Abstract
Water quality has been a major problem in Pakistan owing to a mix of factors such as population expansion, industrial units in urban areas, and agricultural activities. The purpose of this research is to conduct a comprehensive evaluation of water quality monitoring and assessment in Pakistan. The article begins by examining the water sources of Pakistan (i.e., surface water, groundwater, and rainwater). The paper then discusses the methods used by researchers in Pakistan for water quality monitoring and assessment, including chemical, physical, and biological methods. It has been determined that in certain regions in Pakistan, the concentration of arsenic present in the groundwater exceeds the national and international prescribed maximum limits. The range of arsenic concentrations in the Punjab province can vary from 10 to 200 μg/L, while higher concentrations of up to 1400 μg/L have been recorded in Sindh. In the Punjab province, fluoride concentrations vary from 0.5 to 30 mg/L, while in Sindh, the levels can reach up to 18 mg/L. In addition, some of the research has talked about bacteria. A 2017 study found that the fecal coliform concentrations in certain water in different cities of Pakistan surpassed limits and were as high as 1100 CFU/100 mL. Additionally, natural factors such as geological formations and high salinity in some areas contribute to the contamination of water. The effect of water pollution on public health has the potential to cause harm. It is critical to investigate creative strategies for improving water quality, and it is necessary to make investments in research and development, which could include the implementation of sophisticated technologies and the conception of new treatment processes. The review performed in this paper facilitates an understanding of the current water quality in Pakistan, including the types and magnitudes of contaminants present in the water sources. Subsequently, the assessment emphasizes deficiencies and challenges in the existing water quality monitoring frameworks and provides suggestions for improving them. This review is also of significant benefit to all the stakeholders involved in ensuring clean and safe water for human consumption and other purposes in Pakistan, such as policymakers, water managers, researchers, and other stakeholders.
1. Introduction
Pakistan experiences severe shortages of water and water contamination, just like other developing nations throughout the world. The country is regarded as water-stressed and is expected to experience a water shortage in the coming years since its existing water resources have practically depleted [1,2]. The government and officials are in charge of providing inhabitants with access to potable drinking water, but unfortunately, in Pakistan, water shortages and pollution brought on by ineffective water management by the nation’s government agencies are posing a threat to human existence [3]. According to community health surveys and statistics, drinking water of inadequate quality causes 40% of deaths and 50% of waterborne infections in Pakistan [4]. The presence of arsenic in high concentrations in Pakistan’s drinking water may affect up to 60 million people [5]. In the last 4 years, roughly 1832 children lost their lives to waterborne illnesses and drought [6]. Currently, only a fifth of the population has access to safe drinking water, while the rest are forced to rely on water that is contaminated by various pollutants such as chemicals, fertilizer, industrial waste, and sewage [7]. The availability of insufficient and substandard drinking water is a serious human health issue. The release of hazardous industrial chemicals and contaminated trash into water bodies lowers the water quality and has detrimental effects on individual health. Lack of knowledge, outdated treatment methods and apparatuses, unskilled laborers, and insufficient inspection all play a role. It is likely that a war on water will begin both domestically and globally if the current scenario worsens [8]. Issues of sanitation, water, and hygiene have also caused a number of dangers to population health since the probability of contracting waterborne diseases is increasing fast. In Pakistan, 2.5 million cases of diarrheal disease-related fatalities were recorded in 2017; 40% of these deaths and 50% of the country’s disorders are brought on by drinking polluted water [4].
Numerous contaminants, including pathogens and microorganisms, metal poisons, household and industrial waste, pharmaceuticals, and other dangerous medications, are present in the water [9] and need to be monitored [10] and managed [11,12,13]. Changes in climate that affect the annual precipitation, the inadequate construction of water storage structures, and governmental pressures are some of the causes of current water issues in Pakistan [4] Other factors include a rise in demand brought on by a significant expansion of industry and population [14]. Due to insufficient water sanitization, Pakistan faced major economic difficulties in 2019 [15], costing around PKR 343.7 billion (USD 1.5 billion). Additionally, from 2016 to 2017, albeit with UNICEF’s assistance, the cost of distributing facilities for cleaner water grew from PKR 48 billion to PKR 72 billion [15]. It might be claimed that the provision of clean water in Pakistan will need financing because poor facilities are offered to the entire country. Many of the existing problems, including unemployment, the incidence of sickness, and economic instability, are expected to become significantly worse in the near future if things do not change [16].
This paper intends to provide a comprehensive review of the published scientific studies on monitoring, determining, and methodologies related to water quality. Surface water, drinking water, and groundwater sources are the focus of much of this study. Study results on water quality assessment and monitoring in Pakistan during the period of 2012 to 2022 are reviewed in-depth and methodically in this study. Surface water, groundwater, and rainwater are the three categories of water sources in both urban and rural Pakistan, and these categories were used to separate the subject in this paper.
Geography and Water Resources of Study Area
This section provides information about the topography and water resources of the study area. These are the critical characteristics of surface water, groundwater, and rainfall supplies and their present state. The weather data set the tone for readers to better understand the debates on surface and groundwater in Pakistan. The hydrological and geological knowledge is particularly significant since it will assist readers in understanding how hydrogeochemical processes impact the country’s water quality.
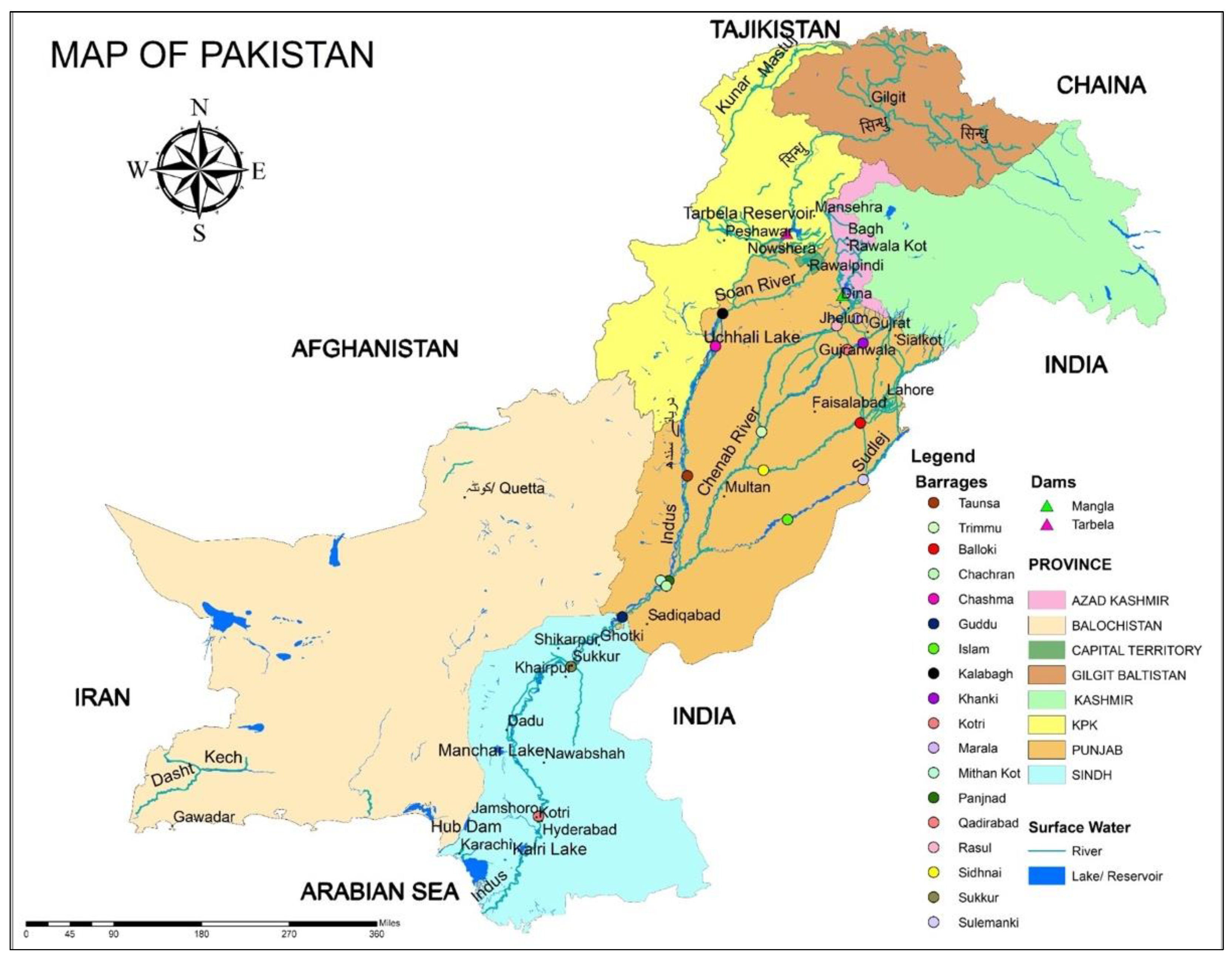
Pakistan is a country in southern Asia that has borders with Afghanistan, India, and China (Figure 1). The Himalayas and the Karakoram are located in eastern Pakistan. There are mountain ranges in the north (Hindukush), hills in the northwest, and a highland plateau in Baluchistan. There is a wide range in the average rainfall, from arid to semiarid, across Pakistan [17]. The Indus River is Pakistan’s most important waterway; it originates in the northern Karakorum Mountains, meanders its way south, and empties into the Arabian Sea. Pakistan’s agricultural sector is vital to the nation’s economy. Wheat, maize, rice, cotton, and sugarcane are the most common agricultural products, and they are grown in 27% of the total area. Increasing the agricultural yield is a common practice to meet the needs of a growing population. Industrial powerhouses such as the textile, pesticide, and fertilizer sectors may be found in the urban hubs of Pakistan [4]. Pakistan has two major river systems: those that flow into the Arabian Sea and those that flow into the Endorheic River basin. The former includes the Indus River basin, the Lyari river, and the Hingol and Hub rivers. The latter includes Mashkal, the Siastan Basin, and the Indus Plain [17]. The Indus Basin, the Kharan Desert system, and Makran coastal drainage make up Pakistan’s three hydrological groups. The Indus Basin is where the majority of surface and groundwater resources are found. Few inter-basin diversions are technically or economically viable due to Pakistan’s topography [18]. The overall water resource quantity is relatively unclear due to a lack of water data (particularly in Balochistan, where the hydrology is very unpredictable) and a lack of solid water accountancy, resulting in only estimated resources. Furthermore, surface groundwater fluxes are poorly measured [18].
Figure 1.
Geography and water resource map of the study area.
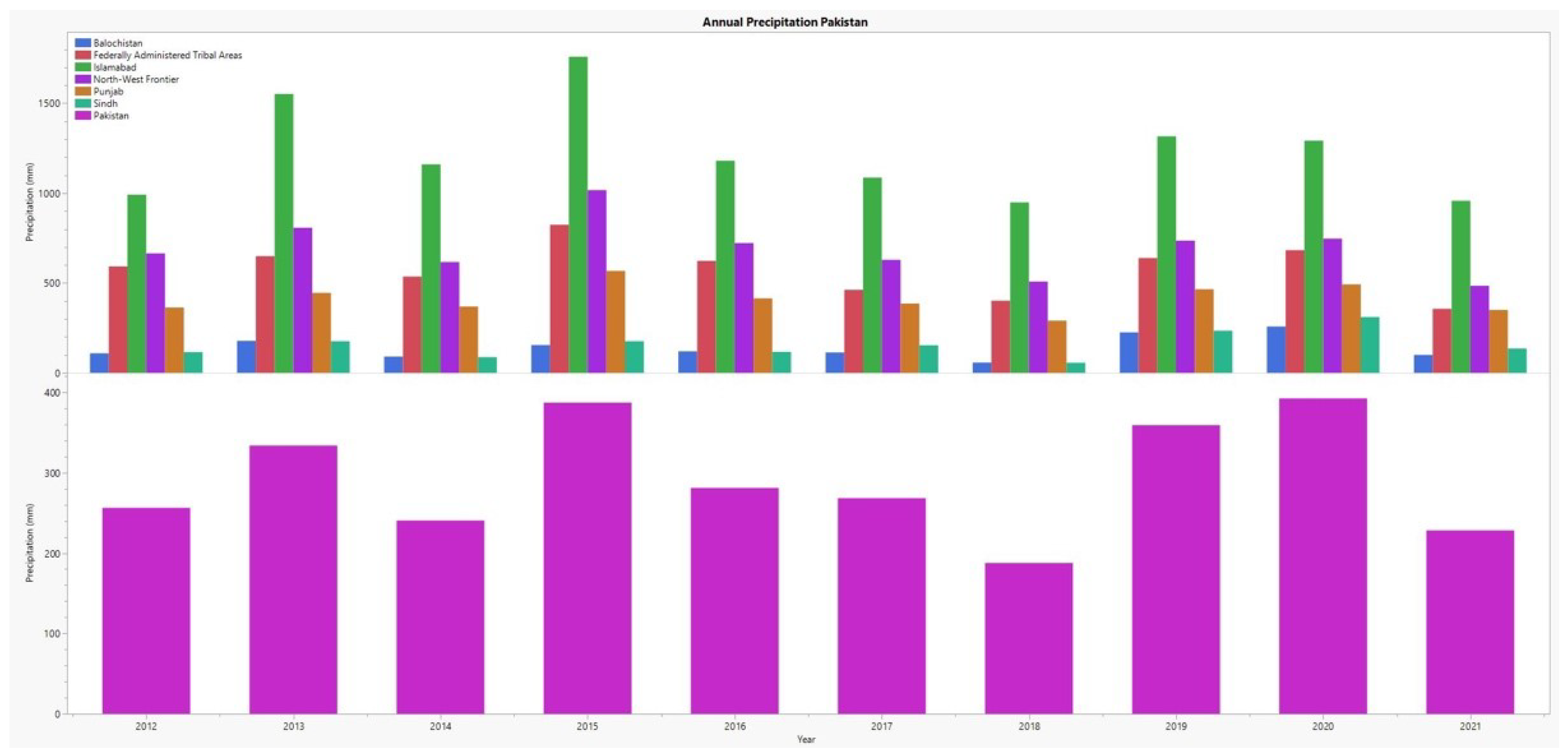
Approximately 70% of the yearly precipitation falls between June and September. This results in the majority of rainwater from the lower Indus valleys being drained into the sea. The pattern of mean annual precipitation in Pakistan exhibits substantial geographical variation. It varies from 125 mm in Balochistan (southeast) to 750 mm in the northwest [19,20]. In the lowlands of Sindh, heavy precipitation falls in July and August, and its strength decreases from the coast to the center of the province. The yearly precipitation in southern Punjab and northern Sindh is less than 152 mm. The regions above the Salt Range, such as some districts of Punjab and Sindh, receive a mean of more than 635 mm of precipitation annually [21]. Winter precipitation is often widespread. During the wintertime, the northern and northwestern regions of NWFP and the northern regions of Balochistan receive a relatively large amount of precipitation. Yearly rainfall over almost 21 million hectares (Mha) of the Indus Plains and Peshawar Basin averages 26 million acre-feet (MAF) (Figure 2). The rainfall yield to crops in irrigated areas is expected to be around 6 MAF [22].
Figure 2.
Annual precipitation in Pakistan and its provinces (source: World Bank Climate change knowledge portal, downloaded on 20 March 2023).
Surface water resources are mostly conditional on the tributaries of the Indus River. The total distance of the Indus River is 2900 km, and its basin is around 966,00 square km. Five main streams join its eastern side: the Jhelum, Chenab, Ravi, Beas, and Sutlej [23]. Additionally, three smaller rivers flow from hilly regions: the Soan, Harow, and Siran. In addition, a number of little streams enter the Indus on its west side. The largest of these is the Kabul River. Rivers in Pakistan have distinct charge characteristics, but all of them begin to increase in the spring and early summer due to the rainy season and snowmelt from the mountains, and they reach their stream flow in July and August. During the months of November through February, the average monthly flows are around one-eighth of those that occur during summertime. In addition to the larger rivers, there are countless tiny rivers and streams whose flow is only seasonal and dependent on precipitation; they carry little flow throughout the winter [24]. Furthermore, the majority of Pakistani groundwater resources are located on the Indus Plain, which stretches from the foothills of the Himalayas to the Arabian Sea and are kept in alluvial layers [25]. The Indus Plain is blessed with a huge aquifer system, which is quickly replacing it as a secondary supply of water for agriculture. It is around 1600 km wide and spans a region of 21 Mha. The aquifer was built over the course of the previous 90 years as a result of direct recharge from rainfall, river flow, and ongoing seepage from a conveyance network of canals, irrigation canals, waterways, and application losses in the irrigated regions [26].
