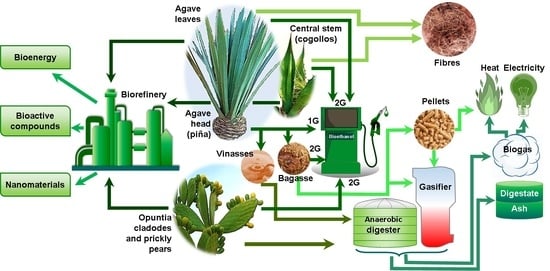
Agave and Opuntia Species as Sustainable Feedstocks for Bioenergy and Byproducts
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
3. Agave (Agavaceae) and Opuntia (Cactaceae) as CAM Crops
4. Characteristics of Production and Cultivation of Agave and Opuntia
4.1. Agave Species
4.2. Productivity of Agave
4.3. Opuntia Species
4.4. Productivity of Opuntia
5. Potential Agave and Opuntia Species for Fuels Production and Energy
5.1. Biofuels, Bioenergy and Byproducts from Agave Species
5.2. Biogas and Energy from the Opuntia Species
6. Challenges and Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bhuyar, P.; Sundararaju, S.; Rahim, M.H.A.; Maniam, G.P.; Govindan, N. Enhanced productivity of lipid extraction by urea stress conditions on marine microalgae Coelastrum sp. for improved biodiesel production. Bioresour. Technol. Rep. 2021, 15, 100696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayakumar, S.; Bhuyar, P.; Pugazhendhi, A.; Rahim, M.H.A.; Maniam, G.P.; Govindan, N. Effects of light intensity and nutrients on the lipid content of marine microalga (diatom) Amphiprora sp. for promising biodiesel production. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 768, 145471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhuyar, P.; Yusoff, M.M.; Rahim, M.H.A.; Sundararaju, S.; Maniam, G.P.; Govindan, N. Govindan Effect of plant hormones on the production of biomass and lipid extraction for biodiesel production from microalgae Chlorella sp. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. Food Sci. 2020, 9, 671–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whangchai, K.; Souvannasouk, V.; Bhuyar, P.; Ramaraj, R.; Unpaprom, Y. Biomass generation and biodiesel production from macroalgae grown in the irrigation canal wastewater. Water Sci. Technol. 2021, 2021195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iizumi, T.; Ramankutty, N. How do weather and climate influence cropping area and intensity? Glob. Food Secur. 2015, 4, 46–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohn, A.S.; VanWey, L.K.; Spera, S.; Mustard, L.K.V.S.A.S.J.F. Cropping frequency and area response to climate variability can exceed yield response. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2016, 6, 601–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, J.E.; Lobell, D.B.; Genova, R.C.; Field, C.B. The Global Potential of Bioenergy on Abandoned Agriculture Lands. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 5791–5794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cushman, J.C.; Davis, S.C.; Yang, X.; Borland, A.M. Development and use of bioenergy feedstocks for semi-arid and arid lands. J. Exp. Bot. 2015, 66, 4177–4193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuevas, E.; Blancas, J.; Caballero, J.; Hinojoza-Díaz, I.A.; Martínez-Ballesté, A. Agricultural management and local knowledge: Key factors for the conservation of socio-ecosystems in the face of the pollinator world crisis. Bot. Sci. 2021, 99, 305–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabrera-Toledo, D.; Vargas-Ponce, O.; Ascencio-Ramírez, S.; Valadez-Sandoval, L.M.; Pérez-Alquicira, J.; Morales-Saavedra, J.; Huerta-Galván, O.F. Morphological and Genetic Variation in Monocultures, Forestry Systems and Wild Populations of Agave maximiliana of Western Mexico: Implications for Its Conservation. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mason, P.M.; Glover, K.; Smith, J.A.C.; Willis, K.J.; Woods, J.; Thompson, I.P. The potential of CAM crops as a globally significant bioenergy resource: Moving from ‘fuel or food’ to ‘fuel and more food’. Energy Environ. Sci. 2015, 8, 2320–2329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owen, N.A.; Fahy, K.; Griffiths, H. Crassulacean acid metabolism (CAM) offers sustainable bioenergy production and resilience to climate change. GCB Bioenergy 2015, 8, 737–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borland, A.M.; Griffiths, H.; Hartwell, J.; Smith, J.A.C. Exploiting the potential of plants with crassulacean acid metabolism for bioenergy production on marginal lands. J. Exp. Bot. 2009, 60, 2879–2896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borland, A.; Hartwell, J.; Weston, D.; Schlauch, K.A.; Tschaplinski, T.; Tuskan, G.; Yang, X.; Cushman, J.C. Engineering crassulacean acid metabolism to improve water-use efficiency. Trends Plant Sci. 2014, 19, 327–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, X.; Zhang, X.; Wang, D. Land Availability for Biofuel Production. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 334–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Food and Agricultural Organization of the United Nations (FAO). Arid Zone Forestry: A Guide for Field Technicians, FAO Conservation Guide, 20; FAO: Rome, Italy, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- United Nations Convention to Combat Desertification (UNCCD), Desertification: A Visual Synthesis; United Nations Convention to Combat Desertification Secretariat: Bonn, Germany, 2011.
