More Than Half of Emitted Black Carbon Is Missing in Marine Sediments
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sediment Core and Dating
2.2. Quantification of Sedimentary BC
2.3. Estimation of BC Fluxes
2.4. Simulation of Historical BC
2.5. BC Emission Inventory and Global Precipitation
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Trends of Sedimentary BC Fluxes in Continental and Marine Sediment Cores
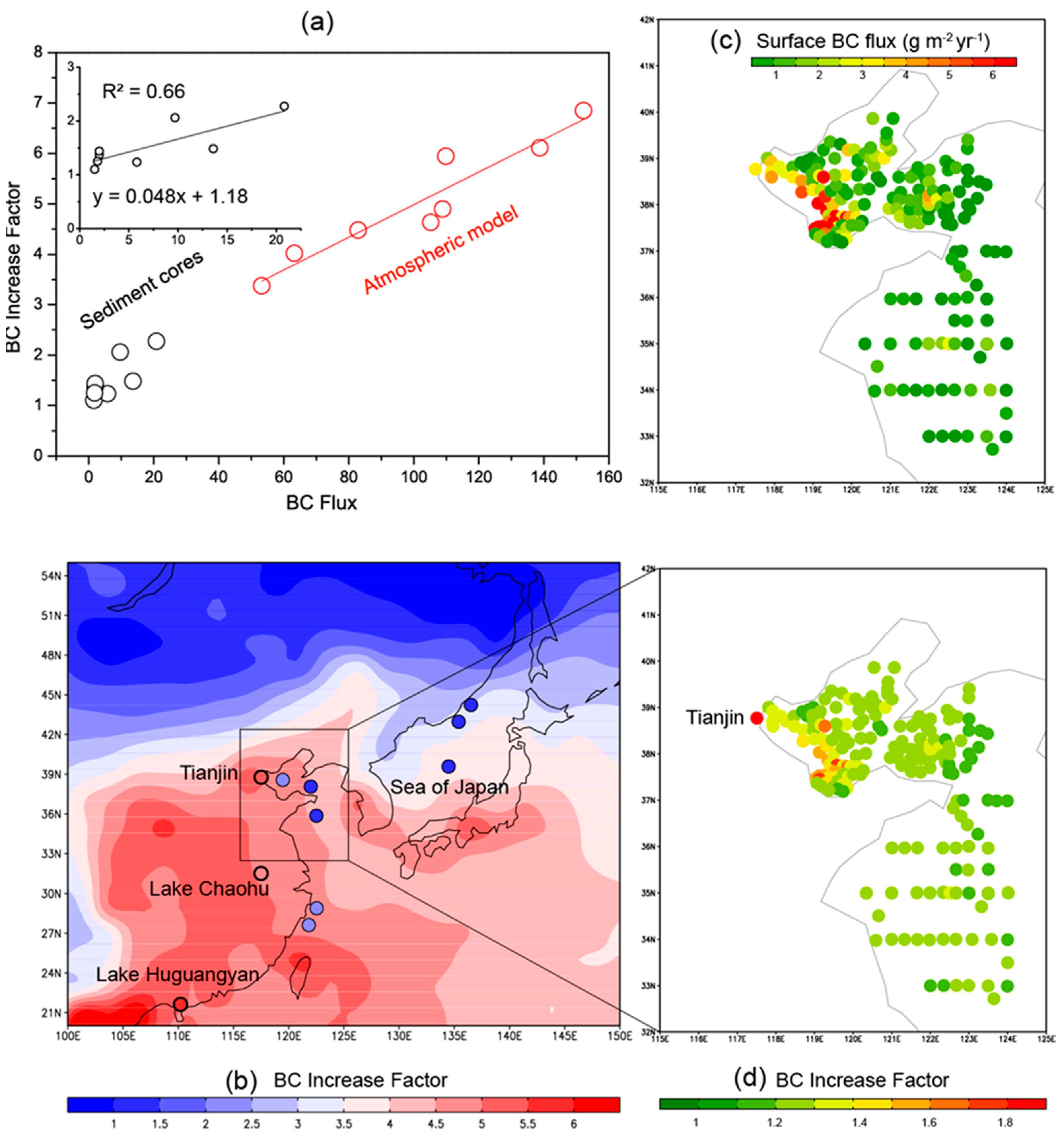
3.2. Sediment Cores and Simulations
3.3. Spatial Variations and Simulations
3.4. BC Missing in Marine Sediments
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ramanathan, V.; Carmichael, G. Global and regional climate changes due to black carbon. Nat. Geosci. 2008, 1, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neupane, B.; Kang, S.; Chen, P.; Zhang, Y.; Ram, K.; Rupakheti, D.; Tripathee, L.; Sharma, C.M.; Cong, Z.; Li, C.; et al. Historical Black Carbon Reconstruction from the Lake Sediments of the Himalayan-Tibetan Plateau. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 5641–5651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruppel, M.M.; Gustafsson, Ö.; Rose, N.L.; Pesonen, A.; Yang, H.; Weckström, J.; Palonen, V.; Oinonen, M.J.; Korhola, A. Spatial and Temporal Patterns in Black Carbon Deposition to Dated Fennoscandian Arctic Lake Sediments from 1830 to 2010. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 13954–13963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coppola, A.I.; Ziolkowski, L.A.; Masiello, C.A.; Druffel, E.R.M. Aged black carbon in marine sediments and sinking particles. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2014, 41, 2427–2433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bond, T.C.; Doherty, S.J.; Fahey, D.W.; Forster, P.M.; Berntsen, T.; Deangelo, B.J.; Flanner, M.G.; Ghan, S.; Kärcher, B.; Koch, D.; et al. Bounding the role of black carbon in the climate system: A scientific assessment. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 5380–5552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhu, Z.; Cao, F.; Tiwari, S.; Chen, B. Source apportionment of absorption enhancement of black carbon in different environments of China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 755, 142685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, S.; Kun, L.; Chen, B. Spatial variability of sedimentary carbon in South Yellow Sea, China: Impact of anthropogenic emission and long-range transportation. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 23812–23823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cong, Z.; Kang, S.; Gao, S.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Q.; Kawamura, K. Historical trends of atmospheric black carbon on Tibetan Plateau as reconstructed from a 150-year lake sediment record. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 2579–2586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurado, E.; Dachs, J.; Duarte, C.M.; Simó, R. Atmospheric deposition of organic and black carbon to the global oceans. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 7931–7939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Feng, T.; Guo, Z.; Li, Y.; Lin, T.; Rose, N.L. Sources and dry deposition of carbonaceous aerosols over the coastal East China Sea: Implications for anthropogenic pollutant pathways and deposition. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 245, 771–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Wang, F.; Li, J.; Tian, L.; Jiang, X.; Yang, J.; Chen, B. Historical variation in black carbon deposition and sources to Northern China sediments. Chemosphere 2017, 172, 242–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, M.W.; De Aragão, L.E.O.C.; Dittmar, T.; De Rezende, C.E.; Almeida, M.G.; Johnson, B.T.; Marques, J.S.J.; Niggemann, J.; Rangel, T.P.; Quine, T.A. Environmental controls on the riverine export of dissolved black carbon. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2019, 33, 849–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Lin, T.; Hu, L.; Tian, C.; Luo, Y.; Yang, X.; Li, J.; Zhang, G. Spatiotemporal Trends of Elemental Carbon and Char/Soot Ratios in Five Sediment Cores from Eastern China Marginal Seas: Indicators of Anthropogenic Activities and Transport Patterns. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 9704–9712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Tian, C.; Wang, X.; Lin, T.; Hu, L.; Li, J.; Zhang, G.; Luo, Y. Cycling and budgets of organic and black carbon in coastal Bohai Sea, China: Impacts of natural and anthropogenic perturbations. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2018, 32, 971–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coppola, A.I.; Wagner, S.; Lennartz, S.T.; Seidel, M.; Ward, N.D.; Dittmar, T.; Santín, C.; Jones, M.W. The black carbon cycle and its role in the Earth system. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2022, 3, 516–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, M.W.; Quine, T.A.; de Rezende, C.E.; Dittmar, T.; Johnson, B.; Manecki, M.; Marques, J.S.J.; de Aragão, L.E.O.C. Do Regional Aerosols Contribute to the Riverine Export of Dissolved Black Carbon? J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2017, 122, 2925–2938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, S.; Jaffé, R.; Stubbins, A. Dissolved black carbon in aquatic ecosystems. Limnol. Oceanogr. Lett. 2018, 3, 168–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coppola, A.I.; Wiedemeier, D.B.; Galy, V.; Haghipour, N.; Hanke, U.M.; Nascimento, G.S.; Usman, M.; Blattmann, T.M.; Reisser, M.; Freymond, C.V.; et al. Global-scale evidence for the refractory nature of riverine black carbon. Nat. Geosci. 2018, 11, 584–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- González-Gaya, B.; Fernández-Pinos, M.C.; Morales, L.; Méjanelle, L.; Abad, E.; Piña, B.; Duarte, C.M.; Jiménez, B.; Dachs, J. High atmosphere–ocean exchange of semivolatile aromatic hydrocarbons. Nat. Geosci. 2016, 9, 438–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Xu, C.; Druffel, E.M.; Xue, Y.; Qi, Y. Two black carbon pools transported by the Changjiang and Huanghe Rivers in China. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2016, 30, 1778–1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, M.W.; Coppola, A.I.; Santín, C.; Dittmar, T.; Jaffé, R.; Doerr, S.H.; Quine, T.A. Fires prime terrestrial organic carbon for riverine export to the global oceans. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 2791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, H.; Niggemann, J.; Luo, L.; Dittmar, T.; Kao, S.J. Aerosols as a source of dissolved black carbon to the ocean. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, M.; Liu, Q.; Cai, W.-J.; Yin, Z.; Meng, F.; Chen, C.-T.A.; Swaney, D.P. Spatial distribution of riverine DOC inputs to the ocean: An updated global synthesis. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sustain. 2012, 4, 170–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaffé, R.; Ding, Y.; Niggemann, J.; Vähätalo, A.V.; Stubbins, A.; Spencer, R.G.M.; Campbell, J.; Dittmar, T. Global charcoal mobilization from soils via dissolution and riverine transport to the oceans. Science 2013, 340, 345–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tranvik, L.J. New light on black carbon. Nat. Geosci. 2018, 11, 547–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Titos, G.; del Águila, A.; Cazorla, A.; Lyamani, H.; Casquero-Vera, J.A.; Colombi, C.; Cuccia, E.; Gianelle, V.; Močnik, G.; Alastuey, A.; et al. Spatial and temporal variability of carbonaceous aerosols: Assessing the impact of biomass burning in the urban environment. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 578, 613–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zheng, G.; Duan, F.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Huang, T.; Kimoto, T.; Cheng, Y.; Su, H.; He, K. Episode-Based Evolution Pattern Analysis of Haze Pollution: Method Development and Results from Beijing, China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 4632–4641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, F.; Zhang, X.; Hao, C.; Tiwari, S.; Chen, B. Light absorption enhancement of particulate matters and their source apportionment over the Asian continental outflow site and South Yellow Sea. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 28, 8022–8035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Tao, S.; Shen, H.; Huang, Y.; Chen, H.; Balkanski, Y.; Boucher, O.; Ciais, P.; Shen, G.; Li, W.; et al. Trend in global black carbon emissions from 1960 to 2007. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 6780–6787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, W.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, J.; Yu, Q.; Cheng, S.; Li, W.; Liu, X.; Tian, H. Variation, sources and historical trend of black carbon in Beijing, China based on ground observation and MERRA-2 reanalysis data. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 245, 853–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Tian, C.; Lin, T.; Hu, L.; Huang, G.; Tang, J.; Li, J.; Zhang, G. Flux and budget of BC in the continental shelf seas adjacent to Chinese high BC emission source regions. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2015, 29, 957–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamashita, Y.; Nakane, M.; Mori, Y.; Nishioka, J.; Ogawa, H. Fate of dissolved black carbon in the deep Pacific Ocean. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Gasser, T.; Ciais, P.; Piao, S.; Tao, S.; Balkanski, Y.; Hauglustaine, D.; Boisier, J.P.; Chen, Z.; Huang, M.; et al. The contribution of China’s emissions to global climate forcing. Nature 2016, 531, 357–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shindell, D.; Kuylenstierna, J.C.I.; Vignati, E.; Van Dingenen, R.; Amann, M.; Klimont, Z.; Anenberg, S.C.; Muller, N.; Janssens-Maenhout, G.; Raes, F.; et al. Simultaneously mitigating near-term climate change and improving human health and food security. Science 2012, 335, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Q.; Streets, D.G.; Carmichael, G.R.; He, K.B.; Huo, H.; Kannari, A.; Klimont, Z.; Park, I.S.; Reddy, S.; Fu, J.S.; et al. Asian emissions in 2006 for the NASA INTEX-B mission. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2009, 9, 5131–5153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Singh, A.K.; Singh, A.K.; Singh, R.; Singh, R.P.; Adams, K.; Dowden, R.L. Subionospheric VLF perturbations observed at a low latitude station Varanasi (L = 1.07). Adv. Space Res. 2015, 55, 576–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.M.; Wei, C.; Huang, R.J.; Bandowe, B.A.M.; Ho, S.S.H.; Cao, J.J.; Jin, Z.D.; Xu, B.Q.; Gao, S.P.; Tie, X.X.; et al. Reconstruction of atmospheric soot history in inland regions from lake sediments over the past 150 years. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 19151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, F.; Zong, Y.Q.; Li, J.F.; Tian, L.Z.; Shang, Z.W.; Chen, Y.S.; Jiang, X.Y.; Yang, J.L.; Yang, B.; Wang, H. Recent Sedimentation Dynamics Indicated by 210Pbexc and 137Cs Records from the Subtidal Area of Bohai Bay, China. J. Coast. Res. 2016, 32, 416–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Shi, X.; Bai, Y.; Fang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Qiao, S.; Liu, S.; Yang, G.; Kornkanitnan, N.; Khokiattiwong, S. Distribution, input pathway and mass inventory of black carbon in sediments of the Gulf of Thailand, SE Asia. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2016, 170, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Cao, J.; An, Z.; Chow, J.C.; Watson, J.G.; Jin, Z.; Fung, K.; Liu, S. Evaluation of the thermal/optical reflectance method for quantification of elemental carbon in sediments. Chemosphere 2007, 69, 526–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-García, L.; Cato, I.; Gustafsson, Ö. The sequestration sink of soot black carbon in the Northern European Shelf sediments. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2012, 26, GB1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, K.; Shen, J.; Wang, G.; Gao, C. Anthropogenic black carbon emission increase during the last 150 years at Coastal Jiangsu, China. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0129680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Taylor, K.E.; Stouffer, R.J.; Meehl, G.A. An Overview of CMIP5 and the Experiment Design. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2012, 93, 485–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, Y.H.; Lamarque, J.F.; Flanner, M.G.; Jiao, C.; Shindell, D.T.; Berntsen, T.; Bisiaux, M.M.; Cao, J.; Collins, W.J.; Curran, M.; et al. Evaluation of preindustrial to present-day black carbon and its albedo forcing from Atmospheric Chemistry and Climate Model Intercomparison Project (ACCMIP). Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 2607–2634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Collins, W.J.; Bellouin, N.; Doutriaux-Boucher, M.; Gedney, N.; Halloran, P.; Hinton, T.; Hughes, J.; Jones, C.D.; Joshi, M.; Liddicoat, S.; et al. Development and evaluation of an Earth-System model—HadGEM2. Geosci. Model Dev. 2011, 4, 1051–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dix, M.; Vohralik, P.; Bi, D.; Rashid, H.; Marsland, S.; O’Farrell, S.; Uotila, P.; Hirst, T.; Kowalczyk, E.; Sullivan, A.; et al. The ACCESS coupled model: Documentation of core CMIP5 simulations and initial results. Aust. Meteorol. Oceanogr. J. 2013, 63, 83–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Salzen, K.; Scinocca, J.F.; McFarlane, N.A.; Li, J.; Cole, J.N.S.; Plummer, D.; Verseghy, D.; Reader, M.C.; Ma, X.; Lazare, M.; et