Abstract
The increased focus on sustainability in response to climate change has given rise to many new initiatives to meet the rise in building load demand. The concept of distributed energy resources (DER) and optimal control of supply to meet power demands in buildings have resulted in growing interest to adopt microgrids for a precinct or a university campus. In this paper, a model for an actual physical microgrid has been constructed in OPAL-RT for real-time simulation studies. The load demands for SIT@NYP campus and its weather data are collected to serve as input to run on the digital twin model of DERs of the microgrid. The dynamic response of the microgrid model in response to fluctuations in power generation due to intermittent solar PV generation and load demands are examined via real-time simulation studies and compared with the response of the physical assets. It is observed that the simulation results match closely to the performance of the actual physical asset. As such, the developed microgrid model offers plug-and-play capability, which will allow power providers to better plan for on-site deployment of renewable energy sources and energy storage to match the expected building energy demand.
Keywords:
Matlab/Simulink; load demands; microgrid; DER; OPAL-RT; digital twin; energy optimization; Gurobi; sustainable building 1. Introduction
Sustainable energy has garnered significant prominence in the contemporary global context. The world is steadfastly progressing toward a more ecologically conscious and energy-efficient paradigm, with an increasing emphasis on sustainable building management. Concurrently, Distributed Energy Resources (DERs), exemplified by renewable energy sources and Battery Energy Storage Systems (BESS), have gained substantial popularity for the purpose of mitigating energy consumption in urban buildings. Furthermore, the concept of microgrids has emerged as a key enabler in this pursuit.
The heightened emphasis on sustainability in response to the challenges posed by climate change has precipitated a surge in novel initiatives aimed at addressing the escalating demand for building energy consumption. This shift in focus has been particularly instrumental in catalyzing the exploration of innovative solutions, such as Distributed Energy Resources (DERs) and sophisticated control strategies for the efficient provision of power within building environments. Consequently, there has been a burgeoning interest in the integration of microgrids within precincts or expansive institutional campuses, notably universities.
In the context of this research endeavor, we present a comprehensive and empirically grounded model for an actual physical microgrid. This model is meticulously designed and realized using the OPAL-RT platform, thus rendering it amenable for real-time simulation studies. To facilitate these simulations, we have gathered extensive datasets encompassing the load demands specific to the SIT@NYP campus, along with the pertinent meteorological data. These datasets, serving as crucial input parameters, are meticulously integrated into the digital twin model representing the DERs of the microgrid.
The primary objective of this study is to scrutinize the dynamic response characteristics exhibited by the microgrid model in the face of varying power generation profiles, which predominantly stem from intermittent solar photovoltaic (PV) sources, and the concurrent variations in building load demands. This examination is rigorously conducted through the execution of real-time simulation studies, with a deliberate intent to draw parallels and distinctions between the responses of the digital twin model and the actual physical assets constituting the microgrid.
A salient observation that emerges from this research is the striking congruence between the simulation results and the performance of the tangible, real-world infrastructure. This observation serves as a testament to the fidelity and accuracy of the developed microgrid model, substantiating its utility as a plug-and-play tool for stakeholders, particularly power providers, who are tasked with strategic planning for the on-site deployment of renewable energy resources and energy storage systems. This endeavor is inherently driven by the overarching objective of harmonizing energy supply with the anticipated building energy demand, thereby fostering a more resilient and sustainable energy ecosystem.
The power usage of HVAC systems is highly cyclical, primarily due to the daily and seasonal variations in environmental factors and human behavior. This fact supports the use of Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs) as the prediction model for forecasting HVAC power consumption. Previous studies [1,2,3] have successfully used neural networks and deep learning for HVAC power forecasts, incorporating diverse input variables. Our study employs a Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) network for this purpose. The flexibility of LSTM allows adaptation to various buildings and locations when appropriately trained with relevant data.
Microgrids constitute a transformative advancement in modern energy systems, departing from conventional centralized power distribution. These self-sufficient, localized grids seamlessly integrate diverse distributed energy resources, including renewables, energy storage, and advanced control systems, fostering both resilience and sustainability. A primary merit lies in their capacity to bolster energy security by providing decentralized power sources, thereby minimizing the impact of grid failures. Furthermore, microgrids empower communities to incorporate renewable energy, facilitating a shift towards cleaner and more sustainable energy practices. The adaptability and versatility of microgrids play a crucial role in optimizing energy efficiency, curbing transmission losses, and enabling the seamless integration of intermittent renewable sources into the broader energy infrastructure. As the global emphasis on constructing resilient and environmentally conscious energy networks intensifies, the significance of microgrids becomes increasingly indispensable in shaping a more sustainable and dependable energy landscape.
2. Experimental Details
Aiming at enhancing predictive power control, the authors introduced an innovative approach by integrating various disciplines. This approach capitalizes on a multi-faceted approach, incorporating Artificial Intelligence (AI), energy optimization, and digital twin technologies. Each of these technological components contributes to the development loop of a sustainable Energy Management System (EMS), collectively working towards achieving resilient, sustainable, and efficient building energy management. This section covers the methodology of our approach.
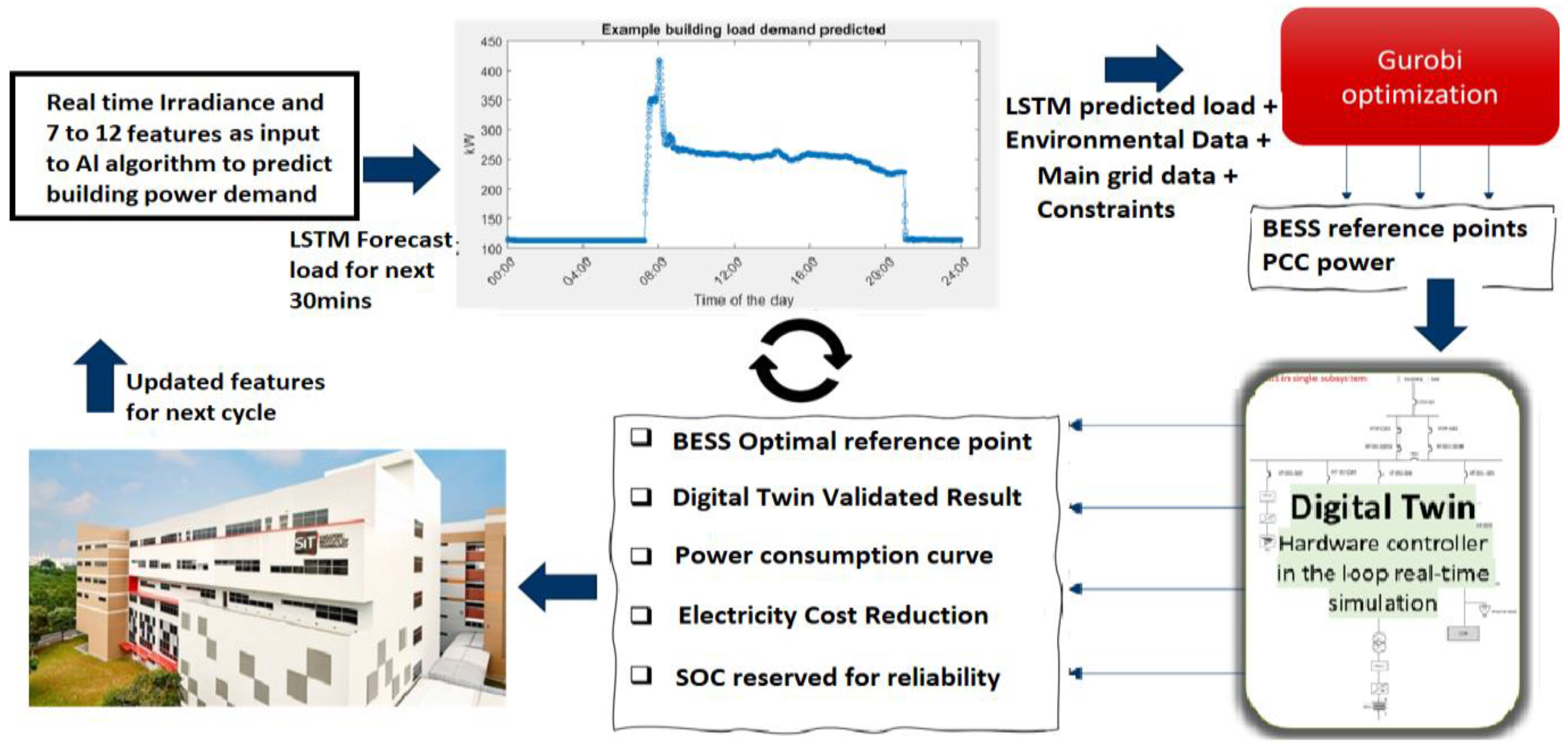
The overarching proposed methodology, outlined in Figure 1, encompasses various stages. In Section 2.1, a comprehensive analysis of the building’s load dynamics is conducted, facilitating the identification of pertinent features crucial for input into the predictive model. Section 2.2 expounds on the utilization of LSTM, an AI algorithm aimed at forecasting the building’s load demand. In Section 2.3, the predictive model for the HVAC building load is developed employing both single-layer and two-layer LSTM architectures across distinct dates. Moving to Section 2.4, the methodology incorporates Gurobi optimization to ascertain the requisite reference point for BESS. Notably, one of the essential inputs for this optimization procedure is the anticipated load demand derived from the LSTM model. Conclusively, the methodology advances by constructing a digital twin model, serving as a parallel system to validate and affirm the efficacy of the proposed predictive building power control. In practical implementation, outcomes derived from the digital twin system furnish the building operator with predictive insights and optimized operational profiles to guide decision-making. The proposed method exhibits versatility, operating either in real-time, thereby reducing human intervention, or functioning as a parallel digital-twin-based system, providing monitoring and predictive consultancy services.
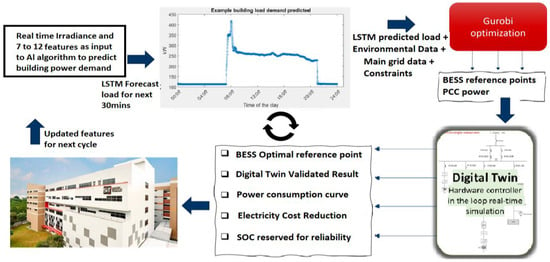
Figure 1.
Overview of predictive building power control using AI, energy optimization, and microgrid digital twin platform.
The research commences with an examination of the cooling system within the Singapore Institute of Technology (SIT) at the Nanyang Polytechnic (NYP) campus (the building reflected in Figure 1).
In the ensuing sections, we provide a comprehensive exposition of the experimental specifics pertaining to each constituent element of the predictive building power control system.