- Galán-Reséndiz, M. Contribución al Entendimiento del Sistema Agroforestal Con Metepantle en Tepetlaoxtoc, México. Master’s in Sciences Thesis. Available online: http://repositorio.chapingo.edu.mx:8080/bitstream/handle/20.500.12098/544/mcads-grm-18.pdf?sequence=2&isAllowed=y (accessed on 7 September 2021).
- Mielenz, J.R.; Rodriguez, M., Jr.; Thompson, O.A.; Yang, X.; Yin, H. Development of Agave as a dedicated biomass source: Production of biofuels from whole plants. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2015, 8, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Lu, M.; Carl, S.; Mayer, J.A.; Cushman, J.C.; Tian, E.; Lin, H. Biomass characterization of Agave and Opuntia as potential biofuel feedstocks. Biomass Bioenergy 2015, 76, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, S.C.; Kuzmick, E.R.; Niechayev, N.; Hunsaker, D.J. Productivity and water use efficiency of Agave americana in the first field trial as bioenergy feedstock on arid lands. GCB Bioenergy 2016, 9, 314–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niechayev, N.A.; Jones, A.M.; Rosenthal, M.D.; Davis, S.C. A model of environmental limitations on production of Agave americana L. grown as a biofuel crop in semi-arid regions. J. Exp. Bot. 2019, 70, 6549–6559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, X.; Corbin, K.R.; Burton, R.A.; Tan, D.K. Agave: A promising feedstock for biofuels in the water-energy-food-environment (WEFE) nexus. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 261, 121283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopkins, W.G.; Hüner, N.P.A. Introduction to Plant Physiology; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Nobel, P.S. Physicochemical and Environmental Plant Physiology, 4th ed.; Elsevier Academic Press: Oxford, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- García-Mendoza, A.J. Distribution of the genus Agave (Agavaceae) and its endemic species in Mexico. Cactus Succul. J. 2002, 74, 177–187. [Google Scholar]
- García-Mendoza, A.J. Los Agaves de México. Ciencias 2007, 87, 14–23. [Google Scholar]
- Esparza, S.S. Distribución Geográfica del Género Opuntia (Cactaceae) en México. Master’s Thesis, Universidad Autónoma de San Luis Potosí, San Luis Potosí, Mexico, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Díaz-Padilla, G.; Sánchez-Cohen, I.; Guajardo-Panes, R.A.; Del Ángel-Pérez, A.L.; Ruíz-Corral, A.; Medina-García, G.; Ibarra-Castillo, D. Mapeo del índice de aridez y su distribución poblacional en méxico. Rev. Chapingo Ser. Cienc. For. Ambient. 2011, XVII, 267–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Palla, K.J.; Hu, R.; Moseley, R.; Mendoza, C.; Chen, M.; Abraham, P.E.; Labbé, J.L.; Kalluri, U.C.; Tschaplinski, T.; et al. Perspectives on the basic and applied aspects of crassulacean acid metabolism (CAM) research. Plant Sci. 2018, 274, 394–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, S.C.; Simpson, J.; Gil-Vega, K.D.C.; A Niechayev, N.; Van Tongerlo, E.; Castano, N.H.; Dever, L.V.; Búrquez, A. Undervalued potential of crassulacean acid metabolism for current and future agricultural production. J. Exp. Bot. 2019, 70, 6521–6537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, S.C.; Dohleman, F.G.; Long, S. The global potential for Agave as a biofuel feedstock. GCB Bioenergy 2010, 3, 68–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chambers, D.; Holtum, J.A.M. Feasibility of Agave as a Feedstock for Biofuel Production in Australia; Publication No. 10/104; Rural Industries Research and Development Corporation: Barton, Australia, 2010; p. 74. [Google Scholar]
- Owen, N.A.; Griffiths, H. Marginal land bioethanol yield potential of four crassulacean acid metabolism candidates (Agave fourcroydes, Agave salmiana, Agave tequilana and Opuntia ficus-indica) in Australia. GCB Bioenergy 2014, 6, 687–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, S.C.; Abatzoglou, J.T.; LeBauer, D.S. Expanded Potential Growing Region and Yield Increase for Agave americana with Future Climate. Agronomy 2021, 11, 2109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Servicio de Información Agroalimentaria y Pesquera (SIAP). Producción Agropecuaria y Pesquera, Producción anual. Estadística de Producción Agrícola, Datos Abiertos, Secretaría de Agricultura, Ganadería, Desarrollo Rural, Pesca y Alimentación. 2020. Available online: http://infosiap.siap.gob.mx/gobmx/datosAbiertos_a.php (accessed on 20 May 2021).
