External Thermal Insulation Composite Systems—Past and Future in a Sustainable Urban Environment
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
- Study of literature and established scientific knowledge. The aim of the research was to achieve an overview of the literature related to the issue of the biodegradation of ETICSs. Articles were evaluated according to keywords, as shown in Figure 1. Studying the articles allowed us to understand the issue in a wider range of presented findings from research. At the same time, it was possible to confront the issue with the results of our research work (Appendix A and Appendix B).
- The comparison of results from conducted research (according to the results of case studies, see Appendix A, selected locations CS 2 and CS 3, and in the text Appendix A) with the results determined according to points outlined above results in the following objectives, namely:
- (a)
- Comparison of results from conducted research include determination of the diversity of microorganisms on the example of 2 selected locations from the case study (a selection of locations with a label CS 2 and CS 3);
- (b)
- To document whether the increasing thicknesses of the ETICS composite, as a result of standard regulations, can have a negative impact on the quality of the internal microclimate;
- (c)
- To document whether the migration of microorganisms from the surface of ETICS towards the internal environment of apartment buildings can be harmful to health or not.
2.1. Study of Literature
2.2. Comparison of Results from Conducted Research
- Orientation of the residential housing towards the world parties,
- Facade shading;
- Proximity to greenery and water bodies;
- The thickness of the ETICS composite (the thickness of the ETICS composite was determined according to the overview in Table 2 and Figure 2 and Figure 3 in accordance with the development of requirements according to standards (code) and legislation (for CZ and the development of requirements according to EU legislation);
- Architectural design of the apartment building, division of the facade and solution of details in the perimeter shell;
- Laboratory diagnostics.
2.2.1. Selection of Locality CS 2 for Defining Species Diversity of Microorganisms for the Area 90 ha
2.2.2. Selection of Locality CS 3 for Defining Species Diversity of Microorganisms for the Area 50 ha
2.2.3. Overview of Monitored Parameters for Selected Locations CS 2 and CS 3
2.3. Diagnostic Options
- Thermal imaging targeting of the external wall and detection of weak points in the external wall;
- Verification of the thermal insulation thickness of the ETICS composite and comparison with the legislation, whether the thickness is satisfactory or not;
- Software modelling of the external wall and comparison of models with the results of thermal imaging;
