Contextual Relationships of Factors Affecting Sustainability 4.0 in the Textile Industry
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Theoretical Background
2.1. Industry 4.0 and Sustainability
- FIS1: Production on demand—a production model that develops goods and merchandise that already have their own demand, a trend in the business market that, as we know, is constantly changing and looking for ways to adapt to generate a more effective result in less time, reducing costs and minimizing waste; after all, only what was already demanded for final consumption/sale will be produced [23,30].
- FIS2: Technological innovation—in a scenario of continuous digital transformation, this innovation consists of implementing resources, based on technology and its tools (AI, IoT, BigData, Blockchain, Machine Learning, etc.), in order to produce positive results for the purpose and processes of the organization, resulting in increased quality and productivity in order to effectively contribute to organizational development [5,38].
- FIS3: Optimization of resources (e.g., energy efficiency)—use of resources, whether inputs, human, or financial, in a more effective and efficient way, reducing waste and costs throughout the execution of processes and enhancing production capacity [39].
- FIS5: Adherence to the Circular Economy—unlike the traditional linear model, where resources are extracted, used, and discarded, the circular economy promotes the reuse and recycling of materials, closing the cycle and reducing dependence on finite resources, seeking to redesign, produce, and market products intelligently, ensuring the efficient use and recovery of resources [42].
- FIS6: Process improvement—continuous improvement in quality and productivity with increased effectiveness and efficiency in the execution of production processes using technologies such as, for example, artificial intelligence, Internet of Things, and robotics [43].
- FIS7: Corporate Socio-Environmental Responsibility—organizations reaffirm their ethical commitment to social, environmental, and economic development, with all their processes guided by the objective of promoting this sustainable production management [44].
- FIS8: Adherence to the Sharing Economy—structured according to new consumer trends, the sharing economy is a business model that is based on the sharing of products and services, as well as the reuse of goods, stimulating the generation of new sources of income and extending the useful life of disused materials, including technology, acting as a catalyst for this economic model, supporting the countless networks that help and drive this model [45].
- FIS9: More conscious consumption—we are facing a generation that is increasingly moving towards conscious and questioning consumption. This consumer, who seeks to understand from the origin of the raw material of that piece of clothing to the end it will have, believes that understanding the entire process and life cycle of a product is fundamental in times when it is necessary to rethink daily habits and how we can adapt them to a planet in need of change [46,47].
- FIS10: Focus on customer experience—taking advantage of technologies such as artificial intelligence, for example, offering solutions to improve customer satisfaction through qualified and relevant experiences of excellence, which have a positive impact; after all, the better the experience, the tendency is for the satisfaction to be greater [48].
- FIS11: Strengthening sustainable fashion—sustainable fashion is related to the generation of an experience associated with social and environmental commitment, uniting the pillars of production and consumption with awareness and commitment to societal issues, considering the entire life cycle of the product, from design to production/manufacturing [49].
- FIS12: Personalization (3D Clothes, Virtual Fitting Rooms, etc.)—technology that facilitates the adaptation of services to the needs of each client, using technologies such as augmented reality and artificial intelligence through, for example, 3D clothes and virtual fitting rooms [4].
- FIS13: Waste reduction—waste management as well as the reduction in its generation together have the responsibility to reduce the environmental impacts arising from industrial production processes, including, for example, practices such as the reuse of inputs and reusing waste, preventing raw materials from being completely discarded [50,51].
- FIS14: Extension of the product’s useful life cycle—the implementation of the extension of the useful life of products is urgent to advance towards more sustainable production and consumption patterns. Extending the useful life of already manufactured products contributes to reducing the use of natural resources and the generation of waste, fundamental factors for accelerating the transition of businesses to a more circular economy [52].
- FIS15: Reduction in the environmental footprint (e.g., reduction in carbon emissions)—the reduction in impacts caused to the biosphere, with the environmental footprint being an indicator of sustainability that monitors the relationship between the biocapacity (or regenerative capacity) of the planet and the demand for natural resources necessary to produce consumer goods and services [53,54].
2.2. Interpretative Structural Modeling (ISM)
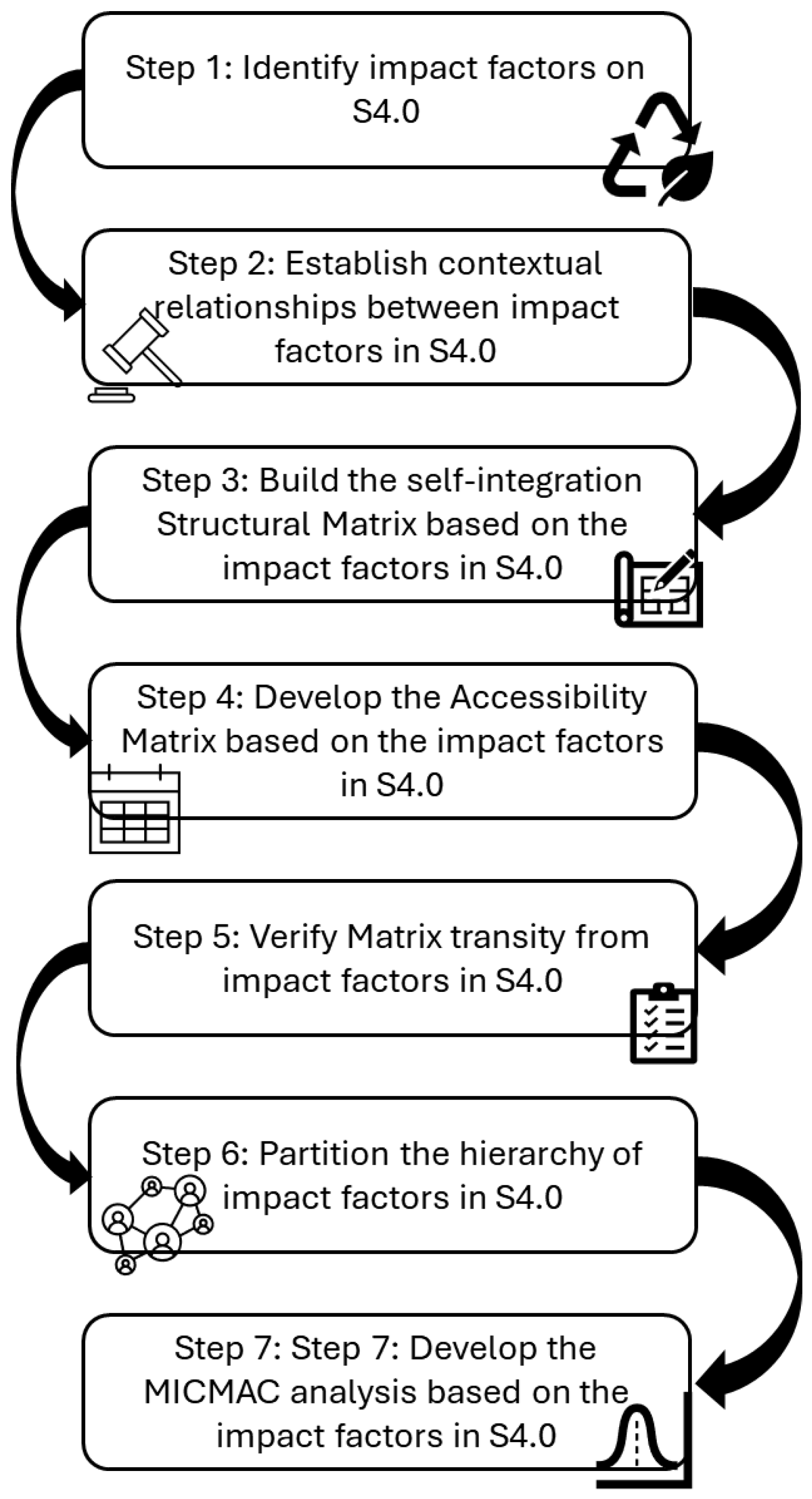
- Identification and exhaustive listing of all factors that will be the subject of study; the identification of factors is the first step in the ISM methodology. For this study, 16 (sixteen) factors that impact Sustainability 4.0 in the textile industry were listed, with 8 (eight) factors being identified for the economic dimension, 4 (four) for the social dimension, and 4 (four) for the environmental dimension [36].
