Abstract
Climate change and urbanization are causing increasingly frequent urban flooding in countries around the world. Various innovative approaches have emerged to address this challenge. In China, the Sponge City was first proposed in 2012 to achieve an urban hydrological balance through natural storage, natural infiltration and natural purification. This article presents a comparative investigation (using a survey method) of new and old communities in Xixian New District and Xi’an in September 2021 to investigate public awareness of the Sponge City and understand levels of satisfaction and acceptance. Individuals of the same age or education residing in the Sponge City generally know more about the Sponge City and were more willing to accept it than those in traditional cities. Moreover, the residents of Sponge City understand the Sponge City concept well, with a majority of the respondents (71.82%) expressing clear understanding on the conception of Sponge City. However, residents in a traditional city exhibited much less understanding of the concept (44.24%). Furthermore, for those living in the same area, people who are younger or have higher education exhibited a clearer understanding of and acceptance of the Sponge City and local government. In this survey, the average scores (assign values to the different responses, then average and percent it) of respondents in Xixian New District with master’s degrees, bachelor’s degrees and high school degrees or below were evaluated at 76.88, 67.94 and 62.15, respectively, compared to 62.07, 50.18 and 50.78 in Xi’an. Lastly, we found that differences in living environment have a significant influence on residents’ perceptions. Residents living in the Sponge City are generally satisfied with the travel and living conditions and greatly support the local government. Meanwhile, this study will help relevant authorities pay more attention to residents’ opinions and help them to formulate policies to spread the concept of Sponge City and encourage residents’ participation.
1. Introduction
Explosive population growth, urbanization, and extreme rainfall are causing urban flooding more frequently, with many countries suffering severe damage [1,2]. Especially in China, critical damage to people’s life and property by urban flooding occurred in a number of cities [2]. For instance, a rare rainstorm in Zhengzhou, Henan province, in July 2021 cost 302 lives and inestimable property losses [3]. A similar incident happened in Xi’an on 24 July 2016 [4]. The risk of urban flooding generated innovative approaches to storm water management [5,6].
First, in 1972, the United States developed BMPs (Best Management Practices). The initial goal was to control non-point source pollution and was gradually extended to water quality and stormwater management [7]. In the 1990s, the WUSD (Water-Sensitive urban Design) [8], NDS (Natural Drainage System) [9], SUDS (Sustainable Urban Drainage System) [10] and LID (Low-Impact Development) [11] concepts were put forward by Australia, Germany, Britain and the United States, respectively. In China, the Sponge City Program (SCP) was proposed in 2012, combined with the current nature-based approaches of constructing urban drainage facilities through natural storage, natural infiltration and natural purification, to simulate natural ecology and optimize the urban environment and urban flood management [12]. Now, numerous sponge facilities and evaluation systems have been proposed and used by researchers. For example, bioretention and permeable pavements were employed in Xi’an and Zhengzhou to effectively reduce the rate of urban flooding [13]. In addition, models such as SWMM [14], BIM [15] and SUSTAIN [10] are wildly used in Sponge City for evaluation and urban flood warning. Various models or technical indicators are commonly used to evaluate the function of sponge facilities, but the actual experience and feelings of residents are generally neglected [15,16]. The perspective of residents should be considered to further promote the development of Sponge City to find the deficiencies in Sponge City planning and awareness development [17,18].
Meanwhile, considering the SCP related to the renewal of old communities and infrastructure, the residents’ participation was also needed to maintain sponge facilities [7,9]. Hence, the building of Sponge City was also affected by the complexity of the residents’ attitudes. However, lacking of residents’ participation and preliminary in-depth investigation may cause some of the residents to oppose the approach, causing potential conflicts in program implementation [7,18]. Consequently, some policy-makers and researchers devoted themselves to improving awareness of Sponge City among residents and tried to explore the feasibility and applicability of encouraging residents to engage in decision-making [19]. For instance, the guidance of “pay attention to raising the public awareness in the importance of Sponge City construction, encourage residents participate in city construction” was put forward by the provincial government of Jiangsu and Zhejiang [20,21]. In addition, the mode of “residents’ participation” was considered to apply in the sponge-style renewal of old communities in several pilot cities [22].
Today, great progress has been achieved in building Sponge City [23]. However, the study of Sponge City has focused on t storm water management and urban flood reduction in the long term [24,25]. There is little research concentrating on the subjective assessment of the effects of and changes made by Sponge City from the perspective of the residents [26,27]. In previous studies, investigation of satisfaction among residents for specific sponge measures and facilities was conducted by several researchers, such as the citizens’ preferences and attitudes towards urban waterfront spaces in Hangzhou and the residents’ satisfaction with sponge-style renewal of an old community in Zhenjiang [7,15]. However, the social effect of building Sponge City has been neglected [28]. Few studies compare the satisfaction among residents between Sponge City and traditional communities [29]. Therefore, more practices are needed to assess the performance of Sponge City and evaluate their social impact by investigating the satisfaction of residents [27,29].
Therefore, it is essential to understand the residents’ awareness perspective, and know the real feelings and attitudes related to the implementation of sponge infrastructure for promoting the building of Sponge City [30,31,32]. To understand the clear changes of citizens’ awareness under the different living environment, we chose the adjacent Xixian New District and Xi’an for the comparison of Sponge City to a traditional city. This choice was intended to reduce the biases related to climate, culture or economic differences. Moreover, Xi’an is much older than the Xixian New District, providing a significant contrast. Three objectives were included to compare Sponge City to a traditional city: (1) the demographic and individual characters of respondents in different communities; (2) the realization of the residents’ attitude and perception towards Sponge City and local government; and (3) the practical social significance during Sponge City’s construction. Field investigation and observation in two communities located in Xi’an and Xixian New District revealed differences among residents with various of ages and educational backgrounds. The study presented here contributes to the field of urban planning and flood control – by assessing perspectives of affected community members and developing technical guidance to improve urban planning in the future.
2. Research Area and Methods
2.1. Situation of the Case Study Area
This study was conducted in Xi’an city and Xixian New District, both located in the north of the Qinlin mountains, referred to as the Guanzhong plain, belonging to the sub-humid climate of China [33]. This area is affected by the warm southeast monsoon in summer and the cold continental monsoon in winter, causing seasonal variability in precipitation [34,35]. The annual average precipitation in this area is about 740 mm, but nearly 43% of it is concentrated in summer, with frequent high-intensity rainstorms [36,37]. The area of the Guanzhong plain accounts for 26.94% of the area of Shaanxi province, but the population and GDP of Guanzhong plain account for 63.35% and 62.35% of population and GDP of Shaanxi province respectively [38]. Population density and urbanization are much higher than in other parts of Shaanxi province, creating greater risk of urban flooding [39,40]. Most residents now have direct experience with extremely climate and the evaluation of the function of an urban drainage system actually exists in their own minds.
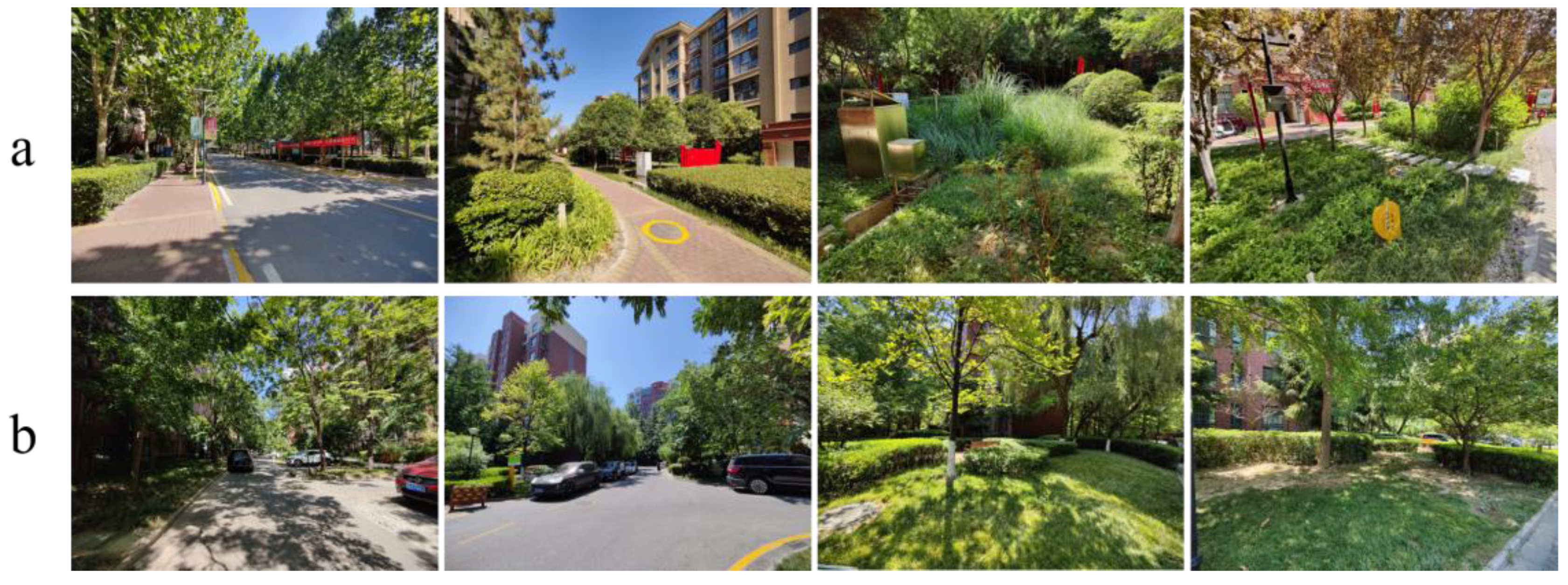
The respondents of Xi’an were from Baihualinjian, with the traditional design, and others were from Tongdejiayuan, with a sponge style design (Figure 1). At the end of 2020, the permanent population of Xi’an was 13.16 million living in an area of 10,108 square kilometers, with 15.65% being 0–14 years old, 68.33% being 15–59 years old and 16.02% being over 60 years old [41]. As the capital of Shaanxi province, the whole designation and construction of Xi’an began earlier than Xixian New District. However, measures were not properly used to reduce the risk of urban flooding in early design philosophy [42,43]. As Figure 2b shows, the greening rate is fair, but there are no sponge facilities such as permeable pavements or bioretention. In addition, the design flow of rainwater cannot meet the daily increased requirement for extreme rainfall conditions [44,45]. For instance, an extreme rainstorm occurred in Xi’an in 2016, causing traffic tie-ups and severe property damage.
