Abstract
Horizontal curves of rural highways are prone to a considerably high number of fatalities because an erroneous perception can lead to unsafe driving. This generally occurs when a driver fails to notice the highway geometry or changes in the driving environment, particularly curved segments. This study aimed to understand the geometric characteristics of curved segments, such as radius and approach tangents, on the driving performance towards minimizing vehicle crashes. Speed profiles and lateral position, the most common indicators of successful negotiation in curves, and eye movements were recorded during an experiment conducted in a fixed-base driving simulator equipped with an eye-tracking system with a road infrastructure (a three-lane highway) and its surroundings. A driving simulator can faithfully reproduce any situation and enable sustainable research because it is a high-tech and cost-effective tool allowing repeatability in a laboratory. The experiment was conducted with 28 drivers who covered approximately 500 test kilometers with 90 horizontal curves comprising nine different combinations of radii and approach tangent lengths. The drivers’ behavior on each curve was classified as ideal, normal, intermediate, cutting, or correcting according to their trajectories and speed changes for analyses of the performance parameters and their correlation conducted by factorial ANOVA and Pearson chi-square tests. The cross-tabulation results indicated that the safest behavior significantly increased when the curve radius increased, and the performance measures of curve radii were greatly affected. However, the driving behavior was not affected by the approach tangent length. The results revealed segments of the road that require a driver’s closer attention for essential vehicle control, critical information, and vehicle control in different parts of the task.
1. Introduction
Curves are the geometric elements of the road alignment characterized by the highest exposure of drivers to the risk of a crash. Drivers intend to operate vehicles at a safe speed based on the roadway’s geometric features. These features are characterized by gradient, horizontal curvature, curve length, tangent sections, and superelevation [1]
Vehicle crashes in horizontal curves are a severe safety concern because their occurrence rate is higher than those in tangent sections of a roadway. Additionally, vehicle crashes on horizontal curves require greater effort to understand driver behavior [2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10]. The probability of road crashes on horizontal curves is high due to the increase in the strain of both driver and vehicle, which leads to an erroneous judgment of speed and trajectory. Consequently, road infrastructure and its interaction with human factors is an essential field of study that has been widely researched to ensure geometric design consistency [11,12].
Previous studies in the driving simulator field have identified several factors associated with driver performance and road safety, e.g., roadway design, road markings, environmental conditions, driver characteristics, and vehicle attributes [13,14]. The literature review identified various studies that have evaluated the effect of different road markings placed before and along the curves on driver behavior [15,16]. Babić et al. [17] presented a systematic review of the most significant academic activities regarding the influence of longitudinal and transverse road markings and road markings for hazard location (curves, intersections, and rural-urban transitions) on driver behavior and overall road safety. Charlton et al. [18] developed two types of experimental road markings (i.e., an “Attentional” set designed to provide visually distinct cues to indicate speed limits of 60, 80, and 100 km/h, and a “Perceptual” set also intended to affect the drivers’ perception of speed). They then compared them to a standard undifferentiated set of markings. The findings indicated that both road markings improved driver compliance with speed limits compared to the control group. One of the recent studies considered horizontal curves, especially those of radii less than 200 m, and showed an increased road accident risk was mainly due to inappropriate speed and failure to maintain proper lateral position [19].
Studies on the association between road design and human factors use performance parameters to measure success in curve negotiation, including speed [5,9,20,21,22], lateral position [11,20,23], lateral acceleration, and driver eye movement [9,24]. Additionally, research on the relationship among those parameters, mainly speed and lateral position in horizontal curves, has been developed [6,25]. Charly and Mathew [4] demonstrated that driving performance measures, such as speed and mean lateral acceleration with geometric parameters, result in reliable estimations of crashes. Barendswaard et al. [2] reported a directly proportional relationship of the maximum prepositioning and swing left behavior of drivers while approaching righthand curves with speed, but inversely proportional to curves radii. However, the relationship between behavioral parameters and the effect of curve geometry on them remains exploitable. In contrast, road strategies and guidelines can significantly enhance driving behavior and its interaction with the highway [26].
Driving simulators provide researchers with a fully controlled environment and the possibility of monitoring various parameters in road safety and sustainable studies with no physical risk associated with driving on real roads. Moreover, they are efficient tools for the inclusion of human factors. They are particularly relevant and promising for research on traffic as they enable studies of driving behavior in different situations (e.g., analysis of driving responses to signalization [27,28], climatic adversities [29,30], visibility [31,32], distraction [33,34], and fatigue [35,36,37]. Using driving simulators to analyze accident aspects in developing countries is a sustainable achievement as naturalistic studies are not always conducted due to their high costs [38].
Curve negotiation requires drivers to anticipate a curve and react to it by adjusting their speed and lane position to accommodate its severity and to apply more attentional resources than driving on a straight section of a road. It can be grouped into four distinct areas, namely, (1) approach, in which drivers locate a curve and make initial speed adjustments, (2) discovery, in which drivers determine the curvature, make additional speed adjustments, and adjust the path for curve entry, (3) entry and negotiation, in which they adjust speed based on curvature and lateral acceleration and maintain proper trajectory and safe lane position, and (4) exit, in which they accelerate towards an appropriate speed and adjust lane position to properly follow their path on the straight segment [39].
The database presented in this research was generated in a controlled experiment performed in a driving simulator equipped with an eye-tracking system that enables the analysis of driver behavior under different geometric conditions of the road. Following the assumption that behavioral parameters are significantly distinct in different road stretches, the main objective of the research was to investigate driver performance and the effects of geometric characteristics of horizontal curves (i.e., radii and approach tangents) on their behavior. This was done by evaluating speed profiles, lateral position, and eye movements.
2. Materials and Methods
This section describes the methodology applied, the sample characteristics, the driving simulator used, the simulation scenario and its development, and the primary data frame used for the analysis.
2.1. Participants
Data were extracted from files of the simulation of Vires Virtual Test Drive® [40] and Smart-Eye Recorder® [41] devices, conducted with 28 volunteers of 26.61 years average age (SD = 4.07 years) ranging from 20 to 38 years. The average driving experience was 7.52 years (SD = 3.97 years).
2.2. Apparatus
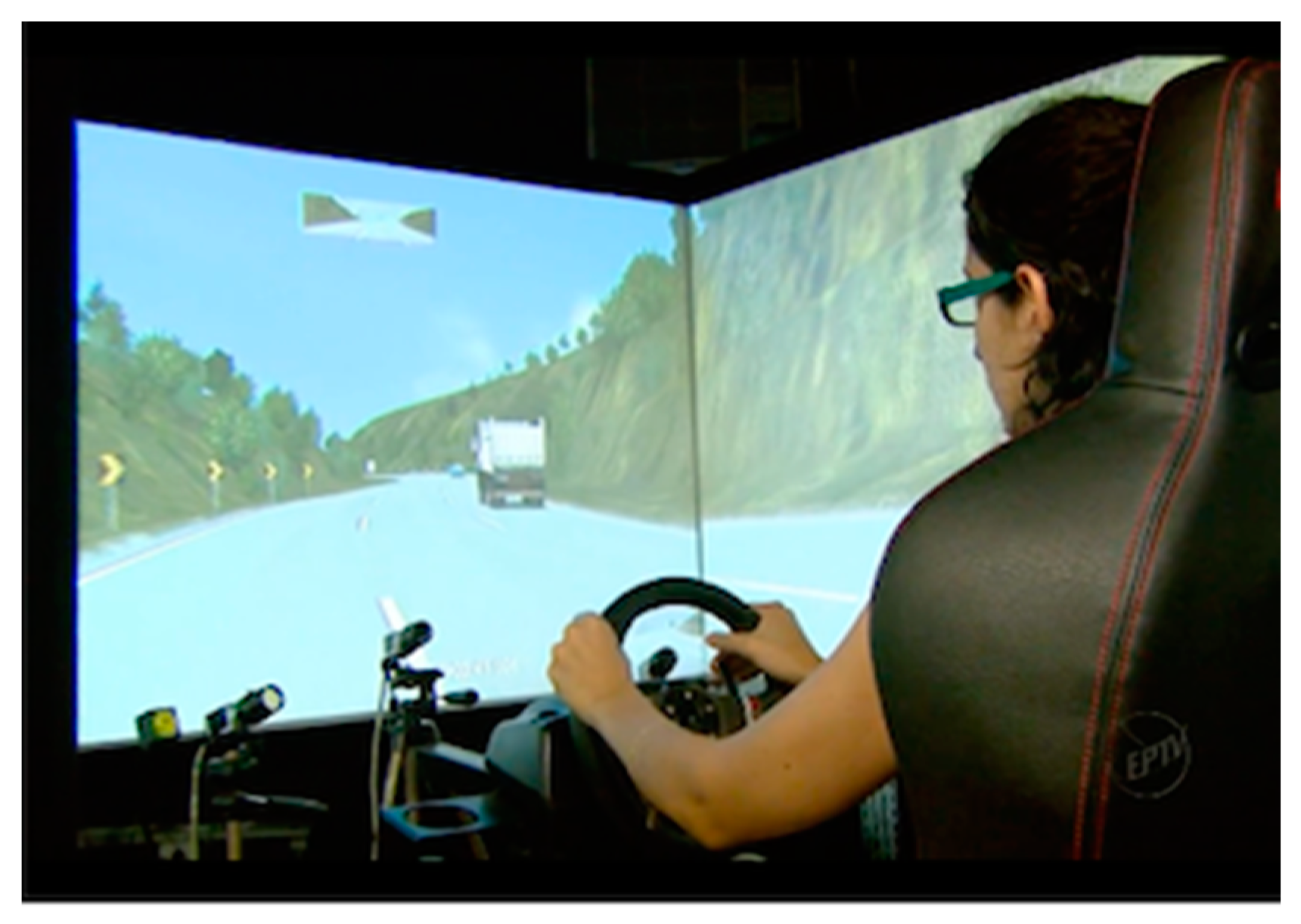
An instrumented driving simulator equipped with an eye-movement tracking system (Pro 5.10® Smart Eye) was used in the experiment (Figure 1). It comprised three front cameras that performed the eye-tracking of the driver and an additional rear camera recording the scenes that the drivers see. The eye-tracking was done by recording eye movements and capturing the direction of the gaze, head position, eyelid opening, blinks, attachment points, pupil size, and other monitoring and measurement. Data on the eye movements of 23 subjects were recorded during the experiment. The simulated environment was projected on a 1.40 × 0.80 m flat panel of 1080 p resolution and 60 Hz projection rate, which also projects rear and lateral mirrors and the speedometer. Speakers reproduce sounds similar to vehicle engines and traffic environments to enhance participant immersion with visual and auditory stimuli.

Figure 1.
The driving simulator used in the experiments.
2.3. Experimental Road
The scenario was based on a Brazilian highway covering 10 km with 20 horizontal curves. Transition curves were designed to create a smooth change between tangents and circular curves. The road had three lanes with a total separation of flows and an 80 km/h speed limit. The lower and upper extreme values of the actual curve radius and approach tangent lengths and their average were taken from the 20 curves in an existing stretch, leading to three different levels for each factor and nine conditions or treatments, as shown in Table 1. The abbreviations for the treatments, provided in the first column of the table, refer to combinations of radius (R) and tangent (T) lengths at different levels, namely small (s), medium (m), and large (l) [42].

