The Digital Economy and Agricultural Modernization in China: Measurement, Mechanisms, and Implications
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Literature Review and Coupling Mechanism Analysis
2.1. Literature Review
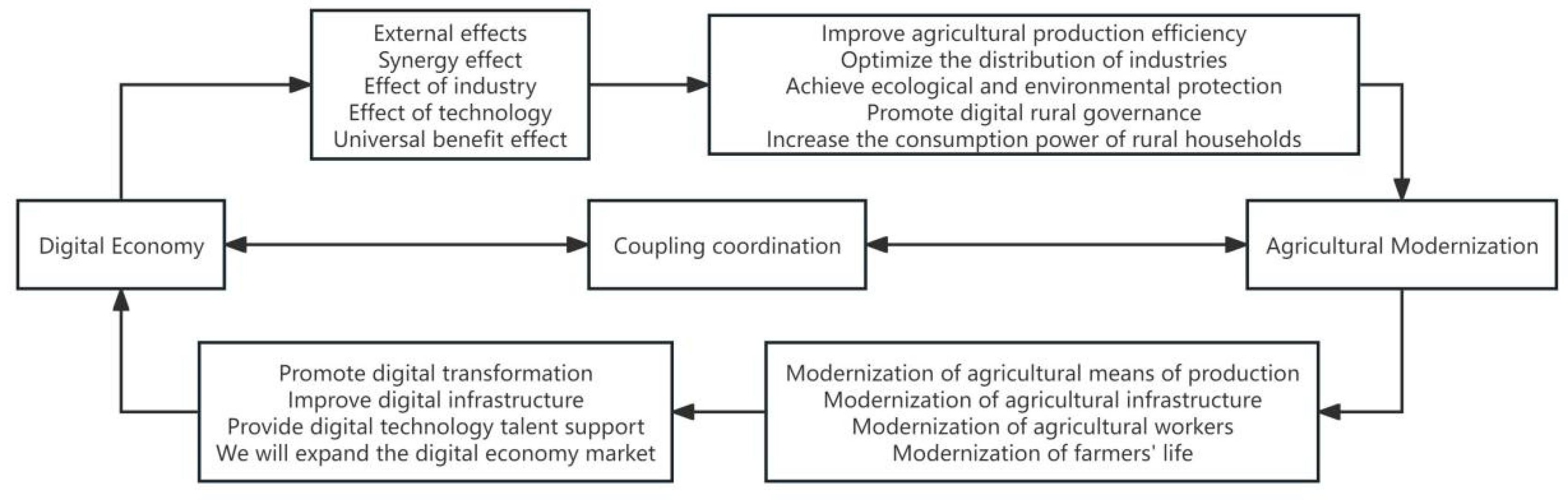
2.2. Analysis of Coupling Mechanism between the Digital Economy and Agricultural Modernization
2.2.1. The Digital Economy Promotes the Development of Agricultural Modernization
2.2.2. Agricultural Modernization Contributes to Digital Economy Transformation
2.2.3. Analysis of Spatial Spillover Mechanism of the Digital Economy and Agricultural Modernization
3. Research Design
3.1. Indicator System Construction
3.1.1. Data Source
3.1.2. Evaluation Indicator System
3.2. Data Processing
3.2.1. Entropy Weight Method
3.2.2. Degree of Coupling Coordination Model
3.2.3. The Kernel Density Function
3.2.4. The Moran Index
3.2.5. Obstacle Degree Model
4. Empirical Analysis
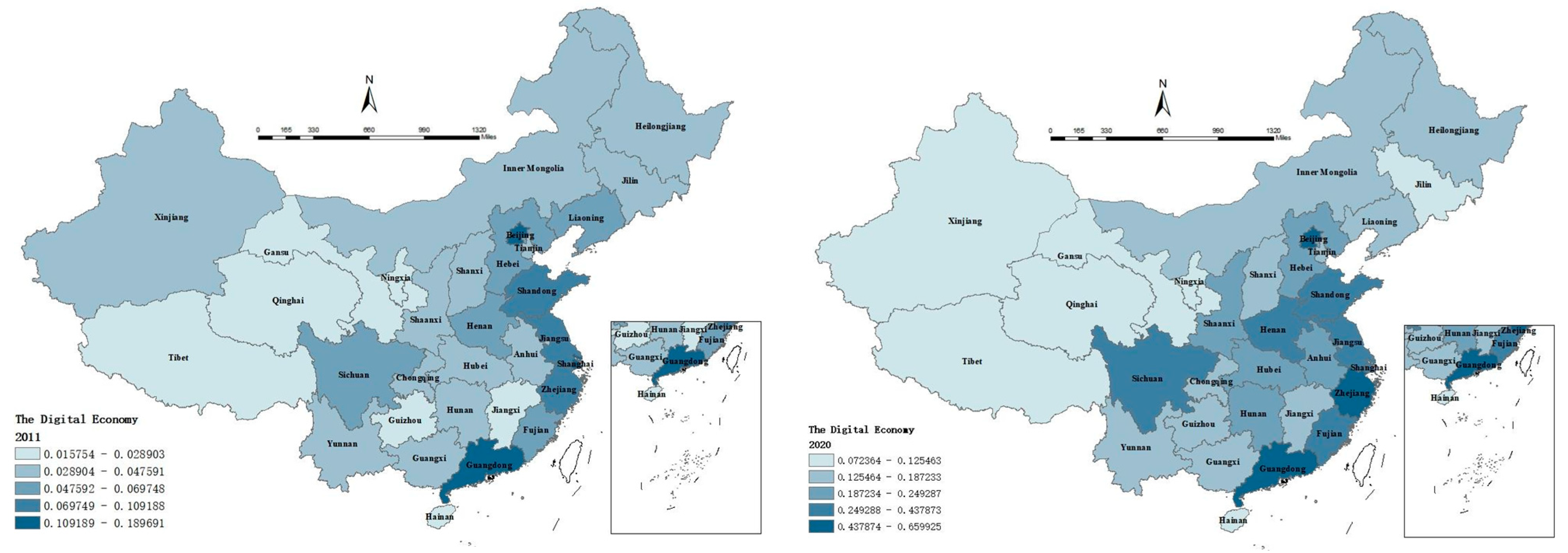
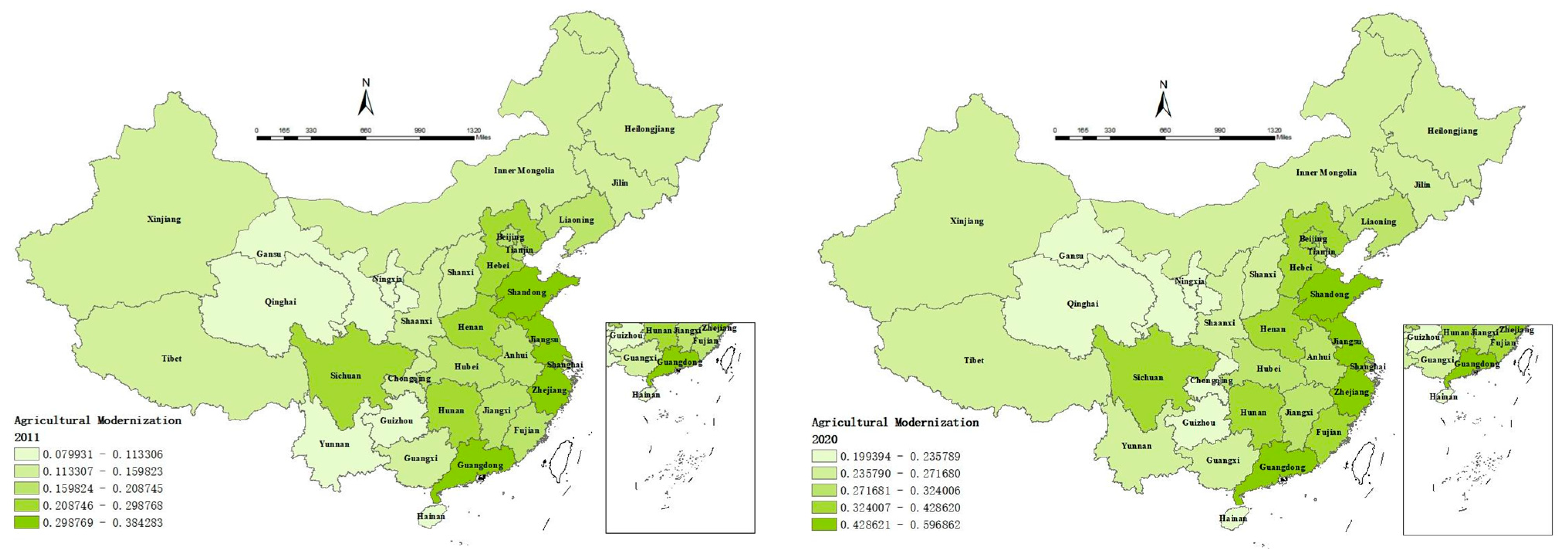
4.1. Characteristics of the Digital Economy–Agricultural Modernization Development Index
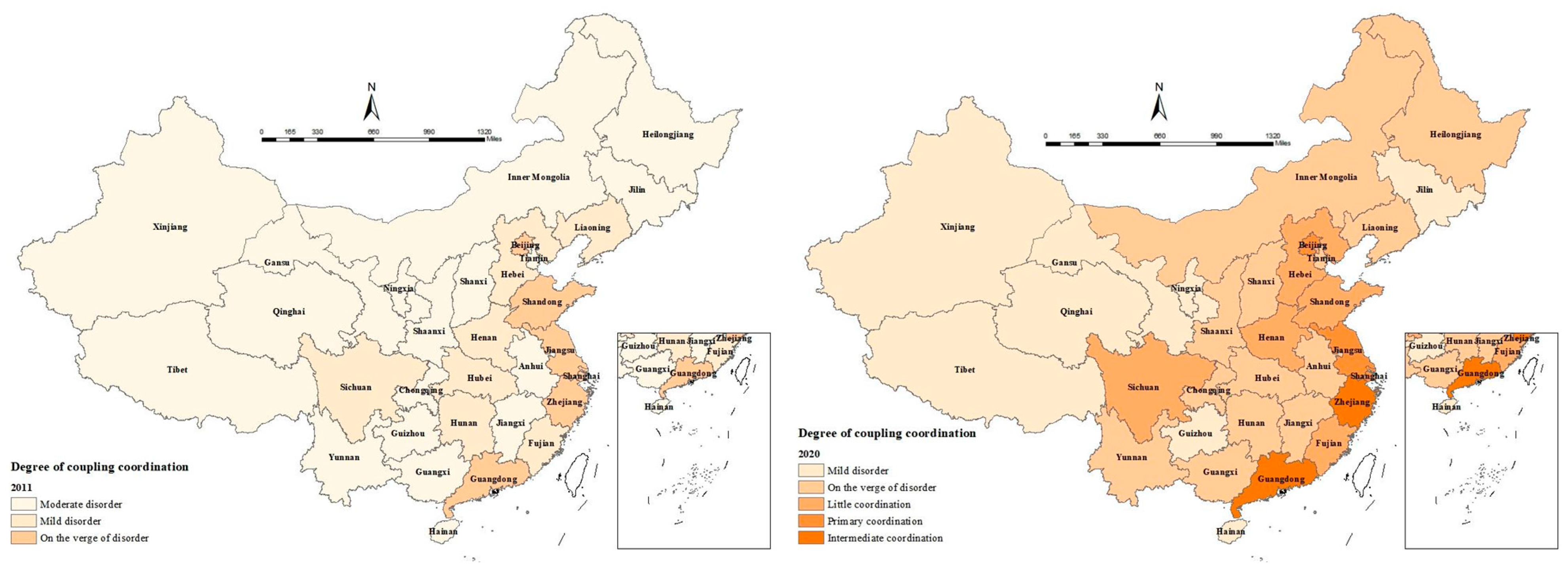
4.2. The Degree of Coupling Coordination between Digitization and Agricultural Modernization
4.3. The Evolution Trend of Coupling Coordination of the Digital Economy and Agricultural Modernization
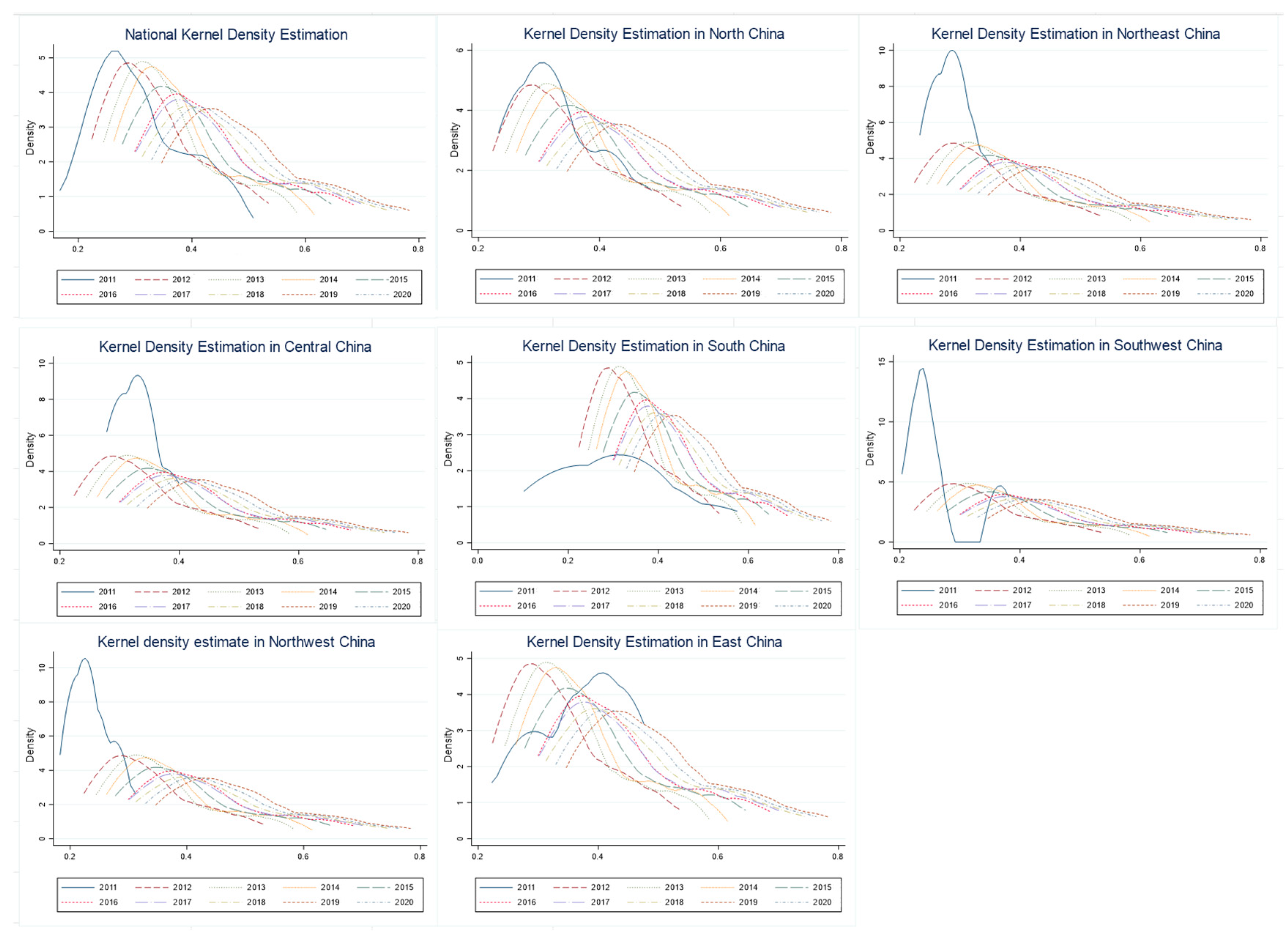
4.3.1. Kernel Density Analysis
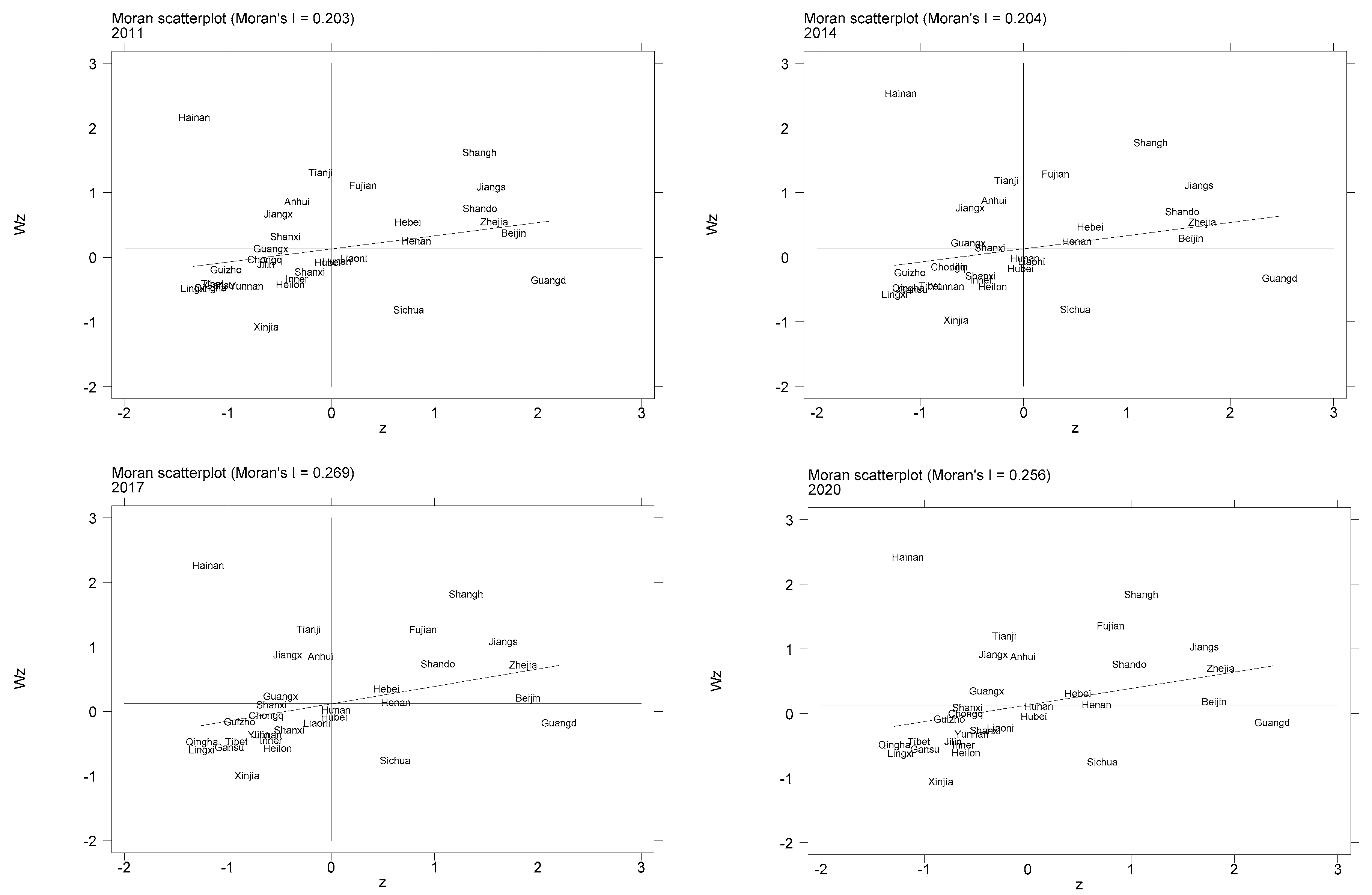
4.3.2. Moran Index Analysis
4.4. Obstacles to the Coupling and Coordinated Development of the Digital Economy and Agricultural Modernization
4.5. Discussion
5. Conclusions and Limitations
5.1. Conclusion
5.2. Research Limitations
6. Practical Implications
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Province | 2012 | 2014 | 2016 | 2018 | 2020 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Beijing | 0.190/0.209 | 0.347/0.233 | 0.524/0.329 | 0.573/0.382 | 0.602/0.429 |
| Tianjin | 0.044/0.184 | 0.082/0.216 | 0.102/0.283 | 0.133/0.304 | 0.187/0.283 |
| Hebei | 0.060/0.299 | 0.111/0.344 | 0.164/0.374 | 0.210/0.358 | 0.249/0.411 |
| Shanxi | 0.035/0.160 | 0.081/0.186 | 0.111/0.213 | 0.134/0.192 | 0.150/0.243 |
| Inner Mongolia | 0.048/0.135 | 0.082/0.170 | 0.100/0.214 | 0.124/0.188 | 0.149/0.259 |
| Liaoning | 0.054/0.204 | 0.094/0.240 | 0.122/0.271 | 0.144/0.241 | 0.175/0.295 |
| Jilin | 0.032/0.139 | 0.062/0.172 | 0.087/0.210 | 0.112/0.186 | 0.125/0.257 |
| Heilongjiang | 0.043/0.136 | 0.084/0.183 | 0.104/0.213 | 0.131/0.185 | 0.159/0.254 |
| Shanghai | 0.161/0.194 | 0.213/0.287 | 0.311/0.355 | 0.339/0.383 | 0.418/0.418 |
| Jiangsu | 0.090/0.374 | 0.184/0.467 | 0.283/0.516 | 0.382/0.510 | 0.438/0.597 |
| Zhejiang | 0.109/0.317 | 0.235/0.374 | 0.408/0.447 | 0.495/0.432 | 0.555/0.524 |
| Anhui | 0.036/0.177 | 0.072/0.219 | 0.121/0.254 | 0.171/0.256 | 0.215/0.324 |
| Fujian | 0.063/0.191 | 0.117/0.241 | 0.223/0.276 | 0.348/0.292 | 0.302/0.354 |
| Jiangxi | 0.029/0.177 | 0.060/0.203 | 0.096/0.227 | 0.135/0.232 | 0.176/0.292 |
| Shandong | 0.082/0.384 | 0.178/0.431 | 0.208/0.465 | 0.262/0.444 | 0.306/0.491 |
| Henan | 0.070/0.276 | 0.106/0.321 | 0.186/0.349 | 0.254/0.341 | 0.312/0.399 |
| Hubei | 0.047/0.186 | 0.087/0.235 | 0.143/0.281 | 0.183/0.266 | 0.219/0.321 |
| Hunan | 0.041/0.230 | 0.079/0.269 | 0.133/0.287 | 0.171/0.290 | 0.213/0.355 |