- Taking samples from the surface of the external wall in the place of significant biodegradation and in the place of windowsills;
- Laboratory diagnostics and determination of the type of microorganism.
3. Results and Discussion
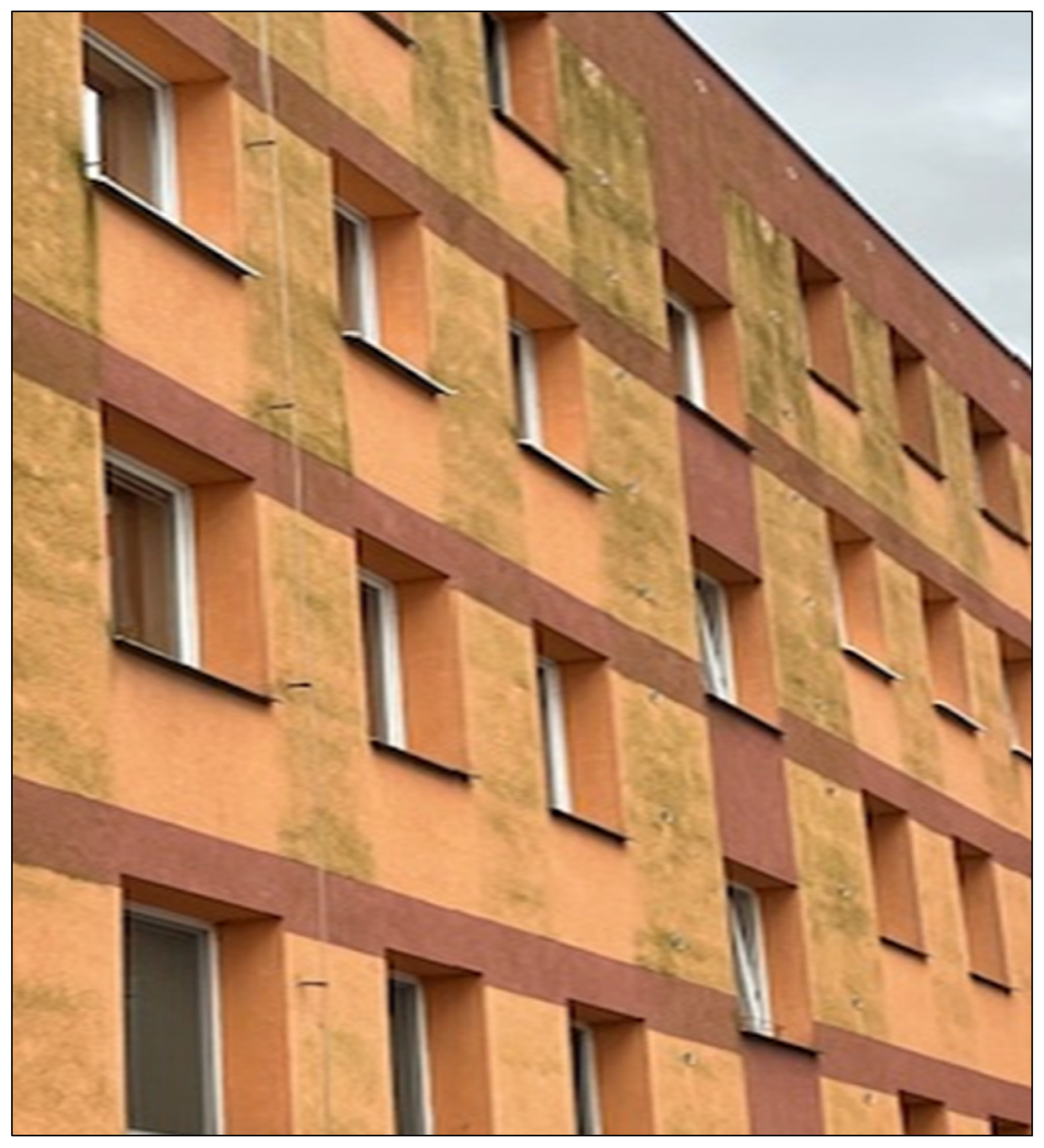
- The results showed that the vegetation near the housing development is affected by the same types of microorganisms as the outer surface of the ETICS composite. Green terrestrial algae Chlorophycae, which are predominant in the case study overview, live locally, in colonies and on other surfaces, such as palisades, gutter walkways, among others. It turned out that the area of greenery or water bodies (forests, parks, rivers) does not have a major influence on the overall extent of colonization of the facade by microorganisms. An important factor for the initiation of biodegradation is the time exposure of the ETICS composite to moisture loading, the orientation of the panel residential housing with respect to the cardinal points and, most likely, the direction of the prevailing winds, which helps the natural transport and migration of microorganisms to other apartment buildings. The adherence to strict technological discipline is also an important factor. The exposure to moisture is documented in Figure A1 (Appendix C).
- The transport of microorganisms into the interior during window ventilation is highly probable. This transport phenomenon can have a negative impact on the health of the population, and a negative impact on human health cannot be ruled out, especially on children or the elderly population, who are more prone to developing health problems. While studying the literature, we did not come across a study that conducted research for ETICS composites in an interdisciplinary manner [50,51,52,53,54,55].
- The predominant areas of research are those that focus on the issues of building microbiology inside buildings, such as the effect of moisture on occupant health, mould formation, etc. The issues of external building microbiology and its link to building indoor quality, taking into account the environmental setting, are addressed to a lesser extent. However, it is important to note that a number of authors state that the issue of building microbiology along with environmental context needs to become an essential part of the criteria for assessing building quality.
- From the point of view of multidisciplinary research “natural sciences, construction and architecture, environment”, the scientific discourse refers to the confirmation or refutation of the fact that the inhalation of undesirable microorganisms from the ETICS composites migrating into the inner space of residential housing through direct ventilation is harmful to health.
