Analysis of Factors Affecting the Extra Journey Time of Public Bicycles
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
3. Methods
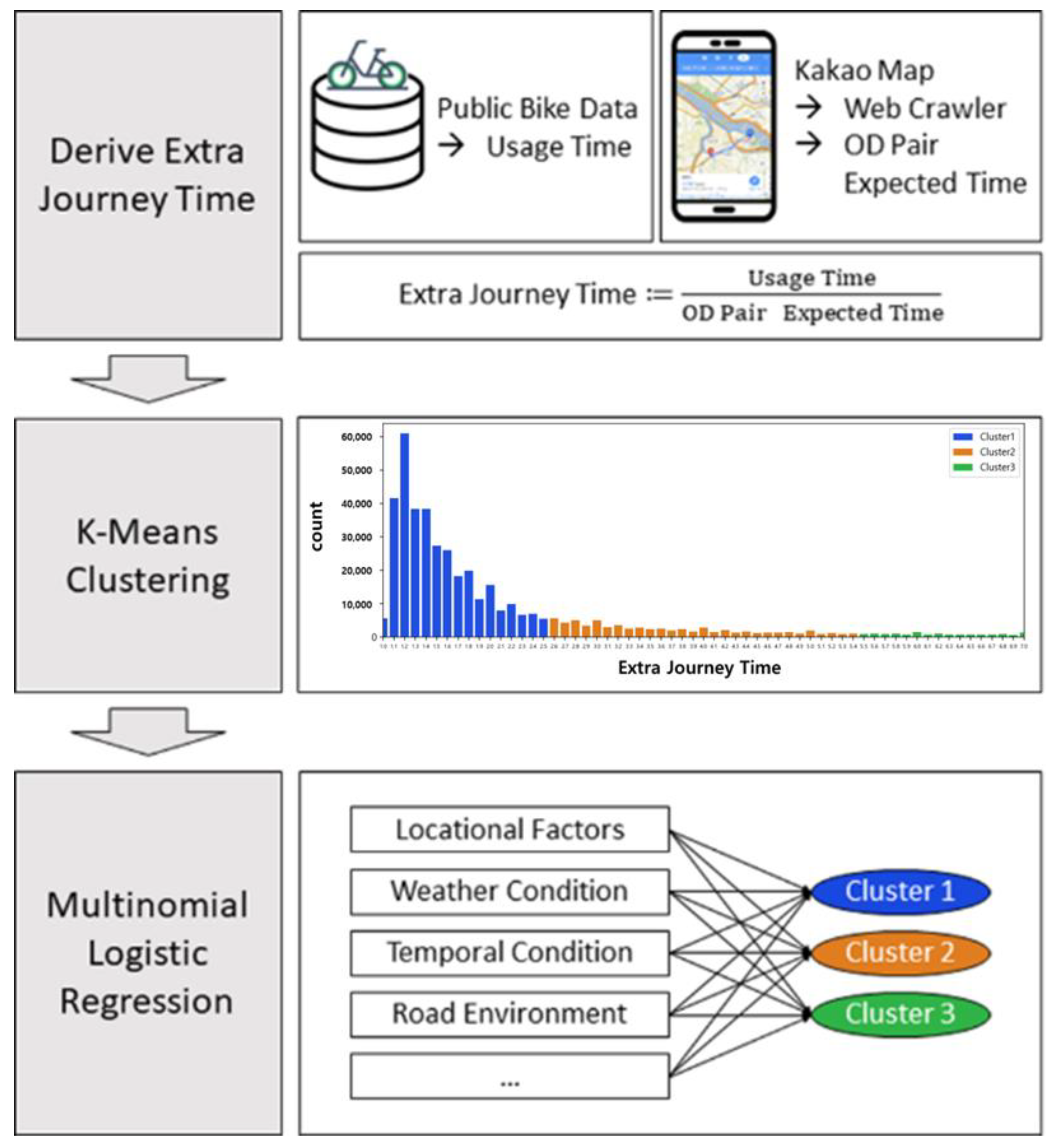
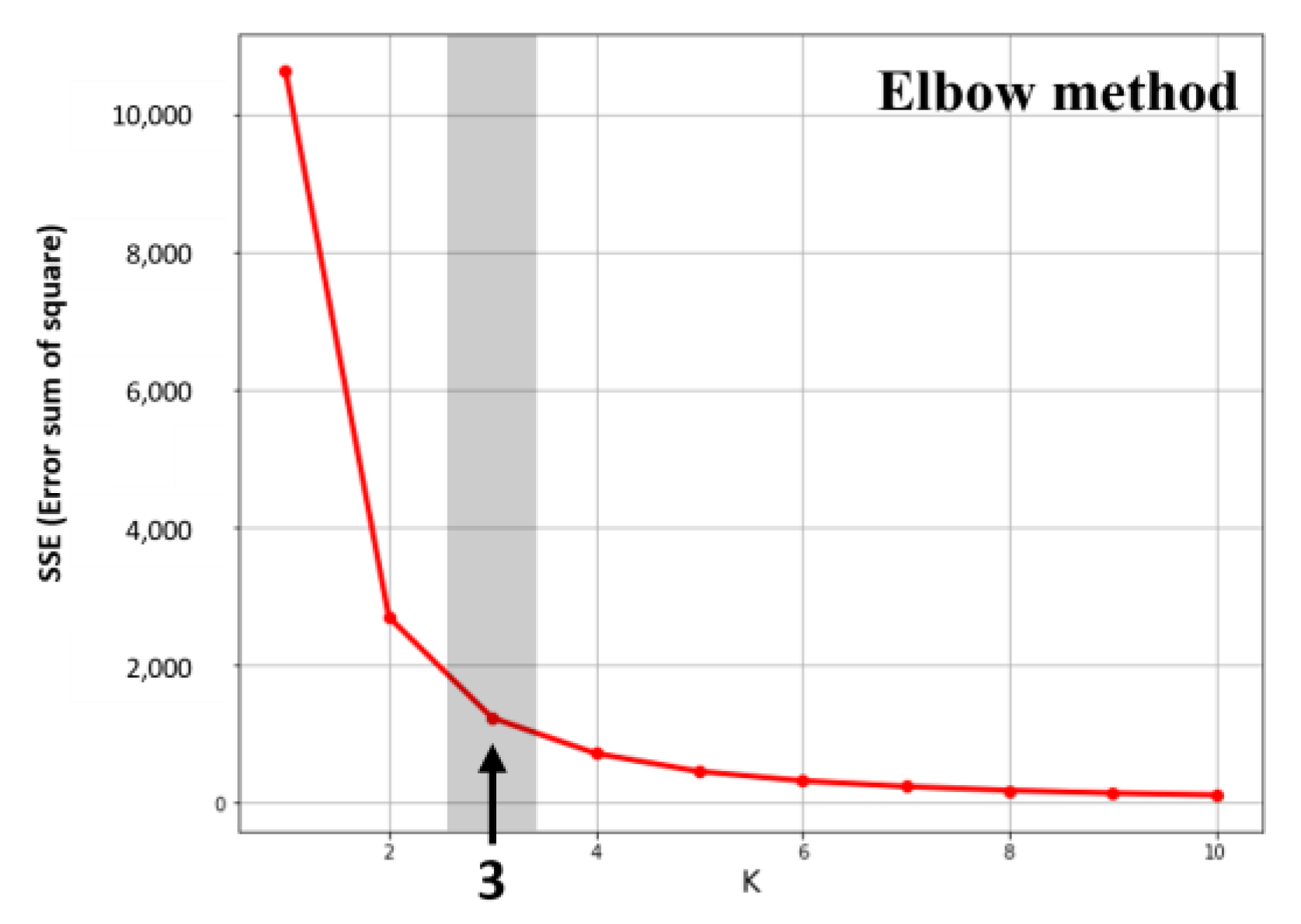
3.1. K-Means Clustering
- Step 1: Randomly set the centroids;
- Step 2: Allocate each object to the cluster closest to the centroid Equation (2);
- Step 3: Update the centroid using Equation (4);
- Step 4: Repeat steps 2 and 3 until convergence.
