Risk Management of Supply Chain Green Finance Based on Sustainable Ecological Environment
Abstract
:1. Introduction
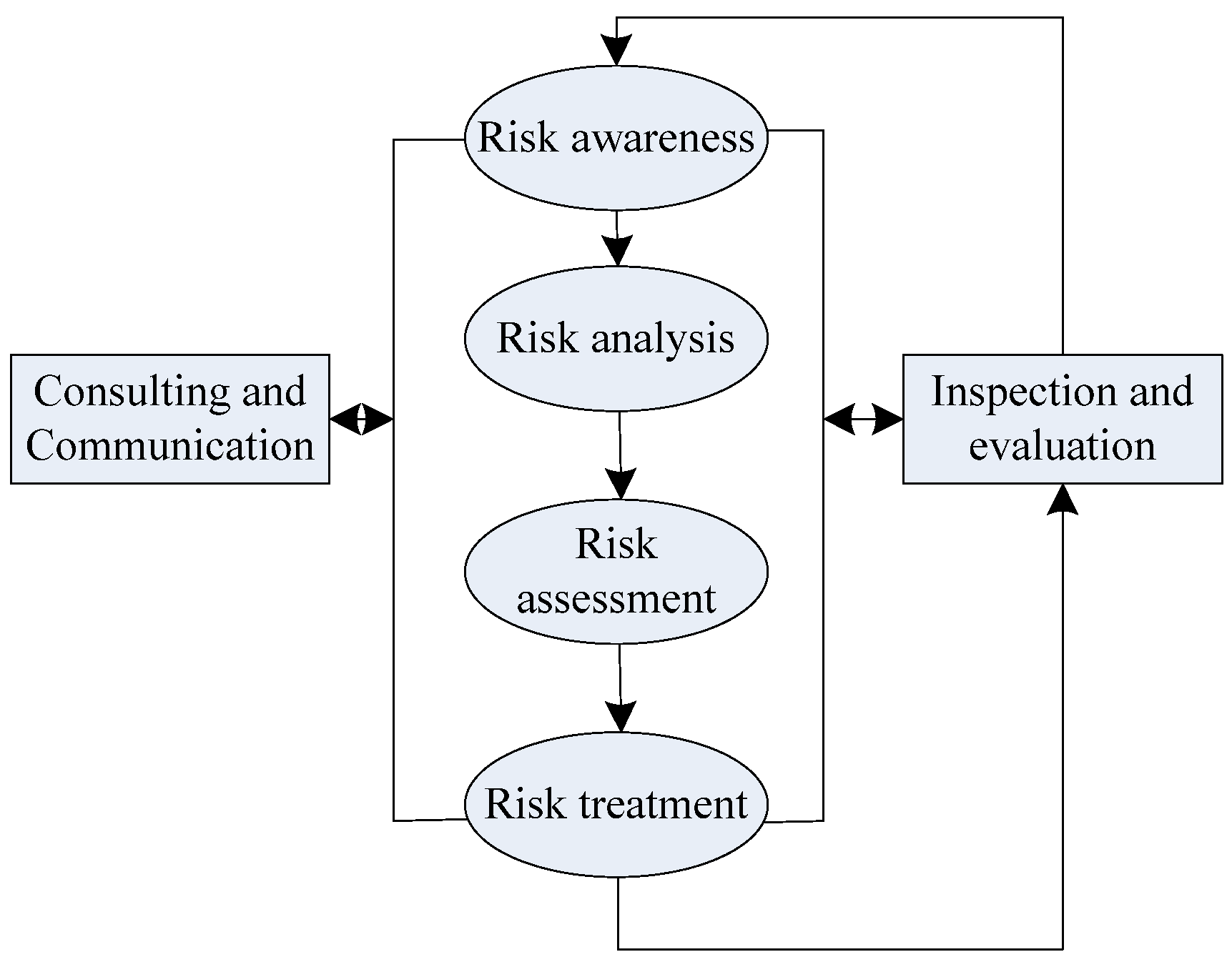
2. Risk Management Methods of Supply Chain Green Finance under Sustainable Ecology
2.1. Green Finance
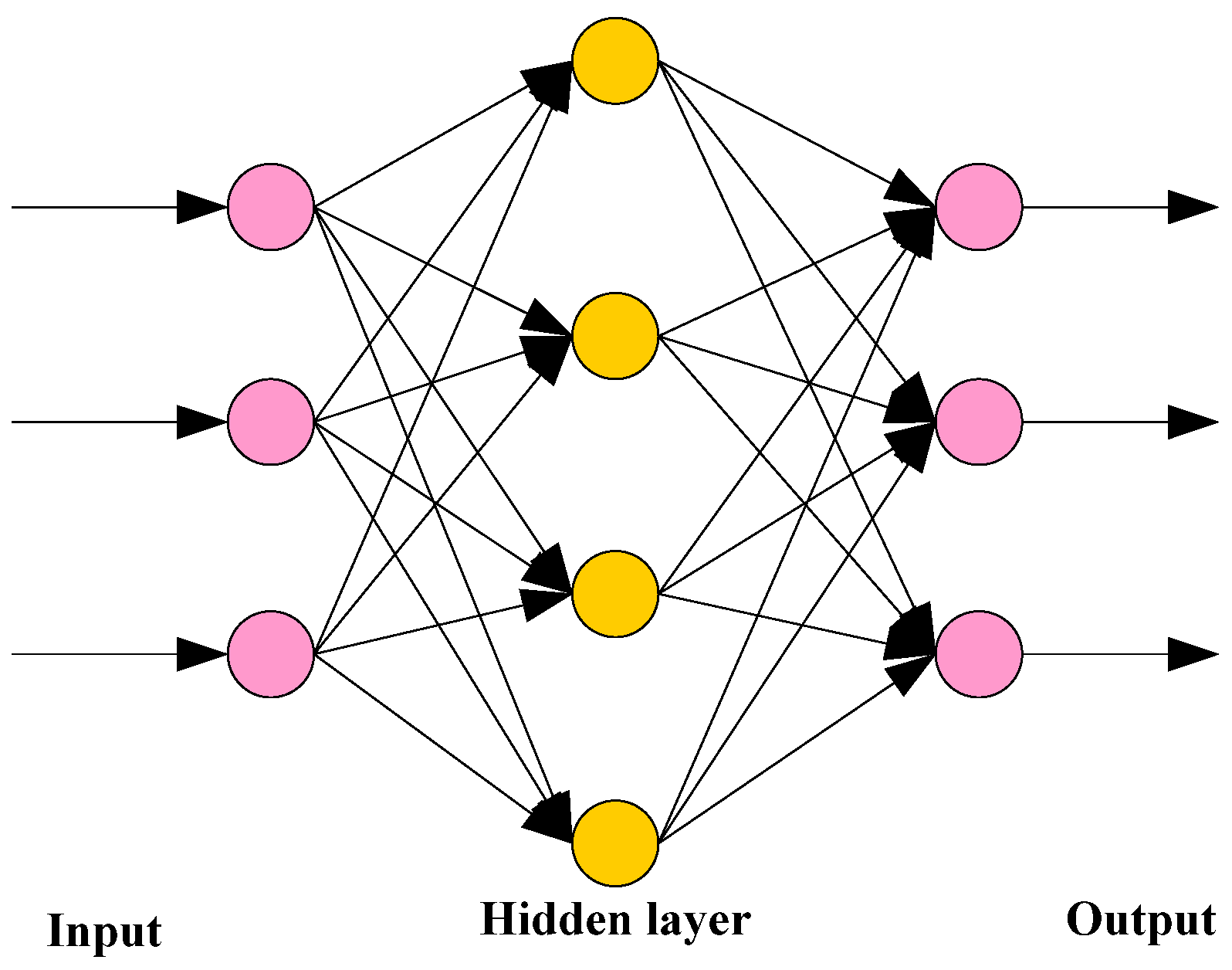
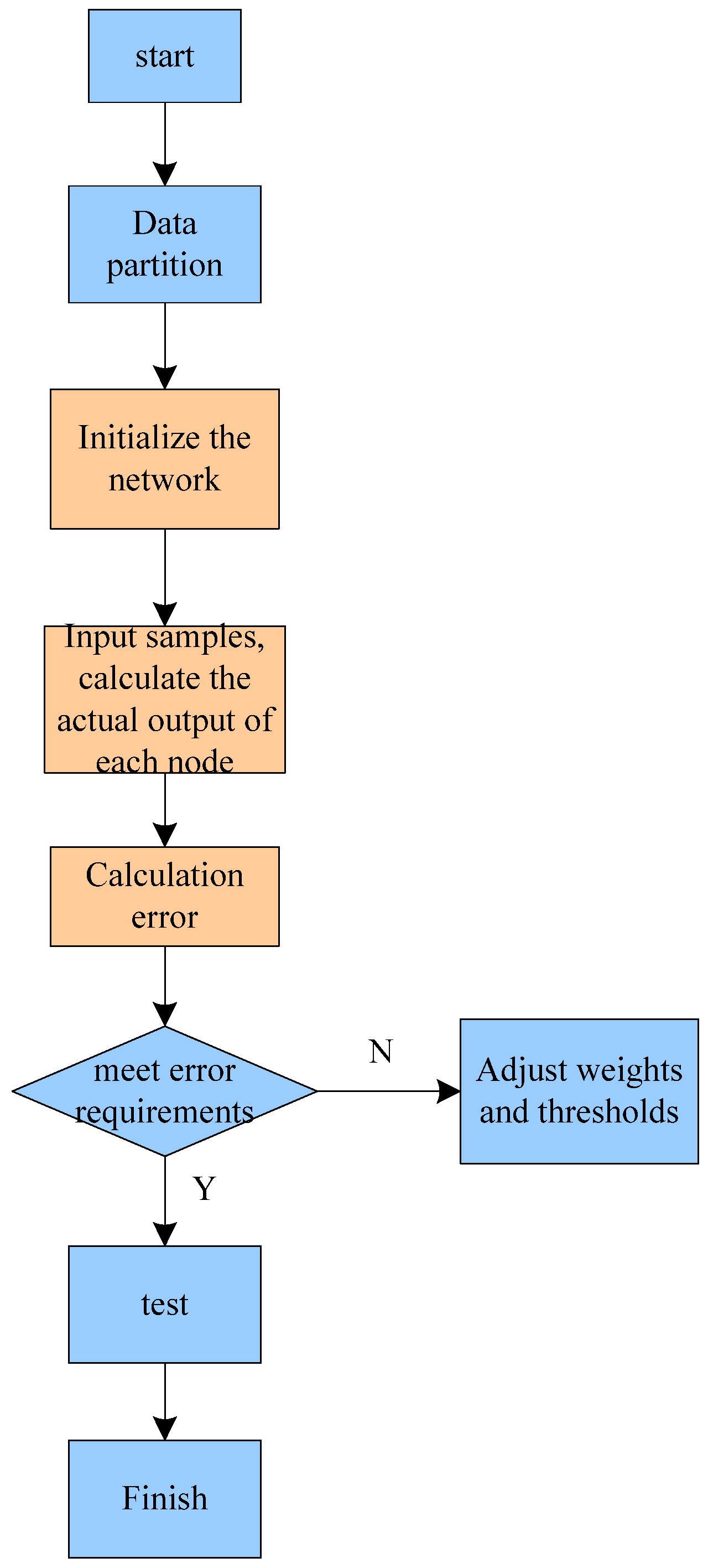
2.2. Research on BP Neural Network under Supply Chain Green Financial Risk Management
- (1)
- Define variables
- (2)
- Forward propagation
- (3)
- Back propagation of error signal
3. Experimental Analysis on Green Financial Risk Management of Sustainable Ecological Supply Chain under BP Neural Network
3.1. Reasons for Risk Management of Green Finance
- (1)
- The indicators cover a wide range. Supply chain green finance business involves various trade financial institutions, agricultural institutions, and other organizations. Analyzing only one aspect can easily lead to biased risk assessments. Therefore, this paper combines the characteristics of each topic and discusses the impact of the financial business on supply chain green finance from different aspects.