| Guangdong | 0.148/0.337 | 0.355/0.404 | 0.497/0.447 | 0.616/0.495 | 0.660/0.579 |
| Guangxi | 0.034/0.138 | 0.068/0.174 | 0.100/0.215 | 0.139/0.209 | 0.180/0.272 |
| Hainan | 0.022/0.080 | 0.046/0.111 | 0.061/0.147 | 0.078/0.142 | 0.091/0.210 |
| Chongqing | 0.036/0.122 | 0.063/0.150 | 0.097/0.181 | 0.131/0.176 | 0.165/0.236 |
| Sichuan | 0.067/0.270 | 0.107/0.313 | 0.185/0.357 | 0.252/0.350 | 0.335/0.387 |
| Guizhou | 0.029/0.093 | 0.048/0.121 | 0.075/0.163 | 0.112/0.157 | 0.151/0.231 |
| Yunnan | 0.031/0.113 | 0.064/0.147 | 0.093/0.184 | 0.129/0.193 | 0.166/0.257 |
| Tibet | 0.016/0.142 | 0.039/0.196 | 0.054/0.211 | 0.066/0.235 | 0.072/0.256 |
| Shaanxi | 0.046/0.157 | 0.075/0.182 | 0.121/0.217 | 0.149/0.184 | 0.196/0.262 |
| Gansu | 0.024/0.102 | 0.047/0.130 | 0.071/0.164 | 0.090/0.162 | 0.105/0.226 |
| Qinghai | 0.021/0.105 | 0.045/0.127 | 0.057/0.143 | 0.071/0.134 | 0.088/0.199 |
| Ningxia | 0.019/0.088 | 0.041/0.116 | 0.055/0.146 | 0.077/0.135 | 0.085/0.202 |
| Xinjiang | 0.033/0.136 | 0.056/0.184 | 0.075/0.230 | 0.093/0.189 | 0.111/0.256 |
| Province | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Beijing | 0.446 | 0.481 | 0.503 | 0.534 | 0.616 | 0.645 | 0.666 | 0.684 | 0.708 | 0.696 |
| Tianjin | 0.299 | 0.325 | 0.351 | 0.365 | 0.380 | 0.413 | 0.420 | 0.448 | 0.461 | 0.455 |
| Hebei | 0.366 | 0.396 | 0.421 | 0.442 | 0.465 | 0.498 | 0.507 | 0.524 | 0.556 | 0.540 |
| Shanxi | 0.273 | 0.297 | 0.335 | 0.350 | 0.369 | 0.392 | 0.379 | 0.400 | 0.426 | 0.413 |
| Inner Mongolia | 0.283 | 0.306 | 0.323 | 0.343 | 0.353 | 0.383 | 0.380 | 0.391 | 0.431 | 0.410 |
| Liaoning | 0.325 | 0.349 | 0.371 | 0.388 | 0.403 | 0.427 | 0.430 | 0.432 | 0.470 | 0.451 |
| Jilin | 0.258 | 0.287 | 0.308 | 0.322 | 0.338 | 0.368 | 0.367 | 0.380 | 0.413 | 0.396 |
| Heilongjiang | 0.277 | 0.303 | 0.334 | 0.352 | 0.361 | 0.386 | 0.386 | 0.394 | 0.429 | 0.411 |
| Shanghai | 0.420 | 0.427 | 0.449 | 0.497 | 0.549 | 0.577 | 0.597 | 0.600 | 0.626 | 0.613 |
| Jiangsu | 0.429 | 0.471 | 0.504 | 0.541 | 0.576 | 0.618 | 0.638 | 0.665 | 0.705 | 0.685 |
| Zhejiang | 0.431 | 0.499 | 0.506 | 0.544 | 0.595 | 0.654 | 0.660 | 0.680 | 0.728 | 0.704 |
| Anhui | 0.282 | 0.312 | 0.333 | 0.354 | 0.391 | 0.419 | 0.434 | 0.457 | 0.497 | 0.477 |
| Fujian | 0.332 | 0.372 | 0.385 | 0.410 | 0.452 | 0.498 | 0.548 | 0.564 | 0.591 | 0.577 |
| Jiangxi | 0.267 | 0.297 | 0.319 | 0.332 | 0.361 | 0.384 | 0.397 | 0.421 | 0.465 | 0.442 |
| Shandong | 0.421 | 0.441 | 0.528 | 0.526 | 0.532 | 0.558 | 0.565 | 0.584 | 0.615 | 0.599 |
| Henan | 0.373 | 0.391 | 0.405 | 0.429 | 0.471 | 0.505 | 0.518 | 0.543 | 0.581 | 0.561 |
| Hubei | 0.305 | 0.334 | 0.353 | 0.378 | 0.421 | 0.448 | 0.449 | 0.469 | 0.510 | 0.489 |
| Hunan | 0.312 | 0.340 | 0.364 | 0.382 | 0.413 | 0.443 | 0.452 | 0.472 | 0.520 | 0.495 |
| Guangdong | 0.473 | 0.535 | 0.584 | 0.615 | 0.645 | 0.687 | 0.701 | 0.743 | 0.783 | 0.763 |
| Guangxi | 0.262 | 0.284 | 0.306 | 0.330 | 0.351 | 0.382 | 0.389 | 0.413 | 0.458 | 0.435 |
| Hainan | 0.204 | 0.224 | 0.248 | 0.268 | 0.288 | 0.308 | 0.309 | 0.324 | 0.366 | 0.345 |
| Chongqing | 0.257 | 0.272 | 0.291 | 0.312 | 0.334 | 0.364 | 0.373 | 0.390 | 0.433 | 0.411 |
| Sichuan | 0.366 | 0.386 | 0.399 | 0.428 | 0.472 | 0.507 | 0.517 | 0.545 | 0.592 | 0.568 |
| Guizhou | 0.228 | 0.242 | 0.263 | 0.277 | 0.303 | 0.332 | 0.343 | 0.364 | 0.422 | 0.392 |