3.2. Multinomial Logistic Regression
4. Study Case
4.1. Data
4.2. Analysis Results
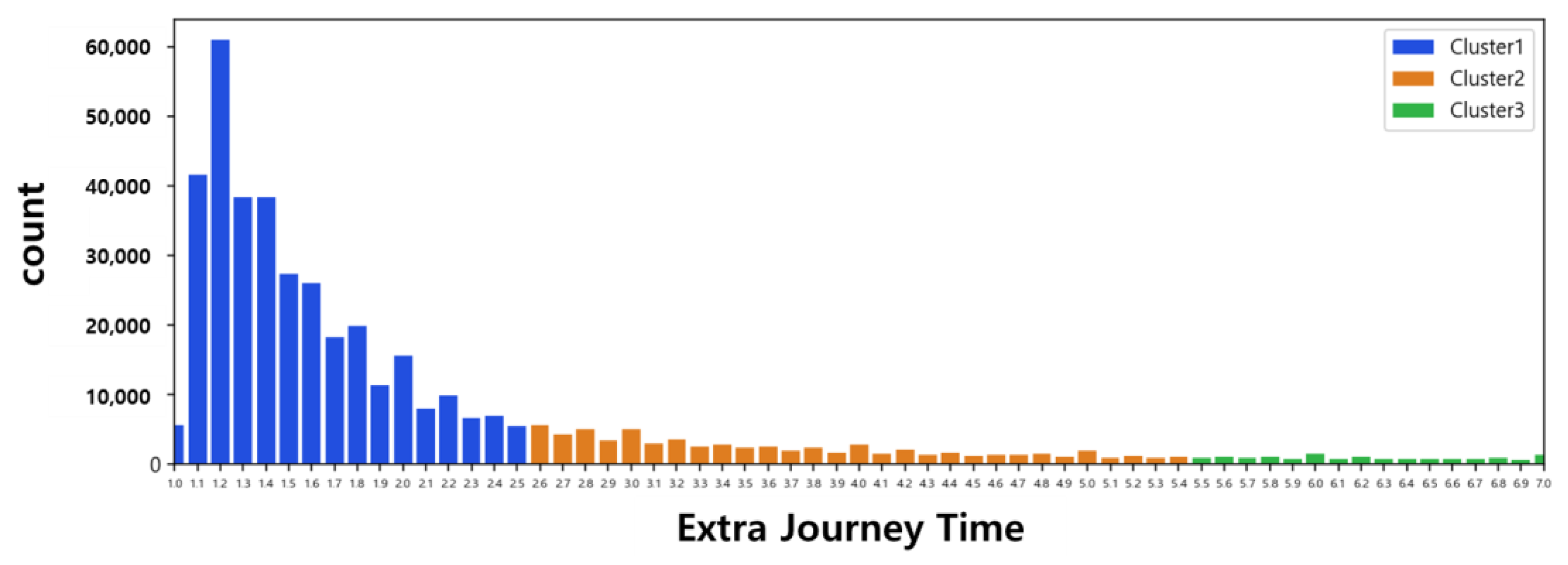
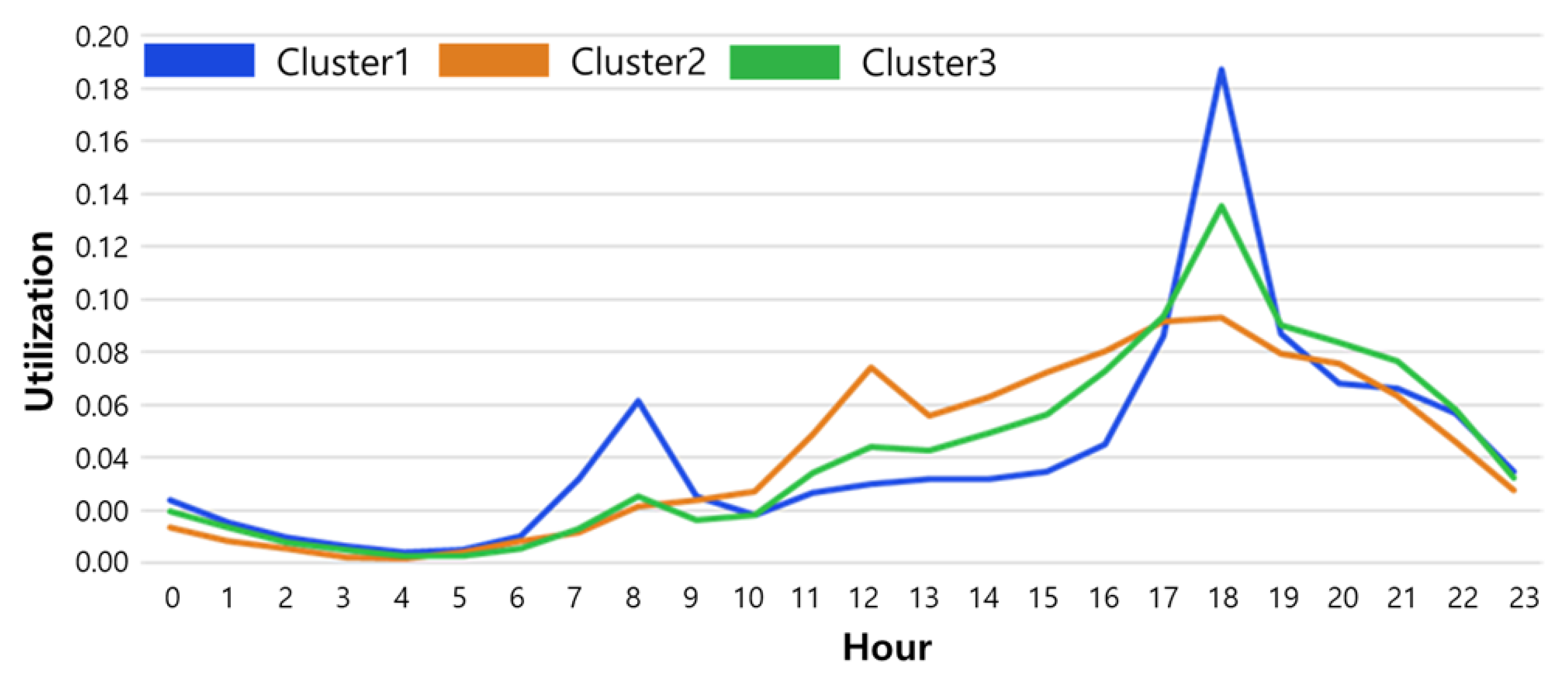
4.2.1. Clustering Results
4.2.2. Multinomial Logistic Regression Results
- (1)
- Performed multinomial logistic regression analysis and k-means clustering to identify and characterize the factors affecting the extra journey time for trips using public bicycles;
- (2)
- Used temporal and spatial variables from various sources to analyze the effects of the different factors affecting public bicycle usage behaviors;
- (3)
- Inferred the public bicycle trip purpose through regression and clustering methods.
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jeong, S.W. Impacts of Automated Vehicles on Running Stability, Traffic Flow and Traffic Safety. Ph.D. Thesis, Hongik University, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Park, H.K. An Analytic Study on Usage Characteristics of the Public Bike Rental Service, “Seoul Bike” at Rush Hours. Master’s Thesis, Seoul City University, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, J.S.; Lee, J.Y.; Park, E.A.; Heo, G.H. A Study on Green Transport Mode Choice and Environmental Awareness; The Korea Transport Institute: Sejong, Republic of Korea, 2011; pp. 1–157.
- Shin, H.C.; Kim, D.J. Impact Analysis on Bike-Sharing and Its Improvement Plan; The Korea Transport Institute: Sejong, Republic of Korea, 2012; pp. 1–310.
