Abstract
As a polymer material, plastic is widely used in passenger vehicles for its light weight and low-cost advantages. China has accumulated a large amount of discarded automotive plastic in recent years, which has put increasing pressure on the environment and the recycling industry. A dynamic material flow model for estimating the plastic stock and waste in passenger vehicles was developed. Additionally, geospatial models were used to study the spatiotemporal evolution trend of passenger vehicle plastics. The results show: (1) passenger-vehicle plastic stock and waste in China increased rapidly from 1985 to 2019. By 2019, the passenger-vehicle plastic stock was 36.94 million tons, and the waste amount was 1.64 million tons, of which polypropylene accounted for the greatest proportion, and polyoxymethylene (POM) accounted for the least. (2) The stock and waste of passenger-vehicle plastics showed spatial dependency. (3) The spatial center of plastic waste was located in Henan Province, and the spatial center is shifting from north to south. (4) The GDP and the annual population are the main driving factors of passenger-vehicle plastic waste. This study will improve plastic waste management, resource recovery, and environmental sustainability decisions.
1. Introduction
Creating a cleaner environment has been the concern of humans for a long time and has become a serious problem in all aspects of human life. Disposing of pollutants in the environment is one of the biggest global issue, and it poses huge risks to human and aquatic health [1]. Therefore, the monitoring and mitigating of the environmental influence of these pollutants are the current concerns of scholars in various fields [2,3,4,5,6,7]. China has become a large country with a high volume of plastic use and a rapidly growing rate of pollution, which may have significant effects on the environment [8]. Plastic, a synthetic or natural high molecular polymer composed of long carbon chains, is widely used in the industrial sector due to its excellent physicochemical properties (light weight, process ability, high durability) and low cost [9]. Plastic is part of everyday life, and its applications are expanding. It has become the fastest-growing engineering material in the last 50 years, and combined with steel, wood, and cements, these four make up the basic construction materials [10,11]. Statistics from the China Plastics Processing Industry Association show that due to a large population and rapid economic growth in China, the cumulative output of plastic products has exceeded 1 billion tons since 1949. China is the largest plastic producer and consumer in the world, contributing to nearly one-third of global plastic production [12]. According to the National Bureau of Statistics, China is also the largest plastic importer, importing more than 4.52 million tons in 2019, and receiving more than 45% of the global plastic waste since 1992 [13].
As a polymer material, plastics are widely used in passenger vehicles for items such as steering wheels, dashboards, bumpers, etc. With the advancement of technology, the proportion of plastics in passenger vehicles is increasing. An increase in urbanization and the demand for vehicles has had a detrimental impact the environment [14,15]. The amount of plastic in vehicles has increased from 10 kg in the 1960s to almost 200 kg to date, which will continue to increase due to the demand for lightweight vehicles [16]. With the rapid development of the domestic automobile industry, the consumption of plastics in passenger vehicles is also increasing rapidly [17]. The continuous increase in the number of passenger vehicles has resulted in the accumulation of a large amounts of passenger-vehicle plastic waste in society. In the future, it will gradually enter the peak period of scrapping, which will exert greater resource recovery and environmental pressure to the automobile recycling and dismantling industry [18,19]. Therefore, it is necessary to study the quantification and evolution of plastics. This can provide data support and reduce recycling pressure for the plastic recycling industry.
There are many studies regarding the quantitative analysis of stocks and waste of different materials, such as plastics and steels [20,21,22]. One of the common techniques is the estimation of stock by material flow analysis and GIS, and the waste is estimated by combining the life distribution model [22]. Zhou et al. [23] used the “top-down” material flow analysis method, combined with the Weibull life distribution function, to build a dynamic model of PVC input and output, and calculated PVC stock and waste emissions in China. Jiang et al. [24] combined the dynamic material flow model and the symmetrically distributed life distribution model to quantify the material stock and flow of plastic from 1978 to 2017. In addition, Ileana et al. [25] used GIS to study agricultural plastics in a region of Italy. Fan et al. [26] established a neural network model to predict the inventory of EU-27 plastic wastes in 2030. In the research method, the material flow analysis combined with the Weibull life distribution model is mainly used. In the research scale, the stock and waste of plastics at the national level were mainly estimated from a macro perspective. There were fewer mesoscale (for a certain region, city, or watershed) studies. In terms of research objects, the focus on plastics as a whole, or on specific types of plastics, or estimates of plastics in a certain industry are rarely mentioned.
Considering the spatial characteristics of different data can lead to more accurate results and a better understanding of the subject of interest [27,28]. Sun et al. [29] analyzed the data from the plastic industry from 2011 to 2017 and explored the spatial distribution of the plastic. The research on plastics in the passenger-vehicle industry was based on the perspective of sustainable development and mainly focused on recycling. Cardamone et al. [30] studied the plastics in end-of-life vehicles from the perspective of sustainable development and evaluated the recycling methods of different types of passenger-vehicle plastics. Zhao and Chen [31] introduced the recycling of automotive plastics in various countries, and put forward the overall idea of design, recycling, research, and development of plastic parts for passenger vehicles in China. According to the existing research, there are some deficiencies in estimating the mesoscale plastics, and the spatial distribution characteristics and evolution trend of passenger-vehicle plastics are not sufficiently explored. In addition, there are many factor analyses for other composites, such as hydroxyapatite-alumina-titanium nanocomposites [32], but there are few factor analyses for plastic. Therefore, it is necessary to systematically estimate the stock and waste of passenger-vehicle plastics in various provinces and to explore the historical pattern and spatial evolution trend of passenger-vehicle plastic stock and waste.
In this paper, a dynamic material flow model was developed to study the stock and waste of the passenger-vehicle plastics from 1985 to 2019. Moreover, combined with GIS technologies such as spatial autocorrelation and center of gravity transfer analysis, this paper analyzed the spatial and temporal evolution trend of passenger-vehicle plastic stock and waste volume in various provinces from 2000 to 2019. It will help to fill the current gaps in previous studies and help the industry to grasp the development dynamics of passenger-vehicle plastic. It can also provide data support for environmental protection policy research of relevant industries. In addition, it offers a theoretical basis for future policy formulation of the plastic recycling industry. In this research work, we will investigate the spatiotemporal variation of various types of plastics used in passenger vehicles. Moreover, the amount of stock plastic is investigated. The amount and spatial distribution of wasted plastic in all provinces of China will be discussed as well. Finally, we examine the influencing factors on the amount and spatiotemporal distribution of plastics in passenger vehicles, through which a route map for the management and recycling of plastics is suggested. The findings of this paper can be used as fundamental information for recycling management and as an aid for sustainable development [33,34].
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. System Boundaries
China, as the largest automotive market in the world, needs to pay special attention to stock of plastics in passenger vehicles and the mass of plastic waste derived from them. Therefore, the spatial boundary of this study is mainland China, and the temporal boundary is the period from 1985 to 2019. Based on the literature reviewed, there are nine types of plastics which are used in passenger vehicles. In this paper, we investigated the amount and spatiotemporal distribution of these nine types: polypropylene (PP), polyethylene (PE), polyvinyl chloride (PVC), acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS), polyurethane (PU), polyamide (PA), polycarbonate (PC), propylene resin (PMMA), and polyoxymethylene (POM).
2.2. Data Sources
The data were mainly collected from statistical yearbooks, industry reports, and related literature. We collected the passenger-vehicle ownership data, at the provincial level, from the China statistical yearbook provided by the national bureau of statistics (http://www.stats.gov.cn/tjsj/ndsj/ (accessed on 15 March 2023)). The market share of passenger vehicles and their sale rate were collected from the statistics of the China Association of Automobile Manufacturers website (http://www.caam.org.cn/ (accessed on 15 March 2023)) and related literature [35]. The data on the use of plastics in passenger vehicles and the proportion of plastics used in passenger vehicles of different brands were extracted from the relevant literature [18]. In addition, data for individual missing years were estimated using linear interpolation. The data of influencing factors (Table 1) were also obtained from the China Statistical Yearbook.

Table 1.
Influencing factors and their abbreviations.
2.3. Quantification of the Passenger-Vehicle Plastic Stocks and Wastes
2.3.1. Dynamic MFA Model
Dynamic material flow analysis (MFA) can be used to investigate the changes in an element during its life cycle. It can be used for any material or combination, especially for materials that are easier to track and whose life cycle data is available [36]. The estimation of plastic stock and flow in passenger vehicles draws on Jiang’s material flow estimation method [18]. The stages that should be followed to implement this analysis are as follows:
First, the stock and waste of passenger vehicles were calculated. The stock was calculated by multiplying the population and the number of vehicles per thousand people (not calculate if there is data in the statistical yearbook of some years). Passenger-vehicles waste was calculated by the inflow, which is the difference between the stock of the given year and its previous year. The calculation of passenger-vehicle stock and waste can be represented by Equations (1) and (2):
where is the per capita passenger-vehicle ownership in year , is the total population in year , is the stock of passenger vehicles in year , is the number of discarded passenger vehicles in year t, is the inflow of passenger vehicles in year t, and is the passenger-vehicle life distribution function.
The bottom-up method is used to estimate the plastic stock of passenger vehicles [37]. According to the website of the China Plastics Processing Industry Association, the amount of plastic used per vehicle by independent brands and foreign brands is not similar. Therefore, we calculated the plastic amount in each category—independent brands and foreign brands—separately. The amount of plastic used per specific brand of vehicle is a weighted average of the total plastic used in all vehicles of that brand. The calculation of plastic proportion and usage can be represented by Equations (3) and (4):
where is the proportion of class I plastics to the total amount of plastics used by passenger vehicles in the year t, and is the average amount of plastics used per passenger vehicle in the year t; , are the proportion of class I plastics in the total plastic consumption of independent brand and foreign brand passenger vehicles in the t year, respectively, and are the amount of plastic used per vehicle of independent brands and foreign brands, respectively, is the market share of independent brand, and is the market share of foreign brand.
According to the amount of plastics used in vehicles and the proportion of various types of plastics, the historical stock and waste of passenger-vehicle plastics was calculated, which can be represented by Equations (5) and (6).
where is the overall stock of i-type plastic in year t, and is the outflow of -type plastic in year .