- Davis, S.C.; Griffiths, H.; Holtum, J.; Saavedra, A.L.; Long, S.P. The Evaluation of Feedstocks in GCBB Continues with a Special Issue on Agave for Bioenergy. GCB Bioenergy 2011, 3, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, S.C.; Lebauer, D.S.; Long, S.P. Light to liquid fuel: Theoretical and realized energy conversion efficiency of plants using Crassulacean Acid Metabolism (CAM) in arid conditions. J. Exp. Bot. 2014, 65, 3471–3478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holtum, J.A.M.; Chambers, D.; Morgan, T.; Tan, D.K.Y. Agave as a biofuel feedstock in Australia. GCB Bioenergy 2010, 3, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Núñez, H.M.; Rodríguez, L.F.; Khanna, M. Agave for tequila and biofuels: An economic assessment and potential opportunities. GCB Bioenergy 2010, 3, 43–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escamilla-Treviño, L.L. Potential of Plants from the Genus Agave as Bioenergy Crops. BioEnergy Res. 2011, 5, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nobel, P.S. Environmental Biology of Agaves and Cacti; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Villacís-Chiriboga, J.; Elst, K.; Van Camp, J.; Vera, E.; Ruales, J. Valorization of byproducts from tropical fruits: Extraction methodologies, applications, environmental, and economic assessment: A review (Part 1: General overview of the byproducts, traditional biorefinery practices, and possible applications). Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2020, 19, 405–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Mendoza, A.J. Flora del Valle de Tehuacán-Cuicatlán; Instituto de Biología, Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México: Mexico City, Mexico, 2011; p. 88. [Google Scholar]
- Gentry, H.S. Agaves of Continental North America; University of Arizona Press: Tucson, AZ, USA, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Colunga-García, M.; Zizumbo-Villarreal, D.; Martínez-Torres, J. Tradiciones en el aprovechamiento de los Agaves mexicanos: Una aportación a la protección legal y conservación biológica y cultural. In En lo Ancestral Hay Futuro: Del Tequila, los Mezcales y Otros Agaves; Colunga-García, M.P., Eguiarte, S.A.L., Zizumbo-Villarreal, D., Eds.; Centro de Investigación Científica de Yucatán, A.C.: Mérida, Yucatán, Mexico, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Comisión Nacional para el Conocimiento y Uso de la Biodiversidad (CONABIO), Red Mundial de Información sobre Biodiversidad (REMIB). 2016. Available online: http://www.conabio.gob.mx/remib/doctos/remibnodosdb.html? (accessed on 19 April 2021).
- Diario Oficial de la Federación (DOF). NORMA Oficial Mexicana NOM-006-SCFI-2012, Bebidas alcohólicas-Tequila-Especificaciones, 13 December 2012. Diario Oficial de la Federación 2012, 912, 5–25. [Google Scholar]
- Sistema Nacional de Investigación y Transferencia Tecnológica para el Desarrollo Rural Sustentable (SNITT). Agenda Nacional de Investigación, Innovación y Transferencia de Tecnología, Agrícola 2016–2022; SNITT- SAGARPA: Ciudad de México, Mexico, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Diario Oficial de la Federación (DOF). Resolución por la que se modifica la declaración general de protección de la denominación de origen Mezcal. Diario Oficial Federación 2001, 578, 72–86. [Google Scholar]
- García-Mendoza, A.J. Sistemática y distribución actual de los Agave spp. mezcaleros; Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México: Instituto de Biología, Bases de datos SNIB-CONABIO, proyecto V029: Mexico, 2003. Available online: http://ipttest.conabio.gob.mx/iptconabiotest/resource?r=SNIB-V029&request_locale=ru (accessed on 5 March 2019).
