Abstract
Wastewater sludge is used as an alternative fuel due to its high organic content and calorific value. However, influent characteristics and operational practices of wastewater treatment plants (WWTPs) can increase the sulfur content of sludge, devaluing it as a fuel. Thus, we investigated the biochemical mechanisms that elevate the sulfur content of sludge in a full-scale industrial WWTP receiving wastewater of the textile dyeing industry and a domestic WWTP by monitoring the sulfate, sulfur, and iron contents and the biochemical transformation of sulfate to sulfur in the wastewater and sludge treatment streams. A batch sulfate reduction rate test and microbial 16S rRNA and dsrB gene sequencing analyses were applied to assess the potential and activity of sulfate-reducing bacteria and their effect on sulfur deposition. This study indicated that the primary clarifier and anaerobic digester prominently reduced sulfate concentration through biochemical sulfate reduction and iron–sulfur complexation under anaerobic conditions, from 1247 mg/L in the influent to 6.2~59.8 mg/L in the industrial WWTP and from 46.7 mg/L to 0~0.8 mg/L in the domestic WWTPs. The anaerobic sludge, adapted in the high sulfate concentration of the industrial WWTP, exhibited a two times higher specific sulfate reduction rate (0.13 mg SO42−/gVSS/h) and sulfur content (3.14% DS) than the domestic WWTP sludge. Gene sequencing analysis of the population structure of common microbes and sulfate-reducing bacteria indicated the diversity of microorganisms involved in biochemical sulfate reduction in the sulfur cycle, supporting the data revealed by chemical analysis and batch tests.
1. Introduction
Wastewater sludge is an inevitable by-product of wastewater treatment plants (WWTP), occurring in solid, semisolid, or slurry forms, which are disposed of into the ambient environment after treatment [1]. The wastewater sludge consists primarily of water (80%), inorganics and organics, microorganisms, biological macromolecules, heavy metals (e.g., As, Fe, Zn, and Pb), and toxic organic compounds that threaten human health and the ecosystem if handled inappropriately [2]. The production of wastewater sludge has increased due to the expansion of sewer networks and treatment systems under industrialization and urbanization [2,3]. The proper handling of wastewater sludge is one of the most urgent issues to ensure the sustainable operation of the entire wastewater system.
The treatment and disposal of wastewater sludge account for 50% of the total operational cost of a WWTP; thus, it is essential to optimize its treatment to reduce operational costs and harmful effects on the environment [4,5]. The main routes of sludge disposal are landfilling; incineration; and other land-based applications, such as soil reinforcement, amendment, and buffering [6]. The disposal of sewage sludge by landfilling has historically been the predominant method because of its simplicity and low cost; however, a shortage of landfill sites threatens human health and the ecosystem if waste is improperly handled [7]. Incineration and land-based applications (e.g., composting) are undesirable because they have the potential to release toxic pollutants (e.g., heavy metals and dioxins) into the ambient environment. Hence, recycling wastewater sludge should be encouraged as an economical and eco-friendly method of treating and disposing of wastewater sludge. Wastewater sludge can be recycled as an energy resource, generating power and heat, and soil fertilizers, providing nutrients (i.e., N and P) and organic matter [6,8,9].
Wastewater sludge is considered a renewable energy source owing to its high potential as a fuel, economic feasibility, and various social and environmental benefits, producing fewer greenhouse gas emissions than fossil fuels [3,10]. For example, for the same amount of heat or energy production, using wastewater sludge as a fuel reduces greenhouse gas emissions by 58% compared to natural gas and by 80% compared to coal or kerosene [10]. Because the calorie content of WWTP sludge is comparable to that of lignite, it has a high potential as an alternative fuel source [11]. In practice, semi-dried sludge cake is pelletized for easy operation and efficient energy recovery [12]. Although wastewater sludge is a good energy source, it should be autothermic and innoxious in applications [13]. Noxious by-products (e.g., NOX, SOX, heavy metals, toxic trace elements, and dioxins) present in some wastewater sludges might diffuse into ambient environments [14]. Therefore, the chemical composition of WWTP sludge and its combustion properties (e.g., calorie and ignition temperature) are crucial for the potential use of sludge as a fuel source.
Sulfur in wastewater sludge is considered one of the most critical elements when sludge is used for combustion or co-combustion with other fuels [15]. Upon combustion, sulfur compounds turn into gaseous oxides of sulfur (SOX), contributing to air pollution and acid rain. [16]. Sulfur is a common element in wastewater sludge and exists as organic (e.g., ester-bonded or carbon-bonded) and inorganic (e.g., sulfates or metal sulfides) compounds [16]. Some industrial or mining wastewater with high sulfate concentrations can eventually cause a high sulfur content in the wastewater sludge. Sulfate-reducing bacteria (SRB) transform sulfate (SO42−) in wastewater into gaseous or ionic sulfides (H2S, HS−, and S2−) while competing with methane-producing archaea and homoacetogenic bacteria for common substrates in an anaerobic digester [17]. Furthermore, high metal concentrations in the anaerobic digester result in insoluble metal sulfide complexes that increase the sulfur content of the sewage sludge cake [18,19]. Ferric chloride is often used as a metal coagulant to precipitate phosphorous and enhance sludge dewaterability in WWTPs [20]. If the dose of the ferric chloride matches the stoichiometric requirement for phosphorous removal and sludge dewatering, ferric ions remain at a small number in the solution to bind the sulfide ions, which are then released as the gaseous hydrogen sulfide. However, ferric chloride is usually overdosed in operational practices, and therefore excessive ferric ions may combine with sulfide ions and form insoluble black precipitates, such as FeS or Fe2S3, in the WWTP sludge [16]. Accumulation of these Fe-S precipitates elevates the sulfur content of the WWTP sludge and devalue the sludge cake as an energy resource.
The sulfur content in the sludge determines the applicability of wastewater sludge as a fuel and is closely correlated with the chemical characteristics of influent wastewater (e.g., sulfate concentration) and the operational practices of a WWTP (e.g., application of metal-containing coagulants). Thus, this study aims to investigate the fate and transformation of sulfate to sulfides or metal–sulfur composites in WWTPs by examining the plant-wide distribution of the concentrations of SO42−, S, and Fe in wastewater and sludge treatment streams. Additionally, the anaerobic digester sludge was subjected to a batch kinetic test to measure the sulfate-reducing rate, alongside a microbial 16S rRNA and dsrB gene sequencing study to correlate the sulfate-reducing rate with SRB abundance and activity. The application of these methods to the experimental and control systems that are an industrial WWTP receiving large quantities of sulfate and a domestic WWTP, respectively, could elucidate the mechanisms of excessive sulfur deposition in wastewater sludge. Although the WWTP sludge as an alternative fuel source becomes popular as a part of carbon neutrality action, excessive sulfur deposition in the sludge, which is an obstacle in practical applications, has not been investigated in earlier studies. In particular, investigation on the mechanisms of sulfur reduction and deposition have not been performed in a full-scale WWTP. This study thus aimed to elucidate the biochemical processes causing excessive sulfur deposition throughout the full-scale industrial and domestic WWTPs. The findings of this study will eventually lead to better utilization of wastewater sludge as an alternative energy source and benefit society.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Site Description
An industrial wastewater treatment plant (IWWTP) and a domestic wastewater treatment plant (DWWTP) in Daegu Metropolitan City, South Korea, were selected as the experimental and control systems, respectively. The IWWTP (the experimental system) receives wastewater from the Daegu Dyeing Industrial Complex, which contains a high sulfate concentration (SO42−) and organics. Before discharge from the industrial complex to the IWWTP, wastewater with a high pH was neutralized by adding a large quantity of sulfuric acid (H2SO4). The DWWTP primarily receives domestic wastewater with a low sulfate concentration.