- Establishment of contextual relationships between factors—for this step, a structured script is used with the aim of establishing the influence relationships between the factors that impact Sustainability 4.0 in the textile industry.
- Preparation of the structural self-interaction matrix referring to the factors under analysis—to identify the contextual relationships that are the subject of research, it is necessary to develop a structural self-interaction matrix based on classification symbols (V, A, X, O) so that the direction between bases i and j can be demonstrated. The “V” classification indicates that there is a relationship only between factor “i” and factor “j”. The “A” classification indicates that there is a relationship only between factor “j” and factor “i”. The “X” classification indicates that there is a relationship in both directions, whether from “i” to “j” or from “j” to “i”. And, finally, the “O” classification points to a lack of relationship in both directions, whether between “i” and “j” or “j” with “i” [60,61].
- Formulation of the Binary Initial Accessibility Matrix for the factors considered—once the structural self-interaction matrix has been developed for the factors that impact Sustainability 4.0 in the textile industry, the Binary Initial Accessibility Matrix must be developed using the classification V, A, X, O, which will be inter-crossed through the relationships between lines and columns according to the following rule [61]:
- ○
- If in the Matrix the entry (i, j) is classified as V, it will be represented by 1 in the entry (i, j) and 0 in the entry (j, i).
- ○
- If the entry (i, j) in the Matrix is classified as A, it will be represented by 0 entry (i, j) and 1 entry (j, i).
- ○
- If the entry (i, j) in the Matrix is classified as X, it will be represented by 1 in the entries (i, j) and (j, i).
- ○
- If the entry (i, j) in the Matrix is classified as O, it will be represented by 0 in the entries (i, j) and (j, i).
- ○
- In the structural self-interaction matrix, diagonal entries will be represented by 1.
- Assessment of transitivity in the structural self-interaction matrix—In this step, we seek to evaluate transitivity to check whether there is conformity in the relationships between different opposing factors [62]. It is important to check the possibility of indirect relationships between the crossed elements in the matrix, the relationships between the two attributes A and B and B and C, respectively, and indicate a relationship between attributes A and C [60,61,62].
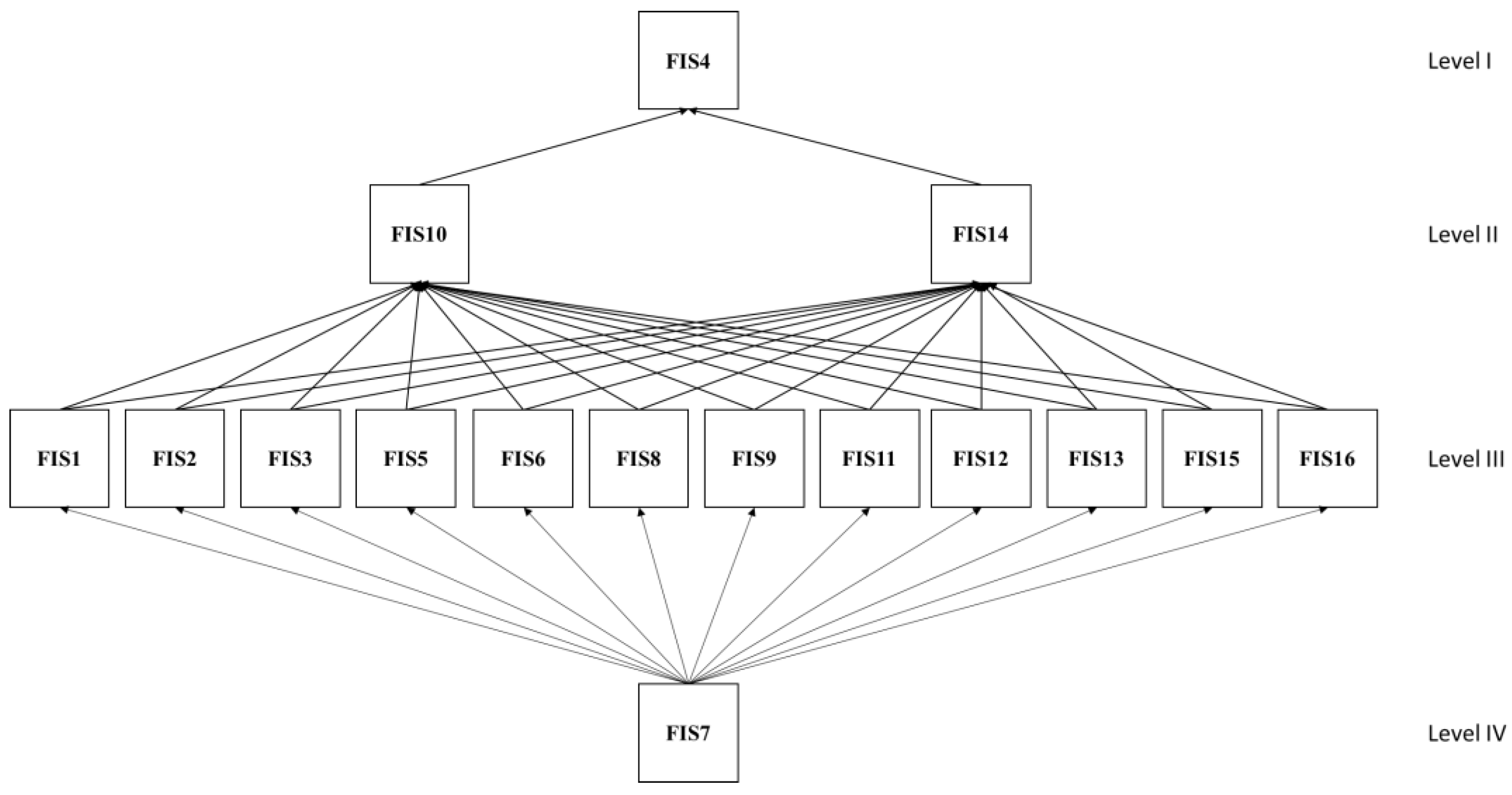
- Definition of partition levels in the Final Accessibility Matrix creation of the diagram ISM—After verifying the transitivity of the matrix, it is necessary to calculate the Power of Direction and Dependence Matrix, in which the summed values in the rows and columns will be represented. It is fundamental for creating a diagram that encompasses the entire ISM model, as well as its fragmentation into different levels [63]. By creating the matrix, it is possible to draw the hierarchical ISM model using a diagram.
