Assessment of Stormwater Quality in the Context of Traffic Congestion: A Case Study in Egypt
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
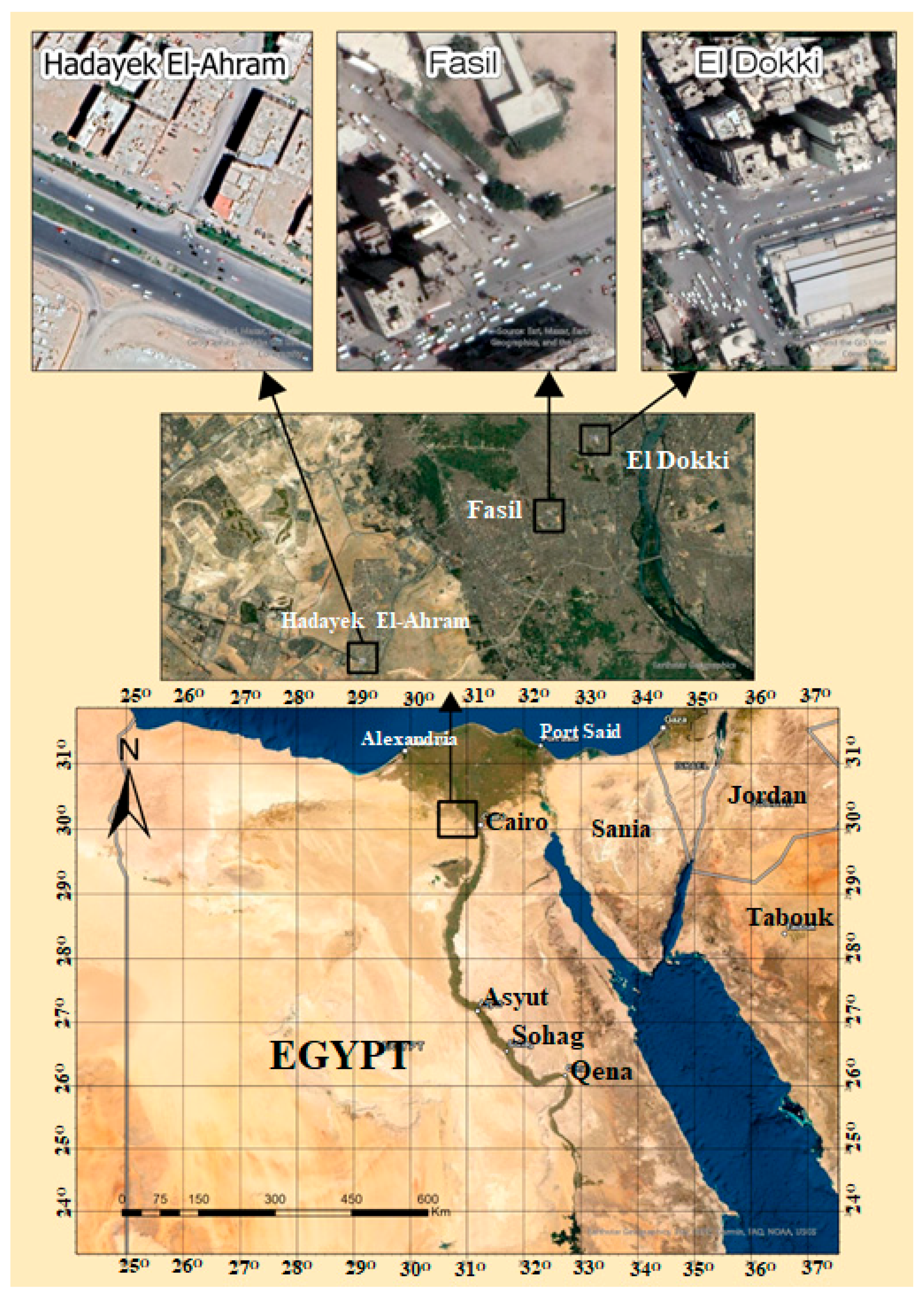
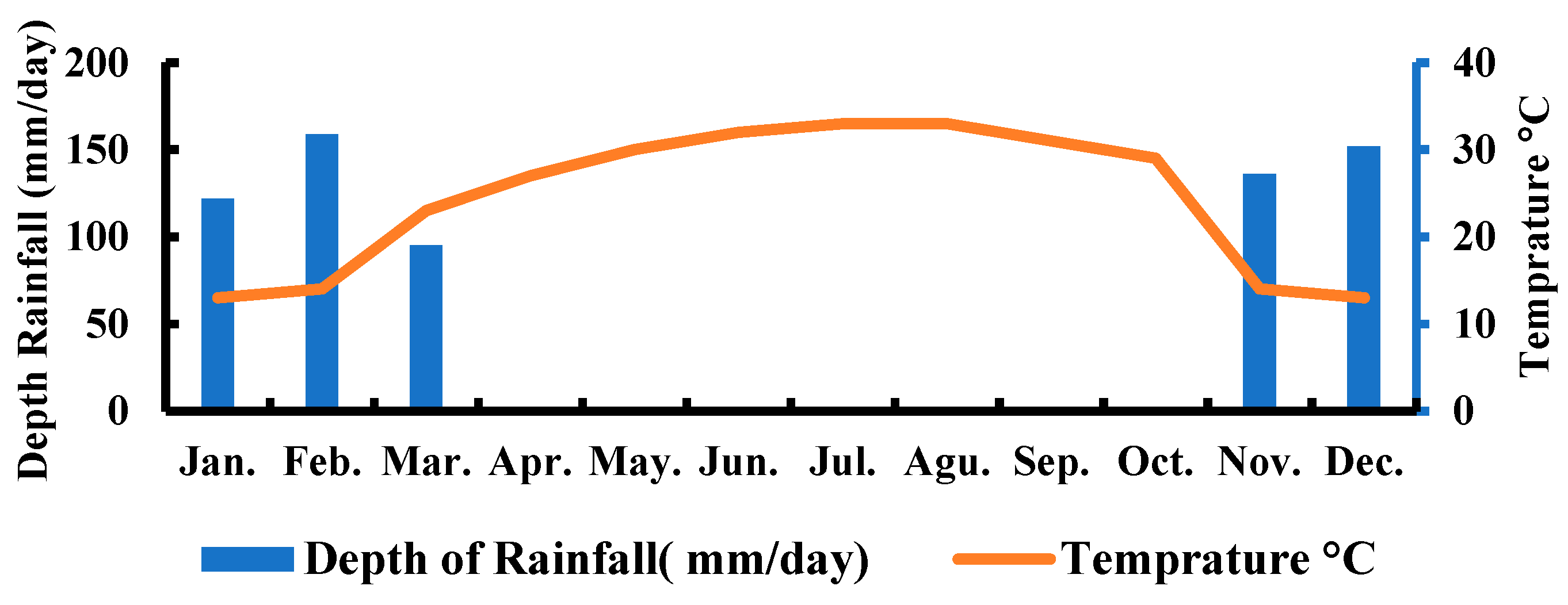
2.1. Study Area
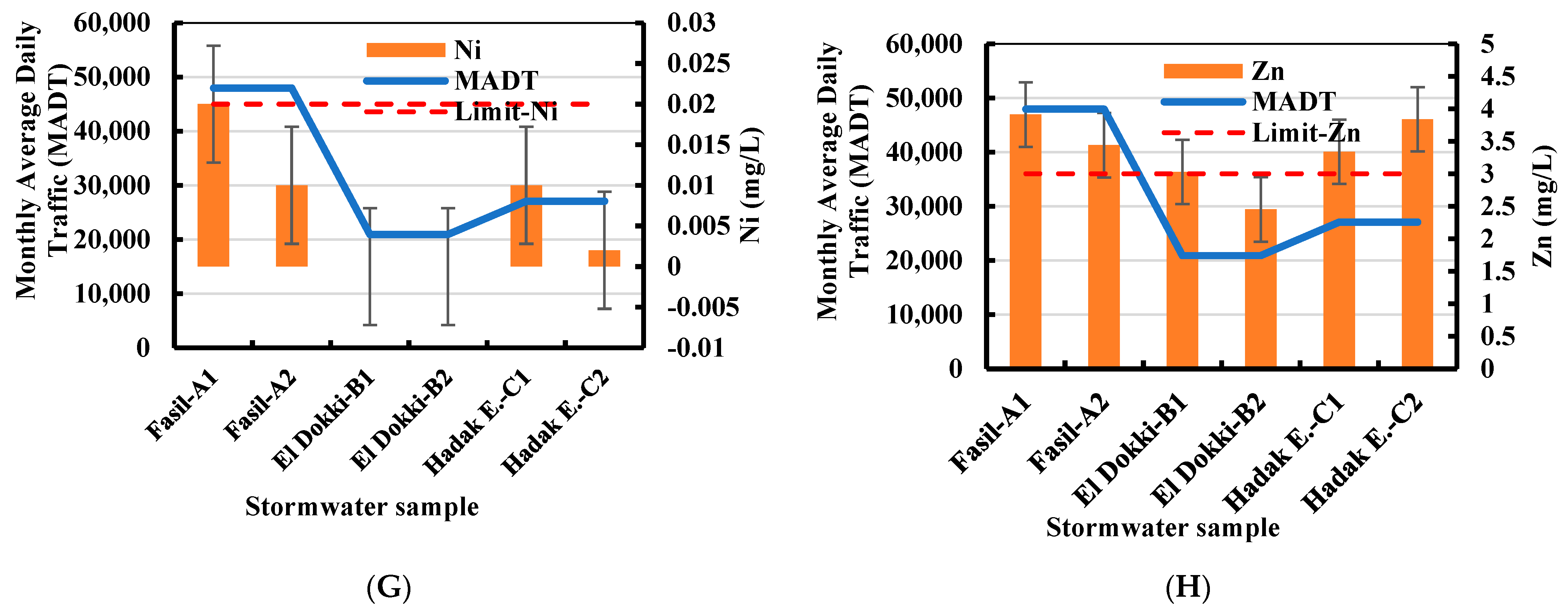
2.2. Traffic Data in the Study Area
2.3. Stormwater-Monitoring Points and the Analyzed Water Quality Parameters
2.4. Water Quality Index (WQI)
2.5. Evaluation of the Suitability of Irrigation Water Quality
3. Results
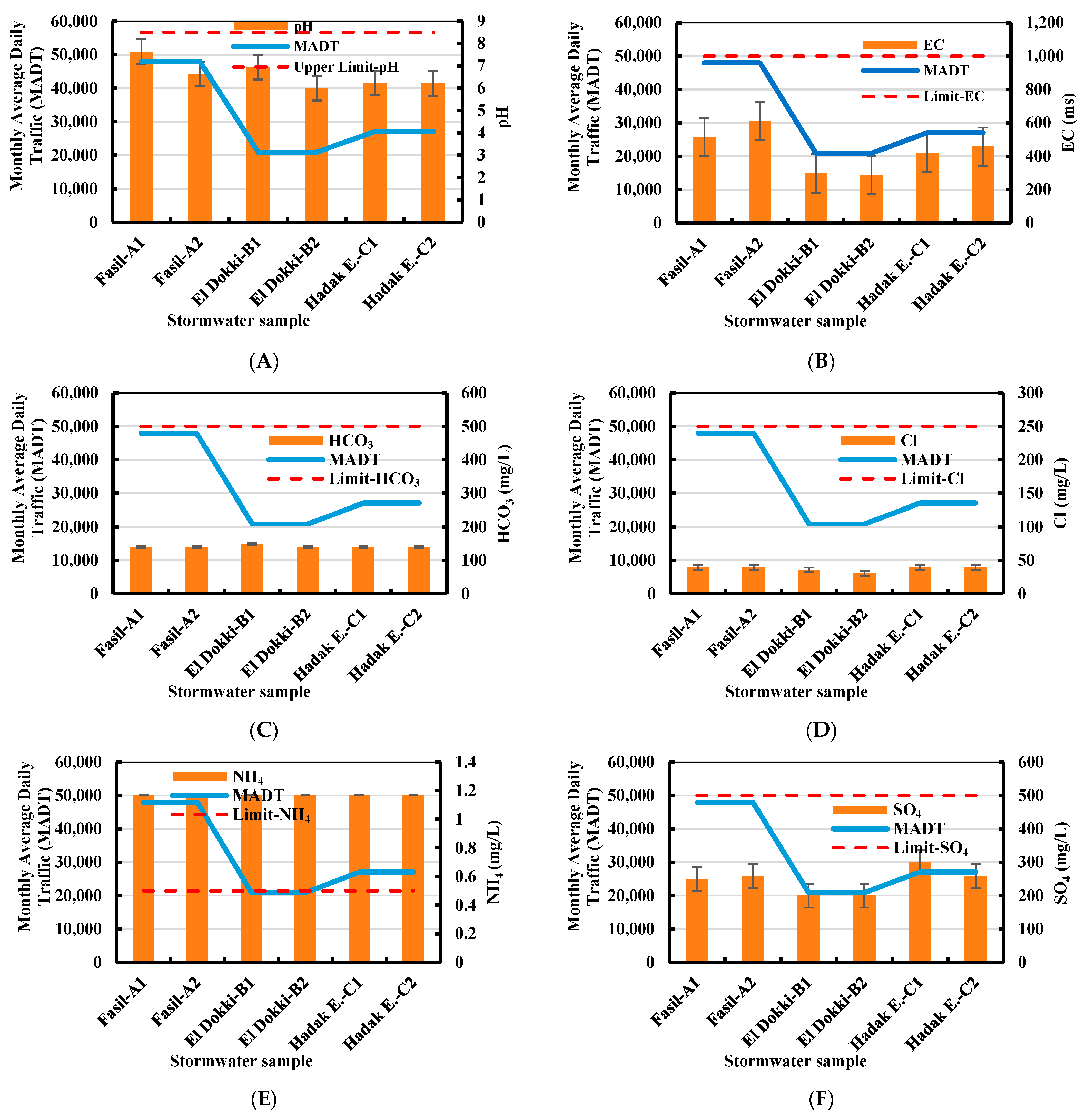