al. The Canadian Fourth Generation Atmospheric Global Climate Model (CanAM4). Part I: Representation of Physical Processes. Atmosphere-Ocean 2013, 51, 104–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jeffrey, S.; Rotstayn, L.; Collier, M.; Dravitzki, S.; Hamalainen, C.; Moeseneder, C.; Wong, K.; Syktus, J. Australia’s CMIP5 submission using the CSIRO-Mk3.6 model. Aust. Meteorol. Oceanogr. J. 2013, 63, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunne, J.P.; John, J.G.; Adcroft, A.J.; Griffies, S.M.; Hallberg, R.W.; Shevliakova, E.; Stouffer, R.J.; Cooke, W.; Dunne, K.A.; Harrison, M.J.; et al. GFDL’s ESM2 Global Coupled Climate–Carbon Earth System Models. Part I: Physical Formulation and Baseline Simulation Characteristics. J. Clim. 2012, 25, 6646–6665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dufresne, J.L.; Foujols, M.A.; Denvil, S.; Caubel, A.; Marti, O.; Aumont, O.; Balkanski, Y.; Bekki, S.; Bellenger, H.; Benshila, R.; et al. Climate change projections using the IPSL-CM5 Earth System Model: From CMIP3 to CMIP5. Clim. Dyn. 2013, 40, 2123–2165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Watanabe, S.; Hajima, T.; Sudo, K.; Nagashima, T.; Takemura, T.; Okajima, H.; Nozawa, T.; Kawase, H.; Abe, M.; Yokohata, T.; et al. MIROC-ESM 2010: Model description and basic results of CMIP5-20c3m experiments. Geosci. Model Dev. 2011, 4, 845–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yukimoto, S.; Adachi, Y.; Hosaka, M.; Sakami, T.; Yoshimura, H.; Hirabara, M.; Tanaka, T.Y.; Shindo, E.; Tsujino, H.; Deushi, M.; et al. A New Global Climate Model of the Meteorological Research Institute: MRI-CGCM3—Model Description and Basic Performance. J. Meteorol. Soc. Japan. Ser. II 2012, 90A, 23–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bentsen, M.; Bethke, I.; Debernard, J.B.; Iversen, T.; Kirkevåg, A.; Seland, Ø.; Drange, H.; Roelandt, C.; Seierstad, I.A.; Hoose, C.; et al. The Norwegian Earth System Model, NorESM1-M—Part 1: Description and basic evaluation of the physical climate. Geosci. Model Dev. 2013, 6, 687–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ekman, A.M.L. Do sophisticated parameterizations of aerosol-cloud interactions in CMIP5 models improve the representation of recent observed temperature trends? J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2014, 119, 817–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Turner, A.G.; Highwood, E.J. Impacts of 20th century aerosol emissions on the South Asian monsoon in the CMIP5 models. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 6367–6378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schmidt, G.A.; Kelley, M.; Nazarenko, L.; Ruedy, R.; Russell, G.L.; Aleinov, I.; Bauer, M.; Bauer, S.E.; Bhat, M.K.; Bleck, R.; et al. Configuration and assessment of the GISS ModelE2 contributions to the CMIP5 archive. J. Adv. Model. Earth Syst. 2014, 6, 141–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adler, R.F.; Huffman, G.J.; Chang, A.; Ferraro, R.; Xie, P.P.; Janowiak, J.; Rudolf, B.; Schneider, U.; Curtis, S.; Bolvin, D.; et al. The version-2 global precipitation climatology project (GPCP) monthly precipitation analysis (1979-present). J. Hydrometeorol. 2003, 4, 1147–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Wang, F.; Li, J.; Tiwari, S.; Chen, B. Assessment of trends and emission sources of heavy metals from the soil sediments near the Bohai Bay. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 29095–29109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.; Tao, S.; Wang, W.; Liu, J.; Shen, H.; Shen, G.; Wang, B.; Liu, X.; Li, W.; Huang, Y.; et al. Black carbon emissions in China from 1949 to 2050. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 7595–7603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.; Xie, S.D. Spatial and temporal variation of anthropogenic black carbon emissions in China for the period 1980-2009. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2012, 12, 4825–4841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Streets, D.G. Sulfur dioxide and primary carbonaceous aerosol emissions in China and India, 1996–2010. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 9839–9864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lei, Y.; Zhang, Q.; He, K.B.; Streets, D.G. Primary anthropogenic aerosol emission trends for China, 1990–2005. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 931–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kurokawa, J.; Ohara, T.; Morikawa, T.; Hanayama, S.; Janssens-Maenhout, G.; Fukui, T.; Kawashima, K.; Akimoto, H. Emissions of air pollutants and greenhouse gases over Asian regions during 2000–2008: Regional Emission inventory in ASia (REAS) version 2. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 11019–11058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Novakov, T.; Ramanathan, V.; Hansen, J.E.; Kirchstetter, T.W.; Sato, M.; Sinton, J.E.; Sathaye, J.A. Large historical changes of fossil-fuel black carbon aerosols. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2003, 30, 1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, S.; Zhao, G.; Wang, T.; Jin, J.; Wang, P.; Lin, Y.; Li, H.; Ying, Q.; Mao, H. Past and future trends of vehicle emissions in Tianjin, China, from 2000 to 2030. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 209, 182–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fohrmann, H.; Backhaus, J.O.; Blaume, F.; Haupt, B.J.; Michels, K.; Mienert, J.; Posewang, J.; Ritzrau, W.; Rumohr, J. Modern ocean current-controlled sediment transport in the Greenland-Iceland-Norwegian (GIN) Seas. In The Northern North Atlantic: A Changing Environment; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2001; pp. 135–154. [Google Scholar]
- Nooteboom, P.D.; Bijl, P.K.; van Sebille, E.; von der Heydt, A.S.; Dijkstra, H.A. Transport Bias by Ocean Currents in Sedimentary Microplankton Assemblages: Implications for Paleoceanographic Reconstructions. Paleoceanogr. Paleoclimatol. 2019, 34, 1178–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, T.J.; Mikkelsen, O.A.; Moller, A.L. Morten Pejrup Deposition and mixing depths on some European intertidal mudflats based on 210Pb and 137Cs activities. Cont. Shelf Res. 2000, 20, 1569–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhou, X.; Ma, Y.; Cao, Z.; Wu, R.; Wang, W. Carbonaceous aerosols over China—Review of observations, emissions, and climate forcing. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 1671–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Decesari, S.; Facchini, M.C.; Matta, E.; Mircea, M.; Fuzzi, S.; Chughtai, A.R.; Smith, D.M. Water soluble organic compounds formed by oxidation of soot. Atmos. Environ. 