The Impact of Corporate Social Responsibility on Speed of OFDI under the Belt and Road Initiative
Abstract
1. Introduction
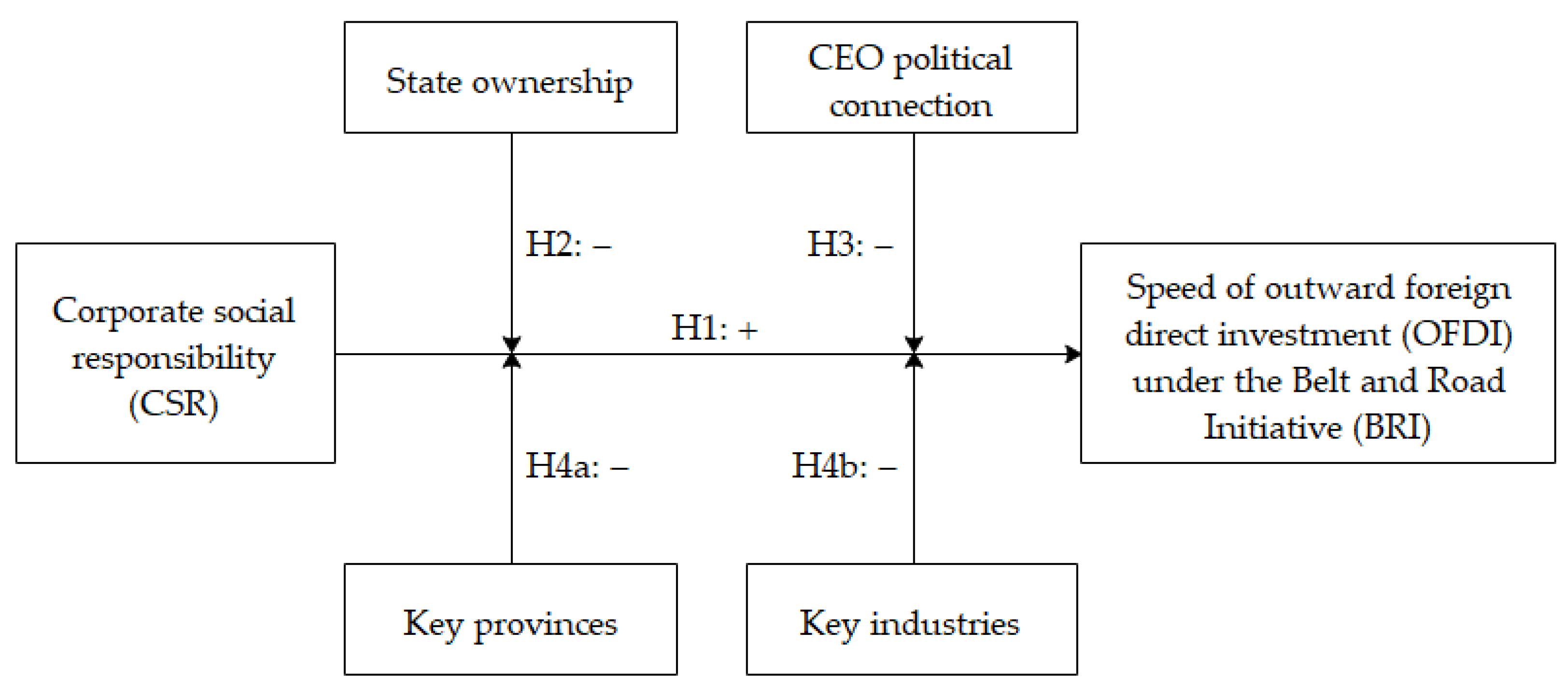
2. Theoretical Development and Hypotheses
2.1. CSR and the Speed of OFDI under BRI
2.2. The Moderating Effect of State Ownership and CEO Political Connection
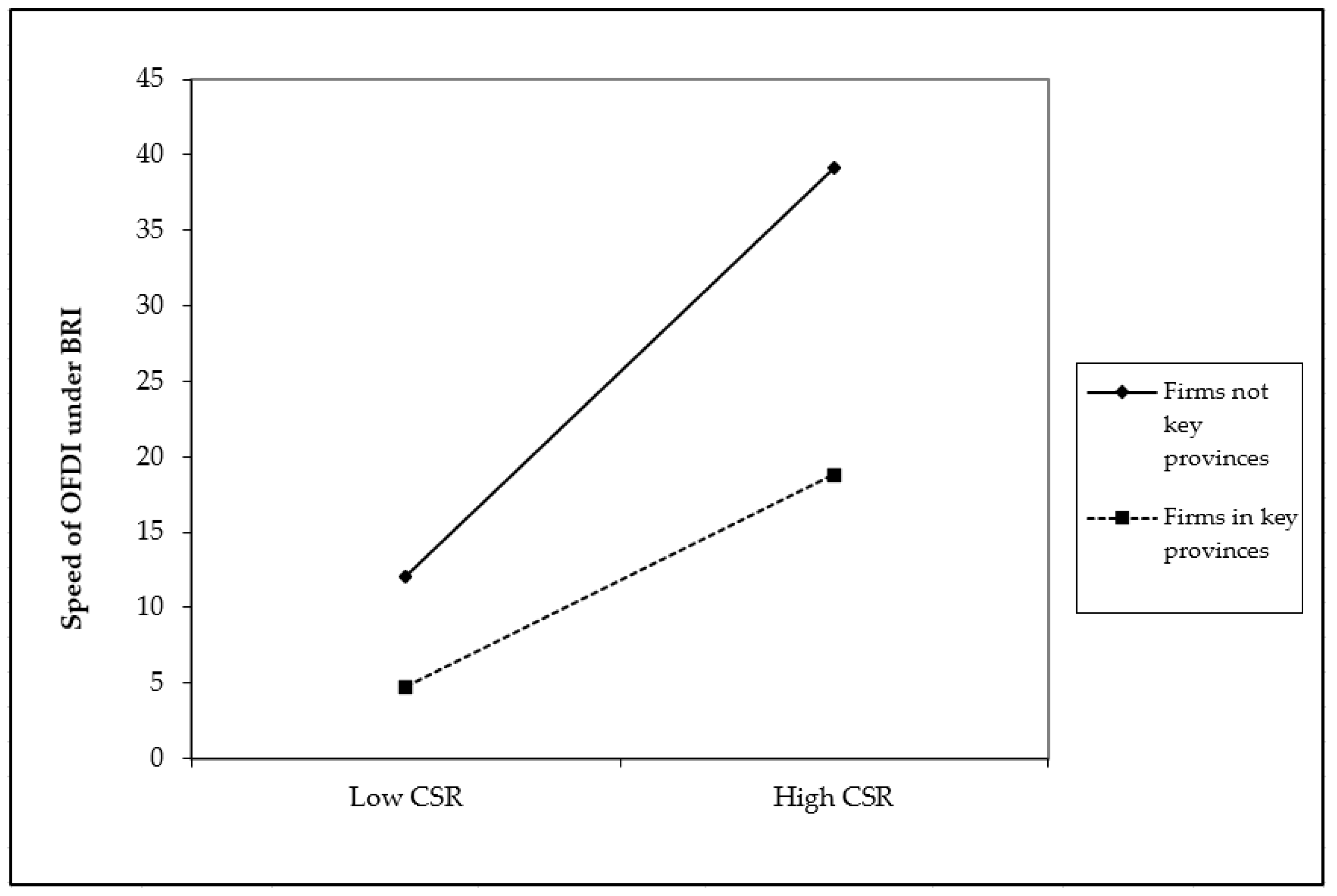
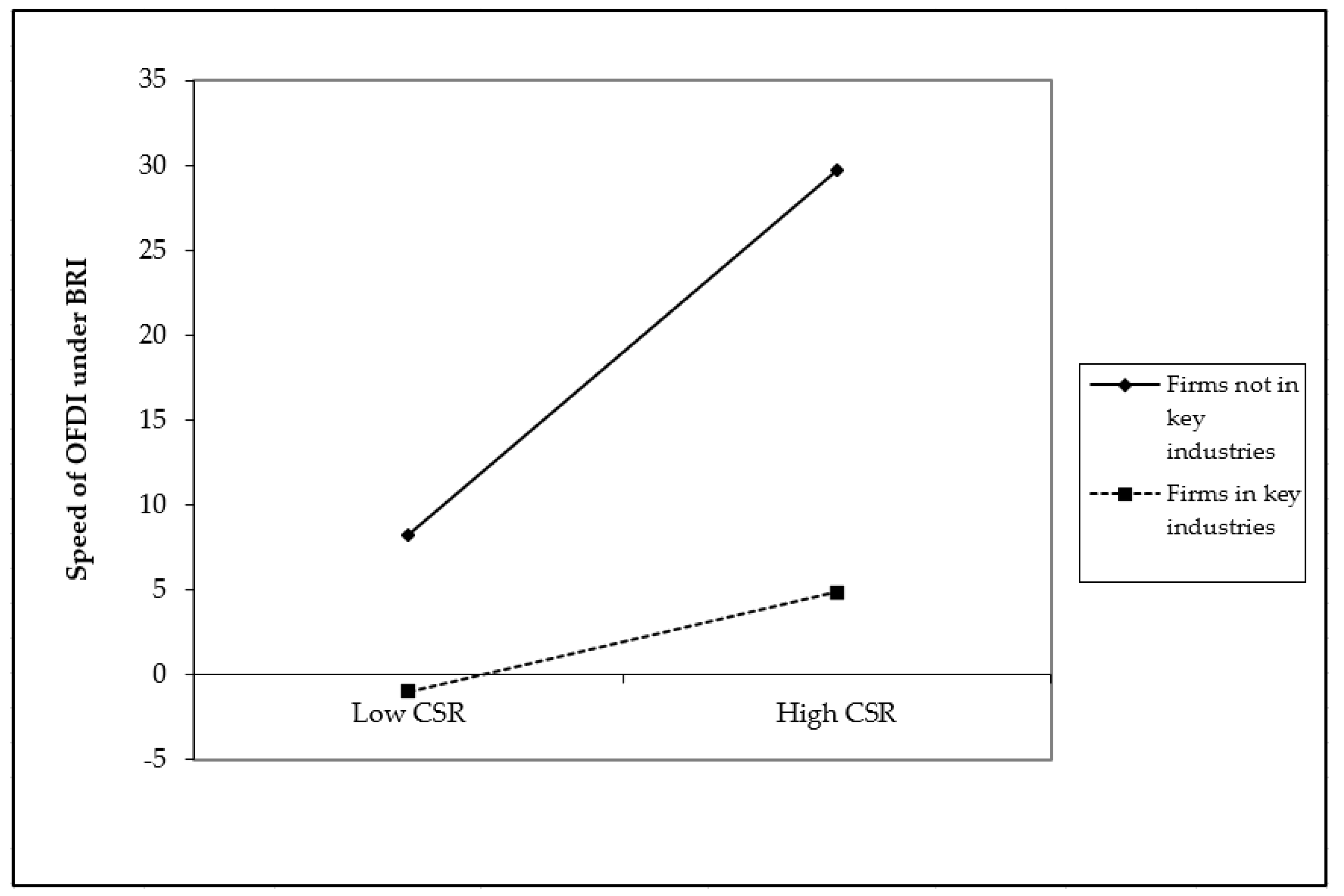
2.3. The Moderating Effect of Key Provinces and Industries along the Belt and Road
3. Methodology
3.1. Data and Sample
3.2. Measures
3.2.1. Dependent Variable
3.2.2. Independent Variable
3.2.3. Moderators
3.2.4. Controls
3.3. Estimation Procedure
4. Results
4.1. Descriptive Statistics and Correlation Analysis
4.2. Results of Regression
4.3. Robustness Check
5. Discussion
5.1. Implications for Research
5.2. Implications for Practice
5.3. Limitations and Future Research
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, J.; Liu, B.; Qian, G. The Belt and Road Initiative, Cultural Friction and Ethnicity: Their Effects on the Export Performance of SMEs in China. J. World Bus. 2019, 54, 350–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Liu, B. State Equity and Outward FDI under the Theme of Belt and Road Initiative. Asia Pac. J. Manag. 2022, 39, 877–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Beule, F.; Zhang, H. The Impact of Government Policy on Chinese Investment Locations: An Analysis of the Belt and Road Policy Announcement, Host-Country Agreement, and Sentiment. J. Int. Bus. Policy 2022, 5, 194–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y. Environmental Risks and Opportunities for Countries along the Belt and Road: Location Choice of China’s Investment. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 211, 14–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, X. Chinese OFDI Responses to the B&R Initiative: Evidence from a Quasi-Natural Experiment. China Econ. Rev. 2020, 61, 101435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Wang, Q. Speed of China’s OFDIs to the Belt and Road Initiative Destinations: State Equity, Industry Competition, and the Moderating Effects of the Policy. J. Int. Bus. Policy 2022, 5, 