Abstract
Sharks occupy an important ecological niche in marine ecosystems. As top predators, they can restrict and control the behavior, numbers and composition of other species through downward effects, and play an essential role in ecosystem stability. Shark fishery data are limited, and for most Chondrichthyes species there is no formal fishery resource assessment at a global level. In this study, we applied the length-based Bayesian biomass (LBB) estimation method to assess the stock status of four common shark bycatch species of which more than 100 samples were collected in coastal waters of the northern South China Sea. Estimates of the length of 50% of individuals captured by gear/the length at first capture that maximized the catch and biomass (Lc/Lc_opt) of a species ranged from 0.49 to 1.4; the draughtsboard shark Cephaloscyllium sarawakensis had the highest value, and the shortnose dogfish Squalus brevirostris had the lowest. Estimates of the collected biomass/biomass of the maximum sustainable yield (B/BMSY) ranged from 0.86 to 1.9. Both C. sarawakensis and the spadenose shark Scoliodon laticaudus were fully exploited, while the spatulasnout catshark Apristurus platyrhynchus and S. brevirostris were in good condition. To verify the stability of the LBB, length frequency data for the most common species S. laticaudus were divided into different size-class intervals; simulations revealed estimated parameters based on these to be insensitive to differences in intervals, except for the smallest (10 mm), which did not affect evaluation results. These results can be used to provide a scientific basis on which shark fisheries in this region can be managed and prior parameters for related resource assessment methods can be determined.
1. Introduction
Sharks occupy an important ecological position, and play an essential role in marine ecosystems. As top predators, they can restrict and control the behavior, abundance, and composition of other species through top-down effects [1,2]. In most marine ecosystems, a decrease in the number of sharks leads to changes in the structure and function of food webs through trophic cascades [3,4,5].
As important marine biological resources, sharks are worth at least USD 1.5 billion annually in fisheries, trade, and tourism [6]. However, high fishing mortality caused by overfishing and the conservative life history characteristics of these animals render many species vulnerable [7,8,9,10,11]. The growing demand for shark-derived commodities (e.g., shark fins, meat, cartilage, liver oil) is the main reason why sharks are subjected to such intense fishing pressure [12,13]. For example, the demand for shark fins in Asian markets has led to the mass killing of sharks [12], increasing shark fin imports more than 214% from 2648 mt in 1985 to 8323 mt in 1998. Similarly, shark fin imports in Thailand increased 42% from 97 to 138 mt. Based on weight, the total estimated number of sharks killed in 2000 was about 100 million, and in 2010 about 97 million, with global estimates ranging from 63 to 273 million sharks annually [11].
Sharks killed for their fins (for which the body is discarded) distort catch data, exacerbating management problems. Distorted production data can cause erroneous assessments of fishing mortality and stock status [13,14], leading to the ill-informed expansion of current global shark fisheries; this is mainly due to serious bycatch and the lack of publicity for shark protection policies. Because of limited and chaotic management policies [11,15,16], a lack of economic incentives, and limited data, current shark fishery management is inadequate [11,17,18,19]. No formal fishery resource assessment exists for most cartilaginous fish in the world [20], and the IUCN Red List cites a square of cartilaginous species as threatened by overfishing, with only one-third of species regarded as safe [1], and 44% of species unable to be accurately assessed because of a lack of data.
In China’s waters, catches of sharks, rays, and skates are estimated to have reduced by 67% between 1950 and 2014 [21]. Highly productive coastal waters are affected by multiple stressors, such as human activity, environmental pollution, and climate change, and fishery resources in this region are declining [22,23]. As an apex predator in coastal waters, coastal sharks experience increasingly severe conditions, and because they are long-living and slow-growing animals with low productivity [24,25,26,27] they are especially vulnerable. Shark recovery from overfishing can take a long time due to habitat degradation and the bioaccumulation and biomagnification of environmental pollutants through the bionet process [28].
Coastal tropical and subtropical waters of the northern South China Sea (NSCS) contain many fishery resources, and are traditional bottom trawl fishing grounds for the Hainan, Guangxi, and Guangdong provinces. Recent increases in the number and power of fishing boats in this region have caused serious declines in offshore fishery resources [29]. Fishing rates declined by 72% from the early 1960s to the late 1990s [30], with the effects of fishing and environmental changes considered primarily responsible [23]. Historically, research on fish in this region has focused on fish morphology, biology, genetics, species composition, and discussions on protection and management strategies [31,32,33,34]. Of the 146 species of shark reported from China’s waters, 13 have been reported in bottom trawl catches from the NSCS [35]. However, because of a lack of accurate catch and survey data, a punctual assessment of shark stocks in this region, and therefore a formulation of science-based fishery management, cannot be achieved. Alternative methods are needed to assess shark stocks in the coastal NSCS.