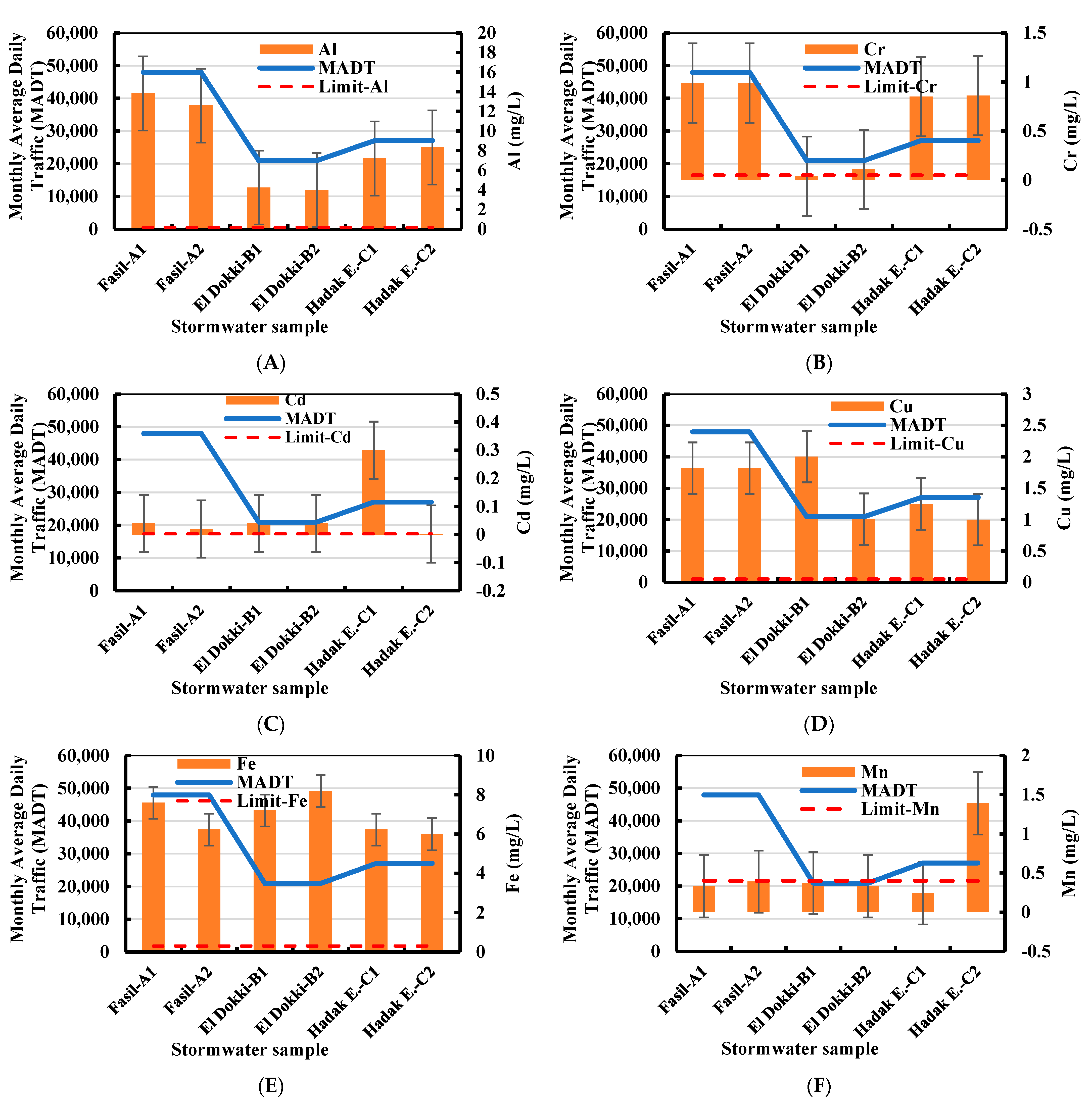
3.1. Stormwater Water Quality
3.2. WQI Results
3.3. Stormwater Quality for Irrigation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abdelazim, N. Conventional water resources and agriculture in Egypt. In The Handbook of Environmental Chemistry; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; Volume 74, pp. 233–241. [Google Scholar]
- Gabr, M.E. Land reclamation projects in the Egyptian Western Desert: Management of 1.5 million acres of groundwater irrigation. Water Int. 2023, 48, 240–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Maksoud, B.M. Estimation of air temperature and rainfall trends in Egypt. Asian J. Adv. Res. Rep. 2018, 1, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radwan, G.; Ellah, A. Water resources in Egypt and their challenges, Lake Nasser case study. Egypt. J. Aquat. Res. 2020, 46, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- UNICEF. Report. 2021. Available online: https://a-z-animals.com/blog/discover-the-most-populated-cities-in-the-world/ (accessed on 10 June 2023).