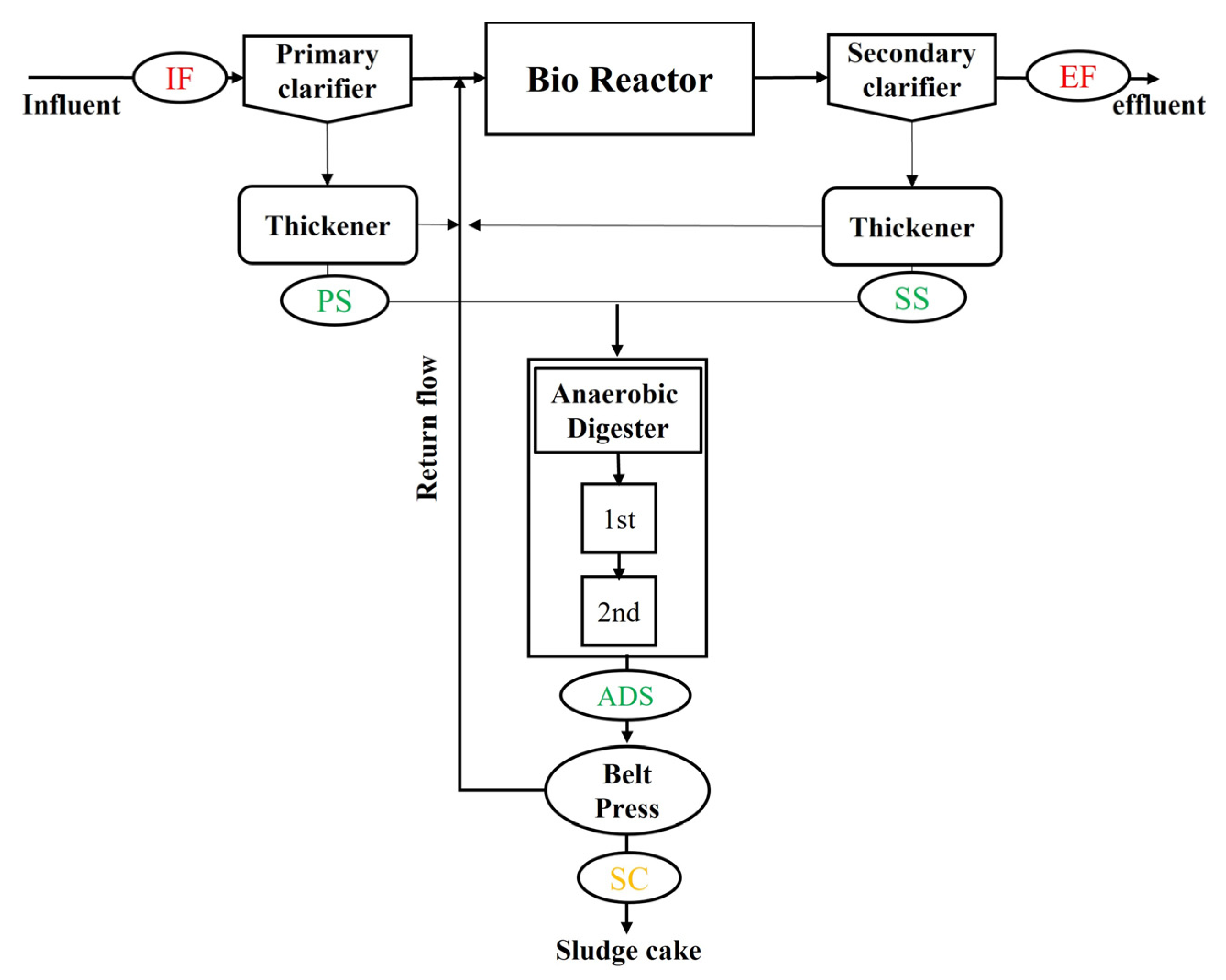
Both the IWWTP and the DWWTP were equipped with conventional wastewater and sludge treatment processes (Figure 1). The wastewater treatment plants consisted of a grit chamber, primary clarifier, bioreactor, and secondary clarifier. An additional coagulation process was applied to remove residual phosphorous, and ferric chloride (FeCl3) was administered as a coagulant. For treatment, the sludge from the primary and secondary clarifier is transferred to the sludge thickener and then to the anaerobic digester to enhance sludge volume reduction and methane gas production. The digested sludge was finally dehydrated into sludge cake by applying centrifuge and belt-press dewatering processes. Methane gas from the anaerobic digester was stored in a gas tank for energy production.
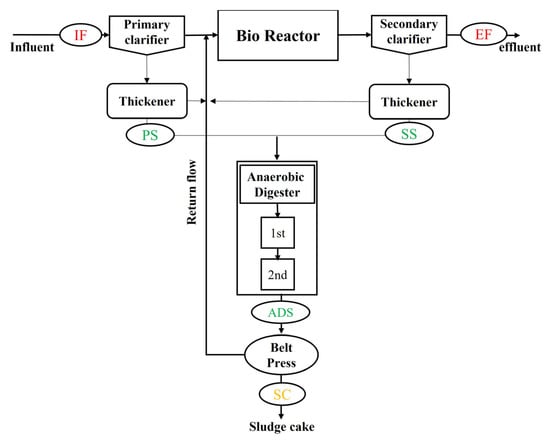
Figure 1.
Schematic diagram of the WWTPs and the sampling points of the wastewater, process water, and sludge samples. IF indicates influent wastewater, EF is effluent wastewater, PS is primary sludge, SS is secondary sludge, ADS is anaerobic digester, and SC is sludge cake.
2.2. Sampling Procedure
The wastewater and sludge samples were collected from sampling locations in the respective WWTPs and analyzed for their chemical composition (1) to investigate the plant-wise behaviors of sulfate, sulfur, and iron, and (2) to perform sulfate-reducing rate tests and microbial community analysis. As shown in Figure 1, influent and effluent wastewater samples were collected before the primary clarifier and after the secondary clarifier, denoted as IF and EF, respectively. The primary and secondary clarifier sludge samples were sampled at the discharges of the primary and secondary sludge thickeners denoted as PS and SS, respectively, and are the input of anaerobic digesters. Digested sludge was obtained at the discharge of the anaerobic digester (output ADS), and the final sludge cake (SC) was collected during the belt-press process. For each sampling location, the composite samples were collected over a certain period, which were then subject to subsequent sample analysis. The wastewater and sludge samples collected from the sampling port of each process were stored in 1 L sterilized polyethylene bottles and kept in an icebox. The samples were transported to the laboratory within 4–8 h and stored at 4 °C until further analysis.