| Yunnan | 0.244 | 0.266 | 0.292 | 0.311 | 0.327 | 0.362 | 0.372 | 0.397 | 0.440 | 0.418 |
| Tibet | 0.217 | 0.252 | 0.273 | 0.295 | 0.316 | 0.326 | 0.340 | 0.352 | 0.362 | 0.357 |
| Shaanxi | 0.292 | 0.311 | 0.323 | 0.341 | 0.364 | 0.403 | 0.399 | 0.407 | 0.461 | 0.433 |
| Gansu | 0.223 | 0.247 | 0.263 | 0.279 | 0.306 | 0.328 | 0.332 | 0.347 | 0.382 | 0.364 |
| Qinghai | 0.216 | 0.240 | 0.265 | 0.275 | 0.283 | 0.300 | 0.301 | 0.313 | 0.347 | 0.329 |
| Ningxia | 0.203 | 0.224 | 0.245 | 0.263 | 0.278 | 0.300 | 0.301 | 0.319 | 0.354 | 0.336 |
| Xinjiang | 0.258 | 0.286 | 0.305 | 0.319 | 0.335 | 0.362 | 0.352 | 0.364 | 0.402 | 0.382 |
References
- Qian, J.F.; Chen, Y.F. Enlightenment of agricultural informatization construction in typical developed countries to China’s agricultural ‘new infrastructure construction’ in China. Sci. Technol. Manag. Res. 2021, 23, 174–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hailu, B.K.; Abrha, B.K.; Weldegiorgis, K.A. Adoption and Impact of Agricultural Technologies on Farm Income: Evidence from Southern Tigray, Northern Ethiopia. Int. J. Food Agric. Econ. 2014, 2, 91–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, T.; Chen, Y.M. The Integrated Development of Digital Economy and Agricultural and Rural Economy: Practical Models, Practical Obstacles and Breakthrough Paths. Issues Agric. Econ. 2020, 7, 118–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Luo, B.L. How Can Small Farmers Be Incorporated into Modern Agricultural Development? Evidence from Wheat-producing Areas of China. Econ. Res. J. 2018, 53, 144–160. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, X.C.; Zhang, M.H. Research on the Scale Measurement of China’s Digital Economy—Basedon the Perspective ofInternational Comparison. China Ind. Econ. 2020, 5, 23–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Gong, Z.M. The lmpact of Digital Economy Level on Green High-quality Development in Chinese Cities. Econ. Geogr. 2022, 42, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, J.; Zhong, M.C. Measurement and analysis of spatial and temporal characteristics of digital economy development level in Chinese provinces. Bus. Econ. 2024, 12–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, M.R. The role of the digital economy in Bangladesh’s economic development. Sustain. Technol. Entrep. 2024, 3, 100054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, B.P.; He, H.C. Empowerment of Digital Economy to High-quality Development: Theoretical Logic, Path Choices and Policy Orientation. Financ. Econ. 2022, 61–75. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, R.R.; Zhang, A.X.; Chen, M. Spatio-temporal Evolution and Driving Factors of Coupling Degree Between Digital Economy and Economic Quality: Numerical Calculation and Empirical Analysis. J. Nanjing Univ. Financ. Econ. 2021, 33–43. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, P.; Gu, Y. Research on the Impact of Digital Economy on Industrial Structure Upgrading—Based on the Perspective of Innovation Output. J. Ind. Technol. Econ. 2022, 41, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.T.; Wen, Z.Y. The impact of digital economy on the high-quality development of manufacturing industry. Stat. Decis. 2022, 38, 109–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.P.; Zhong, G.Z. Spatiotemporal Evolution Characteristics and Influencing Factors of China’sAgricultural and Rural Modernization. Stat. Decis. 2024, 40, 94–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Gu, S.G. Research on agricultural production efficiency measurement and spatial-temporal differentiation—Based on DEA-SBM model analysis. Rural. Econ. Sci.-Technol. 2023, 34, 4–7. [Google Scholar]
