Unlocking the Positive Impact of Bio-Swales on Hydrology, Water Quality, and Biodiversity: A Bibliometric Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Date and Methods
2.1. Literature Search
2.2. Data Processing
3. Results
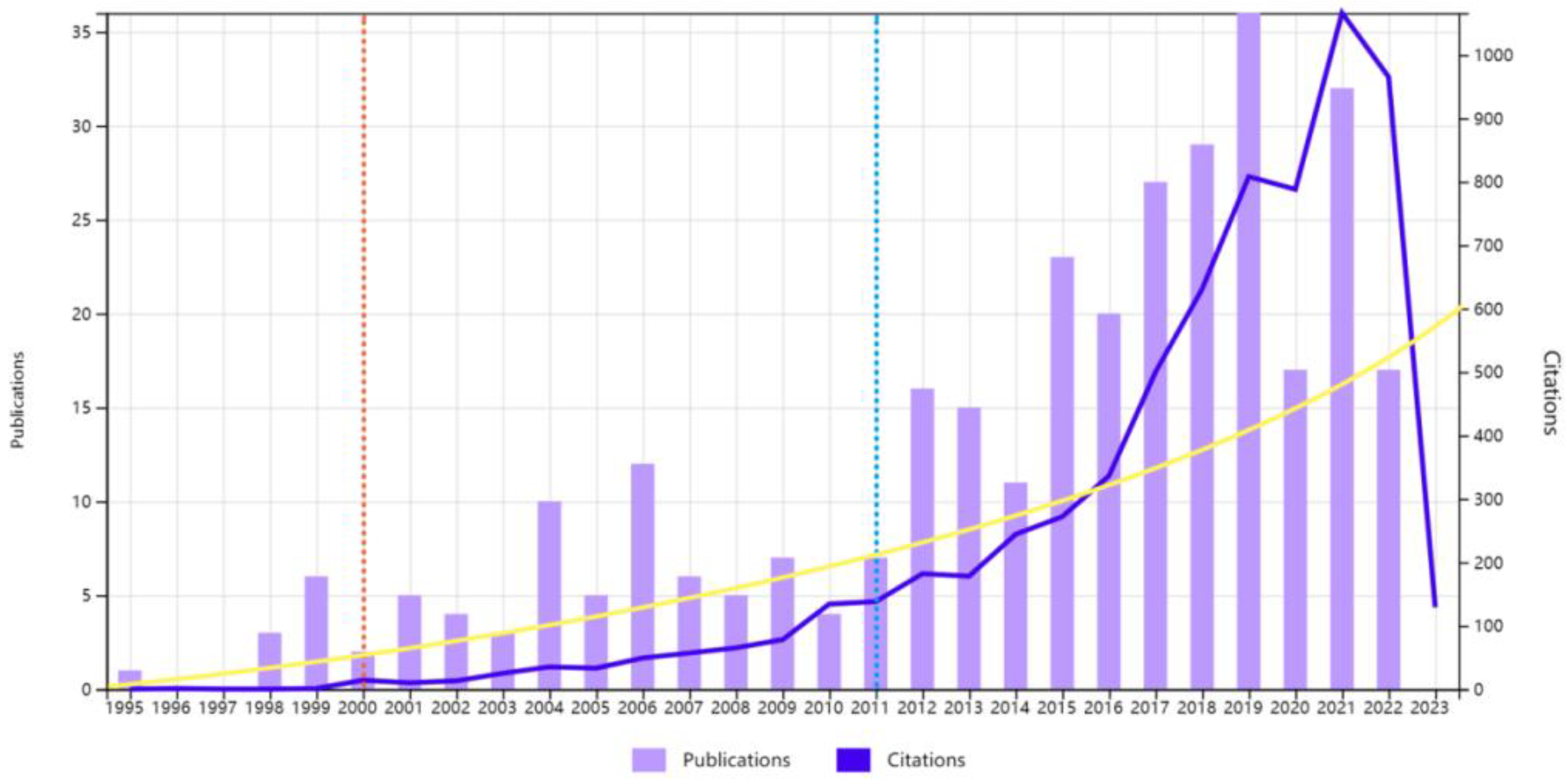
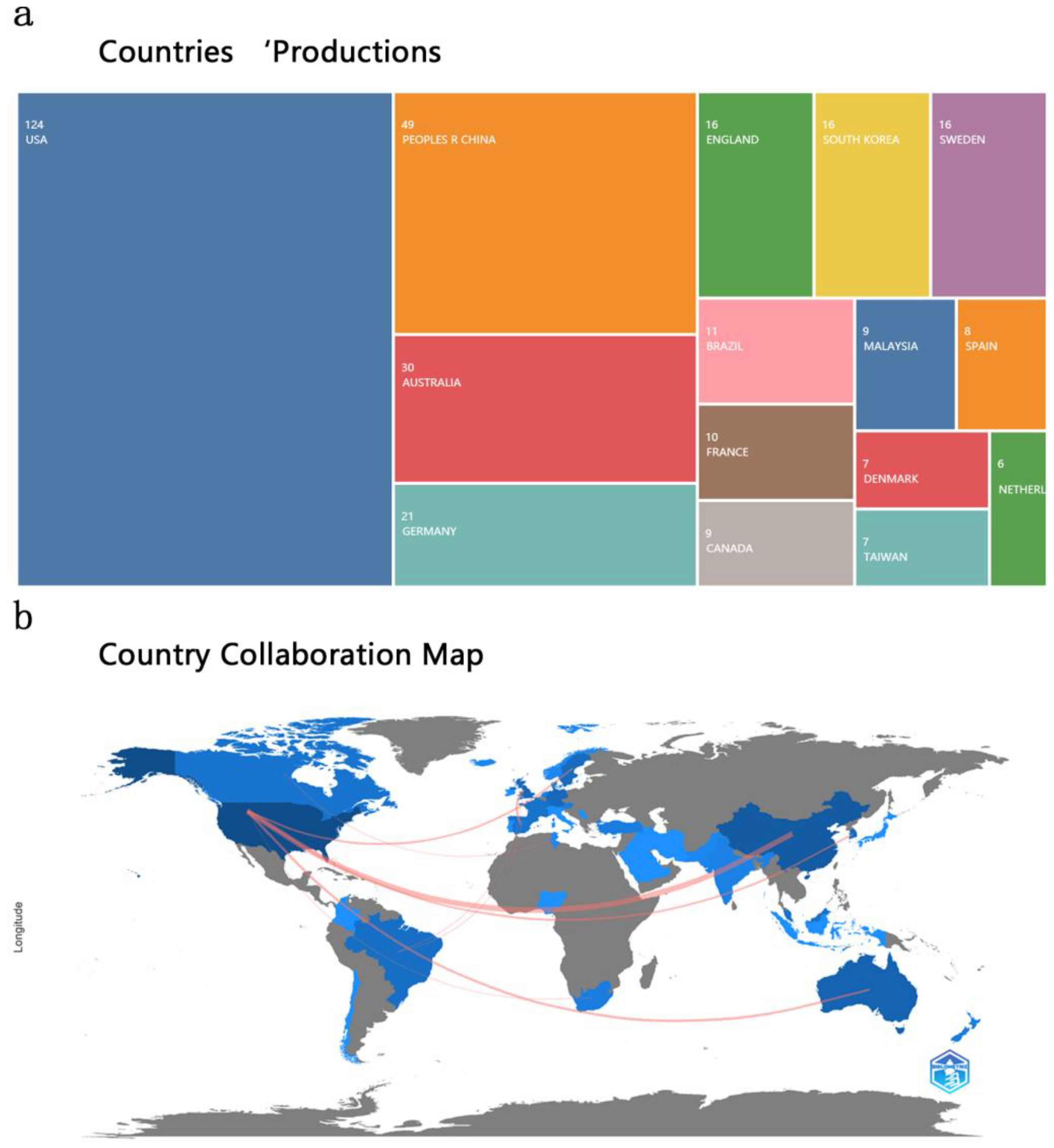
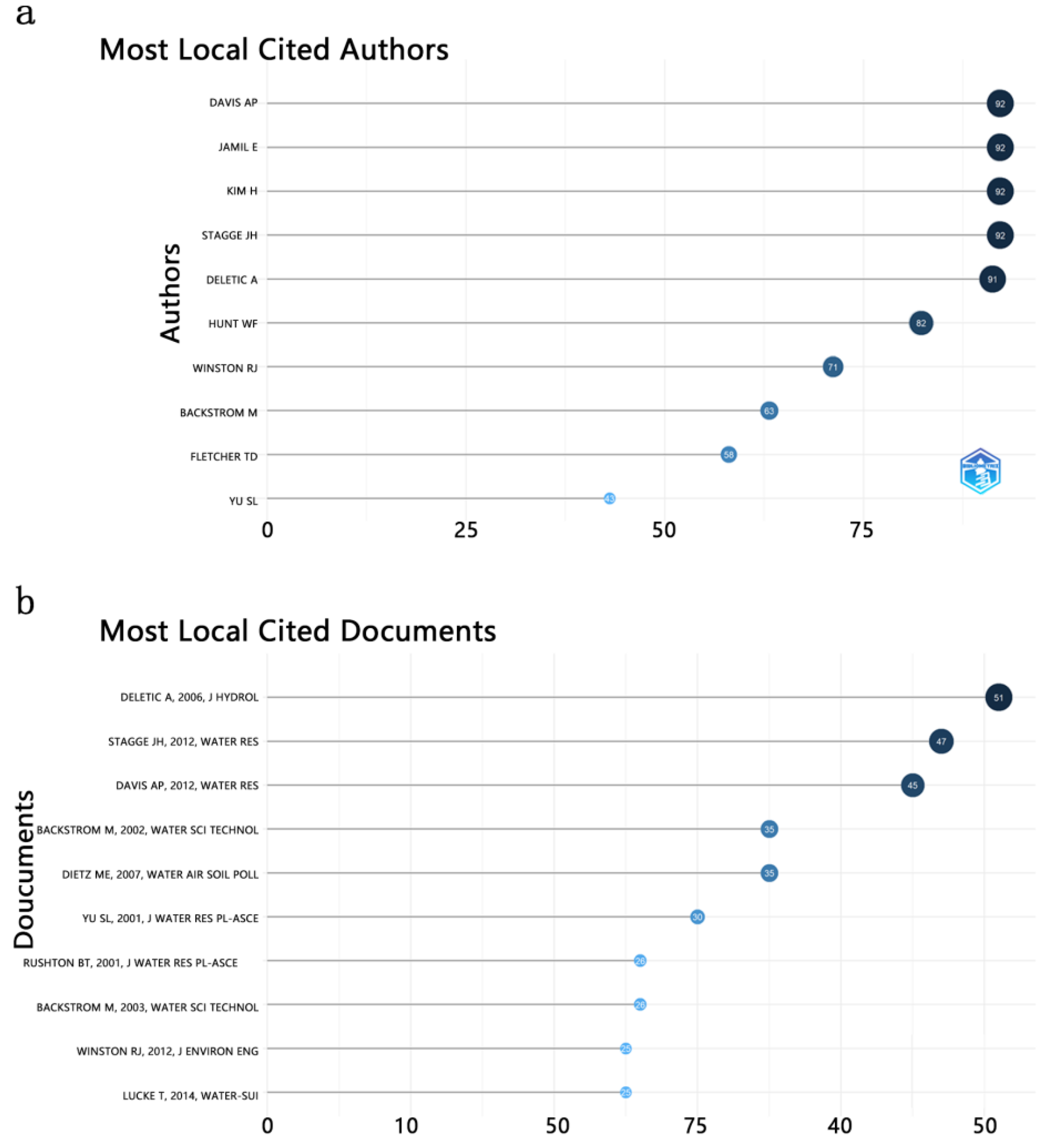
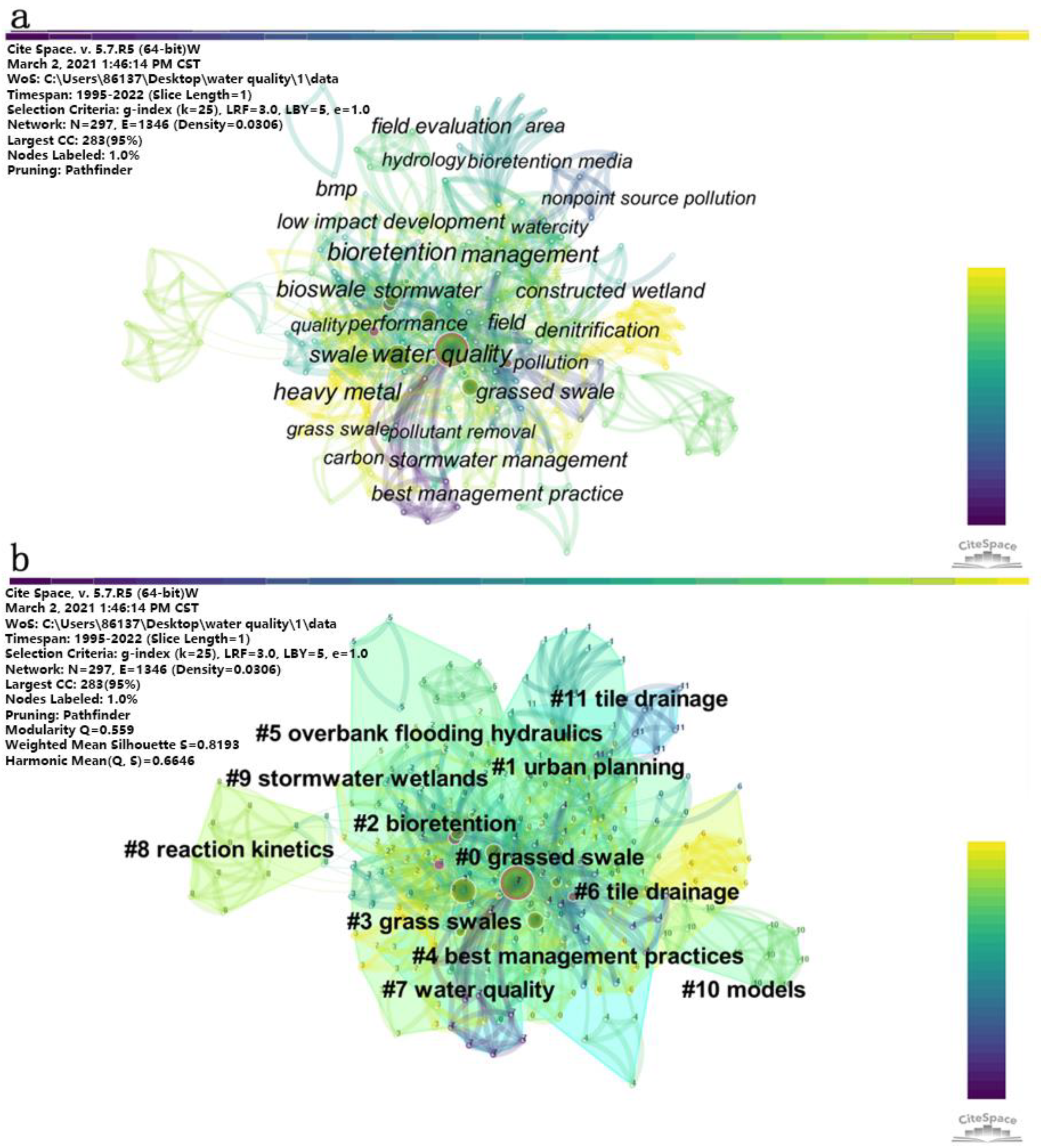
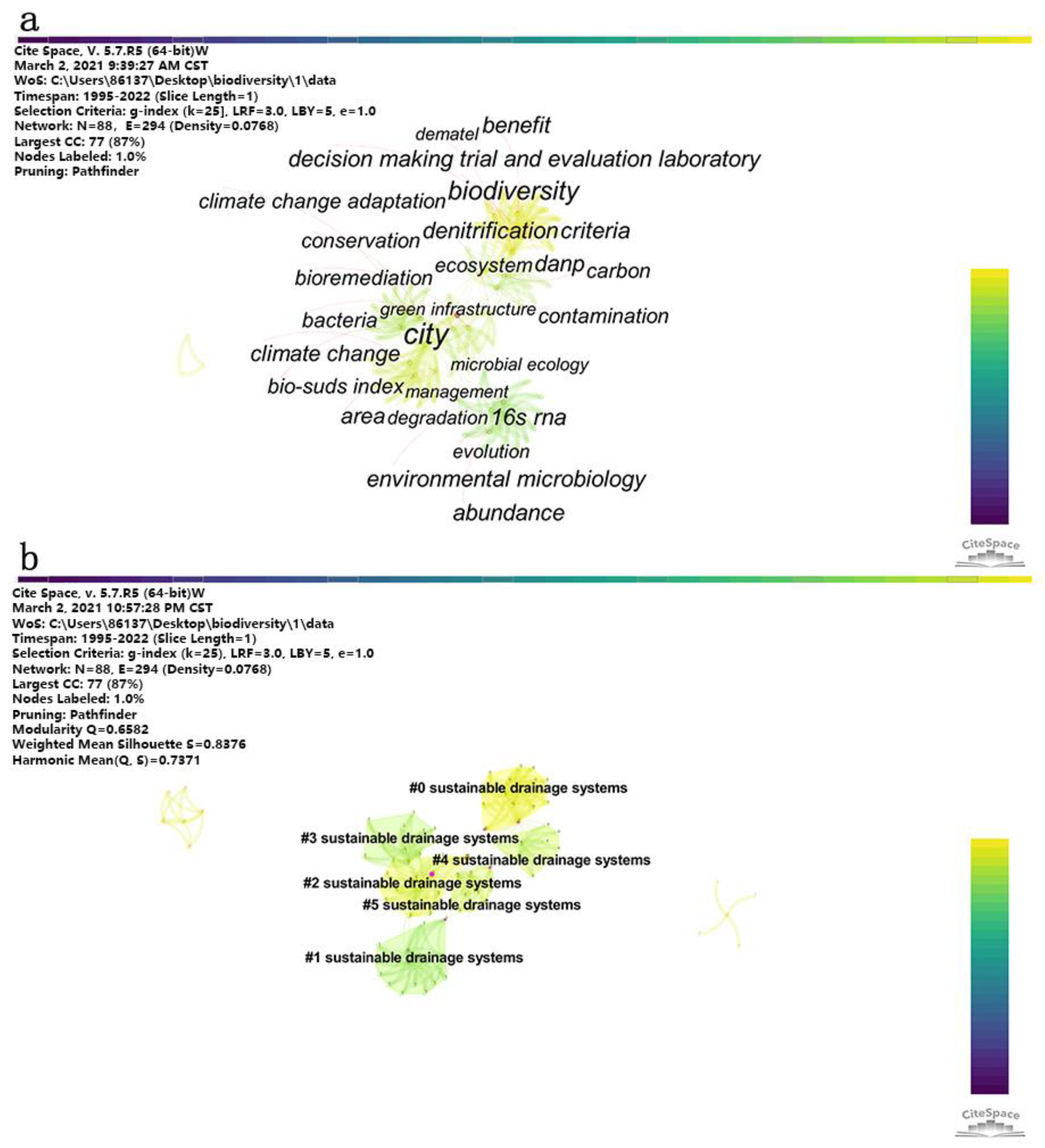
3.1. Status, Development Trends and Hot Topics
3.2. Research on Regulating Services
3.2.1. Hydrology
- (1)
- Influencing factors
- (2)
- Climate
- (3)
- Modeling
3.2.2. Water Quality
- (1)
- Influencing factors
- (2)
- Soil pollution
3.2.3. Biodiversity
- (1)
- Micro level
- (2)
- Macro level
3.3. Future Research Perspectives
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dhakal, K.P.; Chevalier, L.R. Implementing low impact development in urban landscapes: A policy perspective. In World Environmental and Water Resources Congress; Floods, Droughts, and Ecosystems; Webster, V.L., Karvazy, K., Eds.; American Society of Civil Engineers (ASCE): Reston, VA, USA, 2015; pp. 322–333. [Google Scholar]
- Dillman, K.; Czepkiewicz, M.; Heinonen, J.; Fazeli, R.; Árnadóttir, Á.; Davíðsdóttir, B.; Shafei, E. Decarbonization scenarios for Reykjavik’s passenger transport: The combined efects of behavioural changes and technological developments. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2021, 65, 102614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMahon, P.L.; Sorhaindo, C.L.; Barry, W.K. Analysis of low impact development using continuous simulation hydrologic modeling. In International Low Impact Development Conference; Getting in Tune with Green Infrastructure; Hathaway, J., Ed.; American Society of Civil Engineers (ASCE): Reston, VA, USA, 2018; pp. 110–118. [Google Scholar]
- Sanicola, O.; Lucke, T.; Devine, J. Using permeable pavements to reduce the environmental impacts of urbanisation. Int. J. GEOMATE 2018, 14, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafique, M.; Kim, R. Retrofitting the low impact development practices into developed urban areas including barriers and potential solution. Open Geosci. 2017, 9, 240–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahiablame, L.M.; Engel, B.A.; Chaubey, I. Effectiveness of low impact development practices: Literature review and suggestions for future research. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2012, 223, 4253–4273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bichai, F.; Ashbolt, N. Public health and water quality management in low-exposure stormwater schemes: A critical review of regulatory frameworks and path forward. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2017, 28, 453–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Kim, H.Y.; Demarie, F. Facilitators and barriers of applying low impact development practices in urban development. Water Resour. Manag. 2017, 31, 3795–3808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, B.J.; Wang, W.; Sharifi, A.; Liu, X. Progress, knowledge gap and future directions of urban heat mitigation and adaptation research through a bibliometric review of history and evolution. Energy Build. 