Global Challenges and Prospects of Photovoltaic Materials Disposal and Recycling: A Comprehensive Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- (1)
- The available treatment methods for PV waste, with emphasis on recycling technologies as they are the most researched topics. The principles of high-value and closed-loop recycling are introduced and applied in the discussed technologies, since these principles represent best-practices in favor of environmental preservation;
- (2)
- Technological, financial and environmental challenges, which are commonly expected and brought up in parts of the literature;
- (3)
- Current policies and regulations complementing the establishment of a sustainable PV waste management industry worldwide, providing a reference for countries aiming to establish similar legal instruments and infrastructure for EoL management of PV modules;
- (4)
- Discussions and recommendations to improve the EoL management of PV modules. The contradictions and trade-offs arise from conflicting solutions are discussed, offering critical aspects for policymakers or organizations to consider when selecting appropriate treatment types for EoL modules.
2. Methodology
3. Prospects of PV Materials Recycling and Disposal
3.1. PV Modules
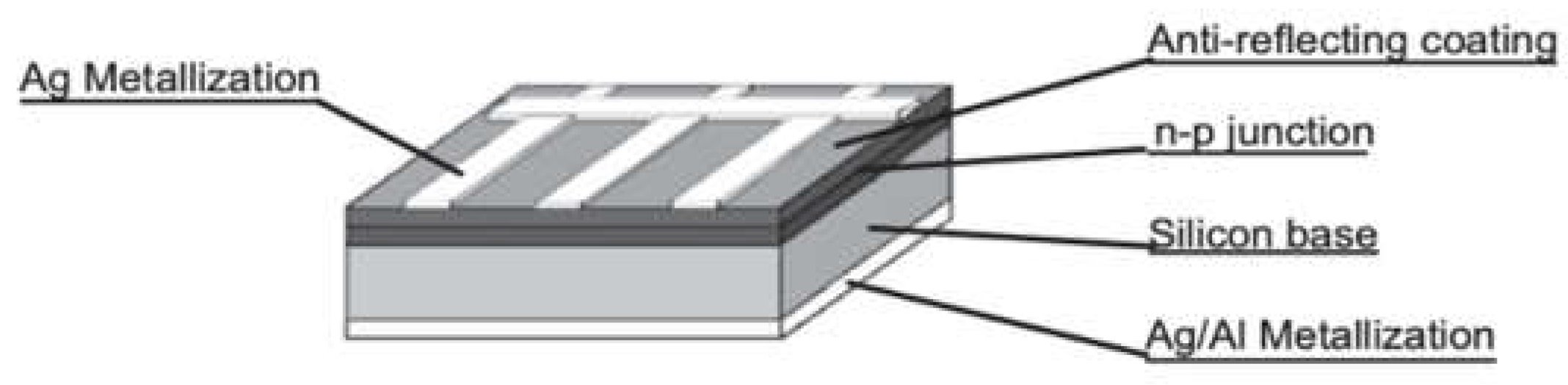
3.1.1. Crystalline Silicon (c-Si) Modules
3.1.2. CdTe and Other Thin-Film Modules
3.2. Disposal of PV Materials
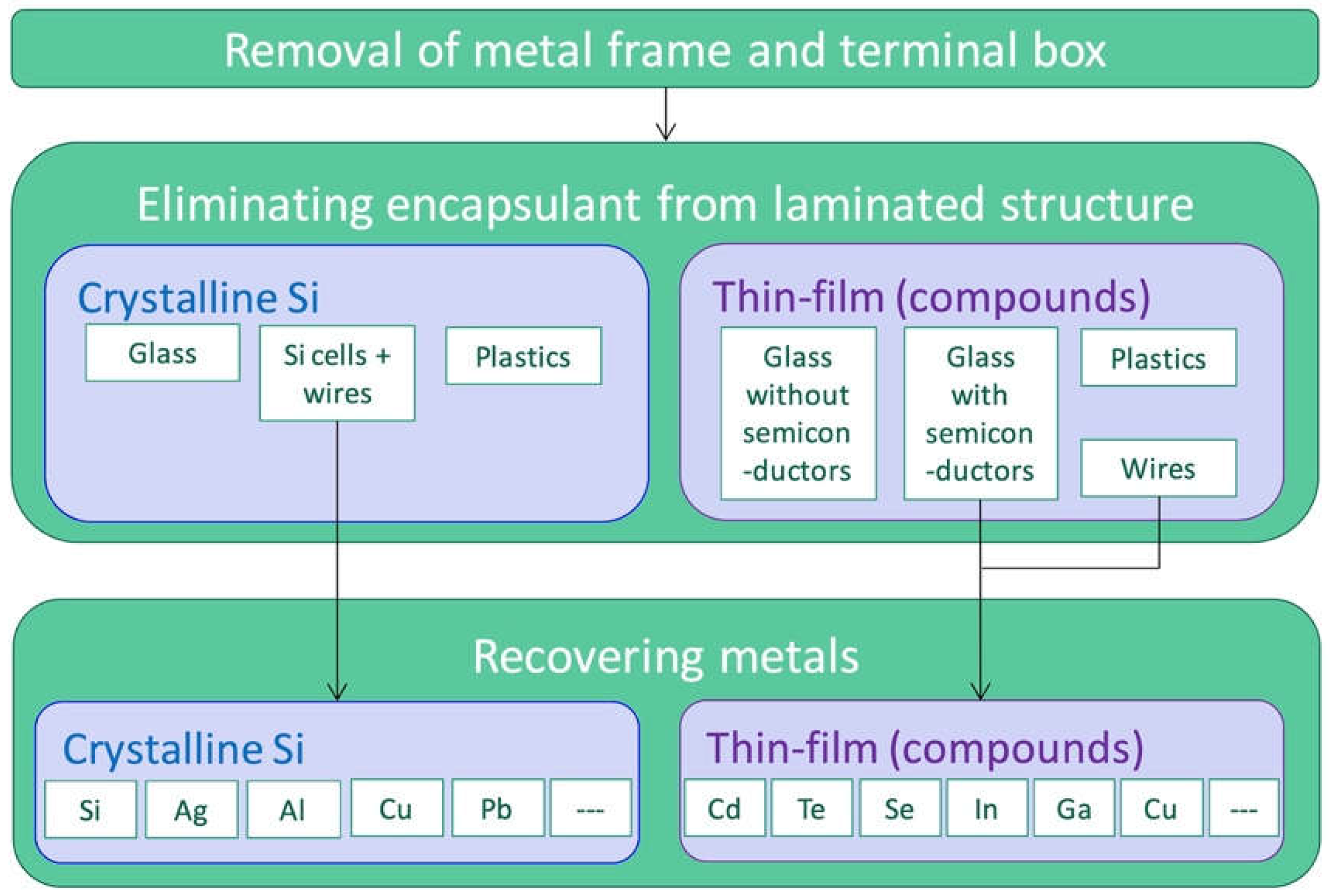
3.3. Recycling of PV Materials
3.3.1. Recycling of c-Si Modules
3.3.2. Recycling of CdTe Thin-Film Modules
3.3.3. Benefits of Recycling
4. Challenges of Recycling PV Materials
4.1. Technological Challenges
4.2. Financial Challenges
4.3. Environmental Challenges
5. Current Policies of PV Materials Disposal and Recycling
5.1. Waste Management Approaches to End-of-Life PV Modules
5.1.1. PV CYCLE
5.1.2. EU WEEE Directive
5.2. Policies for Management of End-of-Life PV Modules in Different Countries
6. Discussions and Recommendations
6.1. Recycling of PV Modules
6.2. Potential Solutions and Future Research
6.2.1. Technological Challenges
6.2.2. Financial Challenges
6.2.3. Environmental Challenges
6.2.4. Contradictions among Proposed Solutions
6.2.5. Prevention and Reduction in EoL PV Module Management
6.2.6. Repair and Reuse in EoL PV Module Management
6.2.7. Recycling in EoL PV Module Management
6.3. Policy and Infrastructural Recommendations
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Farrell, C.C.; Osman, A.I.; Doherty, R.; Saad, M.; Zhang, X.; Murphy, A.; Harrison, J.; Vennard, A.S.M.; Kumaravel, V.; Al-Muhtaseb, A.H.; et al. Technical challenges and opportunities in realising a circular economy for waste photovoltaic modules. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2020, 128, 109911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IEA-PVPS. Snapshot of Global PV Markets 2022; IEA-PVPS: Sydney, Autralia, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Kamarulzaman, A.; Hasanuzzaman, M.; Rahim, N.A. Global advancement of solar drying technologies and its future prospects: A review. Sol. Energy 2021, 221, 559–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IRENA and IEA-PVPS. End-of-Life Management: Solar Photovoltaic Panels; IRENA and IEA-PVPS: Sydney, Autralia, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Domínguez, A.; Geyer, R. Photovoltaic waste assessment of major photovoltaic installations in the United States of America. Renew. Energy 2019, 133, 1188–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.-K.; Fthenakis, V. Design and Optimization of Photovoltaics Recycling Infrastructure. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 8678–8683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kannan, R.; Leong, K.C.; Osman, R.; Ho, H.K.; Tso, C.P. Life cycle assessment study of solar PV systems: An example of a 2.7kWp distributed solar PV system in Singapore. Sol. Energy 2006, 80, 555–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsanakas, I.; van der Heide, A.; Radavičius, T.; Denafas, J.; Lemaire, E.; Wang, K.; Poortmans, J.; Voroshazi, E. Towards a circular supply chain for PV modules: Review of today’s challenges in PV recycling, refurbishment and re-certification. Prog. Photovolt. Res. Appl. 2019, 28, 454–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IEA-PVPS. Snapshot of Global PV Markets 2021; IEA-PVPS: Sydney, Autralia, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Chowdhury, M.S.; Shahahmadi, S.A.; Chelvanathan, P.; Tiong, S.K.; Amin, N.; Techato, K.A.; Nuthammachot, N.; Chowdhury, T.; Suklueng, M. Effect of deep-level defect density of the absorber layer and n/i interface in perovskite solar cells by SCAPS-1D. Results Phys. 2020, 16, 102839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, M.; Fthenakis, V.; Ebin, B.; Steenari, B.M.; Butler, E.; Sinha, P.; Corkish, R.; Wambach, K.; Simon, E.S. Major challenges and opportunities in silicon solar module recycling. Prog. Photovolt. Res. Appl. 2020, 28, 1077–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, M.; Rahman, K.S.; Selvanathan, V.; Hasan, A.M.; Jamal, M.S.; Samsudin, N.A.; Akhtaruzzaman, M.; Amin, N.; Techato, K. Recovery of FTO coated glass substrate via environment-friendly facile recycling perovskite solar cells. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 14534–14541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.A.; Hasanuzzaman, M.; Rahim, N.A. Experimental investigation of on-site degradation of crystalline silicon PV modules under Malaysian climatic condition. Indian J. Pure Appl. Phys. 2018, 56, 226–237. [Google Scholar]
- Mahmoudi, S.; Huda, N.; Behnia, M. Multi-levels of photovoltaic waste management: A holistic framework. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 294, 126252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, M.S.; Rahman, K.S.; Chowdhury, T.; Nuthammachot, N.; Techato, K.; Akhtaruzzaman, M.; Tiong, S.K.; Sopian, K.; Amin, N. An overview of solar photovoltaic panels’ end-of-life material recycling. Energy Strategy Rev. 2020, 27, 100431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Held, M.; Ilg, R. Update of environmental indicators and energy payback time of CdTe PV systems in Europe. Prog. Photovolt. Res. Appl. 2011, 19, 614–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Pandey, S.; Kolhe, M. Global review of policies & guidelines for recycling of solar PV modules. Int. J. Smart Grid Clean Energy 2019, 597–610. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y.; Li, J.; Tan, Q.; Peters, A.L.; Yang, C. Global status of recycling waste solar panels: A review. Waste Manag. 2018, 75, 450–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, R.; Chang, N.L.; Ouyang, Z.; Chong, C.M. A techno-economic review of silicon photovoltaic module recycling. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2019, 109, 532–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norgren, A.; Carpenter, A.; Heath, G. Design for Recycling Principles Applicable to Selected Clean Energy Technologies: Crystalline-Silicon Photovoltaic Modules, Electric Vehicle Batteries, and Wind Turbine Blades. J. Sustain. Metall. 2020, 6, 761–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatachary, S.K.; Samikannu, R.; Murugesan, S.; Dasari, N.R.; Subramaniyam, R.U. Economics and impact of recycling solar waste materials on the environment and health care. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2020, 20, 101130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, B.; Kim, J.Y.; Chung, J. Overview of global status and challenges for end-of-life crystalline silicon photovoltaic panels: A focus on environmental impacts. Waste Manag. 2021, 128, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domínguez, A.; Geyer, R. Photovoltaic waste assessment in Mexico. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2017, 127, 29–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Lu, L.; Yang, H. Review on life cycle assessment of energy payback and greenhouse gas emission of solar photovoltaic systems. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2013, 19, 255–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stolz, P.; Frischknect, R.; Wambach, K.; Sinha, P.; Heath, G. Life Cycle Assessment of Current Photovoltaic Module Recycling. International Energy Agency Photovoltaic Power Systems Programme. 2017. Available online: https://www.google.com.hk/url?sa=t&rct=j&q=&esrc=s&source=web&cd=&cad=rja&uact=8&ved=2ahUKEwic1_T7rfX4AhWkxTgGHfthCwIQFnoECAMQAQ&url=https%3A%2F%2Fiea-pvps.org%2Fwp-content%2Fuploads%2F2020%2F01%2FLife_Cycle_Assesment_of_Current_Photovoltaic_Module_Recycling_by_Task_12.pdf&usg=AOvVaw2EqUJ-SONIc3mihwLEwzTX (accessed on 15 July 2021).
- Mohanty, P.; Muneer, T.; Gago, E.J.; Kotak, Y. Solar Radiation Fundamentals and PV System Components. In Solar Photovoltaic System Applications: A Guidebook for Off-Grid Electrification; Mohanty, P., Muneer, T., Kolhe, M., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 7–47. [Google Scholar]
- Benda, V. 18-Photovoltaics, Including New Technologies (Thin Film) and a Discussion on Module Efficiency. In Future Energy, 3rd ed.; Letcher, T.M., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 375–412. [Google Scholar]