- Xin, L.; Hao, H. The evaluation method of the development level of agricultural modernization in China. Res. Agric. Mod. 2022, 43, 747–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorge-Vazouez, J.; Chivite-Cebolla, M.; Salinas-Ramos, F. The digitalization of the european agri-food cooperative sector. Determining factors to embrace information and communi-cation technologies. Agriculture 2021, 11, 514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.S.; Zhang, D.Y.; Wang, X. Green development effect of agricultural socialized services: An analysis based on farming households’ perspective. Resour. Sci. 2022, 44, 1848–1864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.X.; Chen, H.Q. Chinese Path to Agricultural Modernization: Prerequisites, DynamicCharacteristics and Realistic Path. Chongqing Soc. Sci. 2024, 3, 6–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.R. Research on the Realization Paths of Digitalization of the Circulation of Agricultural Product Boosting the High-quality Development of the Agricultural Economy. China Bus. Rev. 2023, 16, 51–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.M.; Li, C.H. The Impact of Digital Transformation in Agriculture on Green Growth in Agriculture. Chin. J. Agric. Resour. Reg. Plan. 2023, 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, L.Y.; Shi, C.Y.; Yang, X.; Mu, Y.Y. Impact Mechanism of Rural Digitization on China’s Agricultural Resilience: An empirical study based on the coupling coordination degree and mediatingeffect models. J. China Agric. Univ. 2023, 28, 308–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Ruan, L.J. The Expanding Paths and Policy Orientation of Chinese Agricultural and Rural Modernization under the Background of Digital Economy. J. Xi’an Univ. Financ. Econ. 2023, 36, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.M. Mechanism Innovation for the Integrated Development of Digital Economy and Rural Industry. Issues Agric. Econ. 2021, 12, 81–91. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, W.; Li, Y.Q.; Li, C.X.; Guo, J.L.; Jia, H.Q.; Deng, C.D. Digital Economy and Agricultural and Rural Modernization. Front. Sci. Technol. Eng. Manag. 2024, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.G. Digital Economy and High-quality Agricultural Development: Influence Effects and Action Paths. Stat. Decis. 2024, 6, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.C.; Zhang, S.F. An Empirical Test of Modernization of Agricultural Industry Chain Driven by Digital Economy. Stat. Decis. 2024, 40, 22–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y. Research on the Influence of Digital Economy in Agriculture and Rural Areas on the CommonProsperity of Urban and Rural Areas: Based on the Evidence of the Quasi-natural Experimentof E-commerce into Rural Comprehensive Demonstration Counties. J. Tech. Econ. Manag. 2024, 2, 123–128. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, H.; Zhang, Z. Digital Economy Empowers Rural Industry Revitalization: Effect Test and Mechanism Analysis. Rural. Financ. Res. 2023, 5, 44–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.J.; Li, X. Research on the impact and mechanism of the digital economy on rural revitalization—An analysis based on the mediating effect of rural E-commerce. J. Chang. Financ. Coll. 2023, 3, 86–96. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, T. Research on the Integrated Development of Digital Economy and Modern Agriculture. Agric. Econ. 2023, 2, 26–28. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Q.; Li, J.Z.; Hong, Y.S.; Su, Y.Y. The impact of the digital economy on agricultural green development: Evidence from China. Agriculture 2022, 12, 1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.F.; Ji, M.X.; Zheng, X.Z. Digital Economy, Agricultural Technology Innovation, and Agricultural Green Total Factor Productivity. Sage Open 2023, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhakhov, N.V.; Krivoshlykov, V.S.; Slavova, N.A.; Glebova, I.A.; Turchakov, V.V. State Influence on the Development of Digital Economy of Rational Nature Use in Agricultural Sector of the Region’s Economy. In XVIII International Scientific and Practical Conference “Modern Trends in Agricultural Production in the World Economy”; Kuzbass State Agricultural Academy: Kemerovo, Russia, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Li, B.Q.; Zhou, Q.X.; Yue, H.Z. An empirical test of the influence of digital countryside construction on industrial prosperity. Stat. Decis. 2022, 38, 5–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.S.; Yue, X.Y. How to Improve the Efficiency of Rural Digital Governance?—An Analytical Framework based on Data, Technology and Platform. E-Government 2023, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, F.A. Analysis on Technological Empowerment on Modernization Construction of Chinese Rural Communities: Significance, Challenge and Solution. J. Hubei Univ. (Philos. Soc. Sci.) 2022, 49, 134–141+173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T. Opportunities Challenges and Realization Paths of Rural Tourism Development under the Background of Digitalization. Agric. Econ. 2022, 2, 133–135. [Google Scholar]
- Mamai, O.V.; Mamai, I.N.; Kitaeva, M.V. Digitization of the agricultural sector of economy as an element of innovative development in Russia. In Digital Age: Chances, Challenges and Future; Springer International Publishing: Samara, Russia, 2020; pp. 359–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, D.Y.; Lai, D.D. Digital Economy and Urban-Rural Income Gap—Based on the Constraints of Industrial Structure and Environmental Investment. Financ. Account. Commun. 2023, 15, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.A.; Wu, H.A.; Zhao, J.F. Coupling Coordination Measurement and Evaluation of Digital Economyand High-quality Development. J. Stat. Inf. 2022, 37, 22–34. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, M.M.; Liu, J.X. Digital Economy Productivity Helps Common Wealth: Dual Effects and Practical Paths. J. Tech. Econ. Manag. 