2023, 287, 112976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharifi, A.; Pathak, M.; Joshi, C.; He, B.J. A systematic review of the health co-benefits of urban climate change adaptation. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2021, 74, 103190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Fu, X.; Zhang, D.; Chen, F.; Liu, M.; Zhou, S.Q.; Su, J.; Tan, S.K. Assessing urban flooding risk in response to climate change and urbanization based on shared socio-economic pathways. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 880, 163470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, X.J.; Liao, K.H.; Randrup, T.B. Sustainable stormwater management: A qualitative case study of the sponge cities initiative in China. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2020, 53, 101963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- She, L.; Wei, M.; You, X.Y. Multi-objective layout optimization for sponge city by annealing algorithm and its environmental benefts analysis. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2021, 66, 102706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Liu, M.; Zhang, D.Q.; Qi, J.D.; Fu, W.C.; Zhang, Y.; Rao, Q.Y.; Bakhshipour, A.E.; Tan, S.K. Assessing and optimizing the hydrological performance of Grey-Green infrastructure systems in response to climate change and non-stationary time series. Water Res. 2023, 232, 119720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Liu, M.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, Y.; Su, J.; Zhou, S.Q.; Bakhshipour, A.E.; Tan, S.K. Assessing hydrological performance for optimized integrated grey-green infrastructure in response to climate change based on shared socio-economic pathways. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2023, 91, 104436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.S.; Meng, Q.L.; Zou, Y.; Qi, Q.L.; Tan, K.H.; Santamouris, M.; He, B.J. Performance synergism of pervious pavement on stormwater management and urban heat island mitigation: A review of its benefits, key parameters, and co-benefits approach. Water Res. 2022, 221, 118755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Jiang, Z.; Zhang, D.Q.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, M.; Rao, Q.; Li, J.; Tan, S.K. Optimization of integrating life cycle cost and systematic resilience for grey-green stormwater infrastructure. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2023, 90, 104379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Bakhshipour, A.E.; Liu, M.; Rao, Q.Y.; Lu, Z.M. Designing coupled LID–GREI urban drainage systems: Resilience assessment and decision-making framework. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 834, 155267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beecham, S.; Razzaghmanesh, M.; Bustami, R.; Ward, J. The role of green roofs and livingwalls as WSUD approaches in a dry climate. In Approaches to Water Sensitive Urban Design; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2019; pp. 409–430. [Google Scholar]
- Kaykhosravi, S.; Khan, U.T.; Jadidi, A. A comprehensive review of low impact development models for research, conceptual, preliminary and detailed design applications. Water 2018, 10, 1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trenouth, W.R.; Vander Linden, W.K. Canadian low impact development retrofit approaches: A 21st-century stormwater management paradigm. In International Low Impact Development Conference 2018: Getting in Tune with Green Infrastructure; American Society of Civil Engineers (ASCE): Nashville, TN, USA, 2018; pp. 193–202. [Google Scholar]
- Leroy, M.C.; Marcotte, S.; Legras, M.; Moncond’huy, V.; Le Derf, F.; Portet-Koltalo, F. Infuence of the vegetative cover on the fate of trace metals in retention systems simulating roadside infltration swales. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 580, 482–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahiablame, L.; Shakya, R. Modeling flood reduction effects of low impact development at a watershed scale. J. Environ. Manag. 2016, 171, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coffman, L.S.; France, R.L. (Eds.) Handbook of Water Sensitive Planning and Design; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2002; pp. 97–124. [Google Scholar]
- US Environmental Protection Agency. Low Impact Development (LID): A Literature Review; US Environmental Protection Agency, Office of Water and Low Impact Development Center: Washington, DC, USA, 2000.