2.3.2. Life Distribution Model
The material flow analysis is often combined with the life distribution model to calculate the outflow or waste. The life distribution model plays an important role in the metabolism of resources [38]. The commonly used life distribution models were the Weibull life distribution model [39], the normal distribution model [40], etc. Due to the heterogeneity of plastic types [24,38], the absence of detailed information on the life distribution, and in the absence of an official vehicle mandatory end-of-life criteria, a normal distribution is considered to be the best option. Therefore, this paper adopts the normal distribution life model according to the actual life of passenger vehicles. According to the “Regulation on Compulsory Scrapping Standards for Motor Vehicles” published on the official website of the Ministry of Commerce of the People’s Republic of China [41], most of the stipulated scrapping years for vehicles are 10 or 15 years. Considering the automobile technology iteration and style renewal, the average life of passenger vehicles is 13 years. If the vehicle in the 13th year is scrapped, the standard deviation takes 30% of the life expectancy. The normal distribution can be represented by Equation (7).
where is the mean, and is the standard deviation of a random variable.
2.4. Analysis on the Temporal and Spatial Evolution of Passenger-Vehicle Plastic Waste
2.4.1. Spatial Autocorrelation
Spatial autocorrelation refers to the degree of similarity between nearby observations (values). Spatial autocorrelation analysis is a method to test whether the observations of a spatial variable are significantly correlated with those at adjacent spatial points. Spatial correlation is divided into global spatial autocorrelation and local spatial autocorrelation [42]. Global spatial autocorrelation is expressed by Global Moran’s I, which is usually between −1.0 and 1.0. Global Moran’s I > 0 indicates a positive spatial correlation; the greater the value, the more obvious the spatial correlation, and Global Moran’s I < 0 indicates a negative spatial correlation; the smaller the value, the greater the spatial difference, Global Moran’s I = 0, and the spatial randomness. GeoDa spatial analysis software was used to establish spatial weights to calculate the Moran’s I values of passenger-vehicle plastics. The calculation of Global Moran’s I can be represented by Equation (8):
where and refer to the observations of spatial element x in spatial units i and j, respectively, is the mean value of x, is the spatial weight between i and j, and n is the total number of spatial units.
The local spatial autocorrelation is represented by Local Moran’s I, a decomposition of Global Moran’s I. The calculation of Local Moran’s I can be represented by Equation (9):
among them, each element in the formula has the same meaning as Formula (8).
2.4.2. Center of Gravity Transfer Model
The geographical center of gravity can reflect the spatial and temporal distribution characteristics of an element. The migration direction and distance of the center of gravity can reflect the changing range and spatial variation of an element in a certain period of time. The representation of the spatiotemporal distribution pattern based on the barycenter model has become an important element of spatiotemporal evolution law, and it has been widely used in the fields of regional economic disparity [43], population distribution [44], and land-use change [45]. The center of gravity is usually weighted by an attribute value of a geographical phenomenon and then calculated according to the decomposition and composition rules of gravity in physics. QGIS software was used to calculate the center of gravity.
The calculation of the center of gravity of space can be represented by Equation (10)
where , refers to the horizontal and vertical coordinates of the center of gravity in year t; , refers to the horizontal and vertical coordinates of the center of gravity of the i province; n is the number of provinces; is the plastic waste of the i province in year t.
In the gravity transfer model, the direction and distance reflect the gravity migration. A map can directly interpret the migration direction, and the distance is calculated by Equation (11).
where , refers to the horizontal and vertical coordinates of the center of gravity in year t − 1;
2.4.3. Spatiotemporal Evolutionary Tree
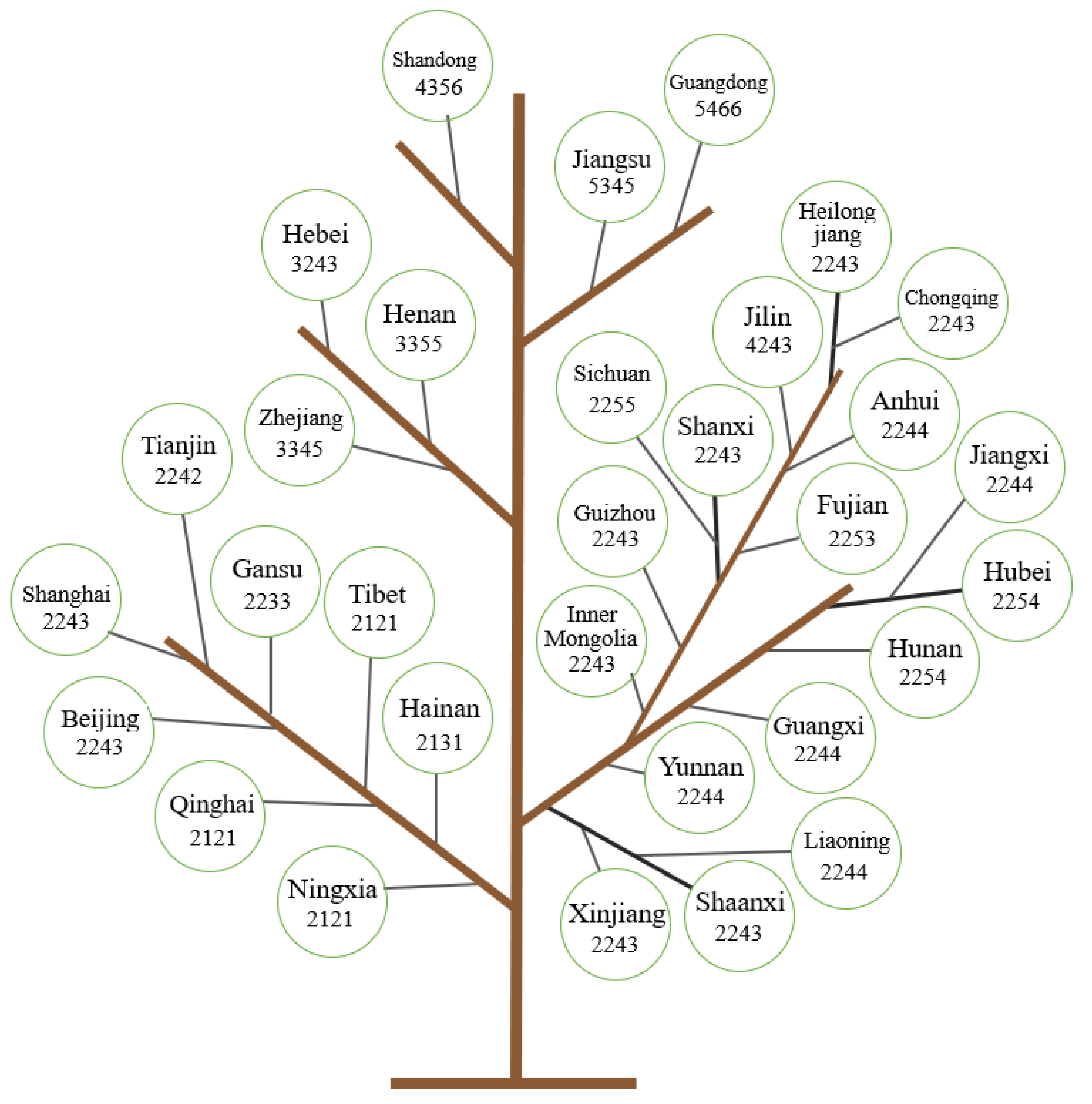
The spatiotemporal evolution tree was used to visualize the historical waste amount of passenger-vehicle plastics, urban development, and the distribution of population. This paper draws on the urban evolutionary tree theory used in Reference [46]. To simplify the evolution tree technique, we combined it with cluster analysis. To construct the spatiotemporal evolution of plastic waste from passenger vehicles, 31 provinces were clustered. In addition, we use GDP to express the urban development stages and divide the city into six development stages. Similarly, the population is also divided into six development stages, according to the actual situation (Table 2). We present the results in a tree structure. Different “branches” represent different types, and the leaves along the branches indicate different urban GDP and population development stages. Each leaf is marked with the name and number of the province. The first number indicates the type of historical waste of passenger-vehicle plastic, the second indicates the urban development stage in 2000, the third indicates the urban development stage in 2019, and the fourth indicates the stage of the city’s population in 2019.

Table 2.
Division of GDP and population in different stages.
2.5. Analysis of Driving Factors of Passenger-Vehicle Plastics
Driver analysis can be done using the geographical detector model [42,47] or Pearson and Spearman correlation analysis [48]. In this study, we choose Spearman correlation analysis; correlation analysis refers to the analysis of two or more variables to examine the strength of the relationship between them. We considered different factors (urbanization rate, GDP, annual population, highway mileage, highway passenger volume, disposable income of urban residents, steel production, car production, number of harmless treatment plants) to investigate their role on the stock of passenger-vehicle plastics and their waste. The Pearson correlation coefficient (−1 ≤ r ≤ 1) is a widely used indicator that shows the influencing power of an independent variable (x) on a dependent variable (y) (Equation (12)).
