Estimating the Amount of Submerged Marine Debris Based on Fishing Vessels Using Multiple Regression Model
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Data
2.2. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
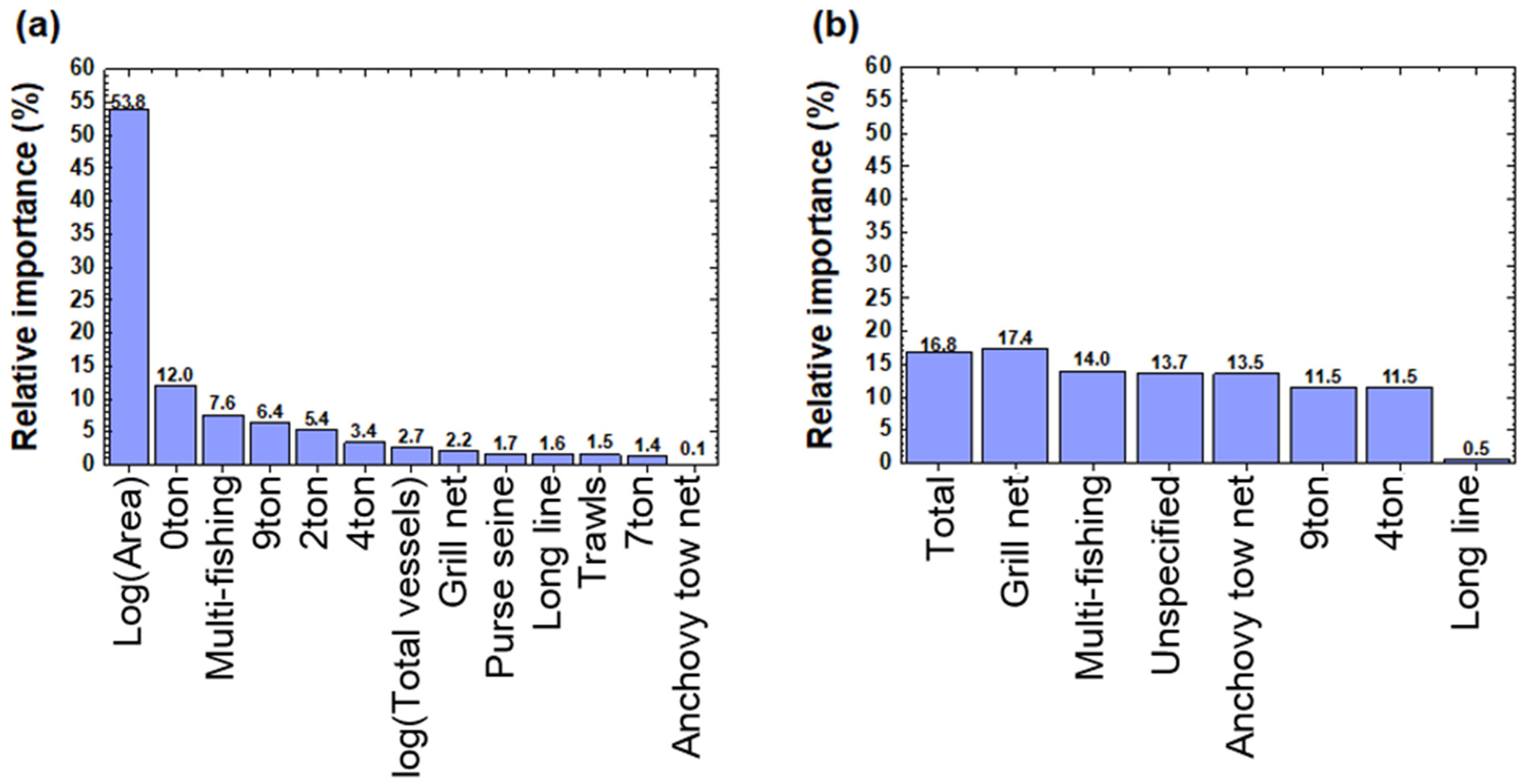
3.1. Correlation between the Amount of Submerged Marine Debris and Fishing Vessels
2.0906(Long line) −0.1556(Grill net) + 6.4046(Trawls) − 1.6425(0 ton) + 0.9655(2 ton) −
0.8039(4 ton) + 0.2336(7 ton) − 1.1761(9 ton) + 26.0916·log(Total vessels) − log(Area)
R2 = 0.667; F = 5.544; p < 0.00002181
0.4141(2 ton) + 0.3819(4 ton) + 16.7435·log(Total vessels) − 3.4292·log(Area)
R2 = 0.511; F = 0.785; p < 0. 6348
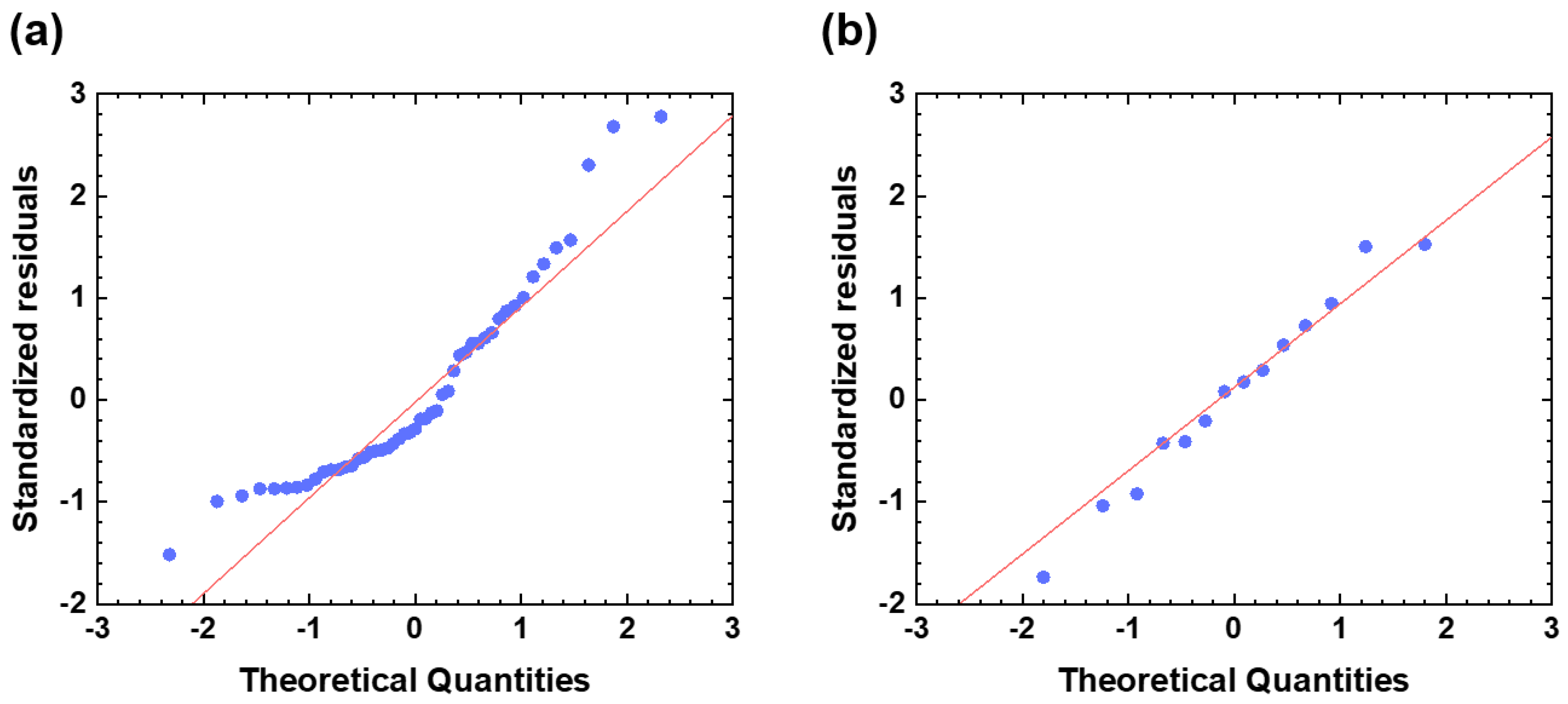
3.2. Model Performance
3.3. Estimation of the Amount of Submerged Marine Debris
4. Discussion
4.1. Comparison of the Estimation Models for the Amount of Submerged Marine Debris
4.2. Variable Analysis
4.3. Limitations and Recommendations for Future Research
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Francois, G.; Georg, H.; Tomak, M. Global Distribution, Composition and Boundance of Marine Litter; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 29–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, S.J.; Kwon, Y.J.; Yoo, S.H. Economic Valuation of Reducing Submerged Marine Debris in South Korea. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 6086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Rivera, S.; Lizaso, J.L.S.; Millán, J.M.B. Spatial and Temporal Trends of Marine Litter in the Spanish Mediterranean Seafloor. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 137, 252–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loulad, S.; Houssa, R.; EL Ouamari, N.; Rhinane, H. Quantity and Spatial Distribution of Seafloor Marine Debris in the Moroccan Mediterranean Sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 139, 163–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tubau, X.; Canals, M.; Lastras, G.; Rayo, X.; Rivera, J.; Amblas, D. Marine Litter on the Floor of Deep Submarine Canyons of the Northwestern Mediterranean Sea: The Role of Hydrodynamic Processes. Prog. Oceanogr. 2015, 134, 379–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez-Llodra, E.; De Mol, B.; Company, J.B.; Coll, M.; Sardà, F. Effects of Natural and Anthropogenic Processes in the Distribution of Marine Litter in the Deep Mediterranean Sea. Prog. Oceanogr. 