- Zhang, Y.; Thomas, T.; Brussel, M.; Van Maarseveen, M. Exploring the impact of built environment factors on the use of public bikes at bike stations: Case study in Zhongshan, China. J. Transport. Geogr. 2017, 58, 59–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, C.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Wu, X.; Yang, X. Exploring multi-scale spatial relationship between built environment and public bicycle ridership. J. Transp. Land Use 2020, 13, 447–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Midgley, P. Bicycle-sharing schemes: Enhancing sustainable mobility in urban areas. In Proceedings of the Commission on Sustainable Development, 19th Session, New York, NY, USA, 2–13 May 2011; United Nations, Department of Economic and Social Affairs: New York, NY, USA, 2011; Volume 8, pp. 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, M.H. Forecasting Public Bicycle Demand of Seoul Based on Time Series Clustering. Master’s Thesis, Hanyang University, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Ricci, M. Bike sharing: A review of evidence on impacts and processes of implementation and operation. Res. Transp. Bus. Manag. 2015, 15, 28–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.Y.; Shin, E.K.; Kim, S.Y. Impacts of the Regional Environment Characteristics on the Public Bicycle Use: Analysis of the Spatial Information Using the Public Bicycles OD Flow-data in Changwon-si. J. Archit. Inst. Korea Plan. Des. 2014, 30, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sa, K.E.; Lee, S.G. Analysis of Physical Characteristics Affecting the Usage of Public Bike in Seoul, Korea: Focused on the Different Influences of Factors by Distance to Bike Station. J. Korea Plan. Assoc. 2018, 53, 39–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, J.M.; Kim, T.H.; Lee, M.Y. A Study on the Seoul Public Bikes Use Characteristics: A Case of the Districts of Yeouido and Sangam. Seoul Stud. 2016, 17, 77–91. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, D.J.; Shin, H.C.; Park, J.S.; Im, H.J. The Impact of Weather on Bicycle Usage: Focus on Usage of Bike-sharing System in Goyang. J. Transp. Res. 2012, 19, 77–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pucher, J.; Komanoff, C.; Schimek, P. Bicycling renaissance in North America?: Recent trends and alternative policies to promote bicycling. Transp. Res. Part A Policy Pract. 1999, 33, 625–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Jeong, K.O.; Shin, H.C. Impact Analysis of Weather Condition and Locational Characteristics on the Usage of Public Bike Sharing System. J. Korean Soc. Transp. 2016, 34, 394–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faghih-Imani, A.; Eluru, N.; El-Geneidy, A.M.; Rabbat, M.; Haq, U. How land-use and urban form impact bicycle flows: Evidence from the bicycle-sharing system (BIXI) in Montreal. J. Transp. Geogr. 2014, 41, 306–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, T.D.; Ovtracht, N.; d’Arcier, B.F. Modeling bike sharing system using built environment factors. Procedia CIRP 2015, 30, 293–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mateo-Babiano, I.; Bean, R.; Corcoran, J.; Pojani, D. How does our natural and built environment affect the use of bicycle sharing? Transp. Res. Part A Policy Pract. 2016, 94, 295–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corcoran, J.; Li, T.; Rohde, D.; Charles-Edwards, E.; Mateo-Babiano, D. Spatio-temporal patterns of a Public Bicycle Sharing Program: The effect of weather and calendar events. J. Transp. Geogr. 2014, 41, 292–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebhart, K.; Noland, R.B. The impact of weather conditions on bikeshare trips in Washington, DC. Transportation 2014, 41, 1205–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puello, L.L.P.; Geurs, K. Modelling observed and unobserved factors in cycling to railway stations: Application to transit oriented developments in the Netherlands. Eur. J. Transp. Infrastruct. Res. 2015, 15, 27–50. [Google Scholar]