When possible, fishery management actions are based on estimates of current stock status and management targets produced from full age-structured stock assessment models; however, most unassessed stocks lack data and commercial importance for a full age-based stock assessment. Three types of assessment models are commonly used in poor-data fishery management: CMSY (catch–maximum sustainable yield), AMSY (abundance—maximum sustainable Yield), and LBB (length-based Bayesian biomass). Catch-based methods cannot be used to assess shark stock for the northern SCS because they are the bycatch of bottom trawl fisheries and the catch data have not been counted. Meanwhile, existing abundance index (e.g., CPUE) data series are not accurate enough to assess the biomass of these species, so the AMSY method is not a good choice for stock assessment. We estimated the parameters of the LBB method directly by a Bayesian Monte Carlo Markov chain process, requiring only length frequency data. This process estimates asymptotic length, length at first capture, relative natural mortality, and relative fishing mortality of a species. The resource statuses of poor-data fish species in China have been previously evaluated using this method [36,37,38]. Thus, we estimated the population parameters of four dominant (bycatch) shark species and assessed their stock status using the LBB method based on length frequency data collected by bottom trawl surveys from 2019 to 2021 in the NSCS. The results provide a scientific basis for regional shark protection and management.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Resource
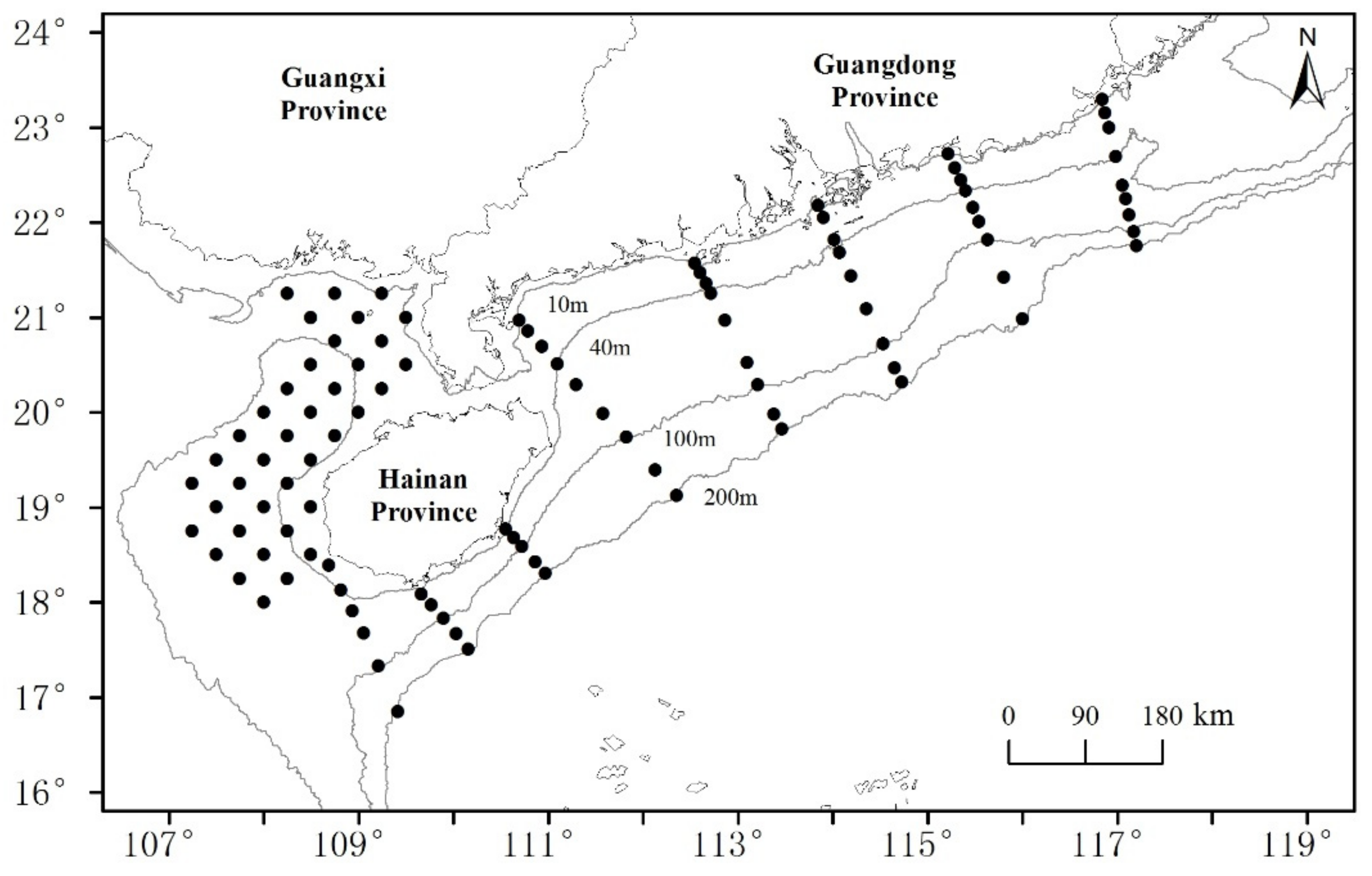
We sourced data for four shark species from bottom trawl surveys (August 2019, March–April 2020, July–September 2020, and January 2021) conducted by the South China Sea Fisheries Research Institute in offshore waters of the NSCS. A steel fishing vessel “Guibeiyu 69068” (engine power 441 kW) was engaged in these surveys. The same gear—a net 80.4 m × 60.54 m (head line: 37.70 m)—was used in each survey. Each site (Figure 1) was trawled once for 1 h at an average speed of 3.5 kn. All shark samples were frozen and then returned to the laboratory for measurement, where their lengths were measured to the nearest 0.1 cm; sharks were identified to species with dichotomy key-based morphological characteristics, and their scientific and common names were verified using FishBase. A total of 952 shark individuals referable to 12 species were collected. Those species, for which more than 100 individuals were retained, were selected for LBB analysis.
Figure 1.
Trawl survey sampling sites, northern South China Sea.
Life history characteristics of these dominant shark species are as follows.
- Cephaloscyllium sarawakensis
This benthopelagic species mainly inhabits the Pacific Ocean. In the South China Sea its distribution extends from southwestern Taiwan, Hong Kong, and Vietnam, to Malaysia, from 10 to 200 m. Males and females attain maximum lengths of 39.7 cm and 44.1 cm, respectively [39].
- Apristurus platyrhynchus
This small shark is found in the western Pacific, the Philippines, South and East China seas, and northward to Suruga Bay, Japan. Maximum male and female lengths are 80.0 cm and 63.0 cm, respectively. It lives mainly on the continental slope, and is oviparous, probably producing a single egg per oviduct at a time [40].
