A Bidirectional Grid-Friendly Charger Design for Electric Vehicle Operated under Pulse-Current Heating and Variable-Current Charging
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. A Novel Bidirectional Grid-Friendly EV Charger
2.1. The Overall Framework
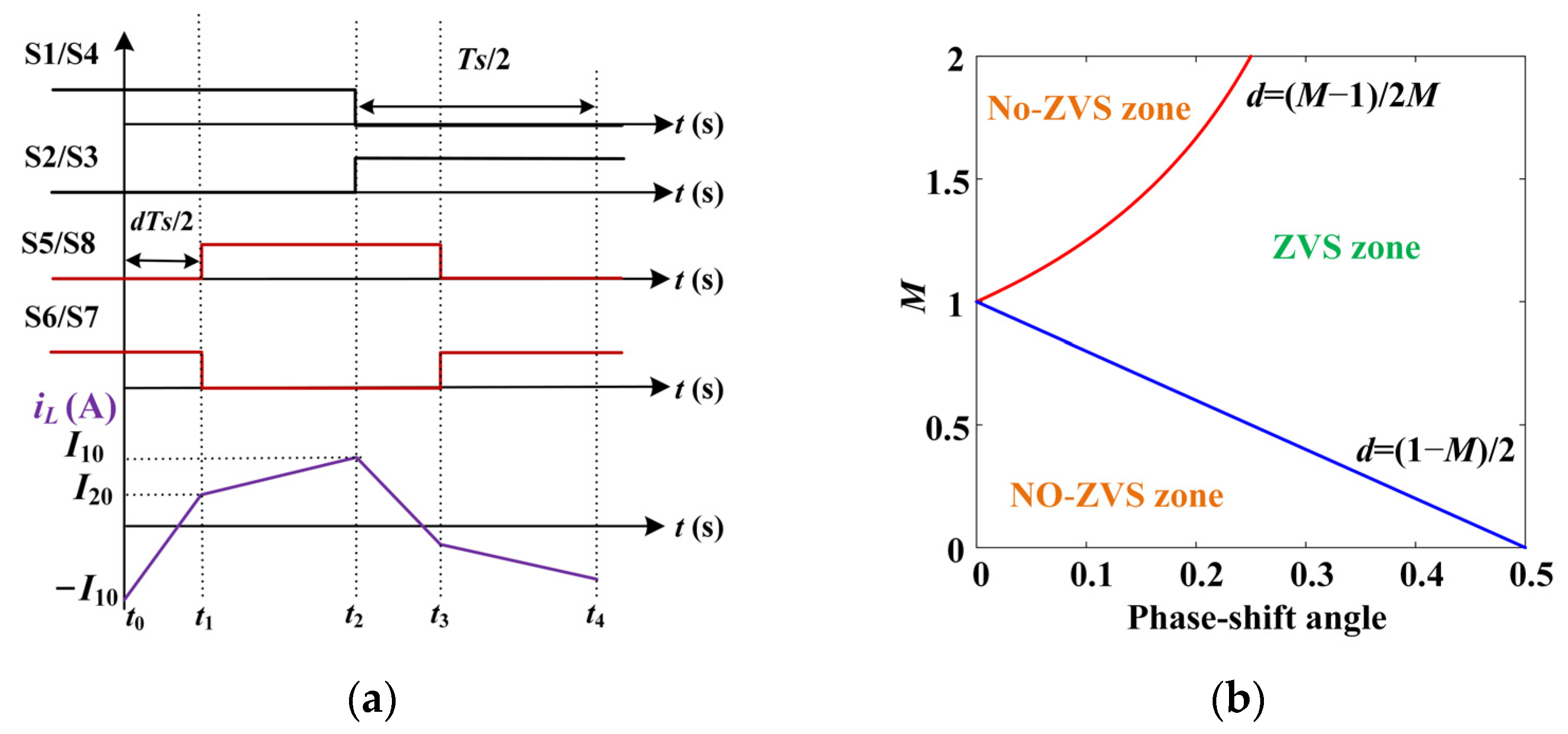
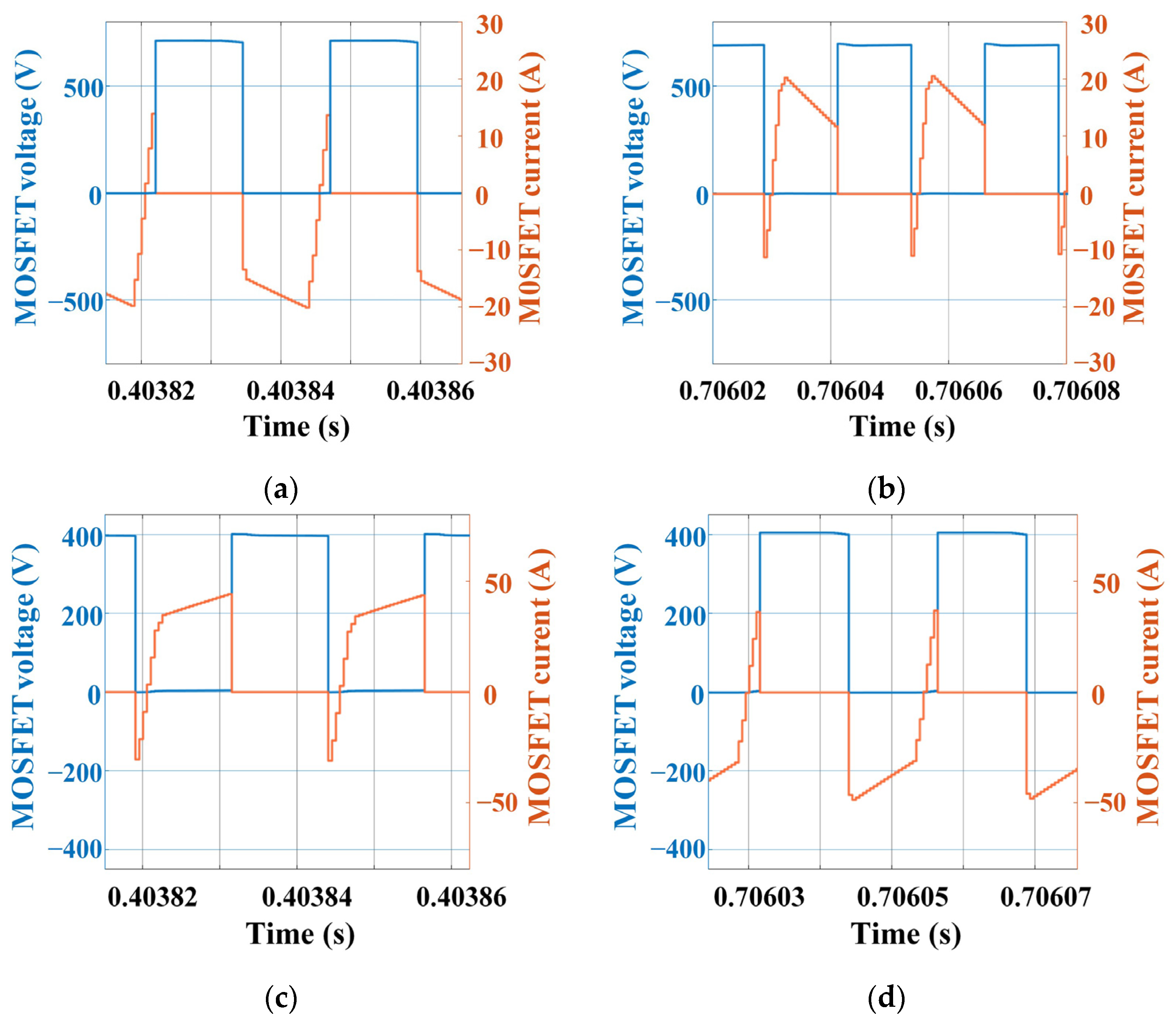
2.2. DAB
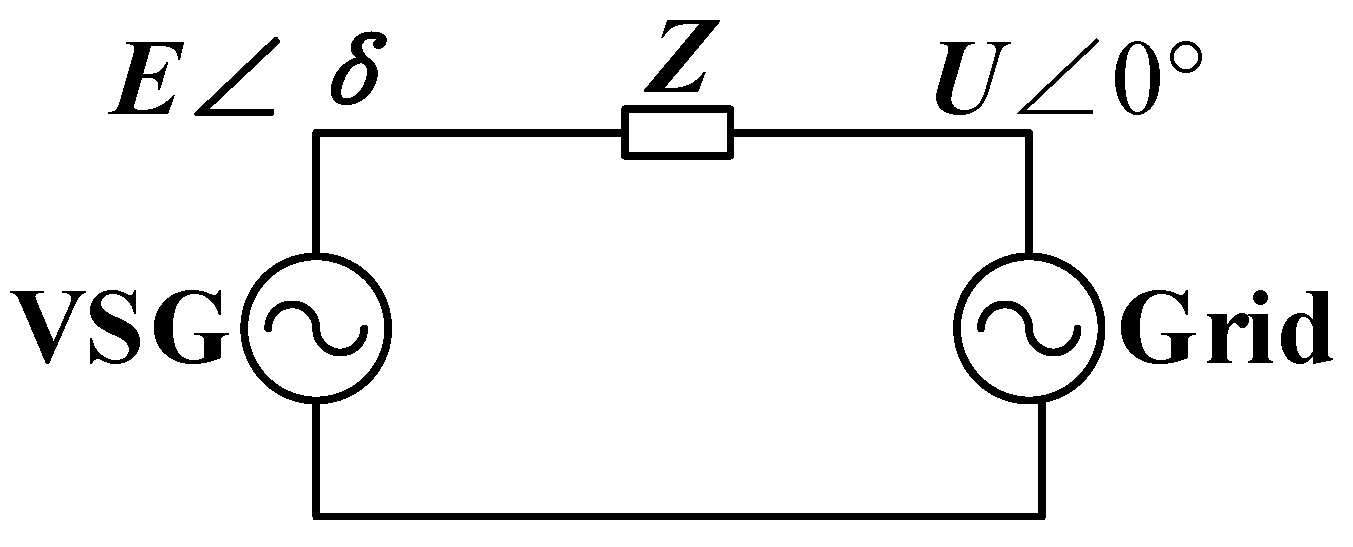