- Su, J.; Wang, M.; Razi, M.A.M.; Dom, N.M.; Sulaiman, N.; Tan, L.-W. A Bibliometric Review of Nature-Based Solutions on Urban Stormwater Management. Sustainability 2023, 15, 7281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Chen, Y.; Yang, R.; Zhao, Y. Exploring the optimal cost-benefit solution for a low impact development layout by zoning, as well as considering the inundation duration and inundation depth. Sustainability 2020, 12, 4990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirby, J.T.; Durrans, S.R.; Pitt, R.; Johnson, P.D. Hydraulic resistance in grass swales designed for small flow conveyance. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2005, 131, 65–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charlesworth, S.M.; Nnadi, E.; Oyelola, O.; Bennett, J.; Warwick, F.; Jackson, R.; Lawson, D. Laboratory based experiment to assess the use of green and food based compost to improve water quality in sustainable drainage (SUDS) device such as swale. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 424, 337–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stagge, J.H.; Davis, A.P.; Jamil, E.; Kim, H. Performance of grass swales for improving water quality from highway runoff. Water Res. 2012, 46, 6731–6742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarukkalige, R.; Priddle, S.; Gamage, D. Evaluation of the impacts of the land use on storm water quality: Case study from Western Australia. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Dev. 2012, 3, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revitt, M.D.; Ellis, B.J.; Lundy, L. Assessing the impact of swales on receiving water quality. Urban Water J. 2017, 14, 839–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, A.P.; Stagge, J.H.; Jamil, E.; Kim, H. Hydraulic performance of grass swales for managing highway runoff. Water Res. 2012, 46, 6775–6786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bäckström, M.; Viklander, M.; Malmqvist, P.-A. Transport of Stormwater Pollutants through a Roadside Grassed Swale. J. Urban Water 2006, 3, 55–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schueler, T.R. Controlling Urban Runoff: A Practical Manual for Planning and Designing Urban BMPs; Metropolitan Washington Council of Governments: Washington, DC, USA, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Gavric, S.; Leonhardt, G.; Marsalek, J.; Viklander, M. Processes improving urban stormwater quality in grass swales and filter strips: A review of research findings. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 669, 431–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aria, M.; Cuccurullo, C. Bibliometrix: An R-tool for comprehensive science mapping analysis. J. Informetr. 2017, 11, 959–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.M. CiteSpace II: Detecting and visualizing emerging trends and transient patterns in scientific literature. J. Am. Soc. Inf. Sci. Technol. 2006, 57, 359–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.M.; Ibekwe-SanJuan, F.; Hou, J. The structure and dynamics of cocitation clusters: A multiple-perspective cocitation analysis. J. Am. Soc. Inf. Sci. Technol. 2010, 61, 1386–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bettencourt, L.M.A.; Kaur, J. Evolution and structure of sustainability science. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 19540–19545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.-B.; Wu, J.; Anderies, J.M. Sustainable landscapes and landscape sustainability: A tale of two concepts. Landsc. Urban Plann. 2019, 189, 274–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.; Xu, C. Mapping research on carbon emissions trading: A co-citation analysis. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 74, 1314–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuanazzi, N.R.; Ghisi, N.d.C.; Oliveira, E.C. Analysis of global trends and gaps for studies about 2,4-D herbicide toxicity: A scientometric review. Chemosphere 2020, 241, 125016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Small, H.; Sweeney, E.; Greenlee, E. Clustering the Science Citation Index using co-citations. I. A comparison of methods. Scientometrics 1985, 7, 391–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, K.K.; Weisenhorn, P.; Gilbert, J.A.; Chu, H.Y. Wheat rhizosphere harbors a less complex and more stable microbial cooccurrence pattern than bulk soil. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2018, 125, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amjad, T.; Shahid, N.; Daud, A.; Khatoon, A. Citation burst prediction in a bibliometric network. Scientometrics 2022, 127, 2773–2790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deletic, A.; Fletcher, T.D. Performance of grass filters used for stormwater treatment—A field and modelling study. J. Hydrol. 2006, 317, 261–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucke, T.; Mohamed, M.A.K.; Tindale, N. Pollutant removal and Hydraulic reduction performance of field grassed swales during runoff simulation experiments. Water 2014, 6, 1887–1904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rushton, B.T. Low-impact parking lot design reduces runoff and pollutant loads. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. 2001, 127, 172–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sañudo-Fontaneda, L.A.; Roces-García, J.; Coupe, S.J.; Barrios-Crespo, E.; Rey-Mahía, C.; Álvarez-Rabanal, F.P.; Lashford, C. Descriptive Analysis of the Performance of a Vegetated Swale through Long-Term Hydrological Monitoring: A Case Study from Coventry, UK. Water 2020, 12, 2781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafique, M.; Kim, R.; Kyung-Ho, K. Evaluating the capability of grass swale for the rainfall runoff reduction from an urban parking lot, Seoul, Korea. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, L.S.; Kuo, J.-T.; Fassman, A.E.; Pan, H. Field test of grassed-swale performance in removing runoff pollution. J. Water Resour. Manag. 2001, 127, 168–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rujner, H.; Leonhardt, G.; Marsalek, J.; Perttu, A.-M.; Viklander, M. The effects of initial soil moisture conditions on swale flow hydrographs. Hydrol. Process 2018, 32, 644–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knight, E.M.P.; Hunt, W.F.; Winston, R.J. Side-by-side evaluation of four level spreader–vegetated filter strips and a swale in eastern North Carolina. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2013, 68, 60–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winston, R.J.; Powell, J.T.; Hunt, W.F. Retrofitting a grass swale with rock check dams: Hydrologic impacts. Urban Water J. 2018, 16, 404–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rujner, H.; Leonhardt, G.; Perttu, A.M.; Marsalek, J.; Viklander, M. Advancing green infrastructure design: Field evaluation of grassed urban drainage swales. In Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Planning and Technologies for Sustainable Management of Water in the City, Lyon, France, 28 June–1 July 2016; GRAIE: Lyon, France, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Fassman, E.A. Monitoring of a series of swales within a stormwater treatment train. In Proceedings of the 33rd IAHR World Congress, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 9–14 August 2009; pp. 7024–7031. [Google Scholar]
- Abida, H.; Sabourin, J.F. Grass swale-perforated pipe systems for stormwater management. J. Irrigat. Drain. Eng. 2006, 132, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Backstrom, M. Sediment transport in grassed swales during simulated runoff events. Water Sci. Technol. 2002, 45, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregory, J.H.; Dukes, M.D.; Jones, P.H.; Miller, G.L. Effect of urban soil compaction on infiltration rate. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2006, 61, 117–124. [Google Scholar]
- Pitt, R.; Chen, S.; Clark, S.E.; Swenson, J.; Ong, C.K. Compaction’s impacts on urban storm-water infiltration. J. Irrigat. Drain. Eng. 2008, 134, 652–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekka, S.A.; Rujner, H.; Leonhardt, G.; Blecken, G.-T.; Viklander, M.; Hunt, W.F. Next generation swale design for stormwater runoff treatment: A comprehensive approach. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 279, 111756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deletic, A. Sediment Behaviour in Overland Flow Over Grassed Areas. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Aberdeen, Aberdeen, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Q.Q. A review of sustainable urban drainage systems considering the climate change and urbanization impacts. Water 2014, 6, 976–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waters, D.; Watt, W.E.; Marsalek, J.; Anderson, B.C. Adaptation of a storm drainage system to accommodate increased rainfall resulting from climate change. J. Environ. Plan. Manag. 2003, 46, 755–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berggren, K. Urban Stormwater Systems in Future Climates—Assessment and Management of Hydraulic Overloading. Ph.D. Thesis, Luleå University of Technology, Luleå, Sweden, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Gavric, S.; Leonhardt, G.; Osterlund, H.; Marsalek, J.; Viklander, M. Metal enrichment of soils in three urban drainage grass swales used for seasonal snow storage. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 760, 144136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaqout, T.; Andradottir, H.O. Hydrologic performance of grass swales in cold maritime climates: Impacts of frost, rain-on-snow and snow cover on flow and volume reduction. J. Hydrol. 2021, 597, 126159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Backstrom, M. Grassed swales for stormwater pollution control during rain and snowmelt. Water Sci. Technol. 2003, 48, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semadeni-Davies, A.; Hernebring, C.; Svensson, G.; Gustafsson, L.G. The impacts of climate change and urbanisation on drainage in Helsingborg, Sweden: Suburban stormwater. J. Hydrol. 2008, 350, 114–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viklander, M. Urban snow deposits—Pathways of pollutants. Sci. Total Environ. 1996, 189, 379–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boger, A.R.; Ahiablame, L.; Mosase, E.; Beck, D. Effectiveness of roadside vegetated filter strips and swales at treating roadway runoff: A tutorial review. Environ. Sci. Water Res. Technol. 2018, 4, 478–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, M.B. Hydrological conditions for contaminant leaching through highway swales. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2004, 158, 169–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, A.H.; Trowsdale, S.A. A review of models for low impact urban stormwater drainage. Environ. Model. Softw. 2007, 22, 394–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.-H.; Barrett, M.E.; Rammohan, P.; Olivera, F.; Landphair, H.C. Documenting stormwater quality on Texas highways and adjacent vegetated roadsides. J. Environ. Eng. 2008, 134, 48–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousef, Y.; Hvitved-Jacobsen, T.; Wanielista, M.; Harper, H. Removal of contaminants in highway runoff flowing through swales. Sci. Total Environ. 