- Walaa, Y.E.; Ahmed, H.E. Managing risks of the Grand Ethiopian Renaissance Dam on Egypt. Ain Shams Eng. J. 2018, 9, 2383–2388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omran, E.S.E.; Negm, A. Environmental Impacts of the GERD Project on Egypt’s Aswan High Dam Lake and Mitigation and Adaptation Options. In Grand Ethiopian Renaissance Dam Versus Aswan High Dam. The Handbook of Environmental Chemistry; Negm, A., Abdel-Fattah, S., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; Volume 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falkenmark, M. Meeting water requirements of an expanding world population. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. B Biol. Sci. 1997, 352, 929–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabr, M.E. Impact of climatic changes on future irrigation water requirement in the Middle East and North Africa’s region: A case study of upper Egypt. Appl. Water Sci. 2023, 13, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djuma, H.; Bruggeman, A.; Eliades, M.; Lange, M.A. Non-conventional water resources research in semi-arid countries of the Middle East. Desalination Water Treat. 2016, 57, 2290–2303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, M.; Al-Zyoud, S.; Elhaddad, E. Surface water quality monitoring for River Nile, Egypt using GIS-Techniques. Open J. Geol. 2018, 8, 161–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabr, M.E.; Al-Ansari, N.; Salem, A.; Awad, A. Proposing a wetland-based economic approach for wastewater treatment in arid regions as an alternative irrigation water source. Hydrology 2023, 10, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabr, M.E.; El Shorbagy, A.M.; Faheem, H.B. Utilizing the harvesting of rainwater to provide safe road transportation efficiency and increase water resources in the context of climatic change. Sustainability 2022, 14, 9656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabr, M.E.; El-Ghandour, H.A.; Elabd, S.M. Prospective of the utilization of rainfall in coastal regions in the context of climatic changes: Case study of Egypt. Appl. Water Sci. 2023, 13, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janke, B.D.; Finlay, J.C.; Hobbie, S.E. Trees and streets as drivers of urban stormwater nutrient pollution. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 9569–9579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunawardena, J.M.A.; Liu, A.; Egodawatta, P.; Ayoko, G.A.; Goonetilleke, A. Influence of Traffic and Land Use on Urban Stormwater Quality: Implications for Urban Stormwater Treatment Design. In Springer Briefs in Water Science and Technology 2018; Springer: Singapore, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Pilone, F.G.; Garcia-Chevesich, P.A.; McCray, J.E. Urban Drool Water Quality in Denver, Colorado: Pollutant Occurrences and Sources in Dry-Weather Flows. Water 2021, 13, 3436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zgheib, S.; Moilleron, R.; Chebbo, G. Priority pollutants in urban stormwater: Part 1—Case of separate storm sewers. Water Res. 2012, 46, 6683–6692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popick, H.; Brinkmann, M.; McPhedran, K. Assessment of stormwater discharge contamination and toxicity for a cold-climate urban landscape. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2022, 34, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.Y.; Toor, G.S. Sources and mechanisms of nitrate and orthophosphate transport in urban stormwater runoff from residential catchments. Water Res. 2017, 112, 176–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwegbue, C.M.A.; Kekeke, E.F.; Tesi, G.O.; Olisah, C.; Egobueze, F.E.; Chukwu-Madu, E.; Martincigh, B.S. Impact of Land-Use Types on the Distribution and Exposure Risk of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Dusts from Benin City, Nigeria. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2021, 81, 210–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, B.; Birch, G. Comparison of heavy metal loads in stormwater runoff from major and minor urban roads using pollutant yield rating curves. Environ. Pollut. 2010, 158, 2541–2545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, H.; Li, Z.; Liu, X. Characteristics of heavy metal pollution in road runoff in the Nanjing urban area, East China. Water Sci. Technol. 2020, 81, 1961–1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shorshani, M.F.; Bonhomme, C.; Petrucci, G.; André, M.; Seigneur, C. Road traffic impact on urban water quality: A step towards integrated traffic, air and stormwater modelling. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2014, 21, 5297–5310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, H.J.; Elmarsafy, M.; Hannan, N.; Gao, V.; Wright, C.; Khan, L.; Gray, D.K. The effects of roadways on lakes and ponds: A systematic review and assessment of knowledge gaps. Environ. Rev. 2022, 30, 501–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunawardena, J.; Egodawatta, P.; Ayoko, G.A.; Goonetilleke, A. Role of traffic in atmospheric accumulation of heavy metals and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 54, 502–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, Z.F.; Zhang, Y.L.; Ding, M.J.; Li, L.H. Identification of traffic-related metals and the effects of different environments on their enrichment in roadside soils along the Qinghai–Tibet highway. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 521–522, 160–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Silva, S.; Ball, A.S.; Huynh, T.; Reichman, S.M. Metal accumulation in roadside soil bourne, Australia: Effect of road age, traffic density and vehicular speed. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 208, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huber, M.; Welker, A.; Helmreich, B. Critical review of heavy metal pollution of traffic area runoff: Occurrence, influencing factors, and partitioning. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 541, 895–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, A.; Liu, L.; Li, D.Z.; Guan, Y.T. Characterizing heavy metals build-up on urban road surfaces, implication for stormwater reuse. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 515–516, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pohjola, M.A.; Kousa, A.; Kukkonen, J.; Harkonen, J.; Karppinen, A.; Aarnio, P.; Koskentalo, T. The spatial and temporal variation of measured urban pm10 and pm2.5 in the Helsinki metropolitan area. Water Air Soil Pollut. Focus 2002, 2, 189–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jandacka, D.; Durcanska, D.; Bujdos, M. The contribution of road traffic to particulate matter and metals in air pollution in the vicinity of an urban road. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2017, 50, 397–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Liu, A.; Li, Y.; Zhang, L.X.; Zhang, G.J.; Guan, Y.T. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons associated with road deposited solid and their ecological risk: Implications for road stormwater reuse. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 563–564, 190–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krein, A.; Schorer, M. Road runoff pollution by polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and its contribution to river sediments. Water Res. 2000, 34, 4110–4115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabr, M.; Soussa, H.; Fattouh, E. Groundwater quality evaluation for drinking and irrigation uses in Dayrout city Upper Egypt. Ain Shams Eng. J. 2021, 12, 327–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Megahed, H.A.; Farrag, A.E.H.A. Groundwater potentiality and evaluation in the Egyptian Nile Valley: Case study from Assiut Governorate using hydrochemical, bacteriological approach, and GIS techniques. Bull. Natl. Res. Cent. 2019, 43, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, R.M.; Clelland, N.L.; Deininger, R.A.; Connor, M.F. A water quality index crashing the physiological barrier. Indic. Environ. Qual. 1972, 1, 173–182. [Google Scholar]
- Davies, J.M. Application and tests of the Canadian Water Quality Index for assessing changes in water quality in lakes and rivers of central North America. Lake Reserve Manag. 2006, 22, 308–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tegegne, A.M.; Lohani, T.K.; Eshete, A.A. Evaluation of groundwater quality for drinking and irrigation purposes using proxy indices in the Gunabay watershed, Upper Blue Nile Basin, Ethiopia. Heliyon 2023, 9, e15263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samy, A.; Eissa, M.; Shahen, S.; Said, M.M.; Shahaba, R.M.A. Geochemistry and assessment of groundwater resource in coastal arid region aquifer (Dahab delta, South Sinai, Egypt). Beni-Suef Univ. J. Basic Appl. Sci. 2023, 12, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egypt Decree No.458; Drinking Water Quality Standards. Ministry of Health and Population in Arabic: Warraq, Egypt, 2007.
- Egypt Decree, 92/2013, “For the Protection of the Nile River and Its Waterways from Pollution”, Decree of Minister of Water Resources and Irrigation no. 92 for Year 2013 for the Executive Regulation of Law 48/1982, 92/2013 (in Arabic). Available online: https://www.mwri.gov.eg/index.php/ministry/ministry-17/12-1984 (accessed on 15 June 2023).
- WHO (World Health Organization). Guidelines for the Safe Use of Wastewater, Excreta and Greywater in: Wastewater Use in Agriculture; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2006; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Gabr, M.E.S. Management of irrigation requirements using FAO-CROPWAT 8.0 model: A case study of Egypt. Model. Earth Syst. Environ. 2022, 8, 3127–3142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- APHA. Standard Method for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 19th ed.; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 1995; p. 500. [Google Scholar]
- Richards, L.A. Diagnosis and Improvement of Saline and Alkali Soils; Handbook; Scientific Publishers: Meerut, India, 1954. [Google Scholar]
- Todd, D.K. Groundwater Hydrology; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Eaton, F.M. Significance of carbonate in irrigation water. Soil Sci. 1950, 62, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doneen, L.D. Notes on Water Quality in Agriculture; Published as a Water Science and Engineering Paper 4001; Department of Water Science and Engineering, University of California: Riverside, CA, USA, 1964. [Google Scholar]
- Raghaunth, H.M. Groundwater; Wiley Eastern Ltd.: New Delhi, India, 1989; p. 563. [Google Scholar]
- Kelley, W.P. Permissible composition and concentration of irrigated waters. Proc. ASCF 1940, 66, 607. [Google Scholar]
- Wilcox, L.V. Classification and Use of Irrigation Waters; Circular 969; USDA: Washington, DC, USA, 1955.
