Spatio-Temporal Evolution Patterns of Hydrological Connectivity of Wetland Biodiversity Hotspots in Sanjiang Plain between 1995 and 2015
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
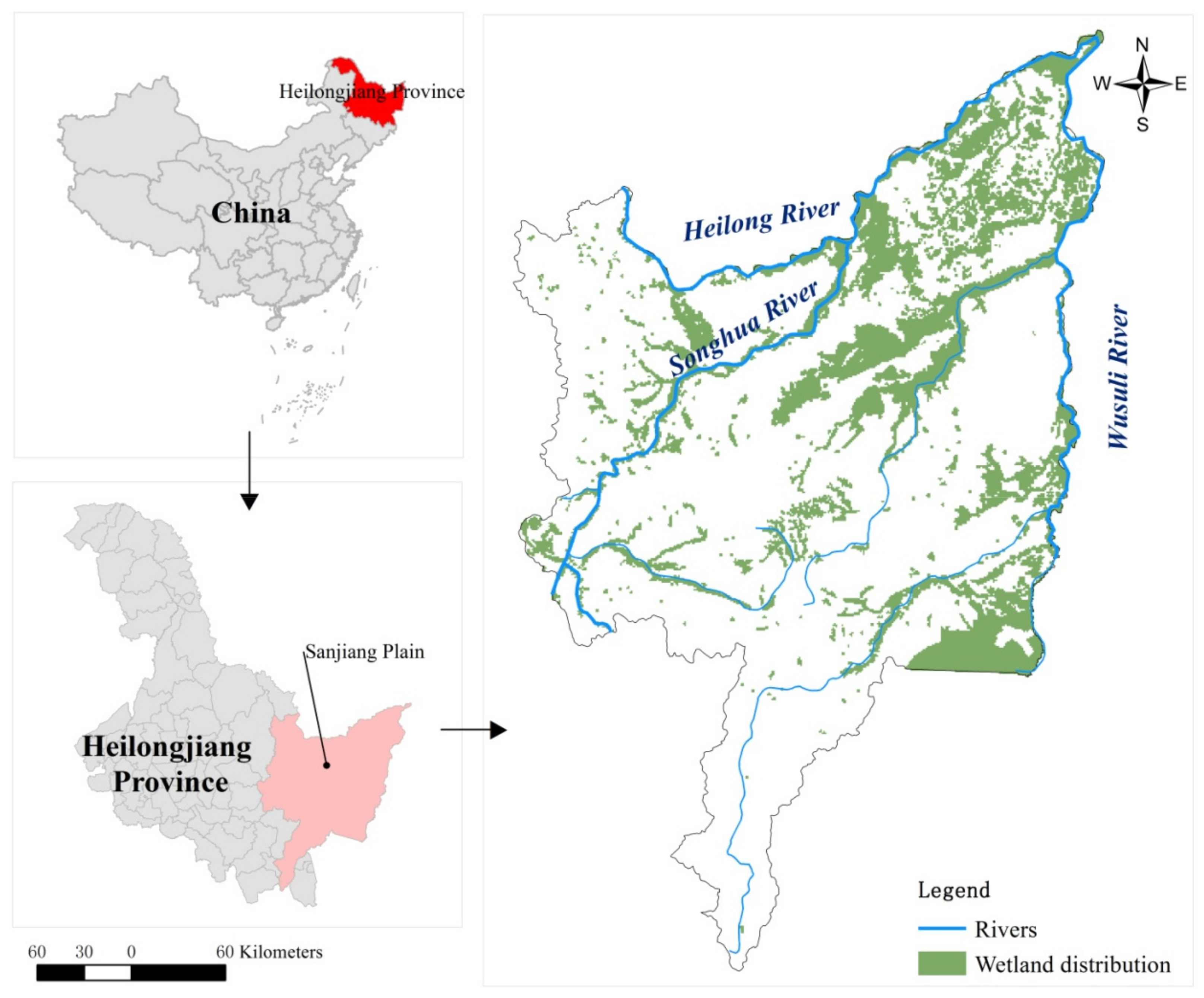
2.1. Overview of the Study Area
2.2. Research Methods
2.2.1. Data Sources
2.2.2. Identification of Wetland Biodiversity Hotspots Based on Systematic Conservation Planning (SCP)
2.2.3. Analysis of Hotspot Structural Hydrological Connectivity Changes Based on Hydrological Connectivity Index
2.2.4. Analysis of Hotspot Functional Hydrological Connectivity Changes Based on MSPA
3. Results
3.1. Spatial Distribution of Wetland Biodiversity Hotspots
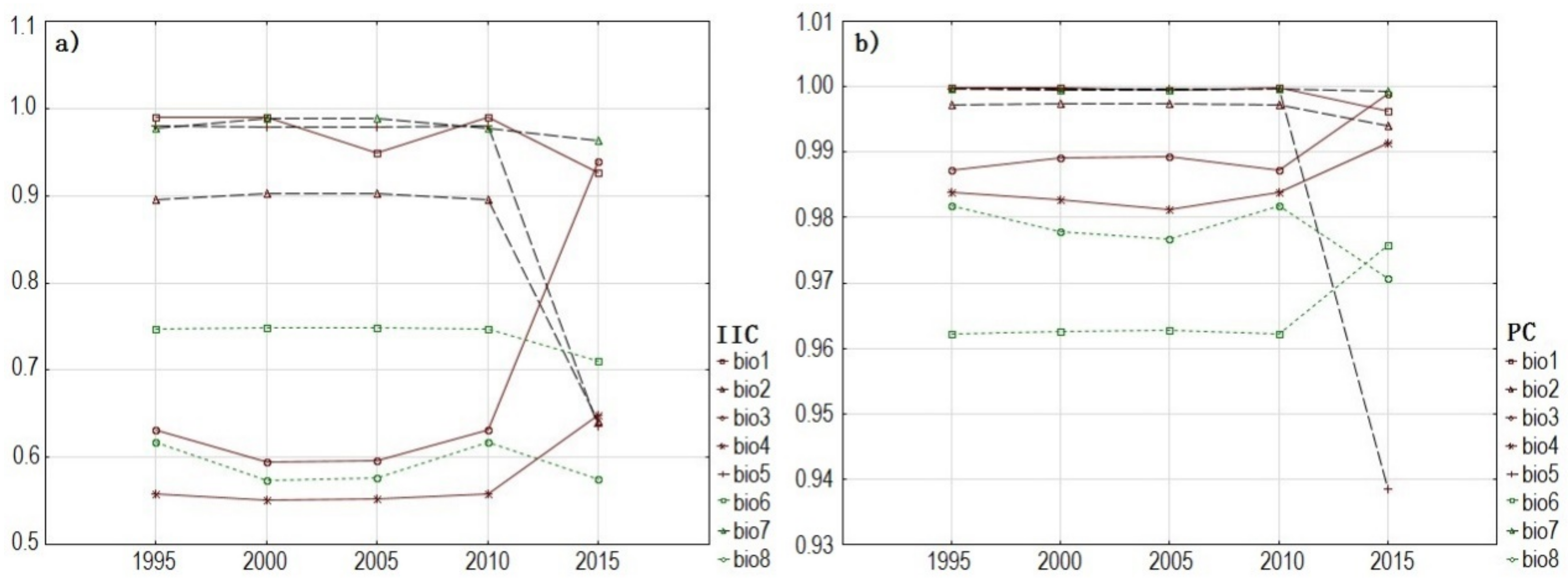
3.2. Analysis of Spatio-Temporal Changes of Biodiversity Hotspots Based on Hydrological Connectivity Index
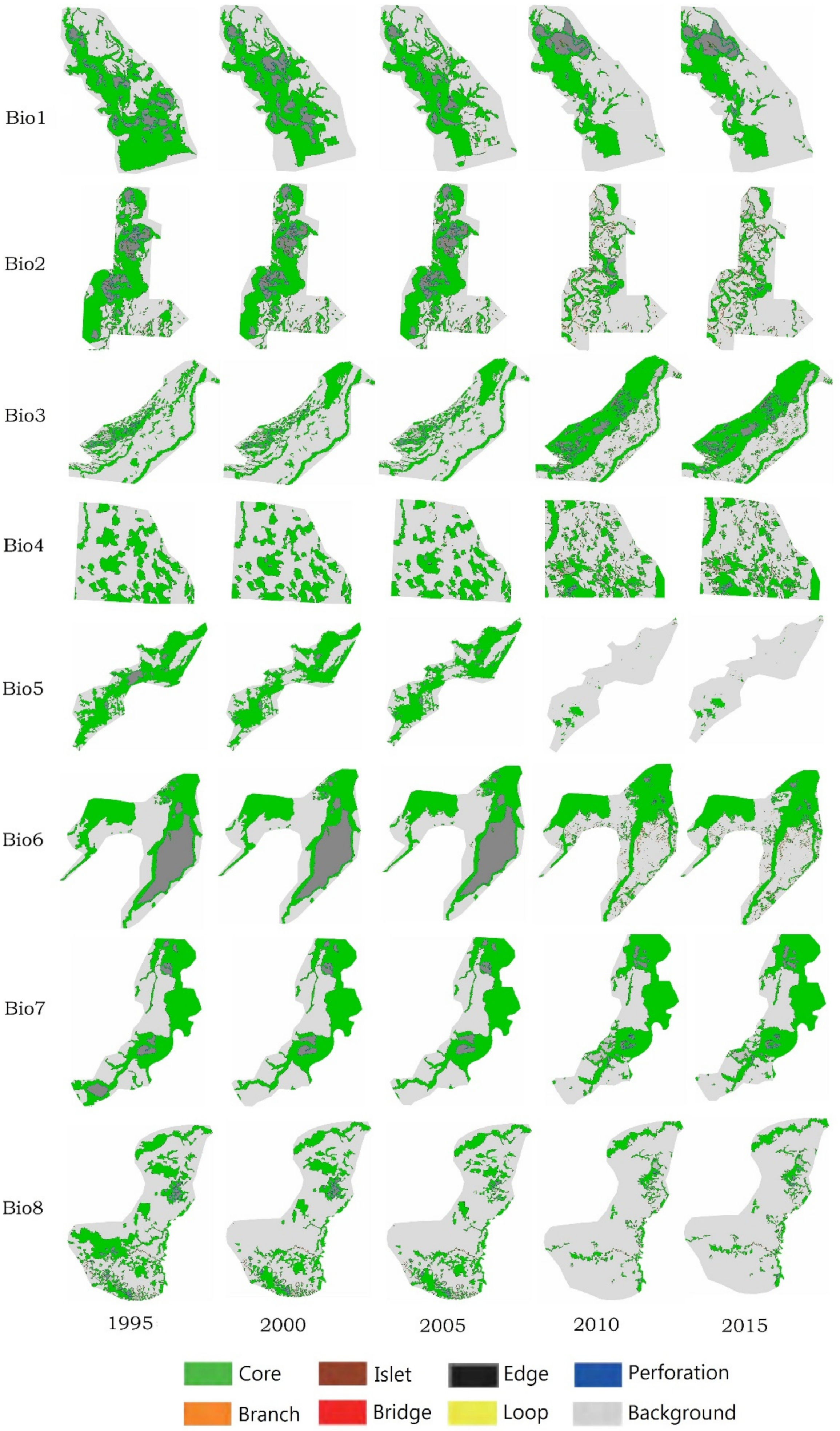
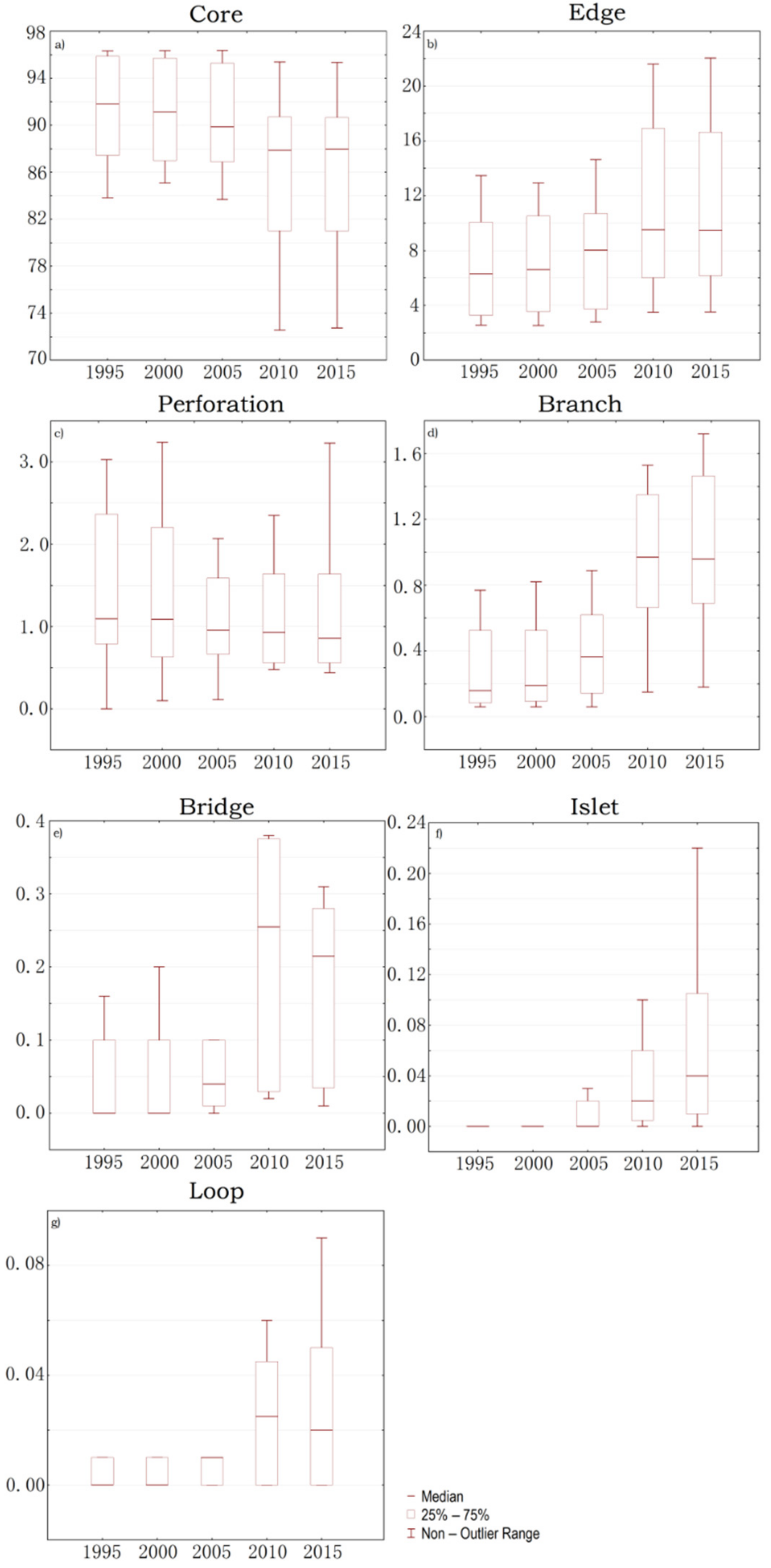
3.3. Spatio-Temporal Analysis of Change in Biodiversity Hotspots Based on MSPA
4. Discussion
4.1. Spatio-Temporal Changes of Biodiversity Hotspots Based on Hydrological Connectivity
4.2. Assessment of the Hydrological Connectivity Indexes
4.3. Implications for the Sustainable Management of Wetland Biodiversity Hotspots
4.4. Future Research
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Grill, G.; Lehner, B.; Lumsdon, A.E.; MacDonald, G.K.; Zarfl, C.; Reidy, L.C. An index-based framework for assessing patterns and trends in river fragmentation and flow regulation by global dams at multiple scales. Environ. Res. Lett. 2015, 10, 015001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.M.; Wu, X.Q. Changes in hydrological connectivity and spatial morphology of Baiyangdian wetland over the last 20 years. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2018, 38, 4205–4213. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, C.J.; Xie, T.; Liu, Z.Z.; Ning, Z.H.; Yu, S.L.; Wang, Q.; Yu, H.L.; Cui, B.S. Effects of hydrological connection on wetland organisms. Environ. Ecol. 2020, 2, 31–39. [Google Scholar]