3. Results
3.1. Historical Patterns of Passenger-Vehicle Plastics Stocks across China
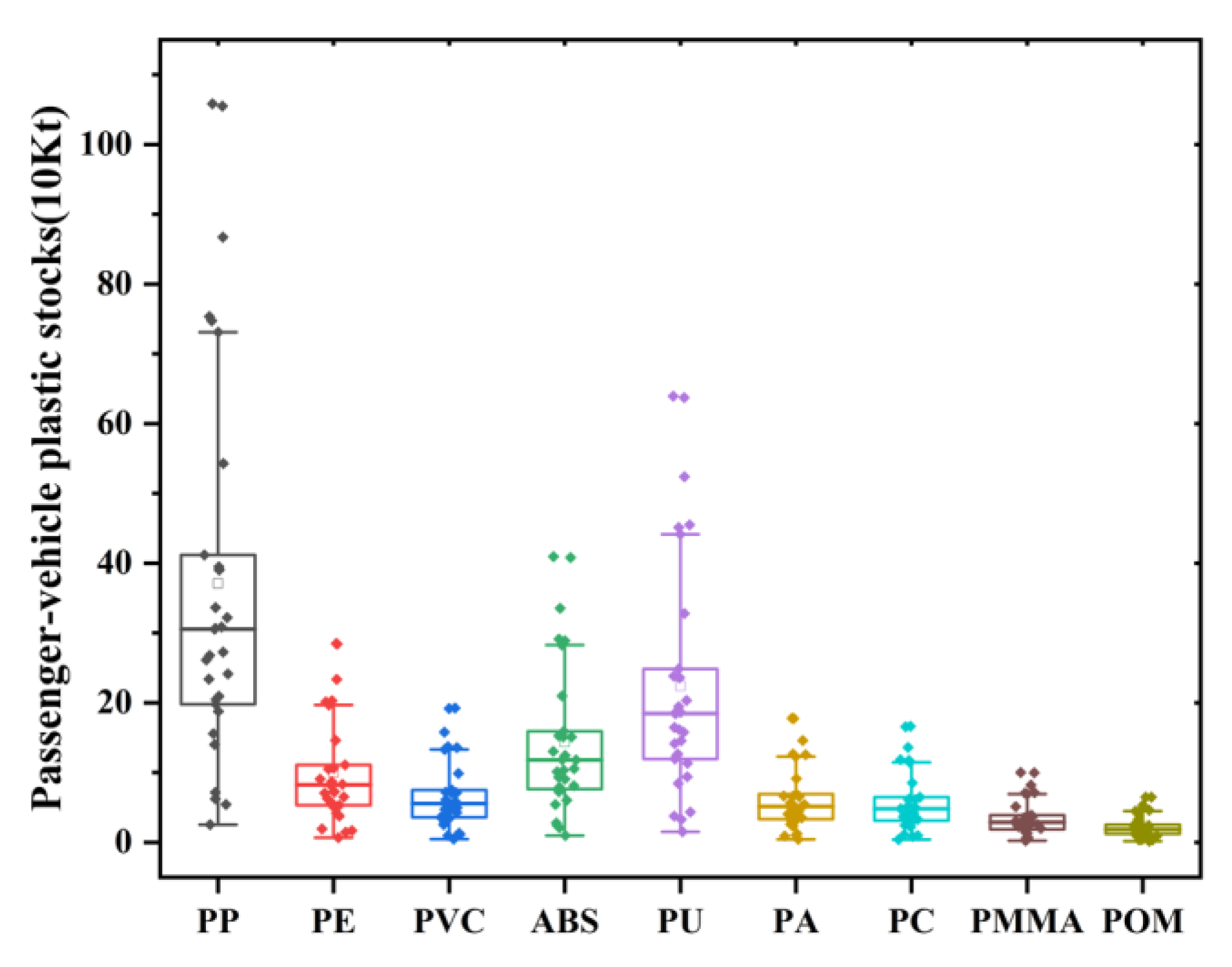
Passenger-vehicle plastics stocks in China showed a clear growth trend from 1985 to 2019, from 260,000 tons in 1985 to more than 30 million tons in 2019. Among these years, the growth was relatively slow from 1985 to 2005, with an increase of only about 400 tons in 20 years. The years 2006 to 2019 represented a stage of rapid growth, from 4.62 million tons to 36.94 million tons, with an average annual growth rate of 17%. In terms of the type of plastics (Figure 1), polypropylene (PP) accounted for the largest share of passenger-vehicle plastic stocks, accounting for 31% of total plastic stocks in 2019, with a stock of 11.5 million tons. The stock of polyurethane (PU) was 6.94 million tons, which together with PP, accounted for half of the passenger-vehicle plastic stocks. In addition, acrylonitrile-butadiene-styrene (ABS), polyethylene (PE), and polyvinyl chloride (PVC) accounted for 12% (4.45 million tons), 8% (3.09 million tons), and 6% (2.09 million tons) of the total plastic stock, respectively. However, polypropylene (PP) accounted for only 15% of automotive plastics in 1985, and other types of plastics accounted for nearly 18%. It can be seen that in the past 30 years, the proportion of polypropylene increased almost two times, and the proportion of other types decreased.
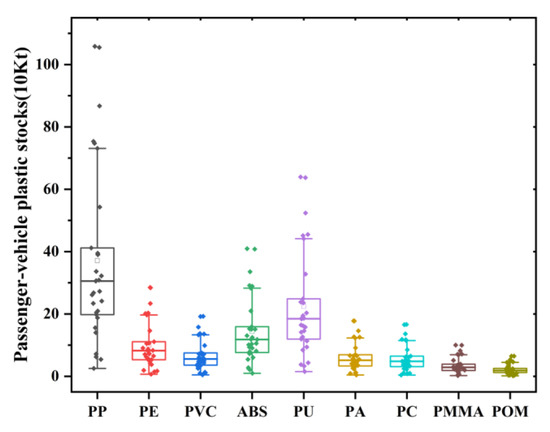
Figure 1.
Plastic stock of all types of passenger vehicles in 2019.
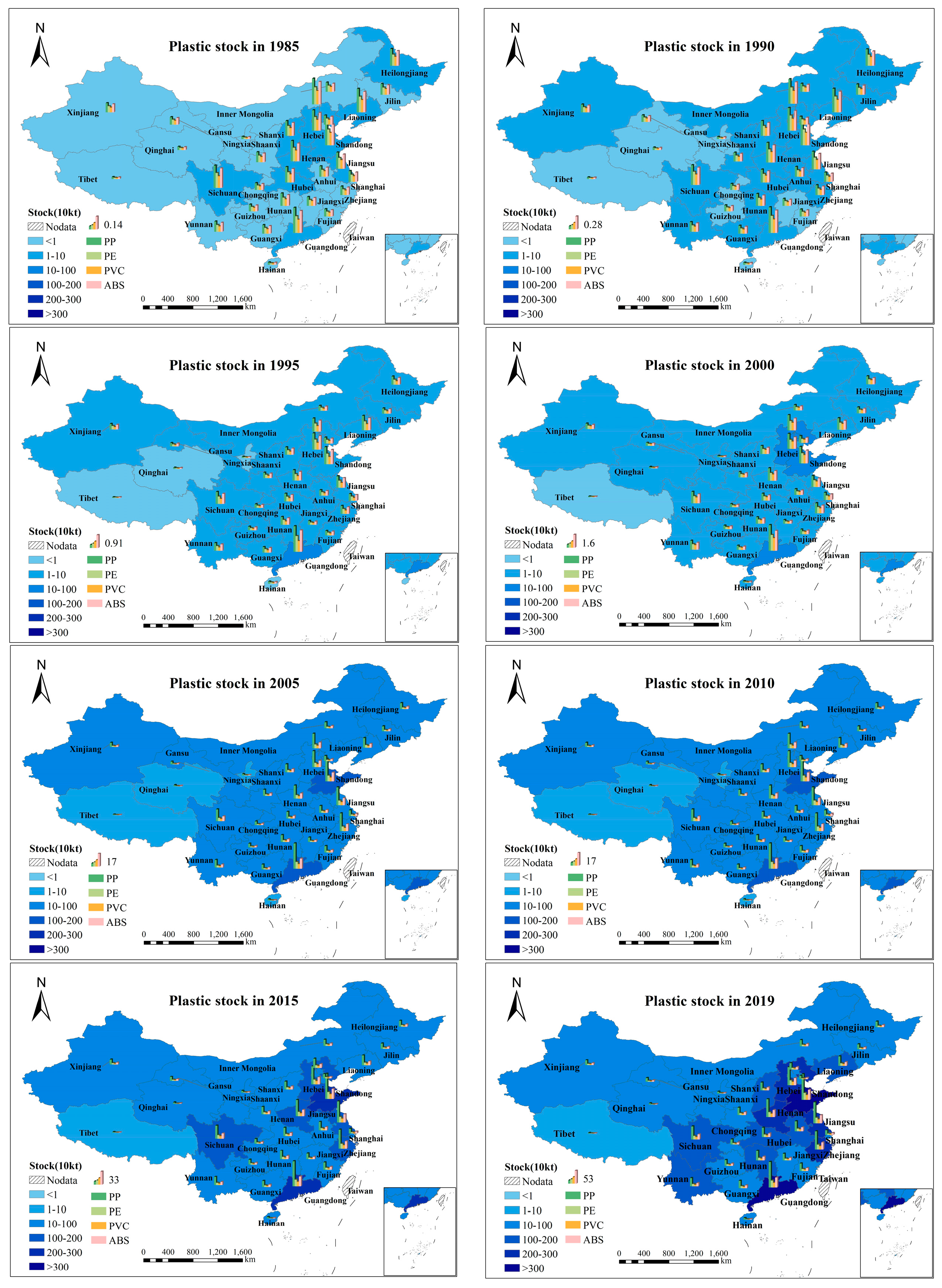
At the region level, the eastern region accounts for the majority of plastic stock. The stocks on the eastern seaboard were the highest, with 18.74 million tons in 2019, accounting for 51% of the total stock in China. The total amount of plastics in the central region is 9.5 million tons, only half of that in the eastern region. The western region has the most significant number of provinces, but the plastic stock here is the lowest. The total amount of plastic in the 12 provinces was only 8.69 million tons.
At the provincial level, there were also significant differences in passenger-vehicle plastics (Figure 2). The top six provinces in 2019 were: Shandong, Guangdong, Jiangsu, Zhejiang, Hebei, and Henan, most of which were eastern coastal provinces. The passenger-vehicle plastic stocks in these provinces were more than 2 million tons, and their average annual growth rate is also very rapid, which is higher than the national average. Among them, the average annual growth rate of Zhejiang Province has reached 19%. The provinces with the lowest plastic stock in passenger vehicles were Hainan, Qinghai, and Tibet. It can be seen from the spatial distribution of plastic stock that the top provinces since 1985 to 2019 are those located in the eastern region, and Guangdong and Shandong have the highest stock. Henan represents the central region, and its plastic stock ranks first in the central region. In the western region, Sichuan has the highest stock, while Tibet, Qinghai, and Ningxia have always been the three regions with the lowest plastic stock during the 35 years of our study.