218–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.Y.; Lu, J.; Jiang, R. Too Slow or Too Fast? Speed of FDI Expansions, Industry Globalization, and Firm Performance. Long Range Plan. 2017, 50, 74–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, P. Knowledge Sourcing by Foreign Multinationals: Patent Citation Analysis in the U.S. Semiconductor Industry. Strateg. Manag. J. 1996, 17, 155–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delios, A.; Beamish, P.W. Survival and Profitability: The Roles of Experience and Intangible Assets in Foreign Subsidiary Performance. Acad. Manag. J. 2001, 44, 1028–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, L.; Pangarkar, N. Performance Implications of Internationalization Strategies for Chinese MNCs. Int. J. Emerg. Mark. 2015, 10, 272–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barney, J. Firm Resources and Sustained Competitive Advantage. J. Manag. 1991, 17, 99–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marano, V.; Tashman, P.; Kostova, T. Escaping the Iron Cage: Liabilities of Origin and CSR Reporting of Emerging Market Multinational Enterprises. J. Int. Bus. Stud. 2017, 48, 386–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonseka, M.; Samarakoon, L.P.; Tian, G.-L.; Seng, R. The Impact of Social Trust and State Ownership on Investment Efficiency of Chinese Firms. J. Int. Financ. Mark. Inst. Money 2021, 74, 101394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aray, Y.; Dikova, D.; Garanina, T.; Veselova, A. The Hunt for International Legitimacy: Examining the Relationship between Internationalization, State Ownership, Location and CSR Reporting of Russian Firms. Int. Bus. Rev. 2021, 30, 101858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Zhang, R. Corporate Social Responsibility, Ownership Structure, and Political Interference: Evidence from China. J. Bus. Ethics 2010, 96, 631–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Gao, J.; Liu, B.; Wang, Z. Big Data-Based Assessment of Political Risk along the Belt and Road. Sustainability 2021, 13, 3935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Tsang, D.; Fuschi, D.L. Chinese Multinationals on the New Silk Route: Managing Political Risk by Branding the Nation. Thunderbird