Investigation of Decentralized Wastewater Treatment System in Urban Wastewater Management: Case Study in Yangon, Myanmar
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methodology
2.1. Research Framework
2.2. Study Area
2.3. Discussions with Residents
2.4. Sustainability Assessment
2.5. Weighted Sum Method (WSM)
- (1)
- Assign equal weights (25%) to each of the four aspects;
- (2)
- In this approach, apply a weight of 0.5 (50%) to the social aspects, while assigning equal weights of 0.1667 (16.667%) to each of the remaining aspects. This scenario should reflect the real-world situations;
- (3)
- Give a weight of 100% to the social aspects and allocate a weight of zero to others.
3. Results and Discussions
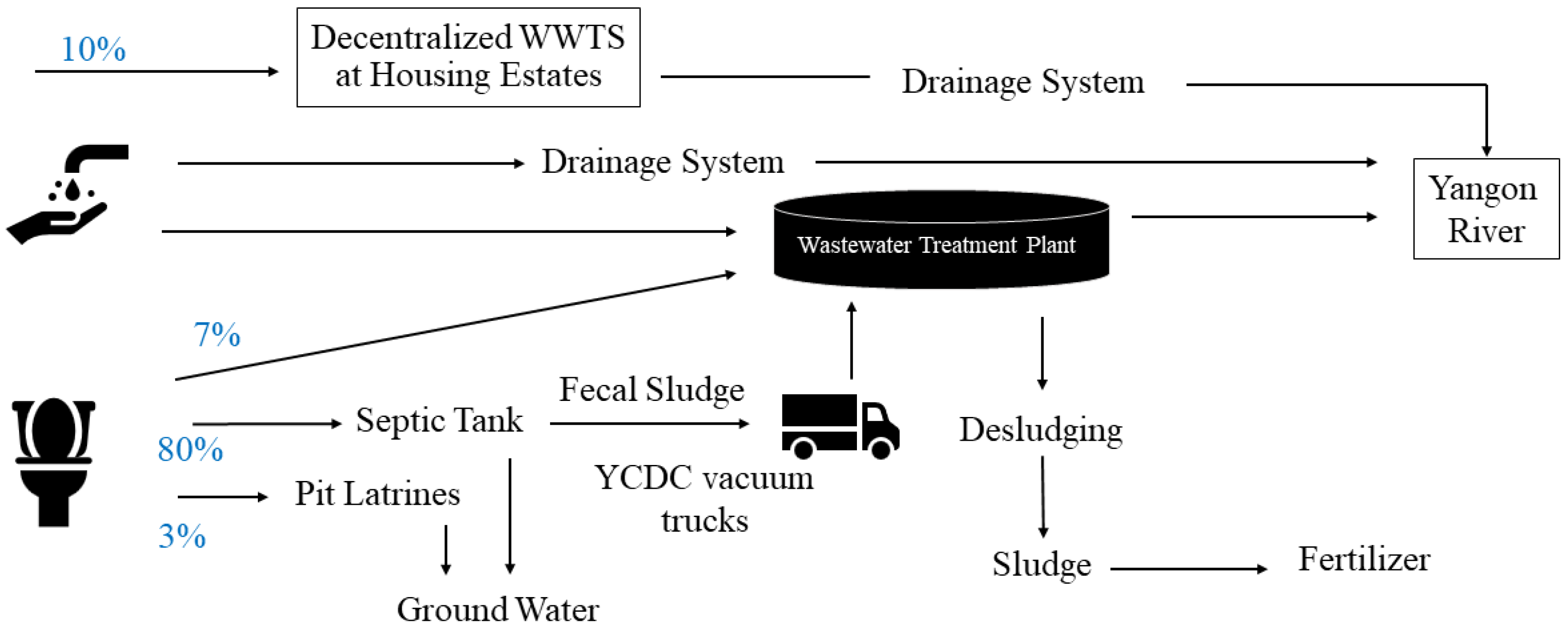
3.1. Investigating Existing Wastewater Treatment Systems in Yangon
3.2. Opinions of Residents
3.3. Wastewater Effluent Quality Results
3.4. Sustainability Assessment
3.5. Scenarios Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Corominas, L.; Neumann, M.B. Ecosystem-based management of a Mediterranean urban wastewater system: A sensitivity analysis of the operational degrees of freedom. J. Environ. Manag. 2014, 143, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aung, H.; Myint, T.Y.; Khaing, N.N. Assessment of surface water quality along Pazundaung Creek, Yangon City. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2020, 496, 012013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Premakumara, D.G.J. Waste Management in Myanmar: Current Status, Key Challenges and Recommendations for National and City Waste Management Strategies; Institute for Global Environmental Strategies: Kanagawa, Japan, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Yangon City Development Committee (YCDC). Existing Yangon City Development Committee Wastewater Treatment Plan and Future Plan; Yangon City Development Committee: Yangon, Myanmar, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Ho, G. Technology for sustainability: The role of onsite, small and community scale technology. Water Sci. Technol. 2005, 51, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varma, V.G.; Jha, S.; Raju, L.H.K.; Kishore, R.L.; Ranjith, V. A review on decentralized wastewater treatment systems in India. Chemosphere 2022, 300, 134462. [Google Scholar]
- Japan International Cooperation Agency (JICA). The Project for Capacity Development on Urban Environmental Management in Yangon City in the Republic of the Union of Myanmar Final Report; Japan International Cooperation Agency: Tokyo, Japan, 2014; Available online: https://openjicareport.jica.go.jp/pdf/1000039704.pdf (accessed on 18 August 2023).