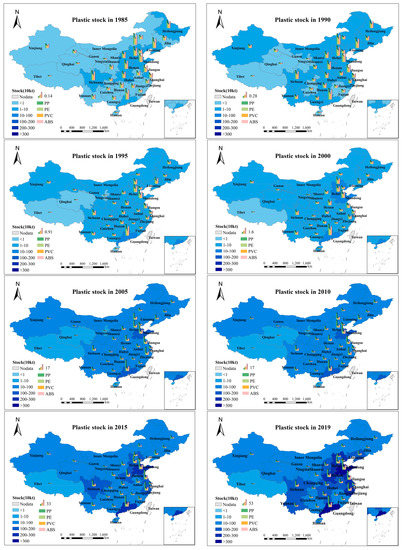
Figure 2.
Spatial distribution map of passenger-vehicle plastic stocks.
3.2. Historical Patterns of Passenger-Vehicle Plastic Wastes across China
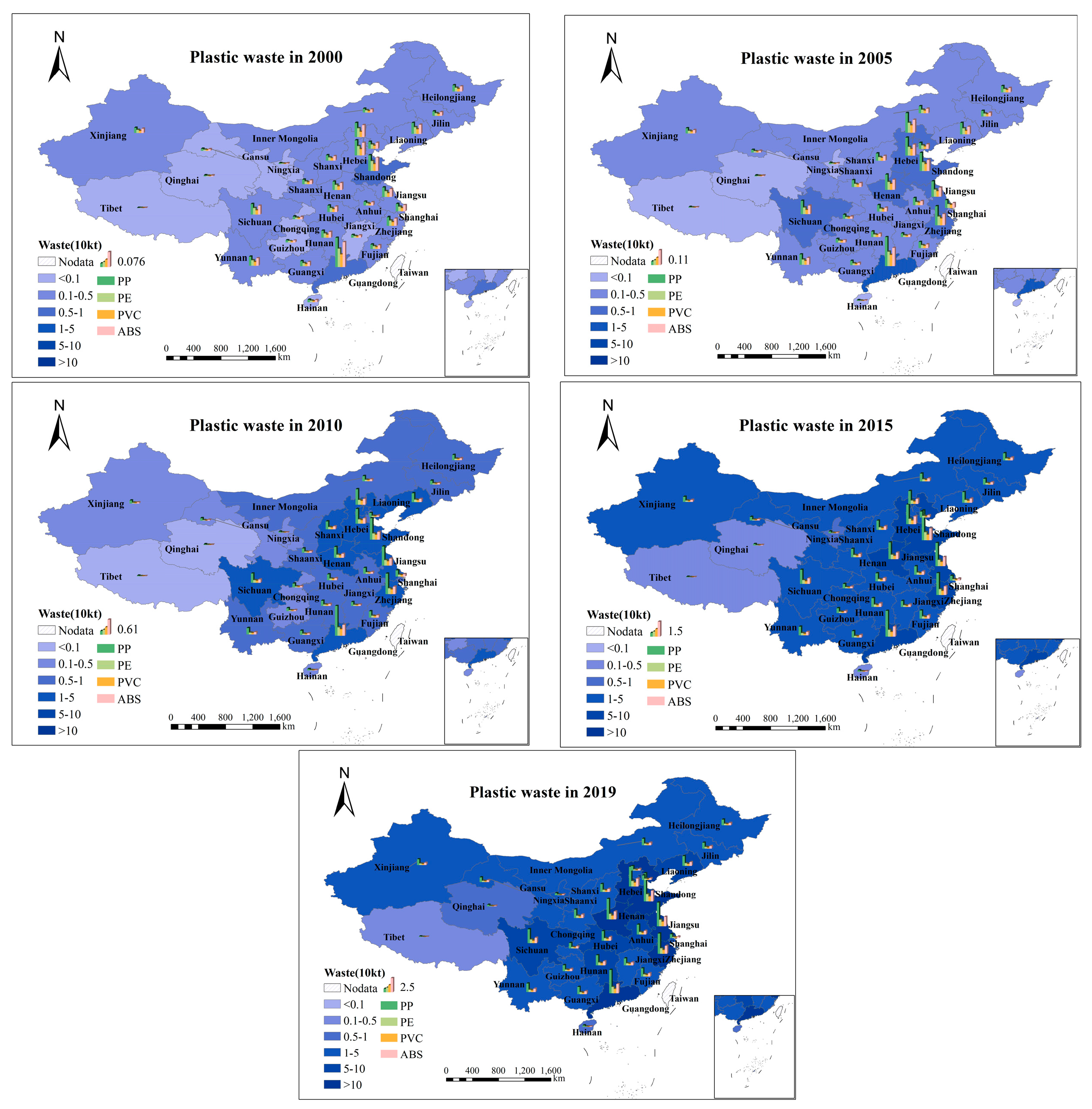
The period of passenger-vehicle plastic waste was from 2000 to 2019, with an exponential growth trend of first slow and then rapid. In terms of the growth rate, the total amount of plastic waste from passenger vehicles in China increased from 68,200 tons to 1.64 million tons in 19 years, an average annual growth rate of 18.2%. Among them, the waste volume of polycarbonate (PC) in 2000 was only 1600 tons, and it reached 79,300 tons in 2019, with the fastest average annual growth rate of 22.6%. The second was polypropylene (PP), with an average annual growth rate of about 22.4% from 2000 to 2019, and the average annual growth rates of propylene resin (PMMA) and polyoxymethylene (POM) were 20.0% and 19.9%, respectively. The average annual growth rate of other plastics was below the level of the total plastic growth rate, but the overall difference was insignificant. The growth rate was above 17%, and polyvinyl chloride (PVC) was the slowest, only 17.1%. Similar to the stock, polypropylene (PP) was the plastic type with the largest waste volume. The waste volume in 2019 was 0.51 million tons, accounting for 31% of the total waste volume. Polyurethane (PU) was second, with 0.31 million tons of waste, 0.20 million tons of acrylonitrile-butadiene-styrene (ABS), 0.14 million tons of polyethylene (PE), and 0.15 million tons of other types of plastics. Of these types of plastics, polyoxymethylene (POM) had the lowest waste volume, at only 31,800 tons. At the regional level, 0.83 million tons of plastic were discarded in the eastern region in 2019, accounting for 50% of the total. The plastic waste in the central region was 0.42 million tons and only 0.40 million tons in the western region.
At the provincial level (Figure 3), Guangdong, Shandong, Hebei, Beijing, Liaoning, and Sichuan were the top six provinces in 2000. The waste amounts in these provinces ranged from 80 to 9525 tons, and the overall cardinality is small. The three provinces with the least amount of waste were Ningxia, Qinghai, and Tibet. Tibet has the least waste, with only 80 tons. It can be seen that there were certain differences in the amount of plastic waste from passenger vehicles between provinces, but the overall amount was small. The top six provinces in 2019 were: Shandong, Guangdong, Jiangsu, Zhejiang, Henan, and Hebei, most of which were eastern provinces. Among them, the plastic waste in Shandong was as high as 0.16 million tons, accounting for 9% of the total waste. Qinghai, Hainan, and Tibet were the three provinces with the least amount of waste. Tibet was still the lowest, with only 3094 tons, which was quite different from Shandong Province. The regional difference in plastic waste in 2019 is noticeable. From the perspective of the average annual growth rate, the province with the highest growth rate from 2000–2019 was Jiangsu, reaching 22.0%. The second was Anhui Province, with an average annual growth rate of 21.8%, and Jiangxi ranked third, with a growth rate of 21.7%. In addition, and the annual growth rate in Henan, Zhejiang, Ningxia, and 12 other provinces is also higher than the national level. The provinces with the lowest growth rate were Hainan, Shanghai, and Beijing, with only 13.3%, 12.4%, and 9.5%.
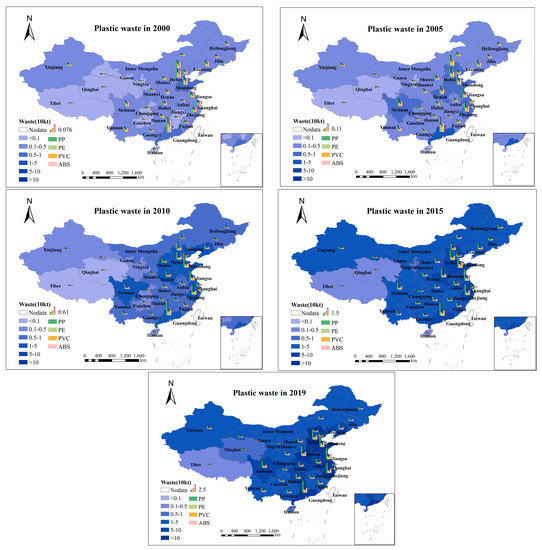
Figure 3.
Spatial distribution map of plastic wastes of passenger vehicle.
3.3. Spatiotemporal Evolution of Passenger-Vehicle Plastics Wastes across China
3.3.1. Spatiotemporal Distribution Pattern of Passenger-Vehicle Plastics Wastes across China
Table 3 shows a certain spatial autocorrelation in the amount of plastic waste from passenger vehicles in China. The Global Moran’s I for 2000, 2005, 2010, 2015, and 2019 were 0.186, 0.184, 0.295, 0.253, and 0.204, respectively, with p < 0.05. The Global Moran’s I results show an overall increasing trend, but the change range is small, which indicates that the plastic waste volume of passenger vehicles has an obvious positive correlation in space, and the degree of aggregation is increasing, but the overall stability is relatively stable. The reason is that the provinces in the same region have the same development and similar passenger-vehicle stock, which leads to the accumulation of plastic waste of passenger vehicles.

Table 3.
Global Moran’s I and p-value of passenger-vehicle plastic waste in China from 2000 to 2019.
