Abstract
Sustainable development has become a concern of all countries globally, and Artificial Intelligence technology emerges at this historic moment. However, few researchers have studied the innovation activities of the Artificial Intelligence industry from the macro-level. This paper focuses on the topological structure and the spatial pattern of the AI patent citation network in China over from 2000–2016. Our main research results are as follows: The network has experienced a striking growth in terms of the size and the number of linkages since 2000, but it has also developed unequally across regions. In the later stages, the network has formed a scale-free network that exhibits small-world property. The network nodes have shown an assortative trait property while weighted preferential attachment has not been significant. In addition, the high values of centrality and numerous linkages between nodes concentrate in the eastern part of China, especially in the Yangtze River Delta, Pearl River Delta, and Bohai Rim. Our results suggest that the AI innovation policies should expand the targets of technological exchange and cultivate more nodes as intermediaries of local knowledge transmission necessary to expand the network and develop the AI industry.
1. Introduction
Under the traditional economic development pattern, the high consumption of production factors and the consequent high pollution are the two persistent issues that hinder sustainable development [1,2,3,4]. Innovation is a new engine of regional growth [5,6]. It has become a key factor in maintaining regional competitiveness and sustainable development [7] since knowledge capital has replaced human and financial capital as a major factor in driving economic development [7,8]. As a shared resource, knowledge could flows freely among innovation objects. The literature has long brought to the fore the role of face-to-face communication and codified knowledge in the transmission of knowledge [9,10,11,12]. For instance, Jaffe et al. (1993) have examined knowledge flows within the US [13], while Maurseth and Verspagen (2002) and Fischer et al. (2006) have focused on European countries [14,15]. In addition, Jaffe and Trajtenberg (2002) and Adams (2002) have compared the source of knowledge flows between colleges and universities, labs, and firms and have examined different channels of transmission [16,17], such as collaboration, talent flow, and a disembodied direct channel of codified information which could facilitate the diffusion of technical knowledge [18].
Furthermore, recent studies have employed social network analysis (SNA) to investigate the structure of an innovation network and its characteristics based on patent data [19,20]. Through four indices of centrality, De Prato and Nepelski (2012) find that the position of a node in the innovation network has a very strong impact on patent collaboration with other nodes [20]. Specifically, a node’s strength and closeness centrality influence positively the technological cooperation between countries, while the degree centrality of nodes shows the opposite result. Based on the example of applied patents in the field of biotechnology, Li et al. (2015) argue that innovation networks can differ in terms of size, degree, linkage, and other network indicators. In addition, they find an obvious expansion in network size over time for both science network and technology network. Furthermore, they highlight the presence of a preferential attachment feature in the patent co-applicant network [21]. Analyzing the citation of US biomedical chemistry patents in Europe, Breschi and Lissoni (2009) describe the evolutionary characteristics of the innovation network and identify the significance of the innovator flow in knowledge spillovers [22]. Another example is Ter Wal (2013) who analyzes the biotechnology patent in Germany and discovers that the importance of geographic proximity in this network has declined over time [23]. It can be seen that the study of the topology structure on innovation networks based on SNA can help to gain insight into the development situations and trends of the industry. At the same time, the geographically presented pattern of innovation networks can provide policy advice for the regional development planning of industries.
Although many researchers have studied the innovation network in China [24,25], most have evaluated all sectors together, hence leading to estimates that did not reflect the heterogeneity across sectors [26,27]. In addition, only a handful of contributions have focused on the country’s Artificial Intelligence (AI) network. AI is a frontier sector in innovation activity, which has been broadly used in various disciplines, supporting to accomplish most of the targets across Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) [28]. AI is explained as the investigation of intelligent problem-solving behavior and the creation of intelligent computer systems [29], which has been a key driver of technological revolution since the beginning of the 21st century, assisting human beings to figure out the issues of economic, social and scientific more efficiently and rapidly [30], such as improving transportation that keeps safety for drivers and pedestrians by applying driverless technology, developing economics that eradicates poverty through boosting productivity, alleviating environmental pollution by increasing resources utilization efficiency [29,31,32]. For China, it is crucial to develop AI to tackle large challenges of societal importance, as seen in an aging population [33], resource shortage [34], economic restructuring, and industrial upgrading [35], which hinder sustainable development. As of 2016, China owned a total of 76,876 AI patents which is slightly more than the US (67,276) and Japan (44,755).
Hence, we are aware of the importance of the AI sector in innovation activity. Meanwhile, we realized that the AI sector has a far-reaching impact on sustainable development, and it had been developed over the past time in China. Thus, discussing the evolution of the AI sector in China is meaningful. To our knowledge, there is no research that depicts the development evolution of the AI sector based on topological and spatial structure. We remedy this gap by focusing on the changes in the AI network across Chinese cities from 2000–2016. We employ social network analysis (SNA) to study the topological structure and the spatial pattern of the Chinese AI patent citation network. Compared to the ordinary innovation network, such as the cooperation network and the inventor network, patent citation provides a document trail [15] that makes it easier to trace and measure the learning process [14,16]. It offers the advantage of formally accounting for the direction and the intensity of the knowledge flows [9]. In addition, while several contributions focus on the factors that explain knowledge flows in the patent citation process [36,37,38,39], this paper lays particular emphasis on highlighting the characteristics of the patent creation-citation network itself. Furthermore, this paper distinguishes itself from the literature by focusing on the innovation network at the urban scale in order to better investigate the spatial heterogeneity present in knowledge transmission that we could not get from a study at the regional or country level [25,40].
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Research Method
Based on graph theory [41,42], we start by constructing the Chinese AI patent citation network noted G = (V, E), where V is the number of nodes in the network, one for each city. E is the number of edges in the network, which represents the citation relationship between cities. We use the degree centrality of cities as the nodes’ weight and the number of citations between cities as the edges’ weight. We employ SNA, which involves Network Centrality Model and Complexity, as our research methods, which are usually used by scholars to analyze the innovation network.
2.1.1. Network Centrality Model
Ponds et al. (2007), Varga and Parag (2009), Alderson et al. (2010), Eisingerich et al. (2010), and Neal (2011) argue that a city’s innovation capacity is tied to that city’s centrality in the network [43,44,45,46,47]. The authors argue that inventors in central areas could receive more information from more partners compared to others who work in peripheral places. We rely on three centrality indices traditionally used in the literature [20] to reflect the position of a city in the innovation network:
(1) Degree centrality, , refers to the number of nodes that connect to the target node [48]. In our case, it corresponds to the number of cities that city is connected with:
where is the cell of an adjacent matrix. If the citation exists, the cell of the matrix is 1; otherwise, it is 0.
(2) Betweenness centrality, , measures the proportion of the shortest paths that go through the target node [49]. When the value is large, the target node has a large controlling power over the network. In our case, it represents the ability of the city to act as the “gatekeeper of the exchange of information”:
where denotes the number of shortest paths between node and node that go through node .
(3) Strength centrality, , is the sum of the weight of the edges that associate with target node [50]. In our case, it means the total number of citations about city:
where denotes the set of adjacent nodes to node and means the total number of citations between nodes and .
2.1.2. Network Complexity
According to Strogatz (2001) and Wagner and Leydesdorff (2005), complex networks are characterized by self-organization, self-similar, scale-free, and small-world features that can be measured through several network indices [51,52]. One of the crucial indices describing the topological features of a network is the degree distribution of nodes [21]. By tradition, the degree distribution is measured through a power-law function which takes the following form: where is a constant, stands for the degree of a node, is an exponent greater than zero that measures the heterogeneity across nodes and stands for the number of nodes. Small values of indicate that the heterogeneity across nodes is strong. Furthermore, when the degree distribution follows a power-law function, the network is called a scale-free network [53].
In addition, Newman (2002) examines assortativity, which tests whether the nodes connect primarily to similar or dissimilar nodes [54]. Barabási and Albert (1999) call this characteristic the ‘preferential attachment’ and define it as the preference behavior of nodes when they choose connections [53]. We define the adjoining neighbors’ average degree centrality of node as:
The adjoining neighbors’ average degree centrality of nodes with degree , is defined as:
where is the connected node of node , is the degree centrality of node , is the number of connected nodes to node , and is the number of nodes connected to node whose degree is .
In the absence of degree correlations, does not depend on , and is a constant. A positive correlation between and means that the nodes tend to connect to other nodes with a similar value of . In contrast, if the nodes with high have a majority of neighbors with low , the correlation is negative, and the network displays a disassortative structure.
However, is defined solely on the basis of the unweighted topological structure. When combined with the weight, the correlation result will provide us with additional insights into the hierarchical and structural organization of the network.