2.3. Measurement of the Liquid Phase Sulfate and Solid Phase Sulfate and Iron
The liquid phase sulfate concentration and solid phase sulfur and iron content in the wastewater and sludge samples were quantified to examine the fate and transformation of sulfate, sulfur, and iron in the experimental and control treatment plants. The solid phase sulfur (S) and iron (Fe) contents of the sludge samples were analyzed using an inductively coupled plasma (ICP) method (Optima 7300 DV, PerkinElmer, Waltham, MA, USA). Before the analysis, the sludge samples were dried at 105 °C for 5 d. The liquid phase sulfate (SO42−) concentration in the wastewater and sludge samples was measured using an ion chromatograph (IC) (ICS-5000 Dionex, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA). The wastewater and sludge samples were filtered through a 0.45 µm in-line PES filter (Sartorius, Goettingen, Germany). The filtrates were then diluted using ASTM Type I (resistivity 18 megohm-cm) filtered and deionized water, which met the specifications for the IC measurement. The gas phase hydrogen sulfide (H2S) concentration of the sample obtained from the anaerobic digester was measured using a UV/VIS spectrometry–methylene blue method based on the Korean standard methods for air pollution (Korean Ministry of Environment, 2021). The gas phase hydrogen sulfide was absorbed in the solution with a zinc–amine complex, and color developed by methylene blue was quantified by measuring the absorbance at a wavelength of 670 nm.
2.4. Sulfate Reduction Rate (SRR) Test
The activity of SRB, as a crucial factor for the transformation of sulfate (SO42−) to sulfide (HS−, S2−) and the deposition of residual sulfur in wastewater sludge, was quantified using the sulfate reduction rate (SRR) test. Sludge samples were collected from the anaerobic digester of the experimental and control systems (IWWTP and DWWTP) and used for the SRR tests. The SRR test method of Lopez-Vazquez et al. (2016) [21] was used with modification. The sludge samples were collected in 2 L sterilized polyethylene bottles and stored in an icebox at 4 °C during transportation to the laboratory. The sludge samples were agitated for approximately 5 min at 300 rpm, and 100 mL of (NH4)2SO4 (1 g/L) stock solution was added to increase the sulfate concentration. The pH of the sludge samples was maintained constant at 7.0 by adding 200 mL of standard phosphate buffer solution (PBS). The homogenized sludge samples were carefully filled up to capacity in 50 mL serum bottles (10 bottles for each sludge sample). The serum bottles were capped tightly with rubber stoppers and aluminum crimps to ensure anaerobic conditions in the sludge samples. The serum bottles were shaken on an orbital table shaker (Daihan, Wonju, Korea) at 100 rpm for 30 min and then at 200 rpm until the completion of the test. Sludge samples were collected from the serum bottles twice a day for the 0–3 d period (6 bottles), once a day for the 4–7 d period (4 bottles), and then once every two days until the SO42− concentration became constant. The sulfate (SO42−) concentration was measured with a DR 3900 HACH spectrophotometer using SulfaVer® 4 Sulfate Reagent Powder Pillows (Hach, Loveland, CO, USA). The specific sulfate reduction rates of the sludge samples were calculated using the slope of the initial decay phase in each SRR test. The equation for calculating the specific sulfate reduction rate is as follows [21]:
where SRRSO4 is the specific sulfate reduction rate, and SO4 final and SO4 initial are the final and initial concentrations of sulfate (mg SO42−/L), respectively, in each batch activity test. Initial biomass concentration, which was determined using the HACH method (method 8164), was classified as volatile suspended solids (VSS).
2.5. Genetic Identification of Archaea, Bacteria, and Sulfate-Reducing Bacteria (SRB)
Primary, secondary (activated), and digested sludge samples were collected from the sludge treatment streams of the experimental system (IWWTP) to analyze the microbial community. Additionally, a digested sludge sample was obtained from the anaerobic digester of the control system (DWWTP). These sludge samples were collected from the sampling ports of the inlet and outlet of the anaerobic digester and stored in 1 L sterilized polyethylene bottles without headspace to maintain anaerobic conditions. The sludge samples were transported to the laboratory within 4–8 h under cold conditions using an icebox.
Archaea, bacteria, and SRB were identified using 16S rRNA and dsrB gene sequencing analysis with a high-throughput Illumina sequencing technique (Illumina MiSeq PE300 platform, Macrogen, Seoul, South Korea). Triplicate-extracted DNA from each sludge sample was mixed to minimize potential variation during the DNA extraction process. DNA was extracted using a DNeasy PowerSoil Kit (QIAGEN, Hilden, Germany) following the manufacturer’s protocol. The DNA quality was examined using gel electrophoresis (1% agarose), and the concentration and purity were further calculated using a NanoDrop 2000 instrument (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA). PCR amplification was performed using primer sets (Table 1) to amplify the 16S rRNA gene (V3–V4 region) and dsrB gene, according to previous studies [22,23,24]. Each reaction was performed in triplicate, and the primers used in this study are listed in Table 1.

Table 1.
Gene primers used for high-throughput sequencing analyses.
The raw sequences from Illumina MiSeq were assigned to samples on the basis of their unique barcode (demultiplexing) and truncated by cutting off the barcode and primer sequences using the Cutadapt (V1.9.1, http://cutadapt.readthedocs.io/en/stable/, accessed on 1 January 2021) tool. Next, quality filtering and denoising of the raw reads were performed under specific filtering conditions to obtain high-quality clean reads and merge pair-end sequences using the DADA2 plugin [25]. The amplicon sequence variants (ASVs) were resolved by removing chimeric sequences with a reference database (Silva database) on the basis of the “consensus” method. Subsequent analyses of richness indices (Chao 1 estimates), diversity indices (Shannon index), and Good’s coverage were performed. In addition, QIIME2 was used to evaluate the similarities in bacterial communities between the sludge samples using the unweighted pair group method with arithmetic mean (UPGMA) clustering based on a weighted UniFrac distance matrix. Finally, unassigned reads were grouped because they did not match any sequences in the database, whereas the reads showing below < 85% query coverage were grouped into an unclassified group. Phylogenetic analysis was performed using the sequence database obtained from National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI). Reads that did not match any sequence in the database were clustered into an unclassified group. Raw sequences of the SRA genes were submitted to the NCBI Sequence Read Archive database (reference no. PRJNA883522).