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
Appendix B
Appendix C
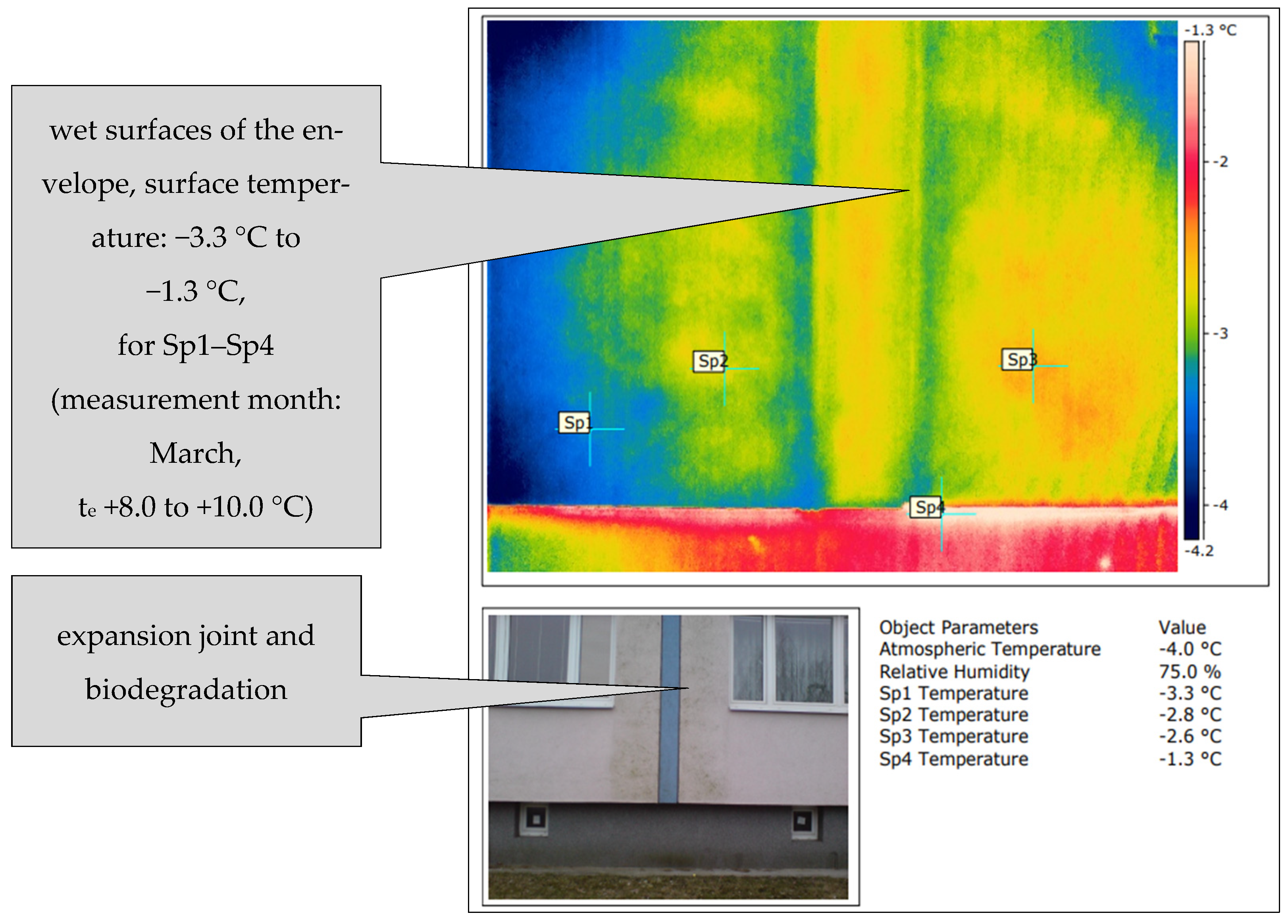
Appendix D
References
- Delivering the European Green Deal (Fit for 55). 2021. Available online: http://energy.ec.europa.eu (accessed on 28 July 2024).
- Witzany, J.; Pašek, J. Prefabricated Structural Systems and Parts of Buildings (KPS 70); CTU: Prague, Czech Republic, 2003; pp. 63–144. [Google Scholar]
- Ryzhova, O.; Khrichenkov, A. Principles of Renovation the Territory of Residential Buildings Dating from 1960s to 1970s: Coping with Modern Housing Crisis. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 481, 2–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubečková, D. The Past and Future of Panel Construction, 1st ed.; VSB-TU: Ostrava, Czech Republic, 2009; pp. 7–13. [Google Scholar]
- Kubečková, D.; Vrbová, M. Historical Development of Thermal Protection of Prefab Residential Housing and Its Future, an Example of the Czech Republic. Energies 2021, 14, 2623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Platform of Building for Future, European Green Deal. 2021. Available online: http://bpie.eu/ (accessed on 28 July 2024).
- Available online: http://renovate-europe.eu (accessed on 28 July 2024).
- CSN 73 2901; Performance of External Thermal Insulation Composite Systems (ETICS). Office for Technical Standardization, Methodology and State Testing: Prague, Czech Republic, 2020.
- Las, E. ETICS, the System We All (Thought to) Know, a Personal View on the “Experience and developments in ETICS”. SSO ETICS, Conference Łochów No. 2022.105. Available online: https://konferencjaetics.com.pl/wp-content/uploads/2022/05/1.-14.10-14.40-Eric-Las-N.2022.105-ETICS-The-fingerprint-and-performance-2022.05.11.pdf (accessed on 28 July 2024).