- Scoliodon laticaudus
This demersal, shallow-dwelling species matures at 34.3 cm (33–35 cm) and reaches a maximum length of 100.0 cm. It is found widely throughout the Indo-West Pacific (Persian Gulf, Somalia, Tanzania, Mozambique, Pakistan, and Java, Indonesia), and the waters of Japan and China. It feeds on small bony fish, shrimps, and cuttlefish. It is viviparous, with litter sizes ranging from 1 to 14, producing pups of about 13–15 cm total length [40].
- Squalus brevirostris
This demersal species is found mainly in the western Pacific, from southern Japan to the South China Sea. Its maximum total length is 60 cm, and it is ovoviviparous [41].
2.2. LBB Method
The LBB method can analyze length frequency data from commercial catches of continuously growing species, such as most commercially exploited fish and invertebrates [36,42]. The key to the LBB method is the von Bertalanffy growth function (VBGF), described as [43]:
where Lt is the length at age t, Linf is the asymptotic length, K is the rate at which Linf is approached, and t0 is the theoretical age at length zero.
If fishing gear operates with full selectivity, the curvature of the catch in the numbers-at-length curve is the value of the total mortality Z relative to K (Z/K); Z comprises natural and fishing mortality (Z = M + F), with the curve expressed by the following equation [44]:
where NL is the number of survivors to length L, NLstart is the number at length Lstart, and Lstart is the minimum length with full selection (all individuals entering the gear are retained by the gear).
Fishing gear selectivity (here assumed trawl-like) for species is given by the following equation:
where SL is the fraction of individuals that are retained by the gear at length L, Lc is the length of 50% of the individuals captured by the gear, and α represents the steepness of the ogive [44].
Parameters Linf, Lc, α, M/K, F/K, and the selection ogive, are estimated by fitting the following two equations [42]:
where NLi is the number of individuals in length class Li, the subindex i in Li represents the serial numbers of length classes, and NLi−1 is the number of individuals in the previous length class. CLi refers to the number of individuals vulnerable to the gear, proportionally represented in the catch for length class Li.
For a given fishing pressure (F/M), the length at first capture Lc_opt that maximizes the catch and biomass can be obtained from:
An index catch per unit of effort (CPUE′/R) is obtained by dividing the relative yield-per-recruit (Y′/R) by F/M, as presented by Froese [42]:
The relative biomass in the exploited situation if no fishing occurs is given by:
where B0′ > Lc denotes the exploitable fraction (>Lc) of the unfished biomass (B0).
The ratio of fished to unfished biomass is described as:
A proxy for the relative biomass that can produce Bmsy/B0 was obtained by re-running Equations (7)–(10) with F/M = 1 and Lc = Lc_opt (Froese [42]).