Pakistan is usually regarded as both water-scarce (limited per capita water availability) and water-stressed. Despite this, crucial facets of Pakistan’s water issues are frequently disregarded. Most evaluations of the water shortage exclude 24 percent of the total supply that is created locally (including the recharging of groundwater by precipitation) [27]. Decades-long population growth has led to a decline in mean availability, which also changes yearly with climatic changes [18]. The present water supply is around 79%. Public health is very at risk when drinking water is supplied improperly or poorly. The release of hazardous chemicals from urban areas and industries into bodies of water without proper treatment causes water pollution and has detrimental effects on human health. Due to rising demand, Pakistan’s water and sanitation administration has been emphasizing the quantity of water over water quality [4]. This is all the result of a lack of knowledge, treatment technology, tools, trained staff, and quality control. One of the main factors in community health in Pakistan is highly polluted water. In this review, we have discussed water quality and the methods used to measure it from 2012 to 2022.
2. Water Quality Parameters and Limits in Pakistan
According to the World Health Organization, “safe drinking water” is any water that does not pose a significant threat to health during use, taking into account any variations in sensitivity between different life stages. Since water is the most frequently consumed liquid, it is thought to be the main means of disease transmission [28]. Bacterial pollution in water causes 80% of all human illnesses in developing countries. Access to potable water is one of Pakistan’s key public health challenges, since the country faces water quality and quantity problems, as recorded in much research. The majority of the water supply, over 70%, is derived from groundwater aquifers throughout the nation [29]. Pakistan is a rich country with many policies. Several policies are directly and indirectly linked to maintaining the standards of water quality, but concerns about drinking water quality in the nation receive less attention since water system organizations prioritize volume over the quality of drinking water. Additionally, the lack of a legislative framework for drinking water quality concerns, poor institutional arrangements, a lack of well-equipped facilities, a lack of routine water quality monitoring, and inadequate institutional arrangements have made the situation worse [30]. In order to solve the major challenges and difficulties in the supply of clean drinking water, the Federal Cabinet of Pakistan passed the National Drinking Water Policy (NDWP) in September 2009. The overarching objective of the policy is to provide cheap, accessible, sustainable, and adequate access to potable water for the entire population and decrease the rate of waterborne disease-related morbidity and mortality. According to the policy, the federal government is in charge of creating special plans of action for underserved and poorly served regions; saline water regions; places vulnerable to natural disasters such as earthquakes, floods, and drought; and areas where women must travel more than 0.5 km to access clean drinking water. A study on Pakistani water quality was published in 2004 by the Pakistan Council of Research in Water Resources (PCRWR) and included suggestions for creating national drinking water quality standards. The World Health Organization (WHO), the Pakistani government, and the Ministry of Health examined the drinking water standards in place for quality assurance, revised them to reflect WHO drinking water quality requirements, and then finalized them (Pak-EPA 2008). The first safe drinking water legislation in Pakistan would be drafted and passed in accordance with the 2009 National Drinking Water Strategy. The policy also proclaimed access to clean water as a basic human right. In order to make the most of the resources available to the local government, cost-effective solutions will be used. The communication of information to all stakeholders regarding the Pakistan National Standards for Drinking Water was held to be the responsibility of the Ministry of Environment (currently the Ministry of Climate Change), the PCRWR, and the Pakistan Standards and Quality Control Authority (PSQCA) [31].
After Pakistan’s 18th amendment to the constitution [32], province EPAs/EPDs were tasked with creating and executing environmental policies within their particular jurisdictions under the Provincial Environmental Protection Act and Policies. Additionally, the law divides up governing duties between the federation and the provinces. Following the passage of the Constitution (Eighteenth Amendment) Act of 2010 (the “18th Amendment”), Parliament is now able to pass laws, exercise executive power over the matters included in the Federal Legislative List in the Fourth Schedule to the Constitution and create extraterritorial legislation. On the other hand, regional assemblies have the authority to enact laws and exercise executive authority over any matter not included in the Federal Legislative List. Furthermore, the Constitution also gives the provinces the freedom to ask Parliament to pass legislation on any issue falling under their purview. The water quality standards of all four provinces and the Pakistan EPA can be found in the following list of websites (Table 1).

Table 1.
Water quality standards.
Samples are typically obtained, categorized for various contaminants and characteristics, compared to all these standards, and highlighted when the findings depart from the benchmarks. In Pakistan, this strategy is used for all sources of drinking water (surface water, groundwater, and rainwater) [33]. Various indicators (such as pH, TDS, heavy metals, and fecal coliforms) have also been used in other research to track water contamination. Studying the macroinvertebrate community, as well as other groups of microorganisms, is part of this. The number and variety of macroinvertebrates and microorganisms are utilized to inductively assess the water quality source even though they are not specifically employed as an indicator [34].
The establishment of the above water quality standards is regarded as a positive move that might serve as a model in addressing Pakistan’s water security issue [35]. Regardless of having extensive national laws and regulations for groundwater resources and control of pollution and a policy structure for the protection of the environment, Pakistan’s organizational and implementation capacity is severely deficient [36]. Local authorities in Pakistan are accountable for water supply and sanitation (WSS); solid waste disposal; and the disposal, treatment, and management of wastewater. The municipal administrations of Tehsil, as well as water and sanitation organizations, are in charge of implementation. Their effectiveness, unfortunately, is generally unregulated. Various national regulations control the water, sanitation, and hygiene (WASH) system; however, because water is a provincial issue, the influence of national organizations is limited. The NSP 2006 was created to encourage public participation, ownership, and management while also freeing up resources to spend on closing the clean water deficit [37]. The Pakistani government established the National Drinking Water Policy (NDWP) in September 2009 with the goal of supplying safe drinking water to all by 2025, with a focus on the poor and vulnerable [31]. The major goal is to distinguish between service provision and control. The right to drink water has priority over all other activities, such as agricultural or industrial water usage. In order to address the issue of water security, Pakistan established the new National Water Policy of Pakistan (NWPP) in 2018. The strategy highlights the need for Pakistan to address present and future challenges to its energy, water, and food security. It addresses a wide range of water-related issues in Pakistan, including the distribution and usage of water based on economic priorities, the sustainability of water basins, agriculture, changing climate impacts, drinking water and sanitation, groundwater, water rights and obligations, hydropower, conservation, sustainable water infrastructure, water-related risks, and regulatory frameworks [38]. Still, there is a lack of a clear framework and a sufficient implementation plan to address the problem, especially in organizational governance systems. However, due to insufficient law enforcement, none of the government’s various projects to address water shortages and pollution in Pakistan have been successfully carried out, and the problems continue to exist. Along with legislation, public awareness is necessary to combat community indifference toward water contamination. Furthermore, official support is presently weak regarding laws, management efforts, and law enforcement, all of which are necessary for citizen education.
3. Methodology
In order to enable future research, recognize gaps in knowledge, and effectively specify study focuses, the goal of this review is to consolidate and categorize research results. This study consistently highlights the future prognosis for water quality monitoring and evaluation, and it goes on to concentrate on the importance of water quality in the environmental sustainability of Pakistan. The literature published on the topic over the previous 10 years was thoroughly searched on Google Scholar and Scopus to find data for this study. The relevant methods have been used in other research, as per Mosley, 2015 and Razali et al., 2018 [39,40]. The search terms used were “water,” “quality,” and “Pakistan”; the country name (Pakistan) was included for this purpose. After that, we narrowed it down to domestic articles in English, along with some other criteria such as the location, origin, document type, and publication year (2012–2022). This was successful in removing any important papers without omitting the pertinent ones. In the context of Pakistan, there are no such contemporary evaluations of this topic, nor are there any with the present breadth of coverage. This supports the originality and importance of such a complex strategy and emphasizes its applicability to a broad variety of Pakistani demographics, including academics, students, authorities, entrepreneurs, and common citizens.
4. Water Quality Assessment in Pakistan
4.1. Surface Water Quality Assessment
The examination and monitoring of the quality of surface waters in Pakistan have been discussed in light of the reported source of contamination, sample location, pollutant parameters, and relevant health issues. Table 2 includes, in reverse chronological order, complete information on the various water sources analyzed in the nation over the last decade (2022–2012), as well as the discovered contaminants. According to an older study by Sial et al. (2006), 1228 of Pakistan’s 6634 recognized enterprises are classified as severely hazardous [2,41]. Industries became a major cause of water pollution in Pakistan because of the high load of organic and poisonous compounds in their wastewater effluents [42]. Textiles, leather, paper, pharmaceuticals, ceramics, petrochemicals, food, steel, oil mills, the sugar industry, and fertilizer plants are the main sectors causing water pollution [43]. These industries generate hundreds of thousands of tons of wastewater loaded with heavy substances such as mercury, magnesium, lead, cadmium, nitrites, chromium, and many more [44]. The majority of companies in Pakistan are concentrated in or near large cities. They directly discharge their waste effluents into surrounding sewers, streams, creeks, lakes, canals, and open or agricultural land. According to Fida et al. (2022) [44], waterborne diseases are caused by bacterial pollutants, including coliforms; toxic components such as Fe, Ni As, Cl, Hg, and F; and pesticides, which have been identified in surface water and groundwater. Forty-one locations all along the Indus River and its tributaries were sampled by Ahmad et al. (2021) [45] to determine the surface quality of the water in Sindh. Only four of the ten physiochemical properties tested (average values of 857 S/cm, 378 mg/L, 8.5 mg/L, and 220 mg/L for EC, TDS, pH, and COD, respectively) fulfilled the standards set by the WHO and the NSDWQ. Contrarily, the levels of TA (1400 mg/L), TH (584 mg/L), DO (6.40 mg/L), and NTU (219) were all above the recommended limits set by the WHO.

Table 2.
Research on surface water quality in Pakistan.
Major Pollutants and Their Sources in the Surface Water of Pakistan
Effective water contaminants may be responsible for the pollution and transmission of infection [115]. Bacteria (microorganisms and infections), chemical contaminants (toxic and heavy metals, salts, and acids), and cations and anions are the most prevalent contaminants [44]. These compounds are toxic if they exceed limits and represent significant physical concerns to individuals and other species in the environment if they exceed certain values [116]. Microbiological contamination; heavy metals, including Pb, As, Hg, and Cd; pesticides; and other anions such as NO3 and F impact the environment and human health throughout Pakistan [8]. Table 2 depicts the primary pollutants discovered in several cities and provinces, as well as the ratios of samples that exceeded the requirements.
The most likely source of drinking water contamination in Pakistan has been identified as coliform pollution [117]. According to numerous studies, the country’s drinking water is heavily contaminated by bacteria [71]; many of the documented bacterial species can have serious health consequences (Table 2). Most parts of the country’s sources of water, including streams, waterways, rivers, and lakes, are heavily contaminated with bacteria. Out of 73 reviewed papers in this study, the authors found 12 studies that found bacterial contamination in their samples (Table 2). These studies also talked about health issues due to this [118]. Ref [2] studied bacteria contamination in the Sutlej River. In their research, they collected 400 samples from 13 different locations around the river. Their model found that E. coli levels in a more polluted environment will show 108% and 173% increases in the near- and mid-future, respectively, and a 251% rise in the distant future compared with the reference time (baseline) levels. In Phuleli Canal, Sindh Province, out of eight water samples, most were found to contain fecal coliforms [56]. Another study in Khairpur found fecal coliform and coliform bacteria in 100% of water samples taken from the water channel, the distribution system, and household taps [119]. The scenario is similar to all other major cities across the country, including Islamabad, Quetta, and Hyderabad. All of these cities’ drinking water was determined to be polluted with bacteria. The major sources of these contaminants were domestic anthropogenic activities and old, open water supply lines [119]. Furthermore, several studies have found health issues due to using bacteria-contaminated water, such as asthma and infections related to the urinary tract, circulation, and other organs. An invasive pathogen creates a range of bloodstream pathogens in patients’ urinary tracts, respiratory tracts, blood, and other ordinarily sterile areas [33].
The physical and chemical characteristics of water, such as pH, EC, DO, and BOD, and the presence of things such as TDS and TSS are used to establish standards and evaluate the physical and chemical water quality. Pesticides and fertilizers are examples of toxic elements that come from factories, ground sediments, and fertilizer waste and end up in water supplies nearby [4]. These water sources have trace-metal contaminants because, as water moves downhill in a hydrological cycle, it dissolves these things [120]. In addition, these metals enter both surface water and groundwater due to human actions such as dumping untreated municipal and industrial waste and using a lot of chemicals in farming. Many of these elements are important for individual health, but too many of them can pollute water and make people and other living things sick [121]. Table 2 is a summary of the different studies that have been conducted from 2012 to 2022 in Pakistan on water pollution caused by physicochemical pollution, such as EC, pH, TDS, TH, and TA. A study by Jabeen et al. (2014) [105] of the Haripur Basin on physicochemical parameters found that a stream sample from the Hattar Industrial Park region had the lowest pH (5.4), whereas a river sample from next to a marble industry area had the highest pH (9.20). Moreover, the surface water had an electrical conductivity range of 0.180 to 1.182 mS/cm. Surface samples from areas near industrial areas often have higher EC values. TDS concentrations in surface water can vary from 116 to 956 mg/L (mean, 322). Mean pH, EC, and TDS values in surface water have been reported to be below the WHO (2008) recommendations. The surface water quality of the Indus River in Sindh was studied by sampling 41 locations all along the river and its tributaries. Only four physicochemical characteristics, namely, EC, TDS, pH, and COD, with average values of 857 S/cm, 378 mg/L, 8.5 mg/L, and 220 mg/L, respectively, were within the WHO-permitted standards. TA (1400 mg/L), TH (584 mg/L), DO (6.40 mg/L), and NTU (219) values, on the other hand, were above the WHO-permitted criteria [45]. Arshad and Imran (2017) [122] found significant As concentrations in two villages in the central Punjab region. Out of 73, most of the studies found low-to-high concentrations of As, COD, BOD, TDS, and other chemicals (Table 2). Furthermore, the sources of these contaminations were industrial and anthropogenic activities and, in some areas, natural inputs [123].
The accumulation of harmful compounds in surface water, particularly harmful heavy metals, is a major environmental and social problem across the world [44]. Heavy metal traces, such as Pb, Mn, Cu, Ni, Fe, and Cr, are substantial environmental contaminants, especially in regions subjected to intense anthropogenic pressure [124]. These pollutants are capable of causing several negative health consequences in humans through the use of heavy-metal-contaminated water [125]. Although certain toxic substances are required for life in low quantities, others, such as Cd, Ni, Hg, and Pb, are physiologically nonessential and extremely dangerous to living creatures [126]. Recent research has found heavy metal pollution in the drinking water of Pakistan, as detailed in Table 2. In the majority of Barandu River samples, heavy metal concentrations of Fe, Pb, Ni, Cr, Mn, and Cd were found to be higher than the WHO-permitted levels for drinking water. People and other living things may have issues as a result of this high concentration of polluted water. Fe is one of the required elements, but if it is present in excess, it can have a negative impact on aquatic life and human health. High levels of Fe harm gastrointestinal tract cells and prevent them from controlling Fe absorption, which results in an unwarranted increase in blood’s Fe concentration [127]. Another study on the Indus Drainage System found that the concentrations of most metals in riverine surface water were well below (Table 2) the guidelines established by the WHO and national agencies, but they showed wide interannual variation when compared with the other river systems. Along with the Indus Drainage System, the general riverine water contamination was higher than that observed in the surface water of the Shatt Al-Arab River [128], the South China Pearl River [129], and Argentine rivers [130] but smaller than those of the stream water of the Ganga River, India [131], and Gadea, Spain [132]. Since the Indus River primarily flows through the populated industrial zones of Faisalabad, Jhang, Sialkot, and Kabul, the heavy metal contamination level of the Chenab River was found to be lower than that of the Indus River [118]. Heavy metals in drinking water can pose significant health risks, including damage to the nervous system, kidney and liver damage, and cancer. In Pakistan, studies conducted between 2012 and 2022 found that high levels of heavy metals, such as lead, chromium, and arsenic, have been detected in drinking water sources (Table 2). It is crucial for Pakistan to tackle heavy metal contamination in drinking water in order to safeguard public health.