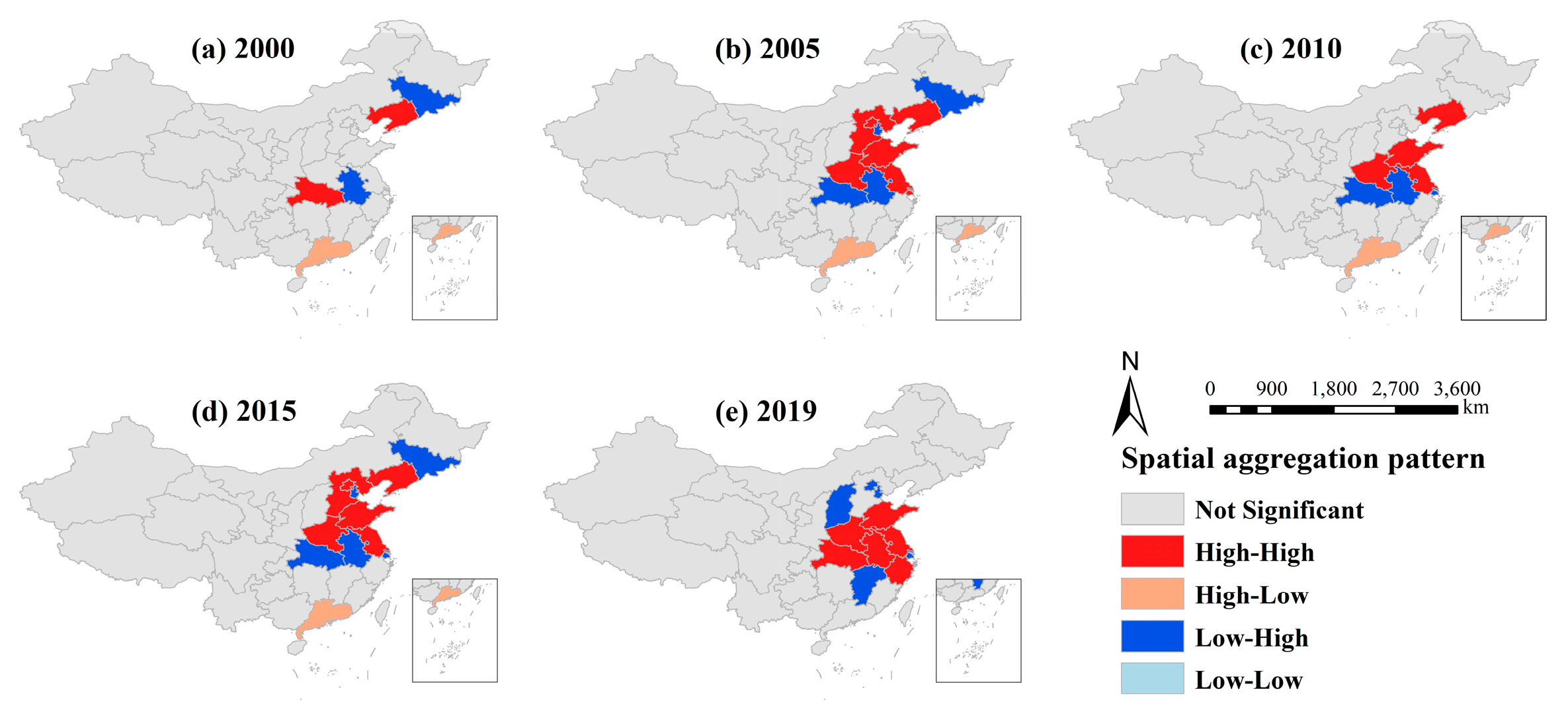
As we can see from Figure 4, Liaoning and Hubei showed a trend of high-high clustering, and Guangdong showed a high-low clustering in 2000. Anhui and Jilin showed a low-high clustering type, and the spatial correlation of other provinces was not significant. The high-high area expanded in the northeast direction in 2005, including six provinces and cities, comprising Henan, Hebei, Tianjin, Shandong, Jiangsu, Shanghai, and Liaoning. The low-high agglomeration area—Hubei, Anhui, Jilin, and Beijing—also expanded, High-low clustering was only observed in Guangdong Province, and the low-low agglomeration type did not appear. In 2010, the high-high agglomeration areas were: Henan, Jiangsu, Shandong, and Liaoning; Tianjin became a low-high agglomeration type, and a high-low agglomeration type area appeared in Guangdong in the same year, and other areas were still insignificant. By 2015, the clustering types of all provinces were basically consistent with those of 2005, while only Shanghai changed from high clustering to low and high clustering. The agglomeration area was relatively concentrated in 2019, mainly in the adjacent provinces. Henan, Shandong, Jiangsu, Anhui, Hebei, and Zhejiang showed high-high clustering, Shanghai and Tianjin were still low-high aggregation types, Tianjin, Shanxi and Jiangxi became low and high aggregation types for the first time, and the spatial correlation of other areas was insignificant.
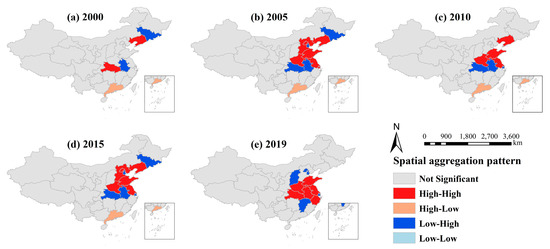
Figure 4.
Spatial agglomeration distribution of passenger-vehicles plastic waste in China from 2000 to 2019.
In general, the high-high agglomeration areas showed a trend of first expanding, then shrinking, and then expanding. In contrast, the low-low agglomeration areas were absent in all years, but there were more types of low-high aggregations. The aggregation area was mainly concentrated in the eastern region, the main aggregation type was high-high aggregation, and the western region showed no spatial autocorrelation. As the eastern region was close to the sea and was a pioneer regarding reform and opening up, its economy has developed rapidly. At the same time, it has driven the development of surrounding areas. The automobile industry developed rapidly, and the number of passenger vehicles was high, resulting in more waste plastics from passenger vehicles. The western region developed relatively late and showed a trend of uneven development. The population density was low, the overall vehicle ownership was relatively small, and the developmental level of different provinces showed a large gap, resulting in low spatial autocorrelation in the western region.
3.3.2. Trajectory of Center of Gravity for Passenger-Vehicle Plastics Waste across China
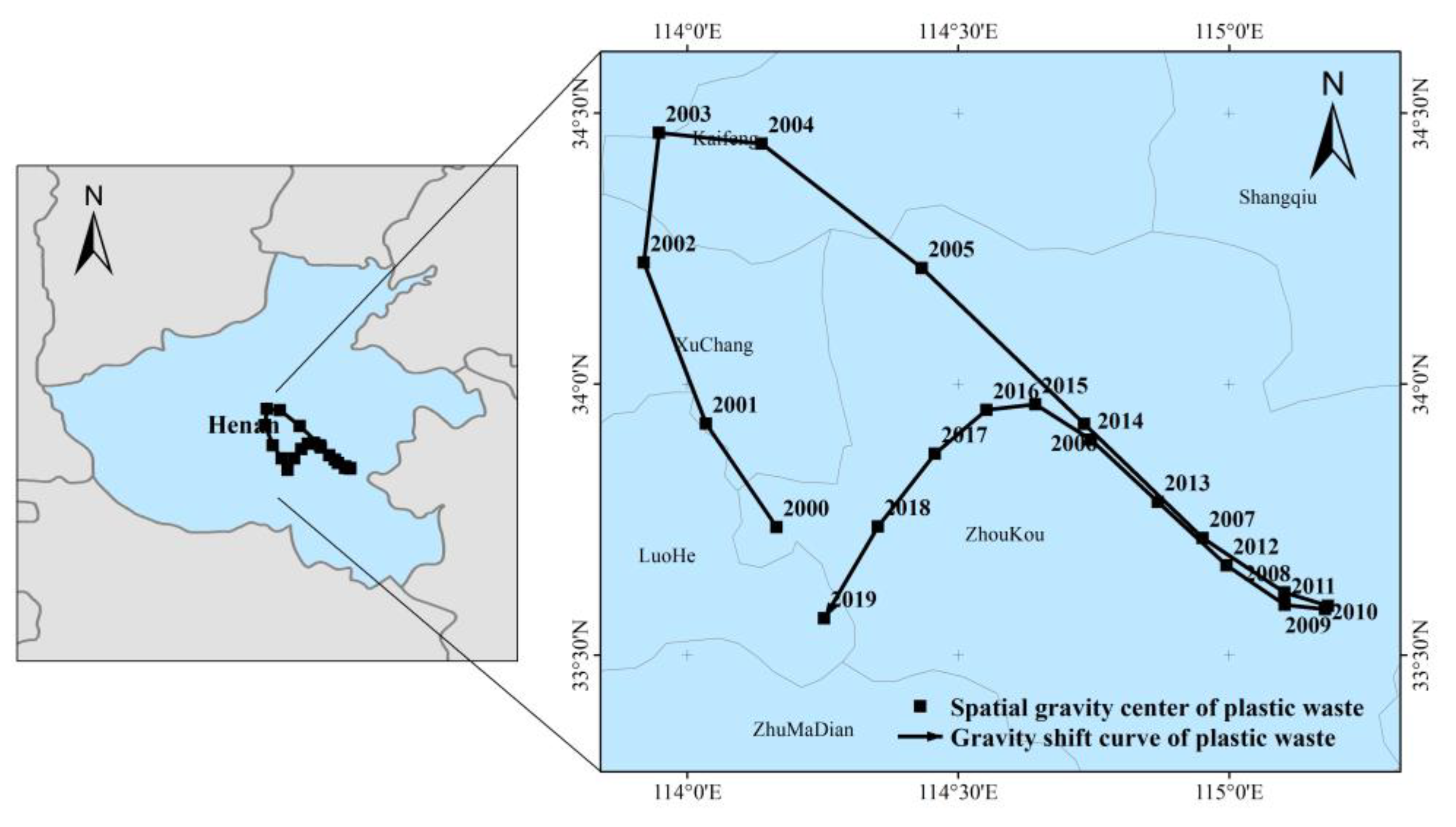
Figure 5 shows the trajectory of the spatial center of gravity of plastic waste from 2000 to 2019. Spatially, the amount of plastic waste was concentrated in the eastern region of China. All of these areas were in Henan province, mainly in Luohe, Zhoukou, Xuchang, and Kaifeng. The change in the spatial center of gravity of the plastic waste volume shifts from north to south, which was mainly divided into four stages. In the first stage, from 2000 to 2003, the spatial center of gravity of passenger-vehicle plastic waste in China was shifted to the northwest direction; in the second stage, from 2003 to 2010, the spatial center of gravity of passenger vehicle plastic waste in China was shifted to the southeast direction; in the third stage, from 2010 to 2016, the spatial center of gravity of passenger vehicle plastic waste China was also shifted to the northwest direction; and in the last stage, from 2016 to 2019, the spatial center of gravity of passenger-vehicle plastic waste in China was shifted to the southwest direction.