- (2)
- The indicators are independent of each other. For the credit risk assessment activities of financial companies in the supply chain, if there is a correlation between the indicators, the accuracy of the financial risk assessment would decrease, and the significance of risk assessment would be lost.
- (3)
- Indicators have relative weights. In empirical research, the selection of indicators should be comprehensive and focused, and indicators and variables should be reasonably selected according to theoretical and actual conditions. Therefore, this paper focuses on the relevant links of the supply chain when selecting the risk assessment indicators for supply chain green finance.
- (4)
- The selection of indicators should be scientific. When conducting experimental analysis, the identification and measurement of indicators and variables is not only theoretical, but must also be scientifically conducted in consideration of the actual situation. This paper fully considers the guiding principles of theory and practical operation when selecting supply chain financial risk assessment indicators, which makes the construction of a supply chain financial rating system more complete.
3.2. Experimental Data
- (1)
- Extraction factor
- (2)
- Factor naming and scoring


3.3. Suggestions on the Sustainable Development of Supply Chain Green Finance Risk Management
- (1)
- Establishing a sound enterprise risk prevention and protection mechanism
- (2)
- Improving market forecasting ability and risk early warning mechanism
- (3)
- Improving supply chain management and strengthening cooperation between green financial enterprises in the supply chain.
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Iwedi, M.; Anderson, O.E.; Barisua, P.S.; Zaagha, S.A. Enterprise risk management practice and shareholders value: Evidence from selected quoted firms in Nigeria. Green Financ. 2020, 2, 197–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jadoon, I.A.; Mumtaz, R.; Sheikh, J.; Ayub, U.; Tahir, M. The impact of green growth on financial stability. J. Financ. Regul. Compliance 2021, 29, 533–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veelen, B.V. Cash cows? Assembling low-carbon agriculture through green finance. Geoforum 2021, 118, 130–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.H.; Lai, K.P. Ecologies of green finance: Greensukukand development of green Islamic finance in Malaysia. Environ. Plan. A Econ. Space 2021, 53, 1896–1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afridi, F.; Jan, S.; Ayaz, B.; Irfan, M. Green finance incentives: An empirical study of the Pakistan banking sector. Rev. Amazon. Investig. 2021, 10, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alieva, I.A.; Altunina, V.V. Current trends in the development of a green finance system: Methodology and practice. Baltic Reg. 2021, 13, 64–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Hu, D.; Yang, C.; Tan, Y. The impact and mechanism of fintech on green total factor productivity. Green Financ. 2021, 3, 198–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colombo, E. From Bushfires to Misfires: Climate-related Financial Risk after McVeigh v. Retail Employees Superannuation Trust. Transnatl. Environ. Law 2022, 11, 173–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X. Research on the Influencing Factors of Internet Financial Risk and Its Prevention Mechanism. Mod. Econ. Manag. Forum 2022, 3, 20–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ermakova, E.P. The Development of The Legal Framework For “Green” Finance In Russia, The EU And China: A Comparative Legal Analysis. Rudn. J. Law 2020, 24, 335–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Song, J.; Wu, H.; Gu, X.; Shi, L. Impact of Financial Technology on Regional Green Finance. Comput. Syst. Sci. Eng. 2021, 39, 391–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junior, W.G.; Kim, B.; Liu, L.; Lai, X. Green Economy Game: A Modular Approach for Sustainable Development Education. Int. J. Des. Learn. 2020, 11, 96–107. [Google Scholar]