- Colunga-García Marín, P.; Zizumbo-Villarreal, D. El tequila y otros mezcales del centro-occidente de México: Domesticación, diversidad y conservación de germoplasma. In En Lo Ancestral Hay Futuro: Del Tequila, Los Mezcales Y Otros Agaves; Colunga-García Colunga-García Marín, P., Larqué, S.A., Eguiarte, L.E., Zizumbo-Villarreal, D., Eds.; Mérida, YucatánMexico: Mérida, Yucatán, Mexico, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Diario Oficial de la Federación (DOF). Declaración General de Protección de la Denominación de Origen Raicilla, 28 June 2019. Diario Oficial Federación 2019, 789, 93–100. [Google Scholar]
- Gardea, A.A.; Findley, L.T.; Orozco-Avitia, J.A.; Bañuelos, N.; Esqueda, M.; Huxman, T.H. Bacanora and Sotol: So Far, So Close. Estud. Soc. 2012, 2, 153–168. [Google Scholar]
- Reynoso-Santos, R.; García-Mendoza, A.J.; López-Báez, W.; López-Luna, A.; Cadena-Iñiguez, P.; Pérez-Farrera, M.A.; Domínguez-Gutiérrez, M.H. Identificación taxonómica de Agaves (Agave spp.) utilizados para la elaboración del licor comiteco en Chiapas, México. Agroproductividad 2012, 5, 9–17. [Google Scholar]
- Nobel, P. Crop ecosystem responses of climatic change. Crassulacean acid metabolism crops. In Climate Change and Global Crop Productivity; Reddy, K., Hodges, H., Eds.; CAB International: Wallingford, UK, 2020; pp. 315–331. [Google Scholar]
- Subedi, R.; Akbar, D.; Ashwath, N.; Rolfe, J.; Rahman, A. Assessing the Viability of Growing Agave tequilana as a Biofuel Feedstock in Queensland, Australia. Int. J. Energy Econ. Policy 2017, 7, 172–180. [Google Scholar]
- Iñiguez-Covarrubias, G.; Díaz-Teres, R.; Sanjuan-Dueñas, R.; Anzaldo-Hernández, J.; Rowell, R.M. Utilization of by-products from the tequila industry. Part 2: Potential value of Agave tequilana Weber azul leaves. Bioresour. Technol. 2001, 77, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montañez, J.L.; Victoria, J.C.; Flores, R.; Vivar, M.Á. Fermentación de los fructanos del Agave tequilana Weber azul por Zymomonas mobilis y Saccharomyces cerevisiae en la producción de bioetanol. Información Tecnol. 2011, 22, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Nobel, P.S. Achievable productivities of certain CAM plants: Basis for high values compared with C3 and C4 plants. New Phytologist 1991, 119, 183–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zúñiga-Estrada, L.; Rosales, R.E.; Yáñez-Morales, M.J.; Jacques-Hernández, C. Characteristics and productivity of a CAM plant, Agave tequilana developed with fertigation in Tamaulipas, Mexico. Rev. Mexicana Cienc. Agric. 2018, 9, 553–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Garcia-Moya, E.; Romero-Manzanares, A.; Nobel, P.S. Highlights for Agave Productivity. GCB Bioenergy 2010, 3, 4–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Corral, J.A.; Pimienta-Barrios, E.; Zañudo-Hernández, J. Optimal and marginal thermal regions for the cultivation of Agave tequilana on the Jalisco state. Agrociencia 2002, 36, 41–53. [Google Scholar]
- Mariles, F.V. Relación entre las clases de tierra y la calidad de Agave angustifolia Haw. En la Soledad Salinas, Quiatoni, Oaxaca, Mexico. Master’s Thesis, Colegio de Postgraduados, Montecillo, Texcoco, Mexico, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Stewart, J.R. Agave as a model CAM crop system for a warming and drying world. Front. Plant Sci. 2015, 6, 684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouaziz, M.A.; Rassaoui, R.; Besbes, S. Chemical Composition, Functional Properties, and Effect of Inulin from Tunisian Agave americana L. Leaves on Textural Qualities of Pectin Gel. J. Chem. 2014, 2014, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SAGARPA. Agave tequilero y mezcalero mexicano. In Planeación Agrícola Nacional 2017–2030; SAGARPA: Ciudad de México, Mexico, 2017; p. 15. [Google Scholar]
- Diario Oficial de la Federación (DOF). Lineamientos de Operación del Programa Sembrando Vida, 24 January 2019. Diario Oficial Federación 2019, 764, 2–32. [Google Scholar]