Int. Bus. Rev. 2020, 62, 291–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.Y.; Karim, Z.A.; Khalid, N.; Zaidi, M.A.S. The Push and Pull Factors of China’s Outward Foreign Direct Investment in BRI Countries. Technol. Econ. Dev. Econ. 2022, 28, 611–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Van Assche, A.; Li, L.; Qian, G. Foreign Direct Investment along the Belt and Road: A Political Economy Perspective. J. Int. Bus. Stud. 2022, 53, 902–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, H.; Yang, L.; Dai, S.; Van Assche, A. Outward FDI, Industrial Structure Upgrading and Domestic Employment: Empirical Evidence from the Chinese Economy and the Belt and Road Initiative. J. Asian Econ. 2021, 74, 101303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, H.; Zhong, M.; Liu, W.; Chen, B. Belt and Road Initiative and OFDI from China: The Paradox of Home Country Institutional Environment between State and Local Governments. Chin. Manag. Stud. 2022, 17, 365–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Q.; Luo, Y.; Maksimov, V. Achieving Legitimacy through Corporate Social Responsibility: The Case of Emerging Economy Firms. J. World Bus. 2015, 50, 389–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.-J.; Rhee, J.H. Rapid FDI Expansion and Firm Performance. J. Int. Bus. Stud. 2011, 42, 979–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, P.W.; Dowling, G.R. Corporate Reputation and Sustained Superior Financial Performance: Reputation and Persistent Profitability. Strateg. Manag. J. 2002, 23, 1077–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitnick, B.M.; Windsor, D.; Wood, D.J. CSR: Undertheorized or Essentially Contested? Acad. Manag. Rev. 2021, 46, 623–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhaliwal, D.S.; Li, O.Z.; Tsang, A.; Yang, Y.G. Voluntary Nonfinancial Disclosure and the Cost of Equity Capital: The Initiation of Corporate Social Responsibility Reporting. Account. Rev. 2011, 86, 59–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Park, M.S.; Wier, B. Is Earnings Quality Associated with Corporate Social Responsibility? Account. Rev. 2012, 87, 761–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, B.; Ioannou, I.; Serafeim, G. Corporate Social Responsibility and Access to Finance: CSR and Access to Finance. Strat. Manag. J. 2014, 35, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Ghoul, S.; Guedhami, O.; Kwok, C.C.Y.; Mishra, D.R. Does Corporate Social Responsibility Affect the Cost of Capital? J. Bank. Financ. 