- Kubečková, D. The Quality of ETICS in the Context of Energy and Social Changes (Case study). Sustainability 2022, 14, 3135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulakatko, V.; Lill, I.; Soekov, E.; Arhipova, R.; Witt, E.; Liisma, E. Towards nearly zero-energy buildings through analyzing reasons for degradation of facades. In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference of Building Resilience, Incorporating the 3rd Annual Conference of the Android Disaster Resilience Network, Salford Quays, UK, 8–10 September 2014; Volume 18, pp. 592–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jasiczak, J.; Girus, K. Maintenance and durability of the concrete externl layer of curtain walls in prefabricated technological Poznan large panel system. In Proceedings of the World Multidisciplinary Civil Engineering-Architecture-Urban Planning Symposium (WMCAUS 2018), Prague, Czech Republic, 18–22 June 2018; IOP Conference Series-Materials Science and Engineering. Volume 245, pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Žák, J. Positive and negative aspects of ETICS. In Proceedings of the 10th International Scientific Conference Building Defects, Ceske Budejovice, Czech Republic, 29–30 November 2018; Volume 279, pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orlik-Koždoň, B. Effect of indoor climatic conditions on the risk of water vapor condensation and mould growth. J. Build. Enginering 2024, 95, 110198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Y.; Fan, Y.; Wang, Z.; Gao, W.; Sun, Z.; Ge, J. Facilitator of moisture accumulation in building envelopes and its influences on condensation and mould growth. Energy Build. 2022, 277, 112528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daugelaite, A.; Dogan, H.; Grazuleviciute, I. Characterizing sustainability aesthetics of buildings and environment: Methodological frame and pilot application to the hybrid environments. Landsc. Archit. Land 2021, 19, 61–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, S.S.; Ellis, C. Sustainability, the environment, and New Urbanism: An assessment and agenda for research. J. Archit. Plan. Res. 2007, 24, 125–142. [Google Scholar]
- Kubečková, D. The influence of architecture and structural creation of details of building envelope structures on the well-being of the indoor environment. In Proceedings of the Conference Defects and Reconstruction of Perimeter Cladding and Roofs, Podbánské, Slovakia, 21–23 March 2005; pp. 81–87. [Google Scholar]
- Blaszczok, M.; Branowski, A. Thermal Improvement in Residential Buildings in View of the Indoor Air Quality—Case Study for Polish Dwelling. Archit. Civ. Eng. Environ. 2018, 11, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Energy Efficiency and IAQ. EfficEPA. 2024. Available online: https://healthenergies.com/ (accessed on 19 September 2024).
- Nakayama, Y.; Nakaoka, H.; Suzuki, N.; Tsumura, K.; Hanazato, M.; Todaka, E.; Mori, C. Prelevance and risk factors of pre-sick building syndrome: Characteristics of indoor environmenat and individual factors. Environ. Health Prev. Med. 2019, 24, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishara, A.; Kramberger-Kaplan, H.; Ptatschek, V. Influence of different pigments on the facade surface temperatures. Energy Procedia 2017, 132, 447–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maltceva, K.; Pridvizhkin, S. Technological, economic and legislative opportunities and barriers for panel apartement buildings energy efficient reconstruction in Russia. In Proceedings of the 10th International Scientific Conference Buildings Defects, Ceske Budejovice, Czech Republic, 29–30 November 2018; Volume 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salčin, M.; Simonović, V.; Habibija, S.D.; Zilić, M. ETICS System of Individual Family Dwellings in Bosnia and Herzegovina. HURBE 2021, 385–394. [Google Scholar]
- Onyszkiewicz, J.; Sadowski, K. Proposal for the revitalization of prefabricated building facades in terms of the principles of sustainable development and social participation. J. Build. Eng. 2022, 46, 103713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Büchl, R.; Raschle, R. Example of practice. In Algae and Fungi on Facades, 1st ed.; MISE: Prague, Czech Republic, 2004; pp. 50–79. [Google Scholar]
- Asere, L.; Mols, T.; Blumberga, A. Assessment of energy efficiency measures on indoor air quality and microclimate in buildings of Liepaja municipality. In Proceedings of the International Scientific Conference-Environmental and Climate Technologies, CONECT 2015, Riga, Latvia, 14–16 October 2015; Volume 95, pp. 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshino, H. Housing Performance and Equipment for Healthy Indoor Environment. In Indoor Environmental Quality and Health Risk Toward Healtheir Environment for All; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 267–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krueger, N.; Hofbauer, W.K.; Thiel, A.; Ilvonen, O. Resilience of biocide-free ETICS to microbiological growth in an accelerated test. Build. Environ. 2023, 244, 110737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antosova, N. Impact of Biocorrosion on the Durability of ETICS and Empirical Findings about the Periodocity of Maintennace. Slovak J. Civ. Eng. 2013, 21, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minarovicová, K. Environmental Aspects of Maintenance of Buildings with ETICS. MATEC Web Conf. 2019, 279, 03005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lembo, F.; Marino, F.P.R. The Pathologies of the ETICS. Recent Dev. Build. Diagn. Tech. 2016, 5, 37–39. [Google Scholar]
