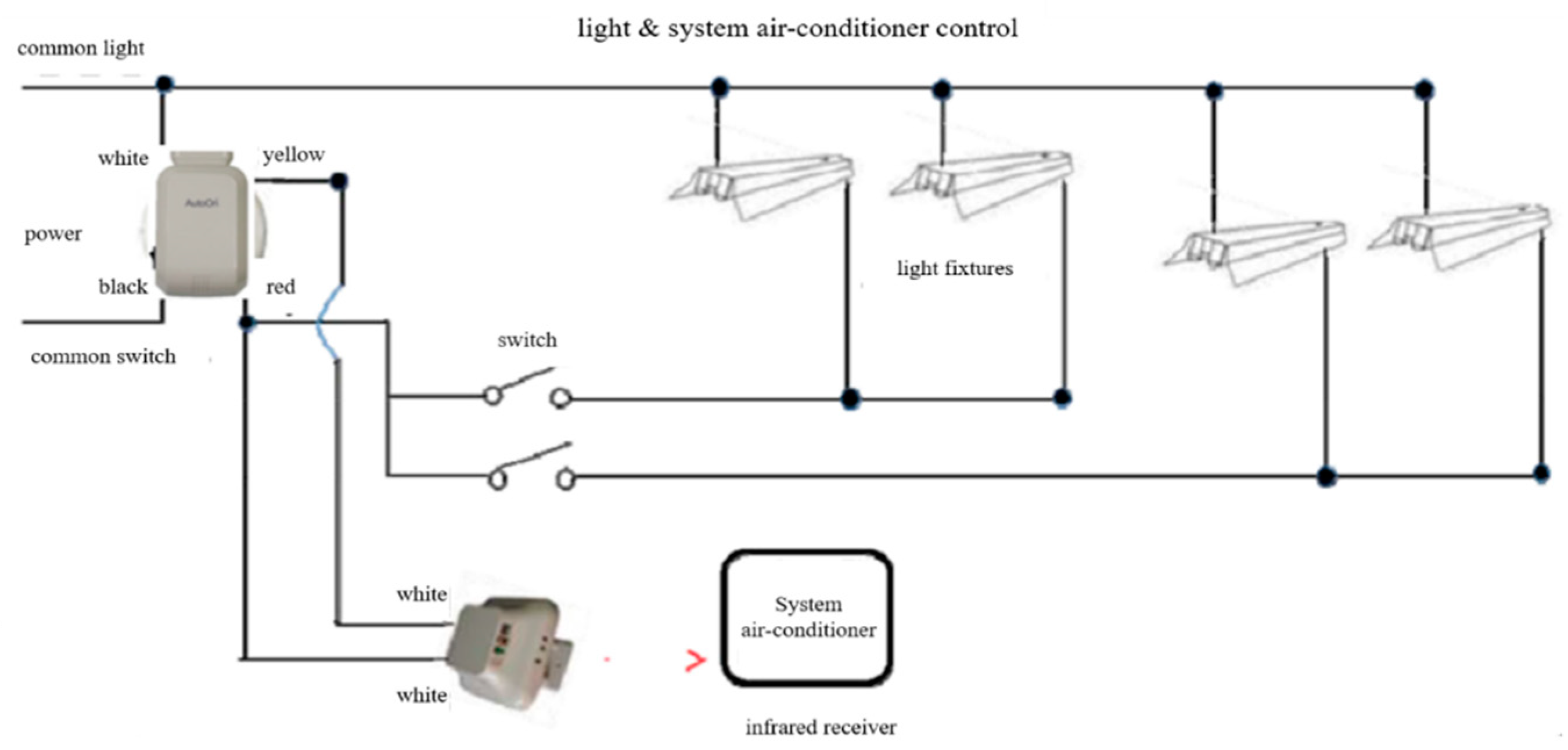
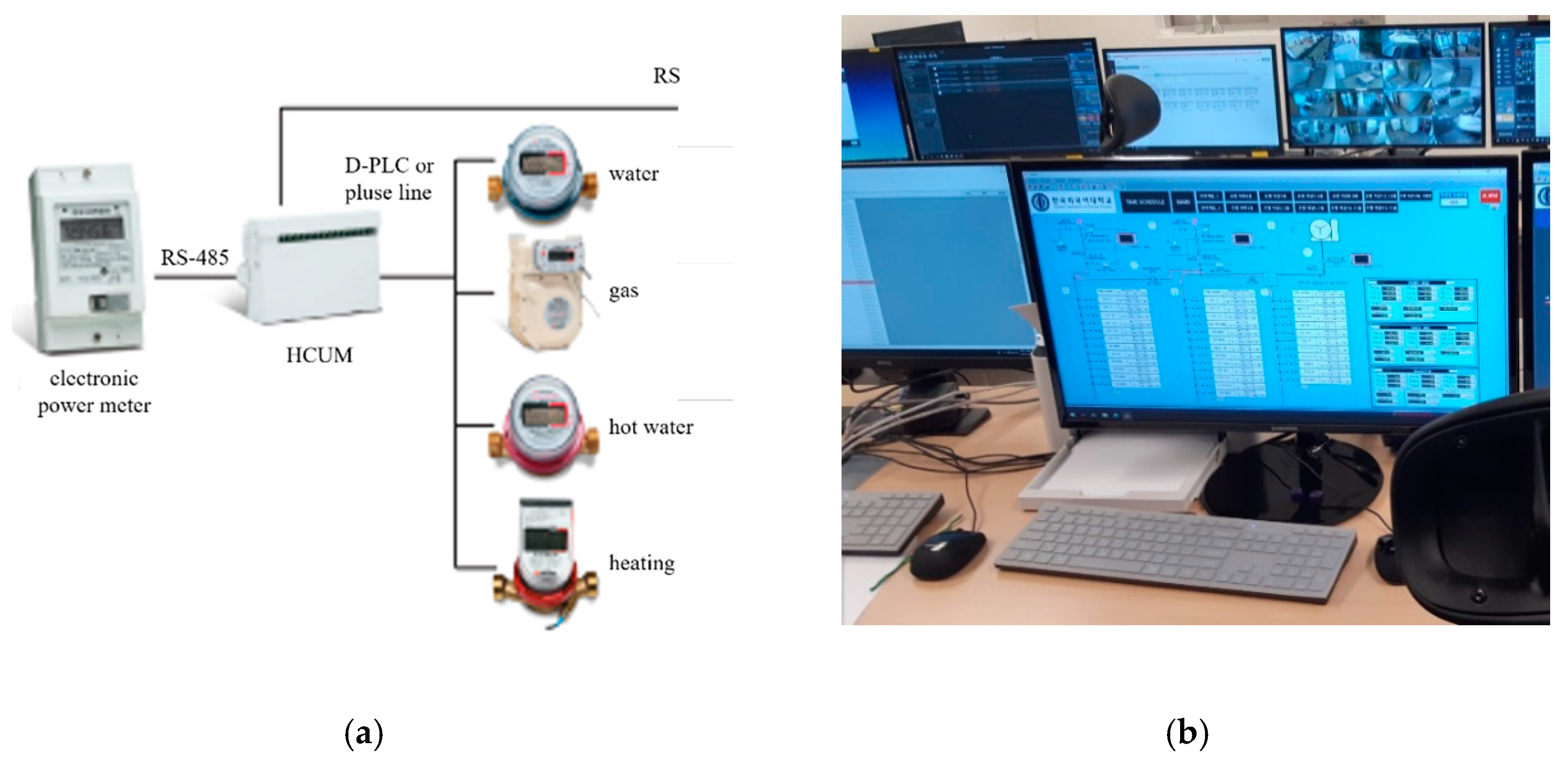
The room management system used in this experiment saves energy by automatically turning off all power sources such as cooling, heating, lighting, electric heat, etc., (except for refrigerators) when a card key is removed from the card reader. Figure 11, Figure 12, Figure 13 and Figure 14 illustrate this system.