Herein, Linf priors are generated as the maximum length obtained from the present study if the maximum length is unknown, or the recorded maximum length in Fishbase (www.fishbase.org, accessed on 15 June 2021) is smaller than that of the present study; otherwise, the recorded maximum length in Fishbase is used for all other situations [42]. All analyses were implemented using LBB_30a.R, an R-code algorithm presented by Froese [42]. Stocks were classified into categories based on B/BMSY values; they were considered overexploited when B/BMSY < 0.8, fully exploited when 0.8 ≤ B/BMSY ≤ 1.2, and non-fully exploited when B/BMSY > 1.2 [45]. A simulation was presented to understand if the estimations were sensitive to different size-class intervals using the LBB method. We set five groups with different size-class intervals (10 cm, 20 cm, 30 cm, 40 cm, and 50 cm) of S. laticaudus to run LBB. We chose S. laticaudus as an example because its length range was wide, from 200 mm to 700 mm.
3. Results
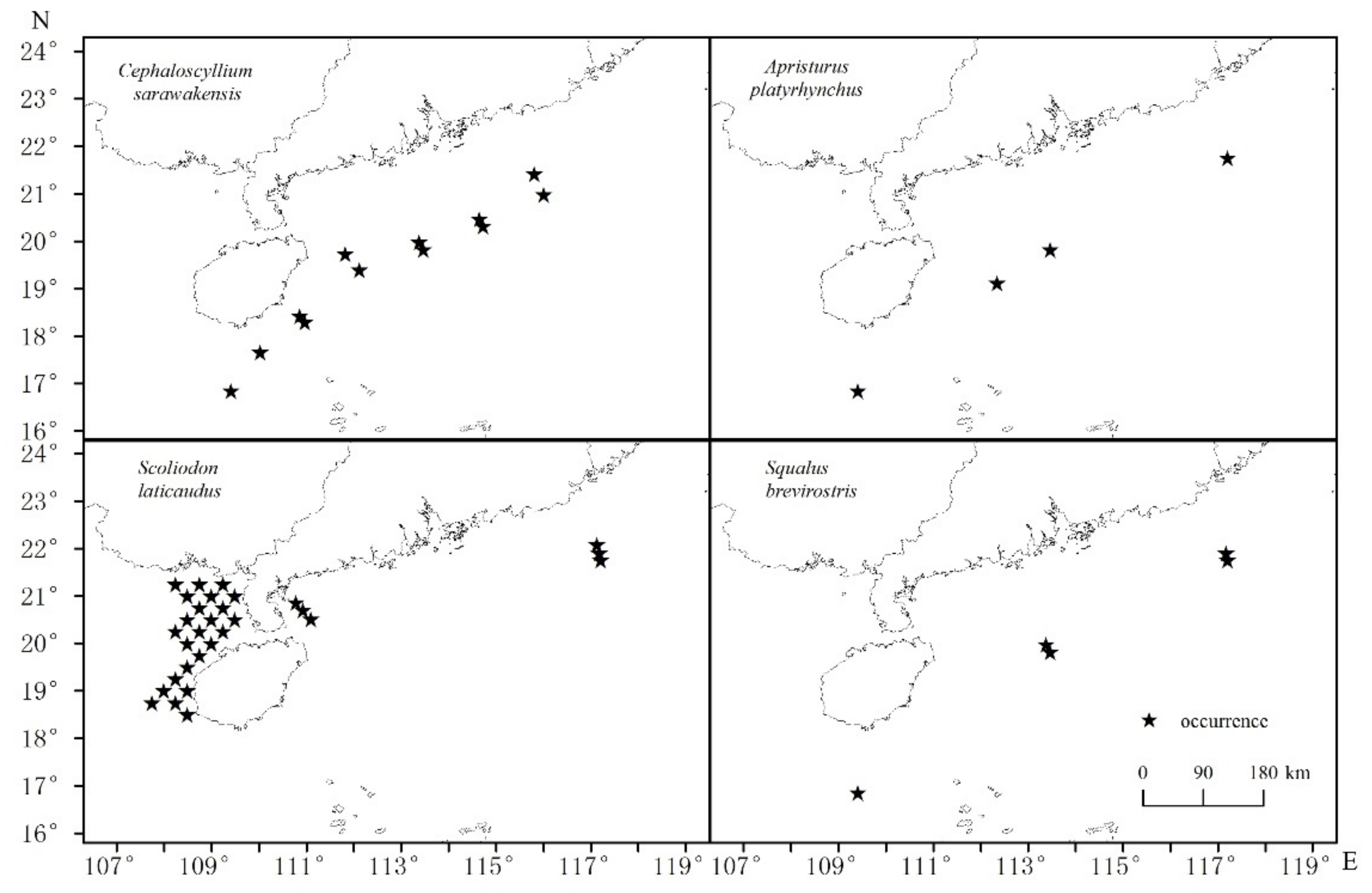
The distributions of each shark species are depicted in Figure 2. A. platyrhynchus was found in the Beibu Gulf, while other species were found on the northern continental shelf of the NSCS and southern waters of Hainan Island, in deep water. Most A. platyrhynchus were found in the shallower eastern part of the Beibu Gulf. Species composition, numbers of sharks retained in trawls, basic information and the priors of four dominant shark species are shown in Table 1 and Table 2.
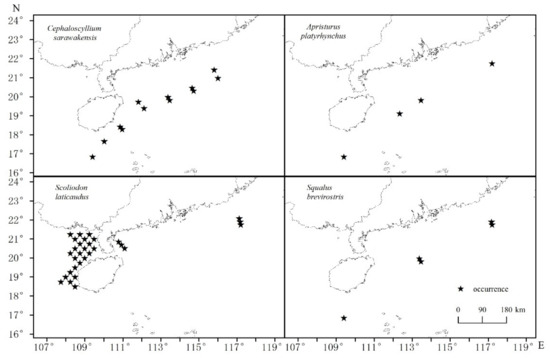
Figure 2.
Distributions of the four shark species in the northern South China Sea.

Table 1.
Species composition and numbers of sharks retained in trawls from the northern South China Sea.

Table 2.
Basic information and priors of model parameters of four dominant shark species from the northern South China Sea.
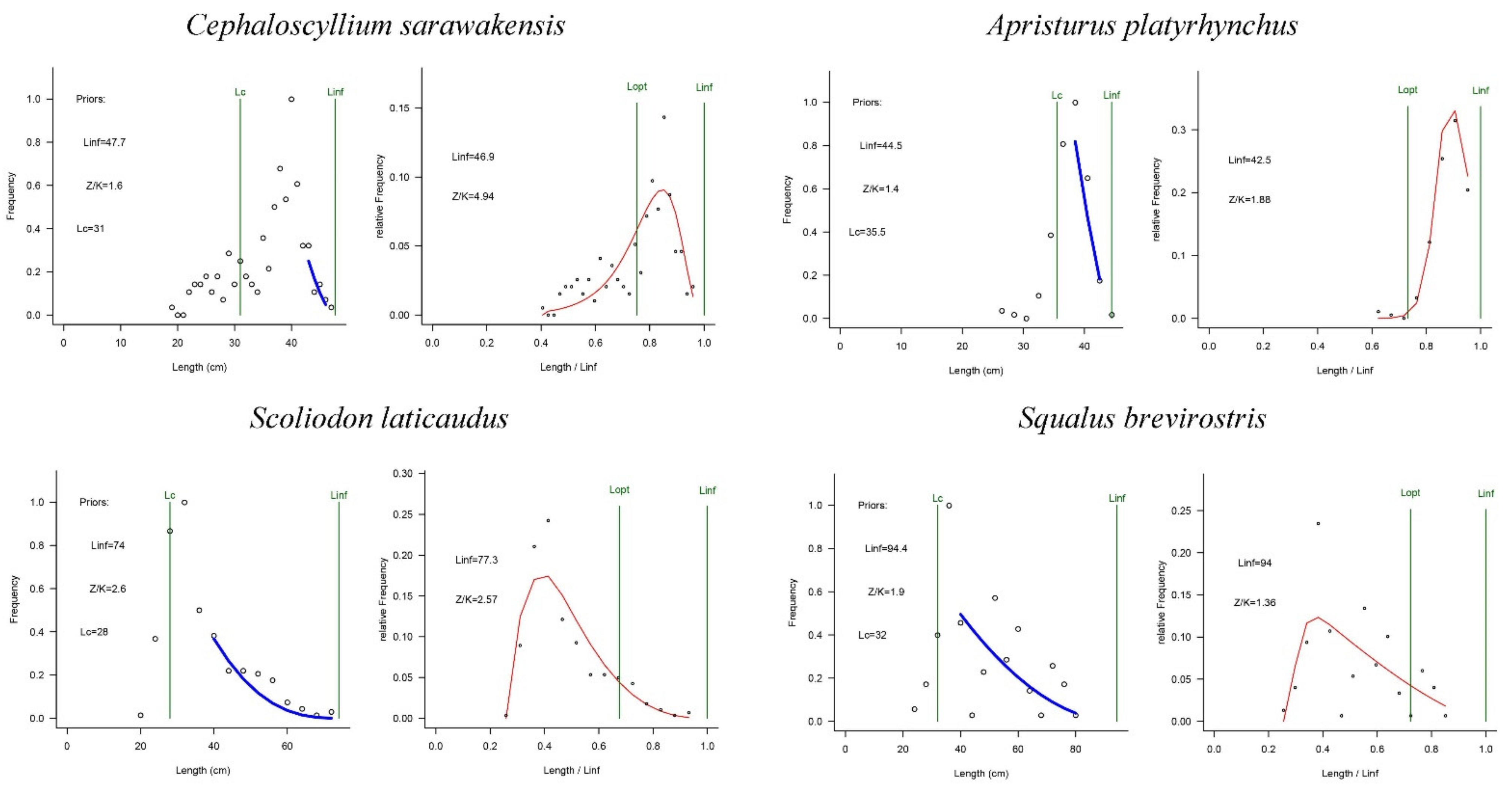
The results of these four shark species in offshore NSCS waters produced by LBB methods are presented in Figure 3 and summarized in Table 3. All length–frequency distributions are unimodal. Estimated Linf values for C. sarawakensis and A. platyrhynchus were smaller than the maximum length (Lmax), while the Lmax was lower than estimated values of Linf for S. laticaudus and S. brevirostris.
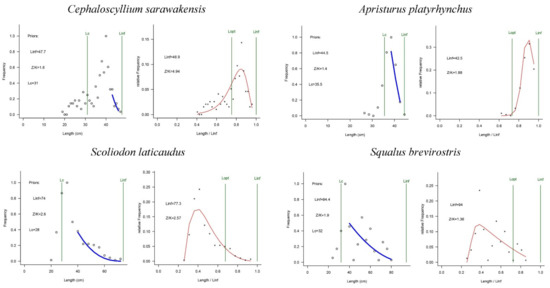
Figure 3.
Trends in population parameters of the four shark species in the northern South China Sea. The left curve shows the LBB model fits to accumulated length frequency data; the right curve indicates the LBB method prediction.

Table 3.
Summary of LBB outputs and status for four dominant shark species in the northern South China Sea.
