Weekly Wellness Variations to Identify Non-Functional Overreaching Syndrome in Turkish National Youth Wrestlers: A Pilot Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Sample Size
2.3. Study Design
2.4. Anthropometric Measurements
2.5. Aerobic Power Test
2.6. Wellness Status Monitoring
2.7. Statistical Analysis
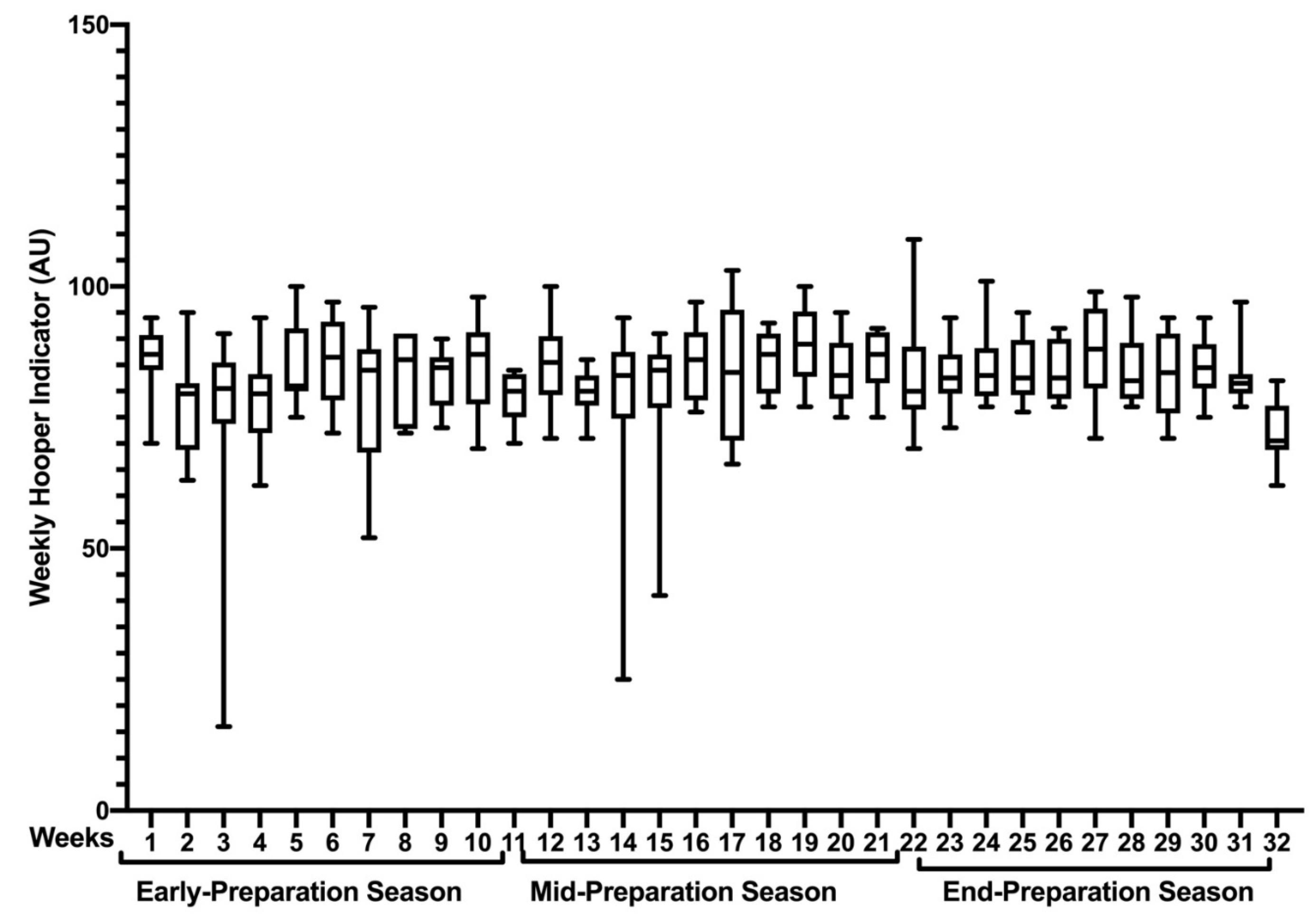
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nobari, H.; Kargarfard, M.; Minasian, V.; Cholewa, J.M.; Pérez-Gómez, J. The effects of 14-week betaine supplementation on endocrine markers, body composition and anthropometrics in professional youth soccer players: A double blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial. J. Int. Soc. Sports Nutr. 2021, 18, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Leeuw, A.-W.; van der Zwaard, S.; van Baar, R.; Knobbe, A. Personalized machine learning approach to injury monitoring in elite volleyball players. Eur. J. Sport Sci. 2021, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meeusen, R.; Duclos, M.; Foster, C.; Fry, A.; Gleeson, M.; Nieman, D.; Raglin, J.; Rietjens, G.; Steinacker, J.; Urhausen, A. Prevention, diagnosis and treatment of the overtraining syndrome: Joint consensus statement of the European College of Sport Science (ECSS) and the American College of Sports Medicine (ACSM). Eur. J. Sport Sci. 2013, 13, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmikli, S.L.; de Vries, W.R.; Brink, M.S.; Backx, F.J. Monitoring performance, pituitary–adrenal hormones and mood profiles: How to diagnose non-functional over-reaching in male elite junior soccer players. Br. J. Sports Med. 2012, 46, 1019–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banfi, G.; Marinelli, M.; Roi, G.; Agape, V. Usefulness of free testosterone/cortisol ratio during a season of elite speed skating athletes. Int. J. Sports Med. 1993, 14, 373–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Passelergue, P.; Lac, G. Saliva cortisol, testosterone and T/C ratio variations during a wrestling competition and during the post-competitive recovery period. Int. J. Sports Med. 1999, 20, 109–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vervoorn, C.; Quist, A.; Vermulst, L.; Erich, W.; De Vries, W.; Thijssen, J. The behaviour of the plasma free testosterone/cortisol ratio during a season of elite rowing training. Int. J. Sports Med. 1991, 12, 257–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clemente, F.M.; Mendes, B.; Palao, J.M.; Silvério, A.; Carriço, S.; Calvete, F.; Nakamura, F.Y. Seasonal player wellness and its longitudinal association with internal training load: Study in elite volleyball. J. Sports Med. Phys. Fit. 2019, 59, 345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorpe, R.T.; Atkinson, G.; Drust, B.; Gregson, W. Monitoring fatigue status in elite team-sport athletes: Implications for practice. Int. J. Sports Physiol. Perform. 2017, 12, S2–S27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wrigley, R.; Drust, B.; Stratton, G.; Scott, M.; Gregson, W. Quantification of the typical weekly in-season training load in elite junior soccer players. J. Sports Sci. 2012, 30, 1573–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebelo, A.; Brito, J.; Seabra, A.; Oliveira, J.; Drust, B.; Krustrup, P. A new tool to measure training load in soccer training and match play. Int. J. Sports Med. 2012, 33, 297–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddad, M.; Stylianides, G.; Djaoui, L.; Dellal, A.; Chamari, K. Session-RPE method for training load monitoring: Validity, ecological usefulness, and influencing factors. Front. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nobari, H.; Barjaste, A.; Haghighi, H.; Clemente, F.M.; Carlos-Vivas, J.; Perez-Gomez, J. Quantification of training and match load in elite youth soccer players: A full-season study. J. Sports Med. Phys. Fit. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, C.M.; Griffiths, P.C.; Mellalieu, S.D. Training load and fatigue marker associations with injury and illness: A systematic review of longitudinal studies. Sports Med. 2017, 47, 943–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooper, S.L.; Mackinnon, L.T. Monitoring overtraining in athletes. Sports Med. 1995, 20, 321–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moalla, W.; Fessi, M.S.; Farhat, F.; Nouira, S.; Wong, D.P.; Dupont, G. Relationship between daily training load and psychometric status of professional soccer players. Res. Sports Med. 2016, 24, 387–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Andrade Nogueira, F.C.; Nogueira, R.A.; Coimbra, D.R.; Miloski, B.; de Freitas, V.H.; Bara Filho, M. Internal training load: Perception of volleyball coaches and athletes. Rev. Bras. Cineantropometria Desempenho Hum. 2014, 16, 638–647. [Google Scholar]
- Clemente, F.M.; Mendes, B.; Nikolaidis, P.T.; Calvete, F.; Carriço, S.; Owen, A.L. Internal training load and its longitudinal relationship with seasonal player wellness in elite professional soccer. Physiol. Behav. 2017, 179, 262–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flatt, A.A.; Esco, M.R.; Nakamura, F.Y. Individual heart rate variability responses to preseason training in high level female soccer players. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2017, 31, 531–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nobari, H.; Aquino, R.; Clemente, F.M.; Khalafi, M.; Adsuar, J.C.; Pérez-Gómez, J. Description of acute and chronic load, training monotony and strain over a season and its relationships with well-being status: A study in elite under-16 soccer players. Physiol. Behav. 2020, 225, 113117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Pallarés, J.; López-Gullón, J.M.; Muriel, X.; Díaz, A.; Izquierdo, M. Physical fitness factors to predict male Olympic wrestling performance. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2011, 111, 1747–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horswill, C.A. Applied physiology of amateur wrestling. Sports Med. 1992, 14, 114–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouergui, I.; Ardigò, L.P.; Selmi, O.; Levitt, D.E.; Chtourou, H.; Bouassida, A.; Bouhlel, E.; Franchini, E. Changes in perceived exertion, well-being, and recovery during specific judo training: Impact of training period and exercise modality. Front. Physiol. 2020, 11, 931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Branco, B.H.M.; Lopes-Silva, J.; da Silva Santos, J.; Julio, U.; Gonçalves Panissa, V.; Franchini, E. Monitoring training during four weeks of three different modes of high-intensity interval training in judo athletes. Arch. Budo 2017, 13, 51–62. [Google Scholar]
- Selmi, O.; Marzouki, H.; Ouergui, I.; BenKhalifa, W.; Bouassida, A. Influence of intense training cycle and psychometric status on technical and physiological aspects performed during the small-sided games in soccer players. Res. Sports Med. 2018, 26, 401–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouergui, I.; Franchini, E.; Selmi, O.; Levitt, D.E.; Chtourou, H.; Bouhlel, E.; Ardigò, L.P. Relationship between Perceived Training Load, Well-Being Indices, Recovery State and Physical Enjoyment during Judo-Specific Training. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 7400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nobari, H.; Silva, R.; Clemente, F.M.; Akyildiz, Z.; Ardigò, L.P.; Pérez-Gómez, J. Weekly Variations in the Workload of Turkish National Youth Wrestlers: A Season of Complete Preparation. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 3832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arazi, H.; Mirzaei, B.; Nobari, H. Anthropometric profile, body composition and somatotyping of national Iranian cross-country runners. Turk. J. Sport Exerc. 2015, 17, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norton, K.; Olds, T. Anthropometrica: A Textbook of Body Measurement for Sports and Health Courses; UNSW Press: Sydney, Australia, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Nobari, H.; Silva, A.F.; Clemente, F.M.; Siahkouhian, M.; García-Gordillo, M.Á.; Adsuar, J.C.; Pérez-Gómez, J. Analysis of Fitness Status Variations of Under-16 Soccer Players Over a Season and Their Relationships With Maturational Status and Training Load. Front. Physiol. 2021, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmat, A.J.; Arsalan, D.; Bahman, M.; Hadi, N.; University of Guilan; Jafari, R.A.; Damirchi, A.; Mirzaei, B.; Nobari, H. Anthropometric and Bio-motor abilities Profile of Young Elite Wrestlers. Phys. Educ. Stud. 2016, 20, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchheit, M. The 30-15 intermittent fitness test: 10 year review. Myorobie J. 2010, 1, 278. [Google Scholar]
- Oliver, J.L.; Lloyd, R.S.; Whitney, A. Monitoring of in-season neuromuscular and perceptual fatigue in youth rugby players. Eur. J. Sport Sci. 2015, 15, 514–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooper, S.L.; Mackinnon, L.T.; Howard, A.; Gordon, R.D.; Bachmann, A.W. Markers for monitoring overtraining and recovery. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 1995, 27, 106–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nobari, H.; Tubagi Polito, L.F.; Clemente, F.M.; Pérez-Gómez, J.; Ahmadi, M.; Garcia-Gordillo, M.Á.; Silva, A.F.; Adsuar, J.C. Relationships between training workload parameters with variations in anaerobic power and change of direction status in elite youth soccer players. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 7934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nobari, H.; Ahmadi, M.; Pérez-Gómez, J.; Clemente, M.; Adsuar, J.; Minasian, V.; Afonso, J. The effect of two types of combined training on bio-motor ability adaptations in sedentary females. J. Sports Med. Phys. Fit. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nobari, H.; Fani, M.; Clemente, F.M.; Carlos-Vivas, J.; Pérez-Gómez, J.; Ardigò, L.P. Intra-and inter-week variations of well-being across a season: A cohort study in elite youth soccer players. Front. Psychol. 2021, 12, 1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopkins, W.G.; Marshall, S.W.; Batterham, A.M.; Hanin, J. Progressive Statistics for Studies in Sports Medicine and Exercise Science. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2009, 41, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kölling, S.; Wiewelhove, T.; Raeder, C.; Endler, S.; Ferrauti, A.; Meyer, T.; Kellmann, M. Sleep monitoring of a six-day microcycle in strength and high-intensity training. Eur. J. Sport Sci. 2016, 16, 507–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nedelec, M.; McCall, A.; Carling, C.; Legall, F.; Berthoin, S.; Dupont, G. The influence of soccer playing actions on the recovery kinetics after a soccer match. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2014, 28, 1517–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, R.; Brito, J.P.; Loureiro, N.; Padinha, V.; Ferreira, B.; Mendes, B. Does the distribution of the weekly training load account for the match results of elite professional soccer players? Physiol. Behav. 2020, 225, 113118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clemente, F.M.; Martinho, R.; Calvete, F.; Mendes, B. Training load and well-being status variations of elite futsal players across a full season: Comparisons between normal and congested weeks. Physiol. Behav. 2019, 201, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chamari, K.; Haddad, M.; Wong, D.P.; Dellal, A.; Chaouachi, A. Injury rates in professional soccer players during Ramadan. J. Sports Sci. 2012, 30 (Suppl. 1), S93–S102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Variables | Season Period | Comparative | Mean Difference (95% CI) | p | Hedge’s g (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| wDOMS (AU) | EarPS: 19.62 (1.30) | EarPS vs. MidPS | 1.1 (−0.1 to 2.4) | 0.194 | 0.8 (−0.1 to 1.7) |
| MidPS: 20.75 (1.38) | EarPS vs. EndPS | 2.0 (1.0 to 3.0) | 0.010 | 1.8 (0.7 to 2.8) | |
| EndPS: 21.63 (0.72) | MidPS vs. EndPS | 0.9 (−0.2 to 1.9) | 0.338 | 0.7 (−0.2 to 1.6) | |
| wFatigue (AU) | EarPS: 20.3 (1.8) | EarPS vs. MidPS | 0.6 (−0.9 to 2.0) | 0.753 | 0.3 (−0.5 to 1.2) |
| MidPS: 20.9 (1.3) | EarPS vs. EndPS | 0.0 (−1.6 to 1.6) | 1.000 | 0.0 (−0.9 to 0.9) | |
| EndPS: 20.3 (1.6) | MidPS vs. EndPS | −0.6 (−1.9 to 0.8) | 1.000 | −0.3 (−1.2 to 0.5) | |
| wStress (AU) | EarPS: 21.2 (0.9) | EarPS vs. MidPS | −0.7 (−1.9 to 0.4) | 0.823 | −0.5 (−1.4 to 0.4) |
| MidPS: 20.5 (1.5) | EarPS vs. EndPS | −1.1 (−2.3 to 0.2) | 0.319 | −0.8 (−1.7 to 0.1) | |
| EndPS: 20.1 (1.6) | MidPS vs. EndPS | −0.4 (−1.8 to 1.1) | 1.000 | −0.2 (−1.1 to 0.7) | |
| wSleep (AU) | EarPS: 20.2 (1.2) | EarPS vs. MidPS | 0.4 (−0.7 to 1.5) | 1.000 | 0.3 (−0.5 to 1.2) |
| MidPS: 20.6 (1.1) | EarPS vs. EndPS | 0.7 (−0.3 to 1.7) | 0.415 | 0.6 (−0.3 to 1.5) | |
| EndPS: 20.9 (0.9) | MidPS vs. EndPS | 0.3 (−0.6 to 1.3) | 1.000 | 0.3 (−0.6 to 1.2) | |
| wHI (AU) | EarPS: 81.3 (3.6) | EarPS vs. MidPS | 1.4 (−2.3 to 5.0) | 0.996 | 0.3 (−0.6 to 1.2) |
| MidPS: 82.7 (4.1) | EarPS vs. EndPS | 1.7 (−1.0 to 4.4) | 0.842 | 0.5 (−0.4 to 1.4) | |
| EndPS: 82.9 (1.9) | MidPS vs. EndPS | 0.3 (−2.7 to 3.3) | 1.000 | 0.1 (−0.8 to 1.0) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nobari, H.; Akyildiz, Z.; Fani, M.; Oliveira, R.; Pérez-Gómez, J.; Clemente, F.M. Weekly Wellness Variations to Identify Non-Functional Overreaching Syndrome in Turkish National Youth Wrestlers: A Pilot Study. Sustainability 2021, 13, 4667. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13094667
Nobari H, Akyildiz Z, Fani M, Oliveira R, Pérez-Gómez J, Clemente FM. Weekly Wellness Variations to Identify Non-Functional Overreaching Syndrome in Turkish National Youth Wrestlers: A Pilot Study. Sustainability. 2021; 13(9):4667. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13094667
Chicago/Turabian StyleNobari, Hadi, Zeki Akyildiz, Maryam Fani, Rafael Oliveira, Jorge Pérez-Gómez, and Filipe Manuel Clemente. 2021. "Weekly Wellness Variations to Identify Non-Functional Overreaching Syndrome in Turkish National Youth Wrestlers: A Pilot Study" Sustainability 13, no. 9: 4667. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13094667
APA StyleNobari, H., Akyildiz, Z., Fani, M., Oliveira, R., Pérez-Gómez, J., & Clemente, F. M. (2021). Weekly Wellness Variations to Identify Non-Functional Overreaching Syndrome in Turkish National Youth Wrestlers: A Pilot Study. Sustainability, 13(9), 4667. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13094667










