Evaluation of Classification Algorithms to Predict Largemouth Bass (Micropterus salmoides) Occurrence
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
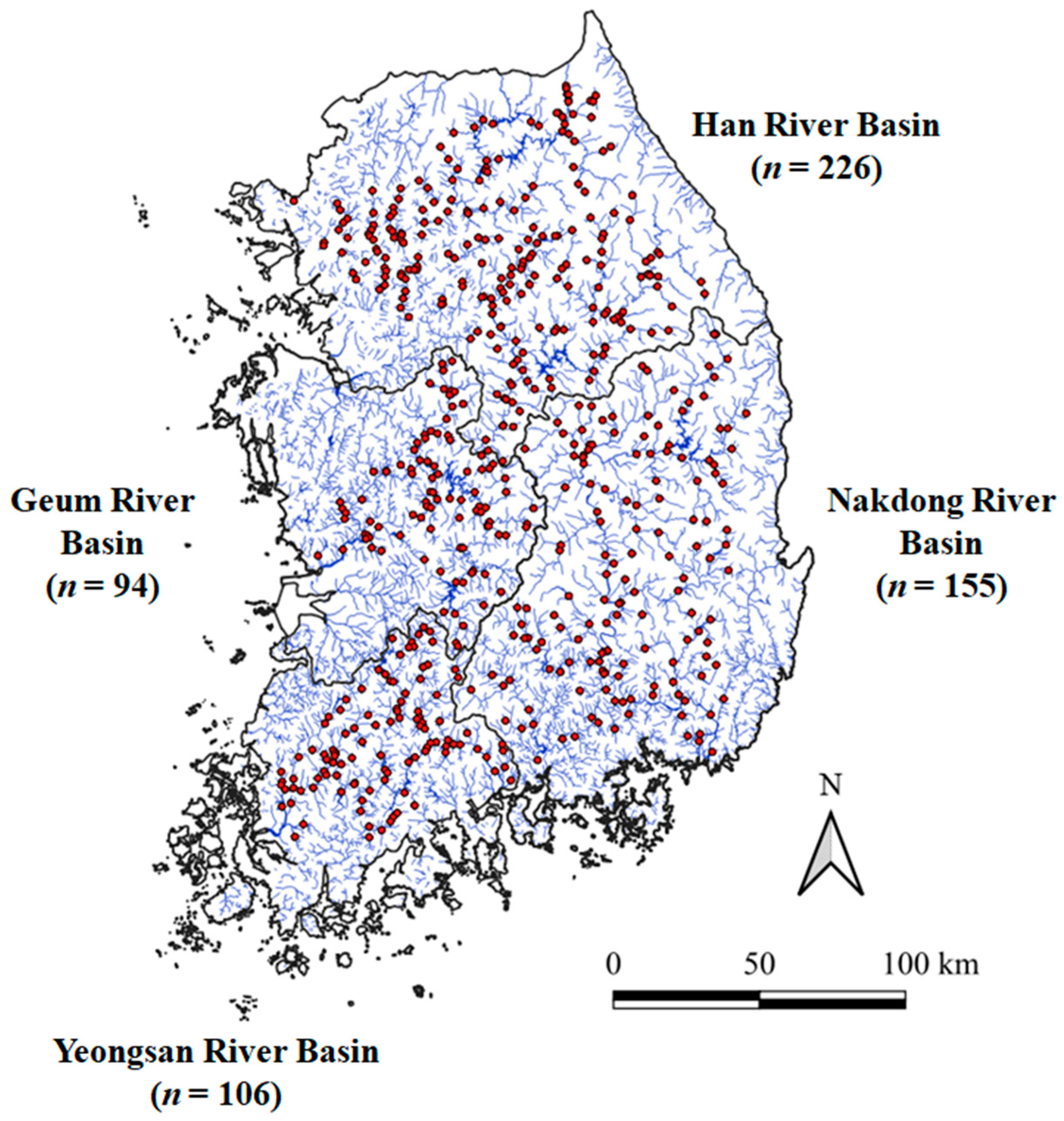
2.1. Study Area and Fish Data
2.2. Environmental Data
2.3. Classification Modeling
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Performance of Classification Algorithms
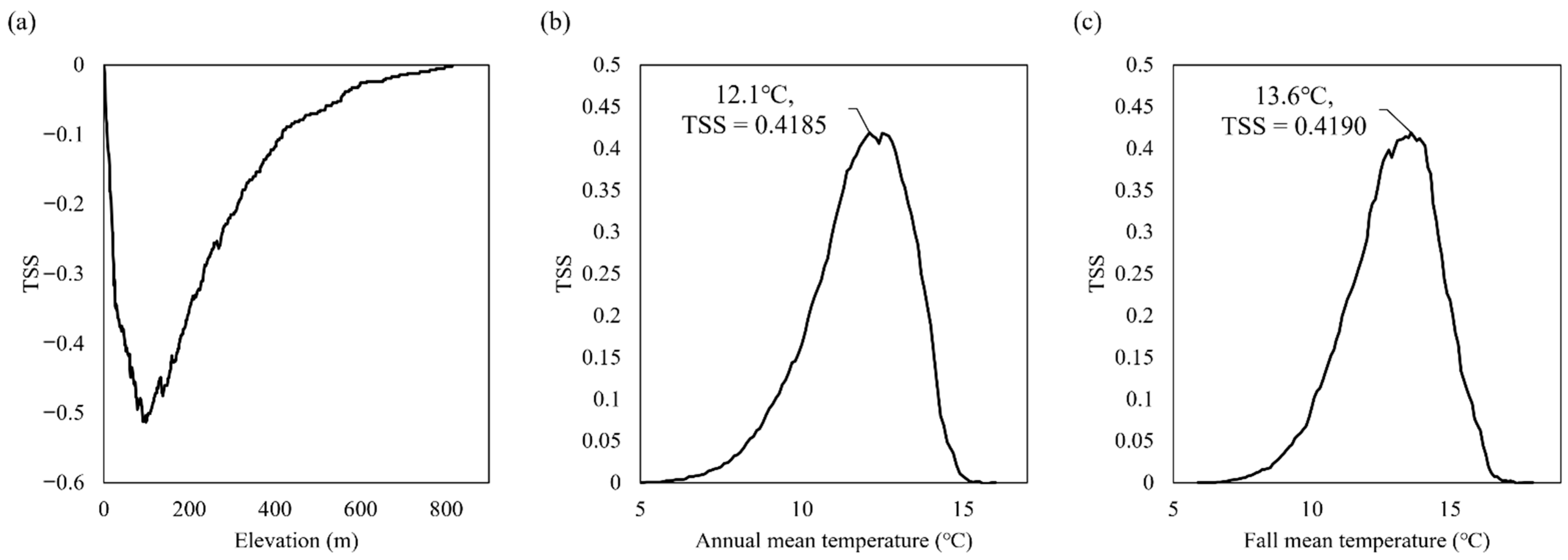
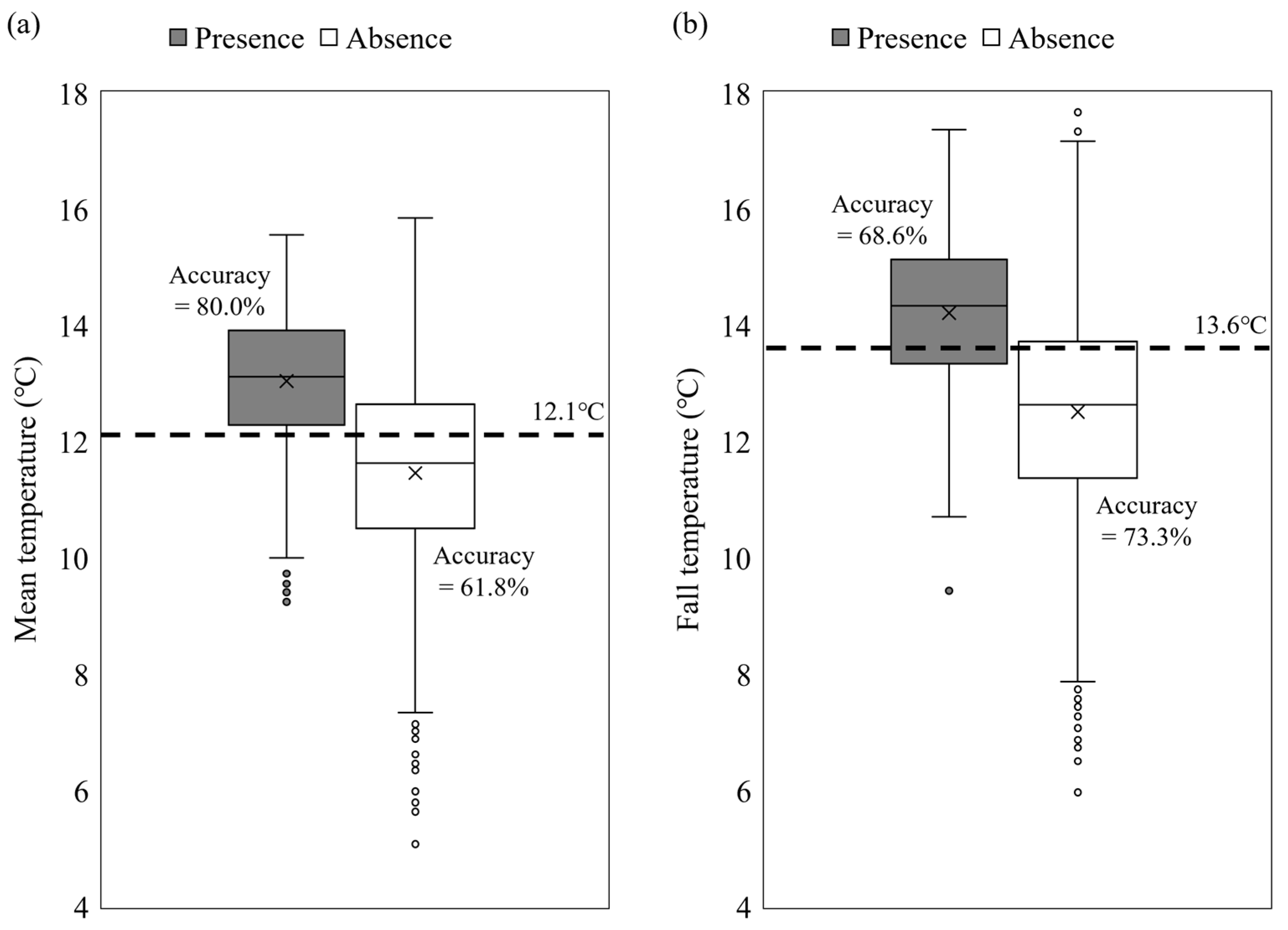
3.2. Role of Environmental Variables
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Grenouillet, G.; Buisson, L.; Casajus, N.; Lek, S. Ensemble modelling of species distribution: The effects of geographical and environmental ranges. Ecography 2011, 34, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNyset, K.M. Use of ecological niche modelling to predict distributions of freshwater fish species in Kansas. Ecol. Freshw. Fish 2005, 14, 243–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vezza, P.; Parasiewicz, P.; Calles, O.; Spairani, M.; Comoglio, C. Modelling habitat requirements of bullhead (Cottus gobio) in Alpine streams. Aquat. Sci. 2014, 76, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraker, M.E.; Keitzer, S.C.; Sinclair, J.S.; Aloysius, N.R.; Dippold, D.A.; Yen, H.; Arnold, J.G.; Daggupati, P.; Johnson, M.