Estimates of Lc/Lc_opt ranged from 0.49 to 1.4, with C. sarawakensis having the highest value, and S. brevirostris the lowest. The maximum and minimum trend in Lc/Lc_opt was the same as the estimate of Z/K, ranging from 1.4 to 4.97. The estimated Lc/Lc_opt value for A. platyrhynchus was higher than that for S. laticaudus, while the estimated Z/K of A. platyrhynchus was lower than that of S. laticaudus.
Estimates of B/BMSY for each species from the northern continental shelf of the NSCS made a difference, ranging from 0.86 to 1.9. In the LBB method, an evaluation of fish resource status can be judged by the ratio of B/BMSY. Combining the results of the model and judgment criteria of Amorim [45], C. sarawakensis and S. laticaudus were both fully exploited, and A. platyrhynchus and S. brevirostris were non-fully exploited.
To verify the stability of the LBB model, S. laticaudus length data were divided into different size-class intervals; simulations revealed estimated parameters (Linf, Lc/Lc_opt, Z/K, B/B0, and B/BMSY) to be insensitive to different intervals, with the exception of the shortest (10 mm) interval (Table 4).

Table 4.
Estimated parameters of the LBB for size-class intervals for a simulated data series for Scoliodon laticaudus.
4. Discussion
This study is the first to assess bottom trawl bycatch shark species resources in the NSCS. The results indicated that the level of relative biomass (B/BMSY) of two species (C. sarawakensis, S. laticaudus) was <1, indicating that these sharks have been considerably impacted by fisheries; for two species (A. platyrhynchus, S. brevirostris) it was >1, indicating they have not been considerably impacted by fisheries. We suggest applying a variety of methods to effectively assess the shark stock status in the NSCS, and formulate optimal fishery management policies.
Length frequency data were sourced from sharks retained in four bottom trawl surveys in the NSCS from 2019 to 2021, from all four seasons. Bottom trawling has poor fishing gear selection [46], and the survey depth range (10–200 m) basically covered the different sizes and habitat of each dominant species. Therefore, our data satisfy the requirements of Froese [42], who emphasized that length–frequency data used in the LBB method should represent the entire target stock.
Globally, the stock status of most shark species cannot be assessed because of a lack of catch data [47], mainly because sharks are caught as bycatch in most fisheries and the bodies are discarded after the fins have been cut off. Traditional stock assessments are only routinely performed on large shark species, such as blue shark Prionace glauca and mako shark Isurus oxyrinchus [48,49,50]. Because of the low economic value of small coastal sharks and a lack of production data because of bycatch, there is currently no specific resource assessment for them in the NSCS. Research is instead focused on species composition, community structure, and life history characteristics which do not require catch or CPUE data [51,52].