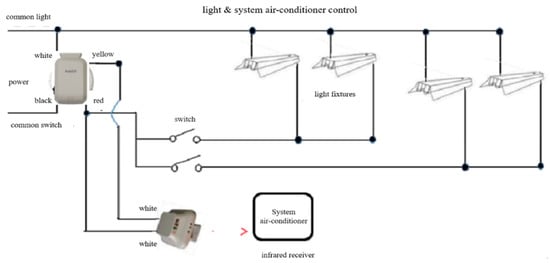
Figure 11.
Control circuit of lighting and air conditioner.
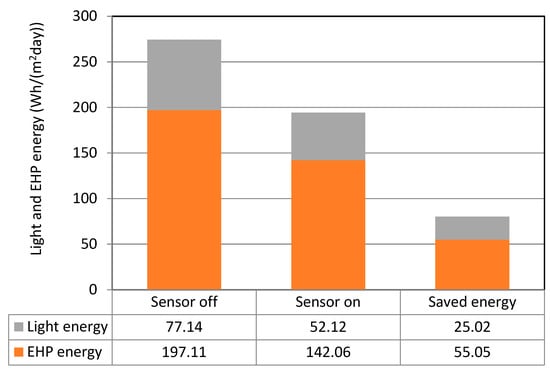
Figure 12.
Classrooms’ average daily electricity consumption.
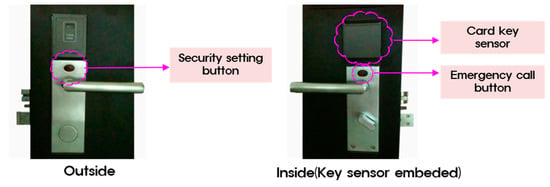
Figure 13.
Card key device of room management system.
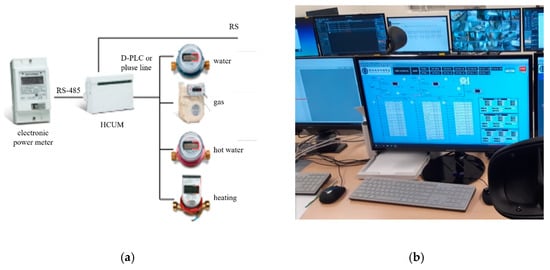
Figure 14.
(a) Remote monitoring system; (b) Management system monitor.
Recently, panel heating has been preferred for dormitory heating systems, as it is easier to control than gas boilers. The experiment was conducted for seven weeks from October to November to evaluate the amount of saved energy.
3.3.2. Experimental Results
This experiment was conducted on a female dormitory. Of the total 195 rooms in the dormitories, 130 rooms were selected for the experiment group, excluding 45 rooms of male users and 20 rooms of female users which was for a different experiment at the same time. To ensure fair and objective results, 10 households for the experiment group and the other 120 households for reference group were chosen randomly. Room management system (RMS) was operated normally for these 120 rooms which were selected as the reference group. Data from the reference group were then used to correct the values of experiments with the experimental group. The average electricity use of both the experimental group and reference group was measured for four weeks prior to the experiment to calculate the correction rate. During this period, the RMS was on for both groups. Then, for the subsequent three weeks, the experimental group’s electricity consumption was evaluated when the room management system was turned off. In contrast, the electricity consumption of the reference group was measured with the RMS turned on.
Data derived from the reference group were used to calculate the average electricity consumption of all 120 rooms. The results are shown in Table 10. Equation (1) was applied to calculate the experimental group’s saved amount.

Table 10.
Weekly electricity consumption of single-room dormitory (kWh).