2011, 35, 2388–2406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, D.; Lee, J.; Chang, S.; Le Breton-Miller, I. Filling the Institutional Void: The Social Behavior and Performance of Family vs Non-Family Technology Firms in Emerging Markets. J. Int. Bus. Stud. 2009, 40, 802–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orlitzky, M.; Schmidt, F.L.; Rynes, S.L. Corporate Social and Financial Performance: A Meta-Analysis. Organ. Stud. 2003, 24, 403–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Branco, M.C.; Rodrigues, L.L. Corporate Social Responsibility and Resource-Based Perspectives. J. Bus. Ethics 2006, 69, 111–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noorbakhsh, F.; Paloni, A.; Youssef, A. Human Capital and FDI Inflows to Developing Countries: New Empirical Evidence. World Dev. 2001, 29, 1593–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kottaridi, C.; Louloudi, K.; Karkalakos, S. Human Capital, Skills and Competencies: Varying Effects on Inward FDI in the EU Context. Int. Bus. Rev. 2019, 28, 375–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahzad, M.; Qu, Y.; Rehman, S.U.; Zafar, A.U.; Ding, X.; Abbas, J. Impact of Knowledge Absorptive Capacity on Corporate Sustainability with Mediating Role of CSR: Analysis from the Asian Context. J. Environ. Plan. Manag. 2020, 63, 148–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingenbleek, P.T.M.; Dentoni, D. Learning from Stakeholder Pressure and Embeddedness: The Roles of Absorptive Capacity in the Corporate Social Responsibility of Dutch Agribusinesses. Sustainability 2016, 8, 1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halkos, G.; Skouloudis, A. Corporate Social Responsibility and Innovative Capacity: Intersection in a Macro-Level Perspective. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 182, 291–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bocquet, R.; Le Bas, C.; Mothe, C.; Poussing, N. CSR, Innovation, and Firm Performance in Sluggish Growth Contexts: A Firm-Level Empirical Analysis. J. Bus. Ethics 2017, 146, 241–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayakawa, K.; Kimura, F.; Lee, H.-H. How Does Country Risk Matter for Foreign Direct Investment? Dev. Econ. 2013, 51, 60–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azam, M.; Khan, M.A.; Iqbal, N. Impact of Political Risk and Uncertainty on FDI in South Asia. Transit. Stud. Rev. 2012, 19, 59–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greve, H.R.; Zhang, C.M. Institutional Logics and Power Sources: Merger and Acquisition Decisions. Acad. Manag. J. 2017, 60, 671–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Lu, J.; Chizema, A. Top Executive Compensation, Regional Institutions and Chinese OFDI. J. World Bus. 2014, 49, 143–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claessens, S.; Djankov, S.; Lang, L.H.P. The Separation of Ownership and Control in East Asian Corporations. J. Financ. Econ. 2000, 58, 81–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhikari, A.; Derashid, C.; Zhang, H. Public Policy, Political Connections, and Effective Tax Rates: Longitudinal Evidence from Malaysia. J. Account. Public Policy 2006, 25, 574–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotler, P.; Manrai, L.A.; Lascu, D.-N.; Manrai, A.K. Influence of Country and Company Characteristics on International Business Decisions: A Review, Conceptual Model, and Propositions. Int. Bus. Rev. 2019, 28, 482–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemati, A.R.; Bhatti, A.M.; Maqsal, M.; Mansoor, I.; Naveed, F. Impact of Resource Based View and Resource Dependence Theory on Strategic Decision Making. Int. J. Bus. Manag. 2010, 5, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, F.; Chan, A.L.-C.; Chen, V.Y.S. Board Political Connections and Tradeoff between Market and Nonmarket Advantages: Evidence from Corporate Financial Information Disclosure. J. Bus. Res. 2023, 164, 113949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ang, Y.Y.; Jia, N. Perverse Complementarity: Political Connections and the Use of Courts among Private Firms in China. J. Politics 2014, 76, 318–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.J.P.; Li, Z.; Su, X.; Sun, Z. Rent-Seeking Incentives, Corporate Political Connections, and the Control Structure of Private Firms: Chinese Evidence. J. Corp. Financ. 