- Freeze, R.A.; Cherry, J.A. Groundwater; Prentice Hall Inc.: Englewood Cliffs, NJ, USA, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, K.; Raju, N.J.; Singh, N.; Sreekesh, S. Heavy metal pollution in groundwater of urban Delhi environs: Pollution indices and health risk assessment. Urban Clim. 2022, 45, 101233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucke, T.; Drapper, D.; Hornbuckle, A. Urban stormwater characterization and nitrogen composition from lot-scale catchments—New management implications. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 619–620, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gustafson, K.R.; Garcia-Chevesich, P.A.; Slinski, K.M.; Sharp, J.O.; McCray, J.E. Quantifying the effects of residential infill redevelopment on urban stormwater quality in denver, colorado. Water 2021, 13, 988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poudyal, S.; Cochrane, T.A.; Bello-Mendoza, R. Carpark pollutant yields from first flush stormwater runoff. Environ. Chall. 2021, 5, 100301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Z.; Chu, J.; Luo, C.; Chen, H. Revealing the characteristics of dissolved organic matter in urban runoff at three typical regions via optical indices and molecular composition. J. Environ. Sci. 2021, 108, 8–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hornig, S.; Bauerfeld, K.; Beier, M. Dynamization of Urban Runoff Pollution and Quantity. Water 2022, 14, 418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Li, J.; Sun, H.; Che, W. Pollutant first flush identification and its implications for urban runoff pollution control: A roof and road runoff case study in Beijing, China. Water Sci. Technol. 2021, 83, 2829–2840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talebnejad, R.; Sepaskhah, A.R. Effect of different saline groundwater depths and irrigation water salinities on yield and water use of quinoa in lysimeter. Agric. Water Manag. 2015, 148, 177–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surendran, U.; Sandeep, O.; Joseph, E.J. The impacts of magnetic treatment of irrigation water on plant, water and soil characteristics. Agric. Water Manag. 2016, 178, 21–29. [Google Scholar]
- Srivastava, S.; Vaddadi, S.; Kumar, P.; Sadistap, S. Design and development of reverse osmosis (RO) plant status monitoring system for early fault prediction and predictive maintenance. Appl. Water Sci. 2018, 8, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathya, K.; Nagarajan, K.; Carlin Geor Malar, G.; Rajalakshmi, S.; Lakshmi, P.R. A comprehensive review on comparison among effluent treatment methods and modern methods of treatment of industrial wastewater effluent from different sources. Appl. Water Sci. 2022, 12, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.; Kyere, F.; Sampene, A.K.; Asante, D.; Yaa, N.; Kumah, G. An investigation on the role of electric vehicles in alleviating environmental pollution: Evidence from five leading economies. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 18244–18259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Engine Oil | Fuel | Tire Wear | Brake Wear | Chassis | Road Paint | Surface Wear for Road | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Al | X | X | X | ||||
| Cr | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| Cd | X | X | X | X | |||
| Fe | X | X | X | ||||
| Cu | X | X | X | ||||
| Mn | X | X | X | X | |||
| Ni | X | X | X | X | X | ||
| Zn | X | X | X | X | X | ||
| Pb | X | X | X | X | X |
| Points of Measurement | The Catchment Area’s Size () | Type of Surface | Monthly Average Daily Traffic (MADT) (Cars) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Faisal | 10,476 | Housing area/Commercial area/Restaurants and parking service/Street/Asphalt | 47,950 |
| El Dokki | 7566 | Housing area/Public station/Main street and commercial area/Street/Asphalt | 20,919 |
| Hadayek El-Ahram | 9870 | Housing area/Main street/Asphalt and grass area | 27,064 |
| Water Parameter | Unit | wi | Wi (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| pH | _ | 2 | 2.56 |
| EC | µs/cm | 2 | 2.56 |
| NO3 | mg/L | 4 | 5.13 |
| NH4 | mg/L | 4 | 5.13 |
| SO4 | mg/L | 2 | 2.56 |
| CO3 | mg/L | 2 | 2.56 |
| HCO3 | mg/L | 2 | 2.56 |
| Cl | mg/L | 2 | 2.56 |
| BOD | mg/L | 4 | 5.13 |
| COD | mg/L | 4 | 5.13 |
| TDS | mg/L | 3 | 3.85 |
| TSS | mg/L | 3 | 3.85 |
| TN | mg/L | 3 | 3.85 |
| TP | mg/L | 3 | 3.85 |
| Na | mg/L | 2 | 2.56 |
| K | mg/L | 2 | 2.56 |
| Mg | mg/L | 2 | 2.56 |
| Ca | mg/L | 2 | 2.56 |
| Al | mg/L | 3 | 3.85 |