Equation for calculating saved energy is given in Equation (1).
where A is energy use of experiment group (before experiment); B is energy use of reference group (before experiment); C is energy use of experiment group (during experiment) and D is energy use of reference group (during experiment)
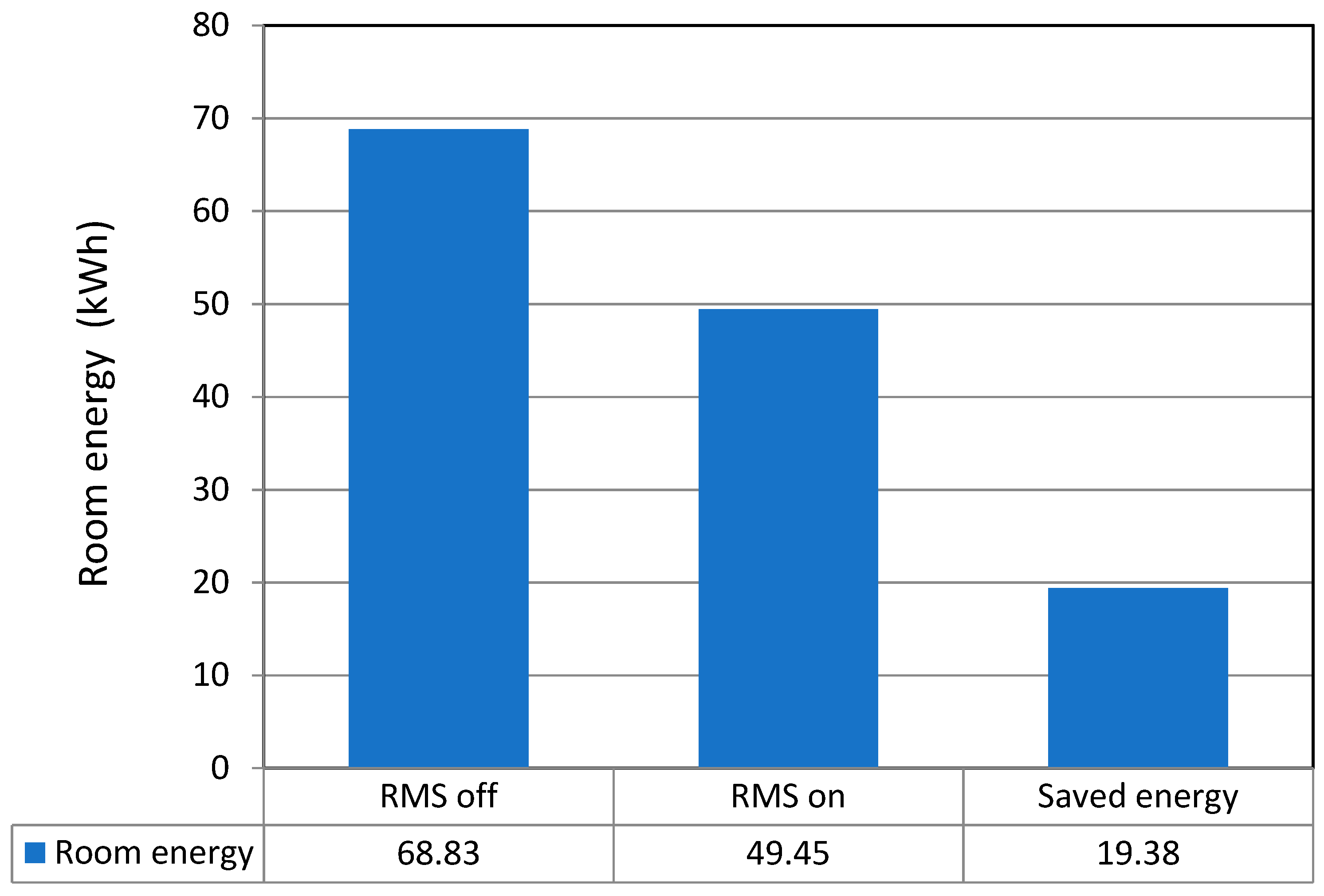
Prior to the experiment, the experimental group’s average weekly electricity use was 24.03 kWh; this value was 25.29 kWh for the reference group. The average weekly electricity use of the experimental group compared to the reference group was 95.0%, indicating that the experimental group used 5.0% less electricity than the reference group. During the experiment, the experimental group’s average weekly electricity use with the RMS turned off was 68.83 kWh. Meanwhile, the reference group’s average weekly electricity use with the RMS still turned on was 52.04 kWh. The average electricity use ratio of the experimental group to the reference group was 132.3%; therefore, the experimental group used 32.3% more electrical energy than the reference group.