In order to figure out the inconsistency, we employ a weighting matrix that includes both weight and topological properties. We put forward the adjoining neighbors’ average strength centrality of node as follows:
where means the number of connected nodes to node , is the strength centrality of node . Similarly, if the correlation between the degree and is positive, the nodes tend to connect to other nodes with a similar value of . In contrast, if the nodes with high have a majority of neighbors with low , the correlation is negative and the network displays a disassortative structure. Otherwise, does not depend on , which means that there is no weighted preferential attachment feature.
In summary, Equation (6) evaluates the weighted assortative properties by checking the actual relationship between the nodes of the network based on the strength of their ties.
2.2. Data Resource
Our analysis is based on data from the Patent Office of the People’s Republic of China. Departing from previous patent extraction (International Patent Classification codes), AI technologies are embedded in various disciplines. Thus, we collect patents based on the patent information keywords, including image recognition, automatic speech recognition, machine learning, neural network, human-computer interaction, robotics, natural language processing, fuzzy system, expert system, and decision-support system, which Derwent innovation suggests. We have extracted information about the address of the inventors, the patent number, the patent description, and all the advanced patents cited by each patent. Due to the extremely low number of AI patents in China before 2000, we limit our study to the 2000–2016 period. It should be noted that using patents as the indicator can not represent individuals’ entire innovation activity and innovation capacity [55]. While in our work, we focus on the directed knowledge flow that some other indicators (e.g., new product avenue) can not express well. Since this paper focuses on the Chinese network, the study area includes mainland China, Hong Kong, Macao, and Taiwan.
3. Topological Structure of AI Innovation Network
3.1. Network Evolution and Agglomeration
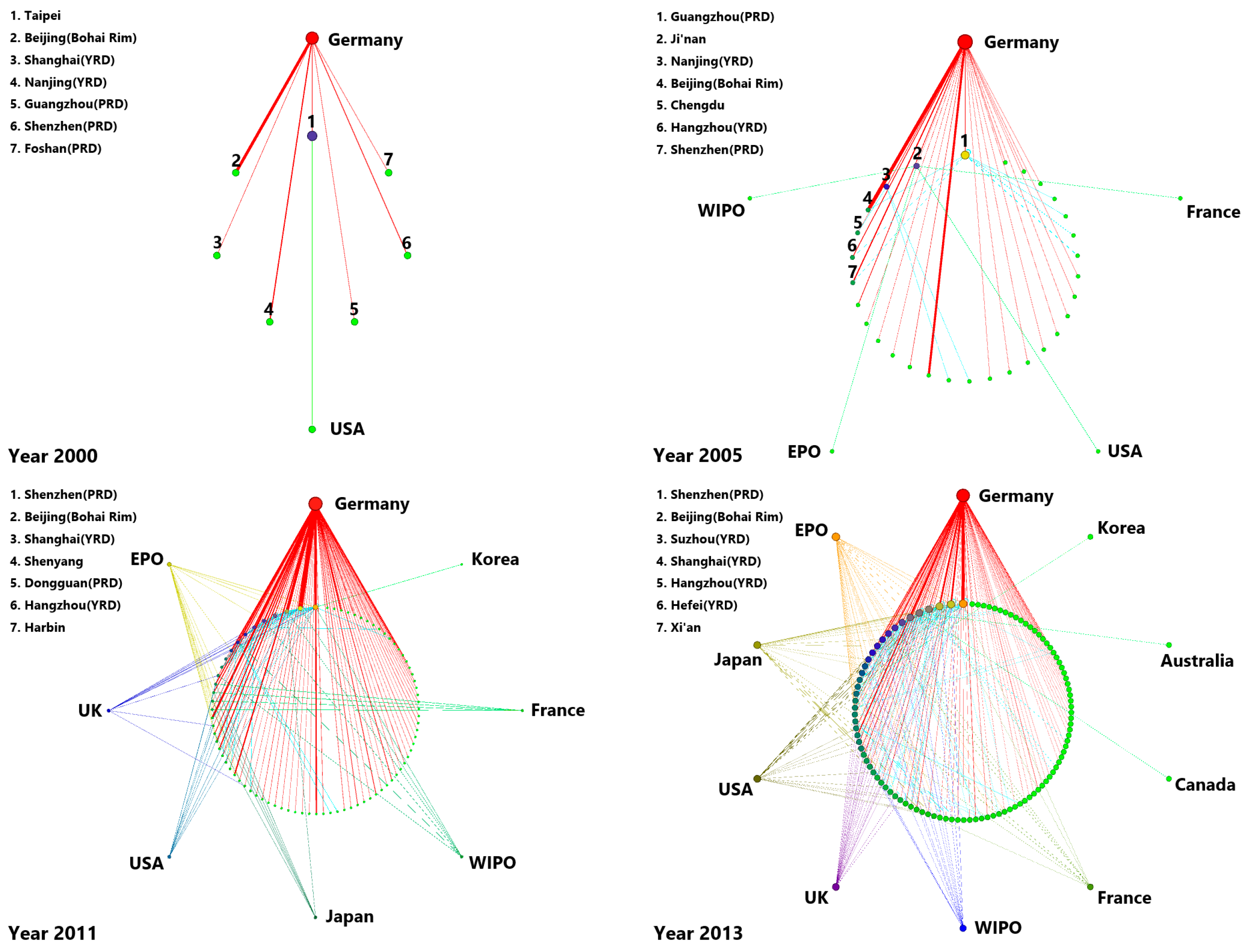
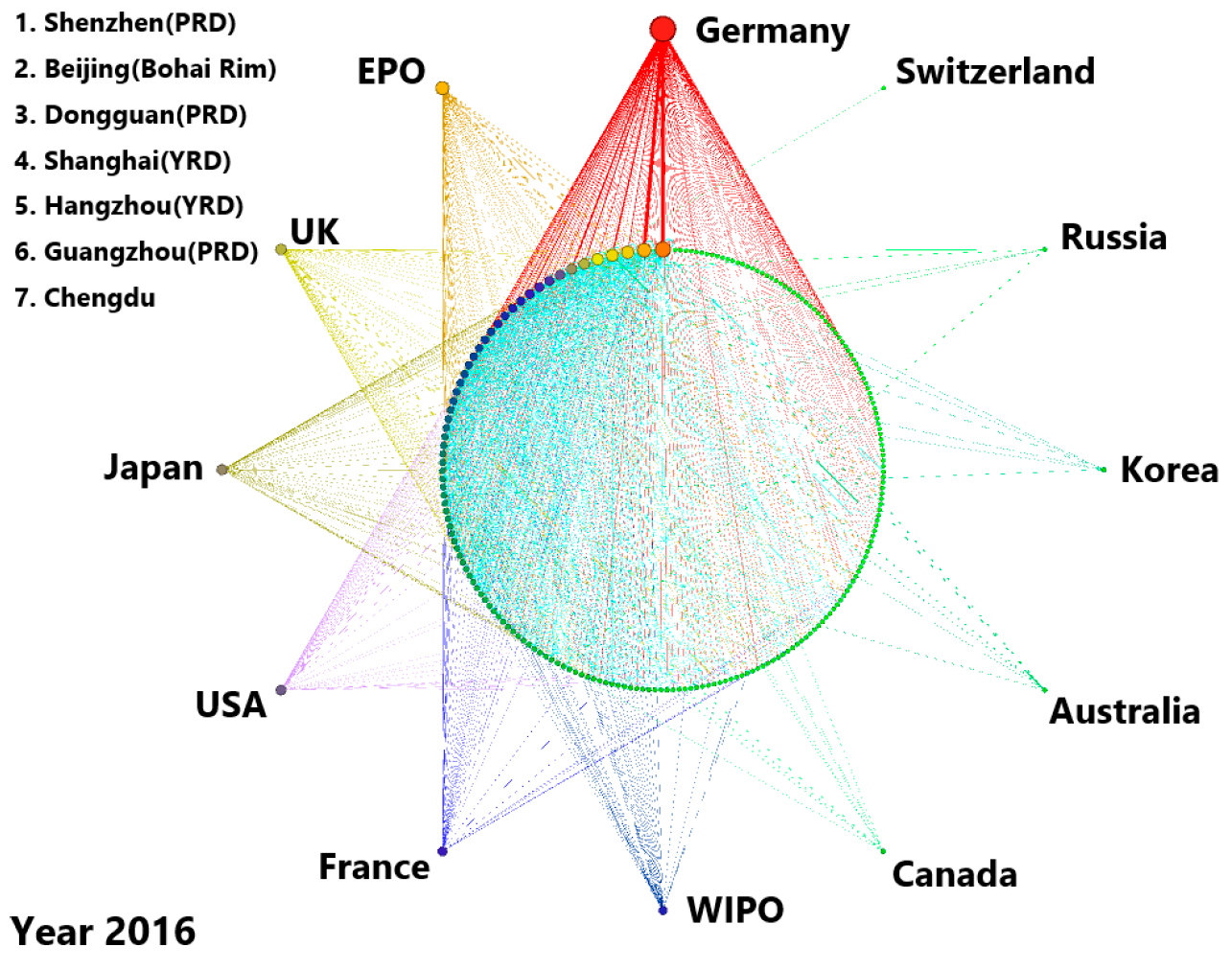
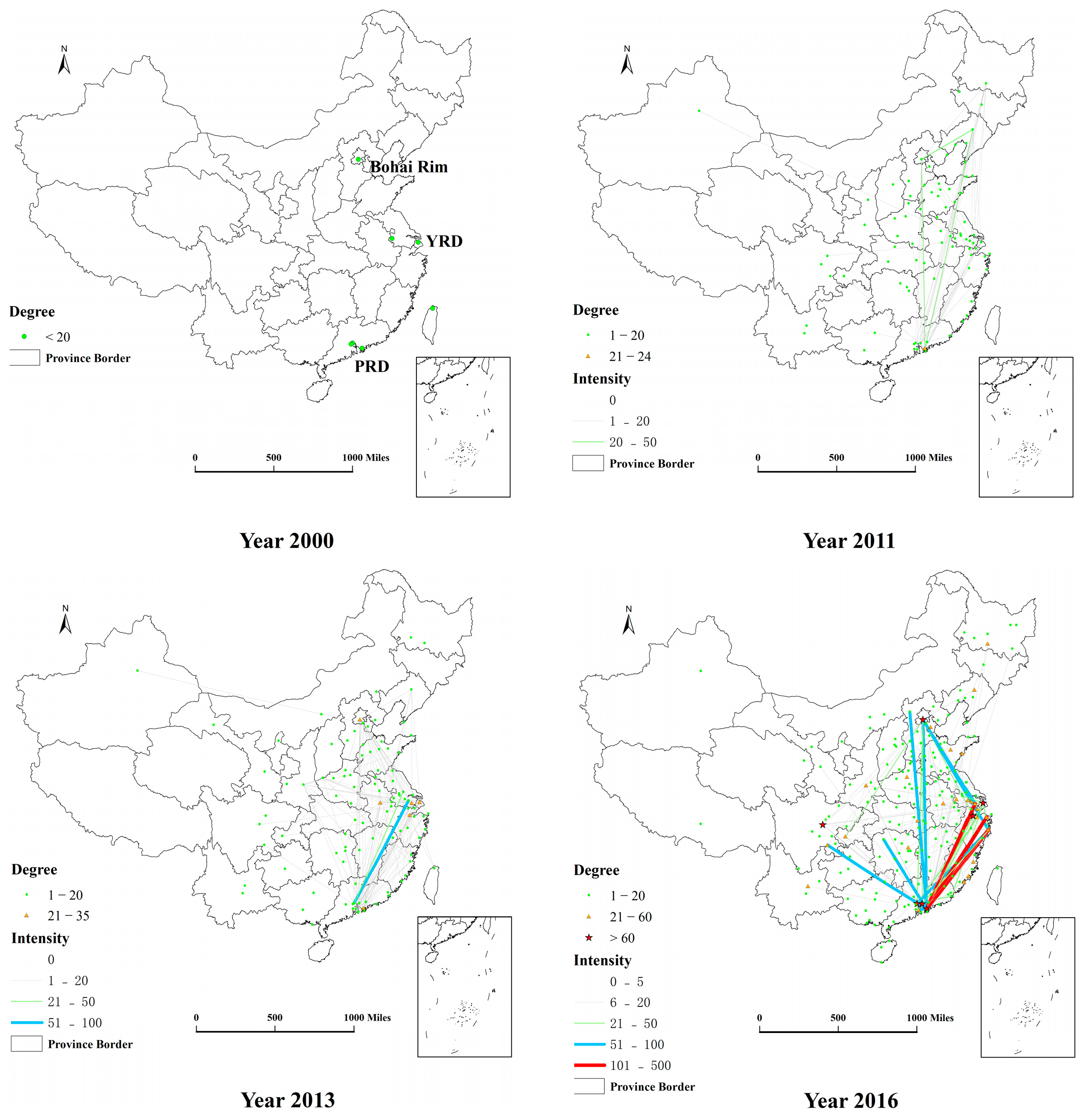
This study employs the Chinese AI patent citation matrix to produce the network graph reported in Figure 1. In addition, the network statistics are presented in Table 1. Both cover the selected years of 2000, 2005, 2011, 2013, and 2016. In Figure 1, the foreign nodes are located in the outer part of the graph while the domestic ones are inside. The size of the nodes shows the degree centrality () of each city. It corresponds to the citation scale that occurs with the current city. The of nodes diminishes in a counter-clockwise direction for both domestic and foreign. The thickness of the line shows the intensity of the citations between cities. We report all the foreign nodes and the top Chinese nodes for each year.
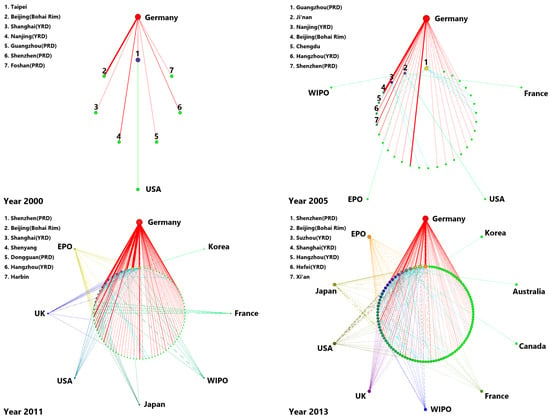

Figure 1.
The topological structure of Chinese AI patent citation network.

Table 1.
Properties of Chinese AI patent citation network.