Figure 1.
The location of study area in Xi’an and Xixian New District, China.

Figure 2.
Environment comparation of Tongdejiayuan (a) and Baihualinjian (b).
Xixian New District, close to Xi’an, has 1.3 million permanent residents living in an area less than one-third of Xi’an’s: 882 square kilometers. Similarly, 18.29% of residents were aged 0–14 years, 69.50% were aged 15–59 years and 12.21% were aged over 60 years in Xixian New District [46]. In 2014, urban flood policies and regulations were released by the local government to reduce the risk of urban flooding [44]. Numerous sponge facilities based on low-impact development (LID) concepts, such as bioretention, permeable pavements and roof gardens, were widely applied, as shown in Figure 2a [47]. Furthermore, the green belt in Qinhuang and Tongyi street were built as bioretention facilities to intercept the runoff and roof gardens were built to purify and reuse the rainwater. Meanwhile, a series of measures were implemented to provide education about Sponge City, such as widespread billboards.
2.2. Methods
A field investigation and survey were used to understand residents’ awareness of Sponge City and feelings of living in different areas. Questions explored the local situation, including green rate, drainage and application of sponge facilities. The detailed study design is described below.
2.2.1. Questionnaire Design
Residents of Baihualinjian and Tongdejiayuan were chosen as the respondents to ensure that most interviewees were permanent residents. There were 120 questionnaires distributed in each city, of which 104 and 110 were returned, respectively. Four survey sections are described below:
The first section focused on basic information about respondents, including gender, age, education and occupation, in order to understand the differences in demographic characteristics between the two areas. This was used to prepare for the following analysis of awareness among different resident groups. The second section was designed to investigate the level of public awareness of Sponge City and specific facilities, including the permeable pavement, bioretention and rainwater gardens. This component aimed to know the differences in awareness to Sponge City between residents living in Xi’an and Xixian New District. The third section concentrated on the feelings of the residents in different communities, and there were four specific questions set to reflect the distinction: the frequency of urban flood, satisfaction with the green rate, sense of living comfort and convenience of travel in rainy days. The aim was to understand the effects of Sponge City construction on the improvement in residents’ life and trips through a comparison. Lastly, we focused on the respondents’ attitudes towards local government. The questions were designed to understand the satisfaction of citizens with government support and policies in order to know the social function of Sponge City’s construction and prepare for in-depth exploration of residents’ participation.
The survey was conducted in September 2021 (Table 1) to ensure the respondents had just experienced the wet-season and that most of the vegetation in both areas was still flourishing. In addition, a weekend evening was selected, when there was a large flow of people, to carry out random surveys at the gate of the community, and we numbered all of the questionnaires and make sure that there are no repeated responses by people.

Table 1.
Composition of Questionnaire Survey.
2.2.2. Statistical Model Design
In previous studies, index evaluation was usually used to explore the relationships of respondents’ activities and awareness, which was most important to determine indications and assign values [46]. Many scholars will take the method of assigning values and averaging them when analyzing such problems. However, confusion would be caused by a general mean score analysis due to the differences in the answer gradients in this survey. Hence, a dimensionless index was developed to serve as a uniform metric:
In the above Equation (1), is the evaluation value representing the level of satisfaction and awareness. Moreover, is the total number of samples for the index, means the different assign value and means the specific number of .
In addition, we used one-way ANOVA to measure the differences among residents in the survey. Analysis of variance is used to test whether the mean of multiple normal populations is equal and then judge whether the influence of various factors on the tested index is significant. The characteristics of social groups generally follow a normal distribution, and when the number of subsamples is greater than 50, it can be considered as representative of the test [48,49]. One-way ANOVA is used to measure whether different levels of a control variable have a significant effect on the observed variable. In mathematics, the magnitude of this difference is denoted by F:
In the above Equation (2), is the number of groups, and n is the number of total samples. and represent the sum of squared deviations between groups and within the group, respectively, and can be calculated as follows:
Presented in Equation (3), and represent the number and average of samples of group i (i = 1,2…r), respectively, and is the total average of all samples. For Equation (4), is equal to (i = 1,2…r), and is the specific value of sample j (j = 1,2…n_i) of group i.
When the confidence level is at 95%, if F > F0.05 (r − 1, n − r), a significant difference can be seen, and if F > F0.01 (r − 1, n − r), that can be seen as an extremely significant difference.
3. Results
3.1. Basic Information of Respondents
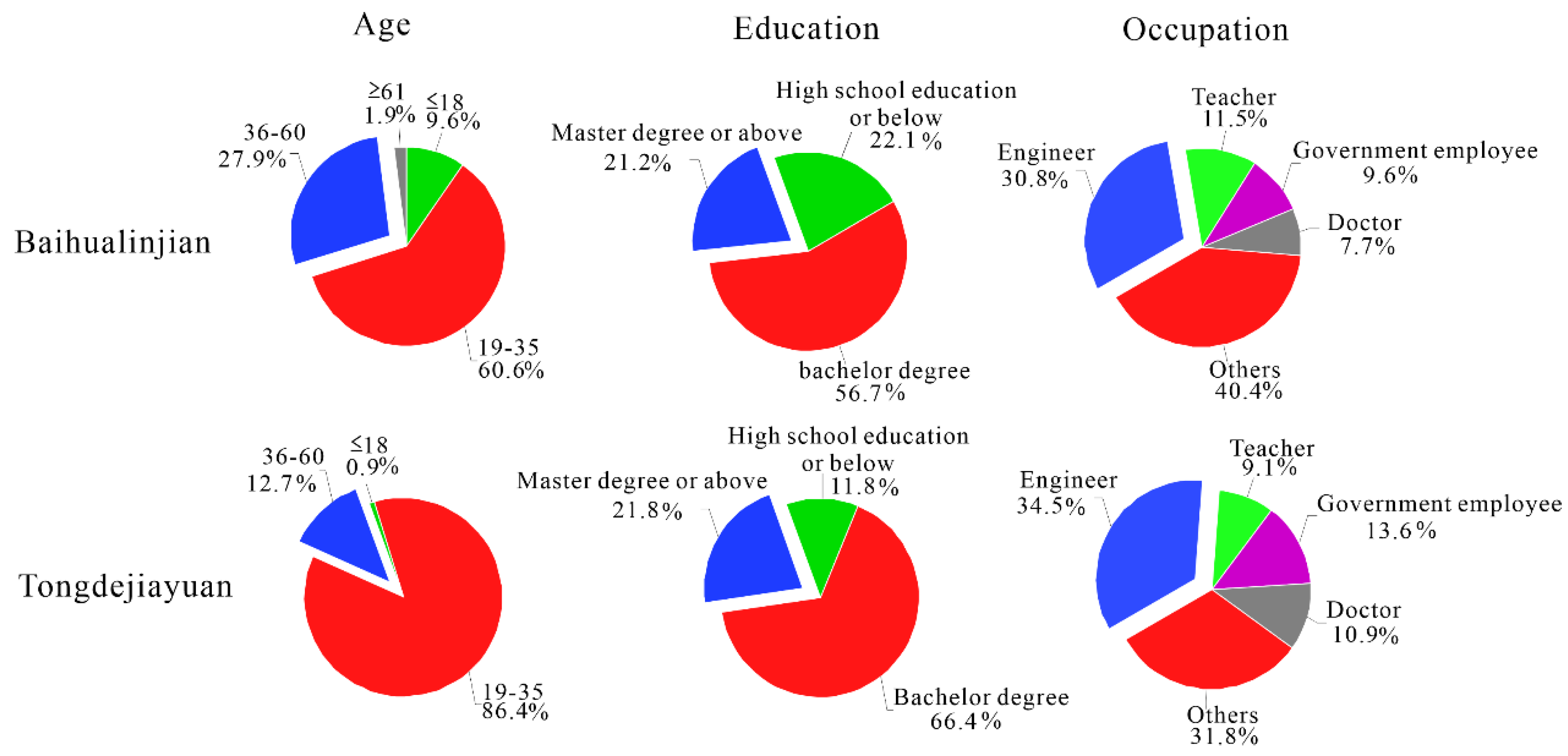
The numbers of male and female respondents in Baihualinjian were 50 and 54, respectively, followed by 50 and 60 in Tongdejiayuan, with no obvious stratification in the gender. In this research, the respondents’ basic information for the two communities was divided into three different parts, shown in Figure 3, with which the investigation of the residents’ characteristics of age, educational background and occupation informed the next analysis.