- Mahmoudi, S.; Huda, N.; Behnia, M. Photovoltaic waste assessment: Forecasting and screening of emerging waste in Australia. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2019, 146, 192–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malandrino, O.; Sica, D.; Testa, M.; Supino, S. Policies and Measures for Sustainable Management of Solar Panel End-of-Life in Italy. Sustainability 2017, 9, 481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Paiano, A. Photovoltaic waste assessment in Italy. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 41, 99–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, S.; Jadhav, N.Y.; Zakirova, B. Socio-Economic and Environmental Impacts of Silicon Based Photovoltaic (PV) Technologies. Energy Procedia 2013, 33, 322–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Panchenko, V.; Izmailov, A.; Kharchenko, V.; Lobachevskiy, Y. Photovoltaic Solar Modules of Different Types and Designs for Energy Supply. Int. J. Energy Optim. Eng. 2020, 9, 74–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.T.; Liu, H.; You, J.C.; Diao, H.W.; Zhao, L.; Wang, W.J. Back EVA recycling from c-Si photovoltaic module without damaging solar cell via laser irradiation followed by mechanical peeling. Waste Manag. 2022, 137, 312–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilias, A.; Rentoumis, M.; Katsigiannis, Y.; Bilalis, N. Integration & assessment of recycling into c-Si photovoltaic module’s life cycle. Int. J. Sustain. Eng. 2018, 11, 186–195. [Google Scholar]
- Klugmann-Radziemska, E.; Ostrowski, P. Chemical treatment of crystalline silicon solar cells as a method of recovering pure silicon from photovoltaic modules. Renew. Energy 2010, 35, 1751–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogacka, M.; Pikoń, K.; Landrat, M. Environmental impact of PV cell waste scenario. Waste Manag. 2017, 70, 198–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vellini, M.; Gambini, M.; Prattella, V. Environmental impacts of PV technology throughout the life cycle: Importance of the end-of-life management for Si-panels and CdTe-panels. Energy 2017, 138, 1099–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Wild-Scholten, M.; Alsema, E. Towards cleaner solar PV: Environmental and health impacts of crystalline silicon photovoltaics. Refocus 2004, 5, 46–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fthenakis, V.M.; Kim, H.C.; Alsema, E. Emissions from Photovoltaic Life Cycles. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 2168–2174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Raugei, M.; Bargigli, S.; Ulgiati, S. Life cycle assessment and energy pay-back time of advanced photovoltaic modules: CdTe and CIS compared to poly-Si. Energy 2007, 32, 1310–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez-Lopez, D.A.; Rasikh, T.; El Mekaoui, A.; Bassam, A.; Vega De Lille, M.; Ricalde, L.J.; Riech, I. Does recycling solar panels make this renewable resource sustainable? Evidence supported by environmental, economic, and social dimensions. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2022, 77, 103539. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, Y.; Liu, X.; Yuan, Z. Life-cycle assessment of multi-crystalline photovoltaic (PV) systems in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2015, 86, 180–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anctil, A.; Fthenakis, V. Critical metals in strategic photovoltaic technologies: Abundance versus recyclability. Prog. Photovolt. Res. Appl. 2013, 21, 1253–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campo, M.D.; Bonnet, D.; Gegenwart, R.; Beier, J. Process for Recycling CdTe/CdS Thin Film Solar Cell Modules. U.S. Patent 6,572,782, 3 June 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Berger, W.; Simon, F.-G.; Weimann, K.; Alsema, E.A. A novel approach for the recycling of thin film photovoltaic modules. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2010, 54, 711–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Cha, K.; Fthenakis, V.M.; Sinha, P.; Hur, T. Life cycle assessment of cadmium telluride photovoltaic (CdTe PV) systems. Sol. Energy 2014, 103, 78–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoden, F.; Detzmeier, J.; Schnatmann, A.K.; Blachowicz, T.; Schwenzfeier-Hellkamp, E. Investigating the Remanufacturing Potential of Dye-Sensitized Solar Cells. Sustainability 2022, 14, 5670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CU-PV. CU-PV: Cradle-to-Cradle Sustainable PV Modules. 2016. Available online: https://www.sustainablepv.eu/fileadmin/sustainablepv/user/doc/POLICY_BRIEF_CU_PV_FINAL_V2.pdf (accessed on 25 May 2022).