- Viegas, C.A.; Borsoi, G.; Moreira, L.M.; Parracha, J.L.; Nunes, L.; Malanho, S.; Veiga, R.; Flores-Colen, I. Diversity and distribution of microbial communities on the surface of External Thermal Insulation Composite Systems (ETICS) facades in residential buildings. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2023, 184, 105658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koste, W.; Shiel, R.J. Rotifera from Australian inland waters.1. Bdelloidea (Rotifera, Dogononta). Aust. J. Mar. Freshw. Res. 1986, 37, 765–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryparová, P.; Rácová, Z. Characterization of Microorganism from Individual Layers of the Building Envelope (ETICS) and Methods of Their Sampling. In Proceedings of the CRRB 2015, Prague, Czech Republic, 12–13 November 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Ryparová, P.; Wasserbauer, R.; Rácová, Z. The cause of occurrence of microorganism in civil engineering and the dangers associated with their growth. Procedia Eng. 2016, 151, 300–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Vrbová, M. Monitoring Report of Biotic Attack; VSB-TU: Ostrava, Czech Republic, 2016–2022. [Google Scholar]
- Vrbová, M. Thesis of Dissertation Work; VSB-TU: Ostrava, Czech Republic, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Report of Nanotechnology Center, Cooperation (Biodegradation); VSB-TU: Ostrava, Czech Republic, 2013–2020.
- Poulíčková, A. Basics of Cyanobacteria and Algae Ecology; Faculty of Science, Palacký University in Olomouc: Olomouc, Czechia, 2011; pp. 11–33. [Google Scholar]
- Report Monitoring of Prefab Residential Housing; VSB-TU: Ostrava, Czech Republic, 2012–2015.
- Thermal Imaging Report; Database of VSB-TU: Ostrava, Czech Republic, 2012–2023.
- Tang, D.; Huang, M. Dilemmas and Solutions for Sustainability-Based Engineering Ethics: Lessons Learned form the Collapse of a Self-Built House in Changsha Hunan, China. Buildings 2024, 14, 2581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barberousse, H.; Ruot, B.; Yéprémian, C.; Boulon, G. An assessment of facade coatings against the colonisation by aerial algae and cyanobacteria. Build. Environ. 2007, 42, 2555–2561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’ORazio, M.; Cursio, G.; Graziani, L.; Aquilanti, L.; Osimani, A.; Clementi, F.; Yéprémian, C.; Lariccia, V.; Amoroso, S. Effects absorption and surface roughness on the bioreceptivity of ETICS comapred to clay bricks. Build. Environ. 2014, 77, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.; Chauhan, M. Influence of Environmental factors on the growth of building deteriorating fungi: Aspergillus Flavus and Penicillium Chrysogenum. Int. J. Phramaceutical Sci. Res. 2023, 4, 425–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez-Figueroa, C.; Beckett, R. Living with buildings, living with microbec: Probiosis and architecture. Arq-Archit. Res. Q. 2020, 24, 155–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicuna, R.; Gonzales, B. The microbial world in a changing environment. Rev. Chil. De Hist. Nat. 2021, 94, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nath, S.; Dewsbury, M.; Douwes, J. Has a singular focus of buildings regulations created unhealthy homes? Archit. Sci. Rev. 2020, 63, 387–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasserbauer, R. Biological Degradation of Buildings; ABF ARCH: Prague, Czech Republic, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Sulakatko, V.; Lill, A.E.; Witt, E. Methodological framework to assess the significance of External Thermal Insulation Composite System (ETICS) on-site activities. Energy Procedia 2016, 96, 446–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ximenes, S.; de Brito, J.; Gaspar, P.L.; Silva, A. Modeling the degradation and service life of ETICS in external walls. Mater. Struct. 2015, 48, 2235–2249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiano, P. Biodegradation of Cultural Heritage: Decay Mechanisms and Control Methods; Seminar Article; Department of Conservation and Restoration, New University of Lisbon: Lisbon, Portugal, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Dornieden, T.; Gorbushina, A.; Krumbein, W. Biodecay of cultural heritage as a space/time-related ecological situation—An evaluation of a series of studies. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2000, 46, 261–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moularat, S.; Hulin, M.; Robine, E.; Annesi-Maesano, I.; Caillaud, D. Airborne fungal volatile organic compounds in rural and urban dwellings: Detection of mould contamination in 94 homes determined by visual inspection and airborne fungal volatile organic compounds method. Sci. Total Environ. 2011, 409, 2005–2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Technical Approval Guideline ETAG 004:2013 External Thermal Insulation Composite Systems with Rendering. Available online: https://www.eota.eu/sites/default/files/uploads/ETAGs/etag-004-february-2013.pdf (accessed on 22 September 2024).