- Chávez-Moreno, C.K.; Tecante, A.; Casas, A. The Opuntia (Cactaceae) and Dactylopius (Hemiptera: Dactylopiidae) in Mexico: A historical perspective of use, interaction and distribution. Biodivers. Conserv. 2009, 18, 3337–3355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffith, M.P.; Porter, J.M. Phylogeny of Opuntioideae (Cactaceae). Int. J. Plant Sci. 2009, 170, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez, H.M.; Godinez, H. Contribución al conocimiento de las cactáceas mexicanas amenazada. Acta Bot. Mex. 1994, 26, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes-Agüero, J.A.; Aguirre Rivera, J.R.; Flores, J.L. Variación morfológica de Opuntia (cactaceae) en relación con su domesticación en la altiplanicie meridional de México. Interciencia 2005, 30, 476–484. [Google Scholar]
- Food and Agricultural Organisation of the United Nations (FAO). Agro-Industrial Utilization of Cactus Pear; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- National Institute of Statistics, Geography and Informatics (INEGI), Land use and vegetation, series VI. 2017. Available online: http://www.inegi.org.mx/geo/contenidos/recnat/usosuelo/Default.aspx (accessed on 23 August 2021).
- Scheinvar, L.; Gallegos, C.; Olalde, G.; Sánchez, V.; Linaje, M. Estado del Conocimiento de las Especies de Nopal (Opuntia spp.) Productoras de Xoconostles Silvestres y Cultivadas (Informe Final); CONABIO: Mexico City, Mexico, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Soberon, J.; Golubov, J.; Sarukhan, J. The Importance of Opuntia in Mexico and Routes of Invasion and Impact of Cactoblastis cactorum (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae). Fla. Èntomol. 2001, 84, 486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores, H.A.; Castillo, I.O.; Martínez, J.M.M.; Rivera, M.G.; Hernández, J.G. Productividad del nopal para verdura (Opuntia spp.) bajo riego por goteo subterráneo en la Comarca Lagunera. Rev. Chapingo Ser. Zonas Áridas (RChSZA) 2004, 3, 99–104. [Google Scholar]
- López-García, J.J.; Fuentes-Rodríguez, J.M.; Rodríguez, R.A. Production and use of Opuntia as forage in Northern Mexico. In Cactus (Opuntia spp.) as Forage; Mondragon-Jacobo, C., Pérez-González, S., Eds.; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2001; pp. 29–38. [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz-Espinoza, F.H.; Alvarado-Mendoza, J.F.; Murillo-Amador, B.; García-Hernández, J.L.; Pargas-Lara, R.; Duarte-Osuna, J.D.; Beltrán-Morales, F.A.; Fenech-Larios, L. Yield and Growth of Green Cladodes of Prickly Pear (Opuntia ficus-indica) Cultivars under Different Plant Densities. J. Prof. Assoc. Cactus Dev. 2008, 10, 22–35. [Google Scholar]
- Nobel, P.S. Environmental productivity indices and productivity for Opuntia ficus-indica under current and elevated atmospheric CO2 levels*. Plant Cell Environ. 1991, 14, 637–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nobel, P.S.; Garcia-Moya, E.; Quero, E. High annual productivity of certain agaves and cacti under cultivation. Plant Cell Environ. 1992, 15, 329–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villegas-Silva, P.A.; Toledano-Thompson, T.; Canto-Canché, B.B.; Larqué-Saavedra, A.; Barahona-Pérez, L.F. Hydrolysis of Agave fourcroydes Lemaire (henequen) leaf juice and fermentation with Kluyveromyces marxianus for ethanol production. BMC Biotechnol. 2014, 14, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Méndez-Gallegos, S.J.; Rössel, D.; Amante-Orozco, A.; Gómez-González, A.; García-Herrera, J.E. El nopal en la producción de biocombustibles. VIII Simposium “Producción y aprovechamiento del nopal”. Rev. Salud Pública Y Nutr. 2010, 5, 70–84. [Google Scholar]