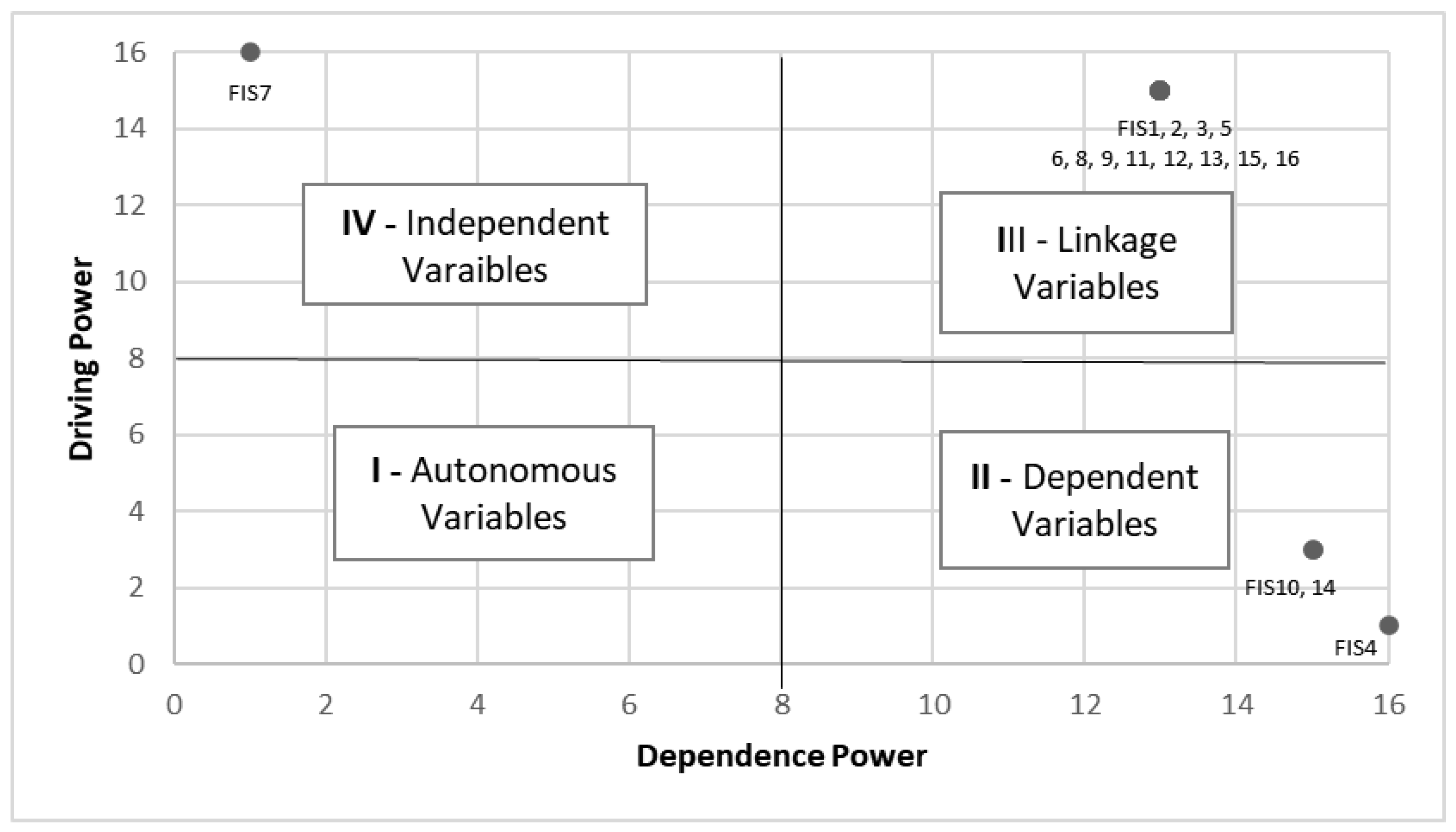
- Carrying out MICMAC analysis in relation to the factors examined—finally, the MICMAC analysis is used to segment the impact factors on Sustainability 4.0 into clusters according to the following classification:
- ○
- Cluster I (Autonomous Variables): the elements of this set are characterized by having low powers of dependence and direction [64].
- ○
- Cluster II (Dependent Variables): the elements of this set are characterized by having high power of dependence and low power of direction. In this group, the elements depend on each other, despite having low power of influence over other factors, therefore representing little relevance [65].
- ○
- Cluster III (Linkage Variables): the elements that make up this set are characterized by having high power of dependence and high power of direction. The factors located in this group influence the other factors, in addition to being influenced themselves [66].
- ○
- Cluster IV (Independent Variables): the elements that compose it are characterized by factors with low power of dependence and high power of direction, that is, it has a high capacity to influence other factors in a stable way [67].
- Review of potential inconsistencies in the ISM Model.
3. Materials and Methods
4. Results
Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- UNIDO—United Nations Industrial Development Organization. INDSTAT 2 2022, ISIC Revision 3. 2020. Available online: https://stat.unido.org (accessed on 11 March 2023).
- Mendes Junior, B.O. Indústria Têxtil. Cad. Setorial Etene 2022, 7, 1–12. Available online: https://www.bnb.gov.br/s482-dspace/handle/123456789/1462 (accessed on 11 March 2023).