2002, 36, 1827–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lelieveld, J.; Klingmüller, K.; Pozzer, A.; Burnett, R.T.; Haines, A.; Ramanathan, V. Effects of fossil fuel and total anthropogenic emission removal on public health and climate. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 7192–7197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Giglio, L.; Randerson, J.T.; Van Der Werf, G.R. Analysis of daily, monthly, and annual burned area using the fourth-generation global fire emissions database (GFED4). J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2013, 118, 317–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Coppola, A.I.; Druffel, E.R.M. Cycling of black carbon in the ocean. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2016, 43, 4477–4482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kuzyakov, Y.; Bogomolova, I.; Glaser, B. Biochar stability in soil: Decomposition during eight years and transformation as assessed by compound-specific 14C analysis. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2014, 70, 229–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamarque, J.F.; Bond, T.C.; Eyring, V.; Granier, C.; Heil, A.; Klimont, Z.; Lee, D.; Liousse, C.; Mieville, A.; Owen, B.; et al. Historical (1850-2000) gridded anthropogenic and biomass burning emissions of reactive gases and aerosols: Methodology and application. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2010, 10, 7017–7039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hansen, J.; Sato, M.; Ruedy, R.; Kharecha, P.; Lacis, A.; Miller, R.; Nazarenko, L.; Lo, K.; Schmidt, G.A.; Russell, G.; et al. Climate simulations for 1880–2003 with GISS modelE. Clim. Dyn. 2007, 29, 661–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smith, R.N.B. A scheme for predicting layer clouds and their water content in a general circulation model. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 1990, 116, 435–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellouin, N.; Rae, J.; Jones, A.; Johnson, C.; Haywood, J.; Boucher, O. Aerosol forcing in the Climate Model Intercomparison Project (CMIP5) simulations by HadGEM2-ES and the role of ammonium nitrate. J. Geophys. Res. 2011, 116, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arora, V.K.; Boer, G.J. Uncertainties in the 20th century carbon budget associ-20ated with land use change. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2010, 16, 3327–3348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maier-Reimer, E.; Kriest, I.; Segschneider, J.; Wetzel, P. The HAMburg Ocean Carbon Cycle model HAMOCC 5.1—Technical Description Release 1.1; Reports on Earth System Science 14; Max Planck Institute for Meteorology: Hamburg, Germany, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Kirkevag, A.; Iversen, T.; Seland, Ø.; Hoose, C.; Kristjansson, J.E.; Struthers, H.; Ekman, A.M.L.; Ghan, S.; Griesfeller, J.; Nilsson, E.D.; et al. Aerosol-climate interactions in the Norwegian Earth System Model—NorESM1-M. Geosci. Model Dev. 2013, 6, 207–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
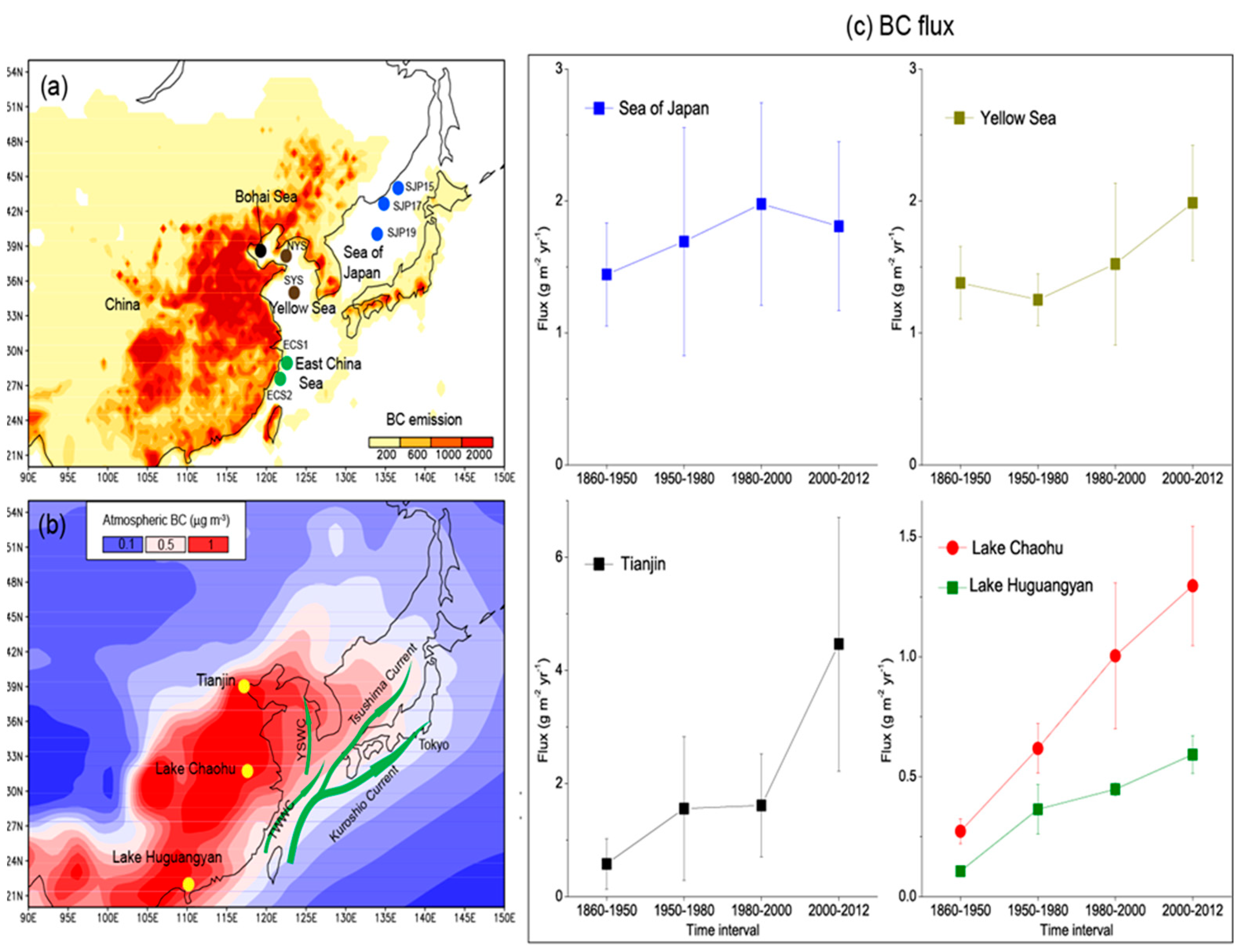

| Site | Longitude, Latitude | Sample Setting | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Marine sediment cores | |||
| SJP15 | 136.49° E, 44.10° N | Sea of Japan, water depth 885 m | This study |
| SJP17 | 134.69° E, 42.85° N | Sea of Japan, water depth 1164 m | This study |
