Development of Bio-Electrochemical Reactor for Groundwater Denitrification: Effect of Electric Current and Water Hardness
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Sludge Acclimatisation and Influent Preparation
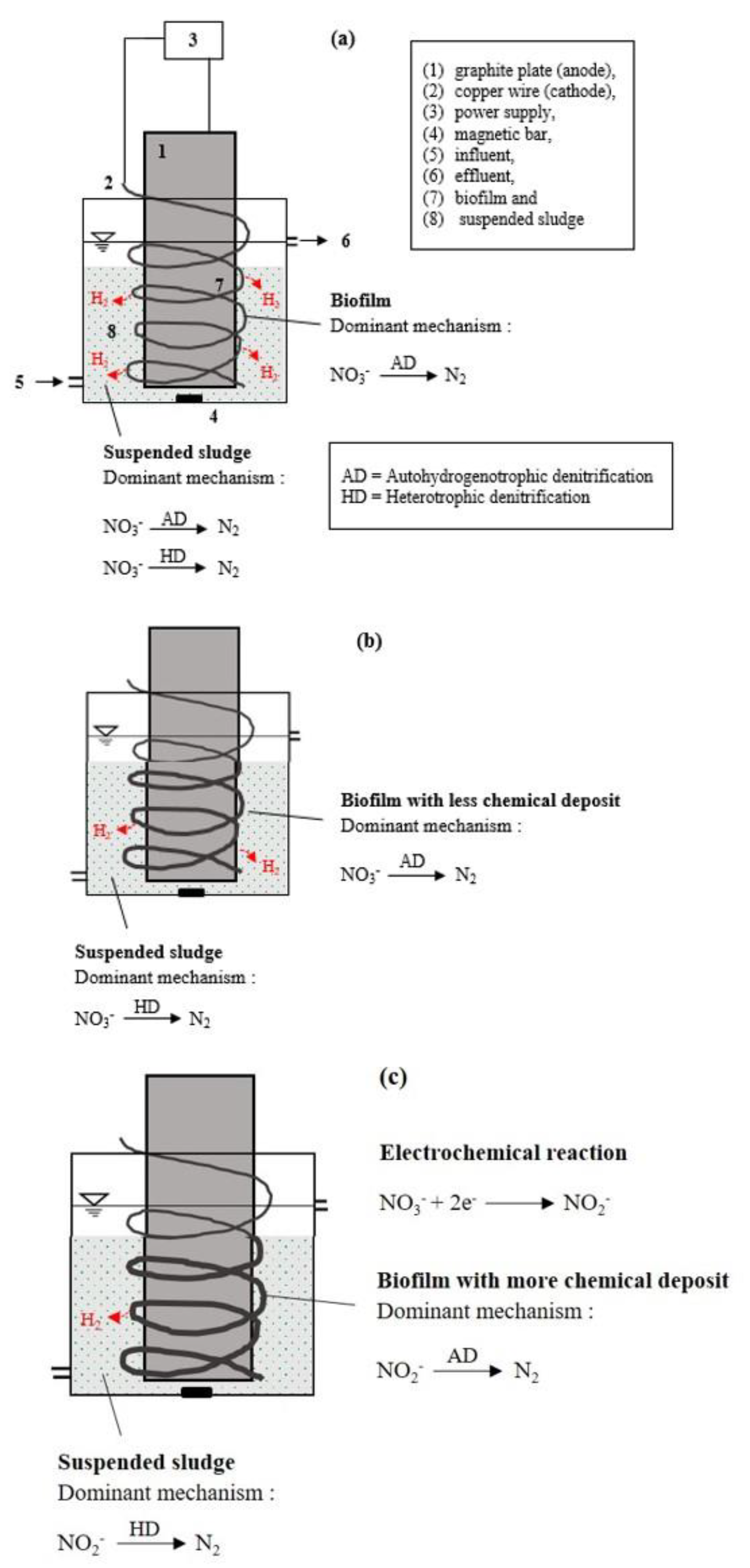
2.3. Experimental Setup and Operation
2.4. Microbial Characterization
2.5. Analytical Method
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Performance at Low Electric Current