- Lwin, C.M.; Maung, K.N.; Murakami, M.; Hashimoto, S. The Implications of Scenarios for Phosphorus flow from Agriculture and Domestic Wastewater in Myanmar. In Proceedings of the Asian Conference on Sustainability, Energy and Environment (ACSEE2017), Kobe, Japan, 8–11 June 2017; pp. 8–10. [Google Scholar]
- Tokich, S.H. Wastewater Management Strategy: Centralized v. Decentralized Technologies for Small Communities; Center for Clean Technology and Environmental Policy: Enschede, The Netherlands, 2006; Volume 27. [Google Scholar]
- United Nations Economic and Social Commission for Asia and the Pacific (UNESCAP). Policy Guidance Manual on Wastewater Management; United Nations Economic and Social Commission for Asia and the Pacific: Bangkok, Thailand, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- United State Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA). Handbook for Managing Onsite and Clustered (Decentralized) Wastewater Treatment Systems; EPA/832-B-05-001; Office of Water, United States Environmental Protection Agency USEPA: Washington, DC, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Kamal, A.S.M.; Goyer, K.; Koottatep, T.; Amin, T.M.N. Domestic wastewater management in South and Southeast Asia: The potential benefits of a Decentralised approach. Urban Water J. 2008, 5, 345–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Du, X.; Zhong, W. Regional Marketization and Corporate Wastewater Treatment Activities: From the Perspective of Government Intervention. Sustainability 2023, 15, 13879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parkinson, J.; Tayler, K. Decentralised wastewater management in peri-urban areas in low-income countries. Environ. Urban. 2003, 15, 75–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sujaritpong, S.; Nitivattananon, V. Factors influencing wastewater management performance: Case study of housing estates in suburban Bangkok, Thailand. J. Environ. Manag. 2009, 90, 455–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wongburi, P.; Park, J.K. Decision making tools for selecting sustainable wastewater treatment technologies in Thailand. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2018, 150, 012013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koottatep, T.; Chapagain, S.K.; Polprasert, C.; Panuvatvanich, A.; Ahn, K.H. Sanitation situations in selected Southeast Asian countries and application of innovative technologies. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2018, 20, 495–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padilla, A.; Morgan, J.; Güereca, L. Sustainability assessment of wastewater systems: An environmental and economic approach. J. Environ. Protection. 2019, 10, 241–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suriyachan, C.; Nitivattananon, V.; Amin, A.N. Potential of decentralized wastewater management for urban development: Case of Bangkok. Habitat Int. 2012, 36, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omran, I.I.; Al-Saati, N.H.; Al-Saati, H.H.; Hashim, K.S.; Al-Saati, Z.N. Sustainability assessment of wastewater treatment techniques in urban areas of Iraq using multi-criteria decision analysis (MCDA). Water Pract. Technol. 2021, 16, 648–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, E.; Carvalho, M.; Martins, S. Sustainable Water Management: Understanding the Socioeconomic and Cultural Dimensions. Sustainability 2023, 15, 13074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obermann, I.; Sattler, K. Comparison of centralized, semi-centralized and decentralized sanitation systems. In Proceedings of the First International Symposium on Urban Development; WIT Press: Billerica, MA, USA, 2013; pp. 159–167. [Google Scholar]
- Massoud, M.A.; Tarhini, A.; Nasr, J.A. Decentralized approaches to wastewater treatment and management: Applicability in developing countries. J. Environ. Manag. 2009, 90, 652–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajakaruna, R.M.A.S.D.; Sewwandi, B.G.N.; Najim, M.M.M.; Baig, M.B.; Alotaibi, B.A.; Traore, A. Sustainable Approaches for Wastewater Treatment: An Analysis of Sludge-Based Materials for Heavy Metal Removal from Wastewater by Adsorption. Sustainability 2023, 15, 14937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghodeif, K. Baseline Assessment Study for Wastewater Treatment Plant for Al Gozayyera Village, West Kantara City, Ismailia Governorate, Egypt. In Network of Demonstration Activities for Sustainable Integrated Wastewater Treatment and Reuse in the Mediterranean; Deutsche Gesellschaft für Internationale Zusammenarbeit (GIZ) GmbH: Bonn, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- AECOM and SANDEC. A Rapid Assessment of Septage Management in Asia: Policies and Practices in India, Indonesia, Malaysia, the Philippines, Sri Lanka, Thailand, and Vietnam; Regional Development Mission for Asia (RDMA); United States Agency for International Development (USAID): Bangkok, Thailand, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization (WHO). Sanitation. 2022. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/sanitation (accessed on 1 September 2023).