4.2. Groundwater Quality Assessment
Pakistan is one of the world’s driest regions, and the majority of the people rely on groundwater to meet their water needs for drinking and other household reasons [133]. Groundwater is a vital resource in Pakistan, providing drinking water and irrigation for agriculture; however, the overuse and overexploitation of this resource have led to a decline in both water quantity and quality in the country [134]. Research on groundwater has largely been studied by authors in Pakistan. We found 97 studies conducted from 2012 to 2022 (using the above method), and 18,220 water samples were collected for water quality analysis (Table 3). Furthermore, these studies were important because groundwater levels in Pakistan have been declining at an average rate of 0.5 m per year over the past decade [135]. This decline is due to the overuse of groundwater resources for irrigation, as well as a lack of effective management and regulation in the groundwater sector [66]. Several studies have also warned that the depletion of groundwater resources could have severe consequences for food security and economic development [136,137]. Groundwater in Pakistan is also being contaminated by a variety of pollutants, including agricultural chemicals, industrial effluents, and sewage (Table 3). Our comprehensive review found that these pollutants are affecting both the quality and the quantity of the groundwater, making it unsuitable for use. Furthermore, studies over the last decade have reported high levels of nitrates, arsenic, and fluoride in groundwater, making it unsafe for drinking and irrigation [138]. To address these issues, researchers have studied the implementation of sustainable groundwater management strategies in Pakistan. This includes the development of water quality assessment methods, policies, and regulations to better manage and conserve groundwater resources, as well as the use of new technologies and practices to reduce water loss and improve water quality. All the information on the many places examined throughout the country over the last decade, as well as the discovered contaminants, can be found in Table 3, listed in reverse chronological order.

Table 3.
Research on groundwater quality in Pakistan.
Major Pollutants and Their Sources in the Groundwater of Pakistan
Chemical (organic and inorganic) and biological pollutants are the two categories of natural pollutants found in groundwater. While inorganic pollutants come from natural origins, the majority of organic pollutants in groundwater are formed by anthropogenic activities. Numerous substances have been identified as inorganic pollutants and claimed to be sensitive aquatic pollutants. Organic pollutants such as oil and pesticides are the most frequent pollutants. Pathogens (bacteria, protozoa, and viruses), water-soluble radioactive compounds, and anions and cations are examples of toxic elements [204]. These compounds are dangerous and may seriously harm people and other ecosystem inhabitants if any amount of them exceeds the allowable limit. Heavy metals, including As, Cd, Pb, and Ni, as well as anions such as NO3 and F, are prominent pollutants and are seen as a danger to groundwater quality in Pakistan [205,206]. Solid trash has increased as a result of population expansion and radical efforts to raise life quality [207]. Municipal waste is distinguished as household, commercial, or institutional garbage, whereas solid waste is categorized as dangerous, clinical, urban, or radioactive [208]. As is clear from the preceding paragraph, solid waste dumps primarily exist in urban areas of developing countries and pose serious risks to groundwater sources, which are an important source of residential water supplies in these places [209]. Groundwater supplies may become contaminated by bacteria and other diseases from municipal waste dumps [149].
Regarding human health, ensuring the bacteriological safety and purity of drinkable water is an ongoing challenge. The transfer of harmful germs, such as microorganisms, infections, and protozoa, occurs through water. In the entire world, 80 percent of illnesses are caused by contaminated water [113]. Fecal and total coliforms in drinking water are indications of the existence of disease-causing microorganisms and pathogens; microbiological safety and groundwater quality are established and monitored by analyzing their occurrence [119]. In both urban and rural parts of Pakistan, bacterial pollution in drinkable water is a major public health concern since it carries germs that can cause infectious illnesses [44]. Multiple studies have found bacterial pollution in groundwater; the country ranks 80th out of 122 nations with low-quality drinking water [117]. In Islamabad, nearly half the samples were polluted with E. coli and fecal coliform bacteria, rendering the water unfit for consumption [190]. A systematic review in 2011 was carried out in four provinces of Pakistan. The study found that coliform bacteria were present in 64% of the samples from Punjab Province, 67% of samples from Khyber Pakhtunkhwa Province, 83% of samples from Sindh Province, and 80% of the samples from Balochistan [210]. Empirical research was conducted recently in Kohistan (MIS1), Shangla (MIS2), and two organizations, namely, Malakand (MIS3) and Mohmand (MIS4). Fecal coliform bacteria were present in the study region at concentrations of BDL-60.0, BDL-32.0, BDL-97.0, and BDL-89.0 colonization units per 100 mL (CFU/100 mL), respectively. The water samples from MIS2 were found to have the lowest mean concentration of fecal bacteria (8.45 CFU/100 mL), whereas the water samples from MIS3 had the highest mean concentration (18.25 CFU/100 mL). In the research region, 78% of groundwater sources had coliform bacteria contamination when contrasted with the permissible threshold (0 CFU/100 mL) of water established by the WHO and Pak-EPA. This high fecal contamination bacteria pollution may be caused by poor sanitation, poor-quality sewage tanks, and animal and human waste [211]. In the Sindh province of Pakistan, this is due to the application of fertilizers in agriculture and the discharge of untreated wastewater into nearby water bodies [125]. A study also found that the presence of nitrates was higher in groundwater samples collected from areas with a higher population density and intensive agricultural activities [4]. In conclusion, the biological contamination of groundwater in Pakistan is a serious problem that is caused by a variety of factors, including the discharge of untreated wastewater, the presence of septic tanks and latrines, the disposal of industrial waste, the use of pesticides in agriculture, and the application of synthetic fertilizers [7]. This problem is particularly severe in areas with a higher population density and intensive agricultural activities, and it poses a significant threat to the health and well-being of the population (Table 3).
The physical and chemical characteristics of groundwater that can determine its quality and appropriateness for different purposes are referred to as physicochemical parameters. Temperature, pH, conductivity, turbidity, dissolved oxygen, and concentrations of different dissolved ions and compounds, such as nitrates, chlorides, and heavy metals, are some of the characteristics that make up this list [87]. These variables can be used to evaluate the general condition of a groundwater system and spot any possible deterioration or pollution. Monitoring these variables over time can also assist in observing changes in groundwater quality and spotting any possible problems. Chemical contaminants such as fertilizers and pesticides come through industry, soil sediments, and fertilizer runoff and then reach surrounding sources of water [44]. These sources of water include harmful metal contaminants as a result of the dissolution of these chemicals during a hydrological cycle [4,44]. Research was conducted to assess the total dissolved solids, hardness, pH, alkalinity, and turbidity of groundwater. Groundwater chemistry analysis data from Lahore were used to assess the quality of drinking water regions using a GIS. The study found that 61% of the zone was excellent, 27% was good, 9% was moderate, and 3% had poor quality. However, when using PSQCA guidelines, only 5% of the region is perfect, 29% is satisfactory, 34% is medium, and 32% is not acceptable for drinking [195]. In a study by Shahab et al. (2016) [188], water samples collected in Sindh were found to be unsafe to drink. In addition, 62.84 percent of EC samples, 34.86 percent of TDS samples, 43 percent of Na+ samples, 17.88 percent of Cl− samples, 26.60 percent of SO42− samples, 39.44 percent of HCO4− samples, 41.7% of turbidity samples, and 35.32 percent of hardness samples were above the WHO standard limit for drinking water. The highest concentrations were recorded in lower Sindh (Thatta, Badin), Tharparker, and central Sindh, where seawater intrusion occurs. Principal component analysis and correlation studies confirm the positive link between As and Fe, which may be the reason for As mobilization in Sindh’s water table. Moreover, in Malakand city, water samples were taken from 75 groundwater sources to determine the quality of drinking water by analyzing the physiochemical characteristics. Among the basic measures, only TH (1500 mg/L) surpassed the WHO and NSDWQ guidelines. These sources of drinking water represent a grave risk to the community’s health [212]. By collecting 10 samples of drinking water from different sources, the physicochemical quality of drinking water in new urban areas of Peshawar was analyzed. The pH fell within the WHO-permitted range; however, TSS levels in five samples and NTU levels in six samples exceeded WHO and NSDWQ recommendations. Pathogens and bacterial illnesses, including diarrhea, nausea, and abdominal pains, can be caused by elevated levels of NTU and TSS [213].
Heavy metal contamination in groundwater is a major concern in Pakistan, and studies have reported the presence of heavy metals such as lead, cadmium, chromium, and nickel in many samples above the permissible limits set by the WHO [161,175]. The sources of heavy metal contamination are varied, including industrial activities, agricultural practices, and municipal waste disposal. It is important to continue research on the extent and sources of the contaminations and implement measures to protect groundwater resources [142]. Trace metals are elements such as iron (Fe), cobalt (Co), and zinc (Zn) that are necessary for the proper growth and functioning of the human body in extremely minute quantities. Heavy metal often relates to a metallic element with a very high density or that is hazardous in trace levels, although excessive amounts of these substances might have negative consequences. Heavy metal examples contain lead (Pb), mercury (Hg), and arsenic (As) [214]. Numerous study studies have been published between 2012 and 2022 stressing the adverse consequences of heavy metals found in drinking water, particularly groundwater. As a result of a lack of economic and technological means, protecting the human population from the harmful consequences of metal poisoning is far more difficult in developing countries than in industrialized nations. Table 3 shows a brief description of the major and heavy metals present in different areas of Pakistan groundwater. Research has examined the levels of various pollutants present in the drinking water and the potential health hazards in Charsadda District, Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, Pakistan. The levels of nitrates in 13 locations exceeded the limit of 10 mg/L set by the US EPA, with concentrations ranging from 10.3 to 14.84 mg/L. Similarly, sulfate levels in nine sites exceeded the limit of 500 mg/L established by the WHO, with concentrations ranging from 505 to 555 mg/L. Additionally, concentrations of Pb, Cd, Ni, and Fe exceeded the permissible limits set by various organizations in certain areas [215]. Nickle is present in groundwater from all of Pakistan’s main cities, with Lahore and Karachi being the worst affected (Table 3). The concentrations range from 0.001 to 3.66 mg/L. The WHO-recommended level is 0.07 mg/L, but PCSQA’s allowed limit is 0.02 mg/L [204]. When it comes to the poisoning of groundwater with arsenic and fluoride, Pakistan is ranked fourth internationally [216]. Regions of Sindh and Punjab have the highest levels of arsenic and fluoride contamination. In Sindh, arsenic and fluoride groundwater contamination has been recorded in the districts of Sukkur, Karachi, Tharparkar, and Hyderabad [204,210]. The groundwater in the Pakistani province of Punjab has significant arsenic concentrations in the districts of Kasur, Lahore, Multan, Sheikhupura, GI Khan, Mianwali, and Vehari. A little under 30,000 wells have been examined as part of this general investigation. As was found in 79% of the wells; 11% had almost 0.01 and 0.05 mg/L, and 10% of the samples had As concentrations of more than 0.05 mg/L [217].
4.3. Research on Filtration Plant Water Quality
The development of water treatment facilities and the encouragement of secure water storage and hygienic practices are only a few of the actions taken by the government of Pakistan to improve the quality of the water supply. However, a lack of financing and infrastructure has hampered many of these initiatives. In Pakistan, there are also a lot of nongovernmental groups that are striving to raise water quality through community-based projects and education. Few studies have been conducted to assess filtration plant water quality (Table 4). One study focused on evaluating the water quality of filtration plants in two populated cities of Pakistan, Rawalpindi and Islamabad. Samples were collected from plants run by the Capital Development Authority in Islamabad and the Water and Sanitation Agency in Rawalpindi. The results showed that several physiochemical parameters and metals were above the acceptable limit set by the World Health Organization. Many samples in both cities were found to be of poor quality with a water quality index greater than 100. The study also found that children are more vulnerable to health hazards from contaminated water. The study suggests that the proper management of limited underground water resources is necessary to ensure the sustainability of safe drinking water in these cities [123]. Another study in the same city assessed the quality of drinking water in the distribution network by collecting 80 samples of water in triplicate from treatment plants and residential taps. Samples were analyzed for various parameters such as free total coliforms, chlorine residue, chloramines, trihalomethanes, total chlorine, total organic carbon, fecal coliforms, and turbidity. The results revealed that some areas of Islamabad City, such as sectors F-6, F-10, and F-11, were free of fecal contamination, while other areas, such as E-7 and F-7, had contamination at a few stations among all the collected samples. The most contaminated areas were found to be sectors F-8, G-9, G-8, I-9, and I-8 of Islamabad, with high levels of E. coli at most sampling stations. Additionally, high concentrations of trihalomethanes and chloroform were detected in sector F-8 [218] (Table 4). It is crucial to evaluate the water quality in filtration facilities since it has a direct influence on people’s health and well-being. The sources of water for these filtration plants were groundwater and surface water [123]. It is essential to systematically research the water quality in filtration facilities in Pakistan, where access to clean drinking water is a key challenge. The scarce water resources are under stress due to a growing population and human activities, making it even more crucial to monitor and preserve them. In developing nations, where water quality monitoring and maintenance are frequently insufficient, the situation is more serious. Given the importance of this problem, it is essential that further research be conducted to thoroughly examine the water quality of Pakistani filtration facilities. The microbiological and health concerns related to water should also be studied, in addition to the physiochemical characteristics. Researchers can then pinpoint issues and provide workable remedies to raise the nation’s water quality. In order to guarantee the population’s access to potable drinking water for the foreseeable future, the research should also take sustainable management of subsurface water resources into account. Furthermore, evaluating the water quality in filtration facilities in Pakistan is essential to safeguarding the population’s health and welfare. To thoroughly examine the water quality and provide practical strategies to enhance it, further research is required. In order to guarantee the population’s access to clean drinking water over the long term, this research should also take sustainable water resource management into account.

Table 4.
Research on filtration plant water quality in Pakistan.
4.4. Research on Rainwater Quality
Rainwater quality assessment is an important field of research in Pakistan since it is a key supply of water for many people. The country’s semiarid and desert regions rely largely on precipitation as a supply of water for drinking, irrigation, and other purposes. However, numerous variables, such as industrial and agricultural operations, urbanization, and climate change, can have an impact on the quality of rainfall [220]. There have been several studies on the rainwater quality in Pakistan in recent years. These studies have focused on various aspects of rainwater quality, including chemical and physical parameters, as well as microbiological and health risks. In order to solve the water scarcity problem in the chosen research region, a study was undertaken to analyze the quality of roof-harvested rainwater. The research team also attempted to discover any potential health risks linked with rainwater drinking in the study location. With the exception of pH, turbidity, and trace amounts of certain elements such as Fe and Pb, the examination of the samples found that all of the physicochemical parameters were within the allowed range stated in the World Health Organization’s drinking water standards. The samples’ mean pH values varied from 5.18 to 6.26, representing mild acidity. The greatest mean turbidity level measured was 5.77 NTU. Furthermore, the mean amounts of Fe and Pb were 0.95 mg/L and 0.056 mg/L, respectively, exceeding the World Health Organization’s drinking water recommendations. The study’s findings show that, while roof-harvested rainwater can be a possible supply of drinking water, it may require further treatment to fulfill the WHO’s drinking water quality requirements [220].