- Melane, M.; Ham, C.; Meincken, M. Characteristics of selected non-woody invasive alien plants in South Africa and an evaluation of their potential for electricity generation. J. Energy South. Afr. 2017, 28, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quiroz, M.; Varnero, M.T.; Cuevas, J.G.; Sierra, H. Cactus pear (Opuntia ficus-indica) in areas with limited rainfall for the production of biogas and biofertilizer. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 289, 125839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrera, I.; Allieri, M.A.; Estupiñan, L.; Martínez, T.; Aburto, J. Technical and economical evaluation of bioethanol production from lignocellulosic residues in Mexico: Case of sugarcane and blue agave bagasses. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2016, 107, 91–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saucedo-Luna, J.; Castro-Montoya, A.J.; Martinez-Pacheco, M.M.; Sosa-Aguirre, C.R.; Campos-Garcia, J. Efficient chemical and enzymatic saccharification of the lignocellulosic residue from Agave tequilana bagasse to produce ethanol by Pichia caribbica. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2011, 38, 725–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez, A.; Dueñas, P.; Hernandez-Sanchez, P.; Guadalajara, Y. The Role of Sustainability Analysis in the Revalorization of Tequila Residues and Wastes Using Biorefineries. Waste Biomass Valorization 2020, 11, 701–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delfin-Ruíz, M.E.; Calderón-Santoyo, M.; Ragazzo-Sánchez, J.A.; Gómez-Rodríguez, J.; Aguilar-Uscanga, M.G. Ethanol Production from Enzymatic Hydrolysates Optimized of Agave tequilana Weber var. azul and Agave karwinskii bagasses. BioEnergy Res. 2021, 14, 785–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corbin, K.R.; Byrt, C.; Bauer, S.; DeBolt, S.; Chambers, D.; Holtum, J.A.M.; Karem, G.; Henderson, M.; Lahnstein, J.; Beahan, C.T.; et al. Prospecting for Energy-Rich Renewable Raw Materials: Agave Leaf Case Study. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0135382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales-Martínez, T.K.; Díaz-Blanco, D.I.; Rodríguez-de la Garza, J.A.; Morlett-Chávez, J.; Castro-Montoya, A.J.; Quintero, J.; Aroca, G.; Rios-González, L.J. Assessment of different saccharification and fermentation configurations for ethanol production from Agave lechuguilla. Bioresources 2017, 12, 8093–8105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortíz-Méndez, O.H.; Morales-Martínez, T.K.; Rios-González, L.J.; Rodríguez-de la Garza, J.A.; Quintero, J.; Aroca, G. Bioethanol production from Agave lechuguilla biomass pretreated by autohydrolysis, Rev. Mex. De Ing. Química 2019, 16, 467–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz-Blanco, D.I.; de La Cruz, J.R.; López-Linares, J.C.; Morales-Martínez, T.K.; Ruiz, E.; Rios-González, L.J.; Romero, I.; Castro, E. Optimization of dilute acid pretreatment of Agave lechuguilla and ethanol production by co-fermentation with Escherichia coli MM160. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2018, 114, 154–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M.L.; Wyman, C.E. Elucidation of native California Agave americana and Agave deserti biofuel potential: Compositional analysis. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0252201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, A.M.; Zhou, Y.; Held, M.A.; Davis, S.C. Tissue Composition of Agave americana L. Yields Greater Carbohydrates From Enzymatic Hydrolysis Than Advanced Bioenergy Crops. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Láinez, M.; Ruiz, H.A.; Arellano-Plaza, M.; Martínez-Hernández, S. Bioethanol production from enzymatic hydrolysates of Agave salmiana leaves comparing S. cerevisiae and K. marxianus. Renew. Energy 2019, 138, 1127–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krümpel, J.; George, T.; Gasston, B.; Francis, G.; Lemmer, A. Suitability of Opuntia ficus-indica (L) Mill. and Euphorbia tirucalli L. as energy crops for anaerobic digestion. J. Arid Environ. 2020, 174, 104047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Texco-López, A.; Álvarez-Cervantes, J.; Cadena-Ramírez, A.; Castro-Rosas, J.; Gómez-Aldapa, C.A.; Téllez-Jurado, A. Effect of hydrothermal pretreating (high pressure) and enzymatic hydrolysis of cladodes of Opuntia ficus-indica on the release of sugars and their potential use in bioethanol production. Rev. Int. De Contam. Ambient. 