Table 1.
Geometric data of the curves.
The experiment considered free-flow conditions, and the direction of the curves, which was randomized, was assumed not to influence driver behavior as there was no opposite flow. A 56° deflection angle (i.e., an intermediate value of the actual stretch), a flat grade, three lanes of 3.6 m width each, and a 1.0 m shoulder on both sides were adopted.
The treatments were randomly ordered until there was no overlap in creating the scenario, which contained different sequences of curves (i.e., sequences of the nine treatments described in Table 1). Each volunteer drove through two of the nine possible sequences, covering 18 km and encountering 18 curves. The sequences were carefully randomized to avoid driver familiarity with the scenario and simulation experience, which might influence their performance.
2.4. Database
Driving simulator data were collected from each driver at a 60 Hz sampling frequency and treated with Python 3.0 programming language. The initial treatment consisted in reading each driver’s file and identifying variables of interest, i.e., those helpful for the study (e.g., simulation time, inertial vehicle coordinates on the track, instant vehicle speed, among others), out of 70 possible ones.
The identification of treatments was necessary for the database lines. Therefore, a separate database contained coordinates related to the beginning and the end of each curve and tangent of the complete scenario, divided into the tangent, entry, and exit spirals and circular sector and their classifications (small, medium, or large). Furthermore, a code identified the treatment and its classification for all lines by crossing and comparing the coordinates of both databases.
The main database file, extracted from the simulator experiments, contains 504 lines resulting from the 28 participants driving through the nine combined treatments twice. Besides the characteristics of both drivers and treatments, each line included speed and lateral placement data, such as mean value, standard deviation, maximum and minimum values, and maximum difference, among others. The statistical analyses presented in what follows were performed by IBM SPSS 24.0® software [43].
2.5. Data Analysis
An analysis of variance (ANOVA) with repeated measures investigated the effects of the geometric characteristics of curves, radii, and approach tangents on the driving speed profiles, trajectories, and eye movements. Because the correct application of ANOVA tests required verification of a few assumptions (e.g., normal distribution of responses, homogeneity of variances between groups, and independence of observations), the data were previously subjected to a Kolmogorov–Smirnov test, which checked if they were normally distributed. They were also subjected to the Levene’s test, which verified the homogeneity of variance. As the experiment adopted repeated measures, the hypothesis of independence between the responses under different conditions would be violated. An additional sphericity assumption was necessary to circumvent this failure, and the Mauchly test evaluated it [44].
- Description of variables:
- ○
- Dependent variables: driving speed, lateral placement, and eye movement information, such as the number of fixations, fixation duration, pupil diameter, and gaze direction.
- ○
- Independent variables: approach tangent lengths and curve radii.
- Factorial ANOVA is an analysis of variance involving two or more independent variables, which is the case of this experiment, as shown in the descriptions of variables above.
- ANOVA with repeated measures consists of an analysis of variance conducted in any design. The independent (predictor) variables were measured using the same subjects under all conditions, which is the case of our experiment. The F-statistic from a repeated measures ANOVA is reported as F (df, dferror) = F-value, p = p-value. The first degree of freedom (df) was calculated as the number of conditions less one, and the second was the product of the first with the number of subjects less one. The following formula explains the F-ratio:where MS is the mean squared error or the mean variability in the data.
- The following tests were performed to check if the assumptions to proceed with the ANOVA with repeated measures were not violated:
- ○
- The Kolmogorov–Smirnov test evaluates if the distribution of scores is significantly different from a normal distribution. A significant p-value indicates a deviation from normality.
- ○
- The Friedman’s ANOVA is a non-parametric test, also known as the non-parametric version of the one-way repeated measures ANOVA. It compares multiple conditions when the same subjects participate in each condition. The resulting data are not normally distributed.
- ○
- The Levene’s test checks if there is any significant difference between the variances of a group and, thus, a non-significant result indicates that the hypothesis was satisfied.
- ○
- The Mauchly test assesses the hypothesis that the variances of differences between conditions are equal. A significant Mauchly’s statistical test (i.e., when it has a probability value less than 0.05), it is conclusive that there are significant differences between the variances of the differences; therefore, the sphericity condition was violated.
- ■
- The Greenhouse–Geisser correction estimates the distance from sphericity. It was used to correct the degrees of freedom associated with the corresponding F ratio when the Mauchly test causes the sphericity condition to be violated.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Driving Speed
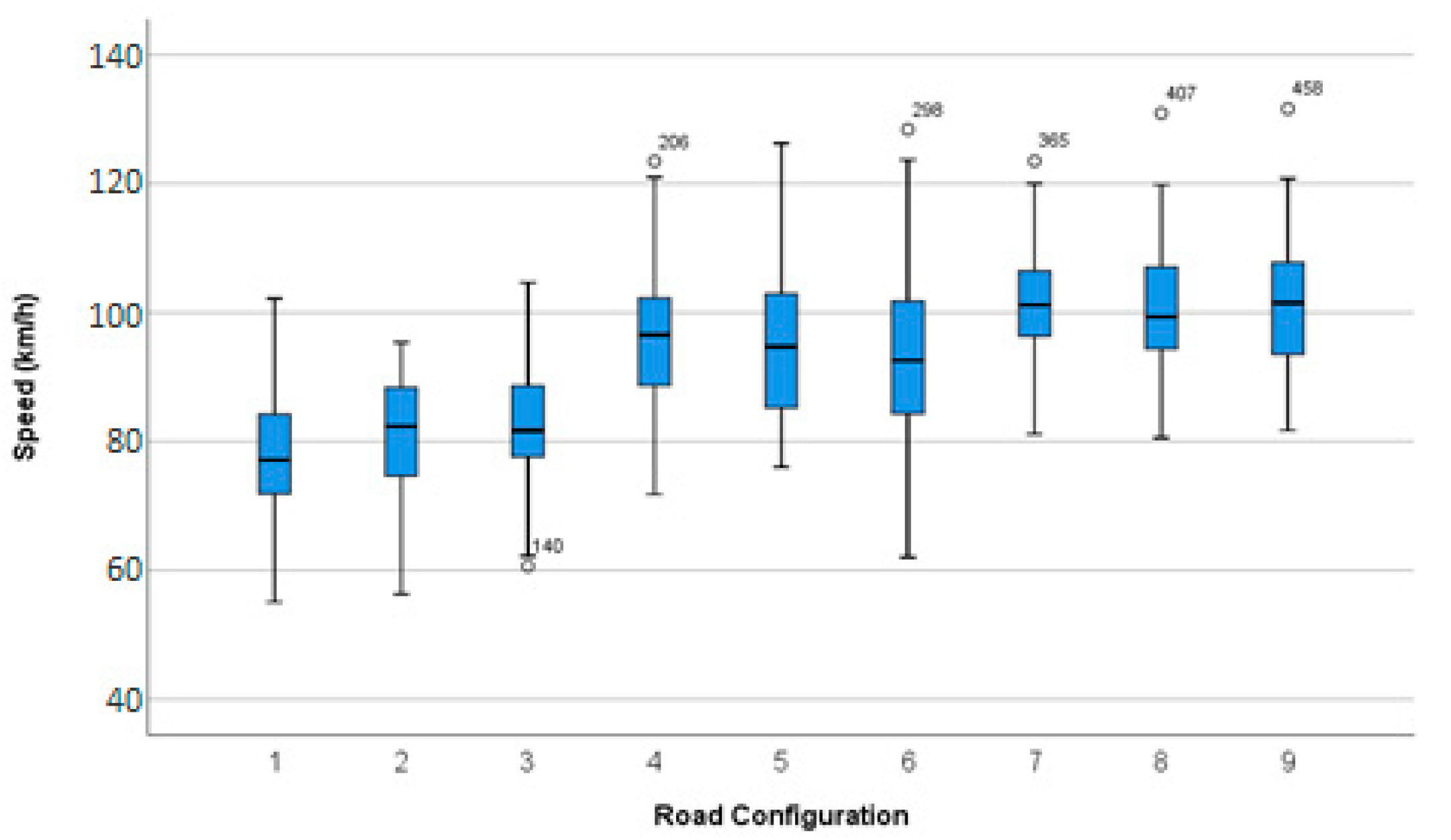
Table 2 summarizes the driving speeds in terms of average values and standard deviations for the combination of approach tangent lengths and curve radii, and the significance values of the Kolmogorov–Smirnov (K–S) normality test, after the removal of visible outliers. Such removal was justified by the rigorous analysis of the recording footage of the experiment, which revealed the values of the average speed of the outliers did not match the real ones reached by the drivers and were considered data recording errors. All curve configurations showed significant results for normal distribution, except the smaller radius with a large approach tangent curve. Figure 2 displays the treatment boxplots also after removing outliers. It can be assumed that the average speed increases with the increase in the curve radii. The variation in the length of the tangents exerted no apparent effect on the average speed between groups. Furthermore, it was observed that, as expected, the driving speed developed by volunteers was close to the design equilibrium speed of the curves because driving below or above the equilibrium speed would impact the safety performance of the curve negotiation.

Table 2.
Driving speed descriptive statistics and normality test for each treatment.
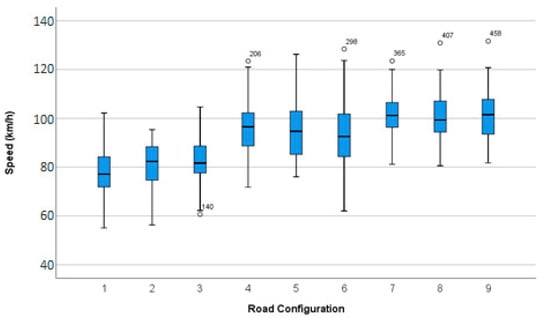
Figure 2.
Treatment boxplots.
Factorial ANOVA with repeated measures was used to check the effect of curve radii and length of approach tangents on the average driving speed along the curves. The Levene’s test revealed that the homogeneity of the variances was not significantly different across groups F (8, 469) = 1.373, p > 0.05. The Mauchly test indicated the sphericity hypothesis was not violated for the main effect of curve radii and approach tangent. Still, it was significant for their interaction (χ2 (9) = 18.37, p < 0.05). Therefore, the degrees of freedom were corrected by Geisser–Greenhouse spherical estimates (ε = 0.58). The test also revealed a significant main effect of curves radii F (2, 469) = 145.55, p < 0.001, Partial Eta Squared = 0.383, and observed power = 1.000, and a non-significant one for approach tangents F (2, 469) = 0.617, p = 0.540, Partial Eta Squared = 0.003, and observed power = 0.153. The ANOVA showed the interaction effect between radii and approach tangent was not significant F (3.466, 173.28) = 2.894, p = 0.055, Partial Eta Squared = 0.055, and observed power = 0.729.
The Bonferroni correction was performed for multiple comparisons. Regarding the main effect of curve radii, a pairwise comparison based on post-hoc tests indicated the average speeds recorded for each level were significantly different. As expected, the lowest speeds were recorded on curves with smaller radii (80.29 km/h), followed by medium curves with a 95.37 km/h average speed. This was significantly higher than that of the first group (average difference = 15.07 km/h, p < 0.001) and lower in comparison with those of larger radii and 100.91 km/h average speed (average difference = 5.54 km/h, p < 0.001). Calvi [3] reported the average speed increases on curves with a wider radius, which is aligned with our results.