2.3. TNPC Based on VSG Control
2.3.1. VSG Outer Ring
2.3.2. VSG Inner Voltage Loop
2.3.3. VSG Inner Current Loop
3. Small-Signal Modeling and Performance Analysis of VSG
3.1. Small-Signal Modeling
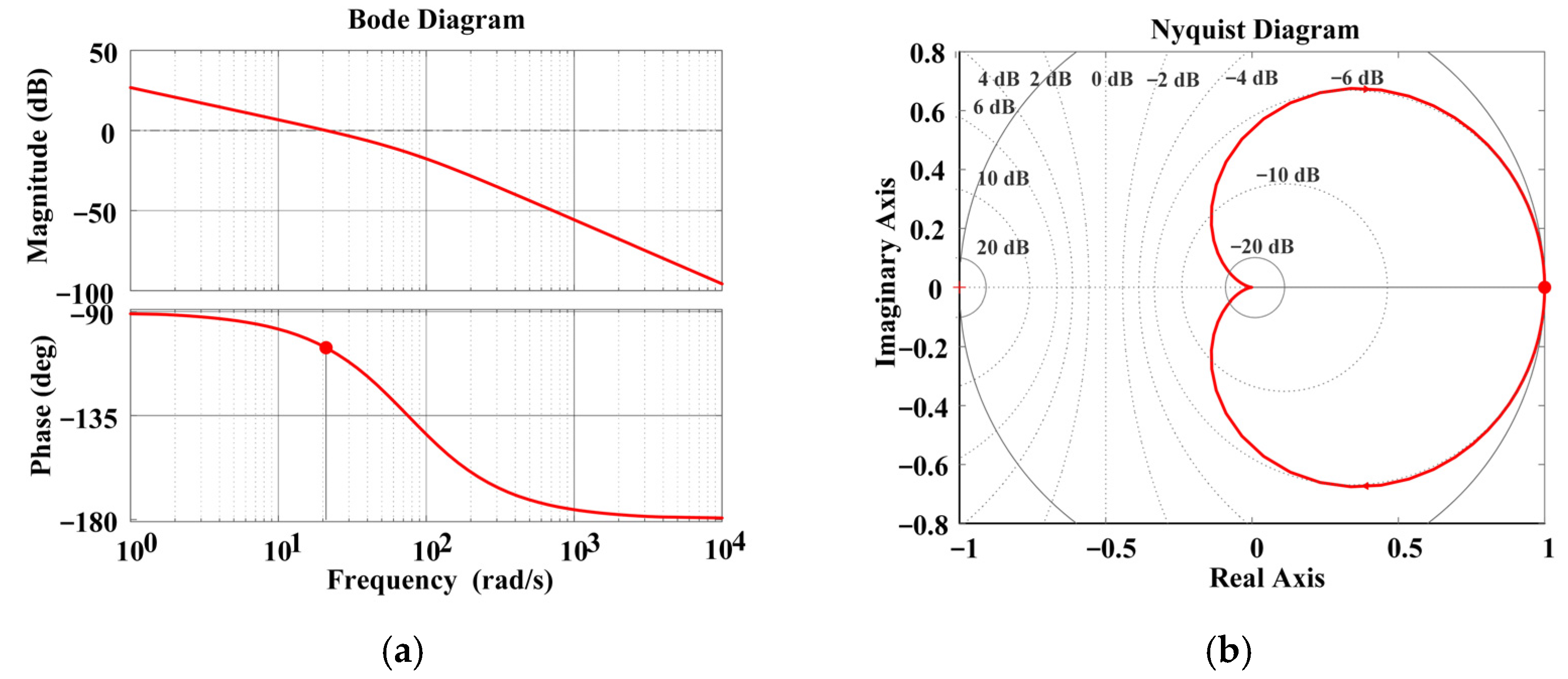
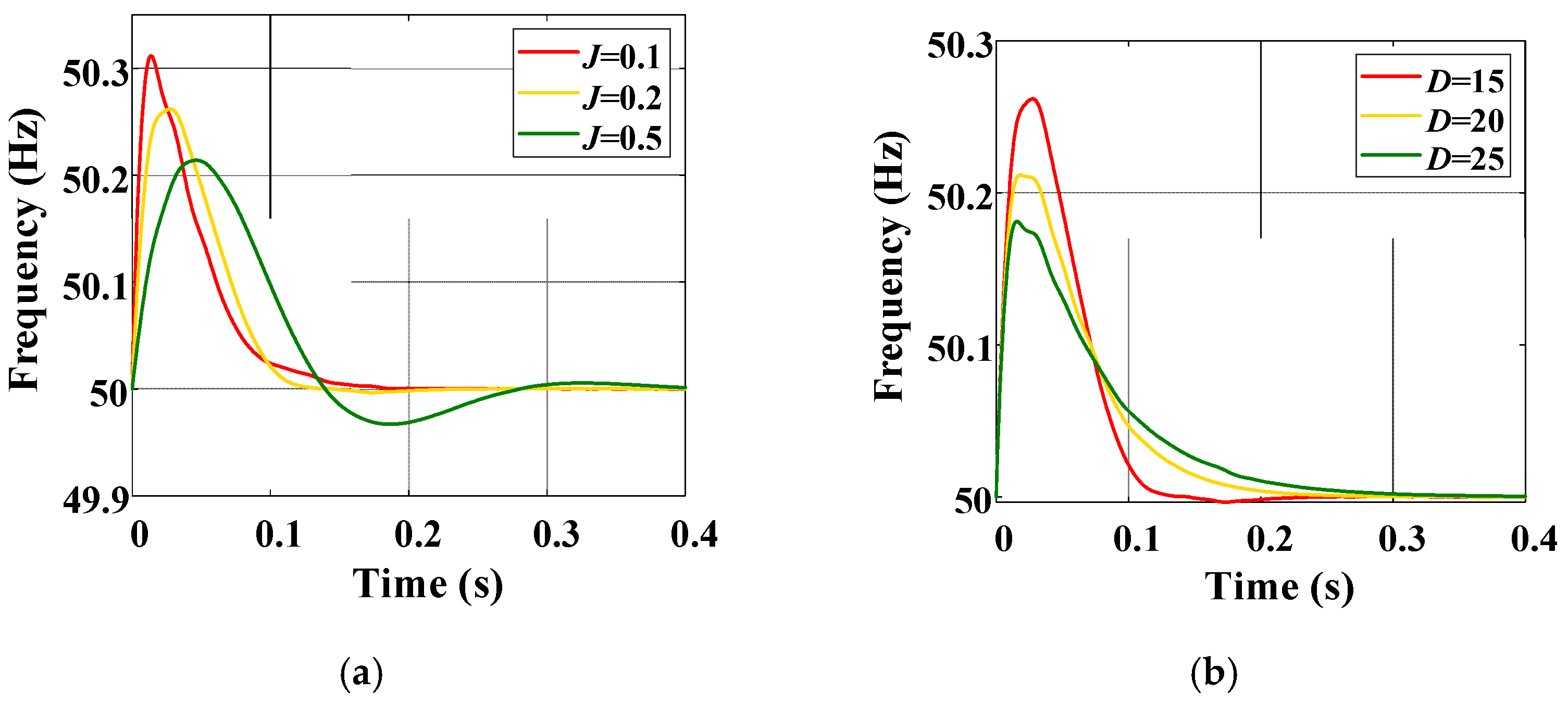
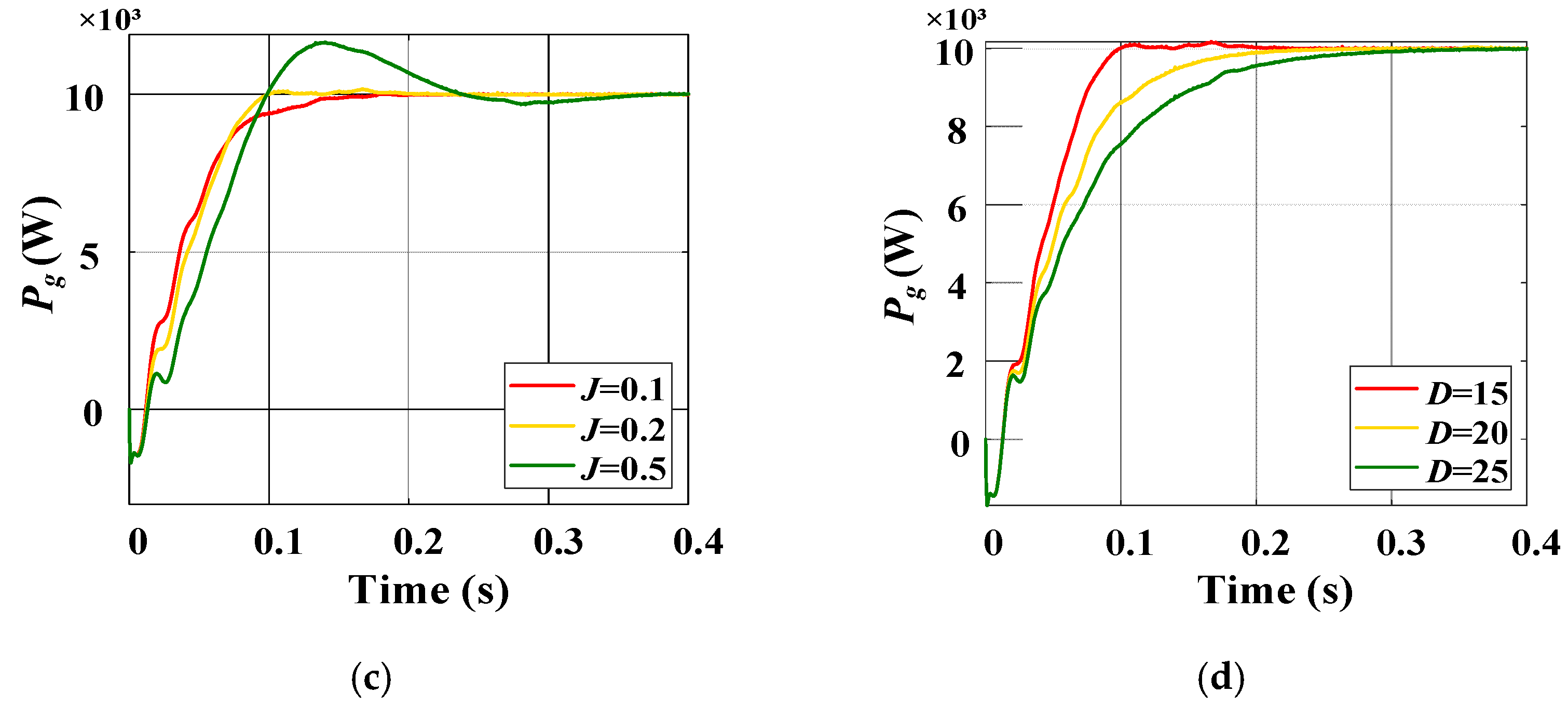
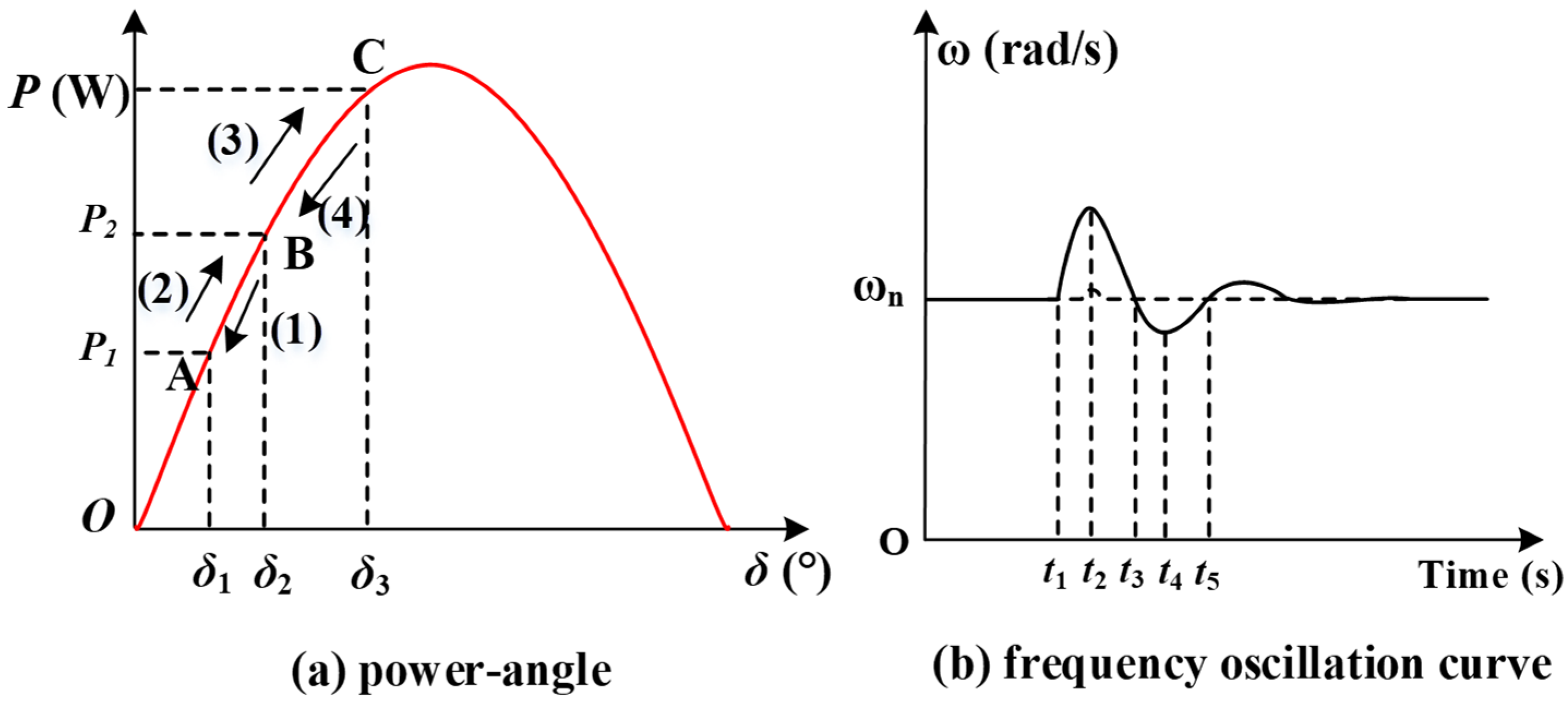