2.1. Cooling System in SIT @ NYP
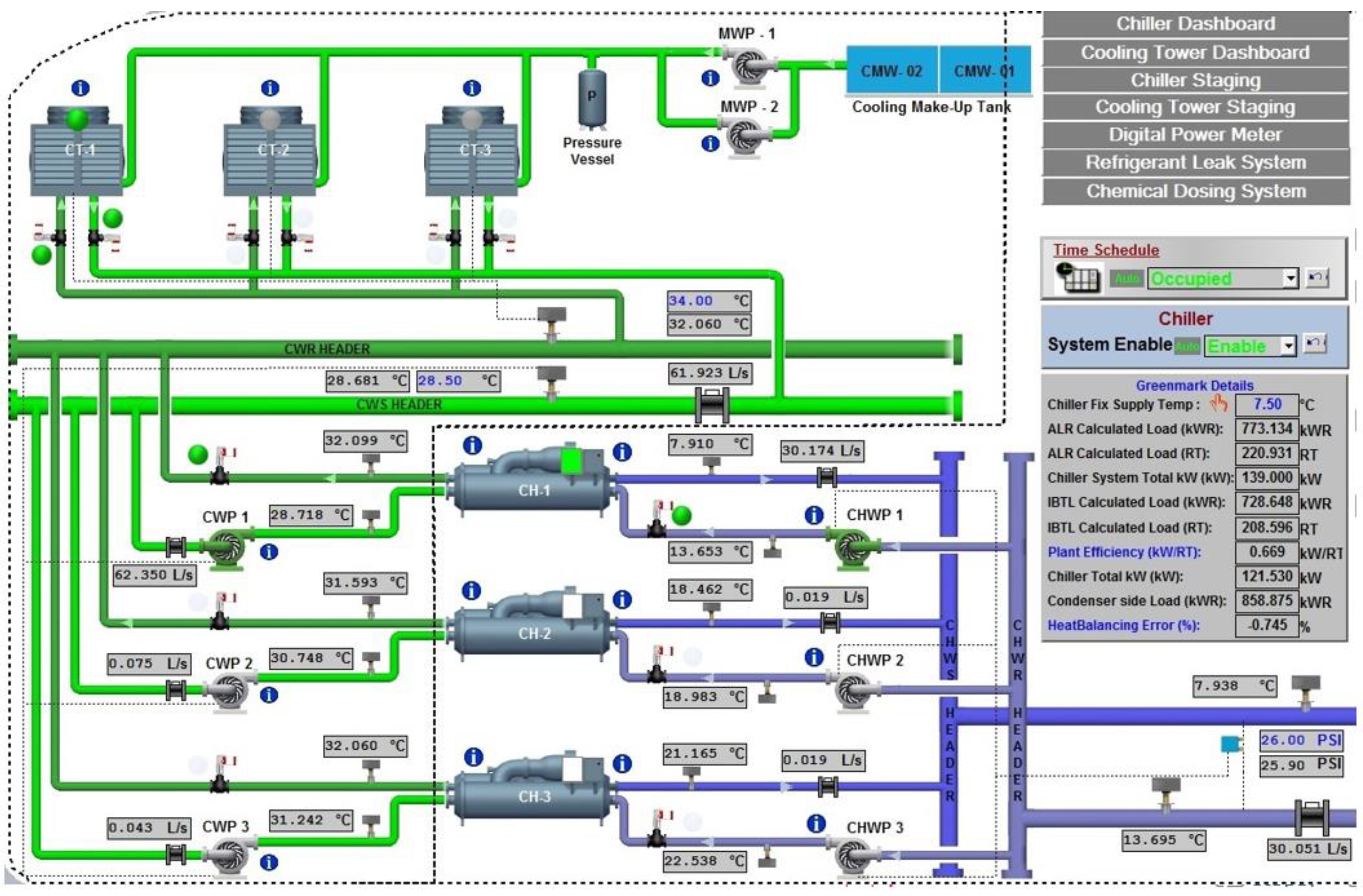
An overview of the cooling system in the SIT @ NYP building is shown in Figure 2. The main components of the cooling system are three units of cooling towers (CT), three units of chillers (CH), three units of chiller water pumps (CWP), three units of condenser water pumps (CHWP), Air Handling Units (AHU), and Fan Control Units (FCU). The system works together to regulate the temperature and flow of chilled water. The chilled water is supplied to AHU and FCU to condition air before it is distributed to the building space. Then, chilled water is returned to the chiller to complete the chilled water circulation. In the chiller (more specific in evaporator), returning chilled water will dump its heat on the refrigerant to lower its temperature before it is supplied to AHU and FCU. The refrigerant’s heat will be released at the condenser water before it is circulated back to the evaporator. The condenser water will be pumped to the cooling tower to reject the heat at the outdoor. Then, condenser water will be returned to the chiller and ready to absorb some heat from the refrigerant. The AHU and FCU take fresh air from outside the building, then filter, dehumidify, and cool the air to the temperature specified by the BMS before it is distributed into the occupied spaces.
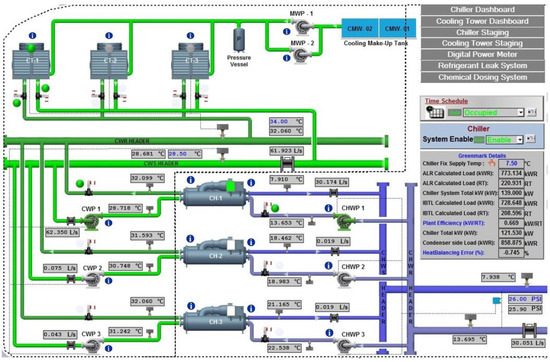
Figure 2.
Overview of SIT @ Nanyang Polytechnic chilled water system.
The building’s cooling system is automatically monitored and controlled by Honeywell Building Management System. It is designed to run only one unit at a time during normal periods but can run multiple units during periods of high demand.
2.2. Brief Description of LSTM
Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs) are ideal for time series prediction problems, where the input and output data are in sequential form. This is because RNNs have a feedback mechanism that allows them to consider previous input data to predict future values. However, one of the challenges of RNNs is the exploding and vanishing gradients that occur during the back-propagation step [4]. This occurs because RNNs have a limited memory and as they go back in time during the back-propagation, the gradients become increasingly small, leading to vanishing gradients. To overcome this problem, Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) networks are a variant of Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs) that have been shown to have more stable gradients [4,5]. Hence, LSTM networks can capture long-term dependencies in data more effectively.
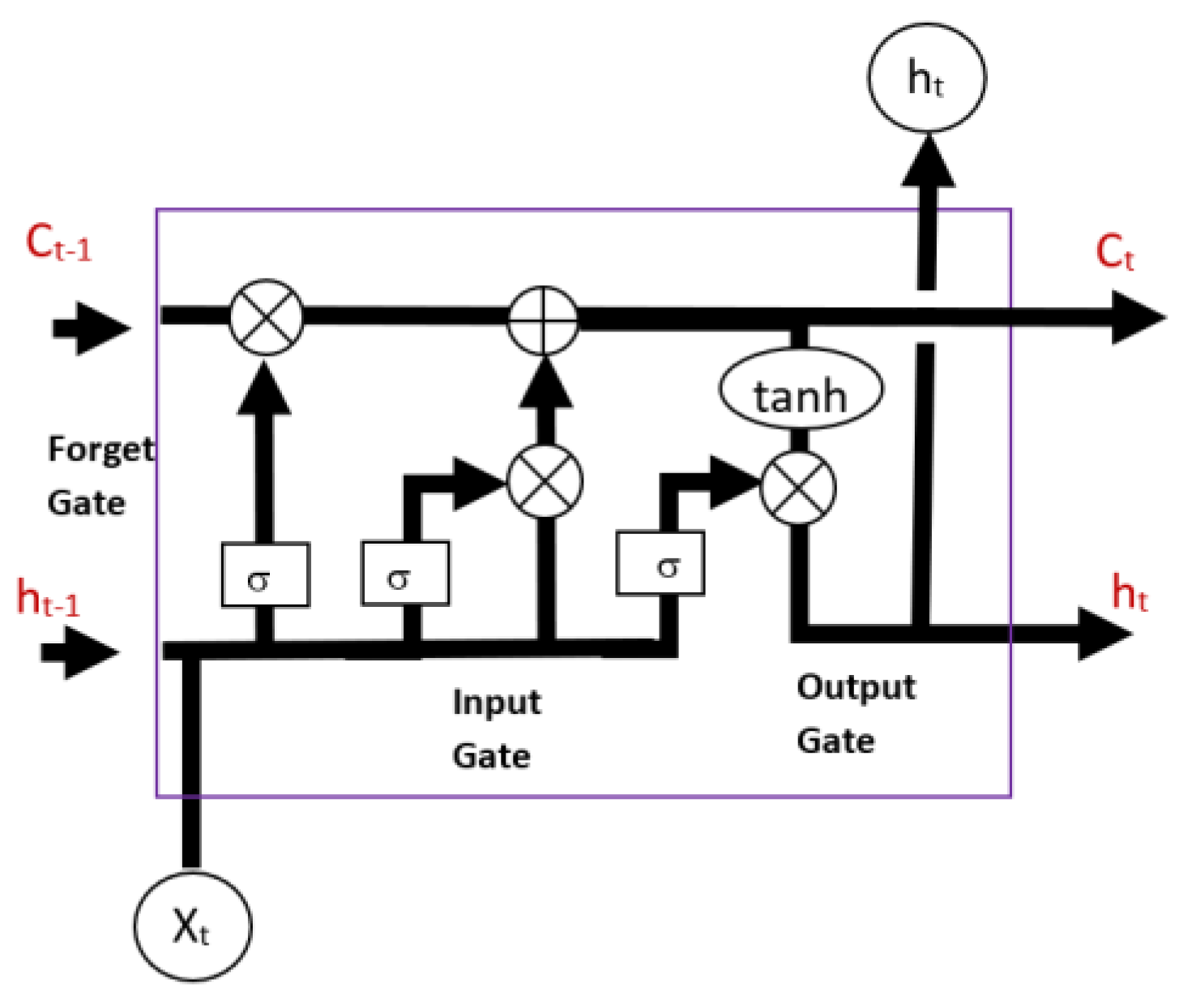
An LSTM network consists of several key components, including the hidden state (ht), cell state (Ct), forget gate, input gate, and output gate as shown in Figure 3. State is a memory unit of the networks that stores information, while gates regulate the flow of information into the state. Input gates control new information added to the new state, forget gates decide what information is discarded, and output gates determine information to be output based on the cell state. The gates employ sigmoid activation functions, while both the cell state and hidden state commonly utilize the hyperbolic tangent (tanh) activation function. Current input (Xt) and previous hidden state (ht−1) are passed through the sigmoid function of the forget gate. If the output value of the forget gate is closer to 0, it means forget, and closer to 1 means to retain. The forget gate determines relevant information to keep from the prior cell state (Ct−1). The input gate decides relevant new information to update in the current cell state (Ct) of the current LSTM unit. The present cell state is determined by the sum of a portion of the previous cell state (factoring in the output of the forget gate) and a fraction of new information (considering both the output of the input gate and the cell state activation function). The output gate is multiplied together with the current cell state to obtain the present hidden state (ht). Information from both the cell state (Ct) and hidden state (ht) will be passed to the next LSTM unit.
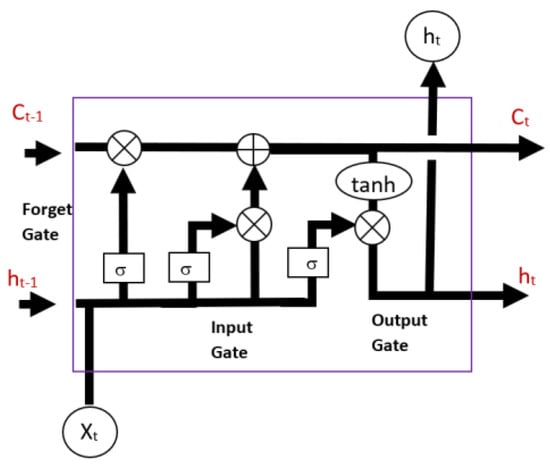
Figure 3.
Illustration of the LSTM network.
2.3. HVAC LSTM Load Predictor Model
The LSTM networks [6,7] with one layer and two layers are examined and compared. The one-layer LSTM network has 100 hidden units, while the two-layer LSTM network has 100 hidden units in each layer. The features used in this study are pre-processed using standard scaling and MinMax scaling techniques.