3. Results
3.1. Fate and Transformation of Sulfate, Sulfur, and Iron
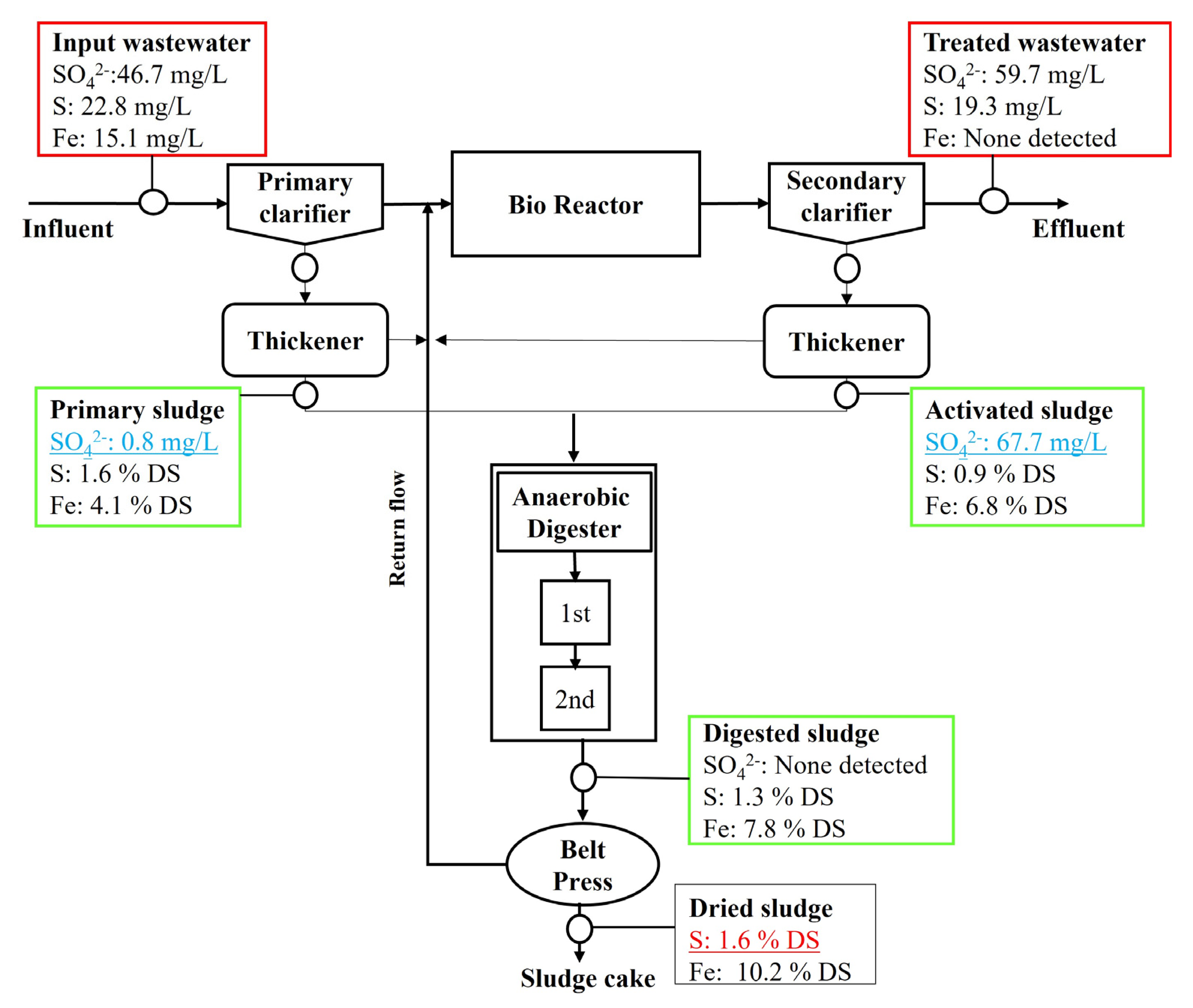
An extraordinarily high sulfate concentration in the influent wastewater of the experimental system (IWWTP) was found to elevate the sulfur content in the wastewater sludge. The sulfate concentration of the influent wastewater of the IWWTP was 1274 mg/L, which is much higher than that of common domestic wastewater, which normally ranges from 10 to 20 mg/L, but reaches up to 200 mg/L in some extreme conditions [26]. The high sulfate concentration in the IWWTP resulted in high sulfur content in the primary and digested sludges, 3.12% and 3.14% (on a total dried weight (DW) basis)), respectively (Figure 2 and Figure 3). These sulfur contents were much higher than those reported for the primary and digested sludges, which typically range from 0.3 to 0.9% and 0.8 to 2.9%, respectively [16,27]. In contrast, the lower sulfate concentration in the influent wastewater of the control system (DWWTP) resulted in relatively lower sulfur contents in the primary and digested sludges and fit within the typical sulfur content range. The sulfur contents in the dried sludges (after Belt press drying, in DW) of the experimental and control systems (IWWTP and DWWTP) were 2.7% and 1.6%, respectively.
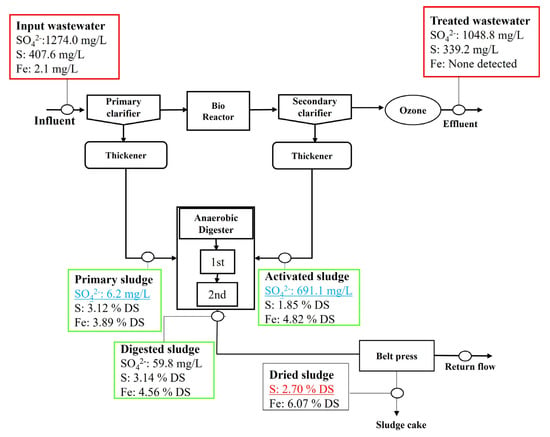
Figure 2.
Concentration of the liquid phase SO42− and solid phase S and Fe in the IWWTP streams.
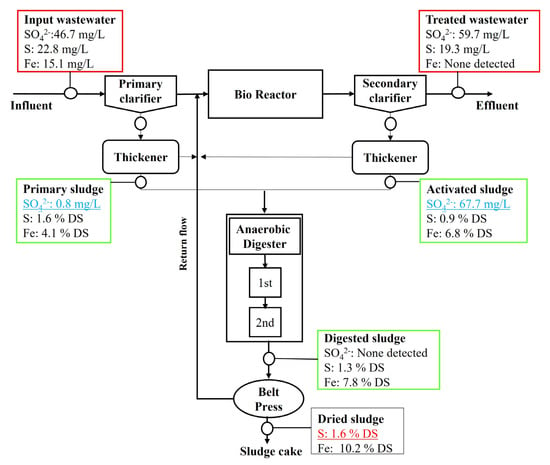
Figure 3.
Concentration of the liquid phase SO42− and solid phase S and Fe in the DWWTP streams.
In both the IWWTP and DWWTP, the primary sludge streams (clarifier and thickener) and anaerobic digester were found to act as the “sink” for sulfate in the entire system. There was a rapid decrease in the high sulfate concentration of the influent wastewater in the primary sludge stream and anaerobic digestor for both the IWWTP and the DWWTP. The sulfate concentration in the IWWTP decreased from 1274 mg/L in the influent to 6.2 and 59.8 mg/L in the primary and anaerobic digested sludges, respectively. Similarly, the sulfate concentration in the DWWTP decreased from 46.7 in the influent to 0.8 mg/L and was not detected (ND) in the primary and digested sludges. The primary sludge stream and anaerobic digester might promote anaerobic conditions in which SRB can thrive and transform sulfate into gaseous and ionic sulfides [17,18].
Iron is also a crucial element that increases the sulfur content in primary, digested, and dried sludge samples. The iron content in the sludge samples was high, ranging from 3.9 to 6.1% and from 4.1 to 10.2% (in DS) for the IWWTP and DWWTP, respectively. The iron contents in the sludge samples were higher than the reported iron contents in the previous research (1.0–6.9% in DS) [27]. In the IWWTP and DWWTP, a large quantity of FeCl3 was added to the bioreactor for phosphorus removal and the dewatering processes for sludge dehydration. Residual Fe3+ may accumulate in processed wastewater and sludge. It might combine with sulfide produced from sulfate transformation by SRB and form Fe-S precipitates under favorable anaerobic conditions (the primary sludge stream and anaerobic digester). Significantly, the excessive use of low-priced iron coagulant might promote the accumulation of iron and sulfur in the primary, digested, and dried sludge, forming Fe-S precipitates.