Table 11 shows the calibration results. The RMS saved electrical energy in the amount of 19.38 kWh per week, with a savings rate of 28.2%. Per unit area and on a daily basis, the savings become 142.42 Wh/(m2day). Figure 15 shows average weekly electricity consumption of a single-room dormitory.

Table 11.
Average weekly electricity consumption of single-room dormitory (kWh).
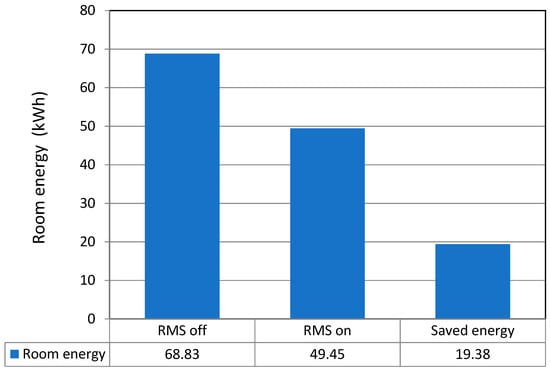
Figure 15.
Average weekly electricity consumption of a single-room dormitory.
4. Conclusions
In order to identify the amount of electrical energy that can be saved with an occupancy detection sensor and room management system in university buildings, we selected underground parking lots, classrooms, and dormitories as experimental sites. We measured and analyzed the amount of power consumed while the RF sensor and room management system were on or off to quantify the reduction. To fulfill this aim, the experiment was conducted on a weekly basis at the experimental sites to measure power consumption. For realistic results, the data were obtained with occupants living their regular lives and activities for a long period of four weeks. The results were then compared and analyzed. The findings are summarized as follows.
- In Experiment 1 (underground parking lot), the average light energy saved by using the RF sensor was 39.5 Wh/m2·day. We found that 77.6% of energy was saved compared to when the sensor was not in use.
- In Experiment 2 (classroom), light energy was reduced from 77.1 Wh/m2·day to 52.1 Wh/m2·day when using the sensor. The reduction rate is 32.4%.
- In Experiment 2 (classroom), cooling energy was reduced from 197.1 Wh/m2·day to 142.1 Wh/m2·day when using the sensor. The reduction rate is 27.9%. Although the savings rate of EHP was low due to shorter operating time (when compared to lighting), the amount was higher.
- In Experiment 3 (dormitory), lights, electrical outlets, and heating all required electrical energy to operate. Using the room management system, the average electrical energy saved was 142.4 Wh/m2·day per room, with a savings rate of 28.2%.
This paper found that underground parking lots were able to achieve the greatest savings, followed by dormitories and then classrooms, which generally coincide with the time of operation of each setting. Universities have different load characteristics than regular offices or houses. Thus, we hope that this paper’s data will be used in the application of systems to reduce electrical energy in the future construction and remodeling of university buildings.