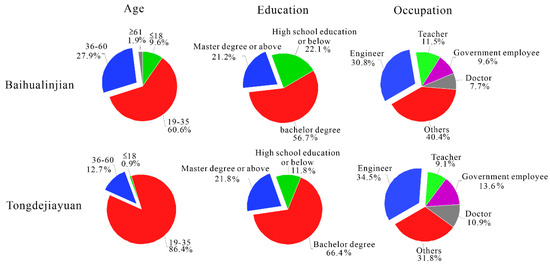
Figure 3.
The individual characteristics in Baihualinjian and Tongdejiayuan.
Four age cohorts were established ≤18, 19–35, 36–60 and ≥61. The proportion of the age group 18 and 61 were 9.6% and 1.9% in Baihualinjian, followed by 0.9% and 0% in Tongdejiayuan, illustrating few very young and very old respondents. The age groups of 19–35 and 36–60 made up 60.6% and 27.9% of the respondents in Baihualinjian, but the proportion of these age groups reached 86.4% and 12.7%, respectively, in Tongdejiauan. By comparing the proportions of different ages, we concluded that the residents of Baihualinjian were younger overall, especially in the age group of 19–35.
In terms of the educational background, people with a bachelor’s degree were predominant in both research areas, but the proportion of Tongdejiayuan was also higher than Baihualinjian, achieving 66.4%. As for the respondents who have a master’s degree or above, nearly equal data were recorded in the two target areas (Baihualinjian, 21.2%; Tongdejiayuan, 21.8%), meaning that the proportion of the residents in Tongdejiayuan with just a high school education was lower than the others. In conclusion, the educational background of Tongdejiayuan in Sponge City was higher than the traditional community. As Figure 3 shows, the proportions of engineers, government employees or doctors in Tongdejiayuan were all beyond those in Baihualinjian; only the number of teachers in Tongdejiayuan was slightly lower than Baihualinjian by 2.4%.
Overall, the total quality of age, educational background and occupation of the residents in Sponge City was higher than the traditional city.
3.2. The Awareness Level of Respondents for Sponge City
Policy implementation is complicated and can be improved by an understanding of citizen perspectives – indeed, feedback from citizens can influence policy and improve project quality awareness [47]. Therefore, it was essential to investigate the awareness level among citizens towards the concept of the Sponge City.
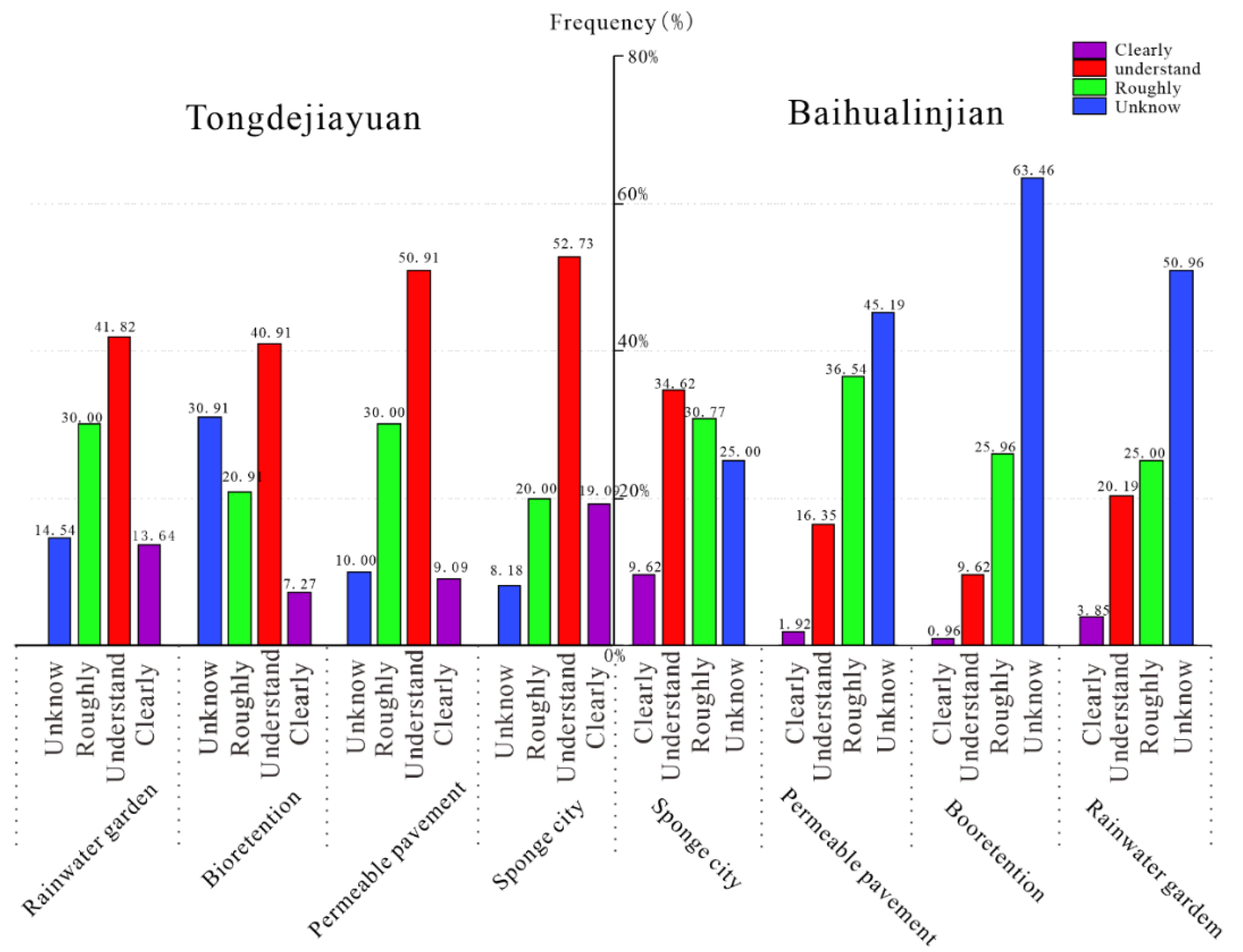
Figure 4 illustrates the distinctions of awareness in typical sponge constructions among residents in both communities. Respondents who expressed “unknown” for survey contents made up the majority in Baihualinjian, while the people of Tongdejiayuan dominantly responded with “understand”. Among Sponge City dwellers, we found that there was still a significant portion of the public that knew about Sponge City and some of the infrastructure, but it is extremely low in Xi’an.
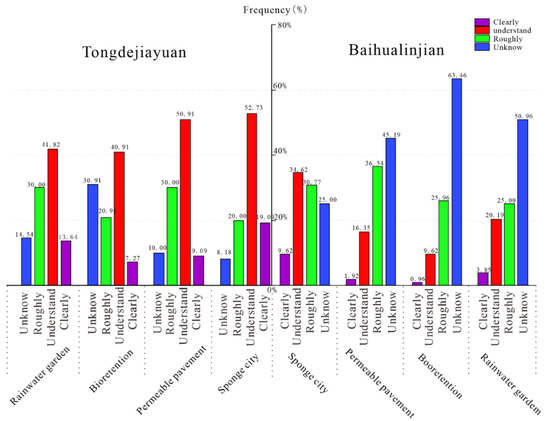
Figure 4.
Respondents’ awareness of Sponge City and types of constructions.
The mean values for the awareness towards Sponge City among the respondents in Tongdejiayuan and Baihualinjian overall were 63.81 and 45.56, respectively, as shown in Table 2; the residents of Sponge City obtained a grade over one-third higher than the residents of the traditional city. Specifically shown in Figure 4, the awareness level of the concept of “Sponge City” among Tongdejiayuan residents reached a peak at 70.68, but the peak for Baihualinjian residents was 57.22. This means that the residents of Xixian New District, with sponge style construction, have a broad understanding of the “Sponge City” concept. In terms of the typical sponge infrastructures, values of Tongdejiayuan were permeable pavement (64.77), bioretention (56.14) and rainwater garden (63.64), which, in Baihualinjian, were 43.75, 37.02 and 44.25, respectively. We calculated that the F was 12.45, which was much higher than the F0.05 (1,6) = 5.99 at the confidence level of 95% but a little lower than the F0.01 (1,6) = 13.75 at the confidence level of 99%. Therefore, we conclude that the inhabitants of Tongdejiayuan have a significantly greater understanding of Sponge City than those of Baihualinjian. It is no doubt that the residents living in the traditional city obtained such a result in this investigation, as the sponge facilities or signs are rarely seen in the streets, and the concept of “Sponge City” occasionally mentioned in social media was one of the few methods for residents to encounter them [48]. Consistently, the highest distinction existed in the awareness of bioretention. For the advanced concept of Sponge City, this project set out to reflect the distinction between respondents, and the residents of Sponge City knew more according to this survey.