Figure 5.
The migration trajectory of the center of gravity of the passenger-vehicle plastic wastes.
The distance and direction of the spatial center of gravity shift in the amount of plastic waste in passenger vehicles basically exhibited a synchronous trend from 2000 to 2019 (Table 4), which showed a cyclical trend of first increasing and then decreasing. The spatial center of gravity of the amount of plastic waste in different periods constantly changes with the change in its direction, and the transfer distance was generally not far. The migration distance of the center of gravity was 24.62 km from 2000–2001, and then the migration distance decreased year by year, until 2004, when the migration distance dropped to the 17.26 km. After 2004, the center of gravity of passenger-vehicle plastic waste shifted in the southeast direction, while the distance of center of gravity migration showed a developing trend of increasing and then decreasing, reaching a minimum value in 2010. From 2010 to 2016, the spatial center of gravity migration distance of passenger-vehicle plastic waste volume first increased and then decreased, and most remained above 10 km. From 2016 to 2019, the distance of the spatial center of gravity shift began to increase, and it exhibited its maximum value in 2019.

Table 4.
Coordinates of the center of gravity and migration distance and direction of plastic waste of passenger vehicles from 2000 to 2019.
3.3.3. Spatiotemporal Evolutionary Tree of Passenger-Vehicle Plastic Wastes across China
The cities all showed a developing trend towards a higher stage (Figure 6). During the study period from 2000 to 2019, all cities developed rapidly, basically rising by two stages, and a few rising by one or three stages. In 2000, there were four cities in the first phase, of which three cities rose to the second phase in 2019, and only one city rose to the third phase. The number of cities in the second stage was the greatest, with 21. By 2019, only 1 city had risen to the third stage, 3 cities had risen to the fifth stage, and the remaining 17 cities had risen to the fourth stage. There were 5 cities in the third stage, and by 2019, 1 city rose to the fourth and sixth stages, and there were 3 cities that had risen to the fifth stage. The only city in the fourth stage in 2000 was Guangdong, which rose to the sixth stage in 2019. The cities that had risen by one stage were Hebei, Jiangsu, Gansu, Tibet, Qinghai, and Ningxia. The cities showing three stages of growth were Sichuan, Fujian, Hubei, and Hunan, and other provinces had risen by two stages.
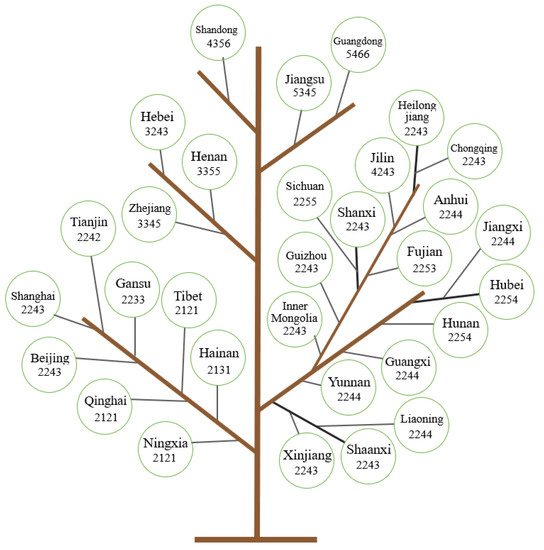
Figure 6.
Spatiotemporal evolutionary tree of passenger-vehicle plastic waste.
According to the results of cluster analysis, plastic waste from passenger vehicles was divided into five types in 2019, with the smallest gathering center of type 2 being 1.6325, followed by type 1, and the gathering center being 4.4424, with 11.2182 for type 3, and 13.3238 and 15.9144 for type 5 and 4, respectively. The average of the historical waste of passenger-vehicle plastics in six types of concentration centers and the stages of development and population in different types of cities (not representing the stages of development, but only the average of the values of the stages of development) is also calculated. In 2000, the averages for urban development stages were 2.0, 1.5, 2.7, 3.0, and 3.5, respectively. It can be seen that the average value of the development stage in 2000 was related to the historical waste amounts of passenger-vehicle plastics in the same type of gathering center; the larger the gathering center was, the larger the average value of the development stage; the smaller the gathering center was, the smaller the development stage average. In 2019, the average value of the urban development stage was 3.1 in the second stage, and the second stage was only 1.6325, which was also the smallest among the agglomeration centers. The fourth type, with the largest average developmental stage, also had the largest agglomeration center. Other stages were similar, with little overall difference. This shows that the amount of plastic waste in urban passenger vehicles was positively related to the GDP. Similarly, the average values of the stage of the population in 2019 were 3.5, 1.9, 4.3, 6.0, and 5.5, respectively, which corresponded to the size of the aggregation center of the type of passenger-vehicle plastic waste. It shows that there was also a positive correlation between the amount of plastic waste in urban passenger vehicles and the urban population.
3.4. Analysis of Driving Factors of Passenger-Vehicle Plastics Wastes
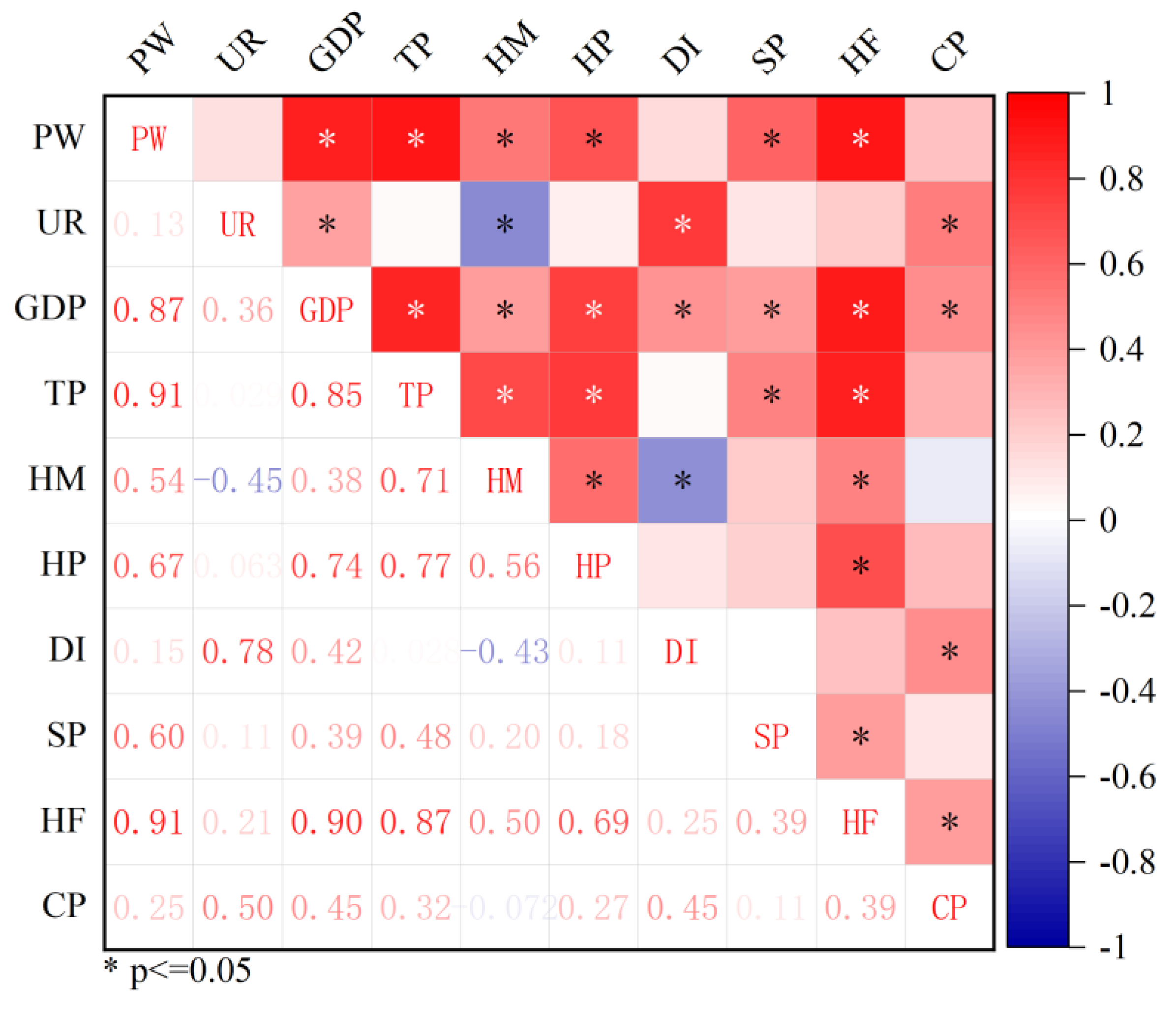
The correlation coefficient was obtained by Pearson correlation analysis on the plastic waste of passenger vehicles in different provinces in 2019 (Figure 7). The number of harmless treatment plants (0.91), the annual population (0.91), and the GDP (0.87) have a strong positive correlation with the volume of passenger-vehicle plastic waste. Highway passenger volume (0.67) and steel production (0.60) also have a positive correlation with passenger-vehicle plastic waste. Highway mileage (0.50), car production (0.24), and urban disposable income (0.15) were also positively correlated with passenger-vehicle plastic waste, but only weakly. The correlation coefficient of the urbanization rate was 0.13, and it was considered that there was no correlation with the amount of plastic waste.