For future research, we would like to study energy consumption of toilets, professors’ offices, administrative rooms, etc., and look for improvement. Sensors will be installed preferentially in places through economic analysis for this follow-up research. In addition, we plan to provide energy feedback (by social media, incentives, penalty, etc.) to students who use a lot of energy in the dormitory. We hope this will enhance users’ consciousness about energy consumption and that they will voluntarily participate in energy saving of electricity, heat energy and water.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.-W.L.; methodology, J.-W.L.; software, Y.I.K.; validation, J.-W.L.; formal analysis, J.-W.L.; investigation, J.-W.L.; resources, J.-W.L.; data curation, J.-W.L.; writing—original draft preparation, J.-W.L.; writing—review and editing, Y.I.K.; visualization, J.-W.L; supervision, Y.I.K.; project administration, Y.I.K.; funding acquisition, Y.I.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant, funded by the Korean Government (Ministry of Science, Technology and Innovation; Ministry of Education).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Chung, M.H.; Rhee, E.K. Potential opportunities for energy conservation in existing buildings on university campus: A field survey in Korea. Energy Build. 2018, 78, 176–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Advanced Information Analysis Technologies Research Group. Information Technology Road Map 2015; Jinhan M&B: Seoul, Korea, 2009; pp. 93–98. [Google Scholar]
- Park, K.H. A Study on the Improvement of Energy Efficiency in University Campus Buildings; Korea Energy Economics Institute: Ulsan, Korea, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Korea Energy Agency. 2017 Energy Statistics Handbook; Korea Energy Agency: Ulsan, Korea, 2017; p. 195. [Google Scholar]
- Alessandro, F.; Francesco, L. CO2 concentration and occupancy detection of educational buildings for energy efficiency purposes an experimental analysis. Preprints 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, L.; Luo, X.; Deng, J. Research and Design of Energy Efficiency Monitoring System for Resource-Saving Campus. In Advances in Engineerings Research, Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Mechanical, Electronic, Control and Automation Engineering (MECAE 2018); Qingdao, China, 30–31 March 2018, Atlantis Press: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; Volume CXLIX, pp. 765–769. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, X.; Feng, X. Campus Building Energy Consumption Quota for Case Analysis. In Proceedings of the 2017 2nd International Conference on Sustainable Energy and Environment Protection, Changsha, China, 23–25 June 2017; pp. 5–11. [Google Scholar]
- Beza, N.G.; Hussain, A.A. Electricity Audit and Reduction of Consumption: Campus Case Study. Int. J. Appl. Eng. Res. 2016, 11, 4423–4427. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, M.K.; Park, G.S.; Kim, S.Y. Energy Efficient Buildings for Creating a Green Campus; Seoul City Research Institute: Seoul, Korea, 2017; pp. 17–26. [Google Scholar]
- Chung, S.W. Energy Performance Improvements and Economic Analysis through Retrofit of Dormitory Buildings. Master’s Thesis, Yonsei University, Seoul, Korea, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, M.K. Foreign Cases and Implications for Energy Efficiency of Campus Buildings. Soc. Air-Cond. Refrig. Eng. Korea 2014, 43, 18–31. [Google Scholar]
- Kolokotsaa, D.; Gobakisa, K.; Papantonioua, S. Development of a web based energy management system for University Campuses: The CAMP-IT platform. Energy Build. 2016, 123, 119–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.P.; Zhou, J.; Luo, Q.M. Research on Campus Energy Consumption Monitoring System Based on IPV6. In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Advanced Education and Management, Singapore, 16–17 December 2017; pp. 558–561. [Google Scholar]
- Ward, S.; Gittens, M.; Rock, N. Campus Monitor: Intelligent Campus Environment Room Monitoring System. In Proceeding of the 2019 ACM SIGUCCS Annual Conference (SIGUCCS ’19), New Orleans, LA, USA, 3–6 November 2019; pp. 165–172. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, T.H.; Seo, J.H.; Choo, S.Y. An Energy Performance Comparison of University Lecture Facilities for Energy Saving Building Design. J. Archit. Inst. Korea Plan. Des. 2018, 34, 105–112. [Google Scholar]
- Jung, J.W. A Study on the Improvement Plans of Energy Performance in University Buildings by Analyzing Case Study. Master’s Thesis, Yeungnam University, Gyeongsan, Korea, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Seo, Y.S. A Study on the Improvement of Facilities and Energy performance by University Dormitory Remodeling. Master’s Thesis, Hanbat National University, Daejeon, Korea, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Son, J.W. A Study on the Energy Consumption Unit Based on Measurement Data in University Dormitory. Master’s Thesis, Kyungpook National University, Daegu, Korea, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.H.; Kim, S.H.; Shin, U.C. Analysis of Hot Water Usage in Hostel. In Proceedings of the 2005 Korean Solar Energy Society Conference, Seoul, Korea, June 2005; pp. 217–222. [Google Scholar]