3.2. Performance at High Electric Current
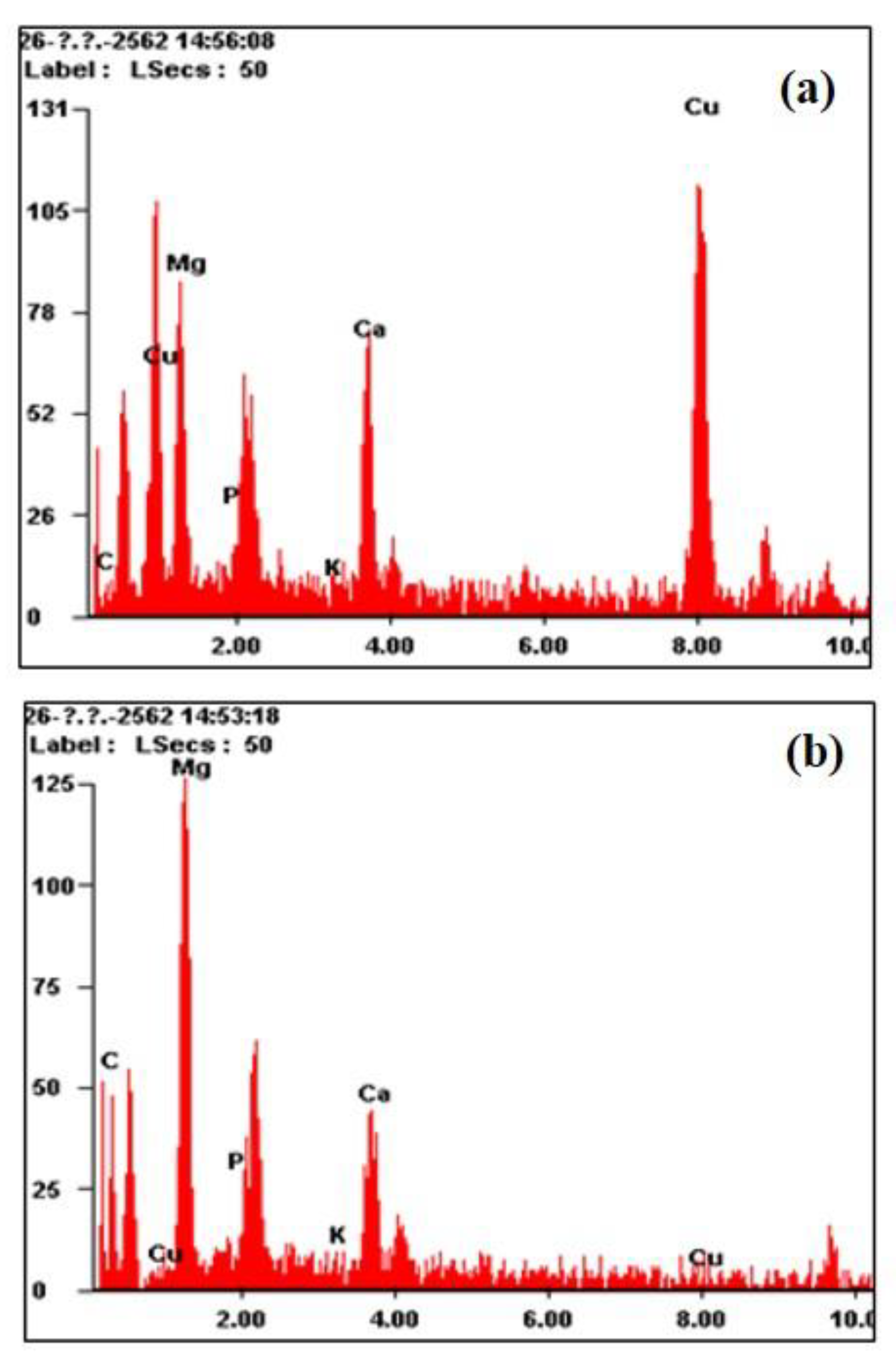
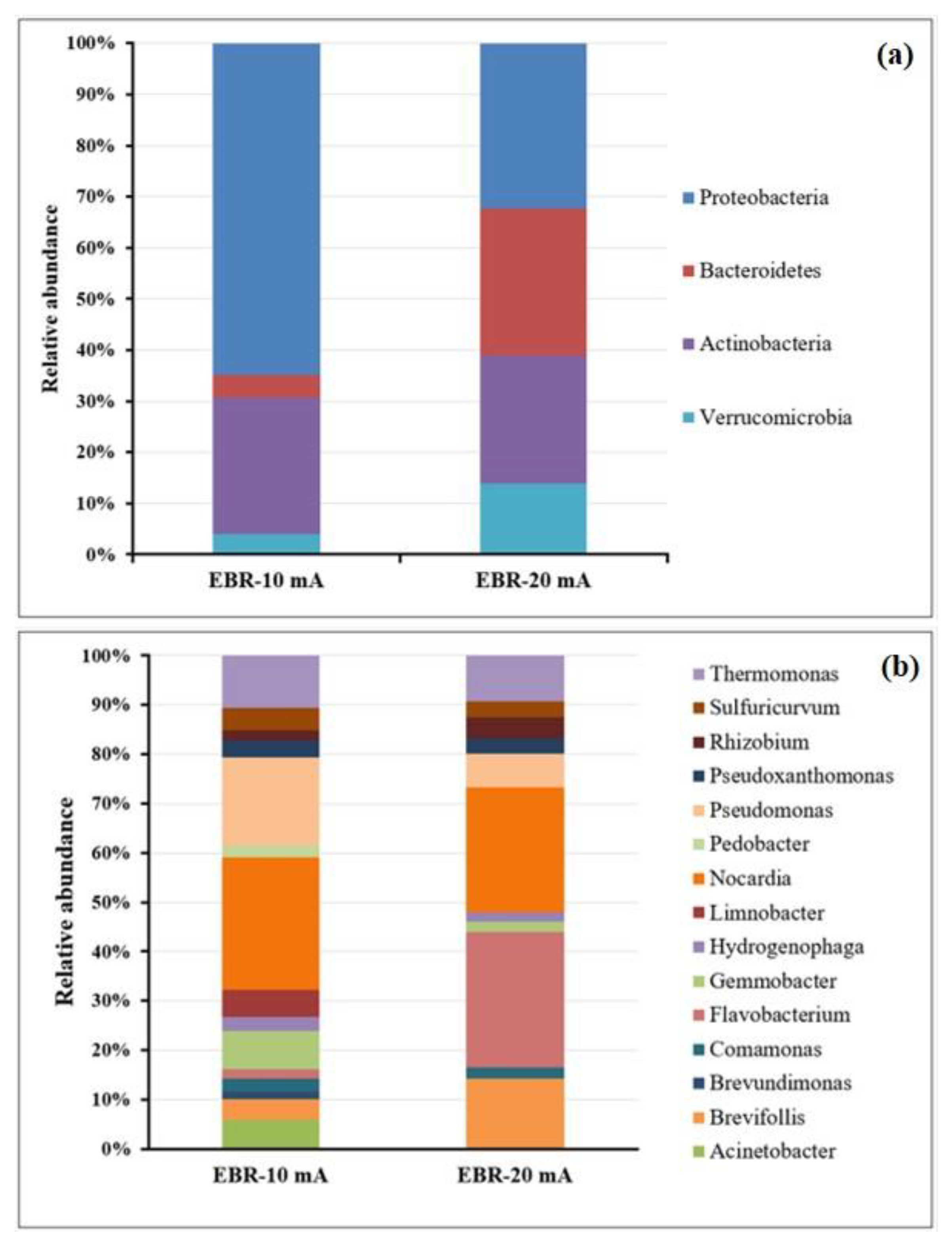
3.3. Bacterial Community of BERs
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bijay, S.; Craswell, E. Fertilizers and nitrate pollution of surface and ground water: An increasingly pervasive global problem. SN Appl. Sci. 2021, 3, 518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.; Yu, G.; Wang, J.; Liu, L.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y. The analysis of groundwater nitrate pollution and health risk assessment in rural areas of Yantai, China. BMC Public Health 2020, 20, 437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality, 4th ed.; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2011.