In 2000, the network was composed of only 9 nodes and 8 edges. Seven Chinese nodes were not associated with any other cities in China but only with US and German. Foshan was the only non-provincial capital among them while the other domestic nodes were core cities. By 2005, just a few new nodes had entered the network, thus adding sparse connections to it. In the second decade of the 21st-century, China followed in the footsteps of numerous developed countries by deploying successive AI development strategies related to Big Data and Internet Plus. More obvious changes occurred in the network scale in 2011 as the number of nodes increased from 35 to 90 and the number of edges changed from 39 to 181. At that time, there were 8 foreign nodes in the network. However, a substantial number of Chinese nodes cited foreign patents heavily while citations between domestic patents remained low (29.28% of all linkages). This result indicates that even though many cities had developed AI, most of them relied on foreign technology mainly. The network configuration changed over 2011–2013 with the emergence of massive connections. While the number of nodes increased by only 24 during this time, the number of edges increased from 181 to 346. This evolution indicates that previously unrelated nodes started to connect with each other. By 2016, the number of nodes and edges increased to 205 and 1457, respectively. More foreign places were cited (up to 12). Without exception, these foreign nodes were technologically advanced regions located in Western Europe (Germany, the UK, and France) and in North America (the US and Canada). Although the number of nodes increased by the same number as in the previous time period, the network doubled its average degree centrality () compared to 2013.
In general, there is a significant growth in each network indicator from 2000–2016. The increase in the number of nodes indicates that more cities had participated in the AI R&D activity. While edges, whether domestic or international, increased rapidly over the study period, we find that the AI inventors cited domestic patents more frequently over the more recent years. In addition, the average degree centrality increased from 0.89 in 2000 to 6.71 in 2016, which shows that the connection choices of nodes became richer. This result also implies that cities are not bounded to their original citation path, they are willing to cite from new technologically-advanced regions. Besides, the increasing average clustering coefficient indicates the level of network cohesiveness was enhanced [53], which suggests a growing network connectivity and a network becoming more mature.
Although the network matured over the study period, the development of the network is unevenly spread across nodes. Based on Figure 1, we find that the majority of nodes had connected with few hubs in 2016. This result is confirmed by a Gini coefficient of 0.680 and a coefficient of variation (CV) of 1.693 for in 2016. As for the other two centrality indices, the Gini coefficient of reached 0.942, and the CV was 4.687 in 2016. The Gini coefficient of was close to 0.890, and the CV was 6.309 in the same year. These two indicators suggest that the high values of , , and are mostly occurring in the minority nodes. In addition, in 2016, newly created patents in China cited past German patents 44,103 times, an amount that was far larger than the sum of citations of other foreign countries or institutions (5124 times).