3.2. Sulfate Reduction Rate (SRR) Test
Accompanying the SRR test and microbial community analysis, the fate and transformation of dissolved sulfate, hydrogen sulfide gas formation, solid sulfur, and iron were also investigated in the anaerobic digester samples, as shown in Figure 4. Because SRB might thrive and function well in the primary sludge stream, the sulfate concentration in the primary sludge was reduced and maintained at a low level at 0.4 and 1.3 mg/L for the IWWTP and DWWTP, respectively. However, the secondary sludge, adapted under aerobic or facultative conditions in the bioreactor, still contained a large quantity of sulfate without substantial sulfate reduction (658 and 51 mg/L in the IWWTP and DWWTP, respectively). These large amounts of sulfate in the secondary sludge were almost completely reduced to sulfide gas (H2S) or ions (HS− or S2−) by the SRB in the anaerobic digester. As discussed in the previous section, the primary sludge stream and anaerobic digester functioned as the “sink” for SO42− and the "source" of sulfide gas (H2S) or ions (HS−, S2−). Because the gaseous H2S concentration released from the anaerobic digester was not remarkably high (36 and 0.05 ppm for IWWTP and DWWTP, respectively), most of the reduced sulfide ions (HS− or S2−) might be utilized to form the Fe-S precipitates. The improvement of Fe-S precipitation and reduction of toxic and caustic H2S is desirable to produce methane gas and maintain the anaerobic digester, but it devalues the sludge as a fuel [28,29].
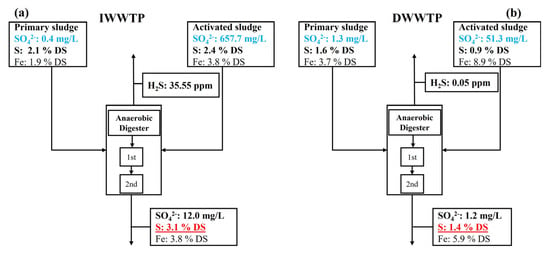
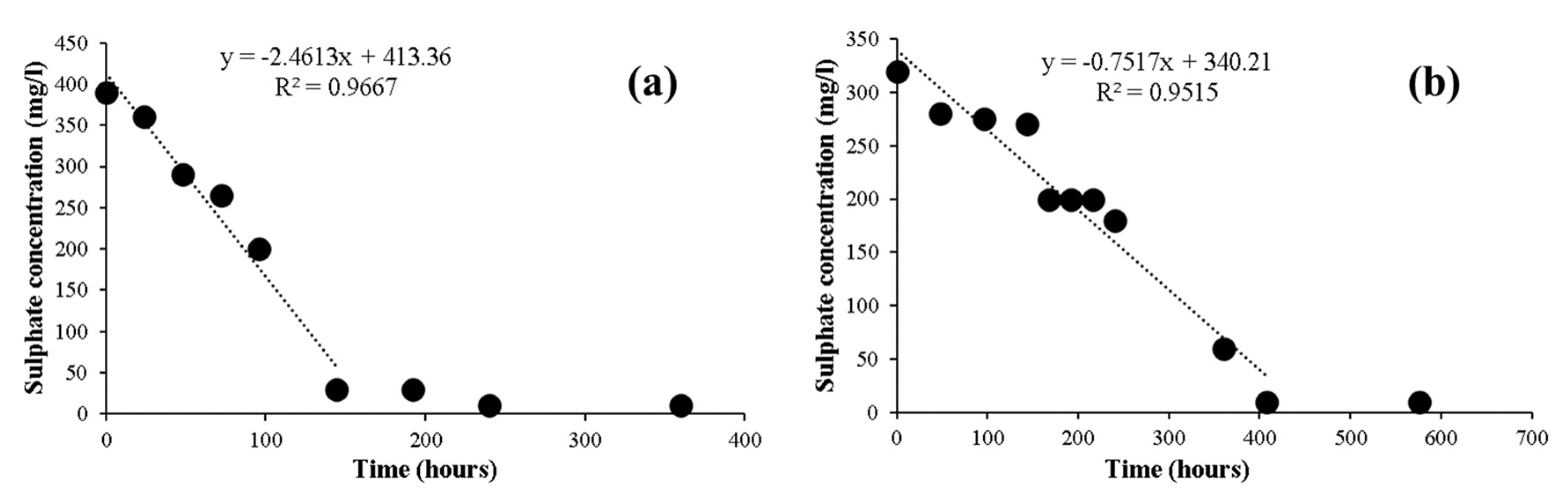
Figure 4.
Concentration of the liquid phase SO42− and solid phase S and Fe in the anaerobic digester streams of the (a) IWWTP and (b) DWWTP.
The SRR of the digested sludge of the IWWTP was much higher than that of the DWWTP, as shown in Figure 5. The sulfate concentration in the SRR test with the IWWTP digested sludge decreased steadily and stabilized after 144 h. In contrast, the SRR test with DWWTP digested sludge required 408 h to reduce sulfate concentration to the background level. On the basis of the observed slope of the initial linear decrease in the sulfate concentration, the specific SRRs of the IWWTP and DWWTP were estimated to be 0.13 mg SO42−/gVSS/h and 0.07 mg SO42−/gVSS/h, respectively. These rates are comparable to those reported in a previous study [30]. The high sulfate concentration seemed to help SRB thrive and function better in the IWWTP sludge, resulting in a higher SRR than that of the DWWTP sludge.
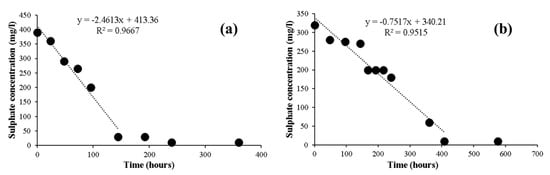
Figure 5.
Sulfate reduction rate tests using the sludges of the (a) IWWTP and (b) DWWTP: reduction of sulfate concentration versus incubation time.
3.3. Identification of Archaea and Bacteria with 16S rRNA Gene Analysis
Primary sludge (IWWTP-PS), anaerobic digester sludge (IWWTP-ADS), and secondary sludge (IWWTP-SS) were collected from the experimental system for microbial community analysis. The anaerobic digester sludge of the control system (DWWTP-ADS) was collected and analyzed as a control sample. A total of 213,903 high-quality 16S rRNA gene sequences with an average length of 410 bp were obtained from the Illumina sequencing analysis of the four sludge samples. Valid sequences were resolved into ASVs, and the data were normalized using a standard sequence number corresponding to the sample with the fewest sequences. Subsequent analyses of the microbial richness and diversity were performed using normalized data from each sample.
More than 34 prokaryotic phyla were detected in all the samples, as shown in Figure 6. Proteobacteria (10.6–36.1%), Bacteroides (11.7–22.6%), Firmicutes (2.2–15.7%), and Chloroflex (4.4–13.6%) were the core phyla, accounting for nearly 88% of the total sequences. IWWTP-SS had the highest relative abundance of Proteobacteria compared to IWWTP-PS, IWWTP-ADS, and DWWTP-ADS. In the sludge samples, three phyla (Euryarchaeota, Crenarchaeota, and Aigarchaeota) of archaea were discovered with a relative abundance of 2.4% (see Figure 6).
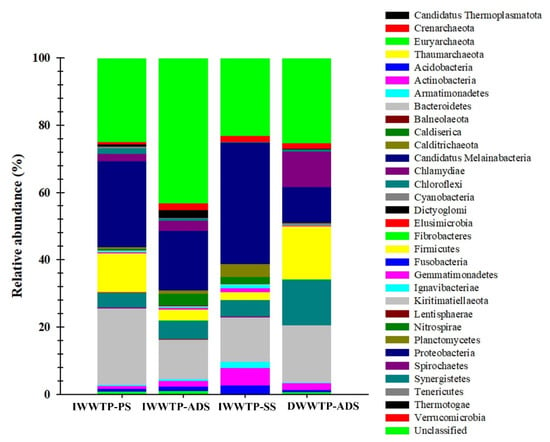
Figure 6.