- BORDA. Decentralized Wastewater Treatment Systems (DEWATS) and Sanitation in Developing Countries: A Practical Guide; Water, Engineering and Development Centre (WEDC), Loughborough University: Loughborough, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Institute for Global Environmental Strategies (IGES). Quick Study on Waste Management in Myanmar: Current Practices and Potential for Sustainable Waste Management; Institute for Global Environmental Strategies: Hayama, Japan, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Wilderer, P.A.; Schreff, D. Decentralised and Centralized Wastewater Management: A Challenge for Technology Developers. Water Sci. Technol. 2000, 41, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, N.B.; Kuyama, T. Decentralized Domestic Wastewater Management in Asia–Challenges and Opportunities. Policy Brief–Series 1, Water Environment Partnership in Asia (WEPA). Institute for Global Environmental Strategies (IGES). 2013. Available online: http://www.wepa-db.net/pdf/1403policy_brief/WEPA_PB1_2013.pdf (accessed on 18 August 2023).
- Eales, K.; Blackett, I.; Siregar, R.; Febriani, E. Review of Community-Managed Decentralized Wastewater Treatment Systems in Indonesia. In Water and Sanitation Program Technical Paper, WSP; World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 2013; Available online: http://hdl.handle.net/10986/1775 (accessed on 10 October 2023).
- World Bank. Environmental Management Plan: Wastewater Treatment Component; The World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 2012; ISBN 0-8213-4740-3. Available online: https://agris.fao.org/agris-search/search.do?recordID=US2012410433 (accessed on 19 April 2023).
- Thin, K.M. Water Supply and Wastewater Management in Mandalay City; United Nations Industrial Development Organization: Mandalay, Myanmar, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Department of Population (DOP). The 2014 Myanmar Population and Housing Census Yangon Region Report. 2015. Available online: http://www.dop.gov.mm/en/ (accessed on 25 July 2022).
- The General Administration Department (GAD). Township Profiles of Yangon Region; Ministry of Home Affairs: Naypyitaw, Myanmar, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Min, T. Current Activities on Domestic Wastewater Treatment in Yangon City, Myanmar. 2018. Available online: https://www.jeces.or.jp/relays/download/257/1391/404/2205/?file=/files/libs/2206/202304181110415669.pdf&file_name=Speaker%20-%206 (accessed on 16 June 2023).
- Starkl, M.; Brunner, N.; Das, S.; Singh, A. Sustainability assessment for wastewater treatment systems in developing countries. Water 2022, 14, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capodaglio, A.G.; Cecconet, D.; Molognoni, D. Small communities Decentralized Wastewater Treatment: Assessment of Technological Sustainability. In Proceedings of the 13th IWA Specialized Conference on Small Water and Wastewater Systems & 5th IWA Specialized Conference on Resources-Oriented Sanitation, Athens, Greece, 14–17 September 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Bakir, H.A. Sustainable Wastewater Management for Small Communities in the Middle East and North Africa. J. Environ. Manag. 2001, 61, 319–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadipour, A.; Rajaee, T.; Hadipour, V.; Seidirad, S. Multi-criteria decision-making model for wastewater reuse application: A case study from Iran. Desalination Water Treat. 2016, 57, 13857–13864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolios, A.; Mytilinou, V.; Lozano-Minguez, E.; Salonitis, K. A Comparative Study of Multiple-Criteria Decision-Making Methods under Stochastic Inputs. Energies 2016, 9, 566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, L.; Xu, Z.; Lv, C.; Hashim, M. Incomplete interval type-2 fuzzy preference relations based on a multi-criteria group decision-making model for the evaluation of wastewater treatment technologies. Measurement 2020, 151, 107137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, P.; Chen, J.; Fung, C.; Naing, Z.; Ouyang, Z.; Nyunt, K. Urbanization, economic development, and environmental changes in transitional economies in the global south: A case of Yangon. Ecol. Process. 