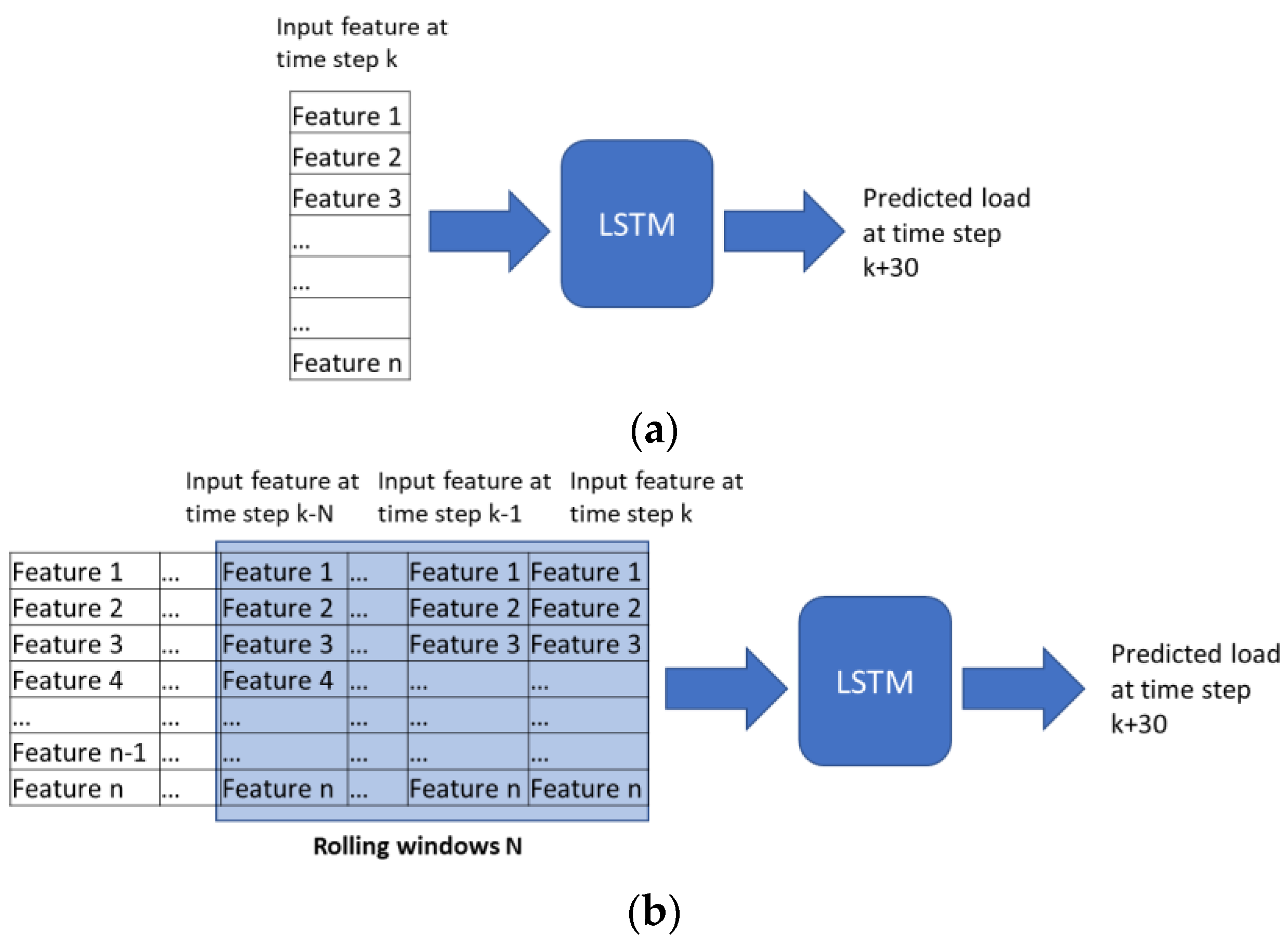
Two approaches are employed for estimating the HVAC load, known as LSTM-1 and LTSM-2. Both LSTMs are used to predict the load for the next 30 min and are based on the features listed in Table 1. All features listed in the table are sourced from the BMS. Apart from different features used in each model, LSTM-1 is trained by using current features, while LSTM-2 is trained by using features in the rolling windows of the past 20 min as shown in Figure 4.

Table 1.
List of features used in both LSTM-1 and LSTM-2.
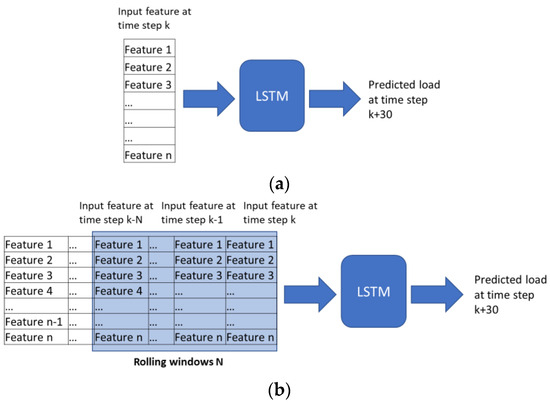
Figure 4.
Time series inputs configuration to LSTM. The network in (a) LSTM-1 requires current input feature and (b) LSTM-2 requires rolling windows N.
2.4. Energy Management Optimization Using Gurobi
The microgrid concept is integral to modern energy systems, where energy storage emerges as an essential component [8]. This is particularly crucial given the dependency of Photovoltaic (PV) power generation on solar irradiance, a variable not subject to human control and contingent upon weather conditions. In the microgrid framework, a key player with high controllability assumes the responsibility of maintaining power and energy balance. This player adeptly adheres to setpoints established by the Microgrid Controller (MGC) or the estates operator. Frequently, BESS is the preferred and commonly employed technology for this purpose, exemplifying its significance in orchestrating the intricate dance of power generation and consumption within a microgrid setting. To ensure optimal functionality, BESS requires precise setpoints which will be dependent on the power control strategy.
To achieve optimal energy management, optimization is a must-do task. It needs to generate the setpoints for BESS. We have used free Gurobi academic license version 10.0.1 is a highly utilized mathematical optimization solver and software bundle designed for addressing intricate linear and nonlinear programming challenges [9]. Energy supply and demand optimization using Gurobi is particularly valuable in the field of energy management, helping the building owner make data-driven decisions to meet the energy demand efficiently, reduce operational costs, and optimize resource utilization while considering various constraints and objectives.
As depicted in Figure 1, the optimization process relies on several key input factors, including power generated by DER, building load demand forecasts generated by LSTM models, the prevailing electrical tariff, BESS, and PV costs. The objective function of the optimization is determined by the building operator’s preferences and could encompass goals such as enhancing energy efficiency, lowering operational expenses, and optimizing resource utilization, among others.
In this section, the focus shifts to employing energy optimization techniques for the generation of Battery Energy Storage System (BESS) setpoints, with consideration given to distinct scenarios.
- (i).
- Scenario 1: the primary objective is to attain the lowest cost of overall building energy consumption. This involves a comprehensive evaluation that considers the electricity tariff from the main grid, as well as the costs associated with Photovoltaic (PV) power generation and BESS operation. The overarching aim is to curtail the total cost, thereby directly benefiting the building user.
- (ii).
- Scenario 2: the optimization process centers on minimizing infeed power fluctuation. High peak-to-peak demand fluctuations pose challenges for the main grid, necessitating additional resources and costs to accommodate sudden increases and decreases in power demand. By mitigating these fluctuations, the burden on the main grid is alleviated, especially in the context of an expanding microgrid landscape. Additionally, this approach contributes to the reduction in equipment sizes and associated costs, offering a dual advantage of enhanced grid stability and economic efficiency.
In Scenario 1: the objective function is to minimize the cost function below.
In Scenario 2: the objective function is to minimize the cost function below.
where Pbat, Ppv, Pgrid are battery, PV, infeed grid active power, respectively. Cbat, Cpv, Cutility are cost of battery, PV, and utility electricity, respectively. is the time step (1 min in the scope of this study). is the average active power demand from the main grid. is the number of time steps involved in the optimization. Depending on the context, can be 30 for half hour predictive control, or 1440 for one day predictive control, etc.
is the total power cost for the period studied. is the variance of the active power exchange with the main grid, which is useful to describe the power fluctuation from the prospect of the main grid. Power fluctuation is a rising concern in modern power systems with renewables.
The constraints are as follows:
- (1)
- Battery SOC should be within given limit at all times.
- (2)
- Battery SOC at the start of the day is the same as the end of the day to ensure continuous operation of BESS.
- (3)
- Maximum infeed power at PCC is 200 kW at any time. And no power flows into the main grid.
- (4)
- Power is balanced at all times and is the output variable which is then used as the BESS setpoint in Section 3.
2.5. Digital Twin Modelling
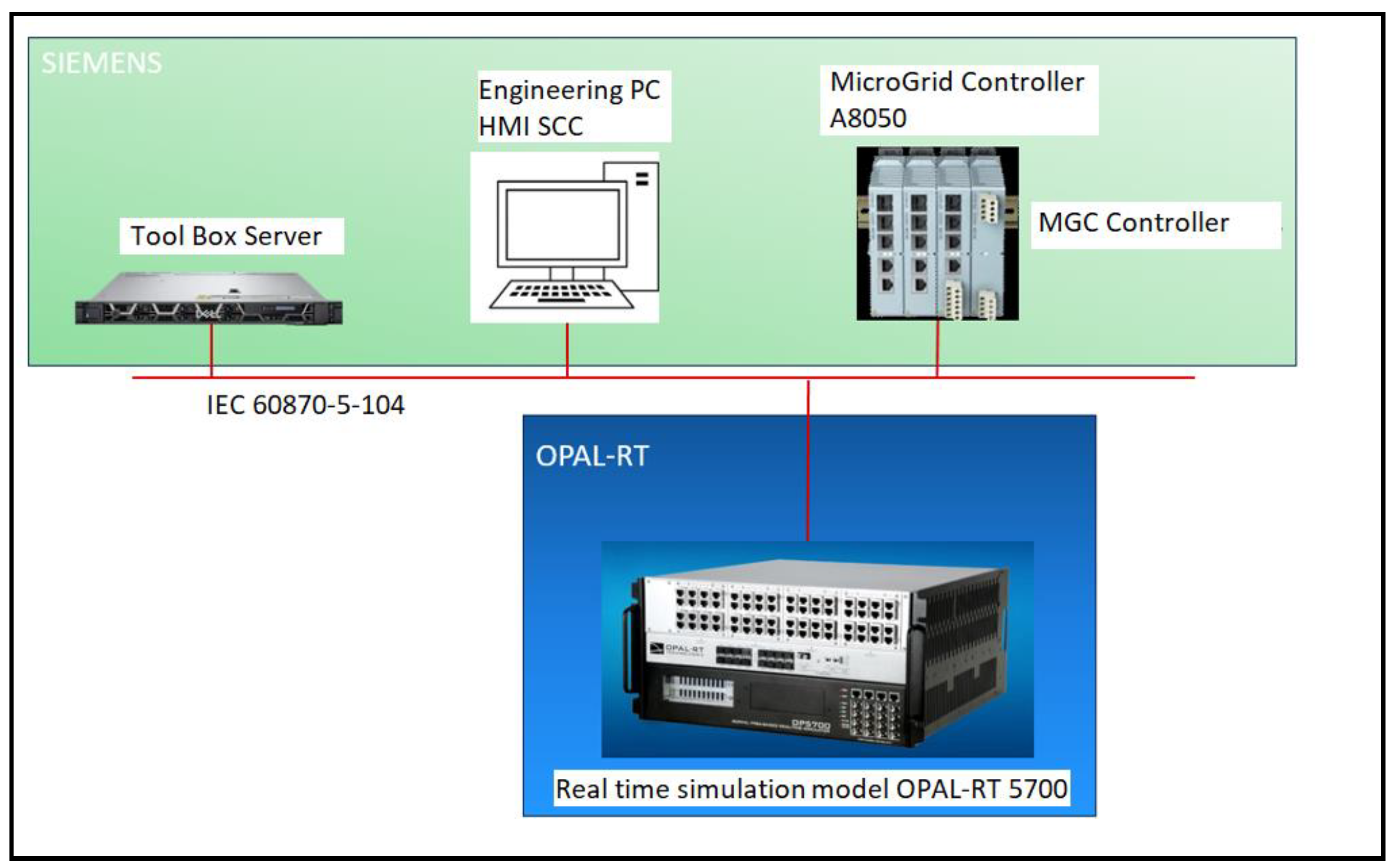
Digital twinning of the microgrid has become critical for effective projection of renewables and power source generation to meet the need of load demand [10]. In this section, the potential application of a microgrid in the building is studied. The microgrid is an experimental microgrid testbed set up in Singapore Power Concept Lab, which is used to create a digital twin using Opal-RT RT-Lab 2019.3 + Matlab 2018b. The digital twin is created using the test data from the experimental microgrid and modeled in detail. It is based on hardware-controller-in-the-loop real-time simulation. The digital twin system architecture is shown in Figure 5. It consists of
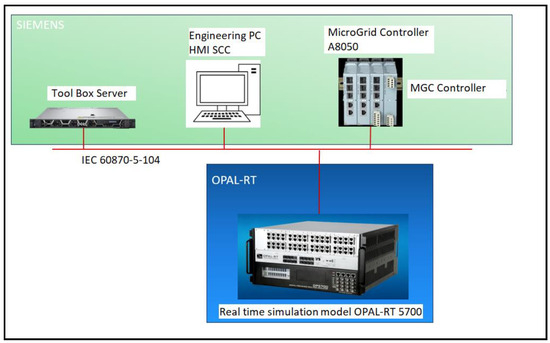
Figure 5.
Digital twin architecture which comprises Siemens MGC, Engineering PC, Real-time simulator, and Toolbox server. The OPAL RT 5700 is sourced from OPAL-RT Technologies Inc, Montreal, Quebec, Canada. The Microgrid controller A8050 is sourced from Siemens, Munich Germany.
- (1)
- Siemens MGC;
- (2)
- Engineering PC;
- (3)
- Real-time simulator;
- (4)
- Toolbox Server.