2013, 118, 273–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cau, A.; Bellodi, A.; Moccia, D.; Mulas, A.; Pesci, P.; Cannas, R.; Pusceddu, A.; Follesa, M.C. Dumping to the Abyss: Single-Use Marine Litter Invading Bathyal Plains of the Sardinian Margin (Tyrrhenian Sea). Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 135, 845–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angiolillo, M.; di Lorenzo, B.; Farcomeni, A.; Bo, M.; Bavestrello, G.; Santangelo, G.; Cau, A.; Mastascusa, V.; Cau, A.; Sacco, F.; et al. Distribution and Assessment of Marine Debris in the Deep Tyrrhenian Sea (NW Mediterranean Sea, Italy). Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 92, 149–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alomar, C.; Compa, M.; Deudero, S.; Guijarro, B. Spatial and Temporal Distribution of Marine Litter on the Seafloor of the Balearic Islands (Western Mediterranean Sea). Deep. Res. Part I Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 2020, 155, 103178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvito, A.; Bellodi, A.; Cau, A.; Moccia, D.; Mulas, A.; Palmas, F.; Pesci, P.; Follesa, M.C. Amount and Distribution of Benthic Marine Litter along Sardinian Fishing Grounds (CW Mediterranean Sea). Waste Manag. 2018, 75, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ioakeimidis, C.; Zeri, C.; Kaberi, H.; Galatchi, M.; Antoniadis, K.; Streftaris, N.; Galgani, F.; Papathanassiou, E.; Papatheodorou, G. A Comparative Study of Marine Litter on the Seafloor of Coastal Areas in the Eastern Mediterranean and Black Seas. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2014, 89, 296–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Botero, C.M.; Zielinski, S.; Pereira, C.I.; León, J.A.; Dueñas, L.F.; Puentes, V. The First Report of Deep-Sea Litter in the South-Western Caribbean Sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 157, 111327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Debrot, A.O.; Vinke, E.; van der Wende, G.; Hylkema, A.; Reed, J.K. Deepwater Marine Litter Densities and Composition from Submersible Video-Transects around the ABC-Islands, Dutch Caribbean. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2014, 88, 361–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiba, S.; Saito, H.; Fletcher, R.; Yogi, T.; Kayo, M.; Miyagi, S.; Ogido, M.; Fujikura, K. Human Footprint in the Abyss: 30 Year Records of Deep-Sea Plastic Debris. Mar. Policy 2018, 96, 204–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Core Team: Vienna, Austria, 2016; Volume 2, pp. 