Several contaminants and characteristics have been identified in rainwater in Pakistan that may constitute a health risk if swallowed. Due to industrial pollution and pesticide usage in agriculture, rainwater in Pakistan has been discovered to have high amounts of heavy metals, such as Pb, Cd, and Cr [221]. Rainwater in Pakistan has also been shown to be rich in bacteria, including E. coli and fecal coliforms, which can cause waterborne illnesses. Furthermore, organic contaminants such as pesticides and herbicides are found in significant concentrations in rainfall samples. These contaminants have the potential to harm aquatic life and taint drinking water supplies [222]. Several studies evaluating rainwater quality in Pakistan have been conducted recently. The studies in Table 5 concentrated on different elements of rainwater quality and demonstrated that a number of variables, such as industrial and agricultural activity, urbanization, and climate change, can have an impact on rainwater quality. According to the research, the good management of rainwater resources is necessary to guarantee that there is enough clean drinking water for the entire population [220].

Table 5.
Research on rainwater quality in Pakistan.
5. Pollution Sources, Assessment Techniques, and Sustainable Development Importance
5.1. Water Pollution Sources in Pakistan
Rising water scarcity and pollution in Pakistan pose a serious danger to the economy and human life, unveiling the importance of the bioeconomy to sustainability [227,228]. Water contamination has been a major concern in the country as the population and economy have grown [44]. The situation is exacerbated by a lack of water treatment technology and knowledge [229]. The overuse of chemical fertilizers and pesticides in agriculture [178], the discharge of industrial waste [175] and untreated sewage into nearby bodies of water [209], and contamination from leaks and malfunctioning pipes used for water delivery are the primary water pollution sources [87]. Industrial wastewater is directly discharged into near water bodies. Pollutants can enter surface water and then groundwater from industrial areas such as textile mills, tanneries, and chemical plants due to leaks or inappropriate waste disposal. Toxic materials such as heavy metals, chemicals, and other harmful substances are examples of pollutants [2,230]. Sewage discharge is another type of groundwater pollution in Pakistan, where improper sewage disposal can contaminate groundwater with bacteria and other contaminants. This can happen when sewage is not adequately treated before disposal or is not disposed of in a way that prevents it from leaking into groundwater [231]. In Pakistan, landfills and the open dumping of solid waste are also sources of surface contamination. Pakistan produces over 48.5 million tons of solid waste yearly [149,156]. Pakistan faces many of the same environmental concerns as other developing countries due to a lack of garbage disposal facilities. The majority of municipal garbage is often burnt, discarded, or dumped in vacant lots in many areas, which has an impact on the well-being of the populace. Major cities in Pakistan are estimated to produce 87,000 tons of solid trash daily by the government (GOP) [51]. Solid waste placed in landfills can produce leachate and harm groundwater [232]. This can happen if the landfill is not adequately planned or managed or if garbage is not confined effectively.
Water quality can be changed by a large number of factors, including agricultural practices, industrial activity, and poor waste disposal. Agricultural activities are a major source of groundwater and surface water pollution in Pakistan [156]. Farmers frequently rely on agrochemicals to keep their crops healthy and protect them from bacterial and insect attacks. However, these pollutants can leach into the soil and eventually pollute groundwater [233]. Furthermore, these chemicals combine with precipitation and run into water bodies, eventually leaking into the sea and contributing to water contamination. Furthermore, pesticides can combine with irrigation and rainwater and penetrate aquifers, polluting these crucial water sources even further. Pesticides and fertilizers include a wide range of hazardous substances that can affect human health and aquatic life [234]. Improper sewage disposal can contaminate groundwater with bacteria and other contaminants. This can occur when sewage is not adequately treated before disposal or is not disposed of in a way that prevents it from leaking into groundwater. This form of pollution may have a considerable influence on the population’s health and well-being, as well as the environment [235].
Mining is another source of groundwater contamination. Water contamination can result from mining minerals in mines [73]. This may happen if the mining activity is not sufficiently monitored or if the mining site is not properly cleaned up afterward. Furthermore, Pakistan is facing many climate change issues. Climate change is also altering the quality and availability of water resources in Pakistan [44,134]. Surface water supplies are being reduced as snow and ice cover in the Himalayas and Hindu Kush Mountains, which feed the Indus River system, decreases. The melting of glaciers has a significant influence on the supply of water for agriculture and residential usage, as well as the region’s hydropower potential [236]. The contamination of both groundwater and surface water is a major concern in Pakistan, putting people’s health and well-being at risk. To address this challenge, important steps must be taken, such as strengthening environmental laws and policies, initiating public education programs, and undertaking more research to identify effective solutions.
5.2. Method Used for the Water Quality Assessment
Water quality assessment is a crucial aspect of ensuring the safety and health of the population. Pakistan faces a number of challenges in terms of providing safe drinking water, including a lack of infrastructure and limited resources [97,237]. However, there have been several methods used in different studies in the period from 2012 to 2022 to assess the drinking water quality in Pakistan. One of the most commonly used methods is lab analysis [92,118]. This involves collecting samples of water from different study areas (such as lakes and rivers) and analyzing them for various contaminants (such as physicochemical ones, bacteria, and heavy metals). Water testing can be performed using various techniques, such as PCR, ELISA, and microscopy. Another method for assessing drinking water quality is through the use of water quality indicators [82,238]. While all WQIs have a similar framework, each was created with one of two goals. These goals may be broader, such as measuring the quality of life in a specific area, or more particular, such as implementing a new water treatment system. These methods have been used for both surface and groundwater. Furthermore, Table 2, Table 3, Table 4 and Table 5 also list, for each of the WQIs under evaluation, the context in which it was created or is being used.
A comprehensive assessment is meant to provide individuals with an idea of the overall water quality, while specialized evaluations are meant to ensure that water is “suitable” for those who want to do certain things with it [65,71]. Some authors also used some recently developed modeling-based methods (SWAT and AI) to assess rain surfaces and groundwater quality [50]. Different studies have used geographical information systems (GISs) to create maps and visualize data, such as water quality test results, and can help identify patterns and trends in water quality. This is useful for identifying areas where water quality is poor and developing plans to improve it [54,239]. Furthermore, community-based monitoring is another important method for drinking water quality assessment in Pakistan. This approach involves engaging local communities in the assessment and monitoring of surface and groundwater quality. Different studies have used the questionnaire survey method to understand water quality and health issues [153,240]. Furthermore, to evaluate data and detect patterns and trends in water quality, statistical analysis methods are extensively employed in water quality evaluation in Pakistan. Principal component analysis (PCA) [168]; cluster analysis (CA) [87]; multivariate statistical techniques (MST), such as factor analysis (FA) and discriminant analysis (DA) [84,198]; and statistical process control are among these methodologies (SPC). In addition, along with these, various other methods are now being used to characterize and evaluate the quality of groundwater. Some of these methods include the blind number approach, the fuzzy mathematical method, cluster analysis, and a collection of pair analysis approaches [241]. These approaches can be used to detect probable sources of pollution, assess the efficacy of water treatment processes, classify water samples, and track water quality over time. Remote sensing technology can be used by future researchers in surface water quality analysis. This involves using satellite imagery and other remote sensing techniques to map and monitor water resources, such as surface water and groundwater bodies. This can provide information on water availability and quality, as well as help identify potential sources of pollution [242,243]. It is important to note that the evaluation of water quality in Pakistan also takes into account other variables, including TDS, BOD, and DO. To obtain a thorough evaluation of water quality in Pakistan, these factors are employed in addition to the ones described above.
Moreover, there are various methods that can be used in the future to assess drinking water quality in Pakistan. These methods can be used in combination to provide comprehensive knowledge of water quality and to identify potential sources of contamination. Recent years have observed an expanding necessity for a real-time sensing system capable of appositely recognizing occurrences of contamination in water distribution systems. A study by Piazza et al. (2020) [9] suggests a numerical optimization methodology that involves the utilization of the NSGA-II genetic algorithm combined with a diffusive–dispersive hydraulic simulator to optimize the efficiency of sensor configurations [244,245,246]. Due consideration of diffusion in the placement of water quality sensors is of the greatest importance if reliable monitoring networks are to be established, according to the findings of the research. Furthermore, the identification of sources of contamination is essential for the successful management of water pollution, which is an important issue in the water sector. The Bayesian method has also been used by different researchers to identify the most contaminating effluents in pressurized distribution systems and urban drainage networks. This can be achieved by the installation of real-time water-quality-measuring sensors [247]. Researchers in Pakistan can potentially utilize these methods in the future to assess water quality.
5.3. Importance of Water Quality in Combating Climate Change and Achieving Sustainable Development
Water quality is an important component of both sustainable development and climate change mitigation [248,249]. Water is a fundamental human right that is required for the existence and well-being of all living creatures. Poor water quality can cause health issues, financial losses, and environmental deterioration. The United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) comprise explicit aims to achieve universal access to and the sustainable management of water and sanitation [250]. This includes Objective 6.1, which seeks to provide universal and equal access to clean and cheap drinking water for all, and Target 6.2, which aims to provide universal and equitable access to sanitation and hygiene for all [251,252]. The lack of access to water, whether resulting from human activity or natural phenomena, can have catastrophic consequences for the health, dignity, and economic prosperity of billions of people around the globe. SDG 6, commonly referred to as the “water goal”, serves as a guideline for achieving water security and is indispensable for the achievement of the goals of the remaining SDGs [253]. Climate change also has an impact on water quality in a variety of ways. Changes in precipitation patterns and rising temperatures can cause more frequent and severe flooding, droughts, and other extreme weather events, contaminating water supplies and disrupting water infrastructure. These occurrences can also cause increased sedimentation and erosion, which can damage water infrastructure and make it more difficult to provide populations with clean and safe water [251,254]. Furthermore, climate change can cause changes in water temperature and chemistry, which can harm aquatic habitats and the animals that rely on them. This can eventually disrupt the entire water cycle, resulting in water shortages and compromising sustainable development goals. Improving water quality is thus critical for attaining a variety of long-term development goals and mitigating the effects of climate change. Investing in water infrastructure and improving water management methods, as well as decreasing pollution and safeguarding water sources, are all part of this [255]. This also entails striving to reduce the effects of climate change by lowering greenhouse gas emissions and adapting to existing changes [256,257]. Water quality is critical not just for human consumption but also for agricultural and industrial applications. Poor water quality can result in lower agricultural yields and higher expenses for farmers and companies. This has an impact on food security and may result in economic losses. Water shortages and poor water quality can also boost rivalry and conflict over water resources, undermining long-term development [258]. Water quality is an important component of both sustainable development and climate change mitigation. Addressing water quality challenges necessitates a multifaceted approach that includes establishing integrated water resource management, investing in water infrastructure, and employing cutting-edge technology. This can eventually lead to better access to clean and safe water, higher food security, and long-term economic prosperity. Furthermore, it is critical to reducing the consequences of climate change, which is increasing water quality problems.
6. Conclusions
This comprehensive review of water quality assessments and monitoring in Pakistan has offered a complete picture of the country’s present water quality situation. In order to properly manage and safeguard Pakistan’s water resources, improved monitoring and evaluation methodologies are required, as evidenced by the data in this research. This review indicates that Pakistan has substantial water quality challenges, including high levels of industrial and agricultural pollution. In addition, restricted access to reliable data and a lack of cooperation between many stakeholders are significant obstacles to successfully resolving these concerns. The assessment found that the quality of water resources in Pakistan, both surface and groundwater, is highly inconsistent and often falls short of the standards set by the WHO and national standards. The presence of pollutants in water sources, including heavy metals, pesticides, and microorganisms, poses a significant danger to human health and the environment. Industrial and agricultural activities have been found to have a serious impact on the water quality of Pakistan’s major rivers, including the Indus and the Chenab. Furthermore, the water quality of groundwater resources is at risk due to excessive extraction and inadequate management. The low availability of reliable data and information on water quality is another key problem. Despite the presence of several monitoring programs, the data collected is frequently insufficient, inconsistent, and difficult for the public to access. This makes it challenging for policymakers and decision-makers to make informed water management and protection decisions. Moreover, a lack of coordination between many stakeholders, such as government agencies, industry, and local populations, limits the effective management of water resources.
This examination also highlighted the necessity of enhanced monitoring and evaluation procedures. Actual monitoring and evaluation methods in Pakistan are frequently out of date and do not correctly reflect the current water quality situation. In addition, our analysis uncovered a lack of ability and resources for monitoring and evaluation at the local level. This makes it challenging for local communities to monitor and manage their water supplies properly. This review recommends a variety of initiatives for governments, businesses, and local communities to adopt to address these challenges. Industry must be held accountable for its effect on water quality. The government should impose more stringent rules on industrial and agricultural activities and hold enterprises accountable for any water contamination caused by their operations. Finally, local communities should be given the authority to actively monitor and safeguard their water supplies. The government should assist local communities with the skills and resources necessary to successfully monitor and manage their water supplies. Additionally, local communities should be included in water management and protection decision-making processes.
Limitations of This Study
Several intriguing discoveries have been made due to this thorough evaluation of water quality monitoring and assessment in Pakistan that might be pursued in future research. The Indus River is the most polluted river in terms of microplastic particles in the world. This river is the principal source of potable water for agriculture and human consumption in Pakistan. Our water sources have not been studied for these contaminants in the past. Future research can examine the presence of pharmaceuticals, soaps, detergents, body lotion, and other personal care items in sources of drinking water. GISs have been used in water quality monitoring and evaluation, although this is still uncommon. This method may be used to collect data on water contamination across a larger area, as opposed to still-popular city-by-city study investigations. In addition, this study has mostly focused on surface and groundwater resources and may have overlooked other significant water sources, such as bottled water, filtered water, rainfall harvesting, and desalination. These water sources are gaining significance, particularly in countries where water shortages are a significant concern. Consequently, future studies may expand into these areas. High levels of pollution from industrial and agricultural sources have been highlighted as the most significant water quality challenges in Pakistan. However, no concrete advice for correcting these difficulties is provided. Therefore, further studies and research are required to comprehend the complexities of water quality challenges and find viable strategies to address them. Furthermore, the economic component of water quality monitoring and evaluation has not been explored. The cost of adopting the proposed solutions has not been analyzed, nor have the potential benefits and costs of these solutions. It is crucial to assess the economic viability of the suggested alternatives. Lastly, there is a lack of studies on the relationship between water quality and its health effects. Therefore, future research should focus on finding the link between water and health.
Author Contributions
L.K., conceptualization, methodology, data curation, and writing—original draft preparation; R.K., writing, resources, and visualization; A.K., literature review, writing, and editing original draft; I.A.T., literature review and editing; C.S., review and editing. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
All data used have been added to the manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
Ministry of Environment, Pakistan (MOE-PAK), biochemical oxygen demand (BOD), copper (Cu), lead (Pb), zinc (Zn), dissolved oxygen (DO), manganese (Mn), molybdenum (Mo), water quality index (WQI). multivariate analysis comprising principal component analysis (PCA), National Water Quality Monitoring (NWQM), spatial distribution using inverse distance weight (IDW), Pakistan Council for Research in Water Resources (PCRWR), electrical conductivity (EC), soil and water assessment tool (SWAT), shared socioeconomic pathways (SSPs), vertical electrical soundings (VES), total suspended solids (TSS), geographical information system (GIS), hierarchical cluster analysis (HCA), pollution source apportionment methodology (PCA/MLR), chemical oxygen demand (COD), Pakistan Environmental Protection Agency (PAK-EPA), World Health Organization (WHO).