The digital twin is wired up using the IEC 60870-104 [11] communication protocol. MGC is the same model as in the experimental setup. MGC logic is replicated to the best effort to provide maximum accuracy in the digital twin. The simulation model is built in details and runs in real-time, enabling the digital twin to be able to model transient dynamic events and compatibility to connecting various hardware in the loop.
As the experimental microgrid and NYP building are of different energy scales, the following rating/capacities are altered to make a better match. The voltage and the rated power/capacity are as shown below.
| Microgrid Parameters | ||
| Unit | Voltage | Rated Power/Capacity |
| PV | 415 V | 300 kW |
| BESS | 275 V/415 V | 300 kW/200 kWh |
| 2 × 1:1 transformer | 415 V/415 V | 400 kVA |
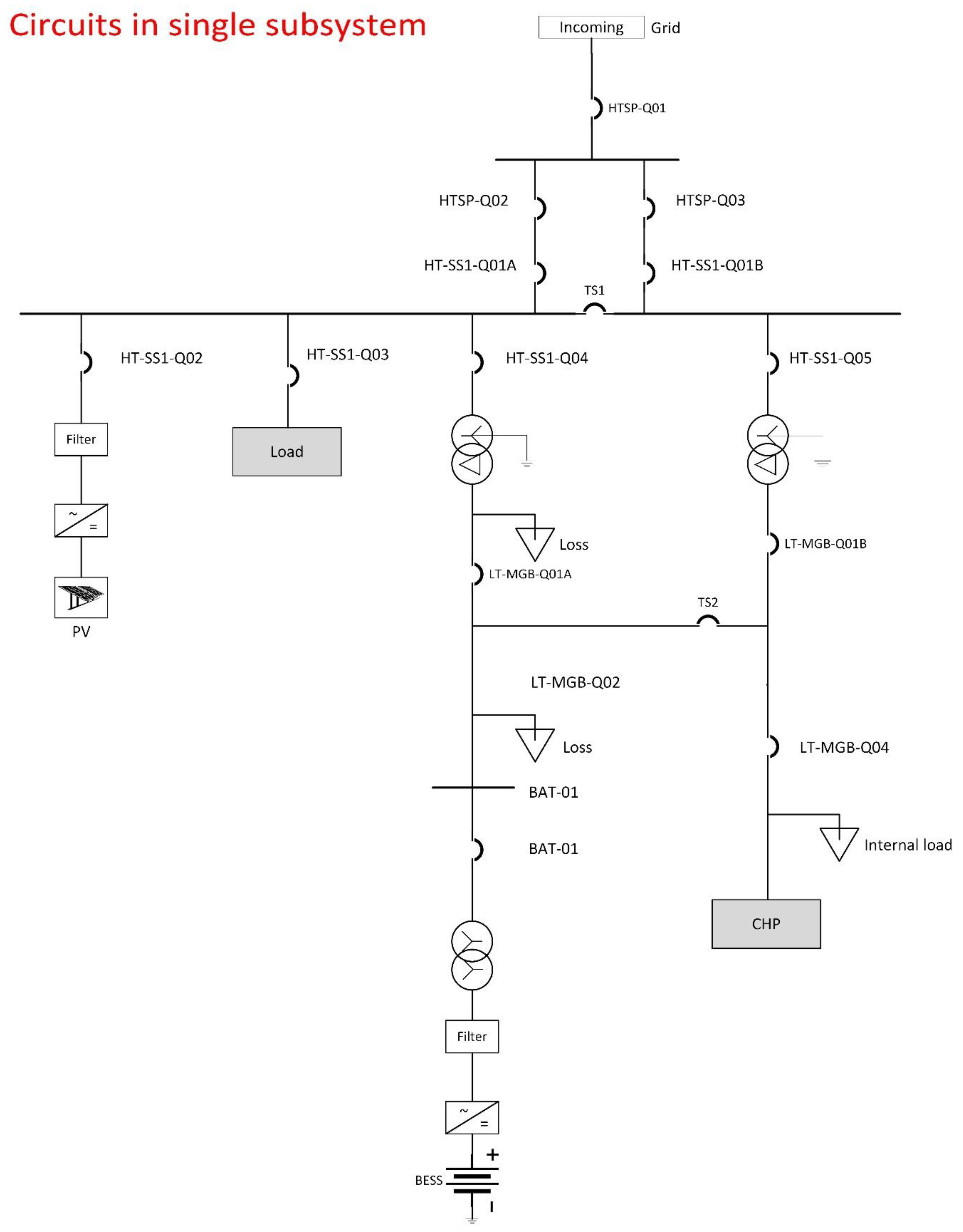
The circuit is shown in the figure below (Figure 6). The experimental microgrid is formed by a common busbar (HT-SS1). The PV is connected through the PV inverter. The NYP load is represented by an aggregated load model. BESS is connected through a step-up transformer and a 1:1 transformer. The latter one is for safety reasons and acting as an isolation barrier in the case of faults on either the building side or BESS side. The same principle applies for a back-up combined heat and power generator (CHP). However, CHP is a back-up for islanded scenarios when there is a power outage on the main grid. CHP is more for energy reliability in contingencies and is not an economic DER in energy optimization. Hence, it is excluded in this paper.
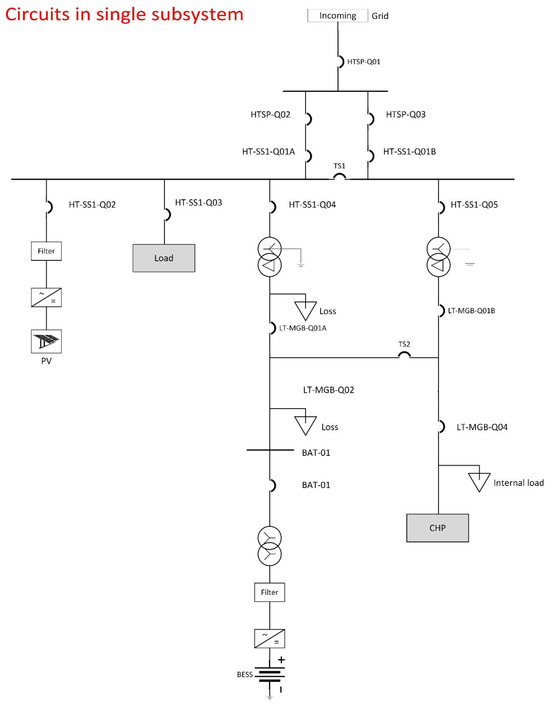
Figure 6.
Circuit in single sub-system.
The digital twin model verification and validation is completed by conducting various simulations and physical experiments. Several test cases are designed, covering from the component level to the system level, from islanded mode to grid connected mode, from dynamic to steady-state scenarios. The test cases are used to verify the simulation model. The comprehensive validation and verification of the digital twin are elaborated upon [12,13], albeit regrettably omitted herein due to constraints imposed by page limitations. The outcomes attained in this study underscore a notable level of fidelity and accuracy [14]. The research leverages the microgrid digital twin as a pioneering tool to substantiate the predictions expounded in Section 3.1 and fine-tune the optimization procedures outlined in Section 3.2. This methodological advancement is poised to significantly enhance the precision of predictive power control mechanisms within the context of sustainable buildings.
2.6. Summary of Section 2
This integrated framework harnesses the strengths of AI, enabling advanced predictive capabilities. Energy optimization techniques are employed to enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of energy usage within the system. Additionally, the utilization of digital twin technology provides a virtual representation of the physical system, facilitating simulation, monitoring, and optimization of operations.
By combining these diverse technologies within the sustainable EMS development loop, the methodology presents a holistic solution for managing building energy. It aims to achieve resilience against fluctuations, sustainability by minimizing environmental impact, and efficiency in energy consumption, thus paving the way for more effective and comprehensive energy management practices.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Cooling Prediction
Different lengths and periods of training data, and different architectures and scaling methods of LSTM (using Matlab 2022b) are studied and discussed in this section.
3.1.1. LSTM-1
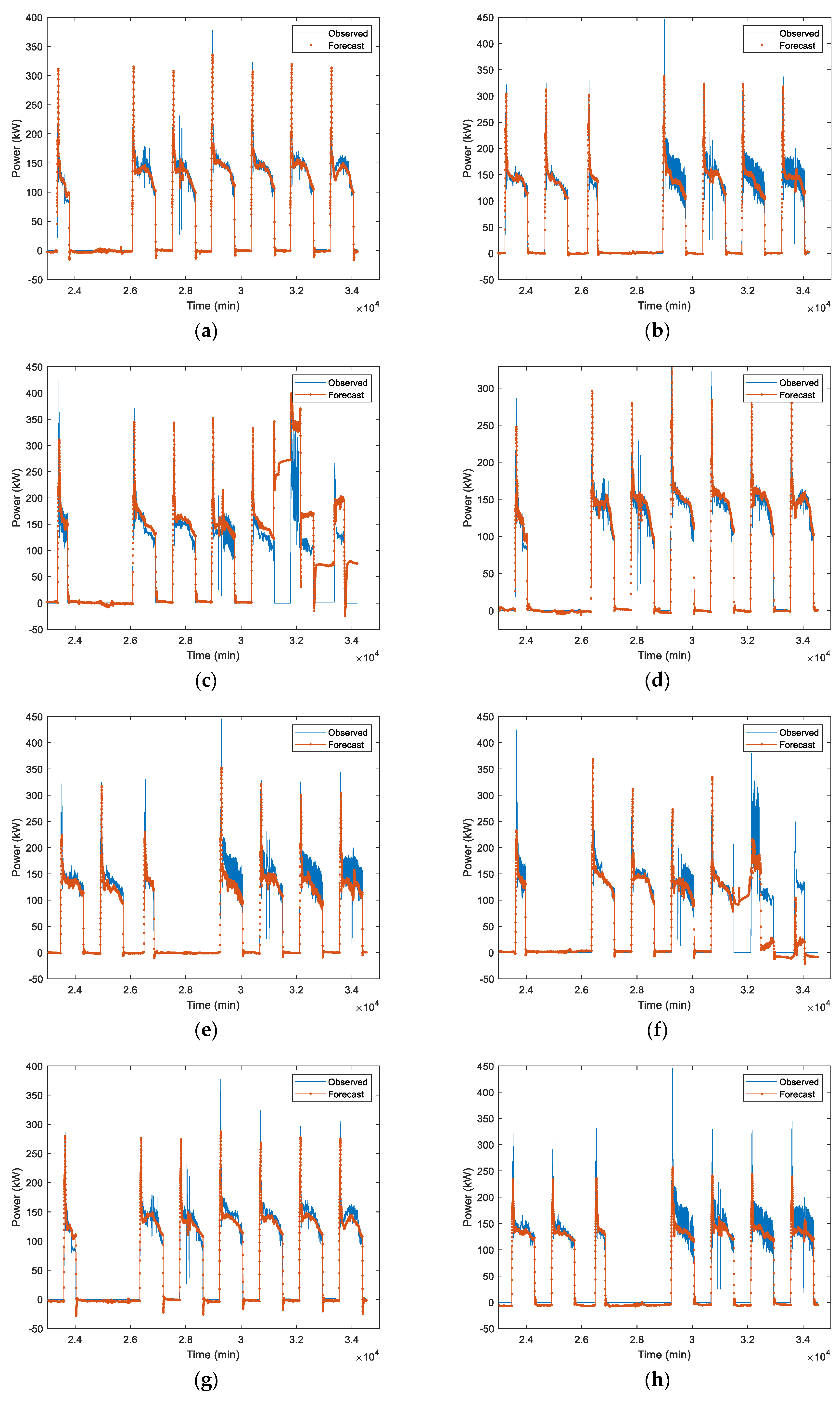
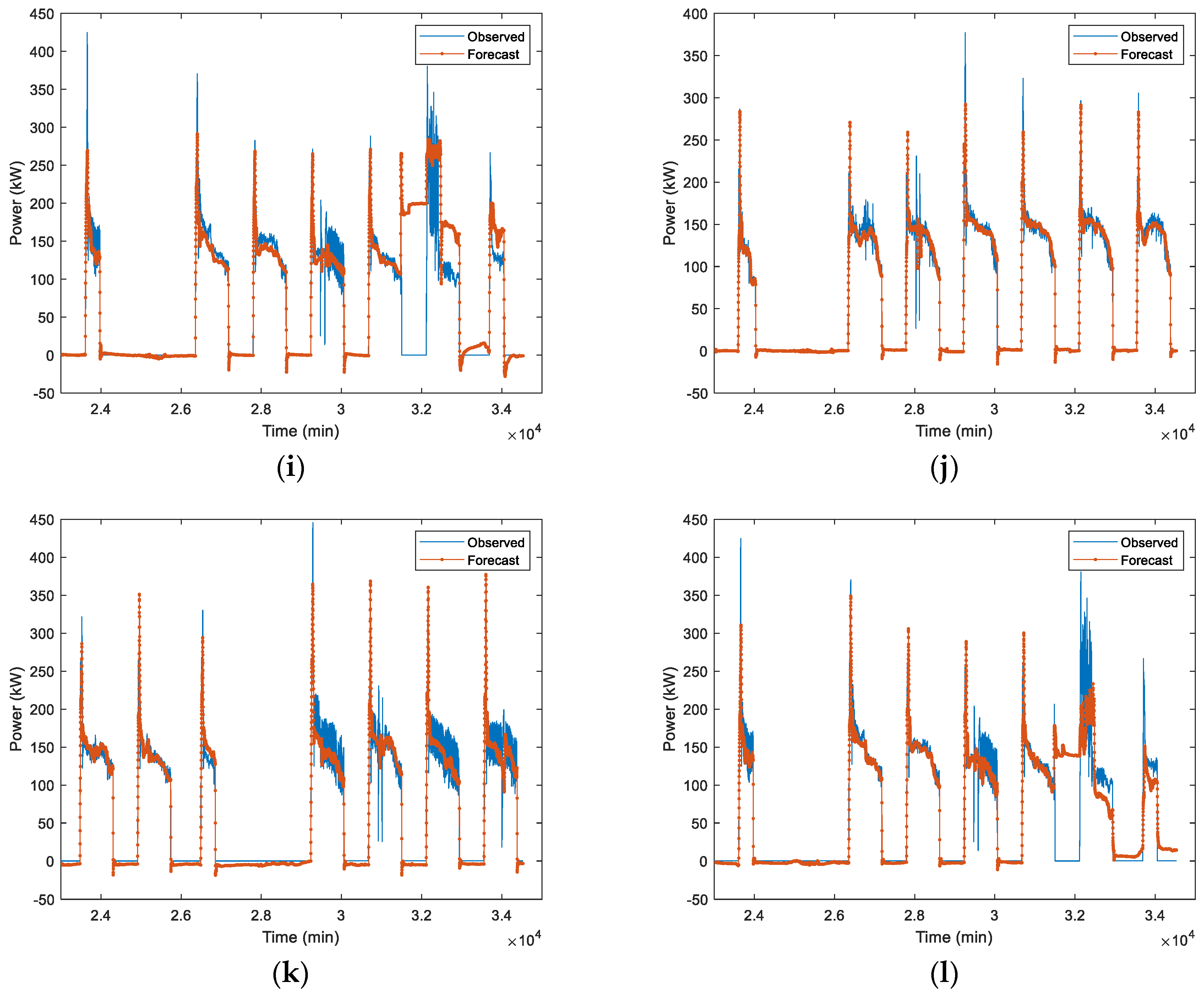