- EOTA: European Organisation for Technical Assessment. Technical Information; EOTA: Brussels, Belgium. Available online: https://eota.eu (accessed on 22 September 2024).
- ASHARE. Information from Events 2022–2024. Available online: https://www.ashrae.org/ (accessed on 22 September 2024).
- Kubečková, D. Regeneration of Panel Housing Estates from the Perspective of Thermal Technology, Sustainability and Environmental Context (Case Study of the City of Ostrava, Czech Republic). Sustainability 2023, 15, 8449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubečková, D.; Kraus, M.; Šenitková, I.J.; Vrbová, M. The Indoor Microclimate of Prefabricated Buildings for Housing: Interaction of Environmental and Construction Measures. Sustainability 2020, 12, 10119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pešta, J.; Tesař, D.; Zwiener, V. Diagnostics of Buildings; Atelier DEC: Rzeszów, Poland, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Plášková, P. Biocorrosion of Inorganic Materials. Master’s Thesis, T. Bati University, Zlín, Czech Republic, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Software Teplo, Svoboda. 2017. Available online: https://kcad.cz/cz/ke-stazeni/teplo/ (accessed on 22 September 2024).

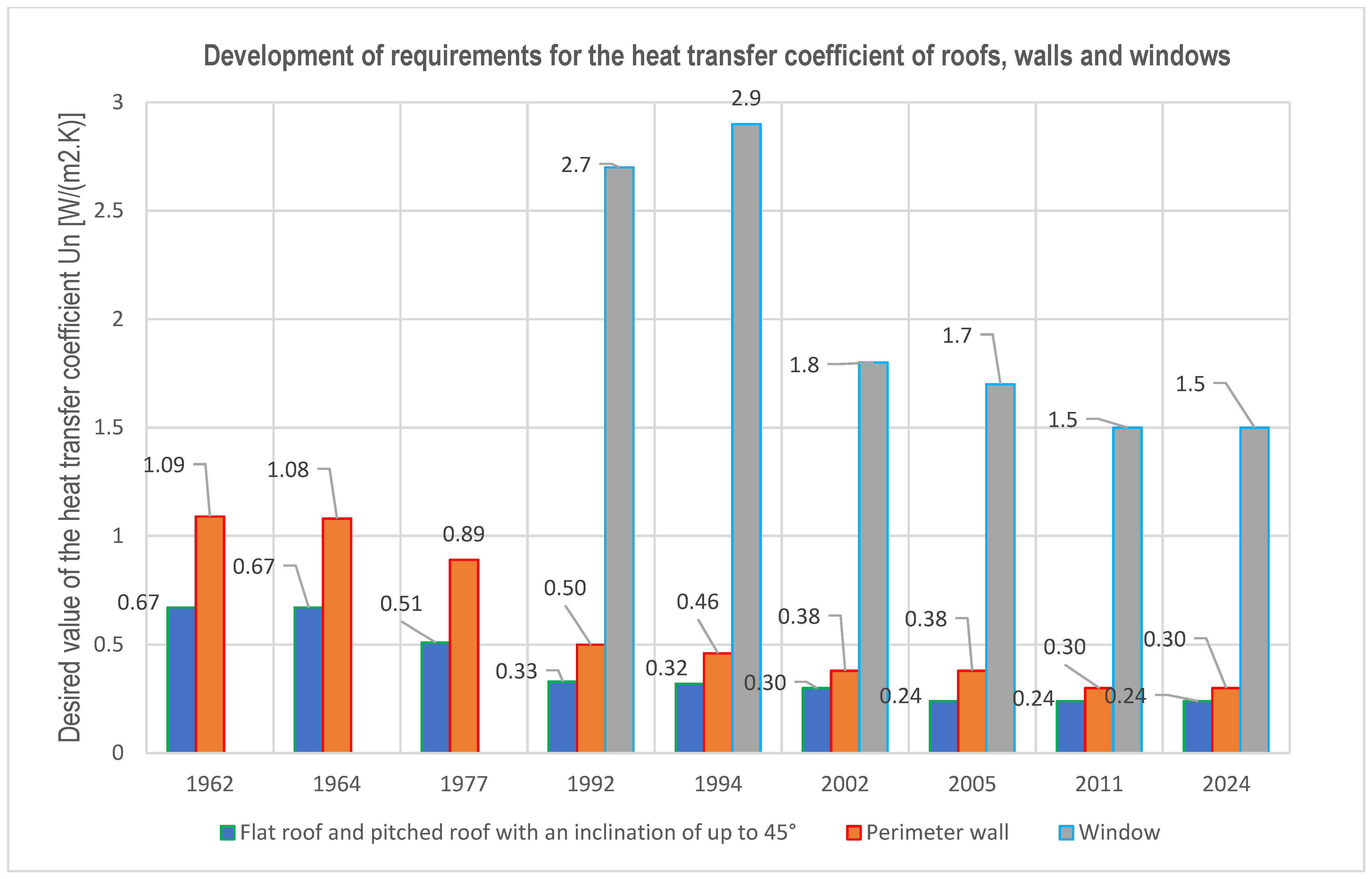
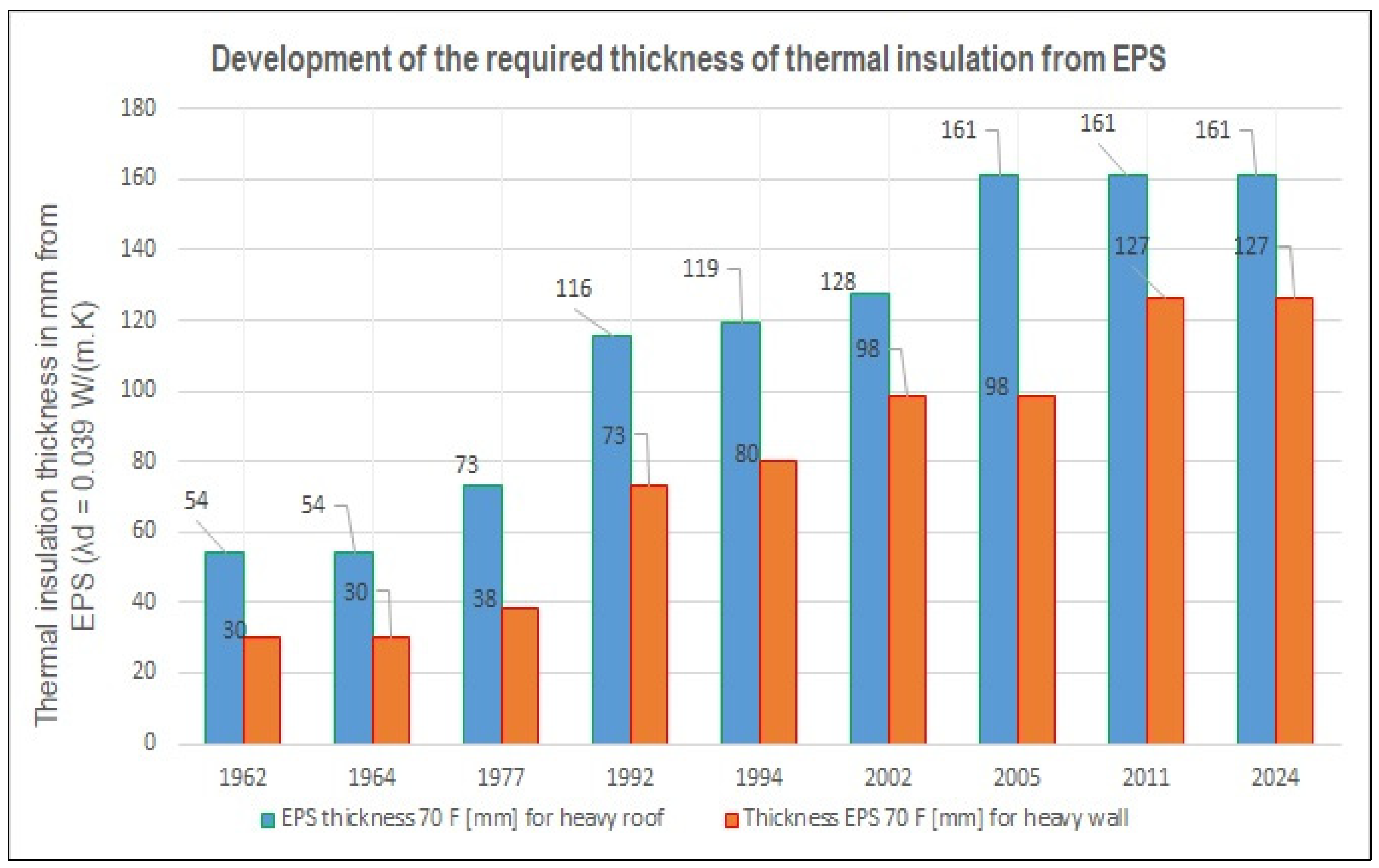


| Year and Country 1995 to 2022 | Environment and ETICS | ETICS and Biodegradation | ETICS and Indoor Microclimate | Environment and Panel Residential Housing | ETICS and Indoor Microclimate of Panel Residential Housing |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Poland | 10 | ||||
| Portugal | 10 | ||||
| Czech Republic | 5 | 2 | 2 | 8 | 2 |