- Fthenakis, V.M. Life cycle impact analysis of cadmium in CdTe PV production. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2004, 8, 303–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jung, B.; Park, J.; Seo, D.; Park, N. Sustainable System for Raw-Metal Recovery from Crystalline Silicon Solar Panels: From Noble-Metal Extraction to Lead Removal. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 4079–4083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uctug, F.G.; Azapagic, A. Environmental impacts of small-scale hybrid energy systems: Coupling solar photovoltaics and lithium-ion batteries. Sci. Total Env. 2018, 643, 1579–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Monier, V.; Hestin, M. Study on Photovoltaic Panels Supplementing the Impact Assessment for a Recast of the WEEE Directive; BIO Intelligence Service: Paris, France, 2011; pp. 1–86. [Google Scholar]
- Faircloth, C.C.; Wagner, K.H.; Woodward, K.E.; Rakkwamsuk, P.; Gheewala, S.H. The environmental and economic impacts of photovoltaic waste management in Thailand. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2019, 143, 260–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, R.; Chang, N.; Lunardi, M.M.; Dias, P.; Bilbao, J.; Ji, J.; Chong, C.M. Remanufacturing end-of-life silicon photovoltaics: Feasibility and viability analysis. Prog. Photovolt. Res. Appl. 2021, 29, 760–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansanelli, G.; Fiorentino, G.; Tammaro, M.; Zucaro, A. A Life Cycle Assessment of a recovery process from End-of-Life Photovoltaic Panels. Appl. Energy 2021, 290, 116727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granata, G.; Pagnanelli, F.; Moscardini, E.; Havlik, T.; Toro, L. Recycling of photovoltaic panels by physical operations. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2014, 123, 239–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IEA-PVPS. End-of-Life Management of Photovoltaic Panels: Trends in PV Module Recycling Technologies; IEA-PVPS: Sydney, Autralia, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Latunussa, C.E.L.; Ardente, F.; Blengini, G.A.; Mancini, L. Life Cycle Assessment of an innovative recycling process for crystalline silicon photovoltaic panels. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2016, 156, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klugmann-Radziemska, E.; Ostrowski, P.; Cenian, A.; Sawczak, M. Chemical, thermal and laser processes in recycling of photovoltaic silicon solar cells and modules. Ecol. Chem. Eng. S 2010, 17, 385–391. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.K.; Lee, J.S.; Ahn, Y.S.; Kang, G.H.; Song, H.E.; Kang, M.G.; Kim, Y.H.; Cho, C.H. Simple pretreatment processes for successful reclamation and remanufacturing of crystalline silicon solar cells. Prog. Photovolt. Res. Appl. 2018, 26, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klugmann-Radziemska, E.; Kuczyńska-Łażewska, A. The use of recycled semiconductor material in crystalline silicon photovoltaic modules production—A life cycle assessment of environmental impacts. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2020, 205, 110259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Kim, W.; Cho, N.; Lee, H.; Park, N. An eco-friendly method for reclaimed silicon wafers from a photovoltaic module: From separation to cell fabrication. Green Chem. 2016, 18, 1706–1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, A.; Wambach, K.; Alsema, E.A. Life Cycle Analysis of Solar Module Recycling Process. MRS Online Proc. Libr. 2011, 895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Lv, F.; Ma, L.Y.; Yang, L.J. The Status and Trends of Crystalline Silicon PV Module Recycling Treatment Methods in Europe and China. Adv. Mater. Res. 2013, 724, 200–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veolia. Veolia Opens the First European Plant Entirely Dedicated to Recycling Photovoltaic Panels. 2018. Available online: https://www.veolia.com/en/newsroom/news/recycling-photovoltaic-panels-circular-economy-france (accessed on 25 May 2022).
- NPC incorporated. PV Panel Recycling Service. 2021. Available online: https://www.npcgroup.net/eng/solarpower/reuse-recycle/recycle-service (accessed on 15 July 2021).