- El Baba, M.; Kayastha, P.; Huysmans, M.; De Smedit, F. Groundwater Vulnerability and Nitrate Contamination Assessment and Mapping Using DRASTIC and Geostatistical Analysis. Water 2020, 12, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huno, S.K.M.; Rene, E.R.; Hullebusch, E.D.; Annachhatre, A.P. Nitrate removal from groundwater: A review of natural and engineered processes. J. Water Supply Res. Technol. AQUA 2018, 67, 885–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bohdziewicz, J.; Bodzek, M.; Wąsik, E. The application of reverse osmosis and nanofiltration to the removal of nitrates from groundwater. Desalin 1999, 121, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiss, I.; Szekeres, S.; Bejerano, T.T.; Soares, M.I. Hydrogen-dependent denitrification: Preliminary assessment of two bio-electrochemical systems. Water Sci. Technol. 2000, 42, 373–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhai, S.; Ji, M.; Zhao, Y.; Pavlostathisc, S.P.; Zhao, Q. Effects of salinity and COD/N on denitrification and bacterial community in dicyclic-type electrode based biofilm reactor. Chemosphere 2018, 192, 328–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mousavi, S.; Mohamed, I.; Arouab, M.K.; Ghafaria, S. Development of nitrate elimination by autohydrogenotrophic bacteria in bio-electrochemical reactors—A review. Biochem. Eng. J. 2012, 67, 251–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Callegari, A.; Bolognesi, S.; Cecconet, D. Operation of a 2-Stage Bioelectrochemical System for Groundwater Denitrification. Water 2019, 11, 959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cecconet, D.; Sabba, F.; Devecseric, M.; Callegaria, A.; Capodaglioa, A.G. In situ groundwater remediation with bioelectrochemical systems: A critical review and future perspectives. Environ. Int. 2020, 137, 105550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarath Prasanth, S.V.; Magesh, N.S.; Jitheshlal, K.V.; Chandrasekar, N.; Gangadhar, K. Evaluation of groundwater quality and its suitability for drinking and agricultural use in the coastal stretch of Alappuzha District, Kerala, India. Appl. Water Sci. 2012, 2, 165–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peungtim, P.; Meesungnoen, O.; Mahachai, P.; Subsoontorn, P.; Do, T.N.; Nakaruk, A.; Khanitchaidecha, W. Enhancement of nitrate removal under limited organic carbon with hydrogen-driven autotrophic denitrification in low-cost electrode bio-electrochemical reactors. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2021, 96, 2520–2528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Feng, C.; Wang, Q.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Sugiura, N. Nitrate removal from groundwater by cooperating heterotrophic with autotrophic denitrification in a biofilm–electrode reactor. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 192, 1033–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhi, S.-L.; Zhang, K.-Q. Hardness removal by a novel electrochemical method. Desalin 2016, 381, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhi, S.; Zhang, S. A novel combined electrochemical system for hardness removal. Desalin 2014, 349, 68–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Z.; Yang, K.; Lin, D. The effect of water hardness on the toxicity of graphene oxide to bacteria in synthetic surface waters. Aquat. Toxicol. 