| Estonia | 4 | ||||
| USA | 29 | ||||
| China | 4 | 16 | |||
| Italy | 7 | ||||
| South Korea | 7 | ||||
| Other countries | 8 | 62 | |||
| 41 | 2 | 2 | 129 | 2 |
| 1949 | 1950–1960 | 1963 | 1979 | 1992–1994 | 1997 | 2002 | 2005 | 2007 | 2000–2020 | 2024–2030 | 2030–2050 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Code 1450 | 1st Code 73 0540 (CZ) for thermal technique | Code 73 0540 | Revision Code 73 0540 | Revision Code 73 0540 Thermal protection of buildings | Code 73 0540—Change 1 | Code 73 0540 Novel of part 2 | Code 73 0540 and its composition of new 4 parts | Code 73 0540 and the introduction of new quantities | EPBD I., EPBD II. | EPBD III, IV. and Emission strategy | Emission strategy |
| Perimeter wall thickness [mm] and material for additional contact insulation | |||||||||||
| 450 Brickwork | 240, 270, 300 Perimeter panels based on lightweight concrete (e.g., slag concrete, gas silicate) | Fit for 55 Emission-free strategy | |||||||||
| Thickness of additional contact insulation based on extruded polystyrene (XPS) or mineral waves (MW) [mm] | |||||||||||
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 60 | 60 80 | 80 100 | 100 120 | 120 150 | 150 180 200 * | Emission free |
| Parameters and Comparison of Selected Locations CS 2 and CS 3 | Location CS 2 with an Area of 90 ha | Location CS 3 with an Area of 50 ha |
|---|---|---|
| Orientation of the residential housing to the cardinal points. | mainly the north | mainly the north |
| Facade shading. | Yes | Yes |
| ETICS composite thickness [mm]. | 120–150 | 120–150 |