- Sasala, R.A.; Bohland, J.; Smigielski, K. Physical and chemical pathways for economic recycling of cadmium telluride thin-film photovoltaic modules. In Proceedings of the 25th IEEE Photovoltaic Specialists Conference, Washington, DC, USA, 13–17 May 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Krueger, L. Overview of First Solar’s Module Collection and Recycling Program. In Proceedings of the 34th PV Specialists Conference, Philadelphia, PA, USA, 7–16 June 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Sinha, P.; Cossette, M.; Menard, J.-F. End-of-Life CdTe PV Recycling with Semiconductor Refining. In Proceedings of the 27th European Photovoltaic Solar Energy Conference and Exhibition, Frankfurt, Germany, 24–28 September 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Ardente, F.; Latunussa, C.E.L.; Blengini, G.A. Resource efficient recovery of critical and precious metals from waste silicon PV panel recycling. Waste Manag. 2019, 91, 156–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohland, J.; Dapkus, T.; Kamm, K.; Smigielski, K. Photovoltaics as hazardous materials: The recycling solution. In Proceedings of the 2nd IEEE World Photovoltaic Specialists Conference, Vienna, Austria, 6–10 July 1998; pp. 716–719. [Google Scholar]
- Celik, I.; Lunardi, M.; Frederickson, A.; Corkish, R. Sustainable End of Life Management of Crystalline Silicon and Thin Film Solar Photovoltaic Waste: The Impact of Transportation. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 5465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocchetti, L.; Beolchini, F. Recovery of valuable materials from end-of-life thin-film photovoltaic panels: Environmental impact assessment of different management options. J. Clean. Prod. 2015, 89, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoudi, S.; Huda, N.; Behnia, M. Environmental impacts and economic feasibility of end of life photovoltaic panels in Australia: A comprehensive assessment. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 260, 120996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corcelli, F.; Ripa, M.; Leccisi, E.; Cigolotti, V.; Fiandra, V.; Graditi, G.; Sannino, L.; Tammaro, M.; Ulgiati, S. Sustainable urban electricity supply chain—Indicators of material recovery and energy savings from crystalline silicon photovoltaic panels end-of-life. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 94, 37–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hunt, A.J.; Matharu, A.S.; King, A.H.; Clark, J.H. The importance of elemental sustainability and critical element recovery. Green Chem. 2015, 17, 1949–1950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fthenakis, V. Considering the Total Cost of Electricity From Sunlight and the Alternatives [Point of View]. Proc. IEEE 2015, 103, 283–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lunardi, M.M.; Alvarez-Gaitan, J.P.; Bilbao, J.I.; Corkish, R. A review of recycling processes for photovoltaic modules. Sol. Panels Photovolt. Mater. 2018, 9–27. [Google Scholar]
- Fthenakis, V.M. End-of-life management and recycling of PV modules. Energy Policy 2000, 28, 1051–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oreski, G. Encapsulant Materials and Degradation Effects—Requirements for Encapsulants, New Materials, Research Trends. 2014. Available online: https://docplayer.net/62873516-Encapsulant-materials-and-degradation-effects-requirements-for-encapsulants-new-materials-research-trends.html (accessed on 25 May 2022).
- Eberspacher, C.; Gay, C.F.; Moskowitz, P.D. Strategies for enhancing the commercial viability of CdTe-based photovoltaics. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 1996, 41, 637–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.-K.; Fthenakis, V. Crystalline silicon photovoltaic recycling planning: Macro and micro perspectives. J. Clean. Prod. 2014, 66, 443–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cucchiella, F.; D’Adamo, I.; Rosa, P. End-of-Life of used photovoltaic modules: A financial analysis. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 47, 552–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Feng, K.; Liu, X.; Wang, P.; Chen, W.Q.; Li, J. Looming challenge of photovoltaic waste under China’s solar ambition: A spatial–temporal assessment. Appl. Energy 2022, 307, 118186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wambach, K.; Schlenker, S.; Muller, A.; Konrad, B.; Sunicon, A.G. A Voluntary Take Back Scheme and Industrial Recycling of Photovoltaic Modules. In Proceedings of the 24th European Photovoltaic Solar Energy Conference, Hamburg, Germany, 21–25 September 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, H.; Heath, G.; Remo, T.; Ravikumar, D.; Silverman, T.; Deceglie, M.; Kempe, M.; Engel-Cox, J. Technoeconomic Analysis of High-Value, Crystalline Silicon Photovoltaic Module Recycling Processes. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2022, 238, 111592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, T.T.; Jirakiattikul, S.; Chowdhury, M.S.; Ali, D.; Niem, L.D.; Techato, K. The Effect of Retail Electricity Price Levels on the FI Values of Smart-Grid Rooftop Solar Power Systems: A Case Study in the Central Highlands of Vietnam. Sustainability 2020, 12, 9209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Adamo, I.; Miliacca, M.; Rosa, P. Economic Feasibility for Recycling of Waste Crystalline Silicon Photovoltaic Modules. Int. J. Photoenergy 2017, 2017, 4184676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogacka, M.; Potempa, M.; Milewicz, B.; Lewandowski, D.; Pikoń, K.; Klejnowska, K.; Sobik, P.; Misztal, E. PV Waste Thermal Treatment According to the Circular Economy Concept. Sustainability 2020, 12, 10562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beyler, C.; Hirschler, M. Thermal decomposition of polymers. In SFPE Handbook of Fire Protection Engineering; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Marín, M.L.; Jiménez, A.; López, J.; Vilaplana, J. Thermal degradation of ethylene (vinyl acetate). J. Therm. Anal. 1996, 47, 247–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez, V. PV CYCLE: Implementing a Voluntary Take-Back and Recycling Scheme for EoL PV modules. In Proceedings of the 34th PV Specialists Conference, Pennsylvania, PA, USA, 11 June 2009. [Google Scholar]
- PV CYCLE. Our R&D Projects. Available online: https://pvcycle.org/our-rd-projects/# (accessed on 27 December 2021).
- CABRISS. Implementation of a CirculAr Economy Based on Recycled, Reused and Recovered Indium, Silicon and Silver Materials for Photovoltaic and Other Applications. Available online: https://www.spire2030.eu/cabriss# (accessed on 27 December 2021).