16S rRNA gene-based relative abundance of microbial communities (bacteria and archaea) at the phylum levels in the sludge samples collected from the IWWTP and DWWTP.
Bacteroidetes were abundant in the IWWTP-PS sample, while Firmicutes and Chloroflex were abundant in the DWWTP-ADS sample. Figure 7 shows microbial genera with an abundance of more than 1% in at least one sample. A total of 38 genera were identified, with the IWWTP-SS sludge sample accounting for 49% (most dominant) of the assigned sequences. The most abundant genera in the samples DWWTP-ADS, IWWTP-PS, IWWTP-ADS, and IWWTP-SS were Moorrella (8.44%), Paludibacter (5.66%), Tangfeifania (2.54%), and Flavilitoribacter (3.23%), respectively (Figure 7). However, unassigned ASVs were found in all samples in the range of 23.2–43%, and were relatively abundant in IWWTP-SS. Thus, the unassigned ASVs were linked to the differences in the microbial community structure found in this study. In wastewater treatment and biogas systems, Proteobacteria, which include various aerobic, anaerobic, and facultative bacteria with different metabolism types, are typically found in the highest abundance [31,32]. Phosphorus and nitrogen removal are generally beneficial to Bacteroidetes and are associated with the hydrolysis and acetogenesis of organic materials [33]. The abundance of archaea in anaerobic digesters was consistent with previous studies that found archaea to be one of the most prevalent phyla in anaerobic digesters [34].
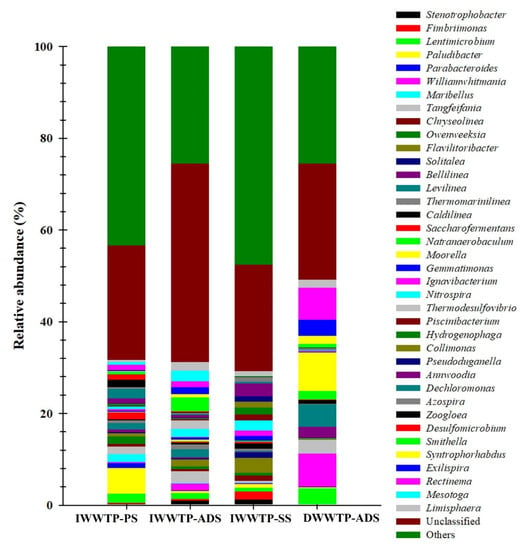
Figure 7.
16. S rRNA gene-based relative abundance of dominant genera (>1%) of microbial communities (bacteria and archaea) in the sludge samples from the IWWTP and DWWTP.
3.4. Identification of SRBs with dsrB Gene Analysis
A total of 15 families in the samples were detected, and most ASVs belonged to Desulfobacteraceae, Desulfobulbaceae, Desulfomicrobiaceae, Syntrophobacteraceae, and Desulfovibrionaceae exhibiting more than 1% abundance. In the IWWTP-PS and IWWTP-SS samples, Desulfobulbaceae (2.12 and 3.37%) and Desulfomicrobiaceae (2.12 and 2.16%) were more abundant, whereas Syntrophobacteraceae (2.26 and 2.64%) was more abundant in IWWTP-SS and DWWTP-ADS samples, respectively. Desulfovibrionaceae (2.71%) was found at relatively high abundance in the IWWTP-ADS sludge samples (Figure 8). All these assigned 15 families were also linked to 28 different genera, with Syntrophobacter (0.79–2.64%), Desulfobulbus (1.48–2.92 %), Desulfovibrio (0.37–2.64%), and Desulfomicrobium (0.14–2.16%) being the most prevalent in the samples (Figure 9).
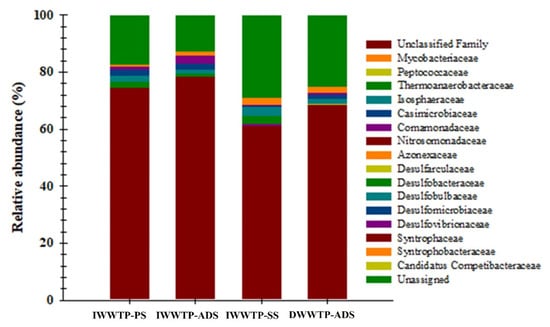
Figure 8.
dsrB gene-based relative abundance of microbial communities (bacteria and archaea) at the family levels in the sludge samples collected from the IWWTP and DWWTP.
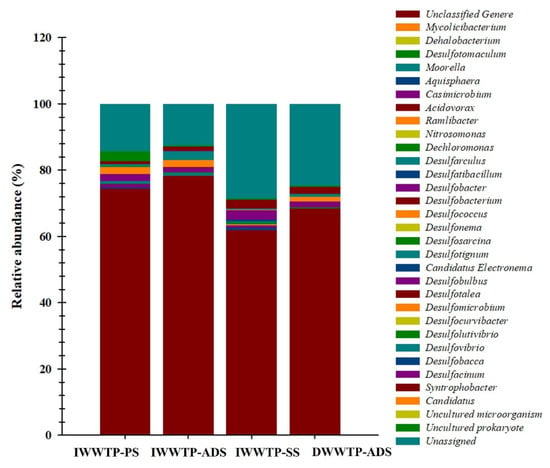
Figure 9.
dsrB gene-based relative abundance of microbial communities (bacteria and archaea) at the genus levels in the sludge samples collected from the IWWTP and DWWTP.
The principal sulfate-reducing microorganisms participating in sulfide generation in the anaerobic process are Desulfobacteraceae, Desulfobulbaceae, Desulfovibrionaceae, Desulfurellaceae, Syntrophaceae, and Syntrophobacteraceae, according to the relative abundance of SRB at the family level [35]. The UPGMA clustering technique based on weighted UniFrac distances was used to quantify the similarities and differences in the microbial communities in different sludge samples. The results of the UPGMA clustering analysis revealed similar microbial (bacteria and archaea) and SRB community structures in the IWWTP-PS and IWWTP-ADS samples (Figure 10), which could be attributed to the similar dynamic conditions between the two sampling stations. This result was in good agreement with Figure 2, which shows that the primary sludge and anaerobic digester processes played a major role in reducing the sulfate concentration.
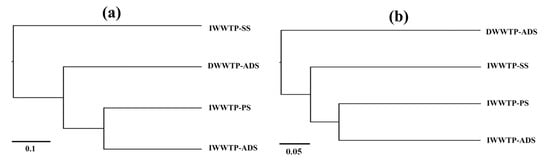
Figure 10.
The tree represents the UPGMA hierarchical clustering results of the weighted UniFrac distance matrix for the dsrB genes (a) and 16S rRNA genes (b) in sludge samples.