In first case, LSTM-1 is trained by using July–September 2020 data. Table 2 shows the forecast accuracy of trained LSTM on different test data (October 2020, September 2022, and October 2022), architecture (one-layer and two-layer), and scaler (MinMax and Standard). These metrics quantitatively assess a model’s accuracy and reliability. The combination ensures a robust evaluation, covering different aspects of prediction accuracy. RMSE considers both magnitude and direction, emphasizing larger discrepancies. MAE evaluates average magnitude without directional consideration, offering a straightforward accuracy measure. Examining bias helps identify systematic errors, crucial for ensuring unbiased forecasts. Performance metrices used in the forecast are RMSE, MAE, and bias. For comparison over different models’ (one-layer LSTM MinMax scaler, one-layer LSTM Standard scaler, two-layer LSTM MinMax scaler, and two-layer LSTM Standard scaler) performance, the average forecast performance of October 2020, September 2022, and October 2022 test data is also presented in Table 2. The average results show that the scaling method has quite a significant influence on the performance of the forecast accuracies. The one-layer LSTM Standard scaler has RMSE 23.8 kW, MAE 11.9 kW, and bias −2.5 kW, while the one-layer LSTM MinMax scaler has RMSE 33.9 kW, MAE 17 kW, and bias 11.5 kW. The two-layer LSTM Standard scaler has RMSE 22.5 kW, MAE 11.1 kW, and bias 0.4 kW, while the two-layer LSTM MinMax scaler has RMSE 28.1 kW, MAE 13.9 kW, and bias 1.6 kW. In both one-layer and two-layer LSTM architecture, the Standard scaler has outperformed the MinMax scaler in terms of performance metrices. This can be attributed to the data being approximately more Gaussian and there being outlier data which MinMax scaling is more sensitive to and hence it is projected as being less accurate. The performance metrices RMSE and MAE of both one-layer and two-layer LSTM in the Standard scaler are very similar. Thus, the one-layer LSTM-1 Standard scaler works well to forecast the load. The forecast output of the HVAC load in time series is presented in Figure 7. The load that we used in our study for the SIT@NYP building is more straight forward but with some outlier data. Hence, one-layer LSTM-1 is adequate to provide accurate prediction, while two-layer LSTMs lead to overfitting with some of the outliers and the dataset is not big considering the training data that were used, the July–September 2020 data.

Table 2.
Prediction results of LSTM-1 based on Jul-September 2020 trained data.
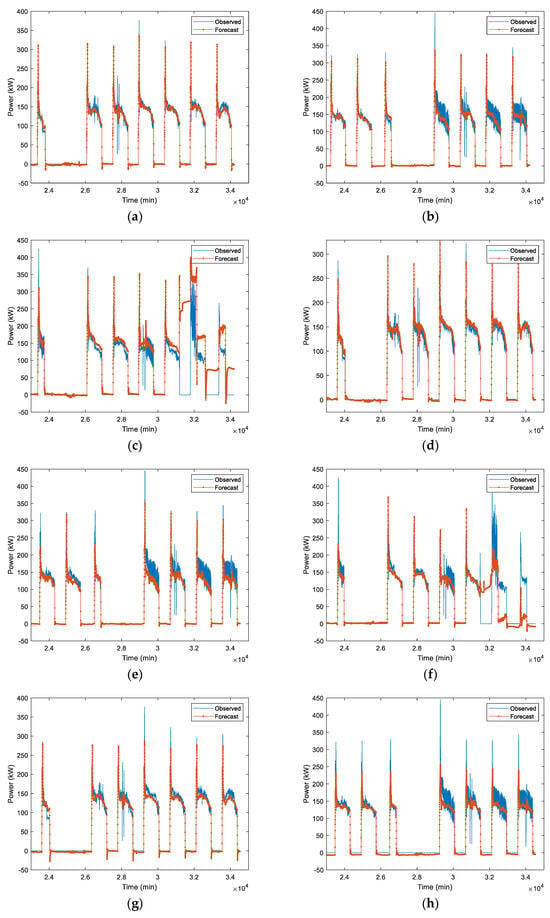
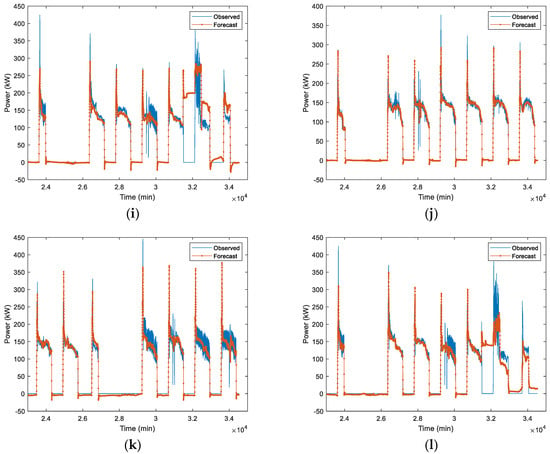
Figure 7.
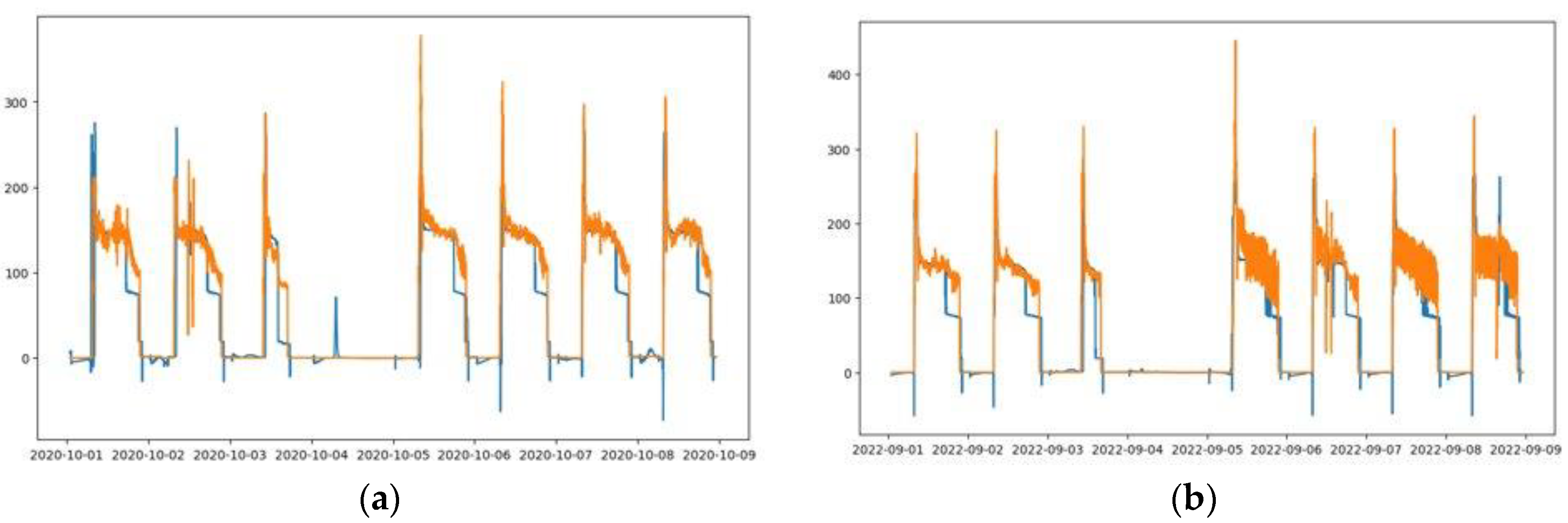
Measured load vs. predicted load. (a–c) One-layer LSTM-1 MinMax scaler; (d–f) One-layer LSTM-1 Standard scaler, (g–i) Two-layer LSTM-1 MinMax scaler, and (j–l) Two-layer LSTM-1 Standard scaler. (a,d,g,j) 1st week of October 2020 test data. (b,e,h,k) 1st week of September 2022 test data. (c,f,i,l) 1st week of October 2022 test data.
In the second case, LSTM-1 is trained by using the short length of data from 1 September 2022 to 6 September 2022 while it makes the forecast for the next two days (7–8 September 2022). This allowed us to see the impact of using less data for training and how it can affect the forecast performance. The forecast performance is presented in Table 3. The one-layer LSTM Standard scaler has RMSE 20.9 kW, MAE 11.9 kW, and bias 0.1 kW, while the one-layer LSTM MinMax scaler has RMSE 21.4 kW, MAE 13.8 kW, and bias 5 kW. The two-layer LSTM Standard scaler has RMSE 22.6 kW, MAE 14.2 kW, and bias 2.1 kW, while the two-layer LSTM MinMax scaler has RMSE 26 kW, MAE 17.8 kW, and bias 11.1 kW. The best model is the one-layer LSTM Standard scaler. In both cases, the one-layer LSTM with Standard scaler outperformed other models and the accuracies of the prediction are not necessary to improve due to the increased number of layers in LSTM. By comparing the result in Table 2 and Table 3, we can also see that the one-layer LSTM Standard MAE value is 8.88 as compared to 11.91. This is also an indication that a richer training data pool helps to make the performance forecast more accurate. This was also observed for the two-layer LSTM for both the MinMax and Standard, where MAE is 11.1 and 9.9 in Table 2 as compared to 17.79 and 14.25 in Table 3.

Table 3.
Prediction results of LSTM-1 based on 1–6 September 2022 trained data.