3.2. Dynamic Performance Analysis and Control Optimization
4. Working Condition Verification
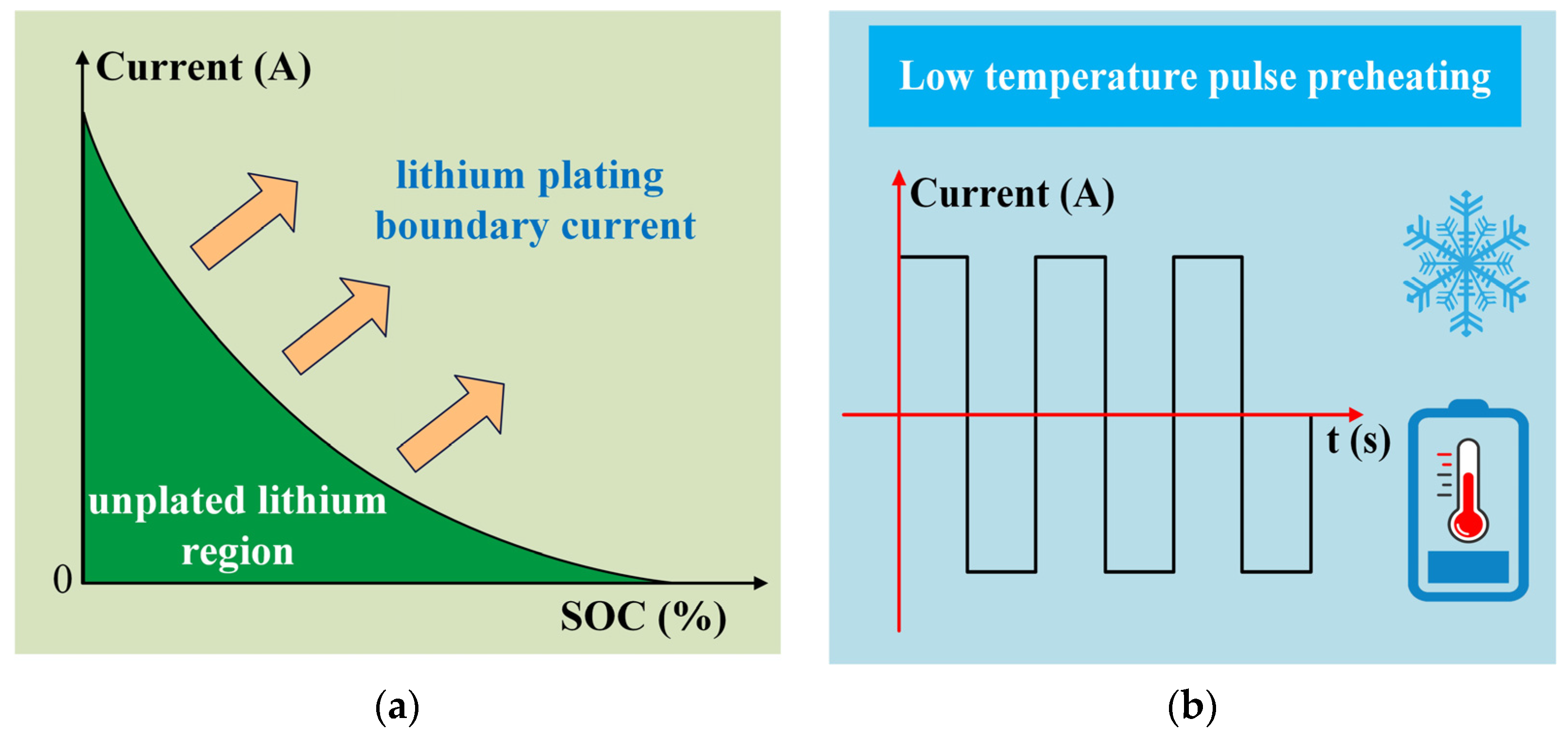
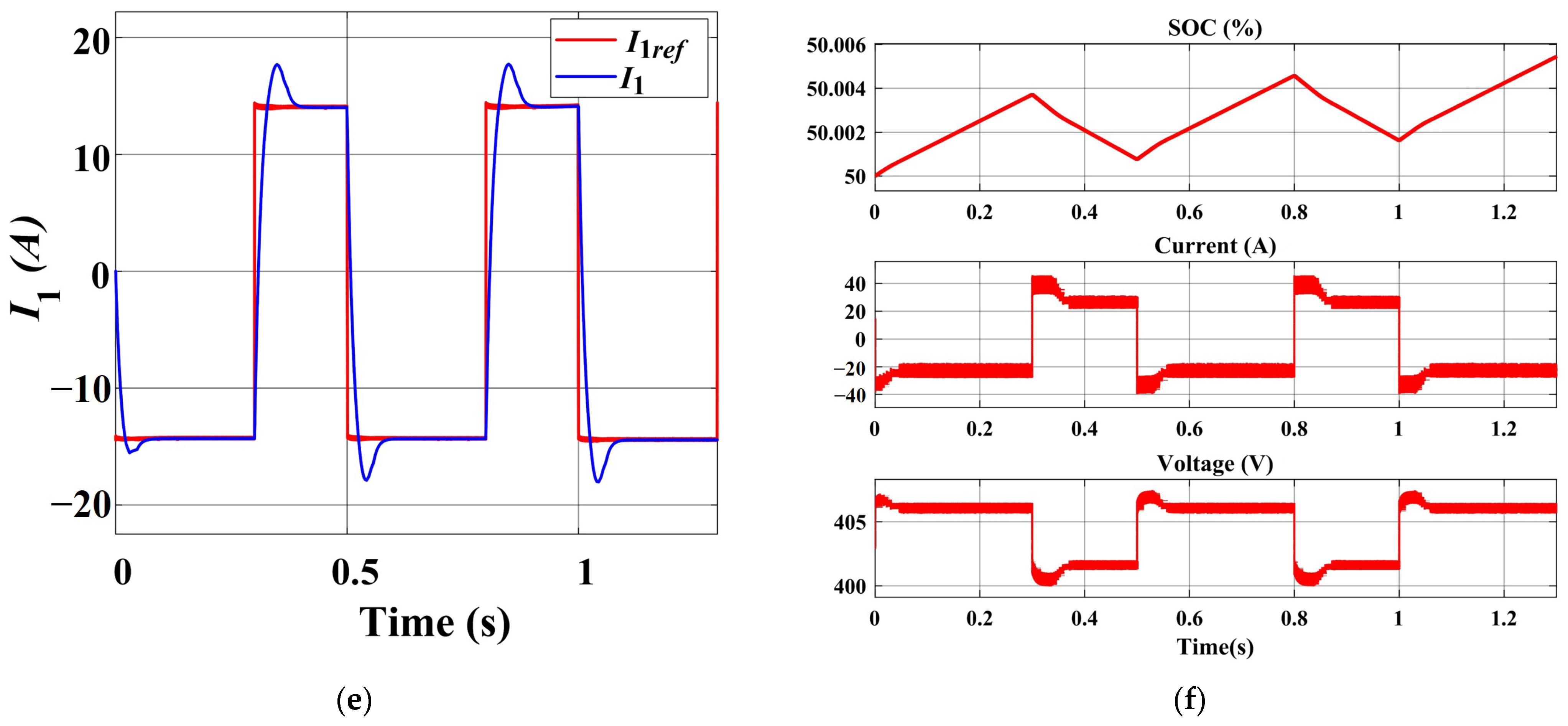
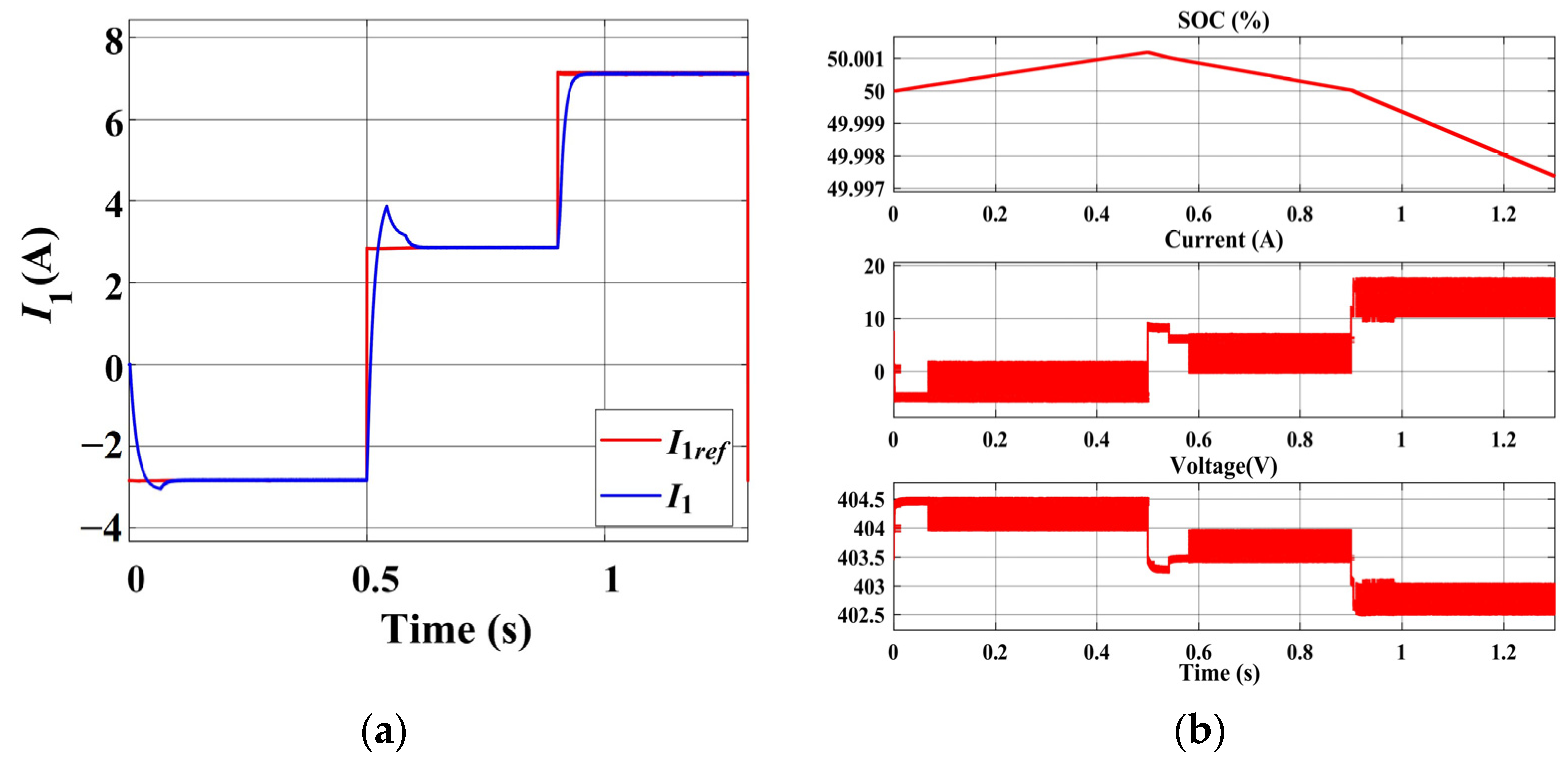
4.1. Low-Temperature Pulse Preheating Stage
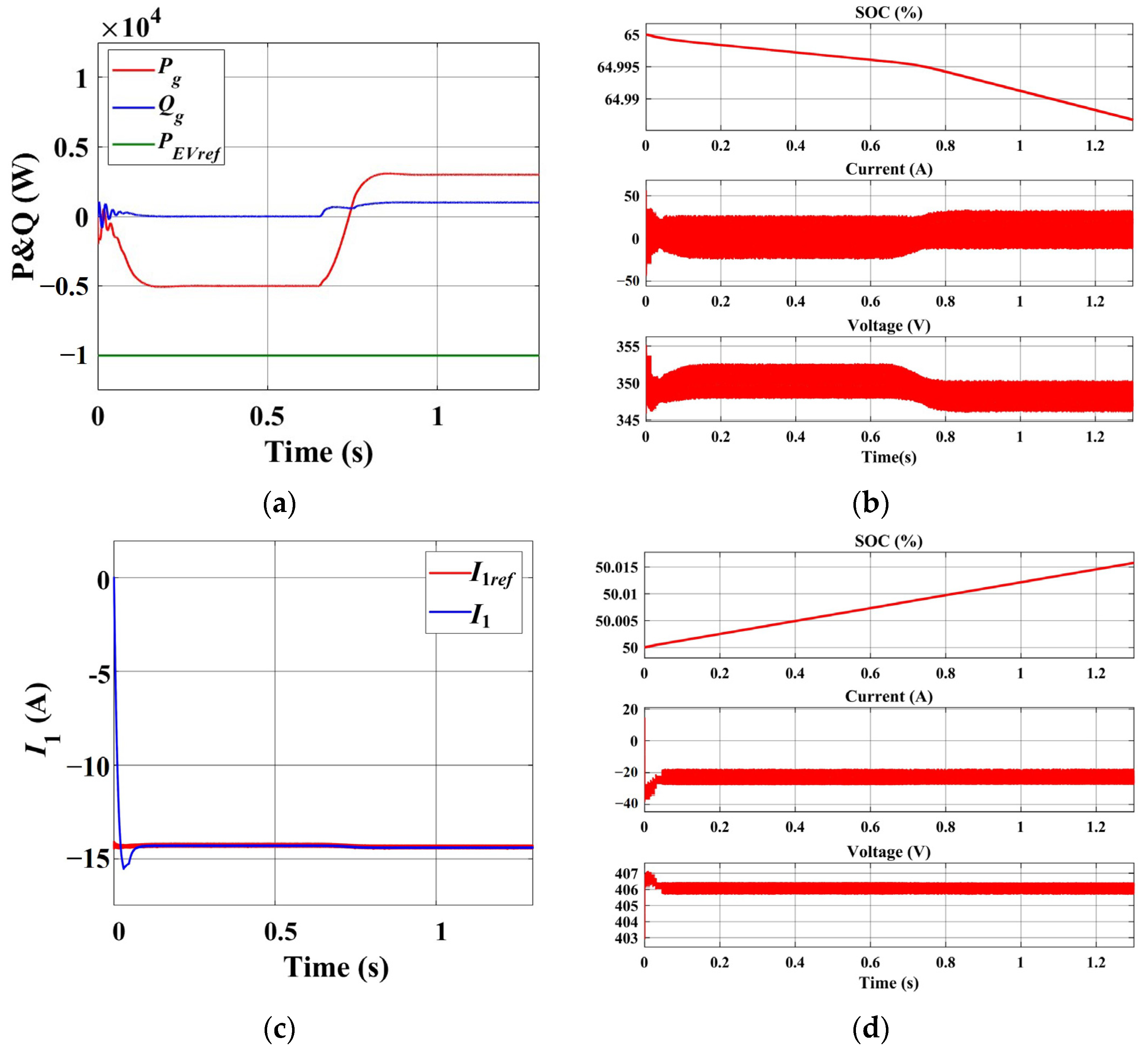
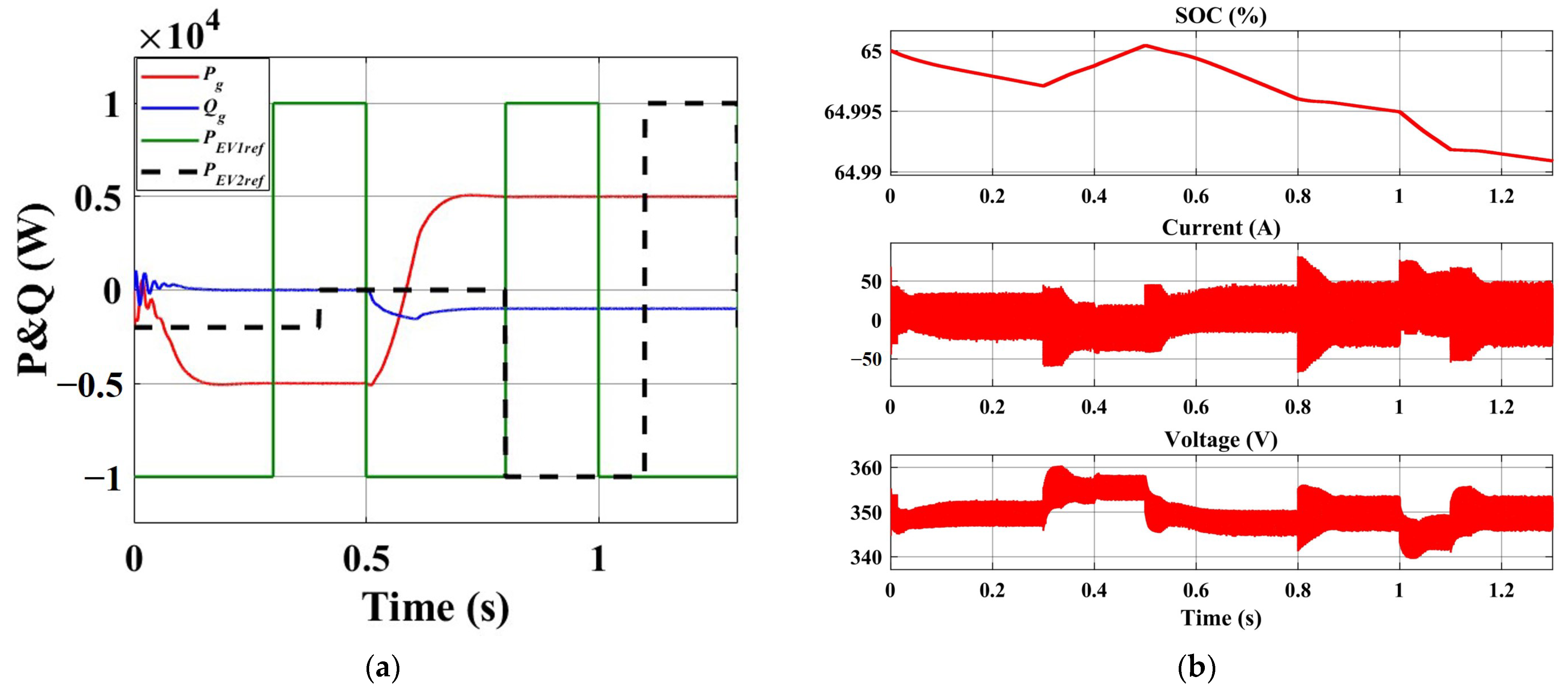
4.2. The Initial Fast Charge Stage
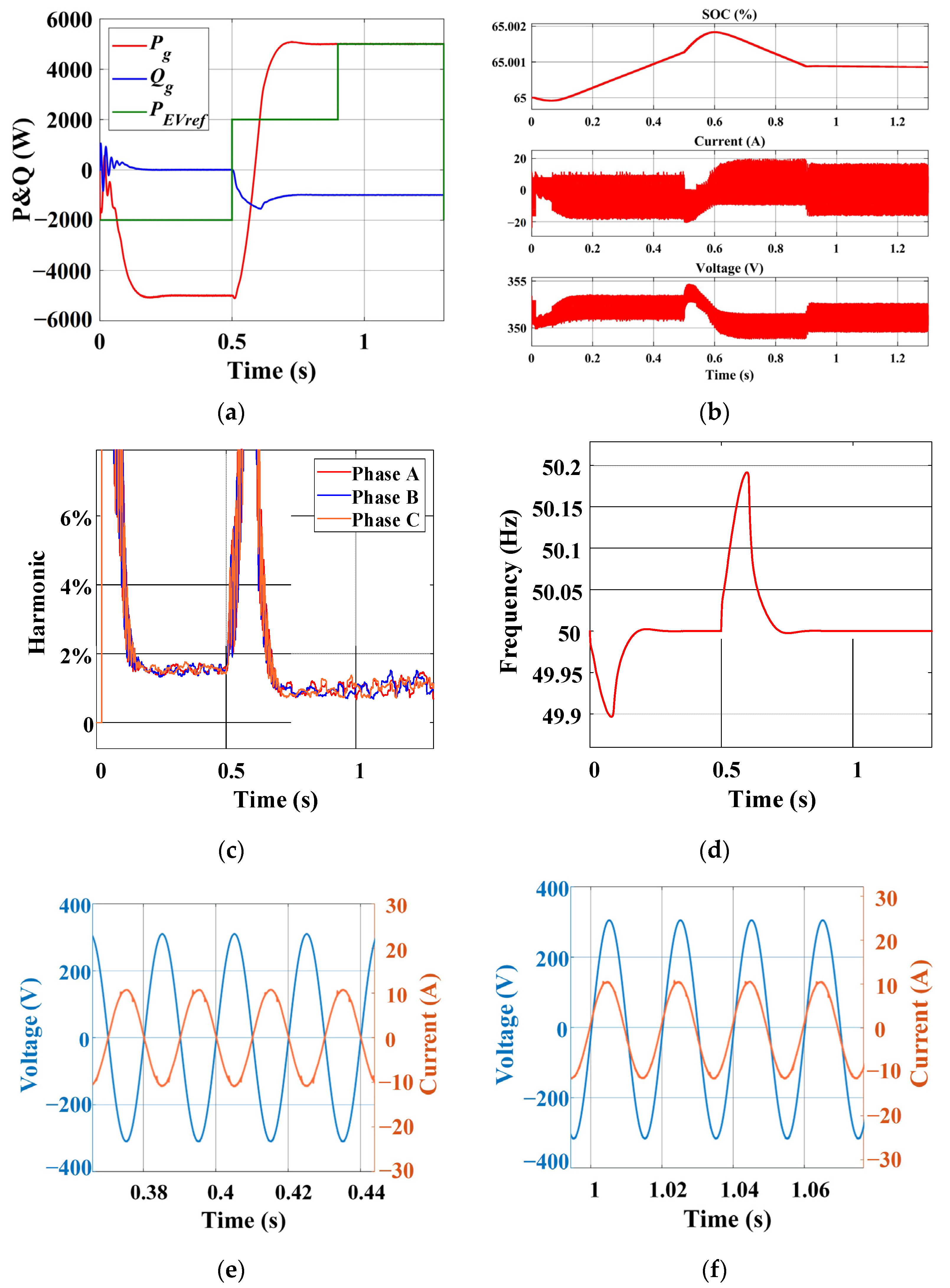