4. Implication
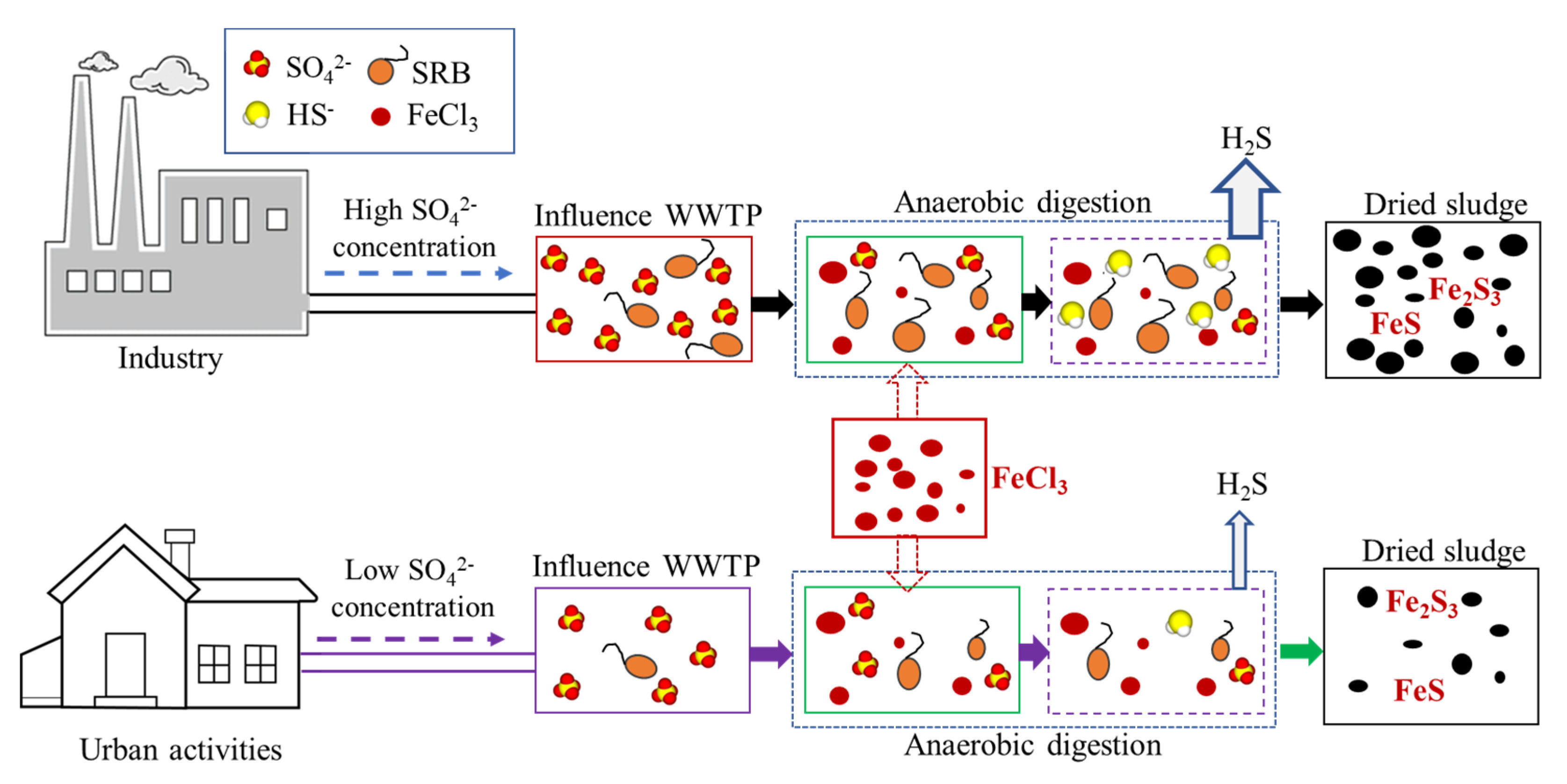
The high sulfur content in the digested and dried sludge via sulfate reduction, Fe-S complexation, and precipitation is shown in Figure 11. This schematic depicts the two distinct mechanisms of sulfate reduction and Fe-S complexation/precipitation that increased the sulfur content in the digested and dried sludge. First, a large amount of sulfate in the influent wastewater of the IWWTP promotes SRB to thrive in the primary sludge stream and anaerobic digester. A healthy microbial community of SRB with many substrates (organics and SO42−) can enhance sulfate reduction and the production of sulfide gas (H2S) and ions (HS−, S2−). Second, iron is a crucial element for increasing the sulfur content in the sludge. Iron chloride has been extensively used as an economical coagulant in industrial and domestic WWTPs to enhance phosphorus removal from wastewater and sludge dewaterability [36]. The surplus iron promotes Fe-S complexation and precipitation as insoluble black precipitates of FeS or Fe2S3 [16]. These mechanisms increase the sulfur content of digested and dried sludge in WWTPs through a synergistic effect. [36]. The complexation and precipitation of FeS or Fe2S3 would be advantageous for WWTP operation because it decreases noxious, caustic H2S gas production but devalues the sludge as a high sulfur content fuel. Operators, managers, and policymakers of WWTPs should balance the stable operation of the sludge treatment processes and quality of sludge for recycling as a fuel.
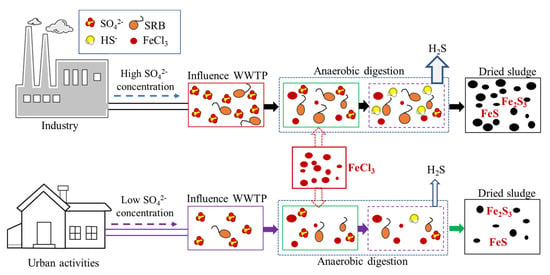
Figure 11.
Schematic diagram depicting the mechanisms of the complexation and precipitation of Fe-S composites in the digested and dried sludge.
5. Conclusions
The biochemical processes involved in increasing the sulfur content in WWTP sludge were investigated in full-scale wastewater treatment plants (IWWTP and DWWTP). The findings of this study are summarized in the following sections:
- The primary clarifier and anaerobic digester played prominent roles in reducing sulfate in the IWWTP and DWWTP because of biological sulfate reduction under anaerobic conditions.
- The activity of SRB in the IWWTP, receiving a large amount of sulfate from the dyeing industrial complex, was much higher than that in the DWWTP. The results from the batch SRR test indicated that the SRR of the IWWTP sludge was twice as high as that of the DWWTP.
- The high-throughput sequencing of the 16S rRNA and dsrB genes achieved almost complete coverage (>99%) and revealed the high diversity, richness, and number of ASV communities in both the WWTPs. The results of 16S rRNA and dsrB gene sequencing analyses also indicated the diversity of microorganisms involved in biochemical sulfate reduction in the sulfur cycle.
- Biological sulfate reduction and Fe-S complexation, induced by excessive sulfate and iron in the WWTP, were the primary causes of the high sulfur content in the WWTP sludge.
The findings of this study on the biochemical mechanisms of sulfate, sulfur, and iron will eventually help researchers find a feasible solution to minimize the sulfur content in wastewater sludge and establish practical and operational guidelines on the use of sludge as an alternative fuel source.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Q.N.H., S.P., T.-U.L., J.-Y.J., Y.-Y.C. and B.J.L.; methodology, Q.N.H., G.B.A., J.K. and B.J.L.; formal analysis, Q.N.H. and G.B.A.; investigation, Q.N.H., G.B.A., J.K., S.P. and B.J.L.; resources, T.-U.L., J.-Y.J., Y.-Y.C. and Y.-H.A.; writing—original draft, Q.N.H.; writing—review and editing, G.B.A., Y.-H.A. and B.J.L.; visualization, Q.N.H. and B.J.L.; supervision, Y.-H.A. and B.J.L.; project administration, J.K.; funding acquisition, T.-U.L., J.-Y.J. and Y.-Y.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the 2021 DEGEC Research Funding Program and the Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF), funded by the Ministry of Education (no. NRF-2020R1I1A3A04036895).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets generated and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding authors upon reasonable request.