-V.V.; Martin, J.F. Projecting the effects of agricultural conservation practices on stream fish communities in a changing climate. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 747, 141112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercado-Silva, N.; Olden, J.D.; Maxted, J.T.; Hrabik, T.R.; Vander Zanden, M.J. Forecasting the spread of invasive rainbow smelt in the Laurentian Great Lakes region of North America. Conserv. Biol. 2006, 20, 1740–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iguchi, K.I.; Matsuura, K.; McNyset, K.M.; Peterson, A.T.; Scachetti-Pereira, R.; Powers, K.A.; Vieglais, D.A.; Wiley, E.O.; Yodo, T. Predicting invasions of North American basses in Japan using native range data and a genetic algorithm. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 2004, 133, 845–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kärcher, O.; Frank, K.; Walz, A.; Markovic, D. Scale effects on the performance of niche-based models of freshwater fish distributions. Ecol. Model. 2019, 405, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conti, L.; Comte, L.; Hugueny, B.; Grenouillet, G. Drivers of freshwater fish colonisations and extirpations under climate change. Ecography 2015, 38, 510–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuda, S.; De Baets, B.; Onikura, N.; Nakajima, J.; Mukai, T.; Mouton, A. Modelling the distribution of the pan-continental invasive fish Pseudorasbora parva based on landscape features in the northern Kyushu Island, Japan. Aquat. Conserv. Mar. Freshw. Ecosyst. 2013, 23, 901–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howeth, J.; Gantz, C.; Angermeier, P.; Frimpong, E.; Hoff, M.; Keller, R.; Mandrak, N.; Marchetti, M.; Olden, J.; Romagosa, C.; et al. Predicting invasiveness of species in trade: Climate match, trophic guild and fecundity influence establishment and impact of non-native freshwater fishes. Divers. Distrib. 2016, 22, 148–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, Y.S.; Bae, M.J.; Hwang, S.J.; Kim, S.H.; Park, Y.S. Predicting potential impacts of climate change on freshwater fish in Korea. Ecol. Inform. 2015, 29, 156–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhn, M. Building Predictive Models in R Using the caret Package. J. Stat. Softw. 2008, 28, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2019; Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 21 May 2020).