References
- Hashmi, I.; Farooq, S.; Qaiser, S. Chlorination and water quality monitoring within a public drinking water supply in Rawalpindi Cantt (Westridge and Tench) area, Pakistan. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2009, 158, 393–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, L.; Deitch, M.J.; Tunio, I.A.; Kumar, A.; Memon, S.A.; Williams, L.; Tagar, U.; Kumari, R.; Basheer, S. Assessment of physicochemical parameters in groundwater quality of desert area (Tharparkar) of Pakistan. Case Stud. Chem. Environ. Eng. 2022, 6, 100232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahim, Z.T. Is Pakistan running dry? In Water Issues in Himalayan South Asia; Palgrave Macmillan: Singapore, 2019; pp. 153–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daud, M.K.; Nafees, M.; Ali, S.; Rizwan, M.; Bajwa, R.A.; Shakoor, M.B.; Arshad, M.U.; Chatha, S.A.S.; Deeba, F.; Murad, W.; et al. Drinking Water Quality Status and Contamination in Pakistan. BioMed Res. Int. 2017, 2017, 7908183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guglielmi, G. Arsenic in drinking water threatens up to 60 million in Pakistan. Science 2017, 24, 15–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabi, G.; Ali, M.; Khan, S.; Kumar, S. The crisis of water shortage and pollution in Pakistan: Risk to public health, biodiversity, and ecosystem. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 10443–10445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilyas, M.; Ahmad, W.; Khan, H.; Yousaf, S.; Yasir, M.; Khan, A. Environmental and health impacts of industrial wastewater effluents in Pakistan: A review. Rev. Environ. Health 2019, 34, 171–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalair, A.R.; Abas, N.; Ul Hasan, Q.; Kalair, E.; Kalair, A.; Khan, N. Water, energy and food nexus of Indus Water Treaty: Water governance. Water Energy Nexus 2019, 2, 10–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piazza, S.; Blokker, E.J.M.; Freni, G.; Puleo, V.; Sambito, M. Impact of diffusion and dispersion of contaminants in water distribution networks modelling and monitoring. Water Sci. Technol. Water Supply 2020, 20, 46–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazbavi, Z.; Sadeghi, S.H.; Gholamalifard, M.; Davudirad, A.A. Watershed health assessment using the pressure–state–response (PSR) framework. Land Degrad. Dev. 2020, 31, 3–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdul, N.A.; Talib, S.A.; Amir, A. Removal Kinetics of Chromium by Nano-Magnetite in Different Environments of Groundwater. J. Environ. Eng. 2020, 146, 04019111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolli, M.K.; Opp, C.; Karthe, D.; Kumar, N.M. Web-Based Decision Support System for Managing the Food–Water–Soil–Ecosystem Nexus in the Kolleru Freshwater Lake of Andhra Pradesh in South India. Sustainability 2022, 14, 2044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, N.M.; Kanchikere, P.M.J. Floatovoltaics: Towards improved energy efficiency, land and water management. Int. J. Civ. Eng. Technol. 2018, 9, 1089–1096. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, D.; Sial, M.S.; Ahmad, N.; Filipe, J.A.; Thu, P.A.; Zia-Ud-din, M.; Caleiro, A.B. Water scarcity and sustainability in an emerging economy: A management perspective for future. Sustainability 2021, 13, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qamar, K.; Nchasi, G.; Mirha, H.T.; Siddiqui, J.A.; Jahangir, K.; Shaeen, S.K.; Islam, Z.; Essar, M.Y. Water sanitation problem in Pakistan: A review on disease prevalence, strategies for treatment and prevention. Ann. Med. Surg. 2022, 82, 104709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howard, G. The future of water and sanitation: Global challenges and the need for greater ambition. J. Water Supply Res. Technol. 2021, 70, 438–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranjan, A. Inter-Provincial water sharing conflicts in Pakistan. Pak. A J. Pak. Stud. 2012, 4, 102–122. [Google Scholar]
- Young, W.J.; Anwar, A.; Bhatti, T.; Borgomeo, E.; Davies, S.; Garthwaite, W.R., III; Gilmont, E.M.; Leb, C.; Lytton, L.; Makin, I.; et al. Pakistan Getting More from Water; World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtar, I.u.H.; Athar, H. Water supply and effective rainfall impacts on major crops across irrigated areas of Punjab, Pakistan. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2020, 142, 1097–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salma, S.; Rehman, S.; Shah, M.A. Rainfall Trends in Different Climate Zones of Pakistan. Pak. J. Meteorol. 2012, 9, 37–47. [Google Scholar]
- Abbas, M.; Shen, S.L.; Lyu, H.M.; Zhou, A.; Rashid, S. Evaluation of the hydrochemistry of groundwater at Jhelum Basin, Punjab, Pakistan. Environ. Earth Sci. 2021, 80, 300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, G.; Sajjad, M.; Kanwal, S.; Xiao, T.; Khalid, S.; Shoaib, F.; Gul, H.N. Spatial–temporal characterization of rainfall in Pakistan during the past half-century (1961–2020). Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 6935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashfaq, M.; Li, Y.; Rehman, M.S.U.; Zubair, M.; Mustafa, G.; Nazar, M.F.; Yu, C.P.; Sun, Q. Occurrence, spatial variation and risk assessment of pharmaceuticals and personal care products in urban wastewater, canal surface water, and their sediments: A case study of Lahore, Pakistan. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 688, 653–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irfan, M.; Qadir, A.; Mumtaz, M.; Ahmad, S.R. An unintended challenge of microplastic pollution in the urban surface water system of Lahore, Pakistan. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 16718–16730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhatti, N.K.; Saand, A.; Keerio, M.A.; Ali, A.; Bhatti, N.-K.; Samo, S.R.; Bhuriro, A.A. Ground Water Quality Assessment of Daur Taluka, Shaheed Benazir Abad. Eng. Technol. Appl. Sci. Res. 2018, 8, 2785–2789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.-H.; Wu, X.; Zhang, D.; Chen, S.; Zhao, J. Demand for green finance: Resolving financing constraints on green innovation in China. Energy Policy 2021, 153, 112255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chilton, P.J.; Jamieson, D.; Abid, M.S.; Milne, C.J.; Ince, M.E.; Aziz, J.A. Pakistan Water Quality Mapping and Management Project; Water Engineering Development Centre, Loughborough University & London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicines: Loughborough, UK, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Ullah, S.; Javed, M.W.; Shafique, M.; Khan, S.F. An integrated approach for quality assessment of drinking water using GIS: A case study of Lower Dir. J. Himal. Earth Sci. 2014, 47, 163–174. [Google Scholar]
- Butt, M.; Khair, S.M. Cost of Illness of Water-borne Diseases: A Case Study of Quetta. J. Appl. Emerg. Sci. 2016, 5, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haydar, S.; Arshad, M.; Aziz, J.A. Evaluation of Drinking Water Quality in Urban Areas of Pakistan: A Case Study of Southern Lahore. Pak. J. Eng. Appl. Sci. 2009, 5, 16–23. [Google Scholar]
- Khwaja, M.A.; Aslam, A. Comparative Assessment of Pakistan National Drinking Water Quality Standards with Selected Asian Countries and World Health Organization; Sustainable Development Policy Institute (SDPI): Islamabad, Pakistan, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, M.; Chaudhry, M.N. Role of and challenges to environmental impact assessment proponents in Pakistan. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2021, 90, 106606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalid, S.; Murtaza, B.; Shaheen, I.; Ahmad, I.; Ullah, M.I.; Abbas, T.; Rehman, F.; Ashraf, M.R.; Khalid, S.; Abbas, S.; et al. Assessment and public perception of drinking water quality and safety in district Vehari, Punjab, Pakistan. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 181, 224–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.H.; Nafees, M.; Muhammad, N.; Ullah, U.; Hussain, R.; Bilal, M. Assessment of Drinking Water Sources for Water Quality, Human Health Risks, and Pollution Sources: A Case Study of the District Bajaur, Pakistan. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2021, 80, 41–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weitzberg, E.; Lundberg, J.O. Novel Aspects of Dietary Nitrate and Human Health. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 2013, 33, 129–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadeem, O.; Hameed, R. Evaluation of environmental impact assessment system in Pakistan. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2008, 28, 562–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haider, H.; Ali, W. Sustainability of Sanitation Systems in Pakistan Solid Waste Management View Project. 2009. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/256191560_Sustainability_of_Sanitation_Systems_in_Pakistan (accessed on 24 February 2023).
- Arfan, M.; Ansari, K.; Ullah, A.; Hassan, D.; Siyal, A.; Water, S.J. Agenda setting in water and IWRM: Discourse analysis of water policy debate in Pakistan. Water 2020, 12, 1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosley, L.M. Drought impacts on the water quality of freshwater systems; review and integration. Earth Sci. Rev. 2015, 140, 203–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razali, A.; Ismail, S.N.S.; Awang, S.; Praveena, S.M.; Abidin, E.Z. Land use change in highland area and its impact on river water quality: A review of case studies in Malaysia. Ecol. Process. 2018, 7, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sial, R.A.; Chaudhary, M.F.; Abbas, S.T.; Latif, M.I.; Khan, A.G. Quality of effluents from Hattar Industrial Estate. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 2006, 7, 974–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasrullah, R.; Bibi, H.; Iqbal, M.; Durrani, M.I. Pollution load in industrial effluent and ground water of Gadoon Amazai Industrial Estate (GAIE) Swabi, NWFP. J. Agric. Biol. Sci. 2006, 1, 18–24. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, L.; Kamil, I.; Ahmad, M.; Naqvi, S.A.; Deitch, M.J.; Amjad, A.Q.; Kumar, A.; Basheer, S.; Arshad, M.; Sassanelli, C. In-house resource efficiency improvements supplementing the end of pipe treatments in textile SMEs under a circular economy fashion. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 1002319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fida, M.; Li, P.; Wang, Y.; Alam, S.M.K.; Nsabimana, A. Water Contamination and Human Health Risks in Pakistan: A Review. Expo. Health 2022, 2022, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, W.; Zubair, A.; Abbasi, H.N.; Nasir, M.I. Water Study of Physical, Chemical and Heavy Metals Parameters in River Indus and its Tributaries, Sindh, Pakistan. Pak. J. Sci. Ind. Res. Ser. A Phys. Sci. 2021, 64, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatima, S.U.; Khan, M.A.; Siddiqui, F.; Mahmood, N.; Salman, N.; Alamgir, A.; Shaukat, S.S. Geospatial assessment of water quality using principal components analysis (PCA) and water quality index (WQI) in Basho Valley, Gilgit Baltistan (Northern Areas of Pakistan). Environ. Monit. Assess. 2022, 194, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dilshad, A.; Taneez, M.; Younas, F.; Jabeen, A.; Rafiq, M.T.; Fatimah, H. Microplastic pollution in the surface water and sediments from Kallar Kahar wetland, Pakistan: Occurrence, distribution, and characterization by ATR-FTIR. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2022, 194, 511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, K.; Younas, M.; Sharif, H.M.A.; Wang, C.; Yaseen, M.; Cao, X.; Zhou, Y.; Ibrahim, S.M.; Yvette, B.; Lu, Y. Heavy metals contamination, potential pathways and risks along the Indus Drainage System of Pakistan. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 809, 151994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naz, S.; Mansouri, B.; Chatha, A.M.M.; Ullah, Q.; Abadeen, Z.U.; Khan, M.Z.; Khan, A.; Saeed, S.; Bhat, R.A. Water quality and health risk assessment of trace elements in surface water at Punjnad Headworks, Punjab, Pakistan. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 61457–61469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, L.; Waheed, H.; Gul, N.; Sheikh, L.; Khan, A.; Iqbal, H. Geochemistry of subsurface water of Swabi district and associated health risk with heavy metal contamination. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2022, 194, 480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatima, S.U.; Khan, M.A.; Alamgir, A.; Mahmood, N.; Sulman, N. Multivariate and spatial methods-based water quality assessment of Chu Tran Valley, Gilgit Baltistan. Appl. Water Sci. 2022, 12, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.; Khan, M.S.; Egozcue, J.J.; Shafique, M.A.; Nadeem, S.; Saddiq, G. Irrigation suitability, health risk assessment and source apportionment of heavy metals in surface water used for irrigation near marble industry in Malakand, Pakistan. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0279083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, M.S.; Islam, M.; Hassan, M.; Bilal, H.; Shah, I.A.; Ourania, T. Modeling the fecal contamination (fecal coliform bacteria) in transboundary waters using the scenario matrix approach: A case study of Sutlej River, Pakistan. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 79555–79566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daud, S.; MonaLisa; Nisar, U. Bin Integrated geophysical, geochemical, and geospatial tools to characterize water resources in GAIE, Eastern Peshawar basin, Pakistan. Environ. Earth Sci. 2022, 81, 390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawab, J.; Rahman, A.; Khan, S.; Ghani, J.; Ullah, Z.; Khan, H.; Waqas, M. Drinking Water Quality Assessment of Government, Non-Government and Self-Based Schemes in the Disaster Affected Areas of Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, Pakistan. Expo. Health 2022, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panhwar, M.Y.; Panhwar, S.; Keerio, H.A.; Khokhar, N.H.; Shah, S.A.; Pathan, N. Water quality analysis of old and new Phuleli Canal for irrigation purpose in the vicinity of Hyderabad, Pakistan. Water Pract. Technol. 2022, 17, 529–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastoi, S.T.; Channa, A.S.; Qureshi, K.M.; Khokhar, W.A. Assessment of Water Quality and Quantity of Surface and Subsurface Drainage System in the Command Area of Bareji Distributary Mirpurkhas, Sindh, Pakistan. QUEST Res. J. 2022, 20, 127–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amrane, A.; Khellaf, N.; Khan, R.U.; Hamayun, M.; Altaf, A.A.; Kausar, S.; Razzaq, Z.; Javaid, T. Assessment and Removal of Heavy Metals and Other Ions from the Industrial Wastewater of Faisalabad, Pakistan. Processes 2022, 10, 2165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, Z.; Imran, M.; Natasha, N.; Murtaza, B.; Amjad, M.; Shah, N.S.; Khan, Z.U.H.; Ahmad, I.; Ahmad, S. Distribution and health risk assessment of trace elements in ground/surface water of Kot Addu, Punjab, Pakistan: A multivariate analysis. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2021, 193, 351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salam, M.; Alam, F.; Hossain, M.N.; Saeed, M.A.; Khan, T.; Zarin, K.; Rwan, B.; Ullah, W.; Khan, W.; Khan, O. Assessing the drinking water quality of educational institutions at selected locations of district Swat, Pakistan. Environ. Earth Sci. 2021, 80, 322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahsan, W.A.; Ahmad, H.R.; Farooqi, Z.U.R.; Sabir, M.; Ayub, M.A.; Rizwan, M.; Ilic, P. Surface water quality assessment of Skardu springs using Water Quality Index. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 20537–20548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.; Mumtaz, R.; Zaidi, S.M.H. Analysis of water quality indices and machine learning techniques for rating water pollution: A case study of Rawal Dam, Pakistan. Water Supply 2021, 21, 3225–3250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.; Khan, A.; Khan, F.A.; Shah, L.A.; Rauf, A.U.; Badrashi, Y.I.; Khan, W.; Khan, J. Assessment of the Impacts of Terrestrial Determinants on Surface Water Quality at Multiple Spatial Scales. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2021, 30, 2137–2147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, M.I.; Javed, M.F.; Abunama, T. Proposed formulation of surface water quality and modelling using gene expression, machine learning, and regression techniques. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 13202–13220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khuhawar, M.Y.; Lanjwani, M.F.; Khuhawar, T.M.J. Assessment of variation in water quality at Right Bank Outfall Drain, including Manchar lake, Sindh, Pakistan. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2021, 00, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setia, R.; Lamba, S.; Chander, S.; Kumar, V.; Dhir, N.; Sharma, M.; Singh, R.P.; Pateriya, B. Hydrochemical evaluation of surface water quality of Sutlej river using multi-indices, multivariate statistics and GIS. Environ. Earth Sci. 2021, 80, 565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtar, F.; Ahmed, M.; Akhtar, M.N. Drinking, Tap and Canal Water Quality Analysis for Human Consumption: A Case Study of Nawabshah City, Pakistan. Mehran Univ. Res. J. Eng. Technol. 2021, 40, 392–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, J.U.; Ahmad, N.; Ullah, N.; Alam, I.; Ullah, H. Health Risks in Different Age Group of Nitrate in Spring Water Used for Drinking in Harnai, Balochistan, Pakistan. Ecol. Food Nutr. 2020, 59, 462–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jadoon, S.; Wang, J.; Mahmood, Q.; Li, X.D.; Zeb, B.S.; Naseem, I.; Hayat, M.T.; Nawazish, S.; Ditta, A. Association of Nephrolithiasis with Drinking Water Quality and Diet in Pakistan. Environ. Eng. Manag. J. 2020, 19, 1289–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jehan, S.; Khattak, S.A.; Muhammad, S.; Ali, L.; Rashid, A.; Hussain, M.L. Human health risks by potentially toxic metals in drinking water along the Hattar Industrial Estate, Pakistan. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 2677–2690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashir, N.; Saeed, R.; Afzaal, M.; Ahmad, A.; Muhammad, N.; Iqbal, J.; Khan, A.; Maqbool, Y.; Hameed, S. Water quality assessment of lower Jhelum canal in Pakistan by using geographic information system (GIS). Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2020, 10, 100357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jehan, S.; Ullah, I.; Khan, S.; Muhammad, S.; Khattak, S.A.; Khan, T. Evaluation of the Swat River, Northern Pakistan, water quality using multivariate statistical techniques and water quality index (WQI) model. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 38545–38558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.J.; Akhter, G.; Gabriel, H.F.; Shahid, M. Anthropogenic effects of coal mining on ecological resources of the central indus basin, Pakistan. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohail, M.T.; Aftab, R.; Mahfooz, Y.; Yasar, A.; Yen, Y.; Shaikh, S.A.; Irshad, S. Estimation of water quality, management and risk assessment in Khyber Pakhtunkhwa and Gilgit-Baltistan, Pakistan. Desalination Water Treat. 2019, 171, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahfooz, Y.; Yasar, A.; Sohail, M.T.; Tabinda, A.B.; Rasheed, R.; Irshad, S.; Yousaf, B. Investigating the drinking and surface water quality and associated health risks in a semi-arid multi-industrial metropolis (Faisalabad), Pakistan. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 20853–20865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imran, U.; Ullah, A.; Shaikh, K.; Mehmood, R.; Saeed, M. Health risk assessment of the exposure of heavy metal contamination in surface water of lower Sindh, Pakistan. SN Appl. Sci. 2019, 1, 589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahab, A.; Qi, S.; Zaheer, M. Arsenic contamination, subsequent water toxicity, and associated public health risks in the lower Indus plain, Sindh province, Pakistan. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 30642–30662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehmood, K.; Ahmad, H.R. Saifullah Quantitative assessment of human health risk posed with chromium in waste, ground, and surface water in an industrial hub of Pakistan. Arab. J. Geosci. 2019, 12, 283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleem, M.; Iqbal, J.; Shah, M.H. Seasonal variations, risk assessment and multivariate analysis of trace metals in the freshwater reservoirs of Pakistan. Chemosphere 2019, 216, 715–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, K.; Lu, Y.; Saeed, M.A.; Bilal, H.; Sher, H.; Khan, H.; Ali, J.; Wang, P.; Uwizeyimana, H.; Baninla, Y.; et al. Prevalent fecal contamination in drinking water resources and potential health risks in Swat, Pakistan. J. Environ. Sci. 2018, 72, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarfraz, M.; Sultana, N.; Jamil, M. Groundwater Quality and Health Risk Assessment in Rural Areas of District Jaffarabad, Baluchistan (Pakistan). Pak. J. Anal. Environ. Chem. 2018, 19, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solangi, G.S.; Siyal, A.A.; Babar, M.M.; Siyal, P. Evaluation of surface water quality using the water quality index (Wqi) and the synthetic pollution index (spi): A case study of indus delta region of pakistan. Desalination Water Treat. 2018, 118, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qaisar, F.U.R.; Zhang, F.; Pant, R.R.; Wang, G.; Khan, S.; Zeng, C. Spatial variation, source identification, and quality assessment of surface water geochemical composition in the Indus River Basin, Pakistan. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 12749–12763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majeed, S.; Rashid, S.; Qadir, A.; Mackay, C.; Hayat, F. Spatial patterns of pollutants in water of metropolitan drain in Lahore, Pakistan, using multivariate statistical techniques. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2018, 190, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahab, A.; Qi, S.; Zaheer, M.; Rashid, A.; Talib, M.A.; Ashraf, U. Hydrochemical characteristics and water quality assessment for drinking and agricultural purposes in District Jacobabad, lower Indus Plain, Pakistan. Int. J. Agric. Biol. Eng. 2018, 11, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, H.H.; Shahid, N.; Qadir, A.; Ahmad, S.R.; Sarwar, S.; Ashraf, M.R.; Arshad, H.M.; Masood, N. Hydrological and ichthyological impact assessment of rasul barrage, river jhelum, Pakistan. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2017, 26, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raza, A.; Farooqi, A.; Javed, A.; Ali, W.; Zafar, M.I. Effect of human settlements on surface and groundwater quality: Statistical source identification of heavy and trace metals of Siran River and its catchment area Mansehra, Pakistan. J. Chem. Soc. Pak. 2017, 39, 296–308. [Google Scholar]
- Javed, S.; Ali, A.; Ullah, S. Spatial assessment of water quality parameters in Jhelum city (Pakistan). Environ. Monit. Assess. 2017, 189, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noreen, M.; Shahid, M.; Iqbal, M.; Nisar, J.; Abbas, M. Measurement of cytotoxicity and heavy metal load in drains water receiving textile effluents and drinking water in vicinity of drains. Measurement 2017, 109, 88–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alamgir, A.; Khan, M.A.; Manino, I.; Shaukat, S.S.; Shahab, S. Vulnerability to climate change of surface water resources of coastal areas of Sindh, Pakistan. Desalination Water Treat. 2016, 57, 18668–18678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleem, M.; Iqbal, J.; Shah, M.H. Assessment of water quality for drinking/irrigation purpose from Mangla dam, Pakistan. Geochem. Explor. Environ. Anal. 2016, 16, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iftikhar, B.; Bashirullah, N.; Ishtiaq, M.; Khan, S.A.; Siddique, S.; Ayaz, T. Chemical quality assessment of drinking water in district peshawar, pakistan. Khyber Med. Univ. J. 2016, 8, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Zulfiqar, H.; Abbas, Q.; Raza, A.; Ali, A. Determinants of Safe Drinking Water in Pakistan: A Case Study of Faisalabad. J. Glob. Innov. Agric. Soc. Sci. 2016, 04, 40–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghanghro, A.B.; Jahangir, T.M.; Memon, A.H.; Jahangir, T.M.; Lund, G.M.; Memon, A.H. Arsenic Contamination in Drinking Water of District Jamshoro Arsenic Contamination in Drinking Water of District Jamshoro, Sindh, Pakistan. Biomed. Lett. 2016, 2, 31–37. [Google Scholar]
- Hussain, S.A.; Hussain, S.A.; Hussain, A.; Fatima, U.; Ali, W.; Hussain, A.; Hussain, N. Evaluation of drinking water quality in urban areas of Pakistan: A case study of Gulshan-e-Iqbal Karachi, Pakistan. J. Biodivers. Environ. Sci. 2016, 8, 64–76. [Google Scholar]
- Nazir, H.M.; Hussain, I.; Zafar, M.I.; Ali, Z.; AbdEl-Salam, N.M. Classification of Drinking Water Quality Index and Identification of Significant Factors. Water Resour. Manag. 2016, 30, 4233–4246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhowmik, A.K.; Alamdar, A.; Katsoyiannis, I.; Shen, H.; Ali, N.; Ali, S.M.; Bokhari, H.; Schäfer, R.B.; Eqani, S.A.M.A.S. Mapping human health risks from exposure to trace metal contamination of drinking water sources in Pakistan. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 538, 306–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Begum, S.; Shah, M.T.; Khan, S. Role of mafic and ultramafic rocks in drinking water quality and its potential health risk assessment, Northern Pakistan. J. Water Health 2015, 13, 1130–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, S.; Hashmi, I.; Saif, M.; Rehman, U.; Qazi, I.A.; Awan, M.A.; Nasir, H. Monitoring of chlorination disinfection by-products and their associated health risks in drinking water of Pakistan. J. Water Health 2015, 13, 270–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mumtaz, M.W.; Adnan, A.; Mukhtar, H.; Danish, M.; Raza, M.A. Determination of toxic metals in water of Lahore canal by atomic absorption spectroscopy. J. Water Chem. Technol. 2015, 37, 73–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandhro, A.J.; Rind, A.M.; Mastoi, A.A.; Almani, K.F.; Meghwar, S.; Laghari, M.A.; Rajpout, M.S. Physico-Chemical Assessment of Surface and Ground Water for Drinking Purpose in Nawabshah City, Sindh, Pakistan. Am. J. Environ. Prot. 2015, 4, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.; Shah, I.A.; Muhammad, S.; Malik, R.N.; Shah, M.T. Arsenic and Heavy Metal Concentrations in Drinking Water in Pakistan and Risk Assessment: A Case Study. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. 2015, 21, 1020–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.S.; Tareen, H.; Jabeen, U.; Mengal, F.; Masood, Z.; Ahmed, S.; Bibi, S.; Riaz, M.; Rizwan, S.; Mandokhail, F.; et al. Quality Assessment of Drinking Water from the Different Colonies of Quetta City, Pakistan according to WHO Standards. Biol. Forum Int. J. 2015, 7, 699–702. [Google Scholar]
- Yousafzai, A.M.; Bari, F.; Ullah, T.; Pakistan, H.B. Assessment of heavy metals in surface water of River Panjkora Dir Lower, KPK Pakistannet. J. Biodivers. Environ. Sci. 2014, 5, 144–152. [Google Scholar]
- Jabeen, S.; Shah, M.T.; Ahmed, I.; Khan, S.; Hayat, M.Q. Physico-chemical parameters of surface and ground water and their environmental impact assessment in the Haripur Basin, Pakistan. J. Geochem. Explor. 2014, 138, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikh, S.A.; Panhwar, A.A.; Channa, M.J.; Merani, B.N.; Nizamani, S.M. Determination of Ground Water Quality for Agriculture and Drinking Purpose in Sindh, Pakistan. J. Pharm. Nutr. Sci. 2014, 4, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Channar, A.G.; Rind, A.M.; Mastoi, G.M.; Almani, K.F.; Lashari, K.H.; Qurishi, M.A.; Mahar, N. Comparative Study of Water Quality of Manchhar Lake with Drinking Water Quality Standard of World Health Organization. Am. J. Environ. Prot. 2014, 3, 68–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.A.; Lang, M.; Shaukat, S.S.; Alamgir, A.; Baloch, T. Water quality assessment of hingol river, balochistan, Pakistan. Middle East J. Sci. Res. 2014, 19, 306–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wattoo, F.H.; Wattoo, M.H.S.; Tirmizi, S.A.; Qadir, M.A. Monitoring of anthropogenic influences on underground and surface water quality of Indus River at district Mianwali-Pakistan. Turk. J. Biochem. J Biochem. 2013, 38, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahir, M.A.; Rasheed, H. Fluoride in the drinking water of Pakistan and the possible risk of crippling fluorosis. Drink. Water Eng. Sci. 2013, 6, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mumtaz, A.; Mirjat, M.S.; Mangio, H.U.R.; Soomro, A. Assessment of Drinking Water Quality Status and its Impact on Health in Tandojam City. Int. J. Humanit. Soc. Sci. 2013, 13, 363–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, A.; Noonari, T.M.; Magsi, H.; Mahar, A. Risk assessment of total and faecal coliform bacteria from drinking water supply of Badin city, Pakistan. J. Environ. Prof. Sri Lanka 2013, 2, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baig, J.A.; Kazi, T.G.; Shah, A.Q.; Kandhro, G.A.; Afridi, H.I.; Khan, S.; Kolachi, N.F.; Wadhwa, S.K. Arsenic speciation and other parameters of surface and ground water samples of jamshoro, Pakistan. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2012, 92, 28–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farooq, M.A.; Shaukat, S.S.; Zafar, M.U.; Abbas, Q. Variation Pattern of Heavy Metal Concentrations During Pre- and Post-Monsoon Seasons in the Surface Water of River Indus (Sindh Province). World Appl. Sci. J. 2012, 19, 582–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Wu, J. Medical Geology and Medical Geochemistry: An Editorial Introduction. Expo. Health 2022, 14, 217–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, A.; He, Y.; Jekel, M.; Reinhard, M.; Gin, K.Y.H. Emerging contaminants of public health significance as water quality indicator compounds in the urban water cycle. Environ. Int. 2014, 71, 46–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azizullah, A.; Khattak, M.N.K.; Richter, P.; Häder, D.P. Water pollution in Pakistan and its impact on public health—A review. Environ. Int. 2011, 37, 479–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasheed, H.; Iqbal, N.; Ashraf, M.; ul Hasan, F. Groundwater quality and availability assessment: A case study of District Jhelum in the Upper Indus, Pakistan. Environ. Adv. 2022, 7, 100148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.; Aziz, T.; Noor-Ul-Ain Ahmed, K.; Ahmed, I.; Nida; Akbar, S.S. Drinking Water Quality in 13 Different Districts of Sindh, Pakistan. Health Care Curr. Rev. 2018, 6, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Liu, Q.; He, Y.; Luo, X.; Zhang, X. Comparison of daily and sub-daily SWAT models for daily streamflow simulation in the upper Huai River Basin of China. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2016, 30, 959–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vardhan, K.H.; Kumar, P.S.; Panda, R.C. A review on heavy metal pollution, toxicity and remedial measures: Current trends and future perspectives. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 290, 111197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arshad, N.; Imran, S. Assessment of arsenic, fluoride, bacteria, and other contaminants in drinking water sources for rural communities of Kasur and other districts in Punjab, Pakistan. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 2449–2463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohail, M.T.; Mahfooz, Y.; Aftab, R.; Yen, Y.; Talib, M.A.; Rasool, A. Water quality and health risk of public drinking water sources: A study of fltration plants installed in Rawalpindi and Islamabad, Pakistan. Desalination Water Treat. 2020, 181, 239–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Li, P. Surface Water Pollution in the Middle Chinese Loess Plateau with Special Focus on Hexavalent Chromium (Cr6+): Occurrence, Sources and Health Risks. Expo. Health 2020, 12, 385–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natasha; Shahid, M.; Khalid, S.; Murtaza, B.; Anwar, H.; Shah, A.H.; Sardar, A.; Shabbir, Z.; Niazi, N.K. A critical analysis of wastewater use in agriculture and associated health risks in Pakistan. Environ. Geochem. Health 2020, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.; Rauf, R.; Muhammad, S.; Qasim, M.; Din, I. Arsenic and heavy metals health risk assessment through drinking water consumption in the Peshawar District, Pakistan. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. 2016, 22, 581–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulk, S.; Azizullah, A.; Korai, A.L.; Khattak, M.N.K. Impact of marble industry effluents on water and sediment quality of Barandu River in Buner District, Pakistan. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2015, 187, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdullah, E.J. Quality Assessment for Shatt Al-Arab River Using Heavy Metal Pollution Index and Metal Index. J. Environ. Earth Sci. 2013, 3, 114–120. [Google Scholar]