- European Parliament and Council of the European Union. Directive 2012/19/EU of the European Parliament and of the Council. 4 July 2012 on waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment (WEEE) Text with EEA Relavance; EU: Brussels, Belgium, 2012; pp. 38–71. [Google Scholar]
- CEI EN 50625-2-4:2017; Collection, Logistics & Treatment Requirements for WEEE—Part 2: Treatment Requirements for Photovoltaic Panels. CEI: Brussels, Belgium, 2017. Available online: https://standards.globalspec.com/std/10401585/cei-en-50625-2-4 (accessed on 19 June 2021).
- Australian Government Department of Agriculture, Water and the Environment. Minister’s Priority List 2021–2022. Available online: https://www.awe.gov.au/environment/protection/waste/product-stewardship/ministers-priority-list/2021-22 (accessed on 24 March 2022).
- Victoria State Government. E-Waste in Victoria. Available online: https://www.environment.vic.gov.au/sustainability/e-waste-in-victoria (accessed on 25 May 2022).
- Stiftung Elektro-Altgeräte Register. Stiftung Elektro-Altgeräte Register. Available online: https://www.stiftung-ear.de/en/home (accessed on 19 June 2021).
- Suresh, S.; Singhvi, S.; Rustagi, V. Managing India’s PV Module Waste. 2019. Available online: https://www.google.com.hk/url?sa=t&rct=j&q=&esrc=s&source=web&cd=&cad=rja&uact=8&ved=2ahUKEwjprNWfrfX4AhWSwzgGHV5GCQsQFnoECAIQAQ&url=https%3A%2F%2Fbridgetoindia.com%2Fbackend%2Fwp-content%2Fuploads%2F2019%2F04%2FBRIDGE-TO-INDIA-Managing-Indias-Solar-PV-Waste-1.pdf&usg=AOvVaw2MQcfP7y7L3ErUzY8t58Bo (accessed on 19 June 2021).
- Komoto, K. Approaches to PV Waste Management in Japan. In Proceedings of the 32nd European Photovoltaic Solar Energy Conference (EU PVSEC), Munich, Germany, 20–24 June 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Mahmoudi, S.; Huda, N.; Behnia, M. Critical assessment of renewable energy waste generation in OECD countries: Decommissioned PV panels. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2021, 164, 105145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellini, E. South Korea to introduce new rules for PV recycling. PV Magazine, 8 October 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, H.; Park, H. PV Waste Management at the Crossroads of Circular Economy and Energy Transition: The Case of South Korea. Sustainability 2018, 10, 3565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jeon, C.H. Chungbuk Province Promotes the Establishment of a Solar Power Recycling Facility; Ministry of Trade, Industry and Energy, Translator; Yonhap News Agency: Seoul, Korea, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- UK Environment Agency. List of Approved Compliance Schemes for WEEE—2014. Available online: https://www.sepa.org.uk/media/36439/approved-pcss.pdf (accessed on 19 June 2020).
- California Legislature. Senate Bill No. 489, Chapter 419, An Act to Add Article 17 (Commencing with Section 25259) to Chapter 6.5 of Division 20 of the Health and Safety Code, Relating to Hazardous Waste, in 489, C. Legislature, Editor. 2015. Available online: https://leginfo.legislature.ca.gov/faces/billTextClient.xhtml?bill_id=201520160SB489 (accessed on 25 May 2022).
- Majewski, P.; Al-shammari, W.; Dudley, M.; Jit, J.; Lee, S.-H.; Myoung-Kug, K.; Sung-Jim, K. Recycling of solar PV panels- product stewardship and regulatory approaches. Energy Policy 2021, 149, 112062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maani, T.; Celik, I.; Heben, M.J.; Ellingson, R.J.; Apul, D. Environmental impacts of recycling crystalline silicon (c-SI) and cadmium telluride (CDTE) solar panels. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 735, 138827. [Google Scholar]
- McDonald, N.C.; Pearce, J.M. Producer responsibility and recycling solar photovoltaic modules. Energy Policy 2010, 38, 7041–7047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Choi, J.K.; Fthenakis, V. Economic feasibility of recycling photovoltaic modules: Survey and model. J. Ind. Ecol. 2010, 14, 947–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goris, M.J.A.A. Recycling Friendly Design: The CU-PV Project for sustainable photovoltaics. In Proceedings of the 29th European Photovoltaic Solar Energy Conference and Exhibition, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 22–26 September 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Einhaus, R.; Bamberg, K.; Franclieu, R.; Lauvray, H. New industrial solar cell encapsulation (NICE) technology for PV module fabrication at drastically reduced costs. In Proceedings of the 19th European PVSEC, Paris, France, 7–11 June 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Heath, G.; Engel-Cox, J. Solar PV recycling: Challenges and approaches. Presented at the Solar Power International and Energy Storage International, Anaheim, CA, USA, 25 September 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Palitzsch, W.; Loser, U. Economic PV waste recycling solutions—Results from R&D and practice. In Proceedings of the 38th IEEE Photovoltaic Specialists Conference, Austin, TX, USA, 3–8 June 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, H. Cost-benefit analysis of waste photovoltaic module recycling in China. Waste Manag. 2020, 118, 491–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, E.-H.; Lee, J.-K.; Lee, J.-S.; Ahn, Y.-S.; Kang, G.-H.; Cho, C.-H. Environmentally friendly recovery of Ag from end-of-life c-Si solar cell using organic acid and its electrochemical purification. Hydrometallurgy 2017, 167, 129–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gernon, M.D.; Wu, M.; Buszta, T.; Janney, P. Environmental benefits of methanesulfonic acid. Comparative properties and advantages. Green Chem. 1999, 1, 127–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LA MIA ENERGIA Scarl. PV-MOREDE: PhotoVoltaic panels MObile REcycling Device; Deliverable D 3.3 Second PV-Morede device Manufactured; LA MIA ENERGIA Scarl: Cassino, Italy.