3.1.2. LSTM-2
Similar with LSTM-1, the LSTM-2 is trained by using the Jul-September 2020 data in the first case; however, it is used for forecasting results over a longer duration period. Table 3 shows the forecast accuracy of trained LSTM on different test data, architectures, and scalers. The average forecast performance of the October 2020, September 2022, and October 2022 test data is presented in Table 4. The one-layer LSTM Standard scaler has RMSE 45.27 kW, MAE 20 kW, and bias 8.58 kW, while the one-layer LSTM MinMax scaler has RMSE 37.03 kW, MAE 18.43 kW, and bias 4 kW. The two-layer LSTM Standard scaler has RMSE 46.17 kW, MAE 20.97 kW, and bias 7.02 kW, while the two-layer LSTM MinMax scaler has RMSE 49.07 kW, MAE 23.8 kW, and bias 6.3 kW. From these results, the one-layer LSTM MinMax scaler has the least RMSE, MAE, and bias error among other models. The forecast output of the HVAC load in time series is presented in Figure 8.

Table 4.
Prediction results of LSTM-2 based on July–September 2020 trained data.
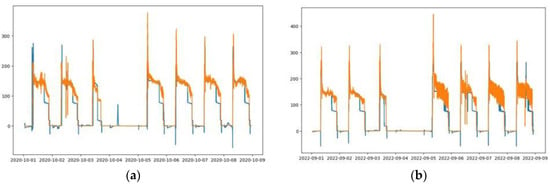
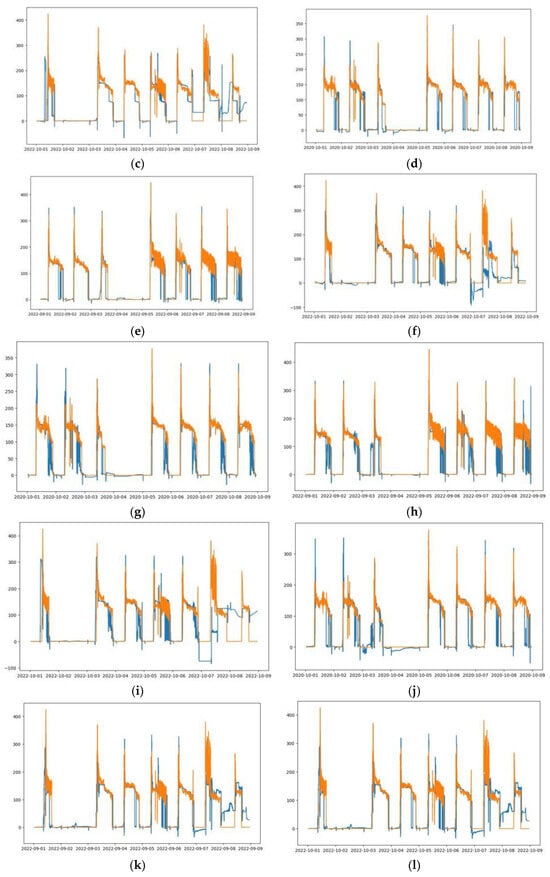
Figure 8.
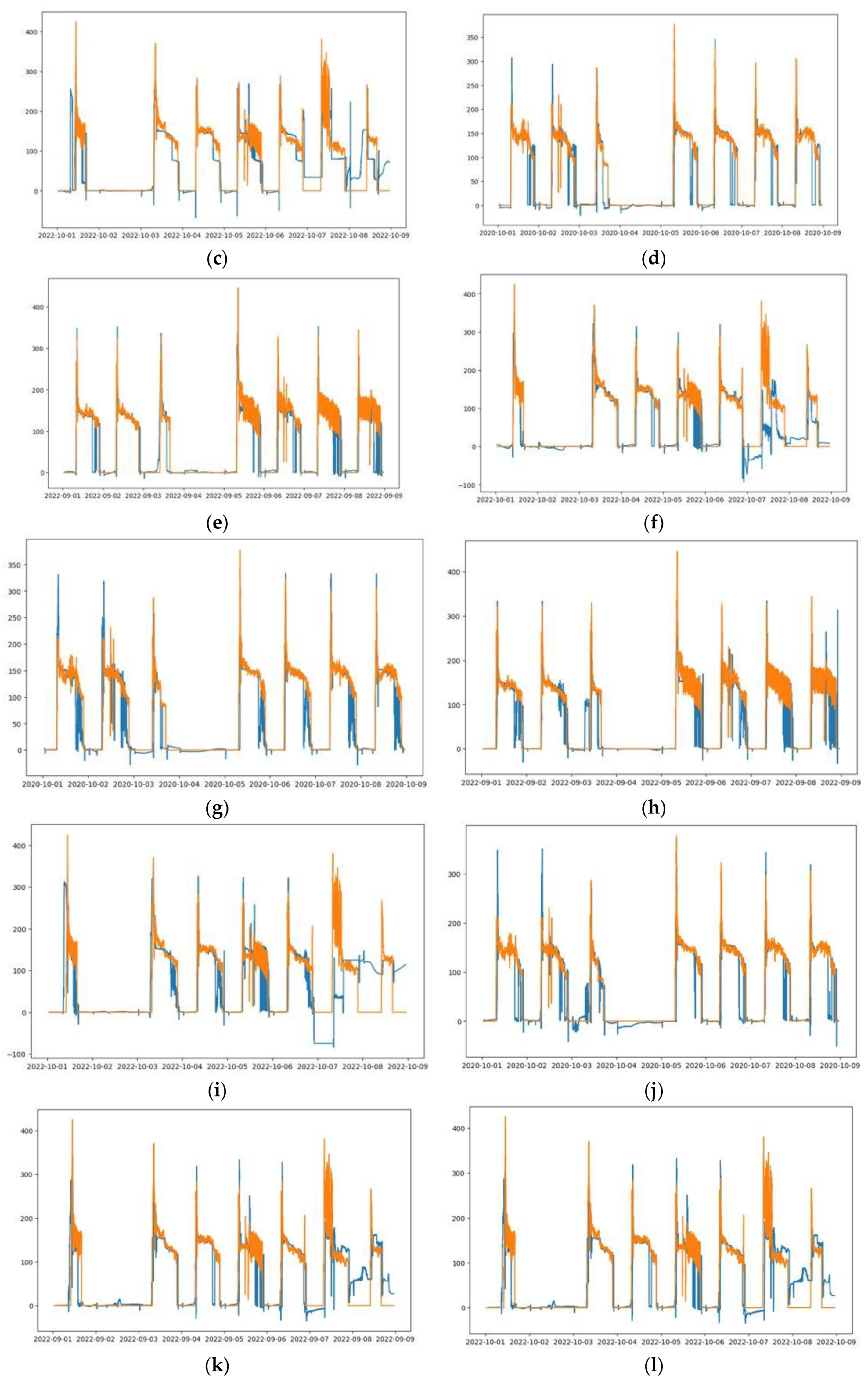
Measured load vs. predicted load. (a–c) One-layer LSTM-2 MinMax scaler; (d–f) One-layer LSTM-2 Standard scaler, (g–i) Two-layer LSTM-2 MinMax scaler, and (j–l) Two-layer LSTM-2 Standard scaler. (a,d,g,j) 1st week of October 2020 test data. (b,e,h,k) 1st week of September 2022 test data. (c,f,i,l) 1st week of October 2022 test data.
Similar with LSTM-1, the LSTM-2 in the second case is trained by using data from 1 September 2022 to 6 September 2022 while the forecasting period is from 7 September 2022 to 8 September 2022. The forecast performance is presented in Table 5. The one-layer LSTM Standard scaler has RMSE 22.41 kW, MAE 13.07 kW, and bias −3.12 kW, while the one-layer LSTM with MinMax scaler has RMSE 21.22 kW, MAE 12.28 kW, and bias −1.52 kW. The two-layer LSTM with Standard scaler has RMSE 23.7 kW, MAE 13.18 kW, and bias −1.57 kW, while the two-layer LSTM with MinMax scaler has RMSE 23.73 kW, MAE 13.18 kW, and bias −2.21 kW. The best model is the one-layer LSTM MinMax scaler, which is similar to the first case.

Table 5.
Prediction results of LSTM-2 based on 1–6 September 2022 trained data.
3.2. Energy Optimization in Microgrid
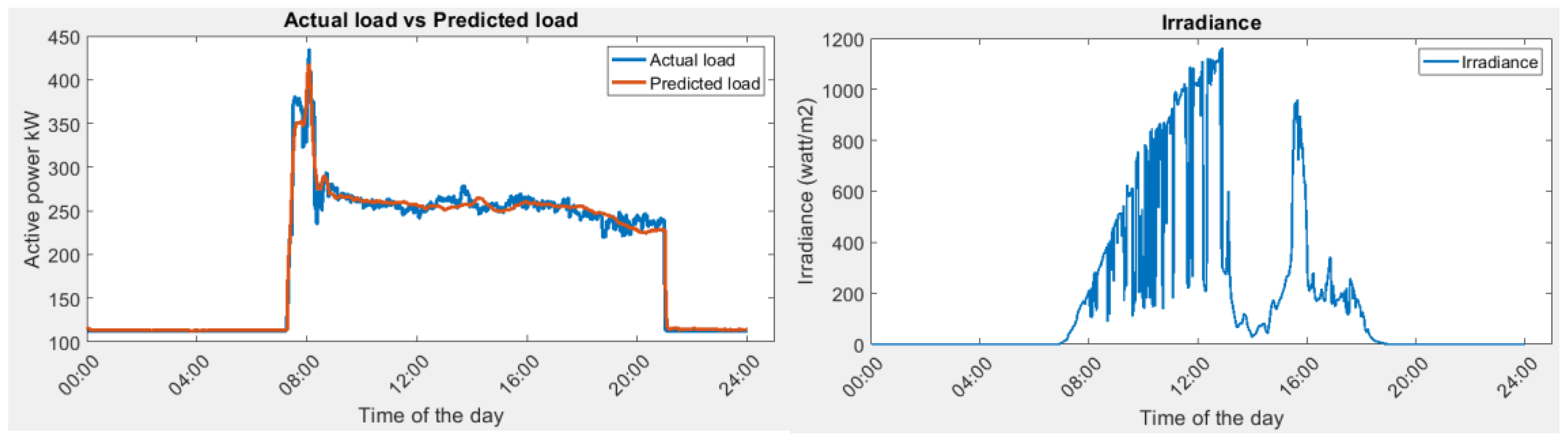
As concluded in Section 3.1, the one-layer LSTM is sufficiently accurate to predict the cooling load. The cooling load in NYP can be accurately predicted. In this section, one day (1 September 2022, trained using July 2020 and September 2020 data, one-layer LSTM) is taken as an example sample to conduct the energy optimization. In addition to the cooling load, there are static loads in the building which are running 24/7, such as the server room. Adding the static load and the cooling load, the total load demand in the building can be obtained. The left figure in Figure 9 is the actual vs. predicted total load in the building. The predicted load colored in orange provides an accurate prediction compared with the actual value. The right figure in Figure 9 is the recorded solar irradiance level. There are frequent fluctuations in the morning, depicting a cloudy day, and the sun is fully covered in the afternoon.
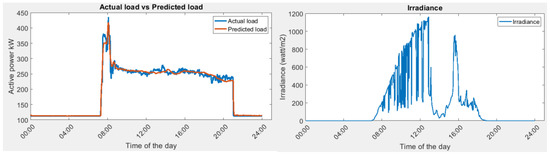
Figure 9.
(Left) Actual load demand vs. predicted load demand. (Right) Irradiance for the day (sensor noise is corrected).
The electric tariff is set to SGD 0.2996/kWh with reference to Singapore’s utility price in the 3rd quarter of 2023. The electrical tariff is assumed to provide an incentive to consumers to use power during the off-peak period. The off-peak price is set to SGD 0.18/kWh. The cost of a battery is set to SGD 0.1715/kWh usage with reference to the cost projection for battery storage provided by the National Renewable Energy Laboratory. The cost of PV is neglected as the PV system can last for 20~30 years with low maintenance costs.
Scenario 1 is further separated into Scenario 1A—lowest cost with Fixed SOC0 and Scenario 1B—lowest cost. SOC0 is the initial battery SOC. In Scenario 1A, SOC0 is fixed at 50%. In Scenario 1B, SOC0 is flexible and becomes one of the variables to solve. In all scenarios, the battery SOC limit is set to 5~95%.
Scenario 1A: lowest cost with Fixed SOC0 (LCFS).