| Cr | mg/L | 3 | 3.85 |
| Cd | mg/L | 3 | 3.85 |
| Fe | mg/L | 3 | 3.85 |
| Cu | mg/L | 3 | 3.85 |
| Mn | mg/L | 4 | 5.13 |
| Ni | mg/L | 3 | 3.85 |
| Zn | mg/L | 4 | 5.13 |
| Pb | mg/L | 4 | 5.13 |
| Sum | 78 | 100 |
| WQI Value | Grade of Water Quality | Possible Usages |
|---|---|---|
| 0–25 | Excellent | Irrigation, drinking, and industrial |
| 25–50 | Good | Irrigation, domestic, and industrial |
| 51–75 | Poor | Irrigation and industrial |
| 76–100 | Very poor | Irrigation |
| 101–150 | Unsuitable | Irrigation is a restricted use |
| >150 | Unfit for drinking | Before use, proper treatment is required |
| Quality Parameter | Applied Formula | Reference | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | SAR | (5) | Richards [46] | |
| 2 | TH | TH = 2.497 + 4.11 | (6) | Todd [47] |
| 3 | SSP | 100 | (7) | Eaton [48] |
| 4 | RSBC | (8) | Doneen [49] | |
| 5 | PI | (9) | Raghaunth [50] | |
| 6 | MAR | (10) | Raghaunth [50] | |
| 7 | KR | (11) | Kelley [51] | |
| Indices | Range | Ranking | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| SAR | <10 mg/L 10–18 mg/L 18–26 mg/L <26 mg/L | Excellent Good Doubtful Unsuitable | Richards [46] |
| EC | <250 μs/cm 250–750 μs/cm 750–2250 μs/cm 2250–5000 μs/cm >5000 μs/cm | Excellent Good Permissible Doubtful Unsuitable | Wilcox [52] |
| TH | 0–75 mg/L 75–150 mg/L 150–300 mg/L | Soft Moderately hard Hard | Todd [47] |
| TDS | 0–1000 mg/L | Freshwater | Freeze [53] |
| RSBC | <5 meq/L 5–10 meq/L >10 meq/L | Safe Marginal Unsatisfactory | Doneen [49] |
| SSP | <20 mg/L 40–80 mg/L <80 mg/L | Excellent Good Fair/permissible Poor | Eaton [48] |
| MAR | <50 mg/L <50 mg/L | Excellent Harmful for soil | Raghaunth [50] |
| KR | <1 >1 | Suitable Excess level | Kelley [51] |
| PI | >75% <25% | Good for irrigation unsuitable | Raghaunth [50] |
| Water Parameter | Unit | A1 | A2 | B1 | B2 | C1 | C2 | Max. | Min. | S.D. | Average | WHO [43] | Egypt Decree [41,42] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | _ | 7.63 | 6.63 | 6.94 | 6 | 6.23 | 6.22 | 7.63 | 6 | 6.6 | 0.6 | 6.5–8.4 | 7.5 |
| EC | µs/cm | 515 | 612 | 297 | 289 | 421 | 458 | 612 | 289 | 432.0 | 114.6 | 500 | 1000 |
| NO3 | mg/L | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 50 | 45 |
| NH4 | mg/L | 1.17 | 1.17 | 1.17 | 1.17 | 1.17 | 1.17 | 1.17 | 1.17 | 1.2 | 0 | 0.5 | 0.5 |
| SO4 | mg/L | 250 | 259 | 200 | 200 | 300 | 259 | 300 | 200 | 244.7 | 35.3 | 250 | 250 |
| CO3 | mg/L | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | N.D. | 300 |
| HCO3 | mg/L | 140.23 | 139.1 | 148.9 | 140.12 | 140.2 | 139.12 | 148.9 | 139.1 | 141.3 | 3.4 | 500 | 500 |
| Cl | mg/L | 39.25 | 39.2 | 36 | 30.3 | 39.3 | 39.2 | 39.3 | 30.3 | 37.2 | 3.3 | 250 | 250 |
| BOD | mg/L | 40 | 38 | 25 | 26 | 45 | 45 | 45 | 25 | 36.5 | 8.2 | 6 | 6 |
| COD | mg/L | 50 | 59.7 | 49.2 | 38.5 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 38.5 | 66.2 | 24.7 | 10 | 10 |
| TDS | mg/L | 329.6 | 320.15 | 190 | 189 | 269.44 | 250.3 | 329.6 | 189 | 258.1 | 55.6 | 500 | 1000 |
| TSS | mg/L | 817 | 750 | 200 | 200 | 790 | 759 | 817 | 200 | 586.0 | 273.8 | 800 | 800 |
| TN | mg/L | 1.2 | 1.17 | 1.17 | 1.17 | 1.17 | 1.17 | 1.2 | 1.17 | 1.2 | 0.0 | 3.5 | 3.5 |
| TP | mg/L | 5.02 | 4.99 | 4.55 | 4.02 | 6 | 6.12 | 6.12 | 4.02 | 5.1 | 0.7 | 2 | 2 |
| Na | mg/L | 90.03 | 91.2 | 119.22 | 90.16 | 70 | 70 | 119.22 | 70 | 88.4 | 16.5 | 200 | 200 |
| K | mg/L | 43.15 | 50.12 | 47.02 | 45.16 | 39.13 | 52.1 | 52.1 | 39.13 | 46.1 | 4.3 | 12 | 12 |
| Mg | mg/L | 46.25 | 40.23 | 50.04 | 48.12 | 40.25 | 50.19 | 50.19 | 40.23 | 45.8 | 4.2 | 30 | 30 |
| Ca | mg/L | 588.41 | 520.19 | 410.03 | 380.03 | 425 | 429.13 | 588.41 | 380.03 | 458.8 | 72.1 | 75 | 75 |
| Al | mg/L | 13.83 | 12.6 | 4.25 | 4 | 7.2 | 8.33 | 13.83 | 4 | 8.4 | 3.8 | 0.2 | 0.2 |
| Cr | mg/L | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.04 | 0.11 | 0.85 | 0.86 | 0.99 | 0.04 | 0.6 | 0.4 | 0.1 | 0.05 |
| Cd | mg/L | 0.04 | 0.02 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.3 | 0.002 | 0.3 | 0.002 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.01 | 0.003 |
| Fe | mg/L | 7.6 | 6.23 | 7.2 | 8.2 | 6.23 | 5.99 | 8.2 | 5.99 | 6.9 | 0.8 | 0.3 | 0.3 |
| Cu | mg/L | 1.82 | 1.82 | 2 | 1.01 | 1.25 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1.5 | 0.4 | 0.05 | 0.05 |
| Mn | mg/L | 0.33 | 0.39 | 0.37 | 0.33 | 0.24 | 1.39 | 1.39 | 0.24 | 0.5 | 0.4 | 0.5 | 0.4 |
| Ni | mg/L | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0 | 0 | 0.01 | 0.002 | 0.02 | 0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.2 | 0.02 |