- Thuiller, W.; Lafourcade, B.; Engler, R.; Araújo, M.B. BIOMOD—A platform for ensemble forecasting of species distributions. Ecography 2009, 32, 369–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallardo, B.; Aldridge, D.C. Inter-basin water transfers and the expansion of aquatic invasive species. Water Res. 2018, 143, 282–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buisson, L.; Thuiller, W.; Casajus, N.; Lek, S.; Grenouillet, G. Uncertainty in ensemble forecasting of species distribution. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2010, 16, 1145–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.B.; Lek, S.; Ye, S.W.; Li, W.; Liu, J.S.; Li, Z.J. Uncertainty in ensemble modelling of large-scale species distribution: Effects from species characteristics and model techniques. Ecol. Model. 2015, 306, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones-Farrand, D.T.; Fearer, T.M.; Thogmartin, W.E.; Thompson, F.R.; Nelson, M.D.; Tirpak, J.M. Comparison of statistical and theoretical habitat models for conservation planning: The benefit of ensemble prediction. Ecol. Appl. 2011, 21, 2269–2282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rokach, L. Ensemble-based classifiers. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2010, 33, 1–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulos, H.M.; Chernoff, B.; Fuller, P.L.; Butman, D. Ensemble forecasting of potential habitat for three invasive fishes. Aquat. Invasions 2012, 7, 59–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, T.X.; Elith, J.; Lahoz-Monfort, J.J.; Guillera-Arroita, G. Testing whether ensemble modelling is advantageous for maximising predictive performance of species distribution models. Ecography 2020, 43, 549–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- García-Berthou, E.; Alcaraz, C.; Pou-Rovira, Q.; Zamora, L.; Coenders, G.; Feo, C. Introduction pathways and establishment rates of invasive aquatic species in Europe. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2005, 62, 453–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maezono, Y.; Miyashita, T. Community-level impacts induced by introduced largemouth bass and bluegill in farm ponds in Japan. Biol. Conserv. 2003, 109, 111–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamerath, M.; Chandra, S.; Allen, B.C. Distribution and impacts of warm water invasive fish in Lake Tahoe, USA. Aquat. Invasions 2008, 3, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodgson, J.R.; Hansen, E.M. Terrestrial prey items in the diet of largemouth bass, Micropterus salmoides, in a small north temperate lake. J. Freshw. Ecol. 2005, 20, 793–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NIER. Survey and Assessment of Stream/River Ecosystem Health (VII); Publication Number: 11-1480523-002181-01; NIER: Incheon, Korea, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Shim, T.; Kim, Z.; Seo, D.; Kim, Y.O.; Hwang, S.J.; Jung, J. Integrating hydraulic and physiologic factors to develop an ecological habitat suitability model. Environ. Model. Softw. 2020, 131, 104760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Z.; Shim, T.; Koo, Y.M.; Seo, D.; Kim, Y.O.; Hwang, S.J.; Jung, J. Predicting the impact of climate change on freshwater fish distribution by incorporating water flow rate and quality variables. Sustainability 2020, 12, 10001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pletterbauer, F.; Melcher, A.H.; Ferreira, T.; Schmutz, S. Impact of climate change on the structure of fish assemblages in European rivers. Hydrobiologia 2015, 744, 235–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pont, D.; Hugueny, B.; Oberdorff, T. Modelling habitat requirement of European fishes: Do species have similar responses to local and regional environmental constraints? Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2005, 62, 163–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yoon, J.D.; Kim, J.H.; Byeon, M.S.; Yang, H.J.; Park, J.Y.; Shim, J.H.; Song, H.B.; Yang, H.; Jang, M.H. Distribution patterns of fish communities with respect to environmental gradients in Korean streams. Ann. Limnol. Int. J. Limnol. 2011, 47, S63–S71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oberdorff, T.; Pont, D.; Hugueny, B.; Chessel, D. A probabilistic model characterizing fish assemblages of French rivers: A framework for environmental assessment. Freshw. Biol. 2001, 46, 399–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huet, M. Profiles and biology of western European streams as related to fish management. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 1959, 88, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Delgado, M.; Cernadas, E.; Barro, S.; Amorim, D. Do we need hundreds of classifiers to solve real world classification problems? J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2014, 15, 3133–3181. [Google Scholar]
- Hermoso, V.; Clavero, M.; Blanco-Garrido, F.; Prenda, J. Invasive species and habitat degradation in Iberian streams: An analysis of their role in freshwater fish diversity loss. Ecol. Appl. 2011, 21, 175–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, T.; Elith, J.; Guillera-Arroita, G.; Lahoz-Monfort, J.J. A review of evidence about use and performance of species distribution modelling ensembles like BIOMOD. Divers. Distrib. 2019, 25, 839–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munoz-Mas, R.; Lopez-Nicolas, A.; Martinez-Capel, F.; Pulido-Velazquez, M. Shifts in the suitable habitat available for brown trout (Salmo trutta L.) under short-term climate change scenarios. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 544, 686–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krogh, A.; Vedelsby, J. Neural network ensembles, cross validation, and active learning. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 1995, 7, 231. [Google Scholar]
- Geman, S.; Bienenstock, E.; Doursat, R. Neural networks and the bias/variance dilemma. Neural Comput. 1992, 4, 1–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, G.; Wyatt, J.; Harris, R.; Yao, X. Diversity creation methods: A survey and categorisation. Inf. Fusion 2005, 6, 5–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, Y.; Chen, H. When does diversity help generalization in classification ensembles? IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Didaci, L.; Fumera, G.; Roli, F. Diversity in classifier ensembles: Fertile concept or dead end? In Proceedings of the International Workshop on Multiple Classifier Systems; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; pp. 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Echelpoel, W.; Boets, P.; Landuyt, D.; Gobeyn, S.; Everaert, G.; Bennetsen, E.; Mouton, A.; Goethals, P.L. Species distribution models for sustainable ecosystem management. In Developments in Environmental Modelling; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; Volume 27, pp. 115–134. [Google Scholar]
- Boets, P.; Landuyt, D.; Everaert, G.; Broekx, S.; Goethals, P.L. Evaluation and comparison of data-driven and knowledge-supported Bayesian Belief Networks to assess the habitat suitability for alien macroinvertebrates. Environ. Model. Softw. 2015, 74, 92–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alofs, K.; Jackson, D. The abiotic and biotic factors limiting establishment of predatory fishes at their expanding northern range boundaries in Ontario, Canada. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2015, 21, 2227–2237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alofs, K.M.; Jackson, D.A.; Lester, N.P. Ontario freshwater fishes demonstrate differing range-boundary shifts in a warming climate. Divers. Distrib. 2014, 20, 123–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meador, M.R.; Brown, L.R.; Short, T. Relations between introduced fish and environmental conditions at large geographic scales. Ecol. Indic. 