| The architectural solution of the residential housing, the division of the facade and the solution of details in the perimeter shell. | partially (loggias, balconies), strip architecture | partially (loggias, balconies), strip architecture |
| Laboratory diagnostics, in situ diagnostics. | Yes | Yes |
| Parameters and Comparison of Selected Locations with Area CS 2 and Area CS 3 | CS 2 with an Area of 90 ha | CS 3 with an Area of 50 ha |
|---|---|---|
| Chlorophycae (algae) [39] Figure 4b | 80% | 90% |
| Dothideomycetes (fungus) [39] Figure 4b | 20% | 10% |
| Other (see Appendix A, Table 3) | - | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kubečková, D.; Kubenková, K.; Afsoosbiria, H.; Musenda, O.K.; Mohamed, K. External Thermal Insulation Composite Systems—Past and Future in a Sustainable Urban Environment. Sustainability 2024, 16, 8500. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16198500
Kubečková D, Kubenková K, Afsoosbiria H, Musenda OK, Mohamed K. External Thermal Insulation Composite Systems—Past and Future in a Sustainable Urban Environment. Sustainability. 2024; 16(19):8500. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16198500
Chicago/Turabian StyleKubečková, Darja, Kateřina Kubenková, Hamed Afsoosbiria, Oskar Kambole Musenda, and Khaled Mohamed. 2024. "External Thermal Insulation Composite Systems—Past and Future in a Sustainable Urban Environment" Sustainability 16, no. 19: 8500. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16198500
APA StyleKubečková, D., Kubenková, K., Afsoosbiria, H., Musenda, O. K., & Mohamed, K. (2024). External Thermal Insulation Composite Systems—Past and Future in a Sustainable Urban Environment. Sustainability, 16(19), 8500. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16198500