- Silva, F.O.; Santos, A.V. Economia Criativa no Mercado da Moda e Sua Influência no Desenvolvimento da Indústria Têxtil no Nordeste. Rev. Econ. Reg. Urbana Trab. 2020, 9, 124–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, T.R.; Silva, F.P.D.; Ruthschilling, E.A. Textile Labs: Um estudo sobre a implementação de tecnologias de fabricação na indústria da moda. Educ. Gráf. 2019, 23, 287–300. [Google Scholar]
- Sousa, J.P.; Oliveira, V.; Maracajá, K.F.B. A sustentabilidade no espaço empresarial: Reflexões sobre a responsabilidade socioempresarial no setor da indústria têxtil da Cidade de Toritama/PE. Ciênc. Gerenc. 2021, 25, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulte, N.K.; Lopes, L.D. Sustentabilidade ambiental: Um desafio para a moda. Actas Diseño 2010, 9, 30–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akter, M.M.K.; Haq, U.N.; Islam, M.M.; Uddin, M.A. Textile-apparel manufacturing and material waste management in the circular economy: A conceptual model to achieve sustainable development goal (SDG) 12 for Bangladesh. Clean. Environ. Syst. 2022, 4, 100070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beier, G.; Matthess, M.; Guan, T.; Grudzien di do, P.; Xue, B.; de Lima, E.P.; Chen, L. Impact of Industry 4.0 on corporate environmental sustainability: Comparing practitioners’ perceptions from China, Brazil and Germany. Sustain. Prod. Consum. 2022, 31, 287–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caires, C.R.B.; Souza, L.A.F.; de Oliveira, A.R.; de Melo Bonini, L.M.; an de Santis SH, D.S. Management of industrial production in fashion: Challenges for sustainability. Rev. Ibero-Am. Humanid. Ciênc. Educ. 2023, 9, 1301–1314. [Google Scholar]
- Toniol, A.P.N.; Albieri, S. O fast-fashion como fenômeno econômico-cultural: Moda e globalização. Braz. J. Bus. 2020, 2, 2316–2327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNeill, L.; Moore, R. Sustainable fashion consumption and the fast fashion conundrum: Fashionable consumers and attitudes to sustainability in clothing choice. Int. J. Consum. Stud. 2015, 39, 212–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bortoluzzi, M.; Gutierrez, J.; Alves, M.F.; Fenerich, A.T. Apoio à tomada de decisão em uma indústria do setor fashion: Novas perspectivas a partir da sustentabilidade e da indústria 4.0. Rev. Eng. Produção 2020, 2, 53–76. [Google Scholar]
- Bullón Pérez, J.J.; Queiruga-Dios, A.; Gayoso Martínez, V.; Martín del Rey, Á. Traceability of ready-to-wear clothing through blockchain technology. Sustainability 2020, 12, 7491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertola, P.; Teunissen, J. Fashion 4.0. Innovating fashion industry through digital transformation. Res. J. Text. Appar. 2018, 22, 352–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albertin, M.R.; Pontes, H.L.J. A Engenharia de Produção na Era da Indústria 4.0: Estudos de Casos e Benchmarking da Indústria 4.0; Editora Appris: Curitiba, Brazil, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Javaid, M.; Haleem, A.; Singh, R.P.; Khan, S.; Suman, R. Sustainability 4.0 and its applications in the field of manufacturing. Internet Things Cyber-Phys. Syst. 2022, 2, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filgueiras, I.F.L.V.; Melo, F.J.C.D.; Guimaraes, D.S., Jr.; Barbosa, A.A.L.; Sobral, E.F.M.; Vital Junior, S.A. Evaluation of the Benefits Generated by Sustainability 4.0: A Study of the Perception of Banking Sector Customers. Sustainability 2024, 16, 2580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfineto, J.J.M. Avaliação da Relação Entre Práticas do Lean Manufacturing e Tecnologias da Indústria 4.0: Aplicação de Modelagem Estrutural Interpretativa (ISM). Master’s Thesis, Escola de Engenharia de São Carlos da Universidade de São Paulo, São Carlos, Brazil, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Pereira, A.; de Oliveira Simonetto, E.; Putnik, G.; de Castro, H.C.G.A. How connectivity and search for producers impact production in Industry 4.0 networks. Braz. J. Oper. Prod. Manag. 2018, 15, 528–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tessarini, G.; Saltorato, P. Impactos da indústria 4.0 na organização do trabalho: Uma revisão sistemática da literatura. Rev. Prod. Online 2018, 18, 743–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Germano, A.X.D.S.; Mello, J.A.V.B.; Motta, W.H. Contribuição das tecnologias da indústria 4.0 para a sustentabilidade: Uma revisão sistemática. Palabra Clave 2021, 11, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, Y.; Choi, J.; Gantumur, M.; Kim, N. Technology-based strategies for online secondhand platforms promoting sustainable retailing. Sustainability 2022, 14, 3259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira Costa, M.F.B.; Zaneti, B.B.; Bruno, I.C. Environmental Impacts of Fast Fashion: The International Textile Dump of Atacama-Chile. 2022. Available online: https://periodicos.utfpr.edu.br/rts/article/view/15794/9040 (accessed on 21 July 2023).
- Brasil. Lei nº 12.305, de 2 de Agosto de 2010. Institui a Política Nacional de Resíduos Sólidos; Altera a Lei no 9.605, de 12 de Fevereiro de 1998; e dá Outras Providências. 2010. Available online: http://www.planalto.gov.br/ccivil_03/_ato2007-2010/2010/lei/l12305.htm (accessed on 8 April 2023).
- United Nations. Our Common Future. 1987. Available online: https://sustainabledevelopment.un.org/content/documents/5987our-common-future.pdf (accessed on 5 October 2022).
- Sugahara, C.R.; Rodrigues, E.L. Desenvolvimento Sustentável: Um discurso em disputa. Desenvolv. Quest. 2019, 17, 30–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EPA United States Environmental Protection Agency. Nondurable Goods: Product-Specific Data. 2021. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/facts-and-figures-about-materials-waste-and-recycling/nondurable-goods-product-specific-data#ClothingandFootwear (accessed on 23 April 2022).
- Barros, S.T. Design na Indústria do Vestuário: Princípios da Sustentabilidade Ambiental como Estratégia para Auxiliar na Redução de Resíduos Têxteis no Segmento de Moda Festa. Master’s Thesis, Faculdade de Arquitetura e Urbanismo e Design da Universidade Federal de Uberlândia, Uberlândia, Brazil, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Mesacasa, A.; Zanette, Y. Análise de uma empresa de moda segundo os princípios da economia circular. Rev. Livre Sustentabilidade Empreendedorismo 2021, 6, 172–200. [Google Scholar]
- Rathore, B. Textile Industry 4.0: A Review of Sustainability in Manufacturing. Int. J. New Media Stud. 2023, 10, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fletcher, K.; Grose, L. Moda & Sustentabilidade: Design para Mudança; Editora Senac: São Paulo, Brazil, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- da Silva, M.F.M.P.; de Moraes, V.B.; de Souza, L.L.; Babinski, V., Jr.; Schulte, N.K. Os Biomateriais Têxteis no Contexto da Indústria 4.0: O Exemplo das Fibras das Teias de Aranhas. In ENSUS 2022—X Encontro de Sustentabilidade em Projeto; Anais eletrônicos...; Uniffespa: Marabá, Brazil, 2022; Available online: https://repositorio.ufsc.br/bitstream/handle/123456789/245081/Vol.%206%20853%20-%20865.pdf?sequence=1&isAllowed=y (accessed on 17 January 2023).