2023, 8, 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, W.F.; Zhang, G.M.; Zhao, F.Y. Digital Economy Empowers Rural Revitalization: Influencing Mechanism and Spatial Effect. J. Financ. Econ. 2023, 3, 32–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, L. Research on the Development Path of Digital Economy to Promote Agricultural Modernization. Econ. Rev. J. 2022, 9, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.X.; Qin, Y. Modernization of Agriculture and Rural Areas: Historical Retrospect, Connotation of Times, Target Positioning and Realization Path. J. Contemp. Econ. Res. 2022, 11, 71–82. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, M.; Buren, M.D. Digital economy, innovation activity and agricultural modernization transformation. J. Tech. Econ. Manag. 2023, 6, 36–41. [Google Scholar]
- Du, Y.H.; Liang, W.Y. Rural Education and Rural Economy Development: The Perspective of Human Capital. J. Beijing Norm. Univ. (Soc. Sci.) 2011, 6, 70–78. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, S.H.; Sun, Y. The Modernization of Rural Education under the Digital Transformation: Value, Blueprint and Strategy. Forum Contemp. Educ. 2023, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.K.; Liu, S.H. Modernization of Rural Education Governance: Its Scientific Connotation, Transformation and Practice Path. Educ. Acad. Mon. 2019, 11, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.D. The Modernization of Peasant lifestyle. Guide Bus. 2015, 6, 182–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J. Research on Global Supply Chain Reconfiguration Path and Digital Transformation of Chinese Manufacturing Industry. China Soft Sci. 2022, 4, 23–34. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Q.Y.; Shan, Z.G.; Ma, C.J. A Review of the Research on the Measurement Index System of Digital Economy at Home and Abroad. World Surv. Res. 2018, 31, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, Y.; Lu, Q.; Li, Z.X. Digital Economy Development Enabling Common Prosperity: Influence effect and Function Mechanism. Secur. Mark. Her. 2022, 5, 2–13. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.Q.; Zeng, F.S. Level Measurement and Regional Difference of Agricultural and Rural Modernization Development in Hunan Province. Econ. Geogr. 2022, 42, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.Y.; Xu, S.W. Study on the construction of an evaluation index system for agricultural and rural modernization in China. Res. Agric. Mod. 2022, 43, 759–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Xin, L.; Zhu, T.H. Research on The Temporal and Spatial Characteristics Andobstacle Factors of The Modernization Level of My Country’Sregional Agriculture And Rural Areas. Chin. J. Agric. Resour. Reg. Plan. 2023, 44, 135–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.Q.; Wang, H.; Tan, Y.H. Spatial-temporal Evolution Characteristics and Regional Differences ofAgriculturaland Rural Modernization Development Level in China. World Agric. 2023, 3, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, D.W.; Fan, Q.; Zhou, X. H. Pattern Conception and Realistic Paths of Deep Integration of Digital Economy and Agriculture. Lanzhou Acad. J. 2022, 12, 131–143. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, F.F.; Qian, Y.L. Coupling Coordination Between Digital Economy and New Urbanization and Obstacle Factors. J. Heihe Univ. 2024, 15, 68–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Xiao, X.P. Study on Spatio-Temporal Evolution of Coupling Coordination between Digital Economy and Agricultural Modernization. Ecol. Econ. 2024, 40, 101–107+125. [Google Scholar]