Table 2.
The mean score and value for awareness level.
Though the distinction in the awareness level of the conception in Sponge City was slight, a huge gap was reflected in the specific projects. For citizens in Xi’an, the official media was the main medium through which they came to know of Sponge City, usually because of the trouble caused by a storm [49,50,51]. Nevertheless, the improvement in urban aesthetic and residents’ transport was enjoyed by people in Xixian New District [52]. Permeable pavement reduced the water-logging in roads, and the bioretention and rainwater gardens regulated the rainwater and improved the urban aesthetics [53,54]. Experience with these projects and commonplace government messaging explain difference in awareness between the two study groups.
3.3. The Investigation of Living Feeling
All of the measures and policies in building Sponge City aim to increase the quality and happiness of the residents’ lives by beautifying the city landscapes, reducing the rate of urban flood and facilitating transportation [53]. Did the wide construction of Sponge City achieve the previous target? How can we really understand the convenience Sponge City provides to normal people? In addition to the evaluation of experts or the reports of governments, the assessment of the residents living in different cities also reflects the changes made by Sponge City [15].
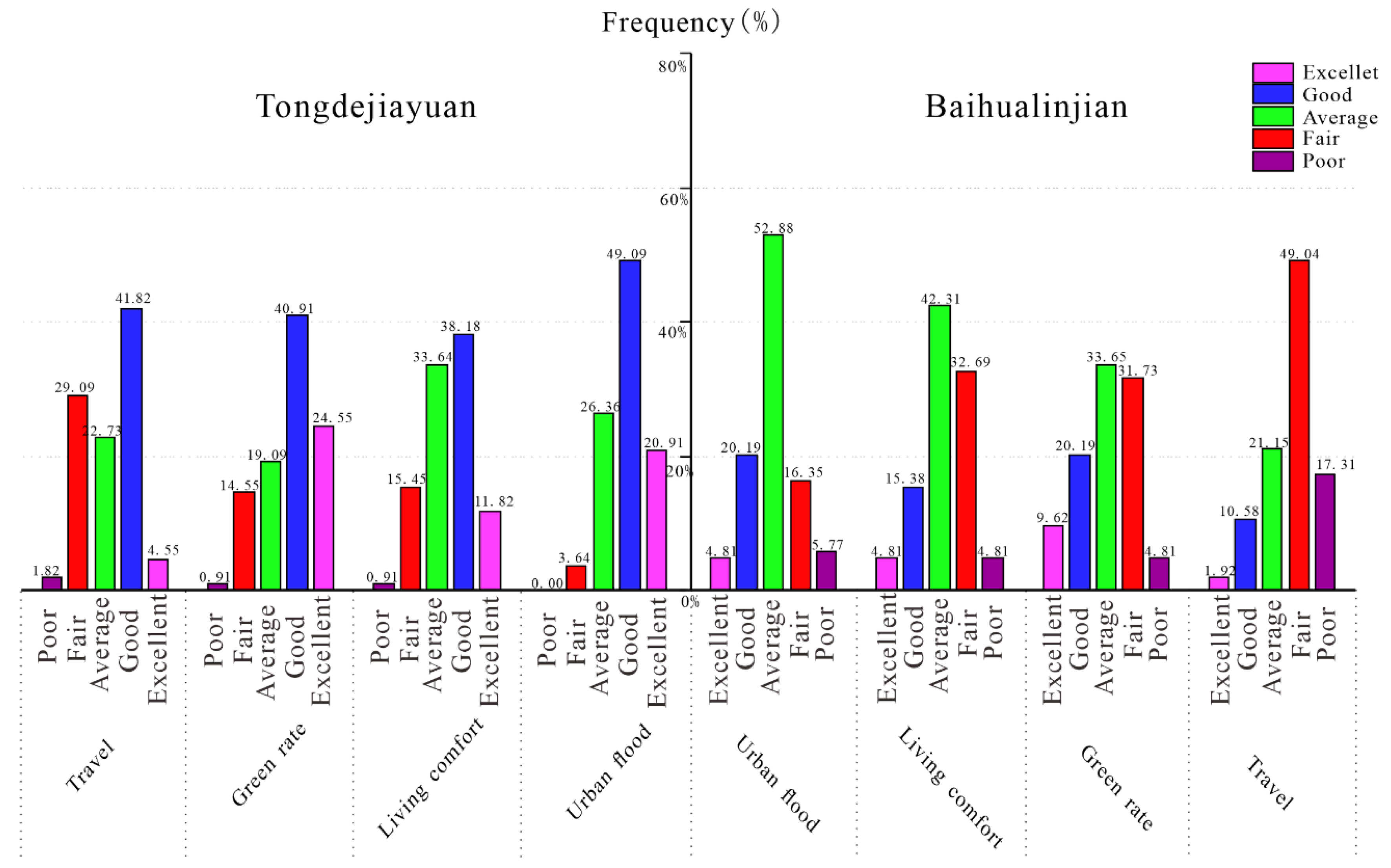
Figure 5 shows the residents’ living feelings in Tongdejiayuan and Baihualinjian. The general evaluation made by most of the respondents in Baihualinjian, and nearly half of the people, gave a “Fair” in “Travel”. Comparably, residents in Tondejiayuan expressed higher satisfaction in all projects and more than a few respondents gave an “excellent” evaluation, which was hardly seen in Baihualinjian.
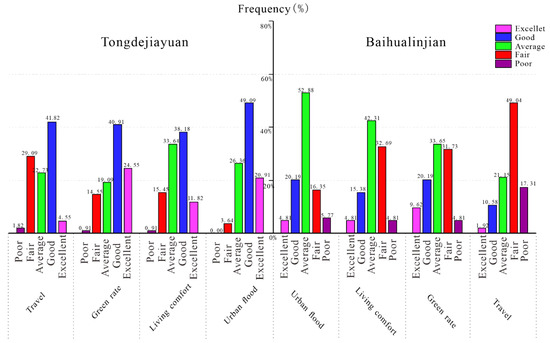
Figure 5.
Residents’ living feeling in Tongdejiayuan and Baihualinjian.
The mean values for the awareness of living feeling of the respondents overall in Xixian New District and Xi’an were 71.2 and 55.7, respectively, followed by the values of 3.56 and 2.79, shown in Table 3. Compared with the data above, the satisfaction of living feeling made great progress. There is no doubt that the value of Tongdejiayuan in urban flood reached its peak at 77.45, but a high value of 60.43 was also achieved in Baihualinjian. The feelings of travel convenience is likely linked with the rate of urban flooding [20]. However, the project “travel” obtains a lowest evaluation of 46.15. Considering the travel conditions varied with numerous factors such as road construction, rush hour or traffic accidents, some of the respondents were asked again about the feeling of daily travel, and most of them expressed that traffic jams frequently occurred in addition to rainy days. Consequently, the living comfort as a comprehensive evaluation index that is influenced by urban floods, green rate and travel, etc., can roughly reflect the satisfaction level of citizens with their home. The values of the satisfaction level of living comfort were 68.91 and 56.54 in Tongdejiayuan and Baihualinjian, respectively. In Figure 5, half of the respondents in Xixian New District gave a positive reply to it, and just 16.36% expressed dissatisfaction, compared to less than one-fifth of the residents in Baihualinjian being satisfied with their living comfort. As for the green rate, the residents of the two areas all gave a proper evaluation, with the lowest gap in all projects. As shown in Figure 5, residents of Xi’an expressed their dissatisfaction in “Travel”, but great progress was made in reducing urban flooding and relieving the traffic by building Sponge City. Similarly, we calculated the F-value to represent the level of difference in living comfort between the two places, which is 11.83: still higher than F0.05 (1,6) = 5.99 but lower than F0.01 (1,6) = 13.75. This means that residents living in sponge cities are more satisfied with their living conditions, a significant difference from Xi’an.

Table 3.
Satisfaction level of respondents for living feeling.
The residents’ attitude and satisfaction with city construction was one of the most important targets in this investigation. In this section, it is demonstrated that building Sponge City greatly contributed to people’s lives, reducing the risk of urban flooding, improving the green rate and improving traffic conditions. Consequently, one of the aims of constructing the pilot Sponge Cites is to observe its influence on society and survey the reflections of the residents [19,22].
3.4. The Investigation of Satisfaction for Government
Planning and decision making are usually modified according to the timely feedback of participants; therefore, it was significant for decision makers to understand the residents’ attitudes and their level of satisfaction towards the government and policies [54]. In addition, trust in government would be enhanced if the building of Sponge City improved people’s lives [19].