- Amaral, J.H.G.; Spers, E.E. Sustainability in the fashion industry: A case study in sericulture. Braz. J. Bus. 2020, 2, 3142–3150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, S.; Miskon, S.; Alabdan, R.; Tlili, I. Towards sustainable textile and apparel industry: Exploring the role of business intelligence systems in the era of Industry 4.0. Sustainability 2020, 12, 2632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, M.J.C. Práticas de sustentabilidade no ensino profissionalizante de moda. In Trilhas da Educação Profissional: Inovação e Criatividade; Cabral, S.N., Mota, L.I.A., Soares, L.S., Tahim, A.P.V.d.O., Eds.; Senac Ceará: Fortaleza, Brazil, 2020; Volume 2, pp. 15–26. [Google Scholar]
- Silva, M.F.V.O.B.; Melo, F.J.C. Sustainability 4.0 In The Fashion Industry: A Systematic Literature Review. Int. J. Adv. Oper. Manag. 2023, 15, 1–31, (ahead-of-print). [Google Scholar]
- Filgueiras, I.F.L.V.; Melo, F.J.C.D. Sustainability 4.0 in services: A systematic review of the literature. Benchmarking 2024, 31, 1771–1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araque González, G.; Suárez Hernández, A.; Gómez Vásquez, M.; Vélez Uribe, J.; Bernal Avellaneda, A. Sustainable manufacturing in the fourth industrial revolution: A big data application proposal in the textile industry. J. Ind. Eng. Manag. 2022, 15, 614–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guizzi, G.; Falcone, D.; De Felice, F. An integrated and parametric simulation model to improve production and maintenance processes: Towards a digital factory performance. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2019, 137, 106052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.W.R.; Chen, M.T.; Tseng, M.L.; Jantarakolica, T.; Xu, H. Multi-objective production programming to systematic sorting and remanufacturing in second-hand clothing recycling industry. Symmetry 2020, 12, 1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, F.B.; Fernandes, P.R.B. A reutilização de resíduos sólidos na economia circular: Estudo de caso no mercado de calçadista. Braz. J. Dev. 2021, 7, 48456–48470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, F.; Yin, S.; Chen, L.; Chen, X. The circular economy in the textile and apparel industry: A systematic literature review. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 259, 120728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ElShishtawy, N.; Sinha, P.; Bennell, J.A. A comparative review of zero-waste fashion design thinking and operational research on cutting and packing optimisation. Int. J. Fash. Des. Technol. Educ. 2022, 15, 187–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorisdottir, T.S.; Johannsdottir, L. Corporate social responsibility influencing sustainability within the fashion industry. A systematic review. Sustainability 2020, 12, 9167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Liu, K. A systematic review and future directions of the sharing economy: Business models, operational insights and environment-based utilities. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 290, 125209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezende, M.V.B.; Dubeux, V.J.C. Ser Sustentável está na Moda? O perfil do consumidor jovem carioca no mercado da moda sustentável. Int. J. Bus. Mark. 2020, 5, 72–84. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, N.; Mohan, D. Sustainable apparel purchase intention: Collectivist cultural orientation and price sensitivity in extended TPB model. J. Revenue Pricing Manag. 2021, 20, 149–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ta, A.H.; Aarikka-Stenroos, L.; Litovuo, L. Customer experience in circular economy: Experiential dimensions among consumers of reused and recycled clothes. Sustainability 2022, 14, 509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sena, T.V. Moda na era digital: Explorando as tendências do metaverso, NFTs e sustentabilidade. Rev. Ensino Artes Moda Des. 2023, 7, 1–26. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, Y.; Deng, K. Sustainable Fashion Innovation Design for Marine Litter. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2021, 1790, 012098. Available online: https://iopscience.iop.org/article/10.1088/1742-6596/1790/1/012098/meta (accessed on 28 July 2023). [CrossRef]
- Juanga-Labayen, J.P.; Labayen, I.V.; Yuan, Q. A review on textile recycling practices and challenges. Textiles 2022, 2, 174–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sodhi, S.; Singh, V.; Arya, V. Upcycling: Innovative way of textile waste management. Pharma Innov. J. 2022, 11, 1247–1248. [Google Scholar]
- Aivazidou, E.; Tsolakis, N. Water footprint management in the fashion supply chain: A review of emerging trends and research challenges. Water Text. Fash. 2019, 77–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, A.; Silva, C. Looking for sustainability scoring in apparel: A review on environmental footprint, social impacts and transparency. Energies 2021, 14, 3032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Memon, H.A.; Wang, Y.; Marriam, I.; Tebyetekerwa, M. Circular Economy and sustainability of the clothing and textile Industry. Mater. Circ. Econ. 2021, 3, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, T.W.; Sun, Y.; Shim, E. Progress of Recycled Polyester in Rheological Performance in Molding, and Economic Analysis of Recycled Fibers in Fashion and Textile Industry; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2023; Available online: https://www.intechopen.com/chapters/81855 (accessed on 27 July 2023).