- Larsen, L.G.; Choi, J.; Nungesser, M.K.; Martha, K.; Harver, J.W. Direction-al connectivity in hydrology and ecology. Ecol. Appl. 2012, 22, 2204–2220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Simioni, J.P.D.; Guasselli, L.A.; Etchelar, C.B. Connectivity among Wetlands of EPA of Banhado Grande, RS. RBRH 2017, 22, e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, X.; Wang, H. Effects of loss of lateral hydrological connectivity on fish functional diversity. Conser. Biol. 2018, 32, 336–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Z.; Wang, X.; Chen, B.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Q. Surface water connectivity of seasonal isolated lakes in a dynamic lake-floodplain system. J. Hydrol. 2019, 579, 124154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahanishakib, F.; Salmanmahiny, A.; Mirkarimi, S.H.; Poodat, F. Hydrological connectivity assessment of landscape ecological network to mitigate development impacts. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 296, 113169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boda, P.; Mora, A.; Várbíró, G.; Csabai, Z. Livin’ on the edge: The importance of adjacent intermittent habitats in maintaining macroinvertebrate diversity of permanent freshwater marsh systems. Inland Waters 2018, 8, 312–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walesiak, M.; Mikusinski, G.; Borowski, Z.; Zmihorski, M. Large fire initially reduces bird diversity in Poland’s largest wetland biodiversity hotspot. Biodivers. Conserv. 2022, 31, 1037–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, B.; Wang, C.; Tao, W.; You, Z.Y. River channel network design for drought and flood control: A case study of Xiaoqinghe River basin, Jinan City, China. J. Environ. Manag. 