4.3. The Later Fast Charge Stage
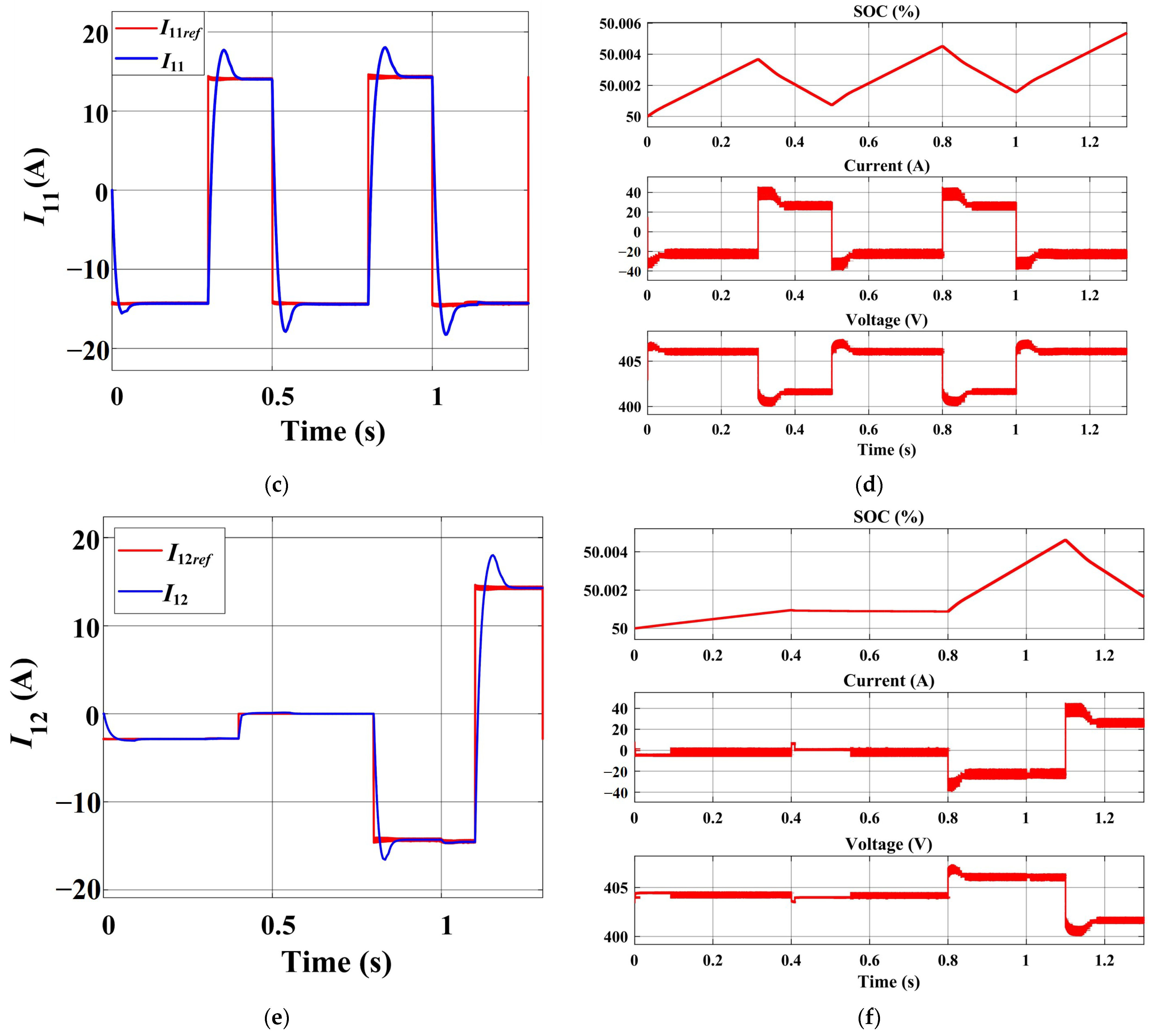
4.4. A Charging Pile with Dual Guns
5. Conclusions and Prospect
- (1)
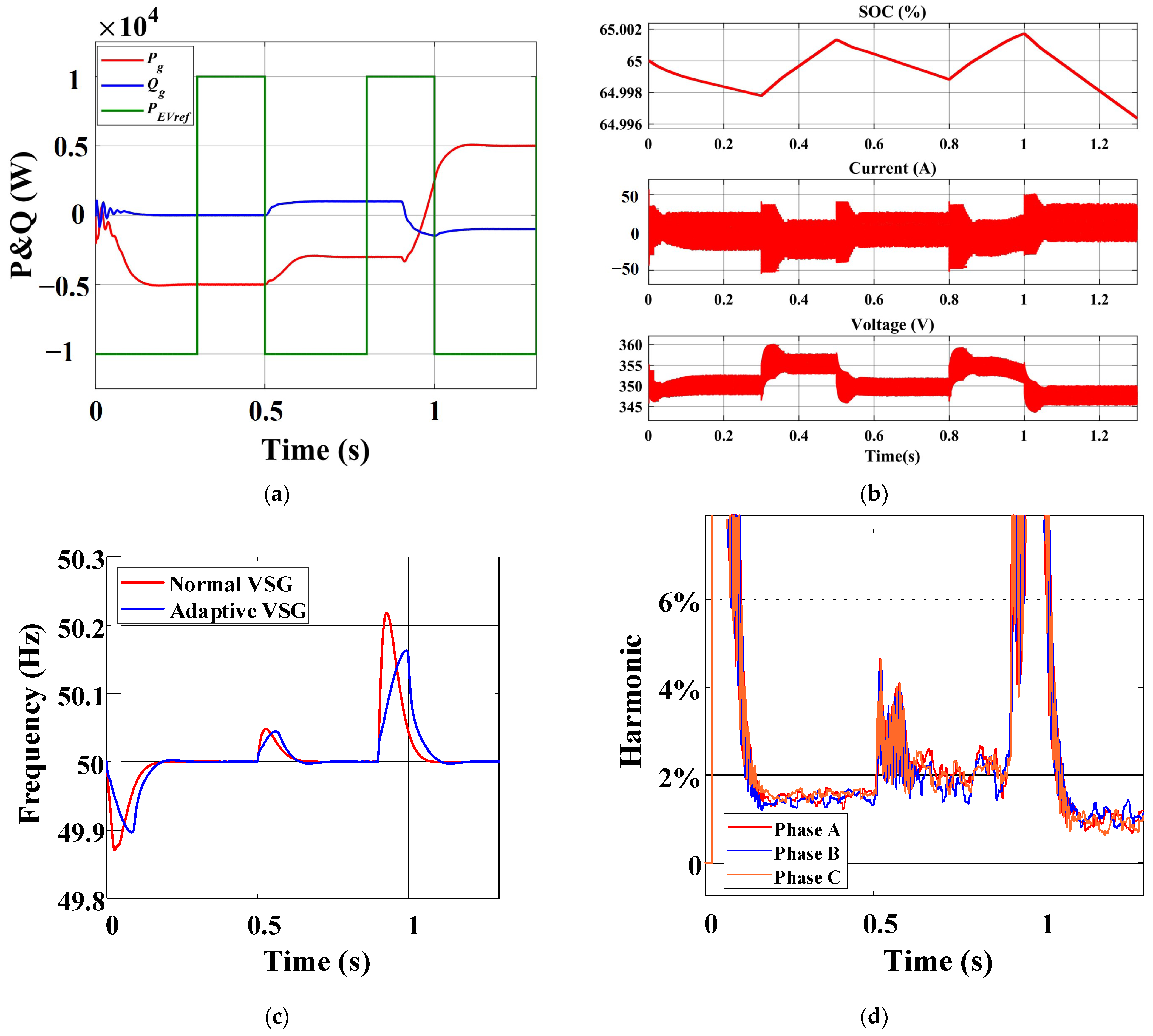
- Within the novel charger, the approximate voltage-source characteristics of the energy storage battery allow for the separate control of EV instructions and grid instructions. The pulse modulation time for EVs consistently achieves a steady state within 0.1 s. The new charger also exhibits a pulse modulation speed twice as fast as that of conventional chargers with identical parameters. Furthermore, the pulse-current heating and variable-current charging of EVs does not generate high-frequency power fluctuations on the grid, and the sequences of grid instructions do not have an impact on the speed of pulse modulation.
- (2)
- Compared to the traditional charger, the new charger exhibits enhanced flexibility and grid-friendliness. The power utilization of fast charging scenarios is improved. Furthermore, the power vector equilibrium is maintained between the EV, energy storage battery, and grid. Without impacting EV requirements, the grid can modify the proportion of supplied energy based on the actual scenario or obtain energy from either the EV or energy storage battery. The adaptive VSG not only supports the power regulation and voltage regulation of the grid but also provides inertia support. The active power can reach a new steady state within 0.2 s, while the reactive power can achieve steady state within 0.1 s.