2019, 35, 1039–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maceda, A.; Soto-Hernández, M.; Peña-Valdivia, C.B.; Trejo, C.; Terrazas, T. Characterization of lignocellulose of Opuntia (Cactaceae) species using FTIR spectroscopy: Possible candidates for renewable raw material. Biomass Convers. Biorefinery 2020, 912, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lueangwattanapong, K.; Ammam, F.; Mason, M.; Whitehead, C.; McQueen-Mason, S.J.; Gomez, L.D.; Smith, J.A.C.; Thompson, I.P. Anaerobic digestion of Crassulacean Acid Metabolism plants: Exploring alternative feedstocks for semi-arid lands. Biores. Technol. 2020, 297, 122262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Ram, C. Agave biomass: A potential resource for production of value-added Products. Environ. Sustain. 2021, 4, 245–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honorato, A.; Sadhukhan, J. Annual biomass variation of agriculture crops and forestry residues, and seasonality of crop residues for energy production in Mexico. Food Bioprod. Process. 2020, 119, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisentraut, A. Sustainable Production of Second-Generation Biofuels. In Potential and Perspectives in Major Economies and Developing Countries, Information Paper; OECD/IEA, International Energy Agency: Paris, France, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Nobel, P.S.; Quero, E. Environmental Productivity Indices for a Chihuahuan Desert Cam Plant, Agave lechuguilla. Ecology 1986, 67, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo-Quiroz, D.; Martínez-Burciaga, O.U.; Ávila-Flores, D.Y.; Castillo-Reyes, F.; Sánchez-Chaparro, J.D. Identification of Potential Areas for Establishment of Plantations of Agave lechuguilla Torr. in Coahuila, Mexico. Open J. For. 2014, 04, 520–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo-Quiroz, D.; Martínez-Burciaga, O.U.; Ríos-González, L.J.; Rodríguez-de la Garza, J.A.; Morales-Martínez, T.K.; Castillo-Reyes, F.; Ávila-Flores, D.Y. Determination of potential areas for Agave lechuguilla Torr. plantations for ethanol production. Acta Quim. Mex. 2014, 4, 5–12. [Google Scholar]
- Martínez-Torres, J.; Barahona-Pérez, F.; García-Marín, P.C.; Magdub-Méndez, A.; Vergara-Yoisura, S.; Larqué-Saavedra, A.; Lappe-Oliveras, P. Ethanol production from two varieties of henequen (Agave fourcroydes Lem). GCB Bioenergy 2010, 3, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SAGARPA. Inauguración de la Planta Piloto para la producción de etanol a través del Agave Mezcalero y Tequilero. 2015. Available online: http://www.sagarpa.gob.mx/Delegaciones/michoacan/boletines/Paginas/B1102015.aspx (accessed on 22 September 2021).
- Duran, G.M.D.; Weber, B.; Jiménez, G.J.; González-Mora, E. The application of solid biofuels as a source of process energy in Mexico: Case studies using agave and coffee waste. Biofuels Bioprod. Biorefining 2021, 15, 1233–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez-Estrada, A.; Mena-Cervantes, V.Y.; Mederos-Nieto, F.S.; Pineda-Flores, G.; Hernández-Altamirano, R. Assessment and classification of lignocellulosic biomass recalcitrance by principal components analysis based on thermogravimetry and infrared spectroscopy. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duran-Cruz, V.; Hernández, S.; Ortíz, I. Evaluation of Steam Explosion Pretreatment and Enzymatic Hydrolysis Conditions for Agave Bagasse in Biomethane Production. BioEnergy Res. 2021, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contreras, S.; Toha, C.J. Biogas production from a suspension of homogenized cladodes of the cactus Opuntia cacti. J. Ferment Technol. 1984, 62, 601–605. [Google Scholar]
- Souvannasouk, V.; Shen, M.-Y.; Trejo, M.; Bhuyar, P. Biogas production from Napier grass and cattle slurry using a green energy technology. Int. J. Innov. Res. Sci. Stud. 2021, 4, 174–180. [Google Scholar]