2003, 3, 81–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glover, D.C.; DeVries, D.R.; Wright, R.A. Growth of largemouth bass in a dynamic estuarine environment: An evaluation of the relative effects of salinity, diet, and temperature. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2013, 70, 485–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasler, C.T.; Suski, C.D.; Hanson, K.C.; Cooke, S.J.; Philipp, D.P.; Tufts, B.L. Effect of water temperature on laboratory swimming performance and natural activity levels of adult largemouth bass. Can. J. Zool. 2009, 87, 589–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]



| Models | Average Rank | Training Set | Test Set | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Accuracy | Kappa | Accuracy | Kappa | ||
| rf | 1.29 (0.78) | 0.999 (0) | 0.998 (0.001) | 0.830 (0.014) | 0.544 (0.041) |
| C5.0 | 2.39 (1.19) | 0.956 (0.031) | 0.884 (0.083) | 0.825 (0.012) | 0.528 (0.036) |
| cforest | 2.90 (0.71) | 0.931 (0.004) | 0.815 (0.011) | 0.822 (0.010) | 0.508 (0.029) |
| knn | 6.25 (2.42) | 0.838 (0.004) | 0.567 (0.010) | 0.804 (0.009) | 0.470 (0.024) |
| svmRadial | 6.30 (2.14) | 0.838 (0.006) | 0.531 (0.023) | 0.813 (0.008) | 0.452 (0.030) |
| svmRadialCost | 6.64 (2.25) | 0.837 (0.008) | 0.525 (0.026) | 0.813 (0.008) | 0.449 (0.029) |
| fda | 7.19 (2.51) | 0.817 (0.006) | 0.515 (0.018) | 0.808 (0.009) | 0.490 (0.025) |
| pcaNNet | 8.19 (2.61) | 0.821 (0.014) | 0.524 (0.033) | 0.801 (0.012) | 0.467 (0.029) |
| bayesglm | 8.21 (2.54) | 0.815 (0.004) | 0.500 (0.012) | 0.808 (0.010) | 0.480 (0.029) |
| svmPoly | 8.49 (2.12) | 0.827 (0.013) | 0.508 (0.036) | 0.808 (0.008) | 0.449 (0.026) |
| avNNet | 9.73 (2.36) | 0.817 (0.008) | 0.495 (0.037) | 0.798 (0.007) | 0.436 (0.033) |
| nnet | 11.64 (2.17) | 0.793 (0.029) | 0.430 (0.154) | 0.776 (0.021) | 0.380 (0.140) |
| pda | 11.90 (1.39) | 0.801 (0.005) | 0.437 (0.017) | 0.795 (0.011) | 0.419 (0.033) |
| Spring | Summer | Fall | Winter | Annual Average | Monthly Difference | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Temp (°C) | 11.53 (1.6) | 23.35 (1.53) | 12.97 (1.82) | −0.32 (2.4) | 11.88 (1.67) | 27.95 (3.75) |
| Prcp (mm/month) | 70.23 (36.66) | 239.14 (85.4) | 79.38 (26.22) | 28.66 (13.94) | 104.29 (25.4) | 332.8 (129.01) |
| Flow (m3/s) | 12.28 (37.17) | 43.15 (107.43) | 26.84 (61.65) | 9.49 (23.89) | 23.06 (51.3) | 88.62 (219.7) |
| TotalN (mg/L) | 1.84 (2.22) | 1.77 (1.71) | 1.94 (1.86) | 2.19 (2.29) | 1.93 (1.94) | 2.12 (1.88) |
| TotalP (mg/L) | 0.15 (0.21) | 0.11 (0.11) | 0.06 (0.09) | 0.14 (0.21) | 0.12 (0.11) | 0.43 (0.57) |
| TotalSS (mg/L) | 24.32 (177.64) | 40.06 (328.12) | 15.05 (83.66) | 20.44 (195.64) | 24.93 (135.39) | 126.92 (840.42) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, Z.; Shim, T.; Ki, S.J.; Seo, D.; An, K.-G.; Jung, J. Evaluation of Classification Algorithms to Predict Largemouth Bass (Micropterus salmoides) Occurrence. Sustainability 2021, 13, 9507. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13179507
Kim Z, Shim T, Ki SJ, Seo D, An K-G, Jung J. Evaluation of Classification Algorithms to Predict Largemouth Bass (Micropterus salmoides) Occurrence. Sustainability. 2021; 13(17):9507. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13179507
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Zhonghyun, Taeyong Shim, Seo Jin Ki, Dongil Seo, Kwang-Guk An, and Jinho Jung. 2021. "Evaluation of Classification Algorithms to Predict Largemouth Bass (Micropterus salmoides) Occurrence" Sustainability 13, no. 17: 9507. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13179507
APA StyleKim, Z., Shim, T., Ki, S. J., Seo, D., An, K.-G., & Jung, J. (2021). Evaluation of Classification Algorithms to Predict Largemouth Bass (Micropterus salmoides) Occurrence. Sustainability, 13(17), 9507. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13179507