2011, 17, 229–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, G.; Liu, B.; Wang, Q. Government Subsidies, State Ownership, Regulatory Infrastructure, and the Import of Strategic Resources: Evidence from China. Multinatl. Bus. Rev. 2018, 26, 319–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.; Pan, X.; Wang, J.; Zhou, Q. Depoliticization and Corporate Cash Holdings: Evidence from the Mandated Resignation of Directors in China. J. Corp. Financ. 2021, 69, 102004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermeulen, F.; Barkema, H. Pace, Rhythm, and Scope: Process Dependence in Building a Profitable Multinational Corporation. Strat. Manag. J. 2002, 23, 637–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, P.; Yang, S.; Boehe, D. Ownership and Corporate Social Performance in China: Why Geographic Remoteness Matters. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 197, 1284–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, P.; Fu, S.; Yang, S. Do Peer Firms Affect Corporate Social Performance? J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 239, 118080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, B.; Lu, W.; Skitmore, M.; Chau, K.W.; Ye, M. Virtuous Nexus between Corporate Social Performance and Financial Performance: A Study of Construction Enterprises in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 129, 223–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Development and Reform Commission; Ministry of Foreign Affairs; Ministry of Commerce. Vision and Actions to Jointly Build the Silk Road Economic Belt and the 21st Century Maritime Silk Road. Available online: http://www.gov.cn/xinwen/2015-03/28/content_2839723.htm (accessed on 10 April 2023).
- National Development and Reform Commission. Article 23 of the Interpretation of the Outline of the 14th Five Year Plan: Promote the High-Quality Development of “the Belt and Road” Initiative; National Development Reform Commission: Beijing, China, 2021.