The operation of speed difference along subsequent highway sections is another parameter widely used in safety evaluations [5,10,12]. The maximum and minimum speeds reached by the drivers in each curve were extracted from the experiment data to calculate maximum speed reduction. If a driver reached the minimum speed on the curve before reaching the maximum, the speed difference assumed a positive value. On the other hand, i.e., if they got their maximum speed before the minimum one, the speed difference was negative.
The calculated speed differences were grouped into three categories, namely substantial speed decrease (SSD), for speed difference values lower than −10 km/h, steady speed (SS), for an absolute value of speed difference lower than or equal to 10 km/h, and substantial speed increase (SSI), for speed differences larger than 10 km/h. Wang and Wang established such a speed change behavior. Table 3 shows the incidence of this speed change classification for the curves. According to the results, SSD was the most common behavior, with a higher proportion for curves with small and medium radii. Those with large radii displayed a more evenly distributed speed change behavior.

Table 3.
Speed change behavior per curve configuration.
3.2. Lateral Placement
The vehicle’s lateral position (LP) was calculated as the distance from the vehicle’s center of gravity to the central road axis, i.e., the middle of the three lanes. A vector cross product identified the side of the vehicle position, i.e., on the right or the left of the track axis—the lateral position assumes a positive value if the vehicle is on the right side of the lane axis and a negative one if it is on the left side of it. A code identified the traffic lane on which the vehicle was driving and the moments when it was crossing or drifting on the lanes.
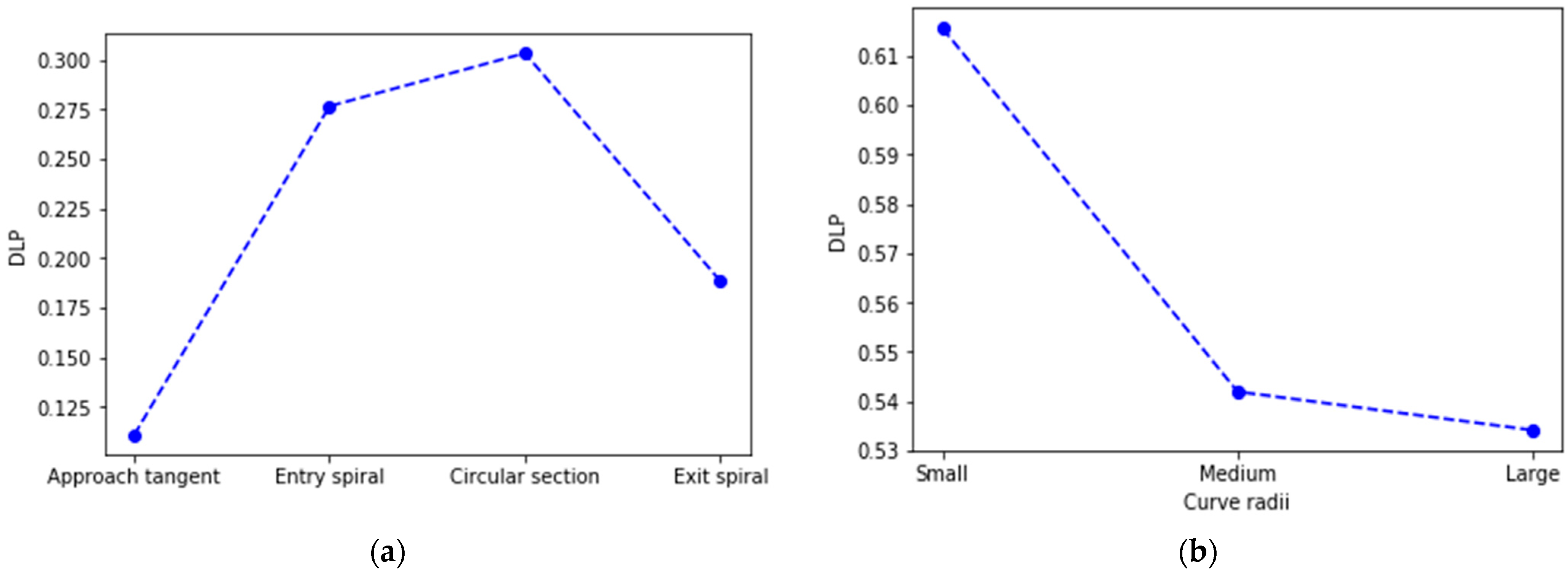
Suh et al. [9] defined Deviation of Lateral Placement (DLP) as an index representing a driver’s steering behavior along a given section of a highway. It can be interpreted as a standard deviation of an individual vehicle’s lateral placement along a given highway section that shows a vehicle’s overall lateral stability. The analysis of the standard deviation of lateral position revealed a higher value in the circular section than in other stretches, as seen in Figure 3a, implying that driving in curvy sections of a road is more challenging. Furthermore, curves with small radii resulted in a significantly greater mean DLP value (Figure 3b), consistent with the fact that the smaller the radius, the more complex the stability maintenance during curve negotiations.
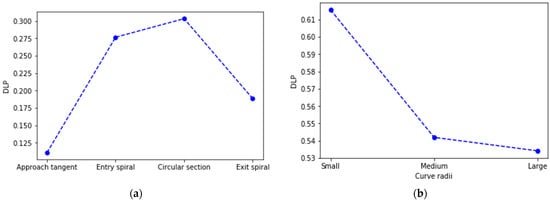
Figure 3.
Deviation of lateral placement per curve section (a) and curve radii (b).
Similar to the speed data, those on the deviation of lateral position per curve configuration group were subject to the Kolmogorov–Smirnov test, which checked whether they were normally distributed. The significant results shown with p-values (p < 0.05) in Table 4 revealed the homogeneity hypothesis had been violated.

Table 4.
Deviation of lateral placement descriptive statistics and normality test.
As the Kolmogorov–Smirnov test indicated deviations in data normality for all curve configurations, Friedman’s ANOVA, a non-parametric test for several related samples, was used to examine the effect of curve radius and approach tangent length on the deviation of lateral position (DLP). It revealed a significant difference across the treatment groups (χ2 (8) = 35.06, p <0.001).
3.3. Driver Classification on Curve Trajectories
Several combinations of lateral position parameters (e.g., mean value, standard deviation, maximum and minimum values, maximum absolute value, maximum absolute difference) maximum value of the lateral acceleration, calculated as the relation between squared vehicle speed and curve radius, provided vehicle trajectories classifications, as shown in Table 5. The curve path classifications and the boundary values for the parameters were adopted from the literature [7]. It was a three-lane highway with a total separation of flows instead of a two-lane rural highway. A lane width was 10 cm larger, resulting in wider limit values for the classifications criteria.

Table 5.
Criteria for the classification of driving behavior.
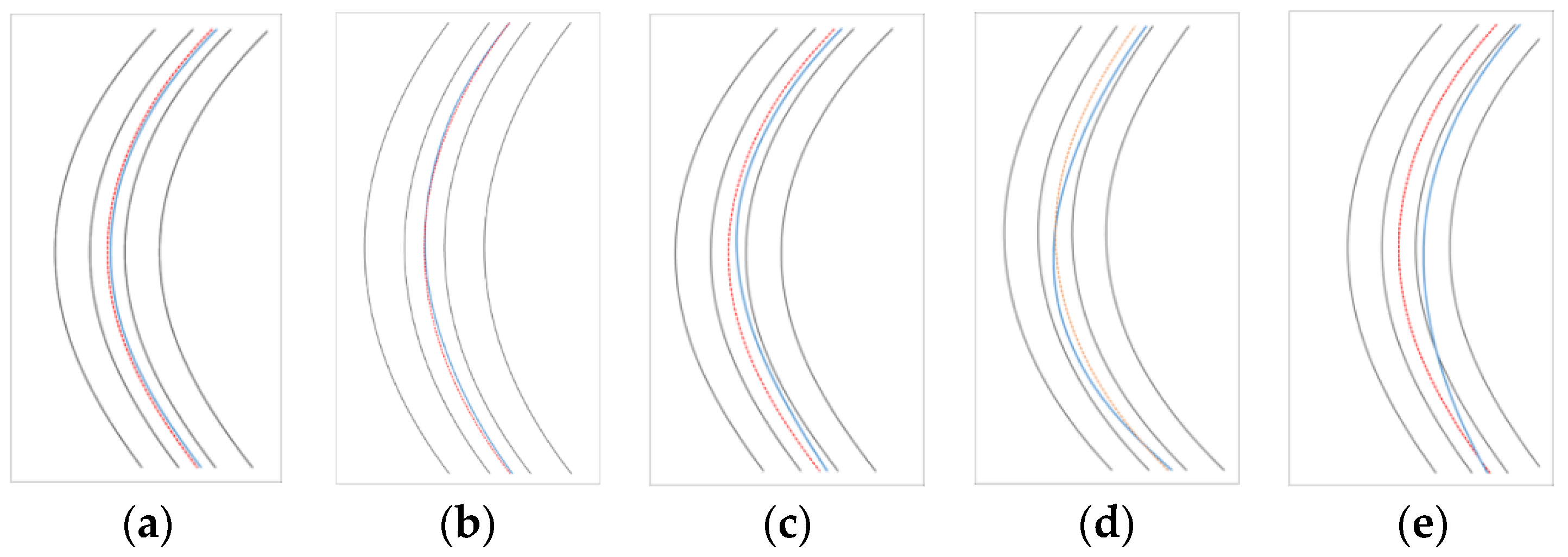
The following five major classes were defined: (1) Ideal behavior, which represents trajectories almost perfectly parallel to any of the lanes’ axes, (2) Normal behavior, which is similar to the previous one, but with greater values for the classification criteria, representing a behavior with no significant errors, (3) Intermediate behavior, characterized by a significant offset toward either the centerline, or the outside in the approach section, (4) Cutting, which represents a conscious driving maneuver to balance centrifugal acceleration by following a trajectory with a greater radius than the geometric one, and (5) Correcting behavior, an unconscious track behavior displayed due to an underestimation or overestimation of road curvature. Trajectories not included in such classes were classified as “others”. Figure 4 shows examples of the trajectory classifications extracted from different driver’s files.
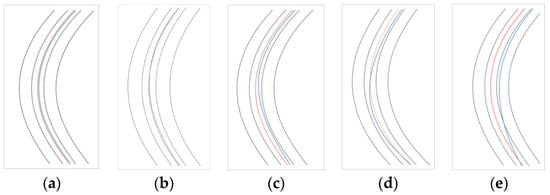
Figure 4.
Examples of different driving behavior paths. (a) Ideal behavior, (b) Normal behavior, (c) Intermediate behavior, (d) Cutting, and (e) Correcting behavior. The gray lines represent road edges, the red line is the middle line axis, and the blue one is the vehicle’s center of gravity path.