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, G. Step Away from Stepwise. J. Big Data 2018, 5, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Survey Period (year) | Number of Marine Debris Removal Projects (site) | Amount of Collected Debris (tonnes) | Collection Area (ha) | The Number of Fishing Vessels on Collection Site (count) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2017 | 24 (35) | 1771.55 | 83,018 | - |
| 2018 | 22 (36) | 710.50 | 66,374 | 958 |
| 2019 | 35 (45) | 1484.16 | 72,057 | 11,314 |
| 2020 | 20 (22) | 1053.68 | 60,661 | 124,379 |
| Accumulation Period * (Year) (Not Defined~Removal Project) | Total (Counts) | |
|---|---|---|
| Collection Sites | Fishing Vessels ** | |
| ~2018 | 25 | 958 |
| ~2019 | 32 | 11,314 |
| ~2020 | 22 | 124,379 |
| Accumulation Period * (Year) (1st Removal Project to 2nd Removal Project) | Overlapped (Counts) | |
|---|---|---|
| Collection Sites | Fishing Vessels ** | |
| 2017~2018 | 4 | 94 |
| 2018~2019 | 13 | 2269 |
| 2019~2020 | 2 | 6143 |
| Variable | Site 1 | Site 2 | Site 3 | Site 4 | Site 5 | Site 6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anchovy tow net | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Multi-fishing | 32 | 11 | 2 | 22 | 1 | 0 |
| Long line | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| Grill net | 111 | 67 | 9 | 15 | 2 | 0 |
| Unspecified | 66 | 27 | 3 | 17 | 6 | 2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Song, K.; Lee, S.; Joung, T.; Yu, J.; Park, J. Estimating the Amount of Submerged Marine Debris Based on Fishing Vessels Using Multiple Regression Model. Sustainability 2023, 15, 15172. https://doi.org/10.3390/su152015172
Song K, Lee S, Joung T, Yu J, Park J. Estimating the Amount of Submerged Marine Debris Based on Fishing Vessels Using Multiple Regression Model. Sustainability. 2023; 15(20):15172. https://doi.org/10.3390/su152015172
Chicago/Turabian StyleSong, Kyounghwan, Seunghyun Lee, Taehwan Joung, Jiwon Yu, and Jongkoo Park. 2023. "Estimating the Amount of Submerged Marine Debris Based on Fishing Vessels Using Multiple Regression Model" Sustainability 15, no. 20: 15172. https://doi.org/10.3390/su152015172
APA StyleSong, K., Lee, S., Joung, T., Yu, J., & Park, J. (2023). Estimating the Amount of Submerged Marine Debris Based on Fishing Vessels Using Multiple Regression Model. Sustainability, 15(20), 15172. https://doi.org/10.3390/su152015172