- Chetty, S.; Johanson, M.; Martín, O.M. Speed of Internationalization: Conceptualization, Measurement and Validation. J. World Bus. 2014, 49, 633–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, T.; del Carmen Triana, M. Demographic Diversity in the Boardroom: Mediators of the Board Diversity-Firm Performance Relationship. J. Manag. Stud. 2009, 46, 755–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolk, A.; Lenfant, F. Multinationals, CSR and Partnerships in Central African Conflict Countries: Multinationals and Partnerships in Central African Conflict Countries. Corp. Soc. Responsib. Environ. Manag. 2013, 20, 43–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghoul, S.E.; Guedhami, O.; Kim, Y. Country-Level Institutions, Firm Value, and the Role of Corporate Social Responsibility Initiatives. J. Int. Bus. Stud. 2017, 48, 360–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, G.F.; Jung, J.C.; Makino, S. Parent Firm Corporate Social Responsibility and Overseas Subsidiary Performance: A Signaling Perspective. J. World Bus. 2020, 55, 101141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buckley, P.J. China’s Belt and Road Initiative and the COVID-19 Crisis. J. Int. Bus. Policy 2020, 3, 311–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Assche, A.; Lundan, S. From the Editor: COVID-19 and International Business Policy. J. Int. Bus. Policy 2020, 3, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Variables | N | Mean | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Speed | 5244 | 2.036 | 1 | ||||
| 2. CSR | 5244 | 21 | 0.244 *** | 1 | |||
| 3. SOE | 5244 | 0.289 | 0.065 *** | 0.061 *** | 1 | ||
| 4. PC | 5244 | 0.294 | −0.008 ** | 0.029 ** | −0.017 | 1 | |
| 5. BRIprov | 5244 | 0.546 | −0.052 *** | −0.013 | −0.096 *** | −0.007 | 1 |
| 6. BRIind | 5244 | 0.610 | 0.049 *** | 0.011 | 0.025 * | −0.023 * | −0.021 |
| 7. Age | 5244 | 2.890 | 0.044 *** | −0.089 *** | 0.157 *** | −0.054 *** | 0.065 *** |
| 8. Size | 5244 | 22.80 | 0.292 *** | 0.259 *** | 0.399 *** | 0.045 *** | −0.074 *** |
| 9. Leverage | 5244 | 0.471 | 0.132 *** | −0.110 *** | 0.310 *** | 0.043 *** | 0 |
| 10. DOL | 5244 | 1.314 | 0.034 ** | −0.005 | −0.034 ** | −0.005 | 0.038 *** |
| 11. Dual | 5244 | 0.300 | −0.023 | 0.002 | −0.275 *** | −0.071 *** | 0.077 *** |
| Variables | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | |
| 6. BRIind | 1 | ||||||
| 7. Age | −0.033 ** | 1 | |||||
| 8. Size | 0.046 *** | 0.156 *** | 1 | ||||
| 9. Leverage | −0.028 ** | 0.202 *** | 0.511 *** | 1 | |||
| 10. DOL | 0.019 | −0.086 *** | −0.103 *** | −0.035 ** | 1 | ||
| 11. Dual | −0.007 | −0.091 *** | −0.170 *** | −0.157 *** | 0.060 *** | 1 |
| Model 1 | Model 2 | Model 3 | Model 4 | Model 5 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CSR | 0.634 *** | 0.877 *** | 1.214 *** | 1.536 *** | 1.219 *** |
| (3.482) | (3.985) | (5.197) | (5.031) | (4.139) | |
| SOE | 0.401 *** | ||||
| (3.295) | |||||
| CSR × SOE | −0.679 * | ||||
| (−1.935) | |||||
| PC | 1.280 * | ||||
| (1.887) | |||||
| CSR × PC | −0.780 ** | ||||
| (−2.029) | |||||
| BRIprov | 1.623 ** | ||||
| (2.308) | |||||
| CSR × BRIprov | −0.736 ** | ||||
| (−2.106) | |||||
| BRIind | 1.626 ** | ||||
| (2.298) | |||||
| CSR × BRIind | −0.888 ** | ||||
| (−2.527) | |||||