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge the financial support of the Daegu Environmental Corporation and Daegu Green Environment Center (2021 DEGEC Research Funding Program) and the National Research Foundation of Korea (project no. NRF-2020R1I1A3A04036895).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Ahuja, S.; Larsen, M.C.; Eimers, J.L.; Patterson, C.L.; Sengupta, S.; Schnoor, J.L. Comprehensive Water Quality and Purification; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, Y.; Raheem, A.; Ding, L.; Chen, W.-H.; Chen, X.; Wang, F.; Lin, S.-L. Pretreatment, modification and applications of sewage sludge-derived biochar for resource recovery-A review. Chemosphere 2022, 287, 131969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirbas, A. Sulfur removal from crude oil using supercritical water. Pet. Sci. Technol. 2016, 34, 622–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, H. Sludge management–future issues and trends. Water Sci. Technol. 2000, 41, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rulkens, W. Sewage sludge as a biomass resource for the production of energy: Overview and assessment of the various options. Energy Fuels 2008, 22, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kacprzak, M.; Neczaj, E.; Fijałkowski, K.; Grobelak, A.; Grosser, A.; Worwag, M.; Rorat, A.; Brattebo, H.; Almås, Å.; Singh, B.R. Sewage sludge disposal strategies for sustainable development. Environ. Res. 2017, 156, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadi, P.; Xu, M.; Ning, C.; Lin, C.S.K.; McKay, G. A critical review on preparation, characterization and utilization of sludge-derived activated carbons for wastewater treatment. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 260, 895–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peccia, J.; Westerhoff, P. We should expect more out of our sewage sludge. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 8271–8276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Syed-Hassan, S.S.A.; Wang, Y.; Hu, S.; Su, S.; Xiang, J. Thermochemical processing of sewage sludge to energy and fuel: Fundamentals, challenges and considerations. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 80, 888–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Đurđević, D.; Blecich, P.; Jurić, Ž. Energy recovery from sewage sludge: The case study of Croatia. Energies 2019, 12, 1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kijo-Kleczkowska, A.; Środa, K.; Kosowska-Golachowska, M.; Musiał, T.; Wolski, K. Combustion of pelleted sewage sludge with reference to coal and biomass. Fuel 2016, 170, 141–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Feng, L.; Peng, X.; Mao, M.; Chi, Y.; Wang, F. Effect of sludge pellets addition on combustion characteristics and ash behaviour of municipal solid waste. Waste Biomass Valorization 2020, 11, 5351–5361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vatachi, N. Wastewater sludge to energy production. A review. In IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering: 2019; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2019; p. 012053. [Google Scholar]
- Leckner, B. Co-combustion: A summary of technology. Therm. Sci. 2007, 11, 5–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werther, J.; Ogada, T. Sewage sludge combustion. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 1999, 25, 55–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewil, R.; Baeyens, J.; Roels, J.; Van De Steene, B. Evolution of the total sulphur content in full-scale wastewater sludge treatment. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2009, 26, 867–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, S.V.; Rao, N.C.; Prasad, K.K.; Sarma, P. Bioaugmentation of an anaerobic sequencing batch biofilm reactor (AnSBBR) with immobilized sulphate reducing bacteria (SRB) for the treatment of sulphate bearing chemical wastewater. Process Biochem. 2005, 40, 2849–2857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elferink, S.J.O. Sulfate-Reducing Bacteria in Anaerobic Bioreactors; Wageningen University and Research: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, J.; Yao, Y.; Li, W.; Shi, K.; Ma, G.; Qiao, Y.; Cheng, D.; Jiang, Q. Insights into the effects of operating parameters on sulfate reduction performance and microbial pathways in the anaerobic sequencing batch reactor. Chemosphere 2023, 311, 137134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Jiang, G.; Wang, Q.; Yuan, Z. Role of indigenous iron in improving sludge dewaterability through peroxidation. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Vazquez, C.; Welles, L.; Lotti, T.; Ficara, E.; Rene, E.; van den Brand, T.; Brdjanovic, D.; van Loosdrecht, M. Activated sludge activity tests. In Experimental Methods In Wastewater Treatment; IWA Publishing: London, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhen, Y.; Mi, T.; He, H.; Yu, Z. Microbial diversity and community structure of sulfate-reducing and sulfur-oxidizing bacteria in sediment cores from the East China Sea. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 2133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michelsen, C.F.; Pedas, P.; Glaring, M.A.; Schjoerring, J.K.; Stougaard, P. Bacterial diversity in Greenlandic soils as affected by potato cropping and inorganic versus organic fertilization. Polar Biol. 2014, 37, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geets, J.; Borremans, B.; Diels, L.; Springael, D.; Vangronsveld, J.; van der Lelie, D.; Vanbroekhoven, K. DsrB gene-based DGGE for community and diversity surveys of sulfate-reducing bacteria. J. Microbiol. Methods 2006, 66, 194–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callahan, B.J.; McMurdie, P.J.; Rosen, M.J.; Han, A.W.; Johnson, A.J.A.; Holmes, S.P. DADA2: High-resolution sample inference from Illumina amplicon data. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado-Vela, J. Nitrogen and Sulfur Cycling during Wastewater Treatment. Ph.D. Thesis, The University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, MI, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Fisher, R.; Alvarez-Gaitan, J.P.; Stuetz, R.; Moore, S. Sulfur flows and biosolids processing: Using Material Flux Analysis (MFA) principles at wastewater treatment plants. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 198, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barton, L.L.; Fardeau, M.-L.; Fauque, G.D. Hydrogen sulfide: A toxic gas produced by dissimilatory sulfate and sulfur reduction and consumed by microbial oxidation. In The Metal-Driven Biogeochemistry of Gaseous Compounds in the Environment; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; pp. 237–277. [Google Scholar]
- Visser, A. The Anaerobic Treatment of Sulfate Containing Wastewater. Ph.D. Thesis, Wageningen University and Research, Wageningen, The Netherlands, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Lens, P.; De Poorter, M.-P.; Cronenberg, C.; Verstraete, W. Sulfate reducing and methane producing bacteria in aerobic wastewater treatment systems. Water Res. 1995, 29, 871–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.-J.; Yang, S.-F.; Li, X.-Y.; Gu, J.-D. Microbial population dynamics during aerobic sludge granulation at different organic loading rates. Water Res. 2008, 42, 3552–3560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundberg, C.; Al-Soud, W.A.; Larsson, M.; Alm, E.; Yekta, S.S.; Svensson, B.H.; Sørensen, S.J.; Karlsson, A. 454 pyrosequencing analyses of bacterial and archaeal richness in 21 full-scale biogas digesters. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2013, 85, 612–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Whitman, W.B. Metabolic, phylogenetic, and ecological diversity of the methanogenic archaea. Ann. N. Y. Acad Sci. 2008, 1125, 171–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Yu, K.; Xia, Y.; Lau, F.T.; Tang, D.T.; Fung, W.C.; Fang, H.H.; Zhang, T. Metagenomic analysis of sludge from full-scale anaerobic digesters operated in municipal wastewater treatment plants. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 98, 5709–5718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, K.; Taylor, M.W.; Turner, S.J. dsrAB-based analysis of sulphate-reducing bacteria in moving bed biofilm reactor (MBBR) wastewater treatment plants. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 98, 7211–7222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bratby, J. Coagulation and Flocculation in Water and Wastewater Treatment; IWA publishing: London, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).