Table 2 lists the top 10 areas for each centrality index and selected year. It is worth noting that not all nodes with a high presented a high value in at the same time, which indicates that not all active nodes played a major role in information transmission. De Prato and Nepelski (2012) claim that there is a strong correlation between and [20]. In our case, however, nodes with high values of do not always display high values of , which demonstrates that nodes have diverse connection properties. This result helps us identify two kinds of nodes: the first type corresponds to nodes with a high but a low at the beginning of the period, which tend to expand their linking target. The second type is nodes with a low but a high . These are nodes that focus on intensifying their strength of existing linkages. As the network develops, the former type experiences a decrease in the value of . This behavior is verified in Table 2 which reports how several nodes that appear in the top list of cities based on but not based on in 2011 fell off from the top list of in 2013 and 2016. These cities followed their own “innovation path dependency” [56] by sticking to cities they absorbed knowledge from in the past. However, these cities seem to have lost their competitive advantages at the end of the period. This result is consistent with observations by Rubera et al. (2016), Almirall and Casadesus-Masanell (2010), and Prabhu et al. (2005) who point out that external searches allow innovative subjects to escape path dependency and broaden their knowledge base [57,58,59]. New network connections help units enter a new innovation path and develop new products [58,59,60,61]. For instance, Shenzhen, which has had the highest since 2011, became the leader of five years later. This phenomenon indicates that absorbing diversified knowledge is more effective in the long-term development of a city than concentrating on limited resources in AI activity.

Table 2.
Centrality Indices.
3.2. Network Complexity
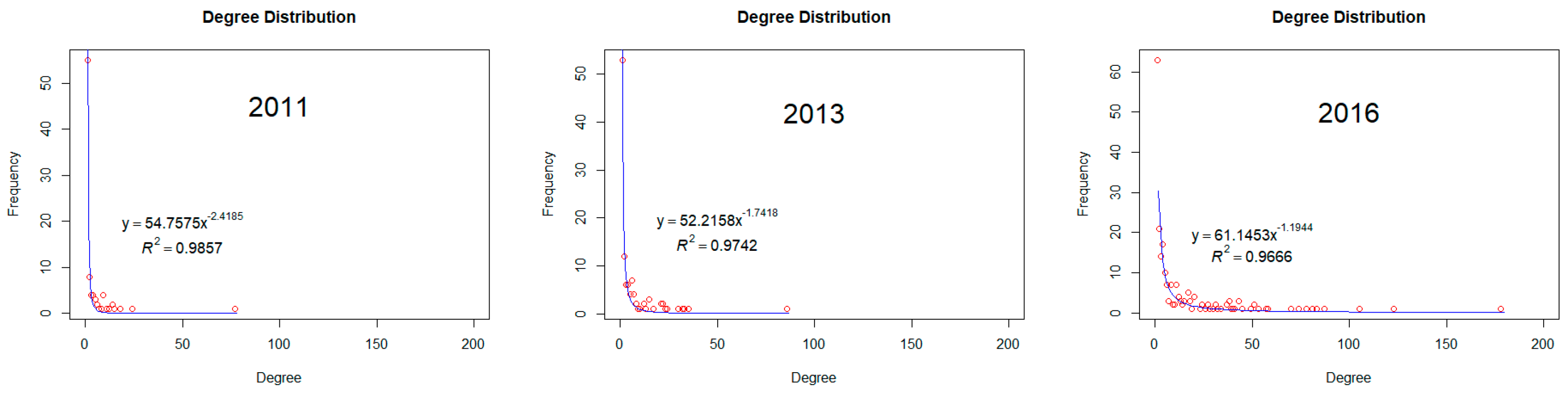
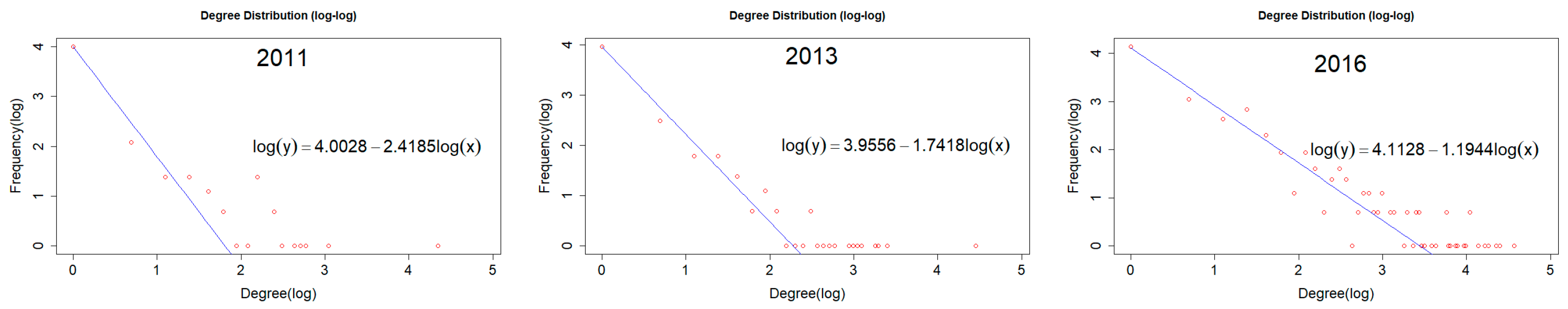
Firstly, we examine the fit of the power function described in Section 2.1.2 based on the value of nodes. Figure 2 shows the fitted curves and associated R2 values.
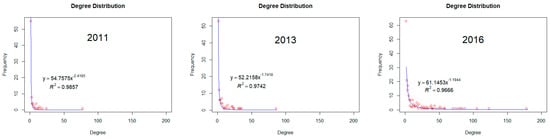

Figure 2.
Power-law function of degree distribution.
We find that the R2 values are between 0.966 and 0.986, hence indicating that the degree distribution of the Chinese AI innovation network follows the power-law function. It means that the majority of the high values of concentrate on the minority nodes and that the network holds the traits of a scale-free network. This result confirms the unbalanced development of the network described in the previous subsection. To be specific, the value of the exponent indicator k decreases from 2.418 in 2011 to 1.194 in 2016, indicating that the discrepancy of nodes in terms of has widened while the network scale expands rapidly. The value of k in 2016 is much smaller than the value in any other year, not only because the of the leading nodes had increased dramatically but also because a large number of fresh nodes with a low have emerged. It is worth noting that even if the degree distribution follows the power-law function, the result didn’t give a conclusive answer that the power-law distribution is favored over alternative distributions [62]. Since the sample size of our case, we can’t tell power-law and log-normal apart after excluding the exponential and stretched exponential or Weibull behaviors.
Secondly, Table 3 reports the correlation between the nodes’ value of and the average of their partners in 2011, 2013, and 2016. These figures are based on Equations (5) and (6).

Table 3.
Preferential attachment.
The results are positive and significant, which means that the network structure presents an assortative trait. However, the result of the weighted preferential attachment is not significant, which demonstrates that there is no obvious tendency for the nodes with high to link with nodes with the same properties. This phenomenon indicates that nodes become attractive based on the number of linkages rather than their intensity.
Furthermore, compared to a random network of the same scale, the average clustering coefficient (C2016 = 0.245) in 2016 is much larger than that of the random one (Crandom = 0.136), and the average path length of both is roughly equal (L~Lrandom). This result exhibits a “small-world behavior”, which is an optimal structure for an efficient diffusion of knowledge [63].
4. Spatial Pattern of AI Innovation Network
In the network graph (Figure 1), two nodes might appear close by based on the intensity of their relationship, even if they are located far away from each other geographically. In this section, we mix the nodes’ information with their geographical location in order to investigate the spatial pattern of the Chinese AI innovation activities.
4.1. Network Connection
Figure 3 maps the geographical distribution of the citations. There are three types of nodes that represent different levels of degree centrality across Chinese cities. The thickness and shade of the links denote the intensity of the AI patent citations.

Figure 3.
Spatial distribution of network connection.
Based on Figure 3, we recognize several domestic nodes without edges, which indicates that these cities cite foreign patents only. All the domestic nodes were insular at the beginning period. As more connections formed between domestic nodes, the citation network in 2011 and 2013 presented a quadrilateral skeleton. Meanwhile, the majority of the edges were located in the eastern part of China, especially between the Yangtze River Delta (YRD), the Pearl River Delta (PRD), and the Bohai Rim. By 2016, more interlaced and sophisticated connections appeared between cities, revealing a diamond shape. At the same time, the proportion of isolated nodes decreased significantly, which suggests an increased focus on domestic AI technology. Yet, several areas remained without nodes or links. They are mostly regions in the western and middle parts of the country as well as some sparsely populated and underdeveloped areas located elsewhere.