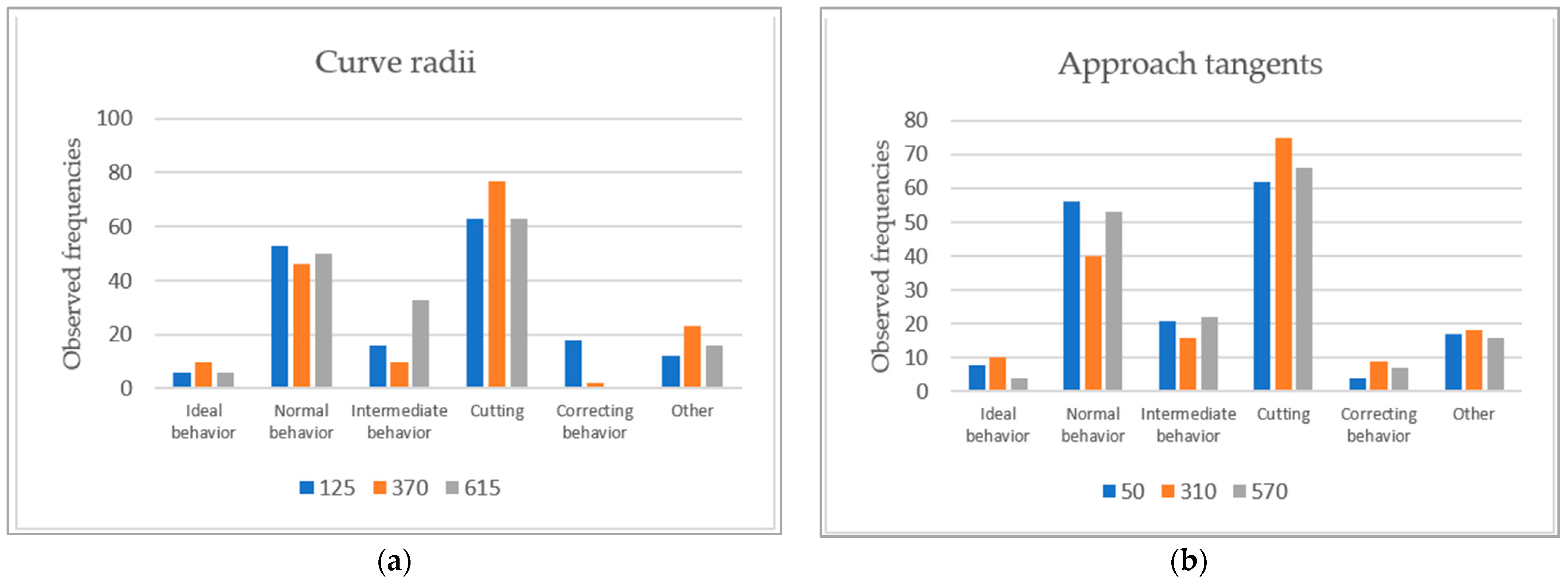
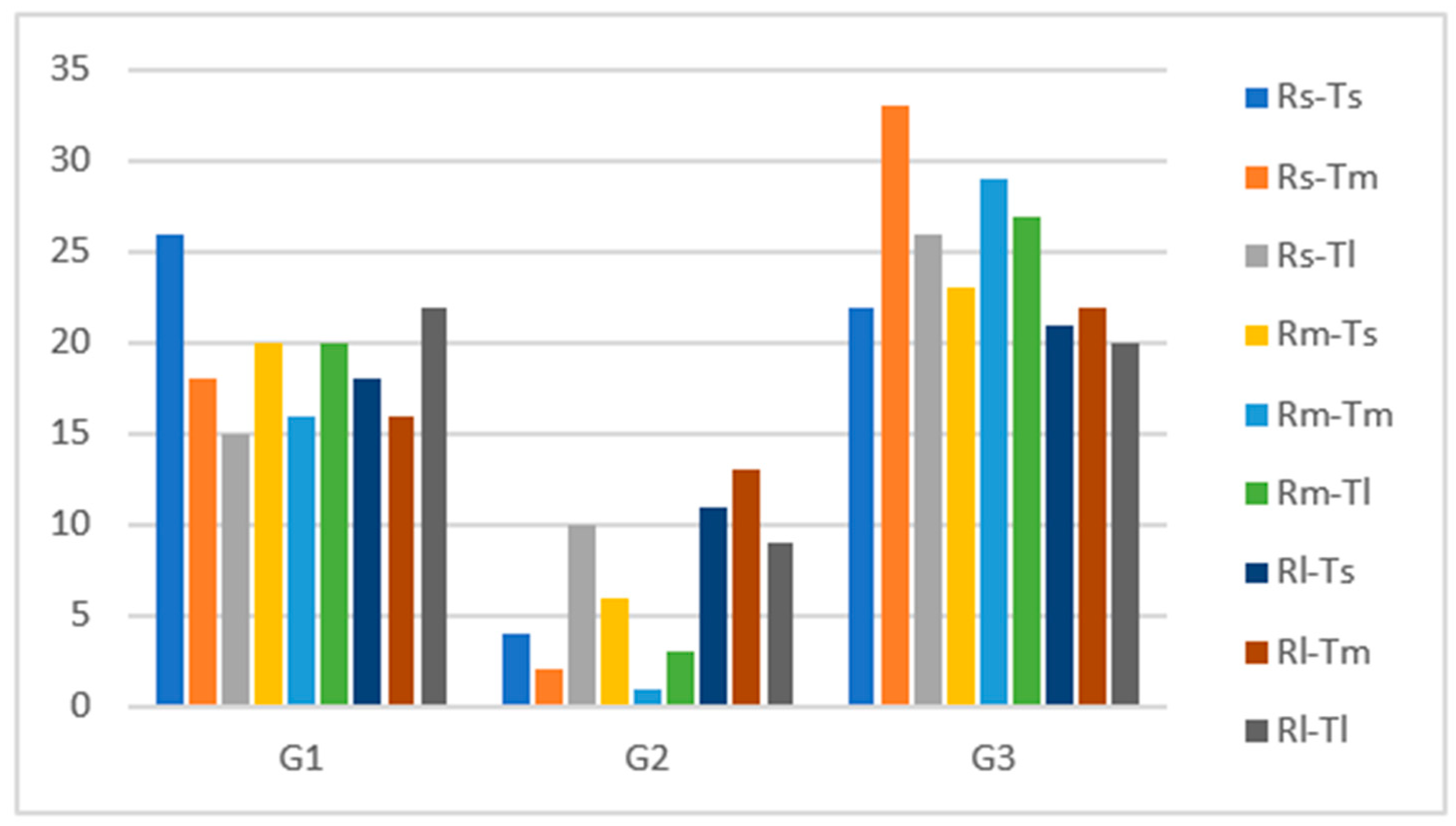
As expected from observations found in the literature review, the curve trajectory classification resulted in a small proportion of ideal behavior (4.37%). Cutting was the most common behavior, observed in 40.28% of trajectories, followed by normal and intermediate behaviors, with 29.56% and 11.71%, respectively. Correcting behavior was the least common result and the most dangerous one, displayed in 3.97% of the instances. These results can be seen better in Figure 5. Curve trajectories classified as “others” were also quite common (10.12%), suggesting the classification criteria can be improved.
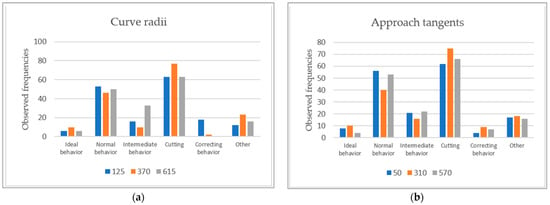
Figure 5.
Driving behavior frequencies per curve radii (a) and approach tangent (b).
Table 6 shows the proportion of the different classes of trajectory disaggregated concerning approach tangents length and curve radii. Pearson chi-square test revealed a significant association between curve radius and trajectories classification results, χ2 (10) = 51.204 (p < 0.001); however, it accepted the null hypothesis of non-association between approach tangent lengths and trajectories classification χ2 (10) = 9.837 (p = 0.455). Testing the association between the trajectories behaviors with the nine curve configurations classes resulted in lower limits of expected frequencies to rely on the Pearson chi-square test.

Table 6.
Disaggregated proportions of driving behaviors.
The trajectories were grouped into three macro-classes to visualize better the effect of different approach tangent lengths and curve radius on curve negotiation. The safest curve negotiation behavior was G1 and included ideal and normal behaviors; macro-class G2 represents the intermediate behavior, and G3 included cutting and correcting behaviors representing the most dangerous behavior.
According to Figure 6, the safest behavior (G1) was more evident in the small approach tangent and radius combination, explained by the higher concentration level demanded on this type of curve. As expected, it was followed by medium and large radii combined with a large approach tangent since the negotiation of wider curves tends to be easier. Intermediate behavior (G2) is slightly more frequent on curves with large radii. At the same time, the incidence of the most dangerous one (G3) significantly decreases in function of curve radius, which is consistent with crash statistics that show a notably higher crash rate on curves with small radii.
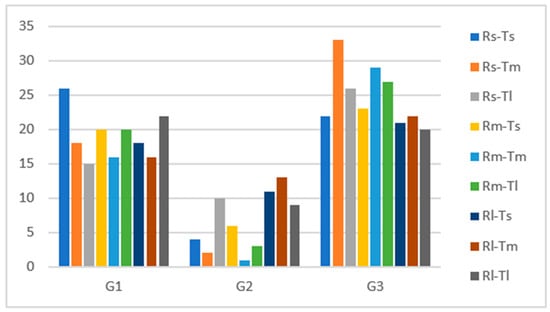
Figure 6.
Classification of macro-classes trajectories per curve configuration.
The Pearson chi-square test showed a significant association between the combination of curves radii and approach tangents length with the macro classification results, χ2 (24) = 33.235 (p < 0.05).
The results revealed trajectories as an emerging safety indicator on horizontal curves as a significant correlation was found between the trajectories identified as dangerous and the radii of the curves. Understanding local driver behavior and identifying driver profiles can significantly contribute to measures that ensure and improve road safety; besides, using a driving simulator has been highly advantageous for this type of study. The research has demonstrated different ways to analyze driving performance, evidencing such an analysis can be shared or replicated, or even bring up reflections towards proposals of regulatory changes by road managers, whether private or governmental agencies.
3.4. Eye-Movements Data Analysis
This section addresses pertinent statistical analyses for a better comprehension of variables to be used and that suit the assumption that driver eye movements differ on curves with distinct geometric characteristics. It also discusses the results and their agreement with what is expected.
The variables extracted from the simulation experiment by Pro 5.10® Smart Eye equipment were the number of fixations, their durations, pupil size, and gaze directions regarding the driver’s visual attention. These were assessed in two different ways, i.e., calculated as the polygon area formed by the drivers’ gaze dispersion for each curve configuration and adopting the relation between the standard deviations of the eye-tracking in the X and Y axes.