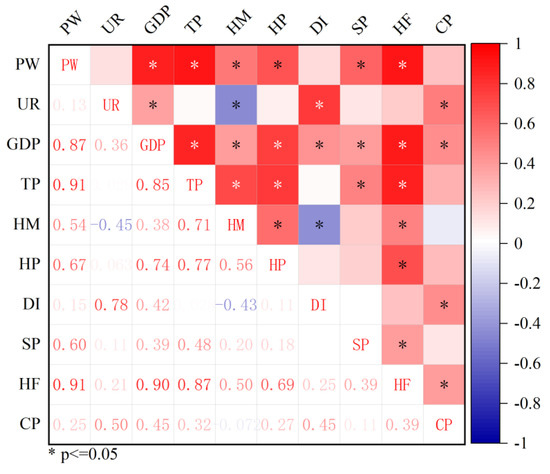
Figure 7.
Heat map of correlation analysis for different provinces of China in 2019.
The number of harmless treatment plants and the amount of plastic waste from passenger vehicles interact with each other. The more harmless treatment plants there were, the more waste the city can handle, and more harmless treatment plants should be built accordingly. When the GDP increases, the overall economic level of the province improves, which means that people’s living standards are better. The speed of vehicle replacement is accelerated, which promotes the growth of passenger-vehicle plastic waste. While the per capita number of passenger vehicles remains constant, the increase in population leads to an increase in the social stock of passenger vehicles, which also leads to an increase in the amount of plastic waste. While the per capita number of passenger vehicles remains constant, the increase in population leads to an increase in the social stock of passenger vehicles, which also leads to an increase in the amount of plastic waste. The increase in highway passenger traffic will affect the carrying capacity of passenger vehicles, thus aggravating the wear and tear of passenger vehicle parts, reducing the service life of passenger vehicles, and accelerating the scrapping of passenger vehicles. The main material of automobiles is steel, the increase in steel production led to an increase in the social stock of passenger vehicles, and the final result was the increase of waste plastics in passenger vehicles. Road mileage has little impact on the stock of passenger vehicles, and the correlation with the amount of plastic waste in passenger vehicles was not high. Taking into account the interaction of harmless treatment plants and plastic waste, it was not a driving factor for passenger-vehicle plastic waste. Therefore, the main driving factors on plastic waste (PW) from passenger vehicles are the annual population and GDP. Guangdong and Shandong had the most plastic waste in 2019. Meanwhile, according to the national bureau of statistics, Guangdong had the largest population and GDP in 2019, and Shandong had the second largest population. This confirms that GDP and population are the main drivers.
4. Discussions
The regional development of passenger-vehicle plastic stocks and waste was unbalanced. According to the estimation results of the material flow analysis, passenger-vehicle plastic stock and waste have grown rapidly across China in the past three decades. Jiang, Wang, Jiang, Xu and Zhu [24] estimated passenger-vehicle plastic stock to be 30.19 million tons in 2018, with a waste volume of 650,000 tons in China. Song et al. [49] estimated that the passenger-vehicle plastic stock would reach 0.6 billion tons and predicted that plastic waste could reach 2 million tons in 2020 under a short-life (12 years) scenario. Our estimate lies in between: the plastic stock grows from 260,000 tons to 40.22 million tons from 1985 to 2020, and the waste reaches 1.75 million tons in 2020. The difference between our results and others is caused by the different life settings of passenger vehicles. When the life of passenger vehicles increases, the amount of plastic waste will decrease accordingly. With the passage of time, the gap between the eastern and western regions has become larger and larger, showing a spatial pattern of more east and less west [50]. Zhang et al. [51] also showed that the eastern region has the largest percentage of abandoned passenger vehicles, consistent with our results. This may be caused by the economic gap between the east and west. The economy of the eastern region has developed rapidly, the automobile industry has developed rapidly, and the number of passenger vehicles is high, resulting in more waste plastics for passenger vehicles. The development of the western region is relatively late and the population density is low, resulting in less plastic waste of passenger vehicles in the western region.
Under the leadership of the reform and opening-up policy, the southeast coastal region has developed rapidly as a pilot area for China to implement opening up to the outside world over the past thirty years. As a result, the center of gravity for plastic waste has been in the eastern region. The western development strategy was formally proposed in 1999, and the western region began to rise, thus shifting the center of gravity to the west. China promulgated the second auto industry “Automobile Industry Development Policy” in 2004 [52], which for the first time combined the auto industry policy and the auto consumption policy into one. Under the guidance of this policy, the automobile industry in China has entered a rapid development stage. The north-south difference increased, the passenger-vehicle plastic waste space center of gravity continued to move south, and the center of gravity shift distance also increasing yearly. The financial crisis broke out in 2008, and the automobile industry in China faced a huge impact. There were more export-oriented production enterprises in the south, and they were more affected by the crisis. Since the spatial center of gravity of passenger-vehicle plastic waste has a certain lag in response to the macro environment, the distance between the spatial center of gravity of passenger-vehicle plastic waste has decreased year by year since 2009. The country entered a phase of economic transformation in 2012. Located in the inland mountainous region of southwest China, economic growth accelerated due to the development dividend brought by infrastructure investment. As a result, the center of gravity of passenger-vehicles plastic waste shifted to the southwest direction, and the speed of the shift became faster and faster as the new economic model took shape.
We suggest the following policy implications and recommendations for the country and society. Our results show that passenger-vehicle plastic waste is growing rapidly, reaching more than 1.64 million tons in 2019. With economic growth, the number of end-of-life vehicles will continue to grow in the next few decades [53,54], which will generate more waste plastics and exert greater pressure to recycle. Therefore, it is necessary to take corresponding measures and introduce relevant policies to slow down the growth of waste plastics, promote the recycling of waste plastics, and balance the regional differences in plastic waste. First, it is vital to improve the process related to automotive production by developing plastic materials that are recyclable, long-lived, easily degradable, and less polluting. The scientific selection of plastic materials for automobiles to facilitate sorting and recycling of waste plastics is also necessary. At the same time, vehicle owners should maintain good driving habits, strengthen the daily maintenance of vehicles, and appropriately extend the scrap life of vehicles while maintaining safety and good performance to increase the life of vehicles and slow down the growth of vehicle waste plastics. Second, it is necessary to strengthen the recycling of passenger-vehicle plastics, and the country needs to improve the relevant legal regulations and industrial policies. Furthermore, drawing on the waste plastic recycling technology of advanced countries, the pollution control and environmental management requirements of passenger-vehicle waste plastics are proposed from the consideration of the whole life cycle of the production, storage, treatment, and reuse of passenger-vehicle plastics, to improve the efficiency of plastic recycling and strengthen the pollution control capacity of waste plastics. Third, the difference between plastic waste in the east and west needs to be balanced: the ecological environment in western China is much worse than that in eastern China, which requires a large amount of plastic films, irrigation facilities, and plastic pipes. There are few harmless treatment plants or circular economy industrial parks in the western region, so circular economy industrial parks should be built there. A portion of the recyclable waste plastics in the eastern region should then be transported to the west for processing, balancing the resource differences between east and west, and maximizing the recycling and utilization of waste plastics.
5. Conclusions
In this study, material flow analysis and the life distribution model are combined to estimate the stock and waste of various passenger-vehicle plastics in China from 1985 to 2019 (35 years). Spatial autocorrelation analysis and center of gravity transfer models were used to reveal the spatiotemporal evolution trend of the plastic waste of passenger vehicles. The driving factors regarding passenger-vehicle plastics are also analyzed. Our results showed a rapid growth in stocks and waste of passenger-vehicle plastics. In 2019, the stocks reached more than 30 million tons, and the waste volume reached more than 1.5 million tons. The east-west gap has grown over time, with the eastern region holding the majority of passenger-vehicle plastic stock and waste. In addition, due to the inconsistent level of economic development, the spatial center of gravity of plastic waste moves from north to south. The GDP and the annual population are the main driving factors of the amount of passenger-vehicle plastic waste. The growth of the GDP and the annual population both promote the amount of passenger-vehicle plastic waste.
The quantitative analysis in our study provides data support for the plastic recycling industry. Moreover, the study of the spatiotemporal evolution of plastics provides a theoretical basis for the layout of a circular economy, and the analysis of the driving factors provides a scientific basis for predicting passenger-vehicle plastic waste. We also put forward some suggestions for the problem of the large-scale and unbalanced development of waste plastics for passenger vehicles. In addition, with the development of science and technology and the requirements of lightweight automobiles, the materials and lifespan of passenger vehicles will change. To further improve the estimation, considering the service life of different types of passenger vehicles, more detailed data is required for future research.