- Fuller, D.; Sahlqvist, S.; Cummins, S.; Ogilvie, D. The impact of public transportation strikes on use of a bicycle share program in London: Interrupted time series design. Prev. Med. 2012, 54, 74–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Palomares, J.C.; Gutiérrez, J.; Latorre, M. Optimizing the location of stations in bike-sharing programs: A GIS approach. Appl. Geogr. 2012, 35, 235–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fishman, E.; Washington, S.; Haworth, N. Bike share: A synthesis of the literature. Transp. Rev. 2013, 33, 148–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Lindsey, G.; Schoner, J.E.; Harrison, A. Modeling bike share station activity: Effects of nearby businesses and jobs on trips to and from stations. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2207.10577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Midgley, P. The role of smart bike-sharing systems in urban mobility. Journeys 2009, 2, 23–31. [Google Scholar]
- Shang, W.-L.; Chen, J.; Bi, H.; Sui, Y.; Chen, Y.; Yu, H. Impacts of COVID-19 pandemic on user behaviors and environmental benefits of bike sharing: A big-data analysis. Appl. Energy 2021, 285, 116429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Y.; Wang, K.; Lu, J.J. Exploring travel patterns and trip purposes of dockless bike-sharing by analyzing massive bike-sharing data in Shanghai, China. J. Transp. Geogr. 2020, 87, 102787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarano, A.; Aria, M.; Mauriello, F.; Riccardi, M.R.; Montella, A. Systematic literature review of 10 years of cyclist safety research. Accid. Anal. Prev. 2023, 184, 106996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McBain, C.; Caulfield, B. An analysis of the factors influencing journey time variation in the cork public bike system. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2018, 42, 641–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathishkumar, V.E.; Cho, Y. Season-wise bike sharing demand analysis using random forest algorithm. Comput. Intell. 2020, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fournier, N.; Christofa, E.; Knodler, M.A., Jr. A sinusoidal model for seasonal bicycle demand estimation. Transp. Res. D Transp. Environ. 2017, 50, 154–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, M.A.; Yamamoto, S.S.; Malik, A.A.; Sauerborn, R. Households’ perception of climate change and human health risks: A community perspective. Environ. Health 2012, 11, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Wang, J.; Xing, Z.; Luan, X.; Jiang, Y. Weather and cycling: Mining big data to have an in-depth understanding of the association of weather variability with cycling on an off-road trail and an on-road bike lane. Transp. Res. Part A Policy Pract. 2018, 111, 119–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McQueen, J. Some methods for classification and analysis of multivariate observations. In Proceedings of the 5th Berkeley Symposium on Mathematical Statistics and Probability, Statistical Laboratory, University of California, Berkeley, CA, USA, 21 June–18 July 1965 and 27 December 1965–7 January 1966; Le Cam, L.M., Neyman, J., Eds.; University of California Press: Durham, NC, USA, 1967; pp. 281–297. [Google Scholar]


| Bike No. | Rental Information | Return Information | Usage Time (min) | Trip Distance (m) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Date | Station No. | Station Name | Date | Station No. | Station Name | |||
| SPB-10324 | 3 July 2018 12:48 | 215 | Yeouido High School | 3 July 2018 13:03 | 209 | Building of Eugene Investment Co. | 14 | 1640 |
| SPB-17638 | 3 July 2018 13:21 | 212 | Exit 1 of Yeouido Subway Station | 3 July 2018 13:32 | 212 | Exit 1 of Yeouido Subway Station | 10 | 1160 |
| SPB-06886 | 3 July 2018 13:23 | 260 | Yeouido Marina Quay | 3 July 2018 13:35 | 206 | Yeouido KBS | 10 | 1600 |
| ⋮ | ||||||||
| Variables | Description | Source | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Usage Factors | Station Size Start/End | Number of rental/return station stands | Seoul public bike rental history (2018) |
| OD-Pair Station Distance (m) | Straight distance in latitude and longitude to the rental/return station | ||
| Usage Distance (m) | User’s actual distance to the rental/return station | ||
| Speed (km/h) | Average riding speed of the bike to the rental/return station | ||
| Day | Time of use of public bikes in rental stations (weekdays/weekend) | ||
| TOD (Time of Day) | AM peak (07:00–10:00), PM peak (18:00–21:00), Interpeak (11:00–17:00), Off peak (22:00–06:00) | ||
| Location Factors | Bike Priority Road | Bike priority road within a 100 m radius of the rental station | Seoul open data plaza (2018) |
| Nearest Subway Dist. Start/End (m) | Distance from the rental/return station to the nearest subway station | ||