| Coupling Subsystem | Target Layer | Indicator Layer | Metric Attributes | Weights |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Digital economy | Digital infrastructure (0.6206) | Domain names | + | 0.1596 |
| Webpages (in 10,000 s) | + | 0.2499 | ||
| Internet broadband access ports (in 10,000 s) | + | 0.0710 | ||
| Broadband internet users (in 10,000 s) | + | 0.0719 | ||
| Long-distance optical cable length (in 10,000 km) | + | 0.0391 | ||
| Mobile phone penetration (%), | + | 0.0290 | ||
| Digitization of agriculture (0.1282) | average service population of rural postal branches (10,000) | + | 0.0990 | |
| Fixed assets invested in agriculture, forestry, animal husbandry and fishery (CNY 100 million) | + | 0.0292 | ||
| Digital industrialization of agriculture (0.2513) | Peking University Digital Financial Inclusion Index (PKU-DFIIC) | + | 0.0299 | |
| Online retail sales (CNY 100 million) | + | 0.2213 | ||
| Modernization of agriculture | Comprehensive production capacity (0.5164) | Grain yield per unit of cultivated land (kg/hectare) | + | 0.0197 |
| Meat product output (10,000 tons) | + | 0.0738 | ||
| Total mechanical power per unit of cultivated land area (10,000 kW/1000 hectares) | + | 0.0639 | ||
| Proportion of effective irrigated area/cultivated land area (%) | + | 0.0550 | ||
| Agricultural electricity consumption (100 million kWh) | + | 0.1780 | ||
| Personnel engaged in scientific and technological activities (person/year) | + | 0.1260 | ||
| Modernization of infrastructure and public services (0.2649) | Household waste disposal rate (%) | + | 0.0086 | |
| Penetration rate of rural access to sanitary latrines (%) | + | 0.0244 | ||
| Medical personnel per 1000 people among the rural population (person/thousand) | + | 0.1087 | ||
| Number of rural cultural stations | + | 0.0680 | ||
| Local government expenditure on education (CNY 100 million) | + | 0.0552 | ||
| Modernization of residents’ ideology and quality of life (0.0959) | Rural residents’ disposable income (CNY) | + | 0.0455 | |
| Engel coefficient of rural households (%) | - | 0.0134 | ||
| Rural residents’ per capita consumption expenditure (CNY) | + | 0.0369 | ||
| Modernization of rural governance systems and capacity (0.1228) | Rural residents’ guaranteed minimum livelihood (per person) | - | 0.0138 | |
| Urban–rural income gap (CNY) | - | 0.0138 | ||
| Number of villagers’ committees | + | 0.0953 |
| Coupling Coordination | Basic Type | Coupling Coordination Level | Coupling Coordination | Basic Type | Coupling Coordination Level |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [0, 0.1) | Low level | Extreme dysregulation | [0.5, 0.6) | High level | Little coordination |
| [0.1, 0.2) | Severe dysregulation | [0.6, 0.7) | Primary coordination | ||
| [0.2, 0.3) | Moderate disorder | [0.7, 0.8) | Intermediate coordination | ||
| [0.3, 0.4) | Moderate level | Mild disorder | [0.8, 0.9) | Extreme level | Good coordination |
| [0.4, 0.5) | On the verge of disorder | [0.9, 1] | High-quality coordination |
| Year | I | E(I) | sd(I) | z | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2011 | 0.191 | −0.033 | 0.109 | 2.053 | 0.020 |