1987, 59, 391–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrett, M.; Lantin, A.; Austrheim-Smith, S. Storm water pollutant removal in roadside vegetated buffer strips. Transp. Res. Rec. 2004, 1890, 129–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winston, R.J.; Anderson, A.R.; Hunt, W.F. Modeling sediment reduction in grass swales and vegetated filter strips using particle settling theory. J. Environ. Eng. 2017, 143, 04016075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, M.A.K.; Lucke, T.; Boogaard, F. Preliminary investigation into the pollution reduction performance of swales used in a stormwater treatment train. Water Sci. Technol. 2014, 69, 1014–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Read, J.; Wevill, T.; Fletcher, T.; Deletic, A. Variation among plant species in pollutant removal from stormwater in biofiltration systems. Water Res. 2008, 42, 893–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, A.P.; Stagge, J.H. Grassed Swale Pollutant Removal Efficiency Studies. In Proceedings of the World Environmental and Water Resources Congress 2006: Examining the Confluence of Environmental and Water Concerns, Omaha, NE, USA, 21–25 May 2006; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Fardel, A.; Peyneau, P.-E.; Béchet, B.; Lakel, A.; Rodriguez, F. Analysis of swale factors implicated in pollutant removal efficiency using a swale database. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 1287–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rommel, S.H.; Ebert, V.; Huber, M.; Drewes, J.E.; Helmreich, B. Spatial distribution of zinc in the topsoil of four vegetated in filtration swales treating zinc roof runoff. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 672, 806–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stevik, T.K.; Aa, K.; Ausland, G.; Hanssen, J.F. Retention and removal of pathogenic bacteria in wastewater percolating through porous media: A review. Water Res. 2004, 38, 1355–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Purvis, R. Bioswale Design Optimization for Enhanced Application and Pollutant Removal; North Carolina State University: Raleigh, NC, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, B.S.; Phillips, B.M.; Voorhees, J.P.; Siegler, K.; Tjeerdema, R. Bioswales reduce contaminants associated with toxicity in urban storm water. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2016, 35, 3124–3134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leroy, M.; Portet-Koltalo, F.; Legras, M.; Lederf, F.; Moncond’huy, V.; Polaert, I.; Marcotte, S. Performance of vegetated swales for improving road runoff quality in a moderate traffic urban area. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 566, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Q.F.; McPherson, E.G. Performance of engineered soil and trees in a parking lot bioswale. Urban Water J. 2011, 8, 241–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auge, R.M. Water relations, drought and vesicular-arbuscular mycorrhizal symbiosis. Mycorrhiza 2001, 11, 3–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Heijden, M.G.A.; Bardgett, R.D.; van Straalen, N.M. The unseen majority: Soil microbes as drivers of plant diversity and productivity in terrestrial ecosystems. Ecol. Lett. 2008, 11, 296–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, A.S.; Lee, A.; McGuire, K.L. Phylogenetic and functional diversity of total (DNA) and expressed (RNA) bacterial communities in urban green infrastructure bioswale soils. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2017, 83, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monberg, R.J.; Howe, A.G.; Ravn, H.P.; Jensen, M.B. Exploring structural habitat heterogeneity in sustainable urban drainage systems (SUDS) for urban biodiversity support. Urban Ecosyst. 2018, 21, 1159–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazemi, F.; Beecham, S.; Gibbs, J. Streetscape biodiversity and the role of bioretention swales in an Australian urban environment. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2011, 101, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, M.; Zhang, D.Q.; Lu, Z.M.; Bakhshipour, A.E.; Liu, M.; Jiang, Z.Y.; Li, J.J.; Tan, S.K. Multi-stage planning of LID-GREI urban drainage systems in response to land-use changes. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 859, 160214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, T.; Wang, M.; Su, J.; Li, J. Unlocking the Positive Impact of Bio-Swales on Hydrology, Water Quality, and Biodiversity: A Bibliometric Review. Sustainability 2023, 15, 8141. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15108141
Chen T, Wang M, Su J, Li J. Unlocking the Positive Impact of Bio-Swales on Hydrology, Water Quality, and Biodiversity: A Bibliometric Review. Sustainability. 2023; 15(10):8141. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15108141
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Tong, Mo Wang, Jin Su, and Jianjun Li. 2023. "Unlocking the Positive Impact of Bio-Swales on Hydrology, Water Quality, and Biodiversity: A Bibliometric Review" Sustainability 15, no. 10: 8141. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15108141
APA StyleChen, T., Wang, M., Su, J., & Li, J. (2023). Unlocking the Positive Impact of Bio-Swales on Hydrology, Water Quality, and Biodiversity: A Bibliometric Review. Sustainability, 15(10), 8141. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15108141