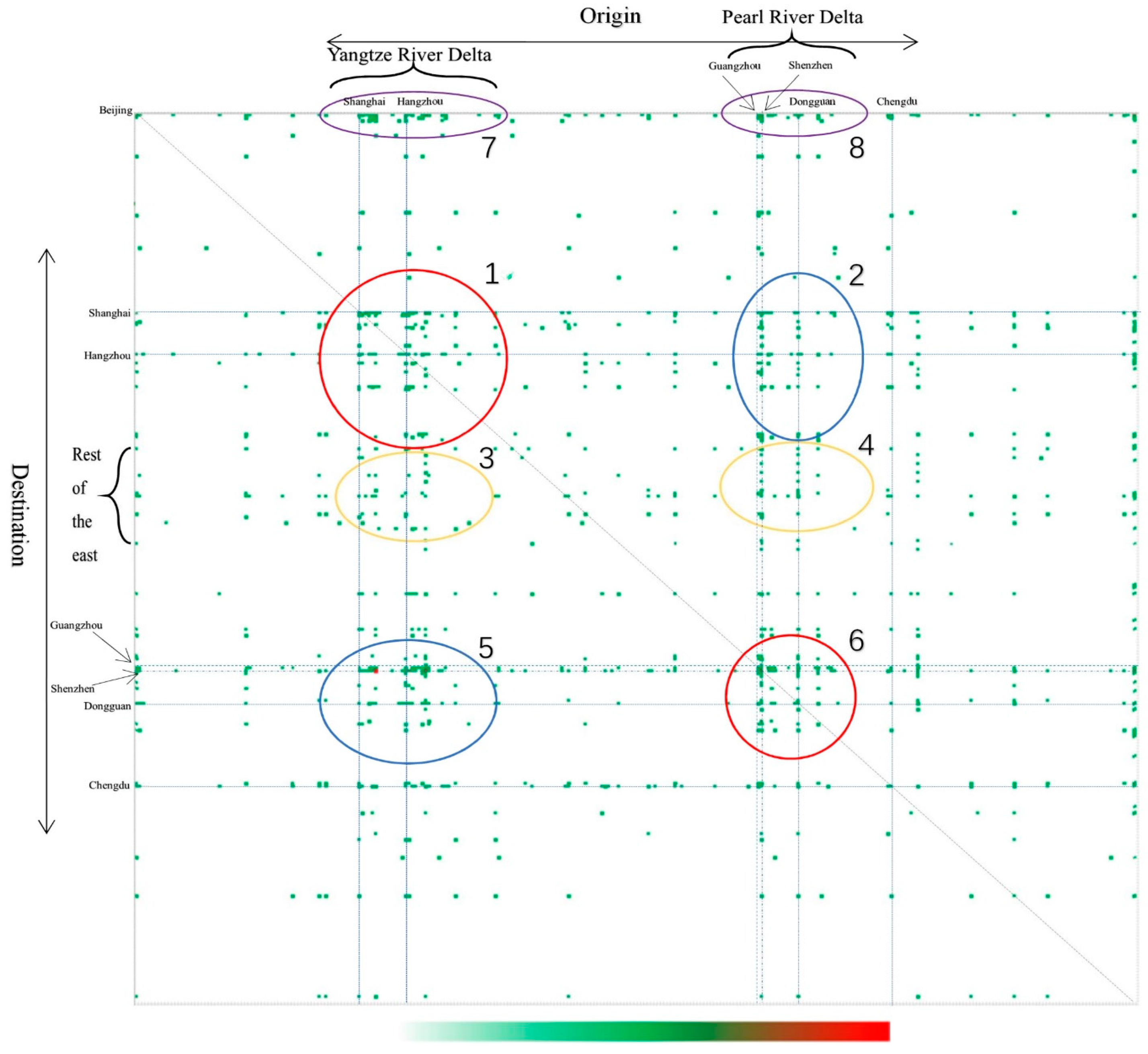
In order to investigate further the geographical distribution of the network and the directionality of the flows, Figure 4 reports the heatmap of the citation intensity for the aggregate data and the entire period. In this figure, the regions are grouped into a two-level hierarchy: 34 provinces or municipalities and 300 prefecture-level cities. The rows of the matrix indicate the origin of the citation and the columns represent the destination. The color of the elements varies from white to green to red, describing the citation intensity from low to high.

Figure 4.
Domestic Citation Matrix.
Figure 4 confirms the dominance of PRD, YRD, and the Bohai Rim described earlier in the patent network. However, these three regions have distinct link behaviors. For PRD, we find that the darker-shaded dots and the highest point density appear in Ellipse 5. It means that AI inventors in PRD favor YRD’s patents. Intra-regional citations, shown on the diagonal of the graph, are mostly present in a few places like Shenzhen and Guangzhou as indicated in Circle 6. In contrast, YRD relies mostly on local rather than remote citations due to the majority of dark-shaded cells appearing in Circle 1. While the point distribution in Circle 1 is much more homogeneous than the intra-citation of PRD (Circle 6), showing that citations inside YRD are relatively dispersed. When it comes to Bohai Rim, we note that the point density is higher in Ellipses 7 and 8 than in other places, which indicates that cities in this area tend to cite patents from YRD and PRD more often than from elsewhere in China.
From the analysis above, we can conclude that, as a whole, the Eastern region dominates the AI patent citation network in China even if the network has developed over the years. We also note that the distribution is heterogeneous in space because several AI-intensive areas display widely different characteristics. YRD focuses more on self-citation and local spillovers, while PRD and Bohai Rim focus on remote transmission. At the same time, linkages within YRD are relatively scattered compared to those within PRD which concentrates in few places. Furthermore, the intensity of the citations between regions are asymmetric. Almost all areas tend to cite more from YRD than from other regions, but the reverse is not true. Thus, the citation intensity varies by citation object and direction.
4.2. Centrality of Node
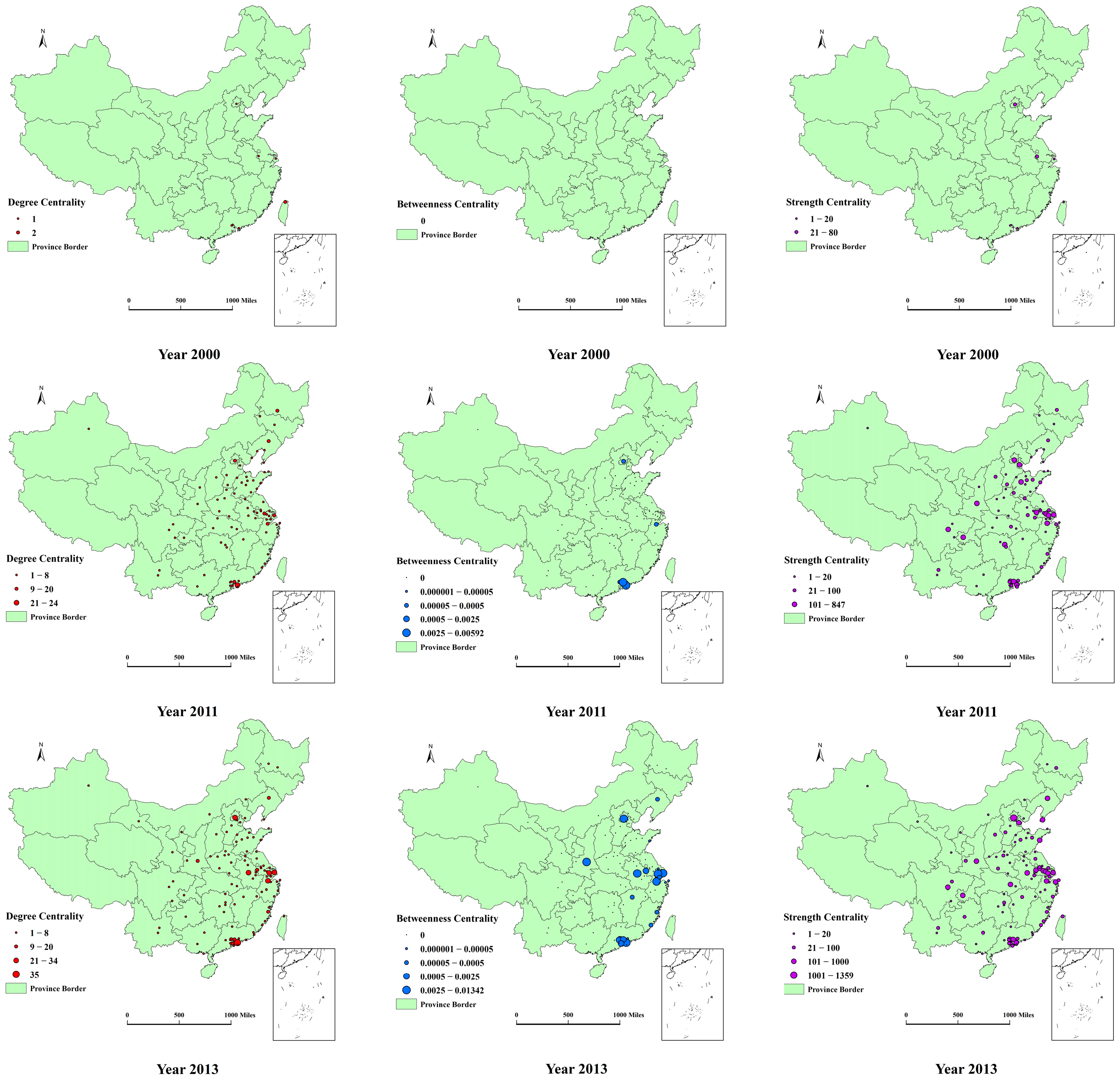
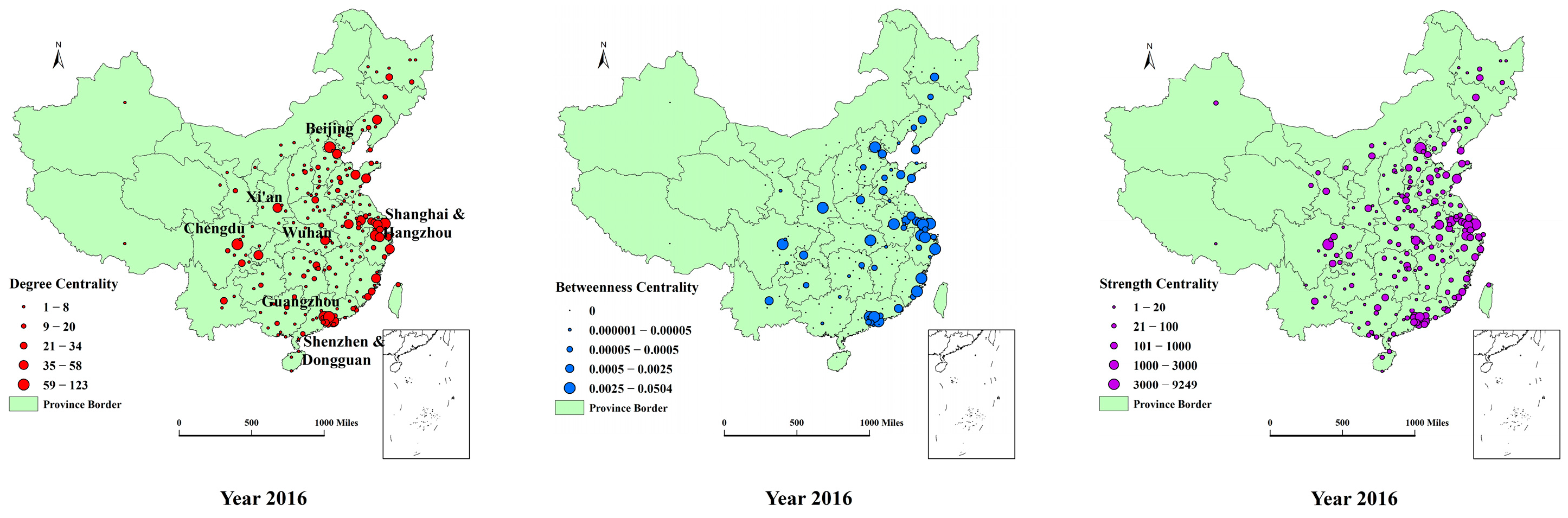
Based on Equations (1)–(3), Figure 5 shows the spatial distribution of Degree (), Betweenness (), and Strength () centrality, respectively, in 2000, 2011, 2013, and 2016. For clarity purposes, we label the core cities in the graph, and for the year 2016 only.
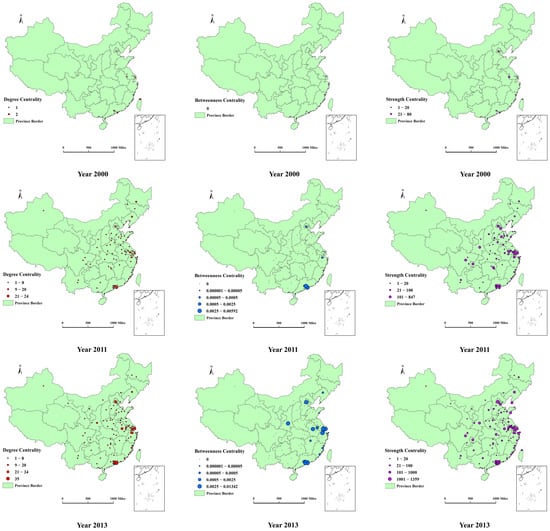

Figure 5.
The spatial distribution of Centrality.
In 2000, all the cities in the network were located in the eastern coastal region. That year Taipei was the city with the highest and it connected Germany and the US. The remaining nodes had relationships with Germany only. However, the city with the highest was Beijing, with a value of 80. At that time, the value of each city was zero because there is no interaction between domestic nodes.
By 2011, more cities had participated in the AI innovation network, including some new creative cities, such as Hangzhou and Dongguan. High values of centrality began to appear in PRD, YRD, and Bohai Rim. Shenzhen had 24 edges, which supersedes Taipei as the location with the most connected domestic node, while the highest was still Beijing, way ahead of Shanghai (2nd) and Shenzhen (3rd). In addition, we find that only five cities (Shenzhen, Dongguan, Hangzhou, Beijing, and Guangzhou) serve as an intermediary agent of the network despite the presence of almost one hundred cities in the network. They are all located in the three AI-developed areas and their value ranged from 1 × 10−4 to 6 × 10−3. The small value indicates the other nodes did not rely heavily on these five transfer stations to connect with others, which reveals that the domestic AI knowledge exchange was scarce at that time.