- NPC Incorporated. Automated PV Panel Disassembly Equipment/Line. Available online: https://www.npcgroup.net/eng/solarpower/reuse-recycle/dismantling (accessed on 25 May 2022).
- Mahmoudi, S.; Huda, N.; Alavi, Z.; Islam, M.T.; Behnia, M. End-of-life photovoltaic modules: A systematic quantitative literature review. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2019, 146, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleiss, G. Estimating Future Recycling Quantities of PV modules in the European Union. In Proceedings of the 32nd European Photovoltaic Solar Energy Conference and Exhibition, Munich, Germany, 20–24 June 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Peeters, J.R.; Altamirano, D.; Dewulf, W.; Duflou, J.R. Forecasting the composition of emerging waste streams with sensitivity analysis: A case study for photovoltaic (PV) panels in Flanders. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2017, 120, 14–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Simón-Martín, M.; Diez-Suárez, A.-M.; Álvarez-de Prado, L.; González-Martínez, A.; De la Puente-Gil, Á.; Blanes-Peiró, J. Development of a GIS Tool for High Precision PV Degradation Monitoring and Supervision: Feasibility Analysis in Large and Small PV Plants. Sustainability 2017, 9, 965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Meena, R.; Kumar, S.; Gupta, R. Comparative investigation and analysis of delaminated and discolored encapsulant degradation in crystalline silicon photovoltaic modules. Sol. Energy 2020, 203, 114–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şevik, S.; Aktaş, A. Performance enhancing and improvement studies in a 600 kW solar photovoltaic (PV) power plant; manual and natural cleaning, rainwater harvesting and the snow load removal on the PV arrays. Renew. Energy 2022, 181, 490–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuan, T.M.; Huang, C.C.; Wu, L.G.; Chan, Y.C.; Yu, C.Y. Process optimization for Potential Induced Degradation improvement on cell level. In Proceedings of the 39th IEEE Photovoltaic Specialists Conference (PVSC), Tampa, FL, USA, 16–21 June 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Kavlak, G.; McNerney, J.; Jaffe, R.L.; Trancik, J.E. Metal production requirements for rapid photovoltaics deployment. Energy Environ. Sci. 2015, 8, 1651–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hocine, L.; Mounia Samira, K. Optimal PV panel’s end-life assessment based on the supervision of their own aging evolution and waste management forecasting. Sol. Energy 2019, 191, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, S.; Sharma, T.; Gupta, A.K. End-of-life management of solar PV waste in India: Situation analysis and proposed policy framework. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2022, 153, 111774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Tong, X. Producer vs. local government: The locational strategy for end-of-life photovoltaic modules recycling in Zhejiang province. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2021, 169, 105484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De la Hoz, J.; Martín, H.; Martins, B.; Matas, J.; Miret, J. Evaluating the impact of the administrative procedure and the landscape policy on grid connected PV systems (GCPVS) on-floor in Spain in the period 2004–2008: To which extent a limiting factor? Energy Policy 2013, 63, 147–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| PV Module | Recycling Processes | Yield of Materials | Suitable for Broken Modules | References | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Disassembly and Delamination | Recovery of Materials | |||||||||
| Mechanical Treatment | Thermal Treatment | Chemical Treatment | Optical Treatment | Mechanical Treatment | Chemical Treatment | Laser Treatment | ||||
| c-Si | ✓ | ✓ | Silicon powder/sheets | Yes | [35] | |||||
| c-Si | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | Pure silicon cells | Yes | [59] | |||
| c-Si | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | Ag Al Silicon wafers | Not specified | [62] | ||||
| c-Si | ✓ | ✓ | Al: 94% Glass Si: 80% Cu: 79% Ag: 90% Pb: 93% | Not specified but chemical etching is applicable to broken cells | [50] | |||||
| c-Si, a-Si and CdTe | ✓ | ✓ | Glass: 80–85% | Not specified but broken modules can be treated together during crushing | [56] | |||||
| c-Si (LGRF) | ✓ | ✓ | Glass: 92% Cu: 41% Al: 74% | Not specified but broken modules can be treated together during crushing | [25,53] | |||||
| c-Si (FRELP) | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | Glass: 99% Cu: 69% Al: 99% Si: 95% Ag: 95% | Not specified | [53,58] | |||
| c-Si (Deutsche Solar AG) | ✓ | ✓ | Glass Al Cu Si Wafers | Yes | [63] | |||||
| c-Si (YingLi Solar) | ✓ | ✓ | Glass Al EVA Si Ag Tedlar | Not specified but broken modules can be treated together during smashing | [8,64] | |||||
| c-Si (Veolia) | ✓ | ✓ | Glass Al Plastic Si Metals | Not specified | [8,65] | |||||
| c-Si (NPC Group) | ✓ | ✓ | Glass Al EVA Solar cells | Not specified | [8,66] | |||||
| CdTe (Solar Cells Inc., currently First Solar) | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | Glass Te sludge: 80% Back metals: 93% Cd: 85% | Yes for chemical treatment but not suitable for water blasting | [67] | |||
| CdTe (First Solar) | ✓ | ✓ | Glass: 90% Cu Unrefined CdTe semiconductor: 95% | Yes | [25,68,69] | |||||
| CdTe and CdS (ANTEC Solar) | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | Glass CdCl2 TeCl4 | Not specified but broken modules can be treated together during milling | [8,44] | ||||
| CdTe and CIS (RESOLVED) | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | Glass Cd Te In | Yes | [45] | |||
| CdTe and CIGS (Loser Chemie) | ✓ | ✓ | Al Glass with EVA layer Glass Metals | Yes | [57] | |||||
| Waste Management Approaches | Examples | |
|---|---|---|
| Voluntary |
|
|
| Public–private |
| PV CYCLE |
| Regulatory |
| European Union WEEE Directive |