| 2012 | 0.193 | −0.033 | 0.108 | 2.093 | 0.018 |
| 2013 | 0.208 | −0.033 | 0.108 | 2.237 | 0.013 |
| 2014 | 0.208 | −0.033 | 0.108 | 2.233 | 0.013 |
| 2015 | 0.217 | −0.033 | 0.108 | 2.305 | 0.011 |
| 2016 | 0.218 | −0.033 | 0.108 | 2.319 | 0.010 |
| 2017 | 0.254 | −0.033 | 0.109 | 2.644 | 0.004 |
| 2018 | 0.254 | −0.033 | 0.108 | 2.651 | 0.004 |
| 2019 | 0.240 | −0.033 | 0.108 | 2.525 | 0.006 |
| 2020 | 0.247 | −0.033 | 0.108 | 2.591 | 0.005 |
| Region | Year | The Main Factor of the Digital Economy Is the Degree of Obstacles | The Main Factor of Agricultural Modernization Is the Degree of Obstacles | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Eastern | 2011 | X1 (55.64) | X2 (10.66) | X3 (24.02) | Y1 (38.50) | Y2 (21.16) | Y3 (7.10) | Y4 (7.55) |
| 2015 | X1 (47.98) | X2 (8.70) | X3 (19.50) | Y1 (35.60) | Y2 (19.05) | Y3 (5.13) | Y4 (7.43) | |
| 2020 | X1 (42.79) | X2 (6.93) | X3 (12.20) | Y1 (33.02) | Y2 (13.27) | Y3 (3.15) | Y4 (7.61) | |
| Mean | X1 (48.80) | X2 (8.77) | X3 (18.57) | Y1 (35.71) | Y2 (17.83) | Y3 (5.13) | Y4 (7.53) | |
| Central | 2011 | X1 (58.96) | X2 (12.06) | X3 (24.70) | Y1 (43.46) | Y2 (20.98) | Y3 (8.22) | Y4 (7.25) |
| 2015 | X1 (55.15) | X2 (10.63) | X3 (23.09) | Y1 (41.96) | Y2 (19.85) | Y3 (6.50) | Y4 (7.17) | |
| 2020 | X1 (49.39) | X2 (9.02) | X3 (20.16) | Y1 (41.42) | Y2 (14.06) | Y3 (4.86) | Y4 (7.44) | |
| Mean | X1 (54.50) | X2 (10.57) | X3 (22.65) | Y1 (42.28) | Y2 (18.30) | Y3 (6.53) | Y4 (7.29) | |
| Western | 2011 | X1 (59.82) | X2 (12.04) | X3 (24.78) | Y1 (46.44) | Y2 (22.62) | Y3 (8.55) | Y4 (9.04) |
| 2015 | X1 (57.88) | X2 (10.95) | X3 (23.47) | Y1 (45.52) | Y2 (21.18) | Y3 (7.07) | Y4 (8.94) | |
| 2020 | X1 (54.39) | X2 (8.66) | X3 (21.93) | Y1 (45.02) | Y2 (15.17) | Y3 (5.49) | Y4 (8.97) | |
| Mean | X1 (57.36) | X2 (10.55) | X3 (23.39) | Y1 (45.66) | Y2 (19.66) | Y3 (7.04) | Y4 (8.98) | |
| Northeastern | 2011 | X1 (59.07) | X2 (11.74) | X3 (24.87) | Y1 (44.57) | Y2 (22.67) | Y3 (7.79) | Y4 (9.01) |
| 2015 | X1 (56.71) | X2 (10.52) | X3 (23.39) | Y1 (43.44) | Y2 (21.85) | Y3 (6.20) | Y4 (8.90) | |
| 2020 | X1 (54.37) | X2 (8.22) | X3 (22.09) | Y1 (43.96) | Y2 (15.54) | Y3 (4.86) | Y4 (8.77) | |
| Mean | X1 (56.72) | X2 (10.16) | X3 (23.45) | Y1 (43.99) | Y2 (20.02) | Y3 (6.28) | Y4 (8.89) | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, J.; Lyu, J. The Digital Economy and Agricultural Modernization in China: Measurement, Mechanisms, and Implications. Sustainability 2024, 16, 4949. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16124949
Guo J, Lyu J. The Digital Economy and Agricultural Modernization in China: Measurement, Mechanisms, and Implications. Sustainability. 2024; 16(12):4949. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16124949
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Jie, and Jiahui Lyu. 2024. "The Digital Economy and Agricultural Modernization in China: Measurement, Mechanisms, and Implications" Sustainability 16, no. 12: 4949. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16124949
APA StyleGuo, J., & Lyu, J. (2024). The Digital Economy and Agricultural Modernization in China: Measurement, Mechanisms, and Implications. Sustainability, 16(12), 4949. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16124949