- Retamal, N.; Durán, J.M.; Fernández, J. Ethanol production by fermentation of fruits and cladodes of prickly pear cactus [Opuntia ficus-indica (L.) Miller]. J. Sci. Food Agric. 1987, 40, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz-Laurel, H.; Rössel-Kipping, D. Energy production balance for biogas generation form cactus prickly in a staged biorefinery. In Proceedings of the International conference of Agricultural Engineering, Zurich, Switzerland, 6–10 July 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Garza, G.E.; Hernández, I.L.; Antonyan, N.; Barrón, L.C.; Vega, V.V.; Barros, M.E.; Rodríguez, C.C.; Meraz, C.D.; Ayora-Peón, R.; Pérez-Suazo, A. Production of nopal-based biogas. In Proceedings of the 2018 IISE Annual Conference, Orlando, FL, USA, 19–22 May 2018; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Panizio, R.M.; Calado, L.F.D.C.; Lourinho, G.; De Brito, P.S.D.; Mees, J.B. Potential of Biogas Production in Anaerobic Co-digestion of Opuntia ficus-indica and Slaughterhouse Wastes. Waste Biomass Valorization 2019, 11, 4639–4647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, B.D.; Banerjee, A.; Acevedo, A.; Halvorsen, K.E.; Eastmond, A. Policies for the Sustainable Development of Biofuels in the Pan American Region: A Review and Synthesis of Five Countries. Environ. Manag. 2014, 56, 1276–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García, C.A.; Manzini, F.; Islas, J.M. Sustainability assessment of ethanol production from two crops in Mexico. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 72, 1199–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tauro, R.; Serrano-Medrano, M.; Masera, O. Solid biofuels in Mexico: A sustainable alternative to satisfy the increasing demand for heat and power. Clean Technol. Environ. Policy 2018, 20, 1527–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watkins, D.W.; De Moraes, M.M.G.A.; Asbjornsen, H.; Mayer, A.S.; Licata, J.; Lopez, J.G.; Pypker, T.G.; Molina, V.G.; Marques, G.F.; Carneiro, A.C.G.; et al. Bioenergy Development Policy and Practice Must Recognize Potential Hydrologic Impacts: Lessons from the Americas. Environ. Manag. 2015, 56, 1295–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selfa, T.; Bain, C.; Moreno, R.; Eastmond, A.; Sweitz, S.; Bailey, C.; Pereira, G.S.; Souza, T.; Medeiros, R. Interrogating Social Sustainability in the Biofuels Sector in Latin America: Tensions Between Global Standards and Local Experiences in Mexico, Brazil, and Colombia. Environ. Manag. 2015, 56, 1315–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Specie | Biomass | Cellulose | Hemicellulose | Lignin |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A. tequilana | Bagasse [23,86,87,88,89] | 10.6–50.0 | 10.6–22 | 6.2–17 |
| Leaf fiber [23,90] | 26.1–49.5 | 15.8–17.8 | 12.7–17.0 | |
| Offshoot bagasse [23] | 19.8 | 13.8 | 13.1 | |
| A. lechuguilla | Cogollos [91,92,93] | 14.65–40.98 | 1.52–12.84 | 9.07–44.25 |
| A. americana | Bagasse [94] | 39.4 | 11.6 | |
| Leaf fiber [90,95] | 5.55–47.2 | 5.6–22.4 | 9.1–9.3 | |
| A. salmiana | Leaf fiber [96] | 20.67 | 3.74 | 23.37 |
| A. karwinskii | Bagasse [89] | 30 | 20 | 14 |
| A. deserti | Bagasse [94] | 54.7 | 17.5 | |
| O. ficus-indica | Cladodes [85,97,98,99] | 3–32.6 | 6.2–18.5 | 3.6–16 |
| O. robusta | Cladodes [99] | 29.1 | 9.9 | 13.1 |
| O. streptacantha | Cladodes [99] | 28.1 | 11.5 | 12.9 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Honorato-Salazar, J.A.; Aburto, J.; Amezcua-Allieri, M.A. Agave and Opuntia Species as Sustainable Feedstocks for Bioenergy and Byproducts. Sustainability 2021, 13, 12263. https://doi.org/10.3390/su132112263
Honorato-Salazar JA, Aburto J, Amezcua-Allieri MA. Agave and Opuntia Species as Sustainable Feedstocks for Bioenergy and Byproducts. Sustainability. 2021; 13(21):12263. https://doi.org/10.3390/su132112263
Chicago/Turabian StyleHonorato-Salazar, José Amador, Jorge Aburto, and Myriam Adela Amezcua-Allieri. 2021. "Agave and Opuntia Species as Sustainable Feedstocks for Bioenergy and Byproducts" Sustainability 13, no. 21: 12263. https://doi.org/10.3390/su132112263
APA StyleHonorato-Salazar, J. A., Aburto, J., & Amezcua-Allieri, M. A. (2021). Agave and Opuntia Species as Sustainable Feedstocks for Bioenergy and Byproducts. Sustainability, 13(21), 12263. https://doi.org/10.3390/su132112263