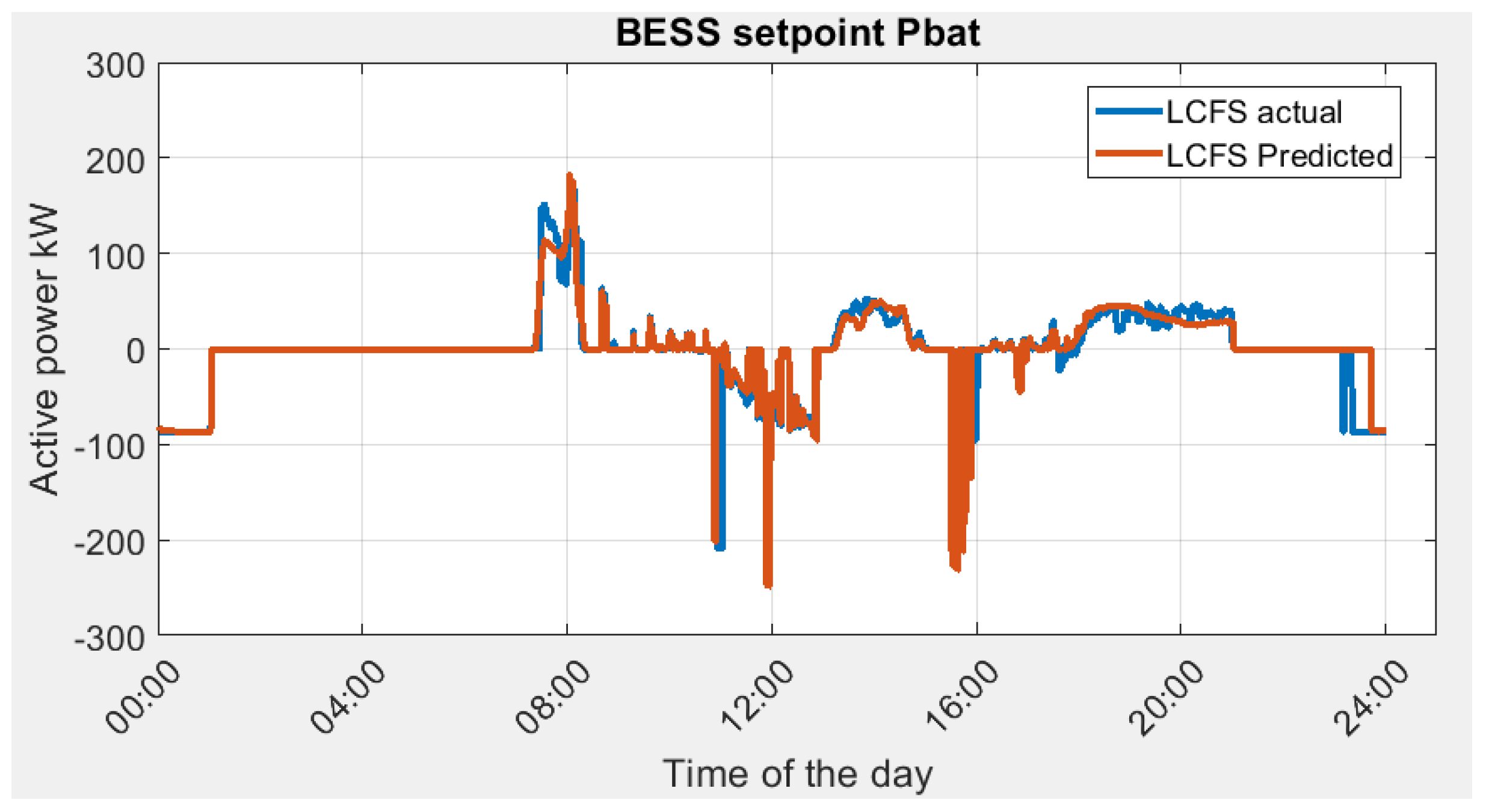
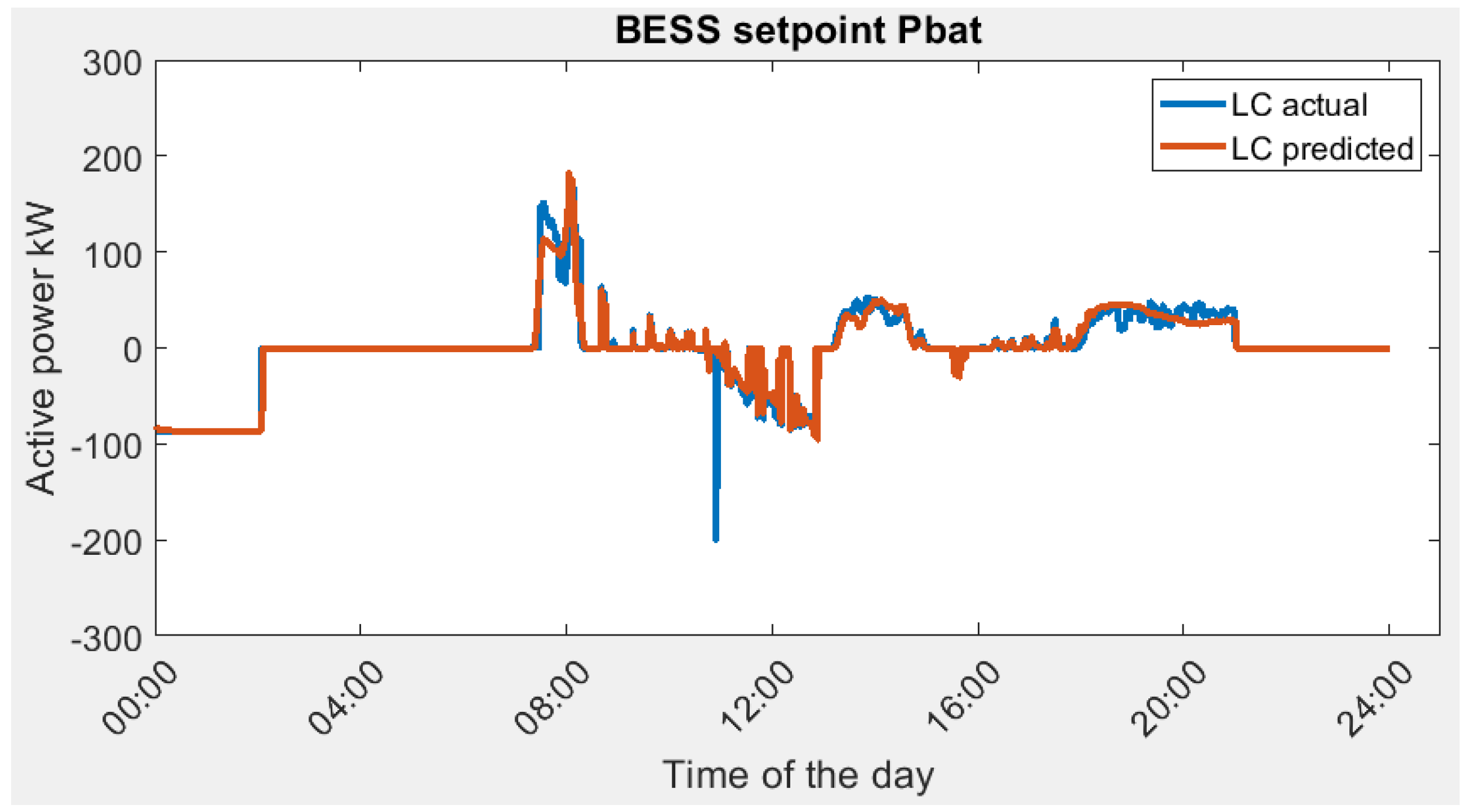
The actual optimal energy management profile (BESS power setpoint) and predicted optimal energy management profile are shown in Figure 10.
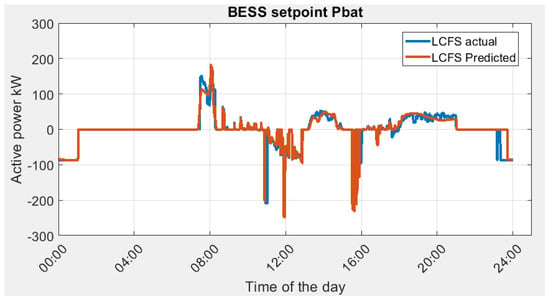
Figure 10.
BESS power setpoint in Scenario 1A, actual optimal vs. predicted optimal.
In general, the LCFS optimization shows a close match between the predicted and actual loading scenarios. This is due to the good prediction accuracy from LSTM as shown in Figure 9. There are several discrepancies noticed:
- (1)
- At 8 am in the morning, there is a power demand surge in the building due to the cooling system. The BESS setpoint is able to follow the power surge with some errors that originated from the load prediction as shown in Figure 9.
- (2)
- At the end of the day, the actual BESS setpoint starts to charge the battery at an earlier time as compared to the predicted case, meaning there is more power discharged from the actual case during the day.
The result reveals that the predicted optimal solution provides an accurate BESS power setpoint. The resulting LCFS predicted electricity cost is SGD 1028.03 as compared to SGD 1027.81 for the actual. Without the microgrid, the electricity cost is 1334.43 SGD. The reduction in energy cost is SGD 306.4.
Scenario 1B: lowest cost (LC).
The actual optimal energy management profile (BESS power setpoint) and predicted optimal energy management profile are shown in Figure 11.
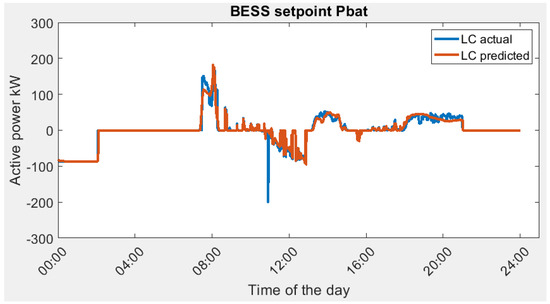
Figure 11.
BESS power setpoint in Scenario 1B, actual optimal vs. predicted optimal.
The graphical representation illustrates that the predicted optimal solution effectively aligns with the true BESS power setpoint. As a consequence, the forecasted LCFS electricity cost amounts to SGD 1017.25, closely approximating the actual cost of SGD 1017.03. In the absence of the microgrid infrastructure, the electricity cost rises to SGD 1334.43. This discernible disparity results in a noteworthy reduction in energy-related expenditures, amounting to SGD 317.18. In this case, the flexible SOC0 provides extra energy reduction. The optimal SOC0 at the beginning of the day is 5%, the defined lower limit of SOC.
A sharp decrease in setpoint is registered in the actual optimal energy management profile at 10:54 am. This was a result of the optimization process recognizing the need to charge the battery at that specific moment. Due to the absence of penalties for abrupt power changes and a consistent electricity price throughout the daytime, the algorithm charged the battery at the maximum allowable rate within the defined constraints. Consequently, it set a −200 kW target at 10:54 am. In essence, multiple optimal solutions exist that yield the same objective value. For instance, when charging the battery, whether done gradually or aggressively, the outcome remains identical in this scenario, provided there is adequate headroom for charging setpoints and the electricity price remains constant during the charging interval.