- Warfield, J.N. Developing interconnection matrices in structural modeling. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 1974, SMC–4, 81–87. [Google Scholar]
- Sage, A.P. Interpretive Structural Modeling: Methodology for Large-Scale Systems; McGraw-Hill: Nova York, NY, USA, 1977. [Google Scholar]
- Feofiloff, P.; Kohayakawa, Y.; Wakabayashi, Y. Uma Introdução Sucinta à Teoria dos Grafos; Editora da Universidade de São Paulo: São Paulo, Brazil, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Melo, F.J.C.; Medeiros, D.D. Applying interpretive structural modeling to analyze the fundamental concepts of the management excellence model guided by the risk-based thinking of ISO 9001: 2015. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. 2021, 27, 742–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, L.B.D.; Melo, F.J.C.D.; Guimaraes, D.S., Jr.; Sobral, E.F.M.; Medeiros, D.D.D. Application of ISM to Identify the Contextual Relationships between the Sustainable Solutions Based on the Principles and Pillars of Industry 4.0: A Sustainability 4.0 Model for Law Offices. Sustainability 2023, 15, 14494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, A.S.; Badhotiya, G.K.; Soni, G.; Kumari, P. Investigating interdependencies of sustainable supplier selection criteria: An appraisal using ISM. J. Glob. Oper. Strat. Sourc. 2020, 13, 195–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashini, R.; Suresh, M. Modelling the ergonomics factors affecting the work system in a hospital: An ISM approach. Int. J. Pure Appl. 2018, 119, 183–198. [Google Scholar]
- Eshtehardi, M.S.A. Structural-interpretative modeling of strategies for achieving the mission of education in an entrepreneurial and community-oriented university. Q. J. Res. Plan. High. Educ. 2022, 28, 33–64. [Google Scholar]
- Ribeiro, A.M.; Arantes, A.; Cruz, C.O. Barriers to the Adoption of Modular Construction in Portugal: An Interpretive Structural Modeling Approach. Buildings 2022, 12, 1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoar, S.; Chileshe, N. Exploring the Causes of Design Changes in Building Construction Projects: An Interpretive Structural Modeling Approach. Sustainability 2021, 13, 9578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Josaiman, S.K.; Faisal, M.N.; Talib, F. Social Sustainability Adoption Barriers in Supply Chains: A Middle East Perspective using Interpretive Structural Modeling. Int. J. Oper. Quant. Manag. 2021, 27, 61–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafiq, M.; Naz, S.; Martins, J.M.; Mata, M.N.; Mata, P.N.; Maqbool, S. A study on emerging management practices of renewable energy companies after the outbreak of covid-19: Using an interpretive structural modeling (ISM) approach. Sustainability 2021, 13, 3420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elhidaoui, S.; Benhida, K.; El Fezazi, S.; Kota, S.; Lamalem, A. Critical success factors of blockchain adoption in green supply chain management: Contribution through an interpretive structural model. Prod. Manuf. Res. 2022, 10, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathvik, S.; Krishnaraj, L.; Awuzie, B.O. Establishing the root causes of unsafe behaviors among construction workers: An integrative interpretive structural modeling analysis. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 7006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaisue, N.; Ketjoy, N.; Kaewpanha, M.; Thanarak, P. The barriers analysis for waste-to-energy project development in Thailand: Using an interpretive structural modeling approach. Energies 2023, 16, 1941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangari, M.S.; Dashtpeyma, M. An integrated framework of supply chain resilience enablers: A hybrid ISM-FANP approach. Int. J. Bus. Excell. 2019, 18, 242–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva Lima, F.S.; Rodrigues, W.; Vergara, F.E.V. O cenário da Política Nacional de Biocombustível no Brasil: Um estudo baseado no Tocantins a partir do método MICMAC. DELOS Desarro. Local Sosten. 2020, 13, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Sheehy, B.; Farneti, F. Corporate social responsibility, sustainability, sustainable development and corporate sustainability: What is the difference, and does it matter? Sustainability 2021, 13, 5965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calza, F.; Sorrentino, A.; Tutore, I. Combining corporate environmental sustainability and customer experience management to build an integrated model for decision-making. Manag. Decis. 2023, 61, 54–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, Y.L.; Yoo, H.S. Environmental, social, and governance activities and firm performance: Global evidence and the moderating effect of market competition. Corp. Soc. Responsib. Environ. Manag. 2023, 30, 2830–2839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denizel, M.; Schumm, C.Z. Closed loop supply chains in apparel: Current state and future directions. J. Oper. Manag. 2024, 70, 190–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Ren, J.; Wan, M.; Cao, J. Financing strategies for a textile and apparel remanufacturing supply chain with the delay in disbursement subsidies. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 437, 140745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Periyasamy, A.P.; Periyasami, S. Rise of digital fashion and metaverse: Influence on sustainability. Digit. Econ. Sustain. Dev. 2023, 1, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eriksson, S.; Käck, J. Sustainable Reverse Logistics in Fast Fashion E-Commerce: A Literature Review-Impact of Sustainable Practices on Customer Satisfaction. 2023. Available online: https://odr.chalmers.se/items/14ead96f-7a83-4334-9347-cb50c5c86945 (accessed on 21 December 2023).
- Liu, C.; Xia, S.; Lang, C. Online luxury resale platforms and customer experiences: A text mining analysis of online reviews. Sustainability 2023, 15, 8137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| j | FSI1 | FSI2 | FSI3 | FSI4 | FSI5 | FSI6 | FSI7 | FSI8 | FSI9 | FSI10 | FSI11 | FSI12 | FSI13 | FSI14 | FSI15 | FSI16 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| i | |||||||||||||||||
| FIS1 | - | X | V | A | V | V | V | A | V | A | A | A | V | A | V | V | |
| FIS2 | - | A | A | V | X | V | V | O | A | A | O | V | A | A | X | ||
| FIS3 | - | A | A | A | V | X | V | A | X | O | V | A | A | O | |||
| FIS4 | - | V | V | O | O | O | V | V | O | V | O | V | V | ||||
| FIS5 | - | A | V | V | V | A | V | V | O | A | V | O | |||||
| FIS6 | - | V | V | O | A | V | V | O | A | V | O | ||||||
| FIS7 | - | A | O | A | O | O | A | A | O | A | |||||||
| FIS8 | - | A | A | V | A | O | A | A | O | ||||||||
| FIS9 | - | A | V | V | O | A | A | O | |||||||||
| FIS10 | - | V | V | O | X | V | V | ||||||||||
| FIS11 | - | X | O | A | V | O | |||||||||||
| FIS12 | - | O | O | V | V | ||||||||||||
| FIS13 | - | A | A | X | |||||||||||||
| FIS14 | - | V | V | ||||||||||||||
| FIS15 | - | V | |||||||||||||||
| FIS16 | - | ||||||||||||||||
| j | FSI1 | FSI2 | FSI3 | FSI4 | FSI5 | FSI6 | FSI7 | FSI8 | FSI9 | FSI10 | FSI11 | FSI12 | FSI13 | FSI14 | FSI15 | FSI16 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| i | |||||||||||||||||
| FIS1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | |
| FIS2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | |
| FIS3 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| FIS4 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | |
| FIS5 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | |
| FIS6 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | |
| FIS7 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| FIS8 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| FIS9 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| FIS10 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |
| FIS11 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | |
| FIS12 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | |
| FIS13 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | |
| FIS14 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |
| FIS15 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | |
| FIS16 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | |
| j | FSI1 | FSI2 | FSI3 | FSI4 | FSI5 | FSI6 | FSI7 | FSI8 | FSI9 | FSI10 | FSI11 | FSI12 | FSI13 | FSI14 | FSI15 | FSI16 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| i | |||||||||||||||||
| FIS1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 * | 1 | 0 | 1 * | 1 * | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | |
| FIS2 | 1 | 1 | 1 * | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 * | 0 | 1 * | 1 * | 1 | 0 | 1 * | 1 | |
| FIS3 | 1 * | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 * | 1 * | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 * | 1 | 1 * | 1 | 0 | 1 * | 1 * | |
| FIS4 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 * | 1 * | 1 * | 1 | 1 | 1 * | 1 | 1 * | 1 | 1 | |
| FIS5 | 1 * | 1 * | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 * | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 * | 0 | 1 | 1 * | |
| FIS6 | 1 * | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 * | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 * | 0 | 1 | 1 * | |
| FIS7 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| FIS8 | 1 | 1 * | 1 | 0 | 1 * | 1 * | 1 | 1 | 1 * | 0 | 1 | 1 * | 1 * | 0 | 1 * | 1 * | |
| FIS9 | 1 * | 1 * | 1 * | 0 | 1 * | 1 * | 1 * | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 * | 0 | 1 * | 1 * | |
| FIS10 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 * | 1 | 1 | 1 | |
| FIS11 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 * | 1 * | 1 * | 1 * | 1 * | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 * | 0 | 1 | 1 * | |
| FIS12 | 1 | 1 * | 1 * | 0 | 1 * | 1 * | 1 * | 1 | 1 * | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 * | 1 * | 1 | 1 | |
| FIS13 | 1 * | 1 * | 1 * | 0 | 1 * | 1 * | 1 | 1 * | 1 * | 0 | 1 * | 1 * | 1 | 0 | 1 * | 1 | |
| FIS14 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 * | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |
| FIS15 | 1 * | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 * | 1 * | 1 * | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 * | 1 * | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | |
| FIS16 | 1 * | 1 | 1 * | 0 | 1 * | 1 * | 1 | 1 * | 1 * | 0 | 1 * | 1 * | 1 | 0 | 1 * | 1 | |
| j | FSI1 | FSI2 | FSI3 | FSI4 | FSI5 | FSI6 | FSI7 | FSI8 | FSI9 | FSI10 | FSI11 | FSI12 | FSI13 | FSI14 | FSI15 | FSI16 | Driving Power | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| i | ||||||||||||||||||
| FIS1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 * | 1 | 0 | 1 * | 1 * | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 13 | |
| FIS2 | 1 | 1 | 1 * | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 * | 0 | 1 * | 1 * | 1 | 0 | 1 * | 1 | 13 | |
| FIS3 | 1 * | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 * | 1 * | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 * | 1 | 1 * | 1 | 0 | 1 * | 1 * | 13 | |
| FIS4 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 * | 1 * | 1 * | 1 | 1 | 1 * | 1 | 1 * | 1 | 1 | 16 | |
| FIS5 | 1 * | 1 * | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 * | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 * | 0 | 1 | 1 * | 13 | |
| FIS6 | 1 * | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 * | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 * | 0 | 1 | 1 * | 13 | |
| FIS7 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | |
| FIS8 | 1 | 1 * | 1 | 0 | 1 * | 1 * | 1 | 1 | 1 * | 0 | 1 | 1 * | 1 * | 0 | 1 * | 1 * | 13 | |
| FIS9 | 1 * | 1 * | 1 * | 0 | 1 * | 1 * | 1 * | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 * | 0 | 1 * | 1 * | 13 | |
| FIS10 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 * | 1 | 1 | 1 | 15 | |
| FIS11 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 * | 1 * | 1 * | 1 * | 1 * | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 * | 0 | 1 | 1 * | 13 | |
| FIS12 | 1 | 1 * | 1 * | 0 | 1 * | 1 * | 1 * | 1 | 1 * | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 * | 1 * | 1 | 1 | 13 | |
| FIS13 | 1 * | 1 * | 1 * | 0 | 1 * | 1 * | 1 | 1 * | 1 * | 0 | 1 * | 1 * | 1 | 0 | 1 * | 1 | 13 | |
| FIS14 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 * | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 15 | |
| FIS15 | 1 * | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 * | 1 * | 1 * | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 * | 1 * | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 13 | |
| FIS16 | 1 * | 1 | 1 * | 0 | 1 * | 1 * | 1 | 1 * | 1 * | 0 | 1 * | 1 * | 1 | 0 | 1 * | 1 | 13 | |
| Dependence power | 15 | 15 | 15 | 1 | 15 | 15 | 16 | 15 | 15 | 3 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 3 | 15 | 15 | ||
| FIS | Reachability Set | Antecedent Set | Intersection Set | Level |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FIS1 | 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 8, 9, 11,12, 13, 15, 16 | 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 8, 9, 10,11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16 | 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 8, 9, 11,12, 13, 15, 16 | |
| FIS2 | 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 8, 9, 11,12, 13, 15, 16 | 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 8, 9, 10,11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16 | 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 8, 9, 11,12, 13, 15, 16 | |
| FIS3 | 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 8, 9, 11,12, 13, 15, 16 | 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 8, 9, 10,11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16 | 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 8, 9, 11,12, 13, 15, 16 | |
| FIS4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | I |
| FIS5 | 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 8, 9, 11,12, 13, 15, 16 | 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 8, 9, 10,11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16 | 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 8, 9, 11,12, 13, 15, 16 | |
| FIS6 | 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 8, 9, 11,12, 13, 15, 16 | 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 8, 9, 10,11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16 | 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 8, 9, 11,12, 13, 15, 16 | |
| FIS7 | 7 | 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9,10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16 | 7 | |
| FIS8 | 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 8, 9, 11,12, 13, 15, 16 | 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 8, 9, 10,11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16 | 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 8, 9, 11,12, 13, 15, 16 | |
| FIS9 | 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 8, 9, 11,12, 13, 15, 16 | 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 8, 9, 10,11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16 | 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 8, 9, 11,12, 13, 15, 16 | |
| FIS10 | 10, 14 | 4, 10, 14 | 10, 14 | |
| FIS11 | 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 8, 9, 11,12, 13, 15, 16 | 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 8, 9, 10,11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16 | 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 8, 9, 11,12, 13, 15, 16 | |
| FIS12 | 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 8, 9, 11,12, 13, 15, 16 | 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 8, 9, 10,11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16 | 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 8, 9, 11,12, 13, 15, 16 | |
| FIS13 | 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 8, 9, 11,12, 13, 15, 16 | 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 8, 9, 10,11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16 | 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 8, 9, 11,12, 13, 15, 16 | |
| FIS14 | 10, 14 | 4, 10, 14 | 10, 14 | |
| FIS15 | 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 8, 9, 11,12, 13, 15, 16 | 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 8, 9, 10,11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16 | 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 8, 9, 11,12, 13, 15, 16 | |
| FIS16 | 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 8, 9, 11,12, 13, 15, 16 | 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 8, 9, 10,11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16 | 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 8, 9, 11,12, 13, 15, 16 |
| FIS | Reachability Set | Antecedent Set | Intersection Set | Level |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FIS1 | 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 8, 9, 11,12, 13, 15, 16 | 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 8, 9, 10,11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16 | 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 8, 9, 11,12, 13, 15, 16 | |