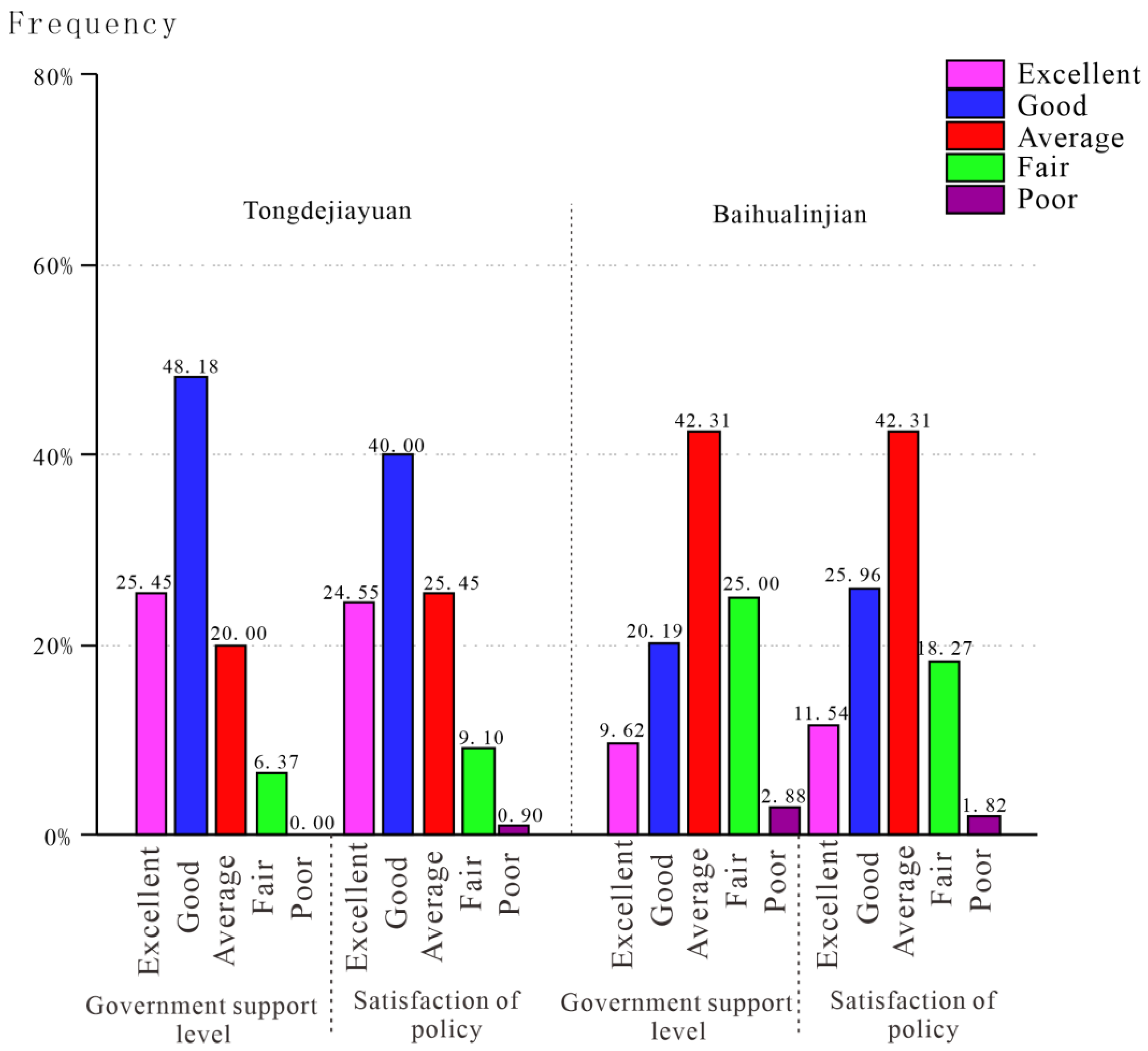
Figure 6 illustrates the respondents’ attitudes to the strengthening of government support in building Sponge City and the effect of policy implementation. In this section, many more residents gave a neutral evaluation. However, obvious differences among respondents could also be found. Nearly three-quarters (73.63%) of respondents in Tongdejiayuan were satisfied with government support, and one-quarter (25.45%) gave the response “Excellent”. As for Baihualinjian, the positive evaluation of respondents of government support was less than half of the proportion of Tongdejiayuan (9.62%—Excellent; 20.19%—Good), and “Good” was the dominant response in Tongdejiayuan, while another area was “Average”. What is more, the satisfaction level with policy was slightly higher than government support in Baihualinjian, with an opposite consequence in Tongdejiayuan, as shown in Figure 6. The mean Y values of satisfaction with government were 77.09 and 63.55 in Tongdejiayuan and Baihualinjian, respectively, shown by Table 4. In addition, the residents of Tongdejiayuan were much more satisfied with the government or its policies than those of Baihualinjian. The F-value of this part is 33.86, which is much higher than the F0.05 (1,3) = 10.13 but a little lower than the F0.01 (1,3) = 34.12. So, we can consider that residents from Tongdejiayuan expressed significant confidence in and support of the government and relevant polices compared with Xi’an.
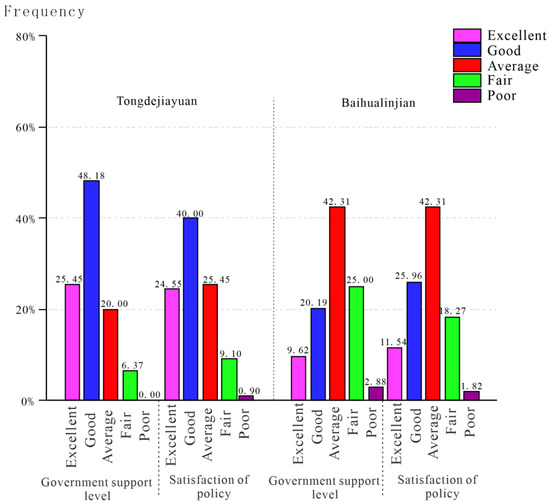
Figure 6.
Evaluation of respondents for government and policies.

Table 4.
Satisfaction level of respondents for government.
At present, the residents of Xi’an seldom have the opportunity to enjoy the convenience provided by Sponge City. In most of their perceptions, the construction of Sponge City has remained in the planning process [48]. Therefore, the low satisfaction with government support and policy expressed by the respondents was to be expected. Comparatively, because of the benefit of the extensive advertisement to residents and the obvious improvements in city aesthetics and quality of life, especially in terms of travel experience on rainy days, the respondents of Xixian New District showed much higher satisfaction with their government in this section.
4. Analysis of Demographics and Sociology
The sections above describe the evaluation for respondents’ conceptions, awareness of Sponge City and satisfaction level with living comfort and government. However, how were respondents with different ages or education backgrounds shown in this investigation? How did the respondents with the same characteristics above but living in different cities evaluate their homes? This will be discussed next.