By 2013, it became obvious that the agglomeration of high values of centrality in PRD, YRD, and Bohai Rim had intensified. Shenzhen was leading in the value of while Beijing was holding its position in terms of . Precisely because of the rapid development, which results in the two cities becoming the major players in the transmission of information across the country’s network. In other words, Beijing ( = 9.07 × 10−3) and Shenzhen ( = 1.34 × 10−2) situated on the shortest path between many dyads. It is worth noting that Xi’an, a city located in the mid-western part of China, started to increase its role in the transmission of knowledge at the regional level. This facilitated the development of local AI around Xi’an as noted by the high value of that appeared across several mid-western cities.
By 2016, an increasing number of nodes with high centrality had concentrated in the eastern part of China, especially in terms of . The eastern coastal cities accounted for eleven of the top fifteen most connected places as determined by the value of . As such, there were nine eastern coastal cities in the top list of . It should be noted that several nodes located in the western or mid-western part of China became more active in the AI business. Here, the most prominent example is Chengdu, a city that was not active in AI during our initial period but occupied the top position across the three centrality indices by 2016, as reported in Table 2. This phenomenon led the spatial distribution of centrality to take a diamond shape. The polygon shape of the innovation network shows that numerous hubs started to emerge and close innovation relationships started to build, as one would expect from a mature network [21]. In addition, more cities became involved in the transmission of information, which improved the knowledge spillovers across cities in several local areas.
5. Conclusions
As a force driving regional development, scientific and technological innovation plays an increasingly important role in regional competitiveness and sustainable development. Past literature shows that the spatial characteristics of innovation activities are becoming a major focus in economic geography [64,65]. This article has built on patent information across Chinese AI businesses to investigate the topological structure and spatial pattern of the innovation network and knowledge spillovers at the urban level from 2000 to 2016.
Based on network indices, we find that the network’s topological structure has experienced a remarkable maturation process over the study period. It has taken the form of an expansion of the network scale and an improvement in connectivity. During this time, most of the high values were concentrated in a few nodes, demonstrating an agglomeration phenomenon that intensified over time in all centrality indices, especially in degree distribution. This pattern is supported by the decreasing exponent of the power-law function, which also shows that a large number of relations were fragile despite the increasing average degree of the network. However, even if the degree distribution follows the power-law function, it is difficult to say the power law is favored over the log-normal distribution. We also find that the degree distribution is indicative of a so-called scale-free network which is characterized by nodes that link to counterparts who possess a similar degree (assortative trait) but not a similar weighted degree. This result indicates that the main driver of connections is the number of cities that one node is linked to instead of the intensity of these relationships. This demonstrates that the innovation objects tend to connect ones who are recognized as good by all rather than just a few. This feature is identical to what Jaffe and de Rassenfosse (2017) found for the US innovation network [66]. Even if the weighted preferential attachment was not significant in our case, future research should consider it for understanding the characteristic of innovation objects in the knowledge learning process accurately. We also find that the Chinese AI network displayed a small-world feature over the course of its maturity, which could facilitate the information diffusion and exchange. In addition, the difference in the ranking of three centrality indices indicates that the key factor for nodes’ long-term development is absorbing diversified knowledge.