2019, 216, 105323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDonough, L.K.; Santos, I.R.; Andersen, M.S.; O’Carroll, D.M.; Rutlidge, H.; Meredith, H.; Oudone, S.; Bridgeman, J.; Gooddy, D.C.; Sorensen, J.P.R. Changes in global groundwater organic carbon driven by climate change and urbanization. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smakman, F.; Hall, A.R. Exposure to lysed bacteria can promote or inhibit growth of neighboring live bacteria depending on local abiotic conditions. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2022, 98, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aloni, A.; Brenner, A. Use of cotton as a carbon source for denitrification in biofilters for groundwater remediation. Water 2017, 9, 714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qiao, L.; Yuan, Y.; Mei, C.; Yin, W.; Zou, C.; Yin, Y.; Guo, Q.; Chen, T.; Ding, C. Reinforced nitrite supplement by cathode nitrate reduction with a bio-electrochemical system coupled anammox reactor. Environ. Res. 2022, 204, 112051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feleke, Z.; Felekea, Z.; Araki, K.; Watanabea, T.; Kuroda, M. Selective reduction of nitrate to nitrogen gas in a biofilm-electrode reactor. Water Res. 1998, 32, 2728–2734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, S.; Suidan, M.T. Electrolytic denitrification: Long term performance and effect of current intensity. Water Res. 1998, 32, 528–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.-H.; Jia, J.-P.; Ying, D.W.; Zhu, Y.-C. Electrochemical effect on denitrification in different microenvironments around anodes and cathodes. Res. Microbiol. 2005, 156, 88–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Green, S.J.; Prakash, O.; Gihring, T.G.; Akob, D.M.; Jasrotia, P.; Jardine, P.M.; Watson, D.B.; Brown, S.D.; Palumbo, A.V. Denitrifying Bacteria Isolated from Terrestrial Subsurface Sediments Exposed to Mixed-Waste Contamination. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 76, 3244–3254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, L.; Han, F.; Zhang, X.; Liu, B.; Fan, D.; Sun, X.; Zhang, Y.; Yana, Z. Simultaneous nitrate and dissolved organic matter removal from wastewater treatment plant effluent in a solid-phase denitrification biofilm reactor. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 314, 123714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Starr, M.P. The Prokaryotes: A Handbook on Habitats, Isolation and Identification of Bacteria; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Duffner, C.; Wunderlich, A.; Schloter, M.; Schulz, S.; Einsiedl, S. Strategies to Overcome Intermediate Accumulation During in situ Nitrate Remediation in Groundwater by Hydrogenotrophic Denitrification. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasiliadou, I.; Siozios, S.; Papadas, I.T.; Bourtzis, K.; Pavlou, S.; Vayenas, D.V. Kinetics of pure cultures of hydrogen-oxidizing denitrifying bacteria and modeling of the interactions among them in mixed cultures. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2006, 95, 513–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, R.; Yuan, Q.; Wang, K. Enrichment of denitrifying bacterial community using nitrite as an electron acceptor for nitrogen removal from wastewater. Water 2020, 12, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deng, M.; Dai, Z.; Senbati, Y.; Li, L.; Song, K.; He, X. Aerobic denitrification microbial community and function in zero-discharge recirculating aquaculture system using a single biofloc-based suspended growth reactor: Influence of the carbon-to-nitrogen ratio. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.-Q.; Li, T.-T.; Li, H.-Q. Biofilm formation monitored by confocal laser scanning microscopy during startup of MBBR operated under different intermittent aeration modes. Process Biochem. 2018, 74, 132–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, L.; Chen, N.; Zhao, J.; Yang, C.; Feng, C. Rice husk-intensified cathode driving bioelectrochemical reactor for remediating nitrate-contaminated groundwater. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 837, 155917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Reactor | Electric Current (mA) | Water Hardness (mg/L as CaCO3) | Chemicals Used in the Influent Preparation (g/L) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MgSO4 | CaCl2 | |||
| BER-10 | 10 | 0 * | 0 | 0 |
| 20 ± 1 | 0.05 | 0.03 | ||
| 40 ± 1 | 0.10 | 0.06 | ||
| 80 ± 2 | 0.20 | 0.11 | ||
| BER-20 | 20 | 0 * | 0 | 0 |
| 20 ± 1 | 0.05 | 0.03 | ||
| 40 ± 1 | 0.10 | 0.06 | ||
| 80 ± 2 | 0.20 | 0.11 | ||
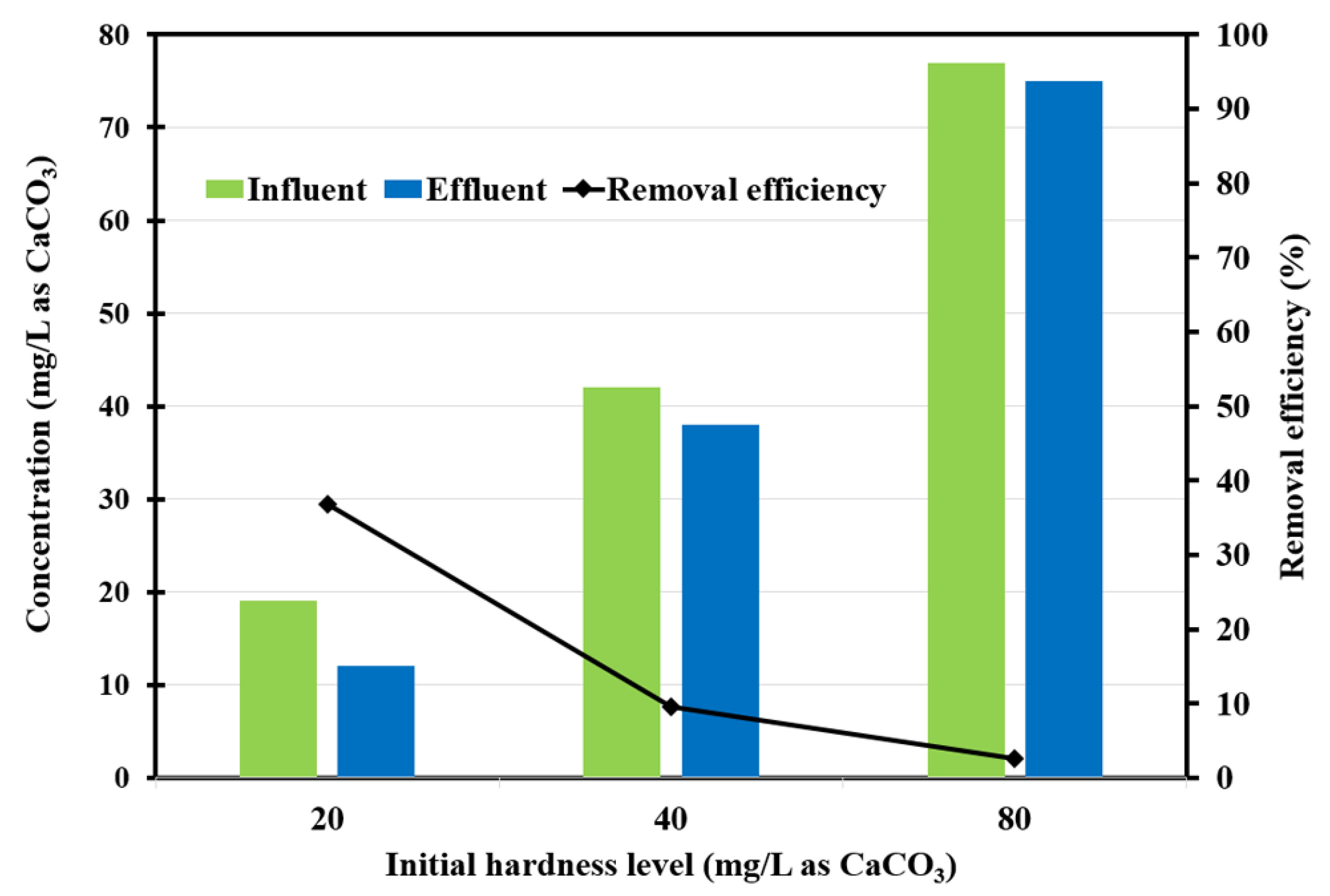
| Water Hardness Condition (mg/L as CaCO3) | Influent NO3-N (mg/L) | Effluent (mg/L) | Efficiency (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NO3-N | NO2-N | NH4-N | Total Nitrogen Removal | NO3-N Removal | ||
| 20 ± 1 | 20 ± 0.5 | 1.5 ± 0.3 | 1.3 ± 0.2 | 0.0 ± 0.1 | 85.6 ± 1.7 | 92.1 ± 1.7 |
| 40 ± 1 | 20 ± 0.5 | 3.8 ± 0.5 | 2.5 ± 0.5 | 0.0 ± 0.0 | 67.1 ± 1.8 | 80.3 ± 2.3 |
| 80 ± 2 | 20 ± 0.5 | 3.6 ± 0.3 | 2.3 ± 0.2 | 0.0 ± 0.0 | 68.4 ± 1.7 | 80.2 ± 2.0 |
| Water Hardness Condition (mg/L as CaCO3) | Influent NO3-N (mg/L) | Effluent (mg/L) | Efficiency (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NO3-N | NO2-N | NH4-N | Total Nitrogen Removal | NO3-N Removal | ||
| 20 ± 1 | 20 ± 0.5 | 1.2 ± 0.1 | 0.3 ± 0.1 | 0.0 ± 0.0 | 92.6 ± 0.8 | 94.1 ± 1.2 |
| 40 ± 1 | 20 ± 0.5 | 1.2 ± 0.4 | 0.1 ± 0.1 | 0.0 ± 0.0 | 93.6 ± 2.3 | 94.0 ± 2.3 |
| 80 ± 2 | 20 ± 0.5 | 0.9 ± 0.3 | 0.0 ± 0.0 | 0.0 ± 0.0 | 95.0 ± 1.4 | 95.3 ± 1.4 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ratananikom, K.; Peungtim, P.; Phuinthiang, P.; Nakaruk, A.; Khanitchaidecha, W. Development of Bio-Electrochemical Reactor for Groundwater Denitrification: Effect of Electric Current and Water Hardness. Sustainability 2022, 14, 9454. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14159454
Ratananikom K, Peungtim P, Phuinthiang P, Nakaruk A, Khanitchaidecha W. Development of Bio-Electrochemical Reactor for Groundwater Denitrification: Effect of Electric Current and Water Hardness. Sustainability. 2022; 14(15):9454. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14159454
Chicago/Turabian StyleRatananikom, Khakhanang, Prarunchaya Peungtim, Patcharaporn Phuinthiang, Auppatham Nakaruk, and Wilawan Khanitchaidecha. 2022. "Development of Bio-Electrochemical Reactor for Groundwater Denitrification: Effect of Electric Current and Water Hardness" Sustainability 14, no. 15: 9454. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14159454
APA StyleRatananikom, K., Peungtim, P., Phuinthiang, P., Nakaruk, A., & Khanitchaidecha, W. (2022). Development of Bio-Electrochemical Reactor for Groundwater Denitrification: Effect of Electric Current and Water Hardness. Sustainability, 14(15), 9454. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14159454