- (3)
- In the absence of the EV, the energy storage battery can independently interact with the grid. Moreover, in a charging pile with dual guns, the instructions between EVs do not interfere with each other. The EV can smoothly connect or disconnect without causing any impact on the grid or the other EV.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, Y.; Wei, Y.; Zhu, F.; Du, J.; Zhao, Z.; Ouyang, M. The path enabling storage of renewable energy toward carbon neutralization in China. eTransportation 2023, 16, 100226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghajan-Eshkevari, S.; Azad, S.; Nazari-Heris, M.; Ameli, M.T.; Asadi, S. Charging and discharging of electric vehicles in power systems: An updated and detailed review of methods, control structures, objectives, and optimization methodologies. Sustainability 2022, 14, 2137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Wu, X.; Li, Y.; Wang, H.; Lu, L.; Ouyang, M. A comprehensive review of DC arc faults and their mechanisms, detection, early warning strategies, and protection in battery systems. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2023, 186, 113674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Tian, G.; Huang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Li, J.; Wu, Y.; Chi, Y. New power system development path mechanism design. Glob. Energy Interconnect. 2023, 6, 166–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, I.A.; Mokhlis, H.; Mansor, N.N.; Illias, H.A.; Awalin, L.J.; Wang, L. New trends and future directions in load frequency control and flexible power system: A comprehensive review. Alex. Eng. J. 2023, 71, 263–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Huang, J.; Quan, H.; Xu, Y.; Liu, Z. Inertial security region estimation and analysis of new power systems considering renewable energy virtual inertial. Energy Rep. 2023, 9, 1836–1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravi, S.S.; Aziz, M. Utilization of electric vehicles for vehicle-to-grid services: Progress and perspectives. Energies 2022, 15, 589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elma, O.; Cali, U.; Kuzlu, M. An overview of bidirectional electric vehicles charging system as a Vehicle to Anything (V2X) under Cyber–Physical Power System (CPPS). Energy Rep. 2022, 8, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, W.; Ahmad, F.; Alam, M.S. Fast EV charging station integration with grid ensuring optimal and quality power exchange. Eng. Sci. Technol. Int. J. 2019, 22, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piao, N.; Gao, X.; Yang, H.; Guo, Z.; Hu, G.; Cheng, H.-M.; Li, F. Challenges and development of lithium-ion batteries for low temperature environments. Etransportation 2022, 11, 100145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, H. Alternating Current Preheating and Fast Charging of Lithium-Ion Batteries with Lithium Plating Prevention at Low Temperatures. Doctoral Dissertation, Tsinghua University, Beijing, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, Y.; Zuo, P.; Chen, X.; Yuan, W.; Huang, R.; Yang, X.; Du, J.; Lu, L.; Han, X.; Ouyang, M. An ultra-fast charging strategy for lithium-ion battery at low temperature without lithium plating. J. Energy Chem. 2022, 72, 442–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Zheng, Y.; Howey, D.A.; Perez, H.; Foley, A.; Pecht, M. Battery warm-up methodologies at subzero temperatures for automotive applications: Recent advances and perspectives. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 2020, 77, 100806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.; Xu, Z.; Xiao, S.; Gao, M.; Bai, J.; Liebig, D.; Lu, L.; Han, X.; Li, Y.; Du, J. Temperature consistency–oriented rapid heating strategy combining pulsed operation and external thermal management for lithium-ion batteries. Appl. Energy 2023, 335, 120659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mateen, S.; Amir, M.; Haque, A.; Bakhsh, F.I. Ultra-fast charging of electric vehicles: A review of power electronics converter, grid stability and optimal battery consideration in multi-energy systems. Sustain. Energy Grids Netw. 2023, 35, 101112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antoun, J.; Kabir, M.E.; Atallah, R.; Moussa, B.; Ghafouri, M.; Assi, C. Impact analysis of EV preconditioning on the residential distribution network. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Conference on Communications, Control, and Computing Technologies for Smart Grids (SmartGridComm), Virtual, 11–13 November 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Antoun, J.; Kabir, M.E.; Atallah, R.; Moussa, B.; Ghafouri, M.; Assi, C. Assisting residential distribution grids in overcoming large-scale EV preconditioning load. IEEE Syst. J. 2021, 16, 4345–4355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Liu, J.; Liu, Z. A generalized droop control for grid-supporting inverter based on comparison between traditional droop control and virtual synchronous generator control. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2018, 34, 5416–5438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, P.; Li, Z.; Jin, H.; Zhao, C.; Fan, J.; Wu, X. An adaptive VSG control strategy of battery energy storage system for power system frequency stability enhancement. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2023, 149, 109039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathore, B.; Chakrabarti, S.; Srivastava, L. A Self-Regulated Virtual Impedance control of VSG in a microgrid. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2021, 197, 107289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Sharma, S. Review of power electronics in vehicle-to-grid systems. J. Energy Storage 2019, 21, 337–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Lu, L.; Li, Y.; Wang, H.; Ouyang, M. Accurate Remaining Available Energy Estimation of LiFePO4 Battery in Dynamic Frequency Regulation for EVs with Thermal-Electric-Hysteresis Model. Energies 2023, 16, 5239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langbroek, J.H.; Franklin, J.P.; Susilo, Y.O. When do you charge your electric vehicle? A stated adaptation approach. Energy Policy 2017, 108, 565–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mou, D.; Yuan, L.; Li, Y.; Wei, S.; Chen, J.; Zeng, Y.; Zhao, Z. Efficiency-oriented circuit parameter optimization of dual active bridge converter. eTransportation 2022, 14, 100208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Bai, H.; Foote, A.; Wang, W. Securing full-power-range zero-voltage switching in both steady-state and transient operations for a dual-active-bridge-based bidirectional electric vehicle charger. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2019, 35, 7506–7519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, Q.; Wen, H.; Wen, J.; Hu, Y.; Du, Y. Transient DC bias elimination of dual-active-bridge DC–DC converter with improved triple-phase-shift control. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2019, 67, 8587–8598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yalçın, S.; Göksu, T.; Kesler, S.; Bingöl, O. Experimental analysis of phase shift modulation methods effects on EMI in dual active bridge DC-DC converter. Eng. Sci. Technol. Int. J. 2023, 43, 101435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Song, Q.; Liu, W.; Sun, Y. Overview of dual-active-bridge isolated bidirectional DC–DC converter for high-frequency-link power-conversion system. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2013, 29, 4091–4106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez Alonso, A.; Vázquez Ardura, A.; González Lamar, D.; Hernando Álvarez, M.M.; Sebastián Zúñiga, F.J. Different purpose design strategies and techniques to improve the performance of a dual active bridge with phase-shift control. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2015, 30, 790–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.; Wang, J.; Zhao, J. General average model of T-type three-level converter for active compensation circuit of distribution network. Energy Rep. 2021, 7, 493–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Q.-C.; Nguyen, P.-L.; Ma, Z.; Sheng, W. Self-synchronized synchronverters: Inverters without a dedicated synchronization unit. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2013, 29, 617–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, T.; Zhu, D.; Zou, X.; Jiang, B.; Peng, L.; Kang, Y. Power coupling mechanism analysis and improved decoupling control for virtual synchronous generator. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2020, 36, 3028–3041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eroğlu, H.; Cuce, E.; Cuce, P.M.; Gul, F.; Iskenderoğlu, A. Harmonic problems in renewable and sustainable energy systems: A comprehensive review. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 2021, 48, 101566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, A.; Wu, Y.; Hu, Z.; Wang, Z.; Wu, T.; Jiang, J.; Peng, Z. Two-stage PV grid-connected control strategy based on adaptive virtual inertia and damping control for DC-link capacitor dynamics self-synchronization. J. Energy Storage 2023, 72, 108659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Zhu, Q.; Lin, S.; Bian, X. A self-adaptive inertia and damping combination control of VSG to support frequency stability. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2016, 32, 397–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Grid Instructions (Pg) | EV Instructions (PEV) | |
|---|---|---|
| Same direction | +x | +y |
| −x | −y | |
| Opposite direction | +x | −y |
| −x | +y |
| Parameters | Symbol | Value |
|---|---|---|
| EV battery voltage | UBattery | 400 V |
| Transformer turns ratio | n | 2 |
| DAB inductance | L | 82 uH |
| Energy storage battery voltage | E1, E2 | 350 V |
| Filter inductance | L1 | 1 mH |
| Filter capacitance | C1 | 10 uF |
| Grid voltage | Uabc | 220 V |
| Grid frequency | fg | 50 Hz |
| Switch frequency | fDC | 40 kHz |
| fAC | 15 kHz | |
| Virtual inertia | J | 0.2 |
| Virtual damping | D | 15 |
| Virtual inductance | Lv | 3.5 mH |
| Inertia adjustment coefficients | Kj | 0.1 |
| Damping adjustment coefficients | Kd | 15 |
| The threshold of J | Tj | 0.6 |
| The threshold of D | Td | 0.6 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jin, N.; Wang, J.; Li, Y.; He, L.; Wu, X.; Wang, H.; Lu, L. A Bidirectional Grid-Friendly Charger Design for Electric Vehicle Operated under Pulse-Current Heating and Variable-Current Charging. Sustainability 2024, 16, 367. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16010367
Jin N, Wang J, Li Y, He L, Wu X, Wang H, Lu L. A Bidirectional Grid-Friendly Charger Design for Electric Vehicle Operated under Pulse-Current Heating and Variable-Current Charging. Sustainability. 2024; 16(1):367. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16010367
Chicago/Turabian StyleJin, Ningzhi, Jianjun Wang, Yalun Li, Liangxi He, Xiaogang Wu, Hewu Wang, and Languang Lu. 2024. "A Bidirectional Grid-Friendly Charger Design for Electric Vehicle Operated under Pulse-Current Heating and Variable-Current Charging" Sustainability 16, no. 1: 367. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16010367
APA StyleJin, N., Wang, J., Li, Y., He, L., Wu, X., Wang, H., & Lu, L. (2024). A Bidirectional Grid-Friendly Charger Design for Electric Vehicle Operated under Pulse-Current Heating and Variable-Current Charging. Sustainability, 16(1), 367. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16010367