| Zn | mg/L | 3.91 | 3.44 | 3.03 | 2.45 | 3.34 | 3.84 | 3.91 | 2.45 | 3.3 | 0.5 | 0.1 | 3 |
| Pb | mg/L | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.12 | 0.12 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.2 | 0.01 |
| Sample | WQI | Grade of Water Quality | Uses |
|---|---|---|---|
| A1 | 776 | Unfit for drinking | Before use, proper treatment is required |
| A2 | 708 | Unfit for drinking | Before use, proper treatment is required |
| B1 | 499 | Unfit for drinking | Before use, proper treatment is required |
| B2 | 426 | Unfit for drinking | Before use, proper treatment is required |
| C1 | 929 | Unfit for drinking | Before use, proper treatment is required |
| C2 | 626 | Unfit for drinking | Before use, proper treatment is required |
| Sample | EC (µs/cm) | TDS (mg/L) | SAR (mg/L) | TH (mg/L) | RSBC (meq/L) | SSP (%) | KR (%) | MAR (mg/L) | PI (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A1 | 515 | 329.6 | 5.1 | 1659.3 | 31.7 | 17.3 | 14.2 | 7.3 | 14.1 |
| A2 | 612 | 320.2 | 5.4 | 1464.3 | 28.2 | 20.1 | 16.3 | 7.2 | 15.8 |
| B1 | 297 | 190.0 | 7.9 | 1229.5 | 22.9 | 26.5 | 25.9 | 10.9 | 22.7 |
| B2 | 289 | 189.0 | 6.2 | 1146.7 | 21.3 | 24.0 | 21.1 | 11.2 | 19.7 |
| C1 | 421 | 269.4 | 4.6 | 1226.7 | 23.5 | 19.0 | 15.0 | 8.7 | 15.3 |
| C2 | 458 | 250.3 | 4.5 | 1277.8 | 23.7 | 20.3 | 14.6 | 10.5 | 14.9 |
| pH | SO4 | HCO3 | Cl | BOD | COD | TDS | TSS | Na | K | Mg | Ca | Al | Cr | Cd | Fe | Cu | Mn | Zn | WQI | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 1.00 | |||||||||||||||||||
| SO4 | −0.07 | 1.00 | ||||||||||||||||||
| HCO3 | 0.30 | −0.57 | 1.00 | |||||||||||||||||
| Cl | 0.40 | 0.78 | −0.21 | 1.00 | ||||||||||||||||
| BOD | −0.01 | 0.93 | −0.65 | 0.81 | 1.00 | |||||||||||||||
| COD | −0.39 | 0.80 | −0.35 | 0.62 | 0.82 | 1.00 | ||||||||||||||
| TDS | 0.50 | 0.67 | −0.56 | 0.76 | 0.69 | 0.20 | 1.00 | |||||||||||||
| TSS | 0.22 | 0.89 | −0.65 | 0.87 | 0.95 | 0.62 | 0.88 | 1.00 | ||||||||||||
| Na | 0.46 | −0.77 | 0.83 | −0.35 | −0.83 | −0.76 | −0.36 | −0.69 | 1.00 | |||||||||||
| K | −0.12 | −0.28 | −0.03 | 0.06 | −0.06 | 0.00 | −0.06 | −0.06 | 0.12 | 1.00 | ||||||||||
| Mg | 0.05 | −0.69 | 0.44 | −0.41 | −0.44 | −0.24 | −0.62 | −0.54 | 0.34 | 0.40 | 1.00 | |||||||||
| Ca | 0.80 | 0.33 | −0.30 | 0.60 | 0.39 | −0.15 | 0.90 | 0.65 | −0.01 | −0.03 | −0.34 | 1.00 | ||||||||
| Al | 0.60 | 0.51 | −0.51 | 0.70 | 0.59 | 0.06 | 0.97 | 0.81 | −0.25 | 0.09 | −0.45 | 0.95 | 1.00 | |||||||
| Cr | 0.24 | 0.84 | −0.69 | 0.83 | 0.90 | 0.53 | 0.93 | 0.99 | −0.64 | 0.02 | −0.57 | 0.71 | 0.87 | 1.00 | ||||||
| Cd | −0.25 | 0.63 | −0.07 | 0.21 | 0.37 | 0.50 | 0.06 | 0.26 | −0.41 | −0.80 | −0.59 | −0.20 | −0.17 | 0.16 | 1.00 | |||||
| Fe | 0.23 | −0.74 | 0.25 | −0.77 | −0.73 | −0.84 | −0.38 | −0.64 | 0.49 | −0.31 | 0.39 | −0.05 | −0.28 | −0.61 | −0.26 | 1.00 | ||||
| Cu | 0.80 | −0.17 | 0.56 | 0.31 | −0.27 | −0.45 | 0.32 | −0.02 | 0.73 | 0.00 | −0.14 | 0.56 | 0.38 | 0.02 | −0.20 | 0.07 | 1.00 | |||
| Mn | −0.28 | 0.11 | −0.25 | 0.25 | 0.40 | 0.54 | −0.06 | 0.24 | −0.42 | 0.71 | 0.50 | −0.16 | 0.02 | 0.22 | −0.41 | −0.48 | −0.46 | 1.00 | ||
| Zn | 0.51 | 0.62 | −0.32 | 0.90 | 0.79 | 0.50 | 0.76 | 0.86 | −0.39 | 0.18 | −0.12 | 0.70 | 0.78 | 0.83 | −0.07 | −0.57 | 0.20 | 0.45 | 1.00 | |
| WQI | 0.18 | 0.94 | −0.42 | 0.76 | 0.81 | 0.60 | 0.73 | 0.84 | −0.58 | −0.53 | −0.75 | 0.47 | 0.56 | 0.79 | 0.71 | −0.53 | 0.06 | −0.19 | 0.58 | 1.00 |
 Positive correlation
Positive correlation  negative correlation.
negative correlation.Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gabr, M.E.; El Shorbagy, A.M.; Faheem, H.B. Assessment of Stormwater Quality in the Context of Traffic Congestion: A Case Study in Egypt. Sustainability 2023, 15, 13927. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151813927
Gabr ME, El Shorbagy AM, Faheem HB. Assessment of Stormwater Quality in the Context of Traffic Congestion: A Case Study in Egypt. Sustainability. 2023; 15(18):13927. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151813927
Chicago/Turabian StyleGabr, Mohamed Elsayed, Amira Mahmoud El Shorbagy, and Hamdy Badee Faheem. 2023. "Assessment of Stormwater Quality in the Context of Traffic Congestion: A Case Study in Egypt" Sustainability 15, no. 18: 13927. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151813927
APA StyleGabr, M. E., El Shorbagy, A. M., & Faheem, H. B. (2023). Assessment of Stormwater Quality in the Context of Traffic Congestion: A Case Study in Egypt. Sustainability, 15(18), 13927. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151813927