3.4.1. Fixations
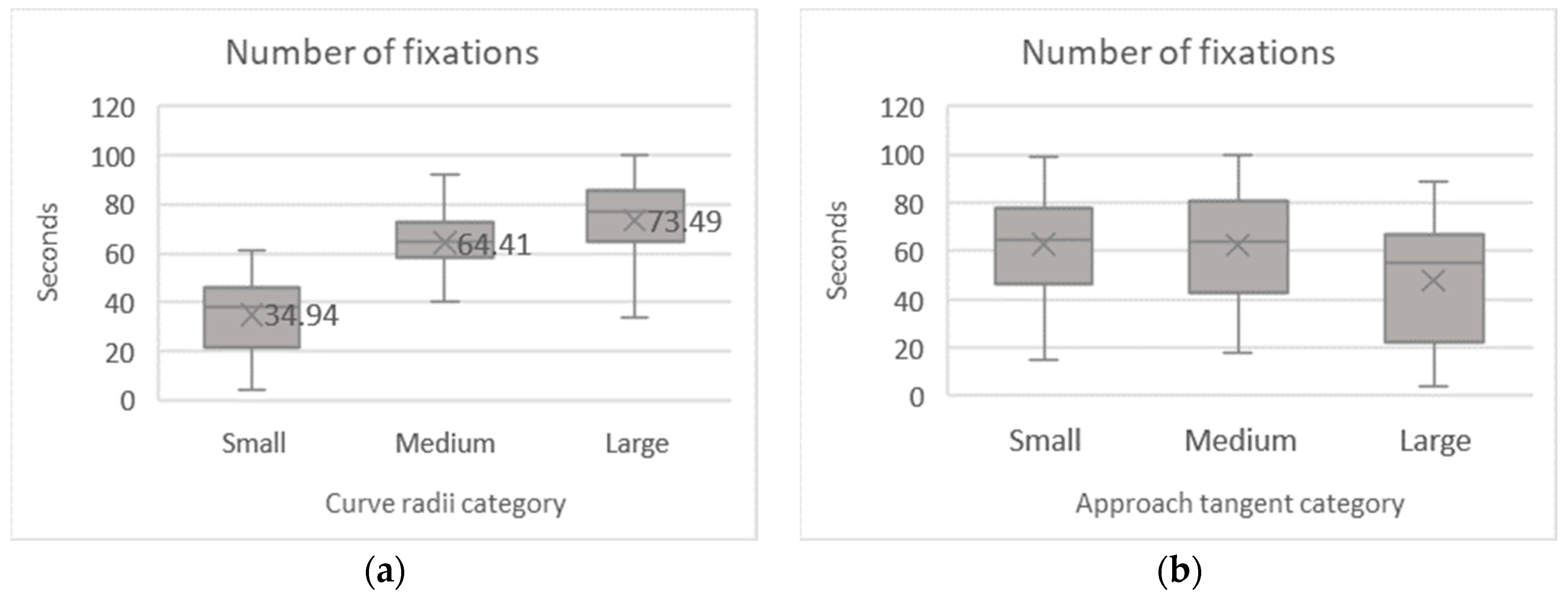
The number of fixations was calculated for each subject in both runs and the nine possible curve configurations (see Table 7 for the mean results). The Kolmogorov–Smirnov test indicated deviations in data normality for most curve configurations. According to the boxplots, the number of fixations is directly proportional to the curve radius increase (Figure 7a). It differs among the studied approach tangent lengths, mainly for the largest one compared to the others. Such significant differences were confirmed by the non-parametric test Friedman’s ANOVA, which revealed relevant effects on the average number of fixations on the curve’s radius (χ2 (2) = 120.139, p < 0.001) and approach tangents (χ2 (2) = 76.712, p < 0.001).

Table 7.
Number of fixations descriptive statistics and normality test.
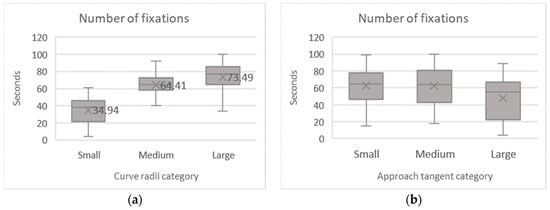
Figure 7.
Mean number of fixations per curve radii (a) and approach tangent (b).
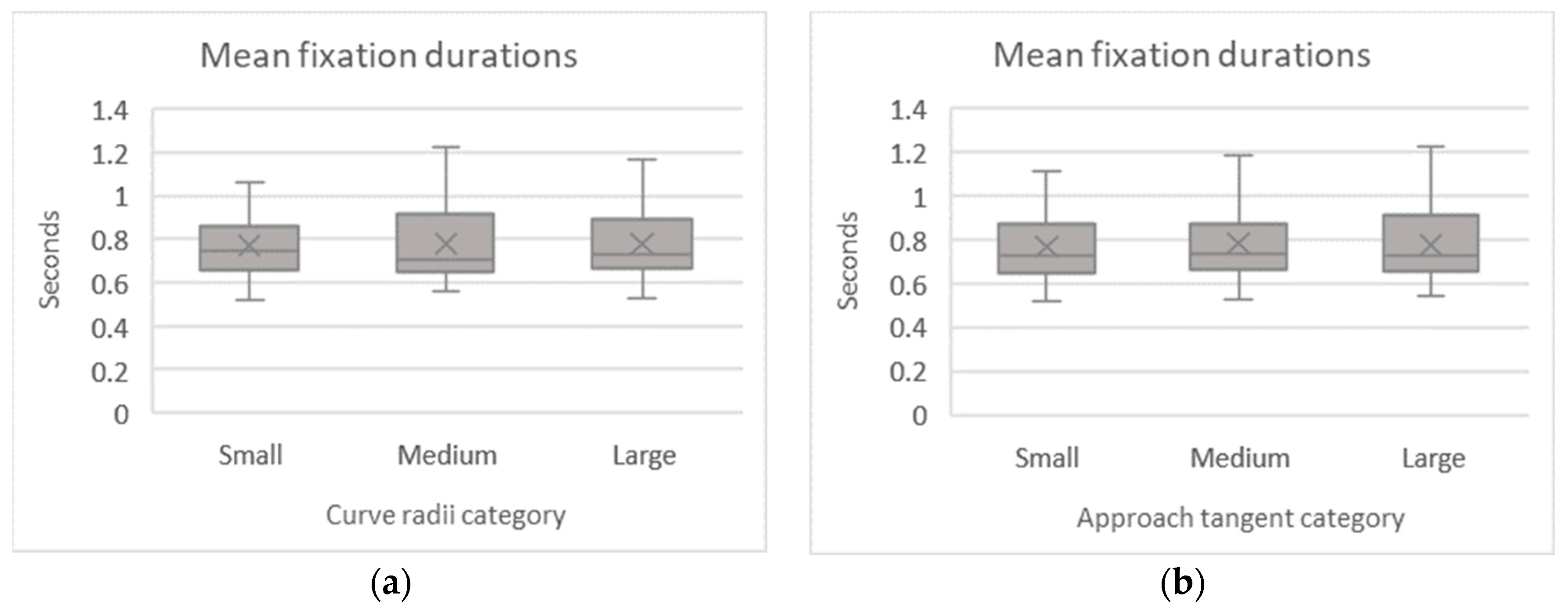
Similarly, for the mean fixation duration, the non-parametric test of Friedman’s ANOVA compared the average duration of the fixations during driving throughout the different curve configurations. The Kolmogorov–Smirnov test demonstrated that the homogeneity hypothesis had been violated, as shown in Table 8. There were no clear differences observable through the boxplots, as shown in Figure 8. Accordingly, Friedman’s ANOVA retained the null hypothesis the mean fixation duration did not change across the radii of the curves (χ2 (2) = 1.246, p = 0.536) and approach tangents groups (χ2 (2) = 2.094, p = 0.351).

Table 8.
Mean fixation duration descriptive statistics and normality test.
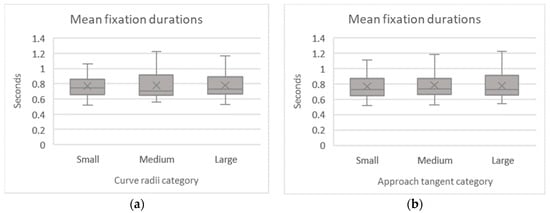
Figure 8.
Mean fixation durations per curve radii (a) and approach tangent (b).
3.4.2. Pupil Diameter Analysis
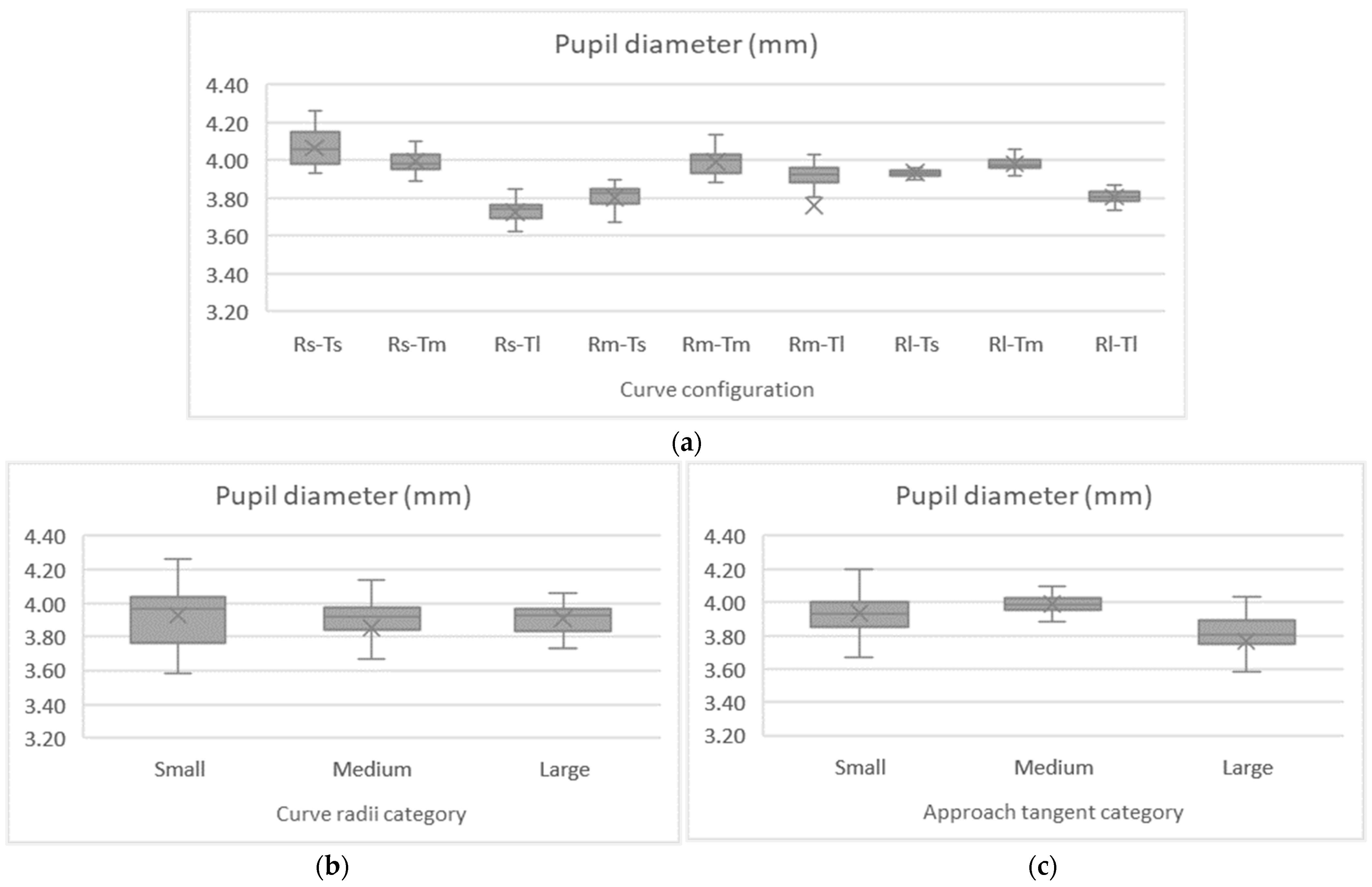
Another eye measurement recorded during the experiment was the pupil diameter, which is strongly associated with the driver’s cognitive abilities. The Kolmogorov–Smirnov test indicated deviations in data normality, as shown in Table 9 and depicted in Figure 9, pointing to Friedman’s ANOVA to examine the effect of the curve configurations on driver pupil size. Analyzing the curve radii and the approach tangent lengths separately, both show significant differences between the observed mean pupil diameters (χ2 (2) = 14.174, p < 0.001) and (χ2 (2) = 29.656, p < 0.001), respectively.