| Restaurants Start/End | Number of restaurants within 100 m of the rental/return station | Business information DB (2018) | |
| Leisure Start/End | The number of tour/entertainment/leisure shops within 100 m of the rental/return station | ||
| Weather Factors | Temperature (°C) | Hourly average temperatures in Yeongdeungpo-gu, Seoul | Weather information DB (2018) |
| Rainfall (mm) | Hourly average rainfall in Yeongdeungpo-gu, Seoul | ||
| Fine Dust (μg/m³) | Daily average fine dust in Yeongdeungpo-gu, Seoul PM10 | ||
| Cluster 1 | Cluster 2 | Cluster 3 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| count | 339,178 | 65,724 | 27,893 |
| mean | 1.5 | 3.6 | 7.4 |
| std | 0.3 | 0.8 | 1.3 |
| min | 0.0 | 2.6 | 5.5 |
| max | 2.5 | 5.4 | 10.0 |
| Cluster 1 | Cluster 2 | Cluster 3 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OD-Pair Station Distance (m) | mean | 2728.48 | 2088.57 | 1006.62 |
| std | 2422.51 | 1561.77 | 651.23 | |
| Usage Distance (m) | mean | 4153.57 | 5261.67 | 5167.34 |
| std | 3940.45 | 4283.70 | 4109.02 | |
| OD-Pair Expected Time (min) | mean | 16.31 | 13.01 | 7.41 |
| std | 21.21 | 7.80 | 3.54 | |
| Usage Time (min) | mean | 24.58 | 45.07 | 53.31 |
| std | 19.10 | 25.68 | 23.50 | |
| Cluster 2 | Cluster 3 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Const. | −4.57 *** | −8.65 | ||
| Usage Factors | Station Size Start | 10–20 | 0.03 ** | 0.01 |
| >21 | 0.02 | 0.10 *** | ||
| (Ref.) < 10 | ||||
| Station Size End | 10–20 | 0.16 *** | 0.24 *** | |
| >21 | 0.22 *** | 0.30 *** | ||
| (Ref.) < 10 | ||||
| OD-Pair Station Distance | 881–1621 m | −1.81 *** | −3.36 *** | |
| 1621–3152 m | −3.62 *** | −7.11 *** | ||
| >3152 m | −5.99 *** | −12.16 *** | ||
| (Ref.) < 881 m | ||||
| Usage Distance | 1581–3120 m | 2.81 *** | 4.26 *** | |
| 3120–6140 m | 5.37 *** | 8.33 *** | ||
| >6140 m | 8.24 *** | 13.04 *** | ||
| (Ref.) < 1581 m | ||||
| Speed | <5 km/h | 5.14 *** | 8.00 *** | |
| 5–10 km/h | 1.48 *** | 2.66 *** | ||
| 10–20 km/h | −0.28 ** | 0.18 | ||
| (Ref.) > 20 km/h | ||||
| Day | Weekday | −0.29 *** | −0.22 *** | |
| (Ref.) Weekend | ||||
| TOD (Time of Day) | AM and PM peak | 0.05 *** | 0.18 *** | |
| Interpeak | 0.37 *** | 0.70 *** | ||
| (Ref.) Off peak | ||||
| Location Factors | Nearest Subway Start | ≤250 m | 0.16 *** | 0.16 *** |
| (Ref.) > 250 m | ||||
| Nearest Subway End | ≤250 m | 0.12 *** | 0.06 *** | |
| (Ref.) > 250 m | ||||
| Restaurants Start | 10–34 shops | −0.42 *** | −0.35 *** | |
| ≥35 shops | −0.41 *** | −0.39 *** | ||
| (Ref.) < 10 shops | ||||
| Restaurants End | 10–34 shops | −0.36 *** | −0.44 *** | |
| ≥35 shops | −0.38 *** | −0.44 *** | ||
| (Ref.) < 10 shops | ||||
| Leisure Start | ≥1 shop | 0.10 *** | 0.11 *** | |
| (Ref.) 0 | ||||
| Leisure End | ≥1 shop | 0.01 | 0.04 * | |
| (Ref.) 0 | ||||
| Bike Priority Road | Yes | 0.31 *** | 0.56 *** | |
| (Ref.) No | ||||
| Weather Factors | Temperature | ≤10 °C | −0.12 *** | −0.08 *** |
| ≥33 °C | −0.05 * | −0.15 *** | ||
| (Ref.) 11–32 °C | ||||
| Rainfall | <10 mm | 0.02 | 0.03 | |
| ≥10 mm | −0.59 | −2.18 ** | ||
| (Ref.) 0 mm | ||||
| Fine dust | Poor/Very poor | −0.05 *** | −0.07 *** | |
| (Ref.) other | ||||
| Model fit statistics | (Ref.) is a reference term | |||
| The reference category is: | Cluster 1 | * This has a significance p-value < 0.10 | ||
| Pseudo-R-squared: | 0.454 | Degrees of Freedom: 60 | ** This has a significance p-value < 0.05 | |
| AIC: | 309,261 | BIC: 309,942 | *** This has a significance p-value < 0.01 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jung, J.; Jung, D. Analysis of Factors Affecting the Extra Journey Time of Public Bicycles. Sustainability 2023, 15, 13804. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151813804
Jung J, Jung D. Analysis of Factors Affecting the Extra Journey Time of Public Bicycles. Sustainability. 2023; 15(18):13804. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151813804
Chicago/Turabian StyleJung, Jongwoo, and Doyoung Jung. 2023. "Analysis of Factors Affecting the Extra Journey Time of Public Bicycles" Sustainability 15, no. 18: 13804. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151813804
APA StyleJung, J., & Jung, D. (2023). Analysis of Factors Affecting the Extra Journey Time of Public Bicycles. Sustainability, 15(18), 13804. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151813804