2022, 11, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naing, W.; Harada, H.; Fujii, S.; Hmwe, C. Informal emptying business in Mandalay: Its reasons and financial impacts. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 65, 122–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Environmental Conservation Department (ECD). National Environmental Quality (Emission) Guidelines; ECD: Naypyitaw, Myanmar, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Than, M. Waste Management in Myanmar: Current Situation, Key Issues, and Challenges; Naypyitaw City Development Committee: Naypyitaw, Myanmar, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Myanmar Water Engineering and Products (MWEP). Water Supply and Wastewater Management in Myanmar; Myanmar Water Engineering and Products: Yangon, Myanmar, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Zin, M.; Soe, S. Reduction of wastewater pollutants of Mandalay City slaughterhouse. In Proceedings of the Second International Conference on Science and Engineering, Yangon, Myanmar, 2–3 December 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Capodaglio, A.G. Integrated, decentralized wastewater management for resource recovery in rural and peri-urban areas. Resources 2017, 6, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chirisa, I.; Bandauko, E.; Matamanda, A.; Mandisvika, G. Decentralized domestic wastewater systems in developing countries: The case study of Harare (Zimbabwe). Appl. Water Sci. 2017, 7, 1069–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Name | Description | Location | Number of Surveys |
|---|---|---|---|
| Area 1 | Lanmadaw Township | 16°46′26.8″ N 96°08′49.1″ E | 4 |
| Area 2 | Latha Township | 16°46′31.9″ N 96°09′04.3″ E | 4 |
| Area 3 | Pazundaung Township | 16°46′29.7″ N 96°10′25.0″ E | 3 |
| Area 4 | Botahtaung Township | 16°46′21.6″ N 96°10′46.0″ E | 3 |
| Area 5 | Kyauktada Township | 16°46′17.3″ N 96°09′49.4″ E | 3 |
| Area 6 | Dagon Township | 16°46′57.2″ N 96°09′29.0″ E | 4 |
| Area 7 | Pabedan Township | 16°46′31.7″ N 96°09′23.7″ E | 4 |
| Area 8 | YCDC Officer Housing Estate | 16°47′23.5″ N 96°10′36.0″ E | 25 residents + 5 officers |
| Area 9 | Centralized wastewater treatment plant | 16°46′02.2″ N 96°11′24.6″ E | 5 officers |
| Aspects | Environmental | Social | Economics | Technical |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DEWATS |
|
|
|
|
| CWTS |
|
|
|
|
| Days | DEWATS | CWTS | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BOD5 (mg/L) | COD (mg/L) | pH (S.U *) | TSS (mg/L) | BOD5 (mg/L) | COD (mg/L) | pH (S.U *) | TSS (mg/L) | |
| Mean Values | 48.3 | 249.1 | 7.25 | 48.2 | 58 | 255 | 7.28 | 61.4 |
| Standard Deviation | 2.4 | 3.5 | 0.2 | 2.4 | 3.3 | 10.6 | 0.1 | 4.9 |
| Environmental | Social | Economic | Technical | Total Score | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DEWATS | 24 | 27 | 23 | 28 | 102 |
| CWTS | 16 | 21 | 18 | 16 | 71 |
| Total Score | 40 | 48 | 41 | 44 |
| Scenario | Weight Combination | Total Importance | Rank |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | W1 = 0.25 | A1WSM-Score = 25.5 | 1 |
| W2 = 0.25 | A2WSM-Score = 17.75 | 2 | |
| 2 | W1 = 0.5 | A1WSM-Score = 26 | 1 |
| W2 = 0.1667 | A2WSM-Score = 18.84 | 2 | |
| 3 | W1 = 1 | A1WSM-Score = 27 | 1 |
| W2 = 0 | A2WSM-Score = 21 | 2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Swan, K.H.; Surinkul, N.; Visvanathan, C. Investigation of Decentralized Wastewater Treatment System in Urban Wastewater Management: Case Study in Yangon, Myanmar. Sustainability 2023, 15, 16756. https://doi.org/10.3390/su152416756
Swan KH, Surinkul N, Visvanathan C. Investigation of Decentralized Wastewater Treatment System in Urban Wastewater Management: Case Study in Yangon, Myanmar. Sustainability. 2023; 15(24):16756. https://doi.org/10.3390/su152416756
Chicago/Turabian StyleSwan, Kaung Htet, Nawatch Surinkul, and Chettiyappan Visvanathan. 2023. "Investigation of Decentralized Wastewater Treatment System in Urban Wastewater Management: Case Study in Yangon, Myanmar" Sustainability 15, no. 24: 16756. https://doi.org/10.3390/su152416756
APA StyleSwan, K. H., Surinkul, N., & Visvanathan, C. (2023). Investigation of Decentralized Wastewater Treatment System in Urban Wastewater Management: Case Study in Yangon, Myanmar. Sustainability, 15(24), 16756. https://doi.org/10.3390/su152416756