Table 9.
Pupil size descriptive statistics and normality test.
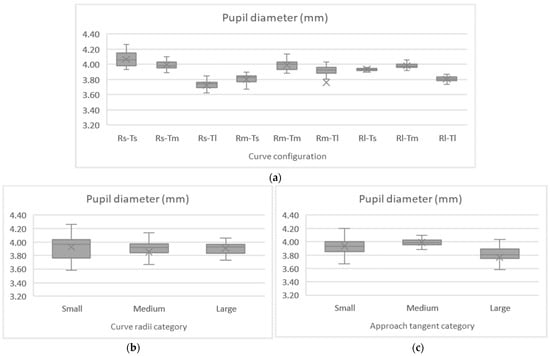
Figure 9.
Mean pupil diameter per curve configuration (a), radii (b), and approach tangent (c).
The Bonferroni correction was performed to adjust significance values. For the main effect of curve radii, a pairwise comparison based on post-hoc tests indicated that the average pupil diameter recorded for the small level was significantly different from the others (p < 0.05), while the difference between the medium and large radii was not (p = 1.000). Similarly, for the main effect of approach tangents, the pairwise comparison also indicated that the average pupil diameter recorded for the small level was significantly different from the others (p < 0.001). In contrast, the difference between the medium and large approach tangents was insignificant (p = 0.993). As expected, the larger the pupil diameter is, the greater the attention devoted to the task is. The largest pupil diameters were recorded on curves with smaller radii and approach tangent (0.418 cm).
3.4.3. Gaze Analysis
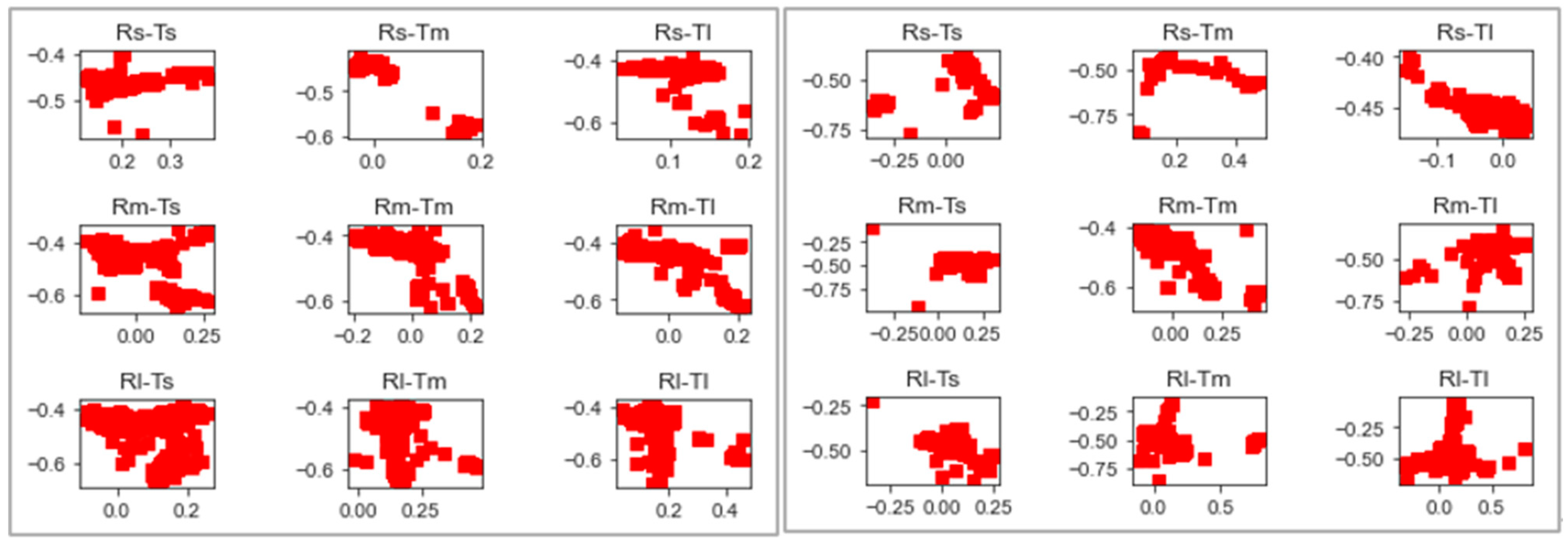
Regarding driver visual attention, the gaze direction was widely explored. Figure 10 shows a comparative search spread between the studied curve configurations for two participants.
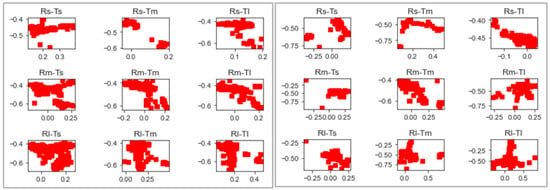
Figure 10.
Spread of search per curve configuration from two subjects.
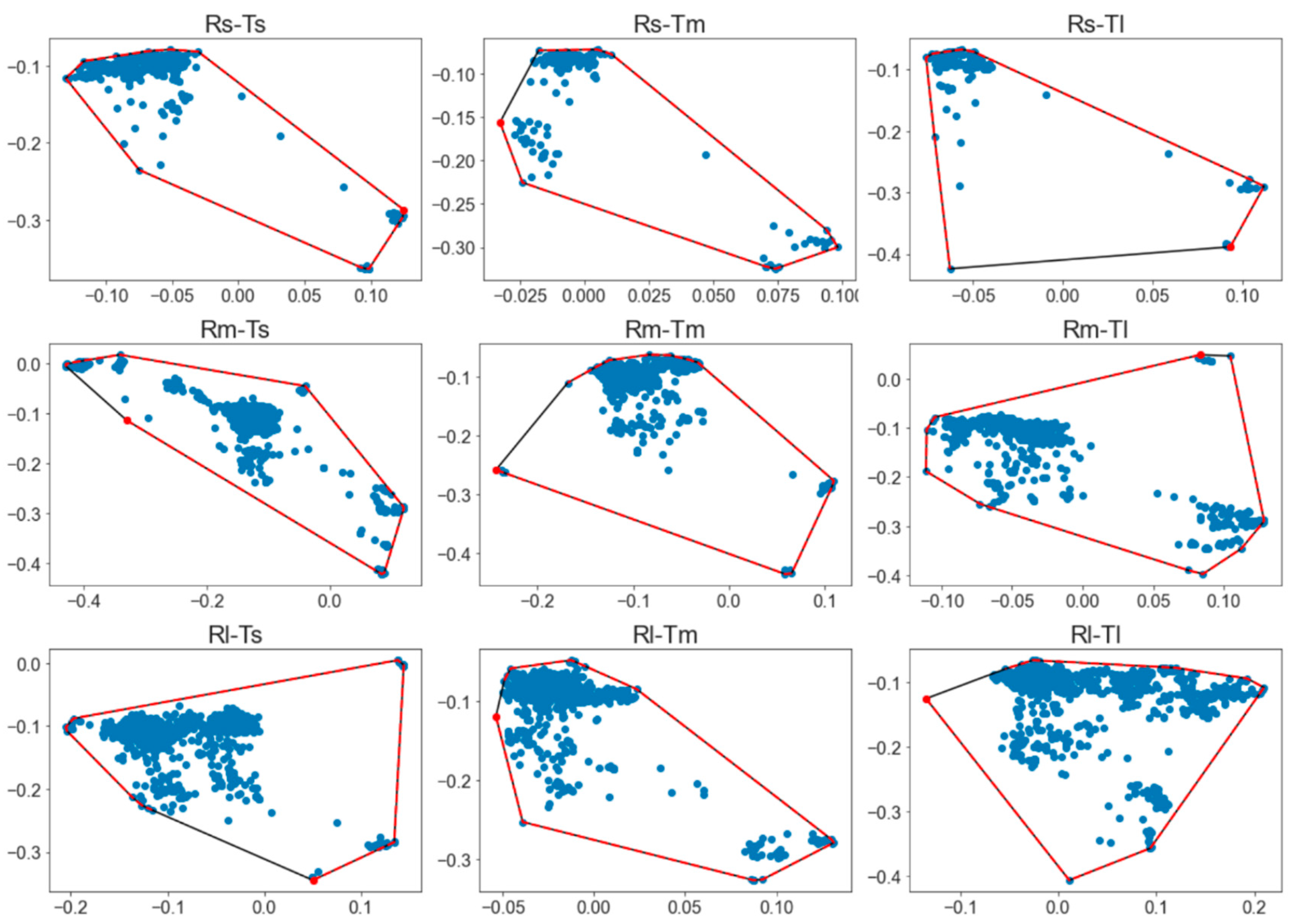
To evaluate the effect of curve radii and approach tangent lengths on the drivers’ visual attention, the polygon’s area shape was calculated by the extreme points of the scatter graphs of each participant for the different curve configurations. This is to be seen in Figure 11, the relation between the standard deviation of the gaze distribution on axis X and Y.
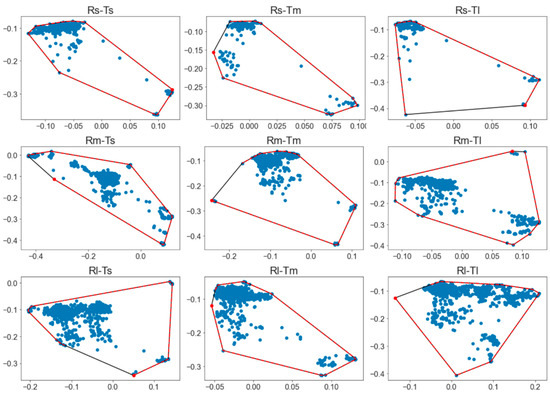
Figure 11.
Gaze distribution areas.