Author Contributions
Y.C. and H.K.: conceptualization and methodology; Y.Q.: verification and writing—original draft; Y.C. and H.K.: supervision and writing—reviewing and editing; X.Y.: re-sources and investigation. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the Hunan Province High-Tech Achievement Transformation and Industrialization Project (No. 2020SK2007) and the Jiangxi University Humanities and Social Sciences Research Project (No. JC20105).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not Applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not Applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data will be available upon request from corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
References
- Karimian, H.; Li, Y.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Z. Evaluation of different machine learning approaches and aerosol optical depth in PM(2.5) prediction. Environ. Res. 2023, 216 Pt 2, 114465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baladi, E.; Davar, F.; Hojjati-Najafabadi, A. Synthesis and characterization of g–C3N4–CoFe2O4–ZnO magnetic nanocomposites for enhancing photocatalytic activity with visible light for degradation of penicillin G antibiotic. Environ. Res. 2022, 215, 114270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hojjati-Najafabadi, A.; Rahmanpour, M.S.; Karimi, F.; Zabihi-Feyzaba, H.; Malekmohammad, S.; Agarwal, S.; Gupta, V.K.; Khalilzadeh, M.A. Determination of tert-butylhydroquinone using a nanostructured sensor based on CdO/SWCNTs and ionic liquid. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci 2020, 15, 6969–6980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Li, D.; Karimian, H.; Wang, S.; Fang, S. The relationship between air quality and MODIS aerosol optical depth in major cities of the Yangtze River Delta. Chemosphere 2022, 308 Pt 2, 136301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Wang, C.; Zhou, P. GVRP considered oil-gas recovery in refined oil distribution: From an environmental perspective. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2021, 235, 108078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Liang, X.S.; Jiang, T. Analyzing the characteristics of soil moisture using GLDAS data: A case study in eastern China. Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haibin, L.; Xie, J.; Xu, J.; Chen, Z.; Liu, T.; Cai, S. Force and torque exerted by internal solitary waves in background parabolic current on cylindrical tendon leg by numerical simulation. Ocean Eng. 2016, 114, 250–258. [Google Scholar]
- Hojjati-Najafabadi, A.; Aygun, A.; Tiri, R.N.E.; Gulbagca, F.; Lounissaa, M.I.; Feng, P.; Karimi, F.; Sen, F. Bacillus thuringiensis Based Ruthenium/Nickel Co-Doped Zinc as a Green Nanocatalyst: Enhanced Photocatalytic Activity, Mechanism, and Efficient H2 Production from Sodium Borohydride Methanolysis. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2023, 62, 4655–4664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Korey, M.; Li, K.; Copenhaver, K.; Tekinalp, H.; Celik, S.; Kalaitzidou, K.; Ruan, R.; Ragauskas, A.J.; Ozcan, S. Plastic waste upcycling toward a circular economy. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 428, 131928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allwood, J.M.; Ashby, M.F.; Gutowski, T.G.; Worrell, E. Material efficiency: A white paper. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2011, 55, 362–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, M.; Cheng, Y.; Li, Q.; Wang, C.; Fang, X.; Yu, J. An effective method for submarine buried pipeline detection via multi-sensor data fusion. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 125300–125309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.D.; Cui, Z.J.; Cui, X.W.; Liu, W.; Wang, X.L.; Li, X.X.; Li, S.X. Life cycle assessment of end-of-life treatments of waste plastics in China. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2019, 146, 348–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.C.; Zuo, J.; Duan, X.G.; Wang, S.B.; Hu, K.S.; Chang, R.D. Impacts and mitigation measures of plastic waste: A critical review. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2021, 90, 106642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, D.; Chu, J.; Han, Q.; Liu, X. How land finance drives urban expansion under fiscal pressure: Evidence from Chinese cities. Land 2022, 11, 253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, X.; Zhang, S.; Li, C.; Xiong, L.; Song, F.; Du, C.; Li, M.; Luo, Q.; Xue, Y.; Wang, S. A carbon neutrality capacity index for evaluating carbon sink contributions. Environ. Sci. Ecotechnol. 2023, 15, 100237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Farzana, R.; Rajarao, R.; Sahajwalla, V. Lightweight expanded aggregates from the mixture of waste automotive plastics and clay. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 145, 283–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.D. Development of Automotive Plastics in China. China Plast. 2004, 18, 2. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, M.; Behrens, P.; Wang, T.; Tang, Z.; Zhu, B. Provincial and sector-level material footprints in China. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 26484–26490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Yu, P.; Lu, J.; Zhang, Y. The mediation effect of land surface temperature in the relationship between land use-cover change and energy consumption under seasonal variations. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 340, 130804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, M.Y.; Zhu, L.X.; An, L.H.; Peng, G.Y.; Li, D. Estimation and prediction of plastic waste annual input into the sea from China. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2018, 37, 26–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciacci, L.; Passarini, F.; Vassura, I. The European PVC cycle: In-use stock and flows. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2017, 123, 108–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Liu, Z.; Karimian, H.; Wang, Z. Mapping the social stock and spatiotemporal distribution of high-tech minerals from wasted mobile phones in China: 2001–2019. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2022, 30, 34306–34318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Yang, N.; Hu, S. Industrial metabolism of PVC in China: A dynamic material flow analysis. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2013, 73, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Wang, T.; Jiang, M.; Xu, M.; Zhu, B. Assessment of plastic stocks and flows in China: 1978–2017. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2020, 161, 104969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ileana, B.; Viviana, L.R.; Carmela, S.; Evelia, S.; Giuliano, V. Agricultural plastic waste mapping using GIS. A case study in Italy. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2018, 137, 229–242. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, Y.V.; Jiang, P.; Tan, R.R.; Aviso, K.B.; Kleme, J.J. Forecasting Plastic Waste Generation and Interventions for Environmental Hazard Mitigation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 424, 127330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Song, L.; Peng, Z.; Yang, J.; Luan, G.; Chu, C.; Ding, J.; Feng, S.; Jing, Y.; Xie, Z. Night-time light remote sensing mapping: Construction and analysis of ethnic minority development index. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Li, Q.; Hou, J.; Karimian, H.; Chen, G. PM2. 5 concentration prediction using convolutional neural networks. Sci. Surv. Mapp. 2018, 43, 68–75. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Z.; Mo, J.; Xiang, Y.; Shan, W. Plastic Industry’s Provincial Comparative Advantages and the Spatial Evolution of Scales of Economy in China from the Perspective of the Belt and Road Initiative. J. Jianghan Univ. (Soc. Sci. Ed.) 2019, 36, 65–81. [Google Scholar]
- Cardamone, G.F.; Ardolino, F.; Arena, U. Can plastics from end-of-life vehicles be managed in a sustainable way? Sustain. Prod. Consum. 2022, 29, 115–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.H.; Chen, M. Automotive plastic parts design, recycling, research, and development in China. J. Thermoplast. Compos. Mater. 2014, 28, 142–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahimi, M.; Mobasherpour, I.; Bafrooei, H.B.; Bidabadi, F.S.; Mansoorianfar, M.; Orooji, Y.; Khataee, A.; Mei, C.; Salahi, E.; Ebadzadeh, T. Taguchi design for optimization of structural and mechanical properties of hydroxyapatite-alumina-titanium nanocomposite. Ceram. Int. 2019, 45, 10097–10105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimian, H.; Li, Q.; Chen, H.F. Assessing Urban Sustainable Development in Isfahan. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2012, 253–255, 244–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Kong, M.; Tong, D.; Zeng, X.; Lai, Y. Property rights and adjustment for sustainable development during post-productivist transitions in China. Land Use Policy 2022, 122, 106379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.Q. Brand structure analysis of the passenger car market in China. Shanghai Auto. 2006, 8, 22–24. [Google Scholar]
- Graedel, T.E. Material Flow Analysis from Origin to Evolution. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 12188–12196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rostkowski, K.; Rauch, J.; Drakonakis, K.; Reck, B.; Gordon, R.B.; Graedel, T.E. “Bottom–up” study of in-use nickel stocks in New Haven, CT. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2007, 50, 58–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krausmann, F.; Wiedenhofer, D.; Lauk, C.; Haas, W.; Tanikawa, H.; Fishman, T.; Miatto, A.; Schandl, H.; Haberl, H. Global socioeconomic material stocks rise 23-fold over the 20th century and require half of annual resource use. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 1880–1885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, W.; Wan, L.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, C.; Lin, L. Short-Lived Buildings in China: Impacts on Water, Energy, and Carbon Emissions. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 13921–13928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Han, J.; Chen, W.Q. Changing patterns and determinants of infrastructures’ material stocks in Chinese cities. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2015, 123, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Commerce of the People’s Republic of China. Regulation on Compulsory Scrapping Standards for Motor Vehicles. Available online: http://www.mofcom.gov.cn/article/swfg/swfgbh/201303/20130300062947.shtml (accessed on 15 March 2023).
- Chen, Y.; Li, H.; Karimian, H.; Li, M.; Fan, Q.; Xu, Z. Spatio-temporal variation of ozone pollution risk and its influencing factors in China based on Geodetector and Geospatial models. Chemosphere 2022, 302, 134843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Liu, H.; Tang, Q. Interprovincial migration in China,1985–2005: A gravity modeling approach. Chin. J. Popul. Resour. Environ. 2014, 12, 146–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, X.H.; Duan, X.J.; Hui, L.I.; Tian, F. The Spatial Structure of The Population’s Education Quality and Its Evolution and Affect on Economic Development in China. Econ. Geogr. 2008, 5, 779–783. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, X.W.; Feng, Z.J.; Ge, J.F. Analysis of Landscape Security Pattern in Western Mountains of Shijiazhuang. In Proceedings of the Geoinformatics 2008 and Joint Conference on GIS and Built Environment, Guangzhou, China, 28–29 June 2008; SPIE: Bellingham, DC, USA, 2008; Volume 7145, pp. 71451P–71451P-8. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.F.; Liu, X.H.; Peng, L.; Chen, H.Y.; Zheng, D. Cities evolution tree and applications to predicting urban growth. Popul. Environ. 2012, 33, 186–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimian, H.; Zou, W.; Chen, Y.; Xia, J.; Wang, Z. Landscape ecological risk assessment and driving factor analysis in Dongjiang river watershed. Chemosphere 2022, 307, 135835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.L.; Li, Q.; Karimian, H.; Chen, X.J.; Li, X.M. Spatio-temporal distribution characteristics and influencing factors of COVID-19 in China. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 3717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, L.L.; Wang, P.; Hao, M.; Dai, M.; Xiang, K.Y.; Li, N.; Chen, W.Q. Mapping provincial steel stocks and flows in China: 1978–2050. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 262, 121393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Li, Z.; Fu, X.; Liu, X.; Li, Z.; Zheng, W. Impact of power on uneven development: Evaluating built-up area changes in Chengdu based on NPP-VIIRS images (2015–2019). Land 2022, 11, 489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Lu, Q.Q.; Yuan, W.; Jiang, S.Y.; Wu, H.J. Characterizing end-of-life household vehicles’ generations in China: Spatial-temporal patterns and resource potentials. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2022, 177, 105979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Development and Reform Commission of China. Automobile Industry Development Policy. Available online: https://www.ndrc.gov.cn/xxgk/zcfb/fzggwl/200506/t20050614_960627.html?code=&state=123 (accessed on 15 March 2023).
- Li, Y.; Liu, Y.H.; Chen, Y.; Huang, S.Y.; Ju, Y.Y. Projection of end-of-life vehicle population and recyclable metal resources: Provincial-level gaps in China. Sustain. Prod. Consum. 2022, 31, 818–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.Z.; Chen, X.H.; Zhang, M.Y.; Lv, X.Q.; Wang, H.H.; Chen, Z.Z.; Huang, X.R.; Zhang, X.X.; Zhang, S.R. End-of-life passenger vehicles recycling decision system in China based on dynamic material flow analysis and life cycle assessment. Waste Manag. 2020, 117, 81–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).