- Nicolae, A.E.; Carutasiu, M.B.; Ionescu, C. Improving the energy efficiency of a student dormitory building by means of simulations. U.P.B. Sci. Bull. C 2018, 80, 189–202. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, M.Y.; Kim, Y.I.; Kim, Y.K. Comparison of Heating and Hot Water Supply Energy Consumption for Medium Capacity Boiler and Multi Boiler of a Dormitory Building. In Proceedings of the 2014 SAREK Summer Conference, Yong-pyong, Korea, 30 October 2014; pp. 594–597. [Google Scholar]
- Narayanan, S.; Apte, M.G.; Haves, P. Systems Approach to Energy Efficient Building Operation: Case Studies and Lessons Learned in a University Campus. In Proceedings of the 2010 ACEEE Summer Study on Energy Efficiency in Buildings, Pacific Grove, CA, USA, 15–20 August 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Song, H. The Effect of Using Smart Plug on Electricity Consumption by Giving Energy Feedback: A Case Study of University Students Living in BTL Dormitory. Master’s Thesis, Seoul National University, Seoul, Korea, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Zanta, S.; Andzej, V.; Rita, V. Research Review of Energy Savings Changing People’s Behavior: A Case of Foreign Country. Procedia-Soc. Behav. Sci. 2015, 191, 1996–2001. [Google Scholar]
- Song, E.B.; Kwon, U.J.; Kim, Y.J. A Classroom Power Management System Using IOT. In Proceedings of the Symposium of the Korean Institute of Communications and Information Sciences, Jeong-sun, Korea, January 2018; pp. 956–957. [Google Scholar]
- Duong, P.R. How Can Occupancy Modeling and Occupancy Sensors Reduce Energy Usage in Academic Buildings: An Application Approach to University of San Francisco. Master’s Thesis, University of San Francisco, San Francisco, CA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Abidin, N.I.A.; Zakaria, R.; Pauzi, N.N.M. Energy Efficiency Initiatives in a Campus Building. Chem. Eng. Trans. 2017, 56, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Jung, K.W.; Seo, C.W. Energy Saving System using Occupancy Sensors and Smart Plugs. J. Inst. Electron. Inf. Eng. 2015, 52, 161–167. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, S.I.; Park, D.W.; Lin, C.H. Implementation of an Efficient Indoor Light Control System using Daylight and Occupancy Detection. In Proceedings of the IEEK Summer Conference 2015, Jeju, Korea, June 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Nam, J.H.; Jang, W.J. The Classroom Lighting Energy Saving plan that used a human body detection sensor. In Proceedings of the KIIEE Annual Conference 2010, Hoeng-sheng, Korea, 6–7 May2010. [Google Scholar]
- Yun, J.H. Energy Consumption Pattern Classification University Buildings Using Change Point Model. Master’s Thesis, Seoul National University, Seoul, Korea, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Shyr, W.J.; Zeng, L.W.; Lin, C.K. Application of an Energy Management System via the Internet of Things on a University Campus. EURASIA J. Math. 2018, 14, 1759–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.-J.; Wei, T. Cost-effective energy saving measures based on BIM technology: Case study at National Taiwan University. Energy Build. 2016, 127, 433–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, N.; Pereira, L.D.; Ferreira, J.; Conceicao, P.; da Silva, P.P. Energy efficiency of higher education buildings: A case study. Int. J. Sustain. High. Educ. 2015, 16, 669–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urfaliglu, O.; Soyer, E.B.; Toreyin, B.U.; Cetin, A.E. PIR-sensor based human motion event classification. In Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE 16th Signal Processing, Communication and Applications Conference, Aydin, Turkey, 20–22 April 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Murayama, R.; Ayaka, K. Evaluation of Fatigue Specimens Using Emats For Nonlinear Ultrasonic Wave Detection. In Proceedings of the 2007 IEEE Ultrasonic Symposium, New York, NY, USA, 26 December 2007; pp. 1836–1839. [Google Scholar]
- Descamps, P.; Vindevoghel, J. Microwave Doppler Sensors for Terrestrial Transportation Applications. IEEE Trans. 1997, 46, 220–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, F.P.; Galeano, F.C. New Microwave Sensors for Intrusion Detection Systems. In Proceedings of the IEEE 33rd Annual 1999 International Carnahan Conference on Security Technology (Cat. No.99CH36303), Madrid, Spain, 5–7 October 1999; pp. 49–53. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).