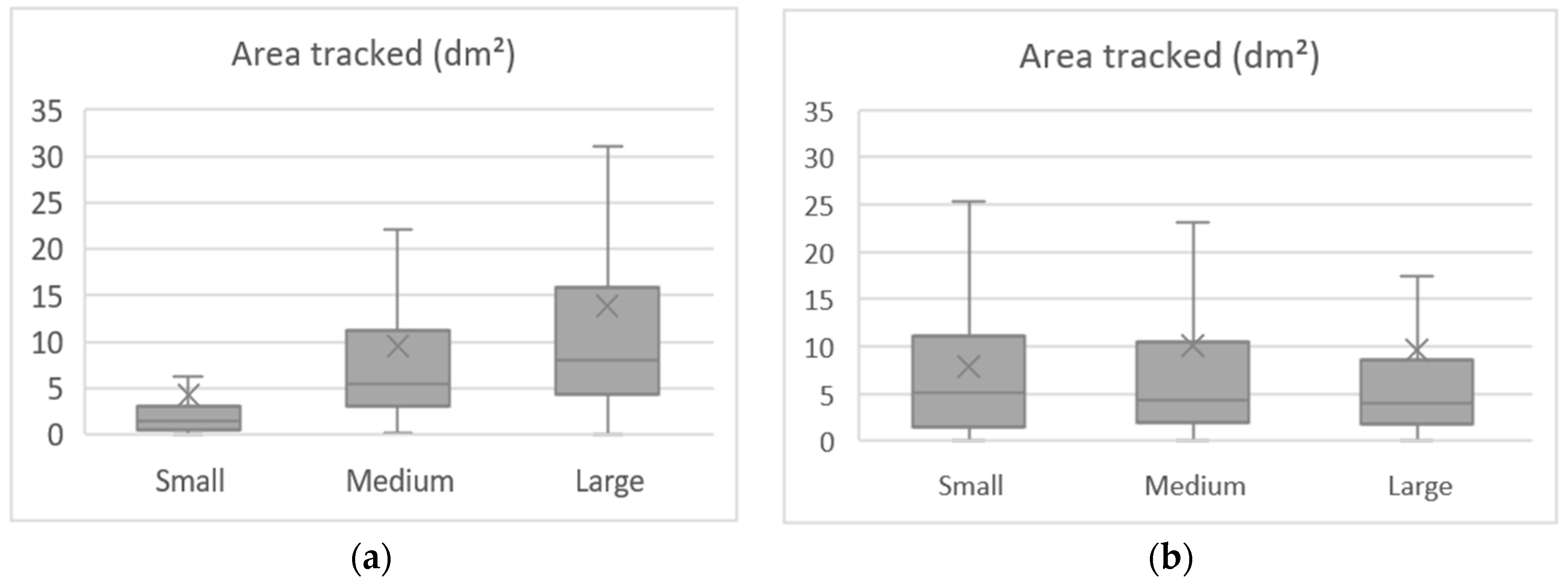
We used the Friedman’s ANOVA test to compare the area tracked while driving in the different curve configurations. The Kolmogorov–Smirnov test revealed the data were not normally distributed, as seen in Table 10 and the average areas tracked. The differences were significant, as proved by the test, resulting in (χ2 (8) = 156.664, p < 0.001). In general, the average areas tracked increased with radius and approach tangent increase, as seen in Figure 12. A smaller spread of drivers’ field of view was related to a greater focus while performing, indicating that the observed result is in line with the literature since shorter curves and tangents tend to demand more attention from the drivers.

Table 10.
Area tracked descriptive statistics and normality test.
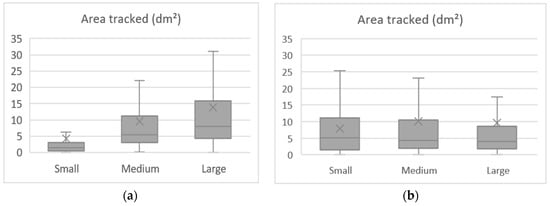
Figure 12.
Mean area tracked per curve radii (a) and approach tangent (b).
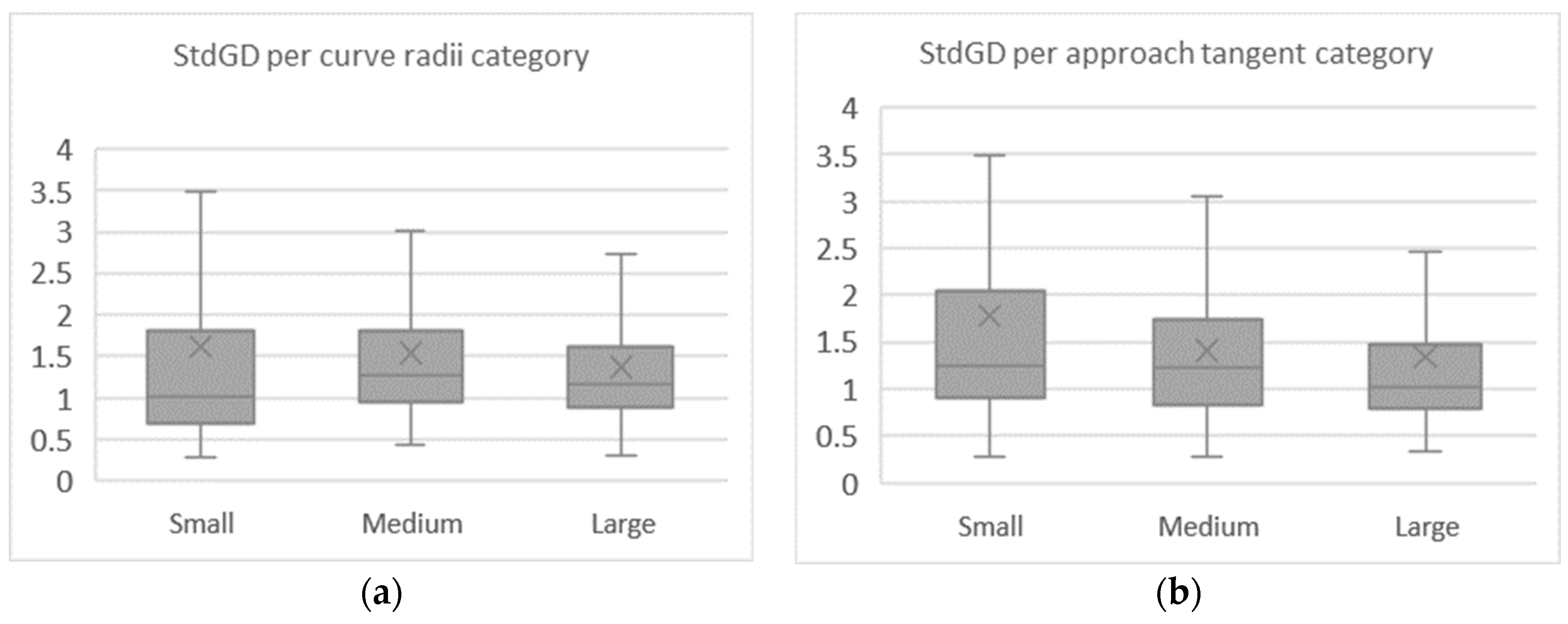
Similarly, the average results obtained by the relation of the standard deviation of the gaze distributions from axis X and Y (StdGD Index) were not normally distributed, as seen by the results of the Kolmogorov–Smirnov test, shown in Table 11. The Friedman’s ANOVA test revealed that this index significantly changes between the studied curve configurations (χ2 (8) = 22.483, p = 0.004).

Table 11.
Deviation of gaze distributions index descriptive statistics and normality test.
Through the boxplots of Figure 13, it is observable that the index value reduced with the increase of the approach tangent length. Meanwhile, there was no clear relation between the index and the curve radius. Evaluating the main effects of curve radii and approach tangents lengths separately for the StdGD index, the Friedman’s ANOVA results demonstrated that the differences observed in the second group were strongly supported with a p-value lower than 0.001, (χ2 (2) = 9.368, p = 0.009) and (χ2 (2) = 17.170, p < 0.001), respectively.
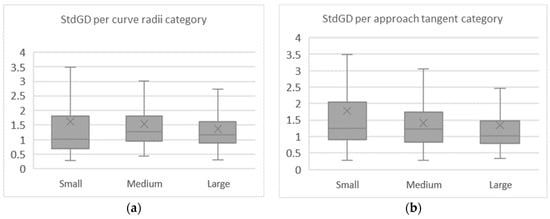
Figure 13.
Mean Standard Deviation of gaze distributions per curve radii (a) and approach tangent (b).
4. Conclusions
This study investigated driver behavior at different approach tangent lengths and radii. The analyses and driver classification were based on speed profiles, lateral position parameters, and eye movements obtained in a driving simulator experiment with twenty-eight drivers. The simulation was performed twice for nine curve configurations, resulting in more than 500 curves, which enabled investigations on the effect of geometric features of horizontal curves on driving performance. Relevant statistical analyses verified the significance of the results. Understanding driver behavior and validating the models in driving simulators are useful and sustainable techniques to improve road safety.
Speed and lateral position were used as measures to assess the driving performance. Initially, a few speeds descriptive analyses and a speed change behavior classification were presented. The lowest speeds were observed on curves with smaller radii, followed by medium- and wider-radius curves, revealing that the average driving speed increased on curves with a wider radius. Repeated measures ANOVA confirmed the effect of the radii of a curve on the average driving speed (F (2, 469) = 145.55, p < 0.001), and the Bonferroni post-hoc test indicated the average speeds were significantly different among the radii of the curves. Speed change behaviors were assessed by the maximum speed reduction achieved by the drivers on each curve, revealing a substantial decrease in speed is the most common behavior observed for the curved configurations with larger radii. However, the driver behavior in curved configurations with smaller radii did not significantly decrease speed.
This research analyzed the drivers’ lateral car position and proposed a curve trajectory classification for a three-lane highway utilizing these measures. The lateral position of the vehicles, assessed by their standard deviation as an index of the driver’s lateral stability, achieved higher values for circular sections compared to other highway stretches and for curves with small radii compared to medium and large curves. The application of Friedman’s ANOVA confirmed the index was significantly different among the treatments (χ2 (8) = 35.06, p < 0.001). The curve trajectories were classified according to lateral position parameters. The incidence of the most dangerous behavior decreased with the increase in the curve radius, supporting the study conducted by Mauriello et al. [7] and consistent with crash statistics, as reported elsewhere. Such first results are in line with those reported in the literature. The most common indicators for successful horizontal curve negotiation (i.e., speed and lateral position) showed a significant association with curve radius but not with the tangent length approach. This signifies their importance as Papadimitriou et al. ranked curve radius as the riskiest factor related to road alignment infrastructure [45]. Further research is necessary to extend the results (e.g., improvements in trajectory classification parameters and development of a multivariate analysis of the variables, such as ordinal logistic regression and inclusion of socioeconomic variables).
Finally, eye measurements were discussed. Relevant analyses grounded the assumption that eye movements differ in different curve configurations, as shown by the statistically significant differences in the mean number of fixations and pupil sizes for the groups. Such movements can assess the driver’s visual attention through the gaze distribution area. No difference was observed among the mean fixation durations; however, the study of the number of fixations requires complementation.
Our results are promising and have confirmed the effectiveness of the driving simulator for road design and driving behavior research and its flexibility for the implementation of different scenarios, which is costly and time-consuming in real-world conditions. Moreover, it provides sufficient data for studies and poses no risk to drivers. By providing a better comprehension of driver behavior, this study helps researchers identify local risky behaviors and their prediction and anticipation, corroborating previous and further studies on road safety and policies through improvements in driving laws and regulations for future road designs and existing highways [46]. The results also showed lateral position, assessed by driver trajectories, is an encouraging surrogate measure for the achievement of driving performance and a road infrastructure safety indicator in horizontal curves. Furthermore, a smart eye data analysis added considerable value to the survey. The correlation between behavioral parameters and driver eye movement can provide traffic engineers with practical suggestions to increase safety in curve sections.