2009, 90, 3675–3686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanderhoof, M.K.; Alexander, L.C.; Todd, M.J. Temporal and spatial patterns of wetland extent influence variability of surface water connectivity in the Prairie Pothole Region, United States. Landsc. Ecol. 2016, 31, 805–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vanderhoof, M.K.; Distler, H.E.; Lang, M.W.; Alexander, L.C. The influence of data characteristics on detecting wetland/stream surface-water connections in the Delmarva Peninsula, Maryland and Delaware. Wetl. Ecol. Manag. 2018, 26, 63–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedroli, B.; Pinto-Correia, T.; Cornish, P. Landscape-What’s in it? Trends in European landscape science and priority themes for concerted research. Landsc. Ecol. 2006, 21, 421–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogt., P.; Riitters, K. Guidos Toolbox: Universal digital image object analysis. Eur. J. Remote Sens. 2017, 50, 352–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.Y.; Fu, Q.; Zhao, Q. Environment Changes of Analysis on the Hydrographic and Water Resources of Marsh Wetland in the Sanjiang Plain. Res. Soil Water Conser. 2007, 14, 298–300. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, Y.X.; Wu, Y.F.; Pan, X.N.; Qi, P.; Dai, Z.L.; Zhang, G.X. Evolution Characteristics of Meteorological and Hydrological Drought in Sanjiang Plain. Res. Soil Water Conserv. 2019, 135, 183–190+195. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, X.G. Biodiversity Change and Sustainable Utilization of Wetland in Sanjiang Plain; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Margules, C.R.; Pessey, R.L. Systematic conservation Planning. Nature 2000, 405, 243–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pressey, R.L.; Cabeza, M.; Watts, M.E.; Richard, M.; Cowling, R.M.; Wilson, K.A. Conservation planning in a changing world. Trens. Ecol. Evol. 2007, 22, 583–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Y.; Sun, G.Q.; Luo, C.Y.; Zeng, X.Y.; Zhang, H.Q.; Murray, N.J.; Xu, N. Identifying restoration priorities for wetlands based on historical distributions of biodiversity features and restoration suitability. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 231, 1222–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S. China Red Data Book of Endangered Animals; Science Press: Beijing, China, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Xie, Y. Chinese Species Red List; Higher Education Press: Beijing, China, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Lagabrielle, E.; Rouget, M.; Bourgeois, T.L.; Payet, K.; Durieux, L.; Baret, S.; Dupont, J.; Strasberg, D. Integrating conservation, restoration and landuse planning in islands Anillustrative case study in Réunion Island (Western Indian Ocean). Landsc. Urban Plan. 2011, 2, 120–130. [Google Scholar]
- Higgins, J.V.; Bryer, M.T.; Khouryk, M.L.; Fitzhugh, T.W. A freshwater classification approach for biodiversity conservation planning. Conservs. Biol. 2005, 19, 432–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carwardine, J.; Rochester, W.A.; Richardson, K.S.; Williams, K.J.; Pressey, R.L.; Possingham, H.P. Conservation planning with irreplaceability: Does the method matter? Biodivers. Conserv. 2007, 16, 245–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrier, S.; Pressey, R.L.; Barrett, T.W. A new predictor of the irreplaceability of areas for achieving a conservation goal, its application to real-world planning, and a research agenda for further refinement. Biol. Conserv. 2000, 93, 303–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascual-Hortal, L.; Saura, S. Comparison and development of new graph-based landscape connectivity indices: Towards the priorization of habitat patches and corridors for conservation. Landsc. Ecol. 2006, 21, 959–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saura, S.; Pascual-Hortal, L. A new habitat availability index to integrate connectivity in landscape conservation planning: Comparison with existing indices and application to a case study. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2007, 83, 91–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saura, S.; Torné, J. Conefor Sensinode 2.2: A software package for quantifying the importance of habitat patches for landscape connectivity. Environ. Modell. Softw. 2009, 24, 135–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riitters, K.H.; Vogt, P.; Soille, P.; Kozak, J.; Estreguil, C. Neutral model analysis of landscape patterns from mathematical morphology. Landsc. Ecol. 2007, 22, 1033–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Oliveira, S.N.; De Carvalho, J.; Osmar, A.; Trancoso, G.; Roberto, A. Landscape-fragmentation change due to recent agricultural expansion in the Brazilian Savanna, Western Bahia, Brazil. Region. Environ. Chang. 2017, 17, 411–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, F.N.; Liu, S.Y.; An, Y.; Sun, Y.X.; Dong, S.K.; Wu, X. Changes of landscape fragmentation and connectivity with urbanization: A case study of Kunming City. Acta Ecrol. Olog. Sin. 2020, 40, 3303–3314. [Google Scholar]
- European Commission Joint Research Centre. Available online: http://forest.jrc.ec.europa.eu/download/software/guidos/mspa/ (accessed on 4 May 2022).
- Hu, P.; Wang, Z.M.; Li, C.J. Remote sensing evaluation of wetland conservation effectiveness in Sanjiang plain. Agric. Sci. J. Yanbian Univ. 2017, 39, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.M.; Han, L.F.; Liu, Q.P.; Li, C.H.; Pan, Z.Y.; Xu, K. Spatial and Temporal Changes in Wetland in Dongting Lake Basin of China under Long Time Series from 1990 to 2020. Sustainability 2022, 14, 3620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.X.; Fu, Q.; Meng, F.X.; Cui, S. Analysis of evolution trend and abrupt changes of annual precipitation in Sanjiang Plain from 1959 to 2013. China Rural Water Hydropower 2016, 9, 201–204. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, H.Y.; Diao, L.M.; Zheng, S.F. Remote Sensing Monitoring of Paddy Field Expansion in Fuyuan during 1990–2013. China Agric. Sci. Bull. 2018, 034, 140–146. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, W.; Song, X.S.; Zhai, J.L. Wetland Protection and Sustainable Utilization of Water Resources in the Flooded Area. Res. Environ. 2000, 3, 58–60. [Google Scholar]