| Countries | Expected PV Panel Waste Volumes by 2050 (Million Tonnes) | PV Waste-Specific Regulations and/or Other Similar Policies and Programmes | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Australia | 0.9–0.95 |
| [4,15,97,98] |
| China | 13.5–19.9 |
| [4,57,84] |
| Germany | 4.3–4.4 |
| [4,99] |
| India | 4.4–7.5 |
| [4,100] |
| Italy | 2.1–8.2 |
| [4,29,30] |
| Japan | 6.5–7.6 |
| [4,18,101,102] |
| Korea | 1.5–2.3 |
| [4,57,103,104,105] |
| Mexico | 0.63–1.5 |
| [4,23,41] |
| UK | 1–1.2 |
| [4,106] |
| US | 7.5–10 |
| [4,5,57,107,108] |
| Literature Works | Findings |
|---|---|
| Vellini et al. [37] |
|
| Celik et al. [72] |
|
| Maani et al. [109] |
|
| McDonald and Pearce [110] |
|
| Challenges | Solutions |
|---|---|
| Delamination of encapsulant layer | R&D to effectively delaminate EVA layer including methods of organic solvent, pyrolysis, and ultrasonic radiation |
| Substitution of EVA layer with thermoplastics | |
| Elimination of encapsulant use ** | |
| Complexity of recycling different materials | New PV modules designed for recycling ** |
| Development of combined recycling process to recycle mixed PV waste or integrated facility with several recycling technologies for different modules ** | |
| Extensive R&D to effectively separate different materials | |
| Optimisation of chemical treatment | Extensive R&D to investigate optimised chemical treatment processes |
| Incomplete recycling of LGRF/mechanical processing | Incorporation of comprehensive recycling processes including thermal and chemical treatments ** |
| Challenges | Solutions |
|---|---|
| Economic value of recovered materials | Prioritized recovery of Al frame |
| Development of pre-treatment step to concentrate valuable elements | |
| Inclusion of thin-film modules among c-Si PV waste ** | |
| Extensive R&D to further refine the quality of recovered materials | |
| Collection and transport system | Bring-in services for small-scale PV systems Pick-up services for large-scale PV systems |
| Establishment of decentralised recycling plants ** | |
| PV industry collective operation to collect and transport waste modules | |
| Insufficient quantities of input PV waste | Cooperation between countries with low PV waste flow through a shared treatment programme |
| Recycling at existing general recycling plants or construction of flexible recycling plants accommodating compatible products ** | |
| Construction of decentralised low-capacity recycling plant ** | |
| Costs of treatment processes | Treatment of PV modules in gaseous environment |
| Usage of aluminium chloride to extract Al from silicon cell | |
| Extensive R&D to reduce consumption of chemicals and costs of recycling technology | |
| Unattractive NPVs | Utilisation of economies of scale ** |
| Recycling at existing general recycling plants or construction of flexible recycling plants accommodating compatible products ** | |
| Proper assessment of economic benefits obtained from secondary material recovery | |
| Financial support from authorities and governmental organisations | |
| Environmental Regulations | Government mandate on recovery of valuable and hazardous materials |
| Showcasing effective PV recycling programme to seek regulatory relief |
| Challenges | Solutions |
|---|---|
| Energy consumption | Increase in renewable energy mix in energy consumption |
| Large-scale thermal treatment to increase the efficiency and economy ** | |
| Heat recovery from thermal treatment | |
| Emission of toxic compounds | Replace toxic chemicals with more environmentally friendly alternatives |
| Effective delamination, substitution or elimination of EVA encapsulant ** | |
| Elimination or reduction in usage of fluorinated polymers | |
| Treatment of gaseous emissions from recycling | |
| Transportation emissions | Establishment of decentralised recycling plants ** |
| PV industry collective operation to collect and transport waste modules | |
| Development of on-site pre-treatment recycling facilities |
| Category | Contradictions/Trade-Offs | References | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Design for Recycling | Elimination of encapsulants
| Performance of PV modules
| [8,20,113] |
Reduction in usage of valuable materials
| Reduced resale value of module components
| [20,43,70,86] | |
| Type/Scale of Recycling Operations | Dedicated PV modules recycling plant
| Bulk recycling at existing general recycling plants
| [1,4,14,25,57] |
Decentralised low-capacity PV recycling plants
| Centralised large capacity PV recycling plants
| [6,57,58,70,83] | |
PV module recycling plant dedicated to one type of PV modules
| PV module recycling plant designed for mixed PV waste
| [56,119] | |
| Types of Remanufacturing | Benchmarks |
|---|---|
| Reuse of recycled metallurgical-grade silicon (MG-Si) |
|
| Reuse of recycled solar-grade silicon (SoG-Si) |
|
| Reuse of recovered intact Si wafers |
|
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, H.F.; Hasanuzzaman, M.; Rahim, N.A.; Amin, N.; Nor Adzman, N. Global Challenges and Prospects of Photovoltaic Materials Disposal and Recycling: A Comprehensive Review. Sustainability 2022, 14, 8567. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14148567
Yu HF, Hasanuzzaman M, Rahim NA, Amin N, Nor Adzman N. Global Challenges and Prospects of Photovoltaic Materials Disposal and Recycling: A Comprehensive Review. Sustainability. 2022; 14(14):8567. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14148567
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Hui Fang, Md. Hasanuzzaman, Nasrudin Abd Rahim, Norridah Amin, and Noriah Nor Adzman. 2022. "Global Challenges and Prospects of Photovoltaic Materials Disposal and Recycling: A Comprehensive Review" Sustainability 14, no. 14: 8567. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14148567
APA StyleYu, H. F., Hasanuzzaman, M., Rahim, N. A., Amin, N., & Nor Adzman, N. (2022). Global Challenges and Prospects of Photovoltaic Materials Disposal and Recycling: A Comprehensive Review. Sustainability, 14(14), 8567. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14148567