Among the assessed species, C. sarawakensis is classified Not Applicable (NA), S. laticaudus as Near Threatened (NT), A. platyrhynchus as Least Concern (LC), and S. brevirostris as Endangered (EN) in the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) Red List of Threatened Species. The relative biomass levels of C. sarawakensis and S. laticaudus were 0.86 and 0.92, indicating that their stocks were fully exploited. The widely distributed C. sarawakensis occurs mainly in deeper coastal waters of the NSCS. Because this species has often been confused with Cephaloscyllium umbratile [53], identifications may have been incorrect in previous related research [51]. The habitat of S. laticaudus is close to the coast and therefore under heavy fishing pressure [54,55], but it is a fertile species, with the female carrying 8–19 embryos [56]. Our results on the status of S. laticaudus are consistent with those from the Bay of Bengal, Bangladesh, using the FiSAT-II evaluation method [57] and the waters around Taiwan [47]. The relative biomass of A. platyrhynchus was 1.4, with that for S. brevirostris even greater (to 1.9). Neither species was non-fully exploited, indicating that regional stocks are in good condition, possibly because those species may live deeper, outside of traditional bottom trawl operation areas, and are not target species due to their low economic value. S. brevirostris was also the dominant shark species in the southwestern sea of the Nansha Islands; combined with the results of this study (non-fully exploited), this indicates that S. brevirostris is widely distributed and abundant in the South China Sea [51]. The Chinese government has tried since the 1980s to restrict fishing in response to inshore fishery depletion caused by demersal trawling and stake nets; however, the status of fishery resources has recovered somewhat in recent years [58].
To verify the influence of body length frequency size-class intervals on model evaluation results, we divided length–frequency data for the most common species S. laticaudus into different length–frequency intervals. While different class intervals do affect results, they do not affect the final evaluation of a stock as being over, fully, or non-fully exploited. To improve this model, a standard class spacing could be considered.
While various concerns have been expressed about the reliability of the LBB method to evaluate resource status [59], for sharks, for which there are limited data, this method enables an evaluation of resource status that is otherwise not possible. Ours is the first study to attempt to analyze the resource status of small sharks in coastal NSCS waters. These results can be used to provide a scientific basis on which shark fisheries in this region can be managed and prior parameters for related resource assessment methods can be determined [60]. Besides, due to the limitations of sampling numbers, the results of this study can only be used as an attempt to study the status of shark resources in this sea area, and provide a preliminary accumulation for further in-depth research in the future.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Z.C. and K.Z.; methodology, K.Z.; formal analysis, Y.X.; resources, Z.C.; data curation, Y.X., M.S. and Z.H.; writing—original draft preparation, Y.X.; writing—review and editing, X.D., Z.C. and K.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the Key Research and Development Project of Guangdong Province (2020B1111030001), the Central Public-interest Scientific Institution Basal Research Fund, CAFS (2020TD05) and Central Public-interest Scientific Institution Basal Research Fund, South China Sea Fisheries Research Institute, CAFS (2021SD01).
Institutional Review Board Statement
The animal study was reviewed and approved by South China Sea Fisheries Research Institute Animal welfare committee.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to the entire crew of the “Zhongyuke 301” and “Guibeiyu 69068” for their participation in the sampling. We appreciate the valuable comments made by four reviewers, which significantly improved our manuscript. We thank Li Su, Yuyan Gong and Yutao Yang for their collaboration on the experiments. We also thank Steve O’Shea from Liwen Bianji (Edanz) for editing the English text of a draft of this manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Dulvy, N.K.; Fowler, S.L.; Musick, J.A.; Cavanagh, R.D.; Kyne, P.M.; Harrison, L.R.; Carlson, J.K.; Davidson, L.N.; Fordham, S.V.; Francis, M. Extinction risk and conservation of the world’s sharks and rays. eLife 2013, 3, e00590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Heupel, M.R.; Simpfendorfer, C.A. Importance of environmental and biological drivers in the presence and space use of a reef-associated shark. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2014, 496, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heupel, M.R.; Knip, D.M.; Simpfendorfer, C.A.; Dulvy, N.K. Sizing up the ecological role of sharks as predators. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2014, 495, 291–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Crooks, K.R.; Soule, M.E. Mesopredator release and avifaunal extinctions in a fragmented system. Nature 1999, 400, 563–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estes, J.A.; Terborgh, J.; Brashares, J.S.; Power, M.E.; Berger, J.; Bond, W.J.; Carpenter, S.R.; Essington, T.E.; Holt, R.D.; Jackson, J.B.; et al. Trophic downgrading of planet Earth. Science 2011, 333, 301–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Penaherrera, C.; Llerena, Y.; Keith, I. Perceptions on the economic value of sharks for the daily diving tourism industry and the souvenir commerce in Santa Cruz Island. In Galapagos Report 2012; Charles Darwin Foundation, Galapagos National Park Directorate and Consejo de Gobierno de Galapagos: Galapagos, Ecuador, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Pacoureau, N.; Rigby, C.; Kyne, P.M.; Sherley, R.B.; Dulvy, N.K. Half a century of global decline in oceanic sharks and rays. Nature 2021, 589, 567–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costello, C.; Ovando, D.; Hilborn, R.; Gaines, S.D.; Deschenes, O.; Lester, S.E. Status and solutions for the world’s unassessed