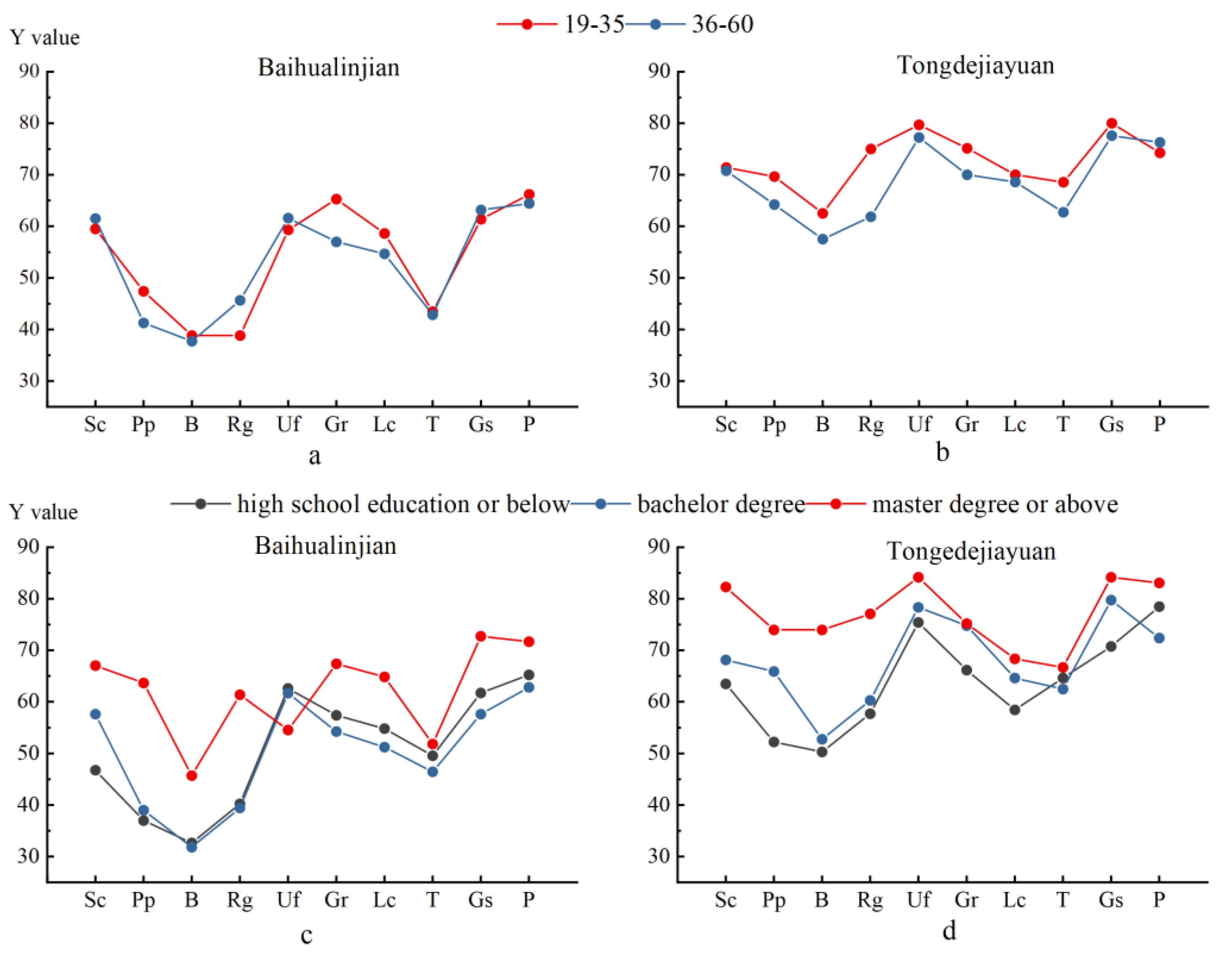
Figure 7 shows the distinctions in the assessments among respondents in different areas and groups towards their cities (the X axis: Sc—Sponge City; Pp—Permeable pavement; B—Bioretention; Rg—Rainwater garden; Uf—Urban flood; Gr—Green rate; Lc—Living comfort; T—Travel; Gs—Government support; P—policy; the Y axis represents the value of ). Four figures, a–d, were established to illustrate the comparative assessment of respondents with different ages and educational backgrounds from Baihualinjian and Tongdejiayuan. Moreover, we calculated the average, Pearson’s r and the F-value to more carefully explain the existing phenomenon. Pearson’s r indicates the similarity level of the trends, and the F-value indicates the significance of the difference.
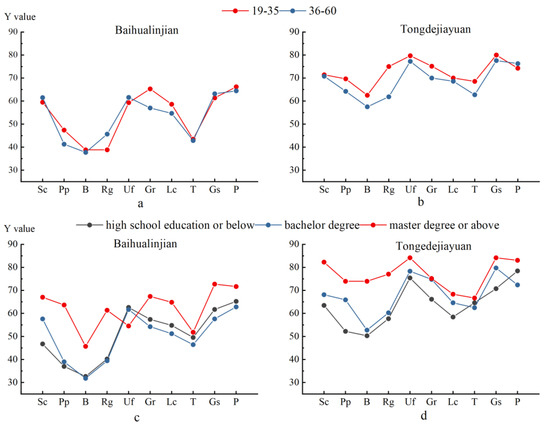
Figure 7.
The assessment in investigation among different respondents.
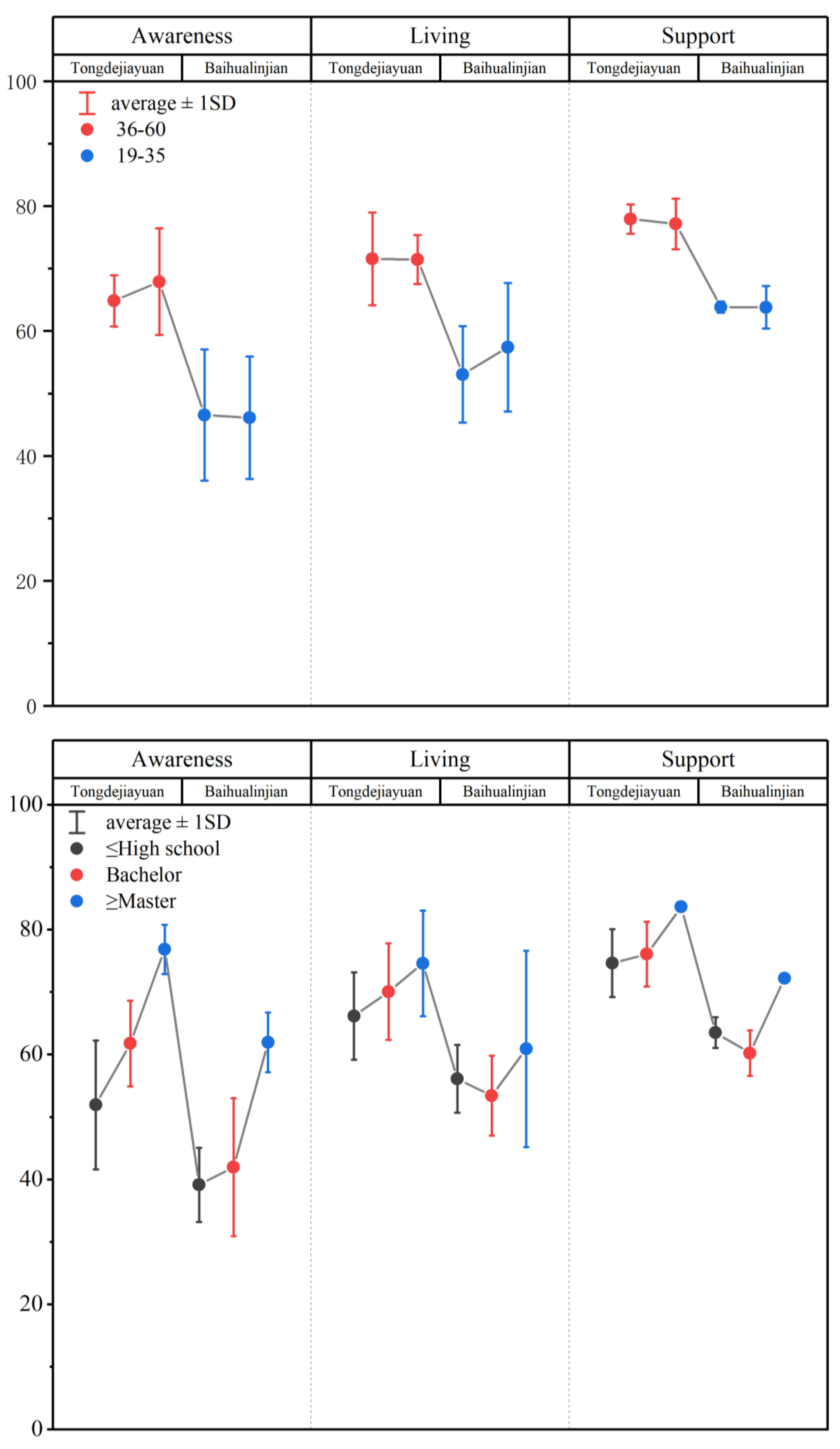
First, in Figure 8, we can easily observe that the average value of each aged group of Baihualinjian (53.87 for younger and 52.99 for older) were greatly lower than Tongdejiayuan (72.63 for younger and 68.68 for older). Then, in Figure 8, we found that the average value of residents living in Tongdejiayuan with master’s, bachelor’s or high school degrees were 76.88, 62.15 and 68.68, respectively, while in Baihualinjian these values were 62.07, 50.18 and 50.78, respectively.
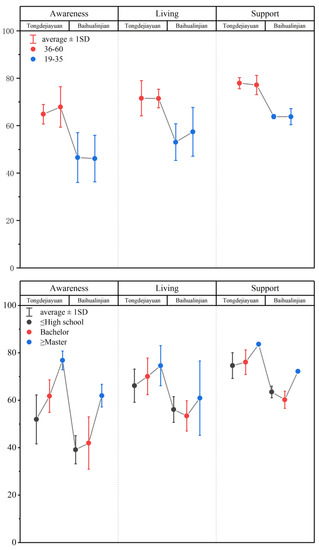
Figure 8.
Comparing evaluation of ages and educational backgrounds.
In comparing the residents with different ages or educational backgrounds who live in the same area, we found the performance was more similar across age groups in Xi’an, with the better curve-fitting degree in Figure 7, and Pearson’s r was 0.91 compared with 0.81 in Xixian New District. Furthermore, at the 95% confidence level, there were no significant differences in the evaluations of different age groups in either Baihualinjian or Tongdejiayuan, FBaihualinjian = 0.036 < FTongdejiayuan = 2.01 < F0.05 (1,18) = 4.41.
For residents in Baihualinjian with different educational backgrounds, the fitting degrees of residents with master’s educations and with bachelor’s or high school degrees were similar; the Pearson’s r were 0.54 and 0.60, respectively, and both of them were much lower than the 0.92 of those with high school education and bachelor’s degrees. The difference between the residents with graduate degrees and those with bachelor’s or high school degrees was significant, Fmaster/bachelor = 7.42 > Fmaster/high school degree = 6.10 > F0.05 (1,18) = 4.41. However, there is no significant difference between the people with high school education and those with bachelor’s degrees, Fbachelor/high school degree = 0.15.