| FIS2 | 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 8, 9, 11,12, 13, 15, 16 | 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 8, 9, 10,11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16 | 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 8, 9, 11,12, 13, 15, 16 | |
| FIS3 | 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 8, 9, 11,12, 13, 15, 16 | 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 8, 9, 10,11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16 | 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 8, 9, 11,12, 13, 15, 16 | |
| FIS5 | 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 8, 9, 11,12, 13, 15, 16 | 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 8, 9, 10,11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16 | 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 8, 9, 11,12, 13, 15, 16 | |
| FIS6 | 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 8, 9, 11,12, 13, 15, 16 | 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 8, 9, 10,11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16 | 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 8, 9, 11,12, 13, 15, 16 | |
| FIS7 | 7 | 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9,10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16 | 7 | |
| FIS8 | 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 8, 9, 11,12, 13, 15, 16 | 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 8, 9, 10,11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16 | 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 8, 9, 11,12, 13, 15, 16 | |
| FIS9 | 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 8, 9, 11,12, 13, 15, 16 | 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 8, 9, 10,11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16 | 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 8, 9, 11,12, 13, 15, 16 | |
| FIS10 | 10, 14 | 10, 14 | 10, 14 | II |
| FIS11 | 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 8, 9, 11,12, 13, 15, 16 | 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 8, 9, 10,11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16 | 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 8, 9, 11,12, 13, 15, 16 | |
| FIS12 | 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 8, 9, 11,12, 13, 15, 16 | 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 8, 9, 10,11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16 | 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 8, 9, 11,12, 13, 15, 16 | |
| FIS13 | 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 8, 9, 11,12, 13, 15, 16 | 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 8, 9, 10,11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16 | 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 8, 9, 11,12, 13, 15, 16 | |
| FIS14 | 10, 14 | 10, 14 | 10, 14 | II |
| FIS15 | 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 8, 9, 11,12, 13, 15, 16 | 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 8, 9, 10,11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16 | 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 8, 9, 11,12, 13, 15, 16 | |
| FIS16 | 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 8, 9, 11,12, 13, 15, 16 | 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 8, 9, 10,11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16 | 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 8, 9, 11,12, 13, 15, 16 |
| FIS | Reachability Set | Antecedent Set | Intersection Set | Level |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FIS1 | 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 8, 9, 11,12, 13, 15, 16 | 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 8, 9, 11, 12, 13, 15, 16 | 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 8, 9, 11,12, 13, 15, 16 | III |
| FIS2 | 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 8, 9, 11,12, 13, 15, 16 | 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 8, 9, 11, 12, 13, 15, 16 | 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 8, 9, 11,12, 13, 15, 16 | III |
| FIS3 | 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 8, 9, 11,12, 13, 15, 16 | 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 8, 9, 11, 12, 13, 15, 16 | 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 8, 9, 11,12, 13, 15, 16 | III |
| FIS5 | 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 8, 9, 11,12, 13, 15, 16 | 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 8, 9, 11, 12, 13, 15, 16 | 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 8, 9, 11,12, 13, 15, 16 | III |
| FIS6 | 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 8, 9, 11,12, 13, 15, 16 | 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 8, 9, 11, 12, 13, 15, 16 | 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 8, 9, 11,12, 13, 15, 16 | III |
| FIS7 | 7 | 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 11, 12, 13, 15, 16 | 7 | |
| FIS8 | 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 8, 9, 11,12, 13, 15, 16 | 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 8, 9, 11, 12, 13, 15, 16 | 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 8, 9, 11,12, 13, 15, 16 | III |
| FIS9 | 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 8, 9, 11,12, 13, 15, 16 | 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 8, 9, 11, 12, 13, 15, 16 | 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 8, 9, 11,12, 13, 15, 16 | III |
| FIS11 | 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 8, 9, 11,12, 13, 15, 16 | 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 8, 9, 11, 12, 13, 15, 16 | 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 8, 9, 11,12, 13, 15, 16 | III |
| FIS12 | 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 8, 9, 11,12, 13, 15, 16 | 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 8, 9, 11, 12, 13, 15, 16 | 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 8, 9, 11,12, 13, 15, 16 | III |
| FIS13 | 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 8, 9, 11,12, 13, 15, 16 | 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 8, 9, 11, 12, 13, 15, 16 | 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 8, 9, 11,12, 13, 15, 16 | III |
| FIS15 | 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 8, 9, 11,12, 13, 15, 16 | 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 8, 9, 11, 12, 13, 15, 16 | 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 8, 9, 11,12, 13, 15, 16 | III |
| FIS16 | 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 8, 9, 11,12, 13, 15, 16 | 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 8, 9, 11, 12, 13, 15, 16 | 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 8, 9, 11,12, 13, 15, 16 | III |
| FIS | Reachability Set | Antecedent Set | Intersection Set | Level |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FIS7 | 7 | 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 11, 12, 13, 15, 16 | 7 | IV |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Silva, M.F.V.O.B.; Melo, F.J.C.d.; Sobral, E.F.M.; Guimarães, D.S.; Albuquerque, A.P.G.d.; Vital, S.A.; Pinto, P.A.L.d.A.; Cruz, T.V.d.Q.F.d.; Andrade, R.C.D.d.; Confessor, K.L.A. Contextual Relationships of Factors Affecting Sustainability 4.0 in the Textile Industry. Sustainability 2024, 16, 5999. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16145999
Silva MFVOB, Melo FJCd, Sobral EFM, Guimarães DS, Albuquerque APGd, Vital SA, Pinto PALdA, Cruz TVdQFd, Andrade RCDd, Confessor KLA. Contextual Relationships of Factors Affecting Sustainability 4.0 in the Textile Industry. Sustainability. 2024; 16(14):5999. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16145999
Chicago/Turabian StyleSilva, Marcella Fernanda Vieira Ottoni Bezerra, Fagner José Coutinho de Melo, Eryka Fernanda Miranda Sobral, Djalma Silva Guimarães, André Philippi Gonzaga de Albuquerque, Silvio André Vital, Pablo Aurélio Lacerda de Almeida Pinto, Tatyane Veras de Queiroz Ferreira da Cruz, Rômulo César Dias de Andrade, and Kliver Lamarthine Alves Confessor. 2024. "Contextual Relationships of Factors Affecting Sustainability 4.0 in the Textile Industry" Sustainability 16, no. 14: 5999. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16145999
APA StyleSilva, M. F. V. O. B., Melo, F. J. C. d., Sobral, E. F. M., Guimarães, D. S., Albuquerque, A. P. G. d., Vital, S. A., Pinto, P. A. L. d. A., Cruz, T. V. d. Q. F. d., Andrade, R. C. D. d., & Confessor, K. L. A. (2024). Contextual Relationships of Factors Affecting Sustainability 4.0 in the Textile Industry. Sustainability, 16(14), 5999. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16145999