fisheries. Science 2012, 338, 517–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Davidson, L.N.K.; Krawchuk, M.A.; Dulvy, N.K. Why have global shark and ray landings declined: Improved management or overfishing? Fish Fish. 2015, 17, 438–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, B.M.; Houk, P.; Russ, G.R.; Choat, J.H. Life histories predict vulnerability to overexploitation in parrotfishes. Coral Reefs 2014, 33, 869–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worm, B.; Davis, B.; Kettemer, L.; Ward-Paige, C.A.; Chapman, D.; Heithaus, M.R.; Kessel, S.T.; Gruber, S.H. Global catches, exploitation rates, and rebuilding options for sharks. Mar. Policy 2013, 40, 194–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fong, Q.S.; Anderson, J.L. International shark fin markets and shark management: An integrated market preference–cohort analysis of the blacktip shark (Carcharhinus limbatus). Ecol. Econ. 2002, 40, 117–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campana, S.E.; Joyce, W.; Manning, M.J. Bycatch and discard mortality in commercially caught blue sharks Prionace glauca assessed using archival satellite pop-up tags. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2009, 387, 241–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Clarke, S.C.; Francis, M.P.; Griggs, L.H. Review of Shark Meat Markets, Discard Mortality and Pelagic Shark Data Availability, and a Proposal for a Shark Indicator Analysis; Ministry for Primary Industries: Wellington, New Zealand, 2013; Volume 65. [Google Scholar]
- Oliver, S.; Braccini, M.; Newman, S.J.; Harvey, E.S. Global patterns in the bycatch of sharks and rays. Mar. Policy 2015, 54, 86–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campana, S.E. Transboundary movements, unmonitored fishing mortality, and ineffective international fisheries management pose risks for pelagic sharks in the northwest atlantic. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2016, 73, 1599–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, S.C.; McAllister, M.K.; Milner-Gulland, E.J.; Kirkwood, G.P.; Michielsens, C.G.J.; Agnew, D.J.; Pikitch, E.L.; Nakano, H.; Shivji, M.S. Global estimates of shark catches using trade records from commercial markets. Ecol. Lett. 2006, 9, 1115–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferretti, F.; Worm, B.; Britten, G.L.; Heithaus, M.R.; Lotze, H.K. Patterns and ecosystem consequences of shark declines in the ocean. Ecol. Lett. 2010, 13, 1055–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dulvy, N.; Simpfendorfer, C.; Davison, L.; Fordham, S.; Brautigam, A.; Sant, G.; Welch, D. Challenges and priorities in shark and ray conservation. Curr. Biol. 2017, 27, R565–R572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cortés, E.; Brooks, E.N.; Gedamke, T. Population dynamics, demography, and stock assessment. In Biology of Sharks and Their Relatives, 2nd ed.; Carrier, J.C., Musick, J.A., Heithaus, M.R., Eds.; CRC Press, Taylor & Francis Group: Miami, FL, USA, 2012; pp. 453–486. [Google Scholar]
- Zeller, D.; Pauly, D. Marine fisheries catch reconstruction: Definitions, sources, methods, and challenges. In Global Atlas of Marine Fisheries: A Critical Appraisal of Catches and Ecosystem Impacts; Island Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2016; pp. 12–29. [Google Scholar]
- Whitmarsh, D.; Palmieri, M.G. Aquaculture in the Coastal Zone: Pressures, Interactions and Externalities. In Aquaculture in the Ecosystem; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; pp. 251–269. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, K.; Guo, J.; Xu, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Chen, Z. Long-term variations in fish community structure under multiple stressors in a semi-closed marine ecosystem in the South China Sea. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 745, 140892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kbjg, A.; Ak, B.; Sp, A.; Saa, C.; Jmb, D.; Cra, E. Fishing for profit or food? Socio-economic drivers and fishers’ attitudes towards sharks in fiji. Mar. Policy 2019, 100, 249–257. [Google Scholar]
- Leeney, R.H.; Mana, R.R.; Dulvy, N.K. Fishers’ ecological knowledge of sawfishes in the Sepik and Ramu rivers, northern Papua New Guinea. Endanger. Species Res. 2018, 36, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Booth, H.; Squires, D.; Milner-Gulland, E.J. The neglected complexities of shark fisheries, and priorities for holistic risk-based management. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2019, 182, 104994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dissanayake, N.G.; Frid, C.; Caswell, B.A. Biodiversity, trait composition and ecological functioning: Impacts of coastal urbanisation on subtropical mudflats. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2020, 71, 1043–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maz-Courrau, A.; López-Vera, C.; Galván-Magaña, F.; Escobar-Sánchez, O.; Rosíles-Martínez, R.; Sanjuán-Muñoz, A. Bioaccumulation and Biomagnification of Total Mercury in Four Exploited Shark Species in the Baja California Peninsula, Mexico. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2001, 88, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Jiang, T.; Wang, X.H.; Duan, L.J.; Li, S.Y. Establishment and analysis of the Ecopath model of the ecosystem in the northern continental shelf of South China Sea. Acta Sci. Nat. Univ. Sunyatseni 2007, 46, 123–127. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Yuan, W. Changes of demersal trawl fishery resources in northern south china sea as revealed by demersal trawling. S. China Fish. Sci. 2008, 4, 8. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.; Huang, Z.R.; XU, Y.W.; Chen, Z.Z. Population genetic structure of brushtooth lizardfish (Saurida undosquamis) based on mitochondrial cytochrome b gene sequences. S. China Fish. Sci. 2019, 15, 41–48. [Google Scholar]
- Shu, L.M.; Qiu, Y.S. Biology analysis of Saurida tumbil in northern South China Sea. J. Fish. Sci. China 2004, 11, 5. [Google Scholar]