Similarly, the curve fitting between the postgraduate education group and other groups was also worse in Tongdejiayuan: the Pearson’s r was 0.61 and 0.64, respectively, as shown in Table 5. A better fitting degree was shown in the groups with bachelor’s degrees and high school degrees or below, for which the Pearson’s r was 0.80. The significant difference was shown in residents with master’s degrees and others, and even an extreme difference occurred in the master’s degrees and high school degrees or below groups, Fmaster/high school degree = 13.42 > F0.01 (1,18) = 8.29 > Fmaster/bachelor = 7.06 > F0.05 (1,18) = 4.41. However, there was no significant difference between those with bachelor’s degrees and high school degrees or below, Fbachelor/high school degree = 1.10 < F0.05 (1,18) = 4.41.

Table 5.
Comparison of different ages and educations in Baihualinjian and Tongdejiayuan.
Based on the data above, the young people in both areas have shown a better awareness and support level towards Sponge City than older people. In addition, with the improvement in education level, residents have a better understanding of Sponge City and exhibit greater government satisfaction. However, on the whole, the difference in scores of residents with different education levels was significantly larger than that between different ages, and the performance of residents with master’s education was most prominent.
Then, we compared the differences among people with the same ages or educational backgrounds but living in different types of cities in this survey. It is found that the higher the education level and the younger the age, the worse the curves fit and the more significant the differences were. In Table 6, the Pearson’s r(19–35) = 0.59 < Pearson’s r(36–60) = 0.94, while F19–35 = 24.68 > F36–60 = 16.17 > F0.01 (1,18) = 8.29. This indicates that the changes in the evaluation of various indicators in this survey were more similar among the older residents, but there was a much more significant difference in the younger group of residents between the two places. Continuously, Pearson’s rhigh school degree = 0.92 > Pearson’s rbachelor = 0.86 > Pearson’s rmaster = 0.44, while FMaster degree = 18.46 > Fbachelor = 17.06 > F0.01 (1,18) = 8.29 > Fhigh school degree = 7.71 > F0.05 (1,18) = 4.41. This means that residents with graduate degrees in Sponge City and the traditional city have extremely significant differences in the performance of the survey and have different trends in the evaluation of various indicators.

Table 6.
Comparison of residents with similar ages or educations in different areas.
In summary, the higher evaluation for Sponge City appeared in those who were younger and with better educational backgrounds. However, among the residents with the same ages and educational backgrounds, those from Sponge City performed better. What is worth noting is that the differences in region are much larger than those in age or educational background. Therefore, based on the results of this survey, we can conclude that the construction of Sponge City has greatly improved residents’ awareness, quality of life and support for the local government.
5. Discussion
A social field investigation and index evaluation were used to compare the differences in awareness and satisfaction among residents living in Sponge City or a traditional city. The empirical results suggest that residents living in Sponge City were more aware of and more satisfied with the urban construction and policies. In the analysis of groups with different ages and educational backgrounds, we found that the proportion of residents with better education or who were younger was much higher in Sponge City than the traditional city. Meanwhile, the younger and more well-educated people exhibited better understanding of Sponge City. Thus, we conclude that a stronger a preference for Sponge City building is demonstrated from the perspective of demographic and social characteristics.
In addition, this study was expected to fill the deficiency in investigating residents’ awareness and feelings in Sponge City construction, which is a long-term, incremental, and explorative process. Making full use of the media to disseminate the concept of Sponge City and creating relevant lessons to educate people would be helpful. Moreover, the survey results suggest several policy measures to ensure that the perspectives of residents are known by decision makers. For instance, some polices could be released to establish a definite and supervised feedback system between the government and residents to coordinate interests and ensure the equal power of all parties in the process of participation. Thus, policies could be designed more precisely and in a timely manner. Consequently, the government should pay attention to improving the level of awareness and acceptance of Sponge City among residents, especially in traditional cities. Encouraging residents to participate in the construction of Sponge City can help to strengthen the relationship between the government and citizens, change the negative attitudes of some people and improve the public’s awareness of Sponge City. Thus, the mode of resident participation in city building could be attempted, and some policy support should be given by the government to encourage residents to engage.
Although the factors that affected the preferences of residents in choosing which community they wanted to live in varied with different aspects, the urban aesthetic, travel convenience on rainy days and urban flood rate cannot be ignored. Based on the survey results, the residents from Xixian New District showed greatly satisfied with their living conditions, due to the travel convenient, highly green rate and the great urban flood management. Therefore, the advantages of Sponge City should be fully used by local governments for making polices to help with employment and urban planning. For instance, a higher subsidy for house purchases towards young and well-educated people would attract those people. For the city itself, young people, especially those with excellent education, are needed for sustainable development. Competitiveness can be continuously enhanced, and the investment in building Sponge City can be returned in other aspects by introducing talents. In addition, the construction of Sponge City will create jobs and attract a large number of related workers such as engineers and building workers, which further promote the development of the city.
Overall, this research is expected to enrich the study of awareness and satisfaction among residents of Sponge City. First, this research can help to examine the outcome of Sponge City and reflect the improving life quality taken by Sponge City from the perspective of residents. Second, this research can inform government to help them understand the satisfaction among residents in different cities and to make targeted measures throughout the process of Sponge City construction. Moreover, this study suggests that it is important to understand the awareness and satisfaction of Sponge City programs among residents using field investigations. There are also a few limitations in this investigation. We were limited by the number and space of the sample, and a deeper analysis of demographic and social characteristics could not be implemented, such as occupational classification. Further research should be more widely and carefully considered in the specific sponge facilities and put emphasis on comparative investigations in different areas.
6. Conclusions
This study enriched the research on the public awareness of Sponge City and directly observed the differences of awareness among residents in two areas. In addition, the difference in awareness and living feelings among residents from sponge cities and traditional cities should be considered, and the government should take measures to reduce this gap. Furthermore, the public awareness of Sponge City was lacking according this survey’s results, so some measures should be taken to spread the concept in society. We should encourage residents to participate in urban construction and conduct more such surveys in the process of construction to understand the real needs of residents and obtain the feedback from residents on the outcome of construction in a timely manner. In the future, the results of this study are expected to be widely applied to support government decision making and examine the effects of urban construction or government policies.