We also find that an increasing number of nodes with high centrality were located in the eastern part of China. Indeed, for each of the three centrality indices, the number of nodes with a high value decrease as one moves westward and the East-West gap has increased as time passes. As such, the greatest mass of intra- and inter-regional connections appeared in the eastern coastal region of China, especially in the Yangtze River Delta, the Pearl River Delta, and the Bohai Rim, so that cities located elsewhere often connect with cities from these three areas. The gap in the AI industry development increased between the eastern part of the country and the hinterland for several reasons. First, the R&D resource endowment of the eastern area is far superior to that of the other places since it was a pioneer of the Chinese reform and opening in 1978. Second, highly-skilled workers and returnees prefer to work in the eastern area [67], because the majority of the AI enterprises set up factories there. By 2016, 44.8%, 28.7%, and 16.9% of all Chinese AI businesses were located in Bohai Rim, YRD, and PRD, respectively. Nine of the top ten AI companies are located in these regions. An example is Huawei, located in Shenzhen (PRD), which created the AI chip and 5G communication, and Alibaba, located in Hangzhou (YRD), which launched Cloud computing, AI Finance, and AI transport. Third, due to its geographical location, the eastern part of China has access to advanced knowledge embedded in international trade and foreign investments [68,69]. Finally, numerous international conferences facilitating the transmission of AI knowledge, such as the World Artificial Intelligence Conference, were held in eastern cities. At the same time, our results highlight that the spatial pattern of network linkages moved from a random distribution to a quadrilateral skeleton over time. We find that the AI citation has not been constrained by the geographical distance at all, since the main citation flows occurred across hubs located far away from each other. Additionally, different regions display diverse citation properties. YRD, for example, was endocentric while PRD was extraverted.
Previous studies demonstrated the connection between AI and sustainable development, and we realize the importance of developing AI for the social, environment, and economy. Our research reveals the evolution of AI in China, which results can lead to several important innovation policy advice to develop the AI sector and support sustainable development. First, we find that one means by which citations could be improved further in the country is by expanding the means of technological exchange and cooperate more broadly. Learning from diversified sources benefits inventors as they can acquire heterogeneous knowledge, which increases the intensity of the innovative relations between cities. Second, our results indicate that a key to the expansion of the citation network has been the increase in nodes with a high value of betweenness centrality. As such, we believe that the government should focus its efforts on this type of node as it has the capacity of promoting AI developments in its surrounding areas. For the central government, they should pay more attention to cultivating more large nodes in the western area. With regards to local government, promoting innovation staff to learn advanced knowledge from the eastern area could develop AI rapidly. Third, we find that intensifying the knowledge and technology exchange with individuals from external areas can greatly promote the development of AI in China. AI is embedded in various disciplines and industries [28], while the resource endowments and industry structure are different across regions due to the vast area of China. Therefore, the grow up of the AI industry requires close inter-regional linkage and exchange. Different from the traditional innovation pattern, open innovation relies not only on internal knowledge and resources of innovation objects but on externals also [70,71,72], which can accelerate the knowledge diffusion and achieve a better innovation performance [72,73,74]. It has become an effective strategy for promoting regional economic growth and strengthening regional competitiveness [75,76,77]. Thus, it is necessary that develop AI with open innovation pattern to facilitate sustainable development of the economy in China. Finally, we believe that AI technology can accelerate China’s progress toward SDGs. However, we can not ignore the negative side of developing AI, such as individual information leakage and cyber security [28]. Thus, the fast growth of AI needs to be supported by the necessary regulatory insight and oversight of AI technologies. Otherwise, it could result in gaps in transparency, safety, and ethical standards.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.T.; methodology, M.T.; software, M.T.; formal analysis, M.T. and S.D.; resources, M.Y.; writing—original draft preparation, M.T.; writing—review and editing, M.T. and S.D.; visualization, M.T.; supervision, S.D. and M.Y.; project administration, M.T., S.D. and M.Y.; funding acquisition, M.Y. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 71303152).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data can be provided upon request from the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
We are grateful for the comments from William Ridley of University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign which will have greatly improved the quality of the manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Ahmad, M.; Chandio, A.A.; Solangi, Y.A.; Shah, S.A.A.; Shahzad, F.; Rehman, A.; Jabeen, G. Dynamic interactive links among sustainable energy investment, air pollution, and sustainable development in regional China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 1502–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halkos, G.; Argyropoulou, G. Using environmental indicators in performance evaluation of sustainable development health goals. Ecol. Econ. 2022, 192, 107263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Y.; Liu, L.; Wang, J.; Ran, Q.; Yang, X.; Shen, J. Assessing the Impact of the National Sustainable Development Planning of Resource-Based Cities Policy on Pollution Emission Intensity: Evidence from 270 Prefecture-Level Cities in China. Sustainability 2021, 13, 7293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, A.; Ahmed, M.; Raza, S.A.; Ali, S. A threshold approach to sustainable development: Nonlinear relationship between renewable energy consumption, natural resource rent, and ecological footprint. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 295, 113073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romer, P.M. Increasing Returns and Long-Run Growth. J. Polit. Econ. 1986, 94, 1002–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crescenzi, R. Innovation and Regional Growth in the Enlarged Europe: The Role of Local Innovative Capabilities, Peripherality, and Education. Growth Chang. 2005, 36, 471–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laperche, B.; Liu, Z. SMEs and knowledge-capital formation in innovation networks: A review of literature. J. Innov. Entrep. 2013, 2, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toivanen, H.; Ponomariov, B. African regional innovation systems: Bibliometric analysis of research collaboration patterns 2005–2009. Scientometrics 2011, 88, 471–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peri, G. Determinants of Knowledge Flows and Their Effect on Innovation. Rev. Econ. Stat. 2005, 87, 308–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powell, W.W.; Koput, K.W.; Smith-Doerr, L. Interorganizational collaboration and the locus of innovation: Networks of learning in biotechnology. Adm. Sci. Q. 1996, 41, 116–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griliches, Z. The Search for R&D Spillovers. Scand. J. Econ. 1992, 94, S29–S47. [Google Scholar]
- Freeman, C. Networks of innovators: A synthesis of research issues. Res. Policy 1991, 20, 499–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaffe, A.B.; Trajtenberg, M.; Henderson, R. Geographic Localization of Knowledge Spillovers as Evidenced by Patent Citations. Q. J. Econ. 1993, 108, 577–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurseth, P.B.; Verspagen, B. Knowledge Spillovers in Europe: A Patent Citations Analysis. Scand. J. Econ. 2002, 104, 531–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, M.M.; Scherngell, T.; Jansenberger, E. The Geography of Knowledge Spillovers between High-Technology Firms in Europe: Evidence from a Spatial Interaction Modeling Perspective. Geogr. Anal. 2006, 38, 288–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaffe, A.B.; Trajtenberg, M. Patents, Citations, and Innovations: A Window on the Knowledge Economy; The MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Adams, J.D. Comparative localization of academic and industrial spillovers. J. Econ. Geogr. 2002, 2, 253–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Noni, I.; Orsi, L.; Belussi, F. The role of collaborative networks in supporting the innovation performances of lagging-behind European regions. Res. Policy 2018, 47, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ter Wal, A.; Boschma, R. Applying Social Network Analysis in Economic Geography: Framing Some Key Analytic Issues. Ann. Reg. Sci. 2009, 43, 739–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Prato, G.; Nepelski, D. Global technological collaboration network. Network analysis of international co-inventions. J. Technol. Transf. 2014, 39, 358–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.D.; Wei, Y.D.; Wang, T. Spatial and temporal evolution of urban innovation network in China. Habitat Int. 2015, 49, 484–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breschi, S.; Lissoni, F. Mobility of skilled workers and co-invention networks: An anatomy of localized knowledge flows. J. Econ. Geogr. 2009, 9, 439–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ter Wal, A.L.J. The dynamics of the inventor network in German biotechnology: Geographic proximity versus triadic closure. J. Econ. Geogr. 2013, 14, 589–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, J.; Yan, Y.; Zhang, J.J. The impact of collaboration and knowledge networks on citations. J. Informetr. 2017, 11, 407–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.C.; Sung, H.Y.; Chen, D.Z.; Huang, M.H. Strong ties and weak ties of the knowledge spillover network in the semiconductor industry. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2017, 118, 114–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anselin, L.; Varga, A.; Acs, Z. Geographical spillovers and university research: A spatial econometric perspective. Growth Chang. 2000, 31, 501–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansfield, E. Academic research underlying industrial innovations: Sources, characteristics, and financing. Rev. Econ. Stat. 1995, 77, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinuesa, R.; Azizpour, H.; Leite, I.; Balaam, M.; Dignum, V.; Domisch, S.; Felländer, A.; Langhans, S.D.; Tegmark, M.; Nerini, F.F. The role of artificial intelligence in achieving the Sustainable Development Goals. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mhlanga, D. Artificial Intelligence in the Industry 4.0, and Its Impact on Poverty, Innovation, Infrastructure Development, and the Sustainable Development Goals: Lessons from Emerging Economies? Sustainability 2021, 13, 5788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordan, M.I.; Mitchell, T.M. Machine learning: Trends, perspectives, and prospects. Science 2015, 349, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Guo, S.; Huang, H.; Liu, W.; Xiang, Y. Information and Communications Technologies for Sustainable Development Goals: State-of-the-Art, Needs and Perspectives. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2018, 20, 2389–2406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palomares, I.; Martínez-Cámara, E.; Montes, R.; García-Moral, P.; Chiachio, M.; Chiachio, J.; Alonso, S.; Melero, F.J.; Molina, D.; Fernández, B.; et al. A panoramic view and swot analysis of artificial intelligence for achieving the sustainable development goals by 2030: Progress and prospects. Appl. Intell. 2021, 51, 6497–6527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Zhu, W.; Tsai, F.S. Social Responsibility toward the Employees and Career Development Sustainability during Manufacturing Transformation in China. Sustainability 2019, 11, 4778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.; Feng, X.; Jin, Z. Sustainable development of China’s smart energy industry based on artificial intelligence and low-carbon economy. Energy Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 243–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.J.; Oh, H. A Study on the Deduction and Diffusion of Promising Artificial Intelligence Technology for Sustainable Industrial Development. Sustainability 2020, 12, 5609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, J.; Liu, N. Exploitative and exploratory innovations in knowledge network and collaboration network: A patent analysis in the technological field of nano-energy. Res. Policy 2016, 45, 97–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, M.M.; Scherngell, T.; Jansenberger, E. Geographic localisation of knowledge spillovers: Evidence from high-tech patent citations in Europe. Ann. Reg. Sci. 2009, 43, 839–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maggioni, M.A.; Uberti, T.E.; Usai, S. Treating Patents as Relational Data: Knowledge Transfers and Spillovers across Italian Provinces. Ind. Innov. 2011, 18, 39–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, D.; Dall’erba, S. An Examination of the Role of Local and Distant Knowledge Spillovers on the US Regional Knowledge Creation. Int. Reg. Sci. Rev. 2016, 39, 355–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.T.; Fang, C.L.; Pang, B.; Wang, S.J. Structure of Chinese city network as driven by technological knowledge flows. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2015, 25, 498–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Euler, L. Leonhard Euler and the Koenigsberg bridges. Sci. Am. 1953, 189, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amstutz, P. Théorie des graphes et ses applications deC. Berge. Ann. Telecommun. 1961, 16, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponds, R.; Van Oort, F.; Frenken, K. The geographical and institutional proximity of research collaboration. Pap. Reg. Sci. 2007, 86, 423–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varga, A.; Parag, A. Academic knowledge transfers and the structure of international research networks. In University Knowledge Transfers Regional Development: Geography, Entrepreneurship Policy; Edward Elgar Publishers: Northampton, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Alderson, A.S.; Beckfield, J.; Sprague-Jones, J. Intercity Relations and Globalisation: The Evolution of the Global Urban Hierarchy, 1981–2007. Urban Stud. 2010, 47, 1899–1923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisingerich, A.B.; Bell, S.J.; Tracey, P. How can clusters sustain performance? The role of network strength, network openness, and environmental uncertainty. Res. Policy 2010, 39, 239–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neal, R.M. MCMC using Hamiltonian Dynamics. In Handbook of Markov Chain Monte Carlo; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Freeman, L.C. Centrality in social networks conceptual clarification. Soc. Netw. 1978, 1, 215–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasserman, S.; Faust, K. Social Network Analysis: Methods and Applications; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Albert, R.; Barabási, A.L. Statistical mechanics of complex networks. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2002, 74, 47–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strogatz, S.H. Exploring complex networks. Nature 2001, 410, 268–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, C.S.; Leydesdorff, L. Network structure, self-organization, and the growth of international collaboration in science. Res. Policy 2005, 34, 1608–1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barabási, A.L.; Albert, R. Emergence of scaling in random networks. Science 1999, 286, 509–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, M.E.J. Assortative Mixing in Networks. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2002, 89, 208701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chabchoub, N.; Niosi, J. Explaining the propensity to patent computer software. Technovation 2005, 25, 971–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coombs, R.; Hull, R. ‘Knowledge management practices’ and path-dependency in innovation. Res. Policy 1998, 27, 237–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubera, G.; Chandrasekaran, D.; Ordanini, A. Open innovation, product portfolio innovativeness and firm performance: The dual role of new product development capabilities. J. Acad. Mark. Sci. 2016, 44, 166–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almirall, E.; Casadesus-Masanell, R. Open versus closed innovation: A model of discovery and divergence. Acad. Manag. Rev. 2010, 35, 27–47. [Google Scholar]
- Prabhu, J.C.; Chandy, R.K.; Ellis, M.E. The impact of acquisitions on innovation: Poison pill, placebo, or tonic? J. Mark. 2005, 69, 114–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahuja, G.; Katila, R. Technological acquisitions and the innovation performance of acquiring firms: A longitudinal study. Strateg. Manag. J. 2001, 22, 197–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laursen, K.; Salter, A. Open for innovation: The role of openness in explaining innovation performance among UK manufacturing firms. Strateg. Manag. J. 2006, 27, 131–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clauset, A.; Shalizi, C.R.; Newman, M.E.J. Power-Law Distributions in Empirical Data. SIAM Rev. 2009, 51, 661–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowan, R.; Jonard, N. Network structure and the diffusion of knowledge. J. Econ. Dyn. Control. 2004, 28, 1557–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howells, J. Tacit Knowledge, Innovation and Economic Geography. Urban Stud. 2002, 39, 871–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howells, J.; Bessant, J. Introduction: Innovation and economic geography: A review and analysis. J. Econ. Geogr. 2012, 12, 929–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaffe, A.B.; de Rassenfosse, G. Patent citation data in social science research: Overview and best practices. J. Assoc. Inf. Sci. Tech. 2017, 68, 1360–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Guo, Y.; Liu, Y. High-level talent flow and its influence on regional unbalanced development in China. Appl. Geogr. 2018, 91, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chien, S.S.; Gordon, I. Territorial Competition in China and the West. Reg. Stud. 2008, 42, 31–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crescenzi, R.; Rodríguez-Pose, A.; Storper, M. The territorial dynamics of innovation in China and India. J. Econ. Geogr. 2012, 12, 1055–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naqshbandi, M.M.; Kamel, Y. Intervening role of realized absorptive capacity in organizational culture–open innovation relationship: Evidence from an emerging market. J. Gen. Manag. 2017, 42, 5–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huizingh, E. Open innovation: State of the art and future perspectives. Technovation 2011, 31, 2–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flor, M.L.; Cooper, S.Y.; Oltra, M.J. External knowledge search, absorptive capacity and radical innovation in high-technology firms. Eur. Manag. J. 2018, 36, 183–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parida, V.; Westerberg, M.; Frishammar, J. Inbound open innovation activities in high-tech SMEs: The impact on innovation performance. J. Small Bus. Manag. 2012, 50, 283–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eppinger, E. How Open Innovation Practices Deliver Societal Benefits. Sustainability 2021, 13, 1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Thomas, V. Inter-country R&D efficiency analysis: An application of data envelopment analysis. Scientometrics 2008, 76, 483–501. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Huang, M.; Wang, H.; Lei, M.; Zhu, D.; Ren, J.; Jabeen, M. International collaboration activity index: Case study of dye-sensitized solar cells. J. Informetr. 2014, 8, 854–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Li, Y.; Li, J.; Chesbrough, H. When do latecomer firms undertake international open innovation: Evidence from China. Glob. Strateg. J. 2022, 12, 31–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).