- Niu, S.F.; Wu, R.X.; Zhai, Y.; Zhang, H.R.; Chen, Y.H. Demographic history and population genetic analysis of Decapterus maruadsi from the northern South China Sea based on mitochondrial control region sequence. PeerJ 2019, 7, e7953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, P.; Huang, C.; Fang, H.; Cai, W.; Li, D.; Li, X.; Yu, H. The abundance, composition and sources of marine debris in coastal seawaters or beaches around the northern South China Sea (China). Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2011, 62, 1998–2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.R.; Chen, Z.Z.; Zeng, X.G. Species composition and resources density of chondrichthyes in the continental shelf of northern South China Sea. J. Oceanogr. Taiwan Strait. 2009, 28, 38–44. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; He, Y.; Du, F.; Liu, M.; Qiu, Y. Using LBB Tools to Assess Miter Squid Stock in the Northeastern South China Sea. Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 7, 518–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, S.; Liang, C.; Xian, W. Stock Assessment Using LBB Method for Eight Fish Species from the Bohai and Yellow Seas. Front. Mar. Sci. 2020, 7, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Zhang, J.; Shi, D.; Chen, Z. Assessment of coral reef fish stocks from the Nansha Islands, South China Sea, using length-based Bayesian biomass estimation. Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 7, 610707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yano, K.; Ahmad, A.; Gambang, A.C.; Idris, A.H.; Solahuddin, A.R.; Aznan, Z. Sharks and Rays of Malaysia and Brunei, Darussalam; SEAFDEC-MFRDMD: Kuala Terengganu, Malaysia, 2005; p. 557. [Google Scholar]
- Compagno, L.J.V. FAO Species Catalogue. Vol. 4. Sharks of the world. An annotated and illustrated catalogue of shark species known to date. Part 2-Carcharhiniformes. FAO Fish. Synop. 1984, 125, 251–655. [Google Scholar]
- Randall, J.E.; Lim, K.K.P. A checklist of the fishes of the South China Sea. Raffles Bull. Zool. Suppl. 2000, 8, 569–667. [Google Scholar]
- Froese, R.; Winker, H.; Coro, G.; Demirel, N.; Tsikliras, A.C.; Dimarchopoulou, D.; Scarcella, G.; Probst, W.N.; Dureuil, M.; Pauly, D. Corrigendum: A new approach for estimating stock status from length frequency data. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2019, 76, 350–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Bertalanffy, L. A quantitative theory of organic growth (inquiries on growth laws. II). Hum. Biol. 1938, 10, 181–213. [Google Scholar]
- Quinn, T.J.; Deriso, R.B. Quantitative Fish Dynamics; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Amorim, P.; Sousa, P.; Jardim, E.; Menezes, G.M. Sustainability status of data-limited fisheries: Global challenges for snapper and grouper. Front. Mar. Sci. 2019, 6, 654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacLennan, D.N. Fishing gear selectivity: An overview. Fish. Res. 1992, 13, 201–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, P.; Chen, M.; Tian, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, S.; Xiao, J. Stock status estimating of 5 shark species in the waters around Taiwan using a length-based Bayesian biomass estimation (LBB) method. Front. Mar. Sci. 2020, 7, 632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleiber, P.; Clarke, S.; Bigelow, K.; Nakano, H.; McAllister, M.; Takeuchi, Y. North Pacific Blue Shark Stock Assessment; U.S. Dep. Commer., NOAA: Washington, DC, USA, 2009; p. 74. [Google Scholar]
- Geng, Z.; Wang, Y.; Kindong, R.; Zhu, J.; Dai, X. Demographic and harvest analysis for blue shark (Prionace glauca) in the Indian Ocean. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2021, 41, 101583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.H.; Liu, K.M. Stock assessment of the shortfin mako shark (Isurus oxyrinchus) in the Northwest Pacific Ocean using per recruit and virtual population analyses. Fish. Res. 2009, 98, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Lin, L.S.; Yuan, L.I.; Song, P.Q.; Chen, Y.J.; Zhang, J. Species composition and quantity distribution of sharks in the southwestern sea of the Nansha Islands and mouth of the Beibu Bay. Mar. Fish. 2018, 1, 27–37. [Google Scholar]
- Gutteridge, A.N.; Huveneers, C.; Marshall, L.J.; Tibbetts, I.R.; Bennett, M.B. Life-history traits of a small-bodied coastal shark. Mar. Freshwater Res. 2013, 64, 54–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakaya, K.; Kawauchi, J. A review of the genus Cephaloscyllium (Chondrichthyes: Carcharhiniformes: Scyliorhinidae) from Taiwanese waters. Zootaxa 2013, 3752, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Riede, K. Global Register of Migratory Species: From Global to Regional Scales: Final Report of the RandD-Projekt 808 05 081; Federal Agency for Nature Conservation: Bonn, Germany, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Thomas, S.; Purushottama, G.B.; Nataraja, G.D.; Kizhakudan, S.J. Fishery and biological characteristics of the spadenose shark Scoliodon laticaudus müller & henle, 1838 from the eastern Arabian Sea. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2020, 34, 101085. [Google Scholar]
- Sen, S.; Chakraborty, S.K.; Zacharia, P.U.; Dash, G.; Joe Kizhakudan, S.; Bharadiya, S.A.; Gohel, J.K. Reproductive strategy of spadenose shark, Scoliodon laticaudus muller and henle, 1839 along north-eastern Arabian Sea. J. Appl. Ichthyol. 2018, 34, 1304–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karim, E.; Qun, L.; Memon, A.M.; Baset, A.; Hoq, M.E.; Shamsuzzaman, M.M.; Das, A. Assessment of some demographic trends of spadenose shark (Scoliodon laticaudus) of the Bay of Bengal, Bangladesh. Indian J. Geo-Mar. Sci. 2017, 46, 1986–1995. [Google Scholar]
- Pauly, D.; Liang, C. The fisheries of the South China Sea: Major trends since 1950. Mar. Policy 2019, 121, 103584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hordyk, A.R.; Prince, J.D.; Carruthers, T.R.; Walters, C.J. Comment on ‘A new approach for estimating stock status from length frequency data’ by Froese et al. (2018). ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2019, 76, 457–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Mamun, M.A.; Liu, Q.; Chowdhury, S.R.; Uddin, M.S.; Sultana, R. Stock Assessment for Seven Fish Species Using the LBB Method from the Northeastern Tip of the Bay of Bengal, Bangladesh. Sustainability 2021, 13, 1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).