- He, Z.; Liu, Z.; Wu, H.; Gu, X.; Yue, X. Research on the Impact of Green Finance and Fintech in Smart City. Complexity 2020, 2020, 6673386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Li, Y.; Jiang, X. Research on the Impacts of Green Finance towards the High-Quality Development of China’s Economy—Mechanisms and Empirical Analysis. Theor. Econ. Lett. 2020, 10, 1338–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claar, S. Green Finance and Transnational Capitalist Classes—Tracing Vested Capital Interests in Renewable Energy Investment in South Africa. J. Entwickl. JEP 2020, 36, 110–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawabata, T. Private governance schemes for green bond standard: Influence on public authorities’ policy making. Green Financ. 2020, 2, 35–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, B.; Bakhshi, P. Green Finance: Fostering Sustainable Development in India. Int. J. Recent Technol. Eng. 2019, 8, 2277–3878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslanishvili, D.; Omadze, K. Green Economy and Access to Finance in Georgia (Going Beyond the Commercial Banking Sector to Finance Businesses in Georgia). J. Econ. Bus. 2019, 2, 761–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novkovska, B. Relationship between shadow and green economy: Less shadow more green. Green Financ. 2019, 1, 130–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, G.L. The allocation of risk and uncertainty in green infrastructure investment with implications for climate change policy. J. Sustain. Financ. Invest. 2019, 9, 116–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakai, K.; Hassan, M.A.; Vairappan, C.S.; Shirai, Y. Promotion of a green economy with the palm oil industry for biodiversity conservation: A touchstone toward a sustainable bioindustry. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2022, 133, 414–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanizdra, M.Y.; Harkushenko, O.M.; Vishnevsky, V.; Kniaziev, S.I. Digital and Green Economy: Common Grounds and Contradictions. Sci. Innov. 2021, 17, 14–27. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, C.; Chen, M. Regional Ecological Security Evolution and Green Economy: An Empirical Study. Math. Probl. Eng. 2021, 2021, 5549048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobby, M.N.; Indira, M.; Peele, K.A.; Venkatesw, T.C.; Krupanidhi, S. Sustainable Nutritional Supplementation for Green Economy through Hydroponics System. Indian J. Ecol. 2021, 48, 85–90. [Google Scholar]

| Element | Initial Eigenvalues | Decimate Sum of Squares and Load | Rotate Square and Load | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | Proportion of Variance | Grand Total % | Total | Proportion of Variance | Grand Total % | Total | Proportion of Variance | Grand Total % | |
| 1 | 6.65 | 19.918 | 19.918 | 6.65 | 19.918 | 19.918 | 4.396 | 13.115 | 13.115 |
| 2 | 4.26 | 12.676 | 32.492 | 4.26 | 12.676 | 32.492 | 4.226 | 12.599 | 25.62 |
| 3 | 2.838 | 8.394 | 40.783 | 2.838 | 8.394 | 40.783 | 3.831 | 11.398 | 36.908 |
| 4 | 2.512 | 7.407 | 48.087 | 2.512 | 7.407 | 48.087 | 2.917 | 8.633 | 45.439 |
| 5 | 2.21 | 6.432 | 54.417 | 2.21 | 6.432 | 54.417 | 2.318 | 6.816 | 52.153 |
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Roa | 0.726 | −0.145 | 0.07 | 0.39 | 0.198 |
| Accounts Receivable Turnover | −0.031 | 0.858 | −0.056 | −0.124 | −0.242 |
| Management level | −0.015 | −0.145 | 0.863 | 0.006 | 0.098 |
| Bank credit rating | 0.212 | −0.014 | 0.218 | 0.784 | 0.095 |
| Financial rules | 0.047 | 0.071 | −0.033 | 0.019 | 0.88 |
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Return on assets | 0.171 | 0.012 | −0.016 | 0.124 | 0.109 |
| Accounts Receivable Turnover | 0.214 | 0.016 | 0.021 | 0.023 | 0.011 |
| management level | 0.005 | 0.045 | 0.28 | −0.057 | 0.045 |
| bank credit rating | 0.005 | 0.055 | 0.025 | 0.296 | 0.081 |
| financial rules | 0.027 | 0.006 | −0.008 | 0.043 | 0.414 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, H. Risk Management of Supply Chain Green Finance Based on Sustainable Ecological Environment. Sustainability 2023, 15, 7707. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15097707
Zhao H. Risk Management of Supply Chain Green Finance Based on Sustainable Ecological Environment. Sustainability. 2023; 15(9):7707. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15097707
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Hailei. 2023. "Risk Management of Supply Chain Green Finance Based on Sustainable Ecological Environment" Sustainability 15, no. 9: 7707. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15097707
APA StyleZhao, H. (2023). Risk Management of Supply Chain Green Finance Based on Sustainable Ecological Environment. Sustainability, 15(9), 7707. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15097707