Author Contributions
Formal analysis, W.Y.; Funding acquisition, S.Z. and Z.W.; Methodology, X.Z. and B.H.; Project administration, A.H.; Validation, Y.W. and D.N.; Writing—original draft, Y.Z.; Writing—review & editing, P.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by National Key R&D Program of China (2018YFE0103800); GDAS Special Project of Science and Technology Development (2020GDASYL-20200102013); Guangdong Foundation for Program of Science and Technology Research (2019QN01L682) and Asia-Pacific Network for Global Change Research APN project (CRRP2020-03MY-He).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Written informed consent has been obtained from the participants to publish this paper.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Yabo, L.; Peng, W. Decrease process analysis of urban system resilience based on the extreme flood simulation. In IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Advances in Energy Resources and Environment Engineering (ICAESEE), Chongqing, China, 20–22 November 2020; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, W.; Ma, C.; Xu, H.; Chen, Z.; Zhao, K.; Han, H. A review on applications of urban flood models in flood mitigation strategies. Nat. Hazards 2021, 108, 31–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wah Yu, C.; Cao, S.-J. Urban Development in the Context of Extreme Flooding Events; SAGE Publications: London, UK, 2022; Volume 31, pp. 3–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiani, W. Analysis on the Current Situation and Development Problem of China’s Sponge City Construction–Case Study on Ningbo Yaojiang-Cicheng Pilot Area. Saudi J. Humanit. Soc. Sci. 2017, 2, 572–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, P.; Luo, M.; Li, F.; Qi, X.; Huo, A.; Wang, Z.; He, B.; Takara, K.; Nover, D.; Wang, Y. Urban flood numerical simulation: Research, methods and future perspectives. Environ. Model. Softw. 2022, 156, 105478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aspacher, M.; Alam, B. Stormwater Best Management Practices: Green Infra-structure in Rural Communities. In Smart Village Technology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 309–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrin, S.; Bertrand, K.; Langlois, E. Avoiding the stigma. A qualitative study of socially included women’s experiences of drug use and dealing, health services and the police in France. Int. J. Drug Policy 2021, 87, 102850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.T.; Ngo, H.H.; Guo, W.; Wang, X.C.; Ren, N.; Li, G.; Ding, J.; Liang, H. Implementation of a specific urban water management-Sponge City. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 652, 147–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luan, Q.; Fu, X.; Song, C.; Wang, H.; Liu, J.; Wang, Y. Runoff effect evaluation of LID through SWMM in typical mountainous, low-lying urban areas: A case study in China. Water 2017, 9, 439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, P.; Xu, C.; Kang, S.; Huo, A.; Lyu, J.; Zhou, M.; Nover, D. Heavy metals in water and surface sediments of the Fenghe River Basin, China: Assessment and source analysis. Water Sci. and Tech. 2021, 84, 3072–3090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choo, K.-S.; Kang, D.-H.; Kim, B.-S. Impact assessment of urban flood on traffic disruption using rainfall–depth–vehicle speed relationship. Water 2020, 12, 926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, N.; Wang, Q.; Wang, Q.; Huang, H.; Wang, X. Upgrading to urban water system 3.0 through sponge city construction. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2017, 11, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, F.; Sun, S.; Lei, T. Understanding China’s urban rainstorm waterlogging and its potential governance. Water 2021, 13, 891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, T.; Li, D.; Zhu, S.; Wang, Y. Does sponge-style old community renewal lead to a satisfying life for residents? An investigation in Zhenjiang, China. Habitat Int. 2019, 90, 102004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Dewancker, B.J.; Qi, Q. Citizens’ preferences and attitudes towards urban waterfront spaces: A case study of Qiantang riverside development. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 45787–45801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Cao, Z.; Luo, P.; Zhu, W. Spatiotemporal Variations and Climatological Trends in Precipitation Indices in Shaanxi Province, China. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Cai, J.; Zuo, J.; Bartsch, K.; Huang, M. Conflict or consensus? Stakeholders’ willingness to participate in China’s Sponge City program. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 769, 145250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, L.; Ren, X.; Gu, R.; Che, Y. Implementation of the “sponge city” development plan in China: An evaluation of public willingness to pay for the life-cycle maintenance of its facilities. Cities 2019, 93, 13–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Sun, M.; Song, B. Public perceptions of and willingness to pay for sponge city initiatives in China. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2017, 122, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhou, W. Impact of the Chinese Sponge City and underground utility tunnel construction on the infrastructure development in developing countries. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Construction and Real Estate Management 2017, Guangzhou, China, 10–12 November 2017; pp. 288–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, P.; Mu, Y.; Wang, S.; Zhu, W.; Mishra, B.K.; Huo, A.; Zhou, M.; Lyu, J.; Hu, M.; Duan, W.; et al. Exploring sustainable solutions for the water environment in Chinese and Southeast Asian cities. AMBIO 2021, 51, 1199–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Palazzo, E. Sponge City and social equity: Impact assessment of urban stormwater management in Baicheng City, China. Urban Clim. 2021, 37, 100829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Li, Y.; Ma, M.; Song, T.; Song, R. Storm water management and flood control in sponge city construction of Beijing. Water 2018, 10, 1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, X.-J.; Liao, K.-H.; Randrup, T.B. Sustainable stormwater management: A qualitative case study of the Sponge Cities initiative in China. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2020, 53, 101963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, J.; Fang, X.; Gong, Y.; Wang, W. Case Studies of the Sponge City Program in China. In Proceedings of the World Environmental and Water Resources Congress, West Palm Beach, FL, USA, 22–26 May 2016; pp. 295–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, T.; Li, D.; Wang, Y. Assessment and Determinants of Residential Satisfaction with Sponge-Style Old Community Renewal: A Case Study in Zhenjiang, China, International Low Impact Development Conference 2018: Getting in Tune with Green Infrastructure, Nashville, TN, USA, 12–15 August 2018; American Society of Civil Engineers: Reston, VA, USA, 2018; pp. 51–63. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, H.S.; Su, Q. Research on constructing sponge city indicator and decision evaluation model with fuzzy multiple criteriamethod. Water Environ. Res. 2020, 92, 1910–1921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Ding, L.; Ren, M.; Li, C.; Wang, H. Sponge city construction in China: A survey of the challenges and opportunities. Water 2017, 9, 594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.; Li, K.; Engel, B.A.; Jia, H.; Leng, L.; Sun, Z.; Shaw, L.Y. Optimal adaptation pathway for sustainable low impact development planning under deep uncertainty of climate change: A greedy strategy. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 248, 109280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.; Zhao, G.; Yu, C.; Wu, Y.J. Smart city development and residents’ well-being. Sustainability 2019, 11, 676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Z. Communication of Tacit Knowledge in Integrated Urban Water Management: The Structural, Cognitive, and Relational Dimensions in China’s Sponge City Programme; University College London: London, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, Y.-J.; Lin, S.-Y. A study on the Relationships of place attachment and individual attributes of residents in different vulnerable districts in Taipei, Taiwan. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 46247–46265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, J.; Cai, H.; He, J.; Wang, H. Performance evaluation of CERES-Wheat model in guanzhong plain of Northwest China. Agric. Water Manag. 2014, 144, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Hoogenboom, G.; Cai, H.; Wang, Z. Winter wheat production on the Guanzhong Plain of Northwest China under projected future climate with SimCLIM. Agric. Water Manag. 2020, 239, 106233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, P.; Liu, L.; Wang, S.; Ren, B.; He, B.; Nover, D. Influence assessment of new Inner Tube Porous Brick with absorbent concrete on urban floods control. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2022, 17, e01236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ounissi, M.; Laskri, H.; Ziouch, O.R.; Justić, D. Riverine and wet atmospheric nutrient inputs to the Southwestern Mediterranean region of North Africa. Mar. Chem. 2021, 228, 103915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.; Wu, J.; Wang, Y.; Elumalai, V.; Subramani, T. Seasonal variation of drinking water quality and human health risk assessment in Hancheng City of Guanzhong Plain, China. Expo. Health 2020, 12, 469–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Su, P.; Lin, Q.; Song, J.; Sun, H.; Cheng, D.; Wang, S.; Peng, J.; Fu, J. Distribution, assessment and coupling relationship of heavy metals and macroinvertebrates in sediments of the Weihe River Basin. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2019, 50, 101665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douglas, I.; Alam, K.; Maghenda, M.; Mcdonnell, Y.; McLean, L.; Campbell, J. Unjust waters: Climate change, flooding and the urban poor in Africa. Environ. Urban. 2008, 20, 187–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, B.; Luo, Z.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, T.; Yang, L. Using Local Climate Zones to investigate Spatio-temporal evolution of thermal environment at the urban regional level: A case study in Xi’an, China. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2022, 76, 103495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coughlin, J.F. Balancing Mobility and Environmental Quality: The Politics of Regional Transportation Infrastructure Investment Planning in the Metropolitan United States; Boston University: Boston, MA, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Maksimovic, C.; Prodanovic, D. Modelling of urban flooding—breakthrough or recycling of outdated concepts. In Proceedings of the Specialty Symposium on Urban Drainage Modeling at the World Water and Environmental Resources Congress 2001, Orlando, FL, USA, 20–24 May 2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnbjerg-Nielsen, K.; Willems, P.; Olsson, J.; Beecham, S.; Pathirana, A.; Bülow Gregersen, I.; Madsen, H.; Nguyen, V.-T.-V. Impacts of climate change on rainfall extremes and urban drainage systems: A review. Water Sci. Technol. 2013, 68, 16–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, C.; Liu, J.; Shao, W.; Mei, C.; Zhou, J. Sponge city construction in China: Policy and implementation experiences. Water Policy 2019, 21, 19–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Hou, J.; Miller, D.; Brown, I.; Jiang, Y. Flood risk management in sponge cities: The role of integrated simulation and 3D visualization. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2019, 39, 101139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powell, R.B.; Ham, S.H. Can ecotourism interpretation really lead to pro-conservation knowledge, attitudes and behaviour? Evidence from the Galapagos Islands. J. Sustain. Tour. 2008, 16, 467–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biber, D. Representativeness in corpus design. Lit. Linguist. Comput. 1993, 8, 243–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, C.; Báscolo, E. Use of research results in policy decision-making, formulation, and implementation: A review of the literature. Cad. Saúde Pública 2006, 22, S7–S19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, B.-J.; Zhu, J.; Zhao, D.-X.; Gou, Z.-H.; Qi, J.-D.; Wang, J. Co-benefits approach: Opportunities for implementing sponge city and urban heat island mitigation. Land Use Policy 2019, 86, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Yu, C.W.; Zhou, D.; Gu, Z. Challenges and Adaptation to Urban Climate Change in China: A Viewpoint of Urban Climate and Urban Planning; SAGE Publications Sage: London, UK, 2019; Volume 28, pp. 1157–1161. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, N.-B.; Lu, J.-W.; Chui, T.F.M.; Hartshorn, N. Global policy analysis of low impact development for stormwater management in urban regions. Land Use Policy 2018, 70, 368–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, Y.; Yang, L.; Wang, X.; Wang, X.; Zhou, Y. Research on distribution characteristics, influencing factors, and maintenance effects of heavy metal accumulation in bioretention systems: Critical review. J. Sustain. Water Built Environ. 2021, 7, 03120001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Fryd, O.; Zhang, S. Blue-green infrastructure for sustainable urban stormwater management—Lessons from six municipality-led pilot projects in Beijing and Copenhagen. Water 2019, 11, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearce, L. Disaster management and community planning, and public participation: How to achieve sustainable hazard mitigation. Nat. Hazards 2003, 28, 211–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).