- Geng, J.; Wang, Y.; Luo, H. Distribution, sources, and fluxes of heavy metals in the Pearl River Delta, South China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 101, 914–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avigliano, E.; Schenone, N.F. Human health risk assessment and environmental distribution of trace elements, glyphosate, fecal coliform and total coliform in Atlantic Rainforest mountain rivers (South America). Microchem. J. 2015, 122, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, H.; Pandey, R.; Singh, S.K.; Shukla, D.N. Assessment of heavy metal contamination in the sediment of the River Ghaghara, a major tributary of the River Ganga in Northern India. Appl. Water Sci. 2017, 7, 4133–4149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cánovas, C.R.; Olías, M.; Nieto, J.M.; Galván, L. Wash-out processes of evaporitic sulfate salts in the Tinto river: Hydrogeochemical evolution and environmental impact. Appl. Geochem. 2010, 25, 288–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatti, M.T.; Anwar, A.A.; Aslam, M. Groundwater monitoring and management: Status and options in Pakistan. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2017, 135, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alamgir, A.; Khan, M.A.; Schilling, J.; Shaukat, S.S.; Shahab, S. Assessment of groundwater quality in the coastal area of Sindh province, Pakistan. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2016, 188, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, Y.; Podgorski, J.; Sadiq, M.; Rasheed, H.; Eqani, S.A.M.A.S.; Berg, M. Monitoring and prediction of high fluoride concentrations in groundwater in Pakistan. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 839, 156058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schewe, J.; Heinke, J.; Gerten, D.; Haddeland, I.; Arnell, N.W.; Clark, D.B.; Dankers, R.; Eisner, S.; Fekete, B.M.; Colón-González, F.J.; et al. Multimodel assessment of water scarcity under climate change. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 3245–3250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoso, S.; Wagan, F.H.; Tunio, A.H.; Ansari, A.A. An overview on emerging water scarcity in pakistan, its causes, impacts and remedial measures. J. Appl. Eng. Sci. 2015, 13, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adnan, S.; Iqbal, J. Spatial analysis of the groundwater quality in the Peshawar district, Pakistan. Procedia Eng. 2014, 70, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, A.S.; Rashid, H.; Khan, S.N.; Akbar, M.U.; Arshad, A.; Rahman, M.M.; Mustafa, S. A Localized Assessment of Groundwater Quality Status Using GIS-Based Water Quality Index in Industrial Zone of Faisalabad, Pakistan. Water 2022, 14, 3342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanjwani, M.F.; Khuhawar, M.Y.; Jahangir Khuhawar, T.M. Assessment of groundwater quality for drinking and irrigation uses in taluka Ratodero, district Larkana, Sindh, Pakistan. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2020, 102, 4134–4157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ur Rehman, H.; Munir, M.; Ashraf, K.; Fatima, K.; Shahab, S.; Ali, B.; Al-Saeed, F.A.; Abbas, A.M.; uz Zaman, Q. Heavy Metals, Pesticide, Plasticizers Contamination and Risk Analysis of Drinking Water Quality in the Newly Developed Housing Societies of Gujranwala, Pakistan. Water 2022, 14, 3787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mughal, A.; Sultan, K.; Ashraf, K.; Hassan, A.; uz Zaman, Q.; Haider, F.U.; Shahzad, B. Risk Analysis of Heavy Metals and Groundwater Quality Indices in Residential Areas: A Case Study in the Rajanpur District, Pakistan. Water 2022, 14, 3551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamali, M.A.; Markhand, A.H.; Agheem, M.H.; Zardari, S.H.; Arain, A.Y.W. Spatial variation in groundwater quality with respect to surface water seepages in Kadhan area District Badin (Indus Delta), Sindh, Pakistan. Int. J. Energy Water Resour. 2022, 7, 105–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamali, M.Z.; Solangi, G.S.; Keerio, M.A.; Keerio, J.A.; Bheel, N. Assessing and mapping the groundwater quality of Taluka Larkana, Sindh, Pakistan, using water quality indices and geospatial tools. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasir, M.J.; Tufail, M.; Ayaz, T.; Khan, S.; Khan, A.Z.; Lei, M. Groundwater quality assessment and its vulnerability to pollution: A study of district Nowshera, Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, Pakistan. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2022, 194, 692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanjwani, M.F.; Khuhawar, M.Y.; Lanjwani, A.H.; Khuahwar, T.M.J.; Samtio, M.S.; Rind, I.K.; Soomro, W.A.; Khokhar, L.A.; Channa, F.A. Spatial variability and risk assessment of metals in groundwater of district Kamber-Shahdadkot, Sindh, Pakistan. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2022, 18, 100784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noor, S.; Rashid, A.; Javed, A.; Khattak, J.A.; Farooqi, A. Hydrogeological properties, sources provenance, and health risk exposure of fluoride in the groundwater of Batkhela, Pakistan. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2022, 25, 102239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, Z.; Imran, M.; Natasha; Rahman, G.; Miandad, M.; Shahid, M.; Murtaza, B. Spatial distribution, health risk assessment, and public perception of groundwater in Bahawalnagar, Punjab, Pakistan: A multivariate analysis. Environ. Geochem. Health 2022, 45, 381–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Israr, M.; Nazneen, S.; Raza, A.; Ali, N.; Khan, S.A.; Khan, H.; Khan, S.; Ali, J. Assessment of municipal solid waste landfilling practices on the groundwater quality and associated health risks: A case study of Mardan-Pakistan. Arab. J. Geosci. 2022, 15, 1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, W.; Iqbal, J.; Nasir, M.J.; Ahmad, B.; Khan, M.T.; Khan, S.N.; Adnan, S. Impact of land use/land cover changes on water quality and human health in district Peshawar Pakistan. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 16526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, M.; Khan, M.J.; Ali, S.S. Environmental security View project Energy and Environmental Security in Developing Countries View project. Pak. J. Sci. 2021, 73. [Google Scholar]
- Lanjwani, M.F.; Khuhawar, M.Y.; Khuhawar, T.M.J.; Lanjwani, A.H.; Soomro, W.A. Evaluation of hydrochemistry of the Dokri groundwater, including historical site Mohenjo-Daro, Sindh, Pakistan. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2021, 103, 1892–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, H.; Khan, M.N.; Sirajuddin, M.; Salman, S.M.; Bilal, M. Assessment of Drinking Water Quality of Different Areas in Tehsil Isa Khel, Mianwali, Punjab, Pakistan. Pak. J. Anal. Environ. Chem. 2021, 22, 376–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalees, M.I.; Farooq, M.U.; Anis, M.; Hussain, G.; Iqbal, A.; Saleem, S. Hydrochemistry modelling: Evaluation of groundwater quality deterioration due to anthropogenic activities in Lahore, Pakistan. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2021, 23, 3062–3076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, S.; Imran, M.; Murtaza, B.; Natasha; Arshad, M.; Nawaz, R.; Waheed, A.; Hammad, H.M.; Naeem, M.A.; Shahid, M.; et al. Hydrogeochemical and health risk investigation of potentially toxic elements in groundwater along River Sutlej floodplain in Punjab, Pakistan. Environ. Geochem. Health 2021, 43, 5195–5209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, J.; Su, C.; Rashid, A.; Yang, N.; Baloch, M.Y.J.; Talpur, S.A.; Ullah, Z.; Rahman, G.; Rahman, N.U.; Earjh; et al. Hydrogeochemical Assessment of Groundwater and Suitability Analysis for Domestic and Agricultural Utility in Southern Punjab, Pakistan. Water 2021, 13, 3589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, S.; Ahmed, M.F. GIS-based spatio-temporal and geostatistical analysis of groundwater parameters of Lahore region Pakistan and their source characterization. Environ. Earth Sci. 2021, 80, 719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, Z.; Talib, M.A.; Rashid, A.; Ghani, J.; Shahab, A.; Irfan, M.; Rauf, A.; Bawazeer, S.; Almarhoon, Z.M.; Mabkhot, Y.N. Hydrogeochemical Investigation of Elevated Arsenic Based on Entropy Modeling, in the Aquifers of District Sanghar, Sindh, Pakistan. Water 2021, 13, 3477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, J.; Ping Wong, L.; Piaw Chua, Y.; Channa, N. Drinking Water Quality Mapping Using Water Quality Index and Geospatial Analysis in Primary Schools of Pakistan. Water 2020, 12, 3382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.J.; Shah, B.A.; Nasir, B. Groundwater quality assessment for drinking purpose: A case study from Sindh Industrial Trading Estate, Karachi, Pakistan. Model. Earth Syst. Environ. 2020, 6, 263–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalid, S.; Shahid, M.; Natasha; Shah, A.H.; Saeed, F.; Ali, M.; Qaisrani, S.A.; Dumat, C. Heavy metal contamination and exposure risk assessment via drinking groundwater in Vehari, Pakistan. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 39852–39864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murtaza, B.; Natasha; Amjad, M.; Shahid, M.; Imran, M.; Shah, N.S.; Abbas, G.; Naeem, M.A.; Amjad, M. Compositional and health risk assessment of drinking water from health facilities of District Vehari, Pakistan. Environ. Geochem. Health 2020, 42, 2425–2437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seelro, M.A.; Ansari, M.U.; Manzoor, S.A.; Abodif, A.M.; Sadaf, A. Comparative Study of Ground and Surface Water Quality Assessment Using Water Quality Index (WQI) in Model Colony Malir, Karachi, Pakistan. Environ. Contam. Rev. 2020, 3, 4–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solangi, G.S.; Siyal, A.A.; Babar, M.M.; Siyal, P. Groundwater quality evaluation using the water quality index (WQI), the synthetic pollution index (SPI), and geospatial tools: A case study of Sujawal district, Pakistan. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. Int. J. 2019, 26, 1529–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, N.; Memon, S.A.; Mahessar, A.A.; Ansari, K.; Qureshi, A. Impact Assessment of Groundwater Quality using WQI and Geospatial tools: A Case Study of Islamkot, Tharparkar, Pakistan. Technol. Appl. Sci. Res. 2020, 10, 5288–5294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahzad, H.; Farid, H.U.; Khan, Z.M.; Anjum, M.N.; Ahmad, I.; Chen, X.; Sakindar, P.; Mubeen, M.; Ahmad, M.; Gulakhmadov, A. An integrated use of gis, geostatistical and map overlay techniques for spatio-temporal variability analysis of groundwater quality and level in the punjab province of pakistan, south asia. Water 2020, 12, 3555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razzaq, S.S.; Naz, S.A.; Zubair, A.; Yasmeen, K.; Shafique, M.; Jabeen, N.; Magsi, A. Detection of Hazardous Contaminants in Ground Water Resources: An Alarming Situation for Public Health in Karachi, Pakistan. Pak. J. Anal. Environ. Chem. 2020, 21, 322–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solangi, G.S.; Munir, B.M.; Siyal, P.; Siyal, A.A.; Babar, M.M. Evaluation of drinking water quality using the water quality index (WQI), the synthetic pollution index (SPI) and geospatial tools in Thatta district, Pakistan. Desalination Water Treat. 2019, 160, 202–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deeba, F.; Abbas, N.; Butt, M.; Irfan, M. Ground Water Quality of Selected Areas of Punjab and Sind Provinces, Pakistan: Chemical and Microbiological Aspects. SSRN Electron. J. 2019, 5, 241–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanoranga; Khalid, S. An assessment of groundwater quality for irrigation and drinking purposes around brick kilns in three districts of Balochistan province, Pakistan, through water quality index and multivariate statistical approaches. J. Geochem. Explor. 2019, 197, 14–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jehan, S.; Khan, S.; Khattak, S.A.; Muhammad, S.; Rashid, A.; Muhammad, N. Hydrochemical properties of drinking water and their sources apportionment of pollution in Bajaur agency, Pakistan. Measurement 2019, 139, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazhar, I.; Hamid, A.; Afzal, S. Groundwater quality assessment and human health risks in Gujranwala District, Pakistan. Environ. Earth Sci. 2019, 78, 634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talib, M.A.; Tang, Z.; Shahab, A.; Siddique, J.; Faheem, M.; Fatima, M. Hydrogeochemical Characterization and Suitability Assessment of Groundwater: A Case Study in Central Sindh, Pakistan. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khuhawar, M.Y.; Khuhawar, M.J.; Ursani, H.-R.; Farooque, M.; Lanjwani; Mahessar, A.A.; Tunio, I.A.; Soomro, A.G.; Rind, I.K.; Brohi, R.-Z.; et al. Assessment of Water Quality of Groundwater of Thar Desert, Sindh, Pakistan. J. Hydrogeol. Hydrol. Eng. Res. 2019, 7, 1000171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masood, N.; Farooqi, A.; Zafar, M.I. Health risk assessment of arsenic and other potentially toxic elements in drinking water from an industrial zone of Gujrat, Pakistan: A case study. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2019, 191, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousaf, S.; Ilyas, M.; Khan, S.; Khan Khattak, A.; Anjum, S. Measurement of physicochemical and heavy metals concentration in drinking water from sources to consumption sites in. J. Himal. Earth Sci. 2019, 52, 36–45. [Google Scholar]
- Mushtaq, N.; Younas, A.; Mashiatullah, A.; Javed, T.; Ahmad, A.; Farooqi, A. Hydrogeochemical and isotopic evaluation of groundwater with elevated arsenic in alkaline aquifers in Eastern Punjab, Pakistan. Chemosphere 2018, 200, 576–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.; Qureshi, F.R. Groundwater Quality Assessment through Water Quality Index (WQI) in New Karachi Town, Karachi, Pakistan. Asian J. Water Environ. Pollut. 2018, 15, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatti, N.B.; Siyal, A.A.; Qureshi, A.L. Groundwater Quality Assessment Using Water Quality Index: A Case Study of Nagarparkar, Sindh, Pakistan. Sindh Univ. Res. J. SURJ Sci. Ser. 2018, 50, 227–234. [Google Scholar]
- Laghari, A.N.; Siyal, Z.A.; Bangwar, D.K.; Soomro, M.A.; Walasai, G.; Shaikh, F.A. Groundwater Quality Analysis for Human Consumption A Case Study of Sukkur City, Pakistan. Technol. Appl. Sci. Res. 2018, 8, 2616–2620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imran, M.; Jahanzaib, S.; Ashraf, A. Using geographical information systems to assess groundwater contamination from arsenic and related diseases based on survey data in Lahore, Pakistan. Arab. J. Geosci. 2017, 10, 450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podgorski, J.E.; Eqani, S.A.M.A.S.; Khanam, T.; Ullah, R.; Shen, H.; Berg, M. Extensive arsenic contamination in high-pH unconfined aquifers in the Indus Valley. Sci. Adv. 2017, 3, 845–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashir, E.; Huda, S.N.; Naseem, S.; Hamza, S.; Kaleem, M. Geochemistry and quality parameters of dug and tube well water of Khipro, District Sanghar, Sindh, Pakistan. Appl. Water Sci. 2017, 7, 1645–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmood, K.; Ul-Haq, Z.; Batool, S.A.; Rana, A.D.; Tariq, S. Application of temporal GIS to track areas of significant concern regarding groundwater contamination. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farooq, A.; Zahid, F.; Asif, S.; Ali, H.Q. Estimation of Fluoride in Drinking Water in Selected Areas of Southern Lahore, Pakistan. Sci. Int. 2016, 28, 391–395. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, R.U.; Khan, P.; Waheed, M.W.; Jan, R.; Author, C.; Ur Rehman, H.; Bibi, S.; Nazir, R.; Shakir, S.K.; Naz, S.; et al. Heavy Metals Analysis in Drinking Water of Lakki Marwat District, KPK, Pakistan. World Appl. Sci. J. 2016, 34, 15–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, A.A.; Khan, M.A.; Kanwal, N.; Bernstein, R. Assessment of safety of drinking water in tank district: An empirical study of water-borne diseases in rural Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, Pakistan. Int. J. Environ. Sci. 2016, 6, 418–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahab, A.; Shihua, Q.; Rashid, A.; Ul Hasan, F.; Sohail, M.T.; Pakistan, R. Evaluation of Water Quality for Drinking and Agricultural Suitability in the Lower Indus Plain in Sindh Province, Pakistan. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2016, 25, 2563–2574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, K.A.; Tzilivakis, J.; Warner, D.J.; Green, A. An international database for pesticide risk assessments and management. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. Int. J. 2016, 22, 1050–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustafa, M.F.; Afreen, A.; Abbas, Y.; Afridi, Z.-U.-R.; Athar, W.; Ur Rehman, Z.; Khan, Q.; ur Rehaman, S.W.; Ali, A. A Study on physio-chemical and biological analysis of drinking water quality from the residential areas of Islamabad, Pakistan. J. Biodivers. Environ. Sci. 2016, 109, 109–125. [Google Scholar]