| Age | 0.406 | 0.376 | 0.458 * | 0.384 | 0.415 |
| (1.576) | (1.457) | (1.776) | (1.506) | (1.609) | |
| Size | 0.262 *** | 0.260 *** | 0.257 *** | 0.263 *** | 0.260 *** |
| (6.057) | (6.024) | (5.951) | (6.225) | (6.017) | |
| Leverage | −0.101 | −0.094 | −0.094 | −0.014 * | −0.102 |
| (−0.694) | (−0.643) | (−0.648) | (−3.649) | (−0.700) | |
| DOI | −0.058 *** | −0.058 *** | −0.058 *** | −0.057 *** | −0.058 *** |
| (−6.508) | (−6.507) | (−6.511) | (−6.499) | (−6.504) | |
| Dual | −0.087 ** | −0.084 ** | −0.094 ** | −0.090 ** | −0.086 ** |
| (−2.060) | (−1.979) | (−2.209) | (−2.136) | (−2.040) | |
| (constant) | −6.440 *** | −6.394 *** | −6.553 *** | −6.642 *** | −6.642 *** |
| (−5.514) | (−5.478) | (−5.610) | (−5.652) | (−5.652) | |
| Year | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Industry | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| N | 5244 | 5244 | 5244 | 5244 | 5244 |
| R2 | 0.255 | 0.257 | 0.258 | 0.263 | 0.256 |
| (1) | |
|---|---|
| L2.CSR | 0.516 *** |
| (2.700) | |
| Age | 0.775 ** |
| (2.319) | |
| Size | 0.202 *** |
| (3.838) | |
| Leverage | −0.231 |
| (−1.330) | |
| SOE | 0.250 ** |
| (1.991) | |
| DOI | −0.118 *** |
| (−9.257) | |
| Dual | −0.070 |
| (−1.438) | |
| (constant) | −6.333 *** |
| (−4.088) | |
| Year | Yes |
| Industry | Yes |
| Province | Yes |
| N | 5244 |
| R2 | 0.272 |
| (1) | |
|---|---|
| CSR | 0.578 *** |
| (3.180) | |
| Age | 0.543 ** |
| (2.099) | |
| Size | 0.257 *** |
| (5.919) | |
| Leverage | −0.095 |
| (−0.651) | |
| SOE | 0.272 ** |
| (2.568) | |
| DOI | −0.067 *** |
| (−6.517) | |
| Dual | −0.084 ** |
| (−1.968) | |
| (constant) | −6.786 *** |
| (−5.083) | |
| Year | Yes |
| Industry | Yes |
| Province | Yes |
| N | 5209 |
| R2 | 0.270 |
| First Stage | Second Stage | |
|---|---|---|
| dv: CSR | dv: Speed | |
| L.CSR | 0.134 *** | |
| (3.532) | ||
| CSR | 4.623 ** | |
| (2.151) | ||
| Age | −0.011 | 0.915 |
| (−0.348) | (1.632) | |
| Size | 0.031 *** | 0.075 |
| (6.163) | (0.772) | |
| Leverage | −0.158 *** | 0.522 |
| (−8.768) | (1.236) | |
| SOE | −0.010 | 0.373 ** |
| (−0.834) | (2.135) | |
| DOI | −0.002 * | −0.075 *** |
| (−1.624) | (−2.691) | |
| Dual | 0.003 | −0.080 * |
| (0.678) | (−1.732) | |
| Year | Yes | Yes |
| Industry | Yes | Yes |
| Province | Yes | Yes |
| N | 3767 | 3767 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, X.; Chen, S.; Wang, Y. The Impact of Corporate Social Responsibility on Speed of OFDI under the Belt and Road Initiative. Sustainability 2023, 15, 8712. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15118712
Wang X, Chen S, Wang Y. The Impact of Corporate Social Responsibility on Speed of OFDI under the Belt and Road Initiative. Sustainability. 2023; 15(11):8712. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15118712
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Xianjing, Shouming Chen, and Yueqi Wang. 2023. "The Impact of Corporate Social Responsibility on Speed of OFDI under the Belt and Road Initiative" Sustainability 15, no. 11: 8712. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15118712
APA StyleWang, X., Chen, S., & Wang, Y. (2023). The Impact of Corporate Social Responsibility on Speed of OFDI under the Belt and Road Initiative. Sustainability, 15(11), 8712. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15118712