- Roelke, D.L.; Spatharis, S.; Mitrovic, S.M. A new hydrology: Effects on ecosystem form and functioning. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2012, 69, 1377–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.P.; Yin, H.W.; Kong, F.H.; Wang, J.J.; Xu, W.B. Analysis of the temporal and spatial pattern of the green infrastructure network in Nanjing, based on MSPA. Chin. J. Ecol. 2016, 35, 1608–1616. [Google Scholar]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, N.; Liang, X.; Zhang, T.; Dong, J.; Wang, Y.; Qu, Y. Spatio-Temporal Evolution Patterns of Hydrological Connectivity of Wetland Biodiversity Hotspots in Sanjiang Plain between 1995 and 2015. Sustainability 2023, 15, 4952. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15064952
Xu N, Liang X, Zhang T, Dong J, Wang Y, Qu Y. Spatio-Temporal Evolution Patterns of Hydrological Connectivity of Wetland Biodiversity Hotspots in Sanjiang Plain between 1995 and 2015. Sustainability. 2023; 15(6):4952. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15064952
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Nan, Xueshi Liang, Tianyi Zhang, Juexian Dong, Yuan Wang, and Yi Qu. 2023. "Spatio-Temporal Evolution Patterns of Hydrological Connectivity of Wetland Biodiversity Hotspots in Sanjiang Plain between 1995 and 2015" Sustainability 15, no. 6: 4952. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15064952
APA StyleXu, N., Liang, X., Zhang, T., Dong, J., Wang, Y., & Qu, Y. (2023). Spatio-Temporal Evolution Patterns of Hydrological Connectivity of Wetland Biodiversity Hotspots in Sanjiang Plain between 1995 and 2015. Sustainability, 15(6), 4952. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15064952