As the next step, we expect to improve this research by applying the same method on another Brazilian roadway in mountainous terrain and evaluate the driver’s behavioral classification on curves based to provide information for the actualization of our manuals of geometric design.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.P.C.L., A.P. and M.E.S.R.; methodology, M.E.S.R. and A.P.C.L.; software, M.E.S.R.; validation, M.E.S.R.; formal analysis, M.E.S.R.; investigation, M.E.S.R., A.P.C.L. and A.P.; resources, A.P.C.L.; data curation, M.E.S.R.; writing—original draft preparation, M.E.S.R. and A.P.C.L.; writing—review and editing, A.P.C.L. and A.P.; visualization, M.E.S.R.; supervision, A.P.C.L.; project administration, A.P.C.L.; funding acquisition, A.P.C.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was financially supported by the Department of Transportation Engineering, São Carlos Engineering School (EESC), University of São Paulo (USP), Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior (CAPES; 001) and São Paulo Research Foundation (FAPESP) for the financial support, grant 2021/10727-1.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted according to the guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Ethical Research Committee of the Faculty of Animal Science and Food Engineering—University of São Paulo (2.184.786).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
No new data were created in this study. Data sharing obtained during the project does not apply to this article due to legal and privacy issues.
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the University of São Paulo’s support of the research activities CAPES, MULTITTECH Engineering, Autopista Régis Bittencourt, ANTT, CNPq grants 307772/2019; 307772/2019-5 and Aurenice Cruz Figueira.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the study design, collection, analysis, or interpretation of data, writing of the manuscript, and decision on the publication of results.
References
- Nama, S.; Maurya, A.K.; Maji, A.; Edara, P.; Sahu, P. Vehicle Speed Characteristics and Alignment Design Consistency for Mountainous Roads. Transp. Dev. Econ. 2016, 2, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barendswaard, S.; Van Breugel, L.; Schelfaut, B.; Sluijter, J.; Zuiker, L.; Pool, D.M.; Boer, E.R.; Abbink, D. Effect of velocity and curve radius on driver steering behaviour before curve entry. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man and Cybernetics (SMC), Bari, Italy, 6–9 October 2019; pp. 3866–3871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvi, A. A Study on Driving Performance Along Horizontal Curves of Rural Roads. J. Transp. Saf. Secur. 2015, 7, 243–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charly, A.; Mathew, T.V. Evaluation of driving performance in relation to safety on an expressway using field driving data. Transp. Lett. 2020, 12, 340–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhari, T.; Maji, A. Effect of Horizontal Curve Geometry on the Maximum Speed Reduction: A Driving Simulator-Based Study. Transp. Dev. Econ. 2019, 5, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallmark, S.L.; Hawkins, N.; Smadi, O. Relationship Between Speed and Lateral Position On Curves. Accid. Reconstr. J. 2014. Available online: https://rosap.ntl.bts.gov/view/dot/26103 (accessed on 9 April 2022).
- Mauriello, F.; Montella, A.; Pernetti, M.; Galante, F. An Exploratory Analysis of Curve Trajectories on Two-Lane Rural Highways. Sustainability 2018, 10, 4248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sil, G.; Nama, S.; Maji, A.; Maurya, A.K. Effect of horizontal curve geometry on vehicle speed distribution: A four-lane divided highway study. Transp. Lett. 2019, 12, 713–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suh, W.; Park, P.Y.-J.; Park, C.H.; Chon, K.S. Relationship between Speed, Lateral Placement, and Drivers’ Eye Movement at Two-Lane Rural Highways. J. Transp. Eng. 2006, 132, 649–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, X. Speed change behavior on combined horizontal and vertical curves: Driving simulator-based analysis. Accid. Anal. Prev. 2018, 119, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charlton, S.G. The role of attention in horizontal curves: A comparison of advance warning, delineation, and road marking treatments. Accid. Anal. Prev. 2007, 39, 873–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llopis-Castelló, D.; Bella, F.; Camacho-Torregrosa, F.J.; García, A. New Consistency Model Based on Inertial Operating Speed Profiles for Road Safety Evaluation. J. Transp. Eng. Part A Syst. 2018, 144, 04018006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bassani, M.; Hazoor, A.; Catani, L. What’s around the curve? A driving simulation experiment on compensatory strategies for safe driving along horizontal curves with sight limitations. Transp. Res. Part F Traffic Psychol. Behav. 2019, 66, 273–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llopis-Castelló, D.; Camacho-Torregrosa, F.J.; Marín-Morales, J.; Pérez-Zuriaga, A.M.; García, A.; Dols, J.F. Validation of a Low-Cost Driving Simulator Based on Continuous Speed Profiles. Transp. Res. Rec. J. Transp. Res. Board 2016, 2602, 104–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ariën, C.; Brijs, K.; Vanroelen, G.; Ceulemans, W.; Jongen, E.M.M.; Daniels, S.; Brijs, T.; Wets, G. The effect of pavement markings on driving behaviour in curves: A simulator study. Ergonomics 2017, 60, 701–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Awan, H.H.; Pirdavani, A.; Houben, A.; Westhof, S.; Adnan, M.; Brijs, T. Impact of perceptual countermeasures on driving behavior at curves using driving simulator. Traffic Inj. Prev. 2019, 20, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babić, D.; Fiolić, M.; Gates, T. Road Markings and Their Impact on Driver Behaviour and Road Safety: A Systematic Review of Current Findings. J. Adv. Transp. 2020, 2020, 7843743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charlton, S.G.; Starkey, N.J.; Malhotra, N. Using road markings as a continuous cue for speed choice. Accid. Anal. Prev. 2018, 117, 288–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babić, D.; Brijs, T. Low-cost road marking measures for increasing safety in horizontal curves: A driving simulator study. Accid. Anal. Prev. 2021, 153, 106013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montella, A.; Galante, F.; Imbriani, L.L.; Mauriello, F.; Pernetti, M. Simulator evaluation of drivers’ behaviour on horizontal curves of two-lane rural highways. Adv. Transp. Stud. 2014, 34, 91–104. [Google Scholar]
- Montella, A.; Galante, F.; Mauriello, F.; Pariota, L. Low-Cost Measures for Reducing Speeds at Curves on Two-Lane Rural Highways. Transp. Res. Rec. J. Transp. Res. Board 2015, 2472, 142–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, T.; Tarko, A.; Tremont, P.J. The influence of combined alignments on lateral acceleration on mountainous freeways: A driving simulator study. Accid. Anal. Prev. 2015, 76, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spacek, P. Track Behavior in Curve Areas: Attempt at Typology. J. Transp. Eng. 2005, 131, 669–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brimley, B.K. Evaluating Unfamiliar Driver Visual Behavior on Horizontal Curves Using Fixation Heat Maps. In Proceedings of the Transportation Research Board 93rd Annual Meeting, Washington, DC, USA, 12–16 January 2014; Volume 14. ISBN 9798459946. [Google Scholar]
- Fitzsimmons, E.J.; Nambisan, S.; Souleyrette, R.R.; Kvam, V. Analyses of Vehicle Trajectories and Speed Profiles Along Horizontal Curves. J. Transp. Saf. Secur. 2013, 5, 187–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobermin, M.P.; Silva, M.M.; Ferreira, S. Driving simulators to evaluate road geometric design effects on driver behaviour: A systematic review. Accid. Anal. Prev. 2021, 150, 105923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Ceunynck, T.; Ariën, C.; Brijs, K.; Brijs, T.; Van Vlierden, K.; Kuppens, J.; Van Der Linden, M.; Wets, G. Proactive evaluation of Traffic Signs using a traffic sign simulator. Eur. J. Transp. Infrastruct. Res. 2015, 15, 184–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larocca, A.P.C.; Ribeiro, R.L.; Figueira, A.D.C.; Oliveira, P.T.M.E.S.D.; Lulio, L.C.; Rangel, M.A.C. Analysis of perception of vertical signaling of highways by drivers in a simulated driving environment. Transp. Res. Part F Traffic Psychol. Behav. 2018, 58, 471–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamdar, S.H.; Qin, L.; Talebpour, A. Weather and road geometry impact on longitudinal driving behavior: Exploratory analysis using an empirically supported acceleration modeling framework. Transp. Res. Part C Emerg. Technol. 2016, 67, 193–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vetturi, D.; Tiboni, M.; Maternini, G.; Bonera, M. Use of eye tracking device to evaluate the driver’s behaviour and the infrastructures quality in relation to road safety. Transp. Res. Procedia 2020, 45, 587–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, K.; Tu, H.; Sun, L.; Sze, N.; Song, Z.; Shi, H. Impacts of reduced visibility under hazy weather condition on collision risk and car-following behavior: Implications for traffic control and management. Int. J. Sustain. Transp. 2019, 14, 635–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Yan, X.; Wong, S. Effects of fog, driver experience and gender on driving behavior on S-curved road segments. Accid. Anal. Prev. 2015, 77, 91–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cassarino, M.; Maisto, M.; Esposito, Y.; Guerrero, D.; Chan, J.S.; Setti, A. Testing Attention Restoration in a Virtual Reality Driving Simulator. Front. Psychol. 2019, 10, 250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, F.S.; Larocca, A.P.C. Drivers’ speed profile at curves under distraction task. Transp. Res. Part F Traffic Psychol. Behav. 2017, 44, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farahmand, B.; Boroujerdian, A.M. Effect of road geometry on driver fatigue in monotonous environments: A simulator study. Transp. Res. Part F Traffic Psychol. Behav. 2018, 58, 640–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Min, J.; Hu, J. Real-time eye tracking for the assessment of driver fatigue. Healthc. Technol. Lett. 2018, 5, 54–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Huysduynen, H.H.; Terken, J.; Eggen, B. The relation between self-reported driving style and driving behaviour. A simulator study. Transp. Res. Part F Traffic Psychol. Behav. 2018, 56, 245–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, Q.; Alhajyaseen, W.K.; Pirdavani, A.; Reinolsmann, N.; Brijs, K.; Brijs, T. Speed perception and actual speed in a driving simulator and real-world: A validation study. Transp. Res. Part F Traffic Psychol. Behav. 2019, 62, 637–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, J.L.; Lichty, M.G.; Brown, J.L.; Richard, C.M.; Graving, J.S.; Graham, J.; O’Laughlin, M.; Torbic, D.; Harwood, D. National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine. In Human Factors Guidelines for Road Systems: Second Edition; The National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OpenSCENARIO, version 1.4; VIRES Simulationstechnologie GmbH: Bad Aibling, Germany, 2018.
- Smart Eye Recorder; Version Pro 5.10; Smart Eye AB: Första Långgatan 28B 413 27, Gothenburg, Sweden, 2020.
- De Torquato, T.L.L. Jerk Como Indicador de Consistência Geométrica Para Rodovias; Universidade de São Paulo: São Paulo, Brazil, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- IBM Corp. IBM SPSS Statistics for Windows, version 24.0; IBM Corp.: Armonk, NY, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Field, A. Descobrindo a Estatística Com SPSS; Artmed: Porto Alegre, Brazil, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Papadimitriou, E.; Filtness, A.; Theofilatos, A.; Ziakopoulos, A.; Quigley, C.; Yannis, G. Review and ranking of crash risk factors related to the road infrastructure. Accid. Anal. Prev. 2019, 125, 85–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kolekar, S.; De Winter, J.; Abbink, D. Human-like driving behaviour emerges from a risk-based driver model. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 4850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).