- Brahman, K.D.; Kazi, T.G.; Afridi, H.I.; Baig, J.A.; Arain, S.S.; Talpur, F.N.; Kazi, A.G.; Ali, J.; Panhwar, A.H.; Arain, M.B. Exposure of children to arsenic in drinking water in the Tharparkar region of Sindh, Pakistan. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 544, 653–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baig, J.A.; Kazi, T.G.; Mustafa, M.A.; Solangi, I.B.; Mughal, M.J.; Afridi, H.I. Arsenic Exposure in Children through Drinking Water in Different Districts of Sindh, Pakistan. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2016, 173, 35–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahessar, A.A.; Memon, N.A.; Leghari, M.E.H.; Qureshi, A.L.; Arain, G.M. Assessment of Source and Quality of Drinking Water in Coastal Area of. IOSR J. Environ. Sci. Toxicol. Food Technol. 2015, 9, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahid, S.U.; Iqbal, J.; Hasnain, G. Groundwater quality assessment and its correlation with gastroenteritis using GIS: A case study of Rawal Town, Rawalpindi, Pakistan. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2014, 186, 7525–7537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, M.A.; Tang, Z.; Mohamadi, B. Contamination Potential Assessment of Potable Groundwater in Lahore, Pakistan. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2014, 23, 1905–1916. [Google Scholar]
- Hassan, A.; Nawaz, M. African Journal of Microbiology Research Microbiological and physicochemical assessments of groundwater quality at Punjab, Pakistan. Afr. J. Microbiol. Res. 2014, 8, 2672–2681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, S.; Akmal, M.; Aziz, F.; Ullah, S.; Khan, K.J. Hand Pumps’ Water Quality Analysis for Drinking and Irrigation Purposes at District Dir Lower, Khyber Pakhtunkhwa Pakistan. Eur. Acad. Res. 2014, 2, 1560–1572. [Google Scholar]
- Arain, M.B.; Ullah, I.; Niaz, A.; Shah, N.; Shah, A.; Hussain, Z.; Tariq, M.; Afridi, H.I.; Baig, J.A.; Kazi, T.G. Evaluation of water quality parameters in drinking water of district Bannu, Pakistan: Multivariate study. Sustain. Water Qual. Ecol. 2014, 3–4, 114–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.; Shahnaz, M.; Jehan, N.; Rehman, S.; Shah, M.T.; Din, I. Drinking water quality and human health risk in Charsadda district, Pakistan. J. Clean. Prod. 2013, 60, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brahman, K.D.; Kazi, T.G.; Afridi, H.I.; Naseem, S.; Arain, S.S.; Ullah, N. Evaluation of high levels of fluoride, arsenic species and other physicochemical parameters in underground water of two sub districts of Tharparkar, Pakistan: A multivariate study. Water Res. 2013, 47, 1005–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, U.; Alvi, S.K.; Perveen, F.; Khan, F.A.; Bhutto, S.; Siddiqui, I.; Bano, A.; Usmani, T.H. Metal contents in the ground waters of Tharparkar district, Sindh, Pakistan, with special focus on arsenic. Pak. J. Sci. Ind. Res. 2012, 55, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashmi, I.; Qaiser, S.; Farooq, S. Microbiological quality of drinking water in urban communities, Rawalpindi, Pakistan. Desalin. Water Treat. 2012, 41, 240–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, M.; Ahmad, N. Potable Water Quality Characteristics of the Rural Areas of District Hangu, Khyber Pakhtunkhwa-Pakistan. Int. J. Multidiscip. Sci. Eng. 2012, 3, 7–9. [Google Scholar]
- Raza, M.; Hussain, F.; Lee, J.Y.; Shakoor, M.B.; Kwon, K.D. Groundwater status in Pakistan: A review of contamination, health risks, and potential needs. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 47, 1713–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayaz, T.; Khan, S.; Khan, A.Z.; Lei, M.; Alam, M. Remediation of industrial wastewater using four hydrophyte species: A comparison of individual (pot experiments) and mix plants (constructed wetland). J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 255, 109833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Memon, Y.I.; Qureshi, S.S.; Kandhar, I.A.; Qureshi, N.A.; Saeed, S.; Mubarak, N.; Khan, S.U.; Saleh, T.A. Statistical analysis and physicochemical characteristics of groundwater quality parameters: A case study. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2021, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usmani, Z.; Kumar, V.; Varjani, S.; Gupta, P.; Rani, R.; Chandra, A. Municipal solid waste to clean energy system: A contribution toward sustainable development. Curr. Dev. Biotechnol. Bioeng. Resour. Recovery Wastes 2020, 2020, 217–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.; Li, W.; Tam, V.W.Y.; Xue, C. Advanced progress in recycling municipal and construction solid wastes for manufacturing sustainable construction materials. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. X 2020, 6, 100036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farid, S.; Baloch, M.K.; Ahmad, S.A.; Khan, I. Water pollution: Major issue in urban areas. Int. J. Water Resour. Environ. Eng. 2012, 4, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soomro, M.; Khokhar, M.; Hussain, W.; Hussain, M. Drinking water Quality challenges in Pakistan. Pak. Counc. Res. Water Resour. Lahore 2011, 17–28. [Google Scholar]
- Nawab, J.; Khan, S.; Khan, M.A.; Sher, H.; Rehamn, U.U.; Ali, S.; Shah, S.M. Potentially Toxic Metals and Biological Contamination in Drinking Water Sources in Chromite Mining-Impacted Areas of Pakistan: A Comparative Study. Expo. Health 2017, 9, 275–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawab, J.; Khan, S.; Ali, S.; Sher, H.; Rahman, Z.; Khan, K.; Tang, J.; Ahmad, A. Health risk assessment of heavy metals and bacterial contamination in drinking water sources: A case study of Malakand Agency, Pakistan. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2016, 188, 286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roohul-Amin; Ali, S.S.; Anwar, Z.; Khattak, J.Z.K. Microbial Analysis of Drinking Water and Water Distribution System in New Urban Peshawar. Curr. Res. J. Biol. Sci. 2012, 4, 731–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noshin, M.; Batool, S.; Farooqi, A. Groundwater pollution in Pakistan. Groundw. Pollut. Pak. 2021, 13, 309–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, K.; Lu, Y.; Khan, H.; Zakir, S.; Ihsanullah; Khan, S.; Khan, A.A.; Wei, L.; Wang, T. Health risks associated with heavy metals in the drinking water of Swat, northern Pakistan. J. Environ. Sci. 2013, 25, 2003–2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jadhav, S.V.; Bringas, E.; Yadav, G.D.; Rathod, V.K.; Ortiz, I.; Marathe, K.V. Arsenic and fluoride contaminated groundwaters: A review of current technologies for contaminants removal. J. Environ. Manag. 2015, 162, 306–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Geen, A.; Farooqi, A.; Kumar, A.; Khattak, J.A.; Mushtaq, N.; Hussain, I.; Ellis, T.; Singh, C.K. Field testing of over 30,000 wells for arsenic across 400 villages of the Punjab plains of Pakistan and India: Implications for prioritizing mitigation. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 654, 1358–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qaiser, S.; Hashmi, I.; Nasir, H. Chlorination at Treatment Plant and Drinking Water Quality: A Case Study of Different Sectors of Islamabad, Pakistan. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2014, 39, 5665–5675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waqar, A.; Ali, M. Different Perspectives on Water Quality of Local Filtration Plants in Pakistan. In Proceedings of the 2nd Conference on Sustainability in Civil Engineering, Islamabad, Pakistan, 12 August 2020; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Rawan, B.; Ullah, W.; Ullah, R.; Akbar, T.A.; Ayaz, Z.; Javed, M.F.; Din, I.; Ullah, S.; Aziz, M.; Mohamed, A.; et al. Assessments of Roof-Harvested Rainwater in Disctrict Dir Lower, Khyber Pakhtunkhwa Pakistan. Water 2022, 14, 3270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaqub, G.; Hamid, A.; Asghar, S. Rain water quality assessment as air quality indicator in Pakistan. Bangladesh J. Sci. Ind. Res. 2019, 54, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathan, M.A.; Lashari, R.A.; Maira, M. Physical and Chemical Contamination Studies of Drinking Water in the Vicinity of Jamshoro Area (Jetharo Village) Sindh, Pakistan. Int. J. Eng. Sci. Comput. 2018, 8, 17985. [Google Scholar]
- Hasan, M.; Shang, Y.; Akhter, G.; Jin, W. Evaluation of Groundwater Suitability for Drinking and Irrigation Purposes in Toba Tek Singh District, Pakistan. Irrig. Drain. Syst. Eng. 2017, 6, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brahman, K.D.; Kazi, T.G.; Afridi, H.I.; Rafique, T.; Baig, J.A.; Arain, S.S.; Ullah, N.; Panhwar, A.H.; Arain, S. Evaluation of fresh and stored rainwater quality in fluoride and arsenic endemic area of Thar Desert, Pakistan. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2014, 186, 8611–8628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chughtai, M.; Mustafa, S.; Mumtaz, M. Study of Physicochemical Parameters of Rainwater: A Case Study of Karachi, Pakistan. Am. J. Anal. Chem. 2014, 2014, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chughtai, M.; Mustafa, S.; Mahmood, R.; Mumtaz, M. Physicochemical Assessment of Rainwater of Karachi, Pakistan. Eur. Acad. Res. 2014, 1, 4099–4108. [Google Scholar]
- D’Adamo, I.; Gastaldi, M.; Morone, P.; Rosa, P.; Sassanelli, C.; Settembre-blundo, D.; Shen, Y. Bioeconomy of Sustainability: Drivers, Opportunities and Policy Implications. Sustainability 2022, 14, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Adamo, I.; Gastaldi, M. Perspectives and Challenges on Sustainability: Drivers, Opportunities and Policy Implications in Universities. Sustainability 2023, 15, 3564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.; Azam, F.; Naveed, H.M.; Abid, W. Impact of Prestigious Indicators on Sustainable Growth of Small and Medium-Sized Enterprises in Pakistan. Asian J. Econ. Empir. Res. 2020, 7, 251–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shehzadi, M.; Afzal, M.; Khan, M.U.; Islam, E.; Mobin, A.; Anwar, S.; Khan, Q.M. Enhanced degradation of textile effluent in constructed wetland system using Typha domingensis and textile effluent-degrading endophytic bacteria. Water Res. 2014, 58, 152–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahid, M.; Niazi, N.K.; Dumat, C.; Naidu, R.; Khalid, S.; Rahman, M.M.; Bibi, I. A meta-analysis of the distribution, sources and health risks of arsenic-contaminated groundwater in Pakistan. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 242, 307–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abiriga, D.; Vestgarden, L.S.; Klempe, H. Groundwater contamination from a municipal landfill: Effect of age, landfill closure, and season on groundwater chemistry. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 737, 140307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Kumar, V.; Shahzad, B.; Tanveer, M.; Sidhu, G.P.S.; Handa, N.; Kohli, S.K.; Yadav, P.; Bali, A.S.; Parihar, R.D.; et al. Worldwide pesticide usage and its impacts on ecosystem. SN Appl. Sci. 2019, 1, 1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.I.; Shoukat, M.A.; Alam, S. Use, Contamination and Exposure of Pesticides in Pakistan: A Review. Pak. J. Agri. Sci 2020, 57, 131–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qureshi, A.S.; McCornick, P.G.; Sarwar, A.; Sharma, B.R. Challenges and Prospects of Sustainable Groundwater Management in the Indus Basin, Pakistan. Water Resour. Manag. 2010, 24, 1551–1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherji, A.; Scott, C.; Molden, D.; Maharjan, A. Megatrends in Hindu Kush Himalaya: Climate Change, Urbanisation and Migration and Their Implications for Water, Energy and Food. In Water Resources Development and Management; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 125–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sleet, P. Water Resources in Pakistan: Scarce, Polluted and Poorly Governed; Future Directions International: Nedlands, Australia, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Haidary, A.; Amiri, B.J.; Adamowski, J.; Fohrer, N.; Nakane, K. Assessing the Impacts of Four Land Use Types on the Water Quality of Wetlands in Japan. Water Resour. Manag. 2013, 27, 2217–2229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakoor, M.B.; Niazi, N.K.; Bibi, I.; Shahid, M.; Sharif, F.; Bashir, S.; Shaheen, S.M.; Wang, H.; Tsang, D.C.W.; Ok, Y.S.; et al. Arsenic removal by natural and chemically modified water melon rind in aqueous solutions and groundwater. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 645, 1444–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, A.H.; Shahid, M.; Khalid, S.; Natasha; Shabbir, Z.; Bakhat, H.F.; Murtaza, B.; Farooq, A.; Akram, M.; Shah, G.M.; et al. Assessment of arsenic exposure by drinking well water and associated carcinogenic risk in peri-urban areas of Vehari, Pakistan. Environ. Geochem. Health 2020, 42, 121–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamrani, S.; Rezaei, M.; Amiri, V.; Saberinasr, A. Investigating the efficiency of information entropy and fuzzy theories to classification of groundwater samples for drinking purposes: Lenjanat Plain, Central Iran. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elhag, M.; Gitas, I.; Othman, A.; Bahrawi, J.; Gikas, P. Assessment of Water Quality Parameters Using Temporal Remote Sensing Spectral Reflectance in Arid Environments, Saudi Arabia. Water 2019, 11, 556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avdan, Z.Y.; Kaplan, G.; Goncu, S.; Avdan, U. Monitoring the Water Quality of Small Water Bodies Using High-Resolution Remote Sensing Data. ISPRS Int. J. Geo Inf. 2019, 8, 553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villa, S.; Sassanelli, C. The Data-Driven Multi-Step Approach for Dynamic Estimation of Buildings’ Interior Temperature. Energies 2020, 13, 6654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sassanelli, C.; Arriga, T.; Zanin, S.; D’Adamo, I.; Terzi, S. Industry 4.0 Driven Result-oriented PSS: An Assessment in the Energy Management. Int. J. Energy Econ. Policy 2022, 12, 186–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Adamo, I. The Profitability of Residential Photovoltaic Systems. A New Scheme of Subsidies Based on the Price of CO2 in a Developed PV Market. Soc. Sci. 2018, 7, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Paola, F.; Sambito, M.; Piazza, S.; Freni, G. Optimal Deployment of the Water Quality Sensors in Urban Drainage Systems. Environ. Sci. Proc. 2022, 21, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Blanc, D. Towards Integration at Last? The Sustainable Development Goals as a Network of Targets. Sustain. Dev. 2015, 23, 176–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osborn, D.; Cutter, A.; Ullah, F. Understanding the Transformational Challenge for Developed Countries. 2015. Available online: https://sustainabledevelopment.un.org/content/documents/1684SF_-_SDG_Universality_Report_-_May_2015.pdf (accessed on 1 March 2023).
- Khan, M.A.; Khan, J.A.; Ali, Z.; Ahmad, I.; Ahmad, M.N. The challenge of climate change and policy response in Pakistan. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcamo, J. Water quality and its interlinkages with the Sustainable Development Goals. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sustain. 2019, 36, 126–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoekstra, A.Y.; Chapagain, A.K.; van Oel, P.R. Advancing Water Footprint Assessment Research: Challenges in Monitoring Progress towards Sustainable Development Goal 6. Water 2017, 9, 438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, N.K.; Mishra, I. Sustainable development goal 6: Global Water Security. Environ. Sustain. 2022, 5, 271–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera, V. Reconciling global aspirations and local realities: Challenges facing the Sustainable Development Goals for water and sanitation. World Dev. 2019, 118, 106–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azadi, F.; Ashofteh, P.S.; Loáiciga, H.A. Reservoir Water-Quality Projections under Climate-Change Conditions. Water Resour. Manag. 2019, 33, 401–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, L.; Nadeem, F.; Sloan, M.; Restle-Steinert, J.; Deitch, M.J.; Naqvi, S.A.; Kumar, A.; Sassanelli, C. Fostering Green Finance for Sustainable Development: A Focus on Textile and Leather Small Medium Enterprises in Pakistan. Sustainability 2022, 14, 11908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michels-Brito, A.; Rodriguez, D.A.; Cruz Junior, W.L.; de Souza Vianna, J.N. The climate change potential effects on the run-of-river plant and the environmental and economic dimensions of sustainability. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 147, 111238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukate, S.; Wagh, V.; Panaskar, D.; Jacobs, J.A.; Sawant, A. Development of new integrated water quality index (IWQI) model to evaluate the drinking suitability of water. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 101, 348–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).