| SJP19 | 133.96° E, 40.05° N | Sea of Japan, water depth 732 m | This study |
| NYS | 122.48° E, 38.16° N | Northern Yellow Sea, water depth 50 m | [13] |
| SYS | 123.50° E, 34.99° N | Southern Yellow Sea, water depth 76 m | [13] |
| Bohai Sea | 119.27° E, 38.60° N | Central mud area in the Bohai Sea, water depth 27 m | [13] |
| ECS1 | 122.50° E, 29.00° N | East China Sea, northern Min Zhe coastal mud area, water depth 50 m | [13] |
| ECS2 | 121.66° E, 27.64° N | East China Sea, southern Min Zhe coastal mud area, water depth 50 m | [13] |
| Sediment cores in China | |||
| Tianjin | 117.51° E, 38.77° N | Three parallel cores from a wetland/marsh in the south of Tianjin, north China | This study |
| Lake Chaohu | 117.50° E, 31.50° N | One of the famous “five freshwater lakes” in Anhui Province of eastern China. Average water depth is ~2.7 m | [37] |
| Lake Huguangyan | 110.28° E, 21.15° N | A maar lake with a natural sediment trap in southeastern China. Average water depth is ~20 m | [37] |
| 1860–1950 | 1950–1980 | 1980–2000 | 2000–2012 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average | S.D. # | Average | S.D. # | Average | S.D. # | Average | S.D. # | |
| Fluxes (g m−2 yr−1) | ||||||||
| Bohai Sea | 4.7 | 0.6 | 6.0 | 1.0 | 5.8 | 1.5 | 9.7 | 2.1 |
| Yellow Sea | 1.4 | 0.3 | 1.3 | 0.2 | 1.5 | 0.6 | 2.0 | 0.4 |
| East China Sea | 9.2 | 2.8 | 9.4 | 2.4 | 13.6 | 5.2 | 20.8 | 4.9 |
| Sea of Japan | 1.4 | 0.4 | 1.7 | 0.9 | 2.0 | 0.8 | 1.8 | 0.6 |
| Tianjin | 0.6 | 0.4 | 1.6 | 1.3 | 1.6 | 0.9 | 4.5 | 2.2 |
| Lake Chaohu | 0.3 | 0.1 | 0.6 | 0.1 | 1.0 | 0.3 | 1.3 | 0.2 |
| Lake Huguangyan | 0.11 | 0.02 | 0.36 | 0.10 | 0.45 | 0.03 | 0.59 | 0.08 |
| Increase Factor | ||||||||
| Bohai Sea | 1.0 | 1.3 | 1.2 | 2.1 | ||||
| Yellow Sea | 1.0 | 0.9 | 1.1 | 1.4 | ||||
| East China Sea | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.5 | 2.3 | ||||
| Sea of Japan | 1.0 | 1.2 | 1.4 | 1.3 | ||||
| Tianjin | 1.0 | 2.7 | 2.8 | 7.7 | ||||
| Lake Chaohu | 1.0 | 2.3 | 3.7 | 4.7 | ||||
| Lake Huguangyan | 1.0 | 3.4 | 4.2 | 5.6 |
| Site | 1950–1980 | 1980–2000 | 2000–2012 | Surface | Average | S.D. # |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bohai Sea | 50.6 | 74.8 | 69.9 | 74.0 | 67.3 | 11.3 |
| Yellow Sea | 62.4 | 75.4 | 75.8 | 73.3 | 71.7 | 6.3 |
| East China Sea | 58.9 | 68.0 | 62.8 | N.A. | 63.2 | 4.6 |
| Sea of Japan | 36.5 | 59.4 | 68.8 | N.A. | 54.9 | 16.6 |
| Total Average | 52.1 | 69.4 | 69.3 | 73.7 | 65.1 | 11.1 |
| Total S.D. | 11.5 | 7.4 | 5.3 | 0.5 | 7.1 | 5.4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, B.; Tiwari, S.; Liu, K.; Zou, J. More Than Half of Emitted Black Carbon Is Missing in Marine Sediments. Sustainability 2023, 15, 9739. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15129739
Chen B, Tiwari S, Liu K, Zou J. More Than Half of Emitted Black Carbon Is Missing in Marine Sediments. Sustainability. 2023; 15(12):9739. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15129739
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Bing, Shani Tiwari, Kun Liu, and Jianjun Zou. 2023. "More Than Half of Emitted Black Carbon Is Missing in Marine Sediments" Sustainability 15, no. 12: 9739. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15129739
APA StyleChen, B., Tiwari, S., Liu, K., & Zou, J. (2023). More Than Half of Emitted Black Carbon Is Missing in Marine Sediments. Sustainability, 15(12), 9739. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15129739