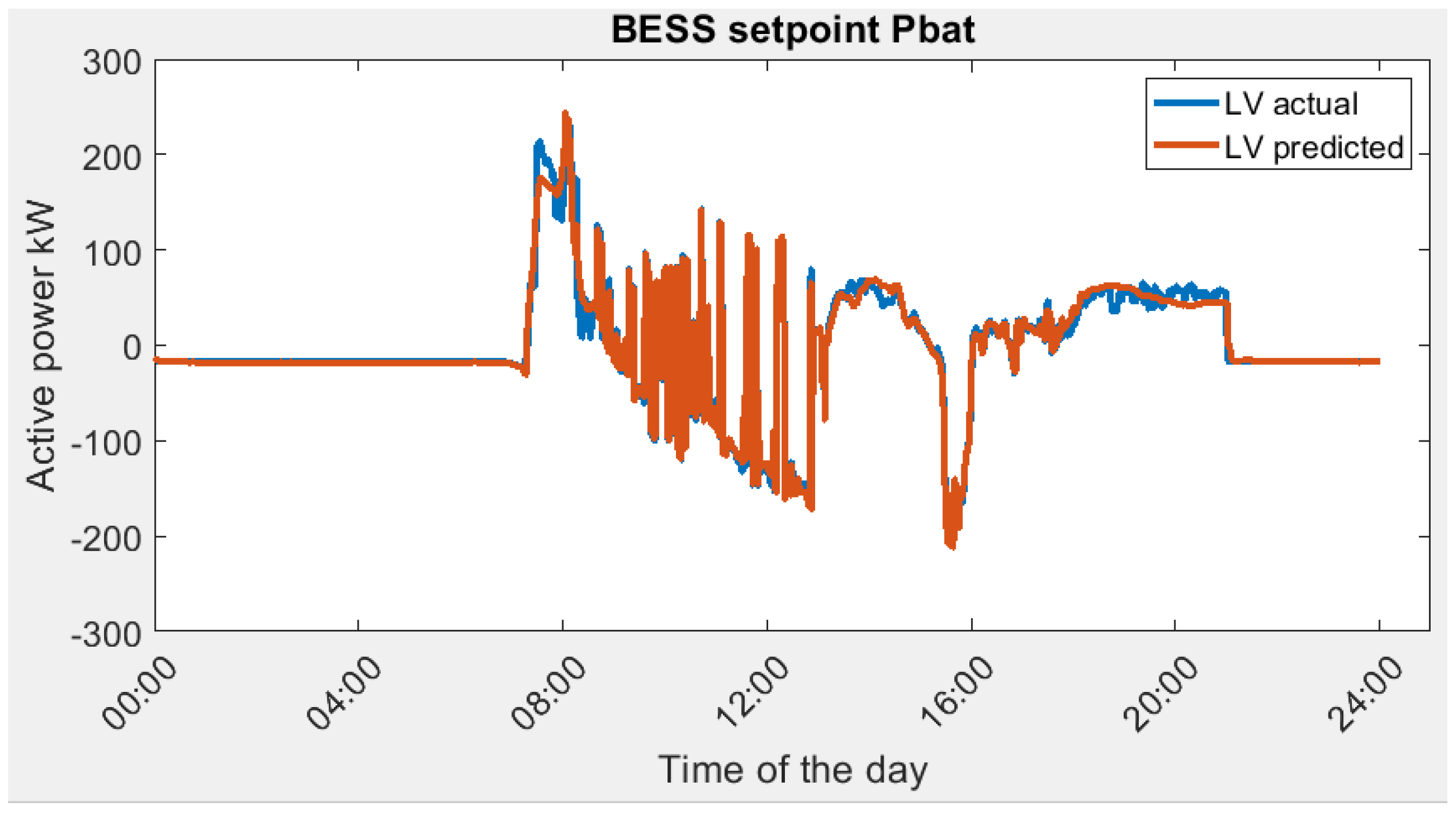
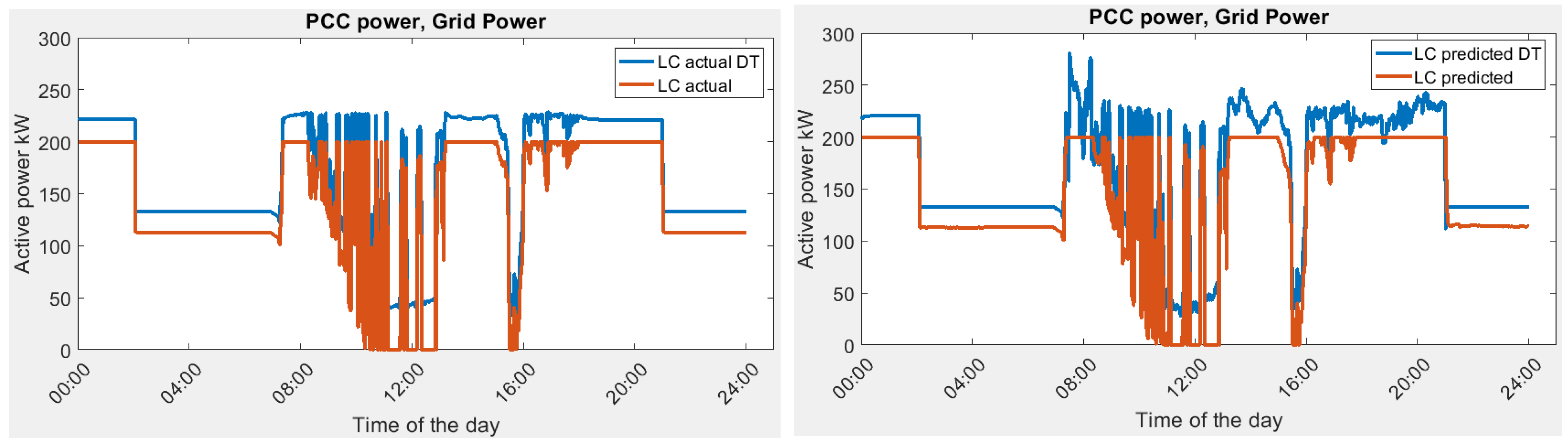
Scenario 2: lowest Variance (LV). The actual optimal energy management profile (BESS power setpoint) and predicted optimal energy management profile based on lowest Variance (LV) are as shown in Figure 12.
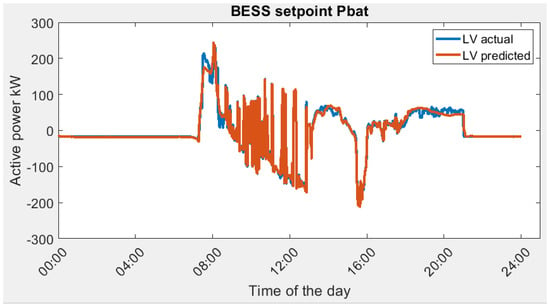
Figure 12.
BESS power setpoint in Scenario 2, actual optimal vs. predicted optimal.
The variance of grid power serves as a pivotal metric denoting the oscillation in power load. As exemplified by the observed electrical load requisites, the zenith of power demand culminates at 428.85 kW. In the context of high-tension power supplies, the rate applied to contracted capacity is more favorable in comparison to uncontracted capacity, signifying an economic incentive for responsible capacity planning. It is imperative to acknowledge that an elevated variance in power consumption substantially heightens the likelihood of incurring expenses related to uncontracted capacity, accentuating the financial significance of minimizing load fluctuations and optimizing capacity utilization.
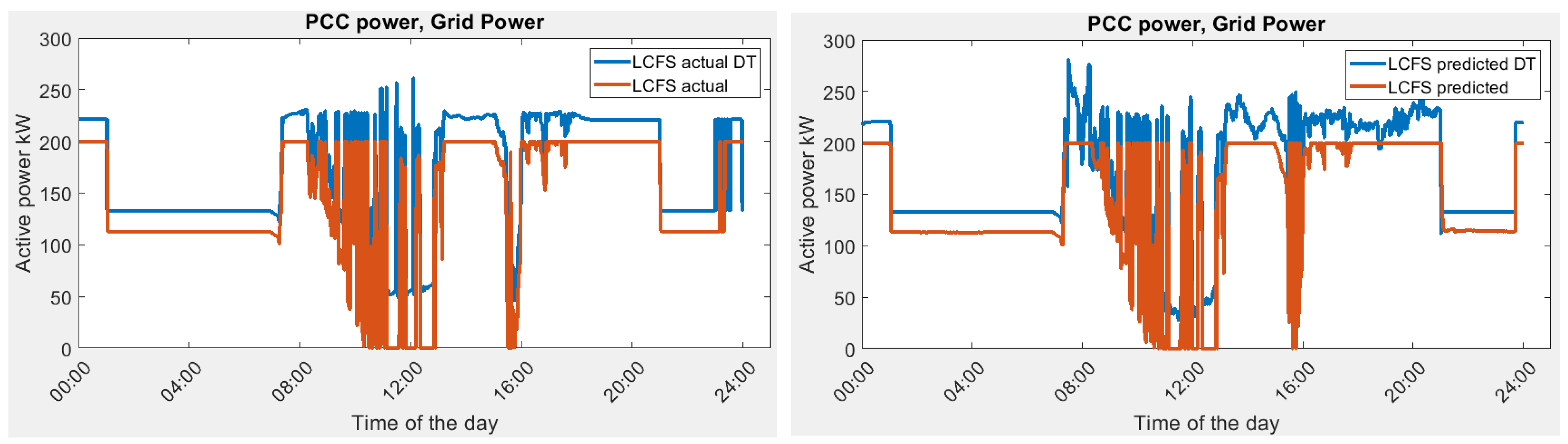
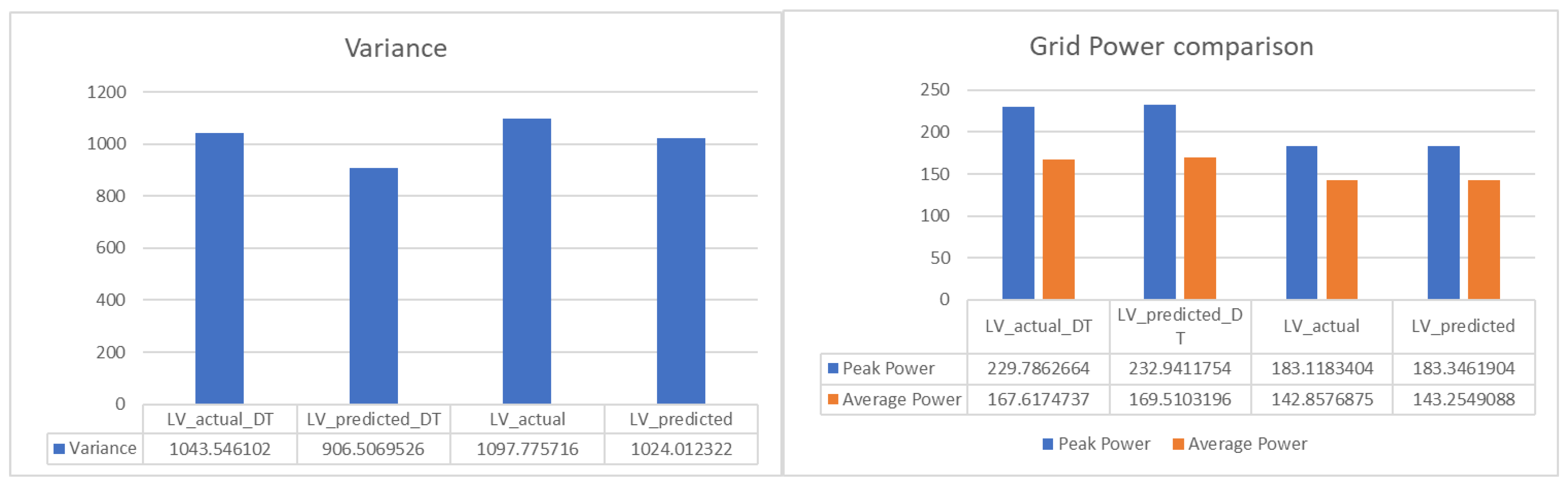
The result of LV optimization for actual load demand and predicted load demand is shown in Figure 13. The LV optimization using predicted load data is 1024.01 , which is lower than 1097.78 . This is due to more fluctuation in the actual load demand than the prediction. The results of the optimization process are summarized in Table 6.
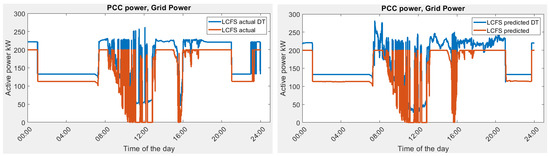
Figure 13.
Grid power demand in Scenario 1A, actual vs. predicted in optimization and DT simulation.

Table 6.
Optimization result with varying scenarios.
3.3. Microgrid Digital Twin Result and Discussion
Following Section 3.2, the optimized setpoints are used as the reference in the microgrid digital twin system. The result achieved reveals a close-to-reality performance of microgrid integration with the SIT@NYP campus. The objective is to verify the results from Section 3.1 and Section 3.2. The findings from the microgrid digital twin reveal the discrepancies due to the physical microgrid and give feedback to the building’s predictive power control.
Scenario 1A: lowest cost with Fixed SOC0 (LCFS).
In this scenario, the actual power demand that is required from the grid is plotted as in Figure 13.
The actual power needed from the grid is based on the optimization of the actual building load, which is the optimal energy management in an ideal scenario. The predicted power needed from the grid is based on the optimization of the predicted building load demand using LSTM. The result shows a close match between two scenarios. The battery is charging during the mid-night period. During charging, the battery charging solution is not unique, and the time of charging is flexible given that it will not affect the value of the objective function. Hence, the grid power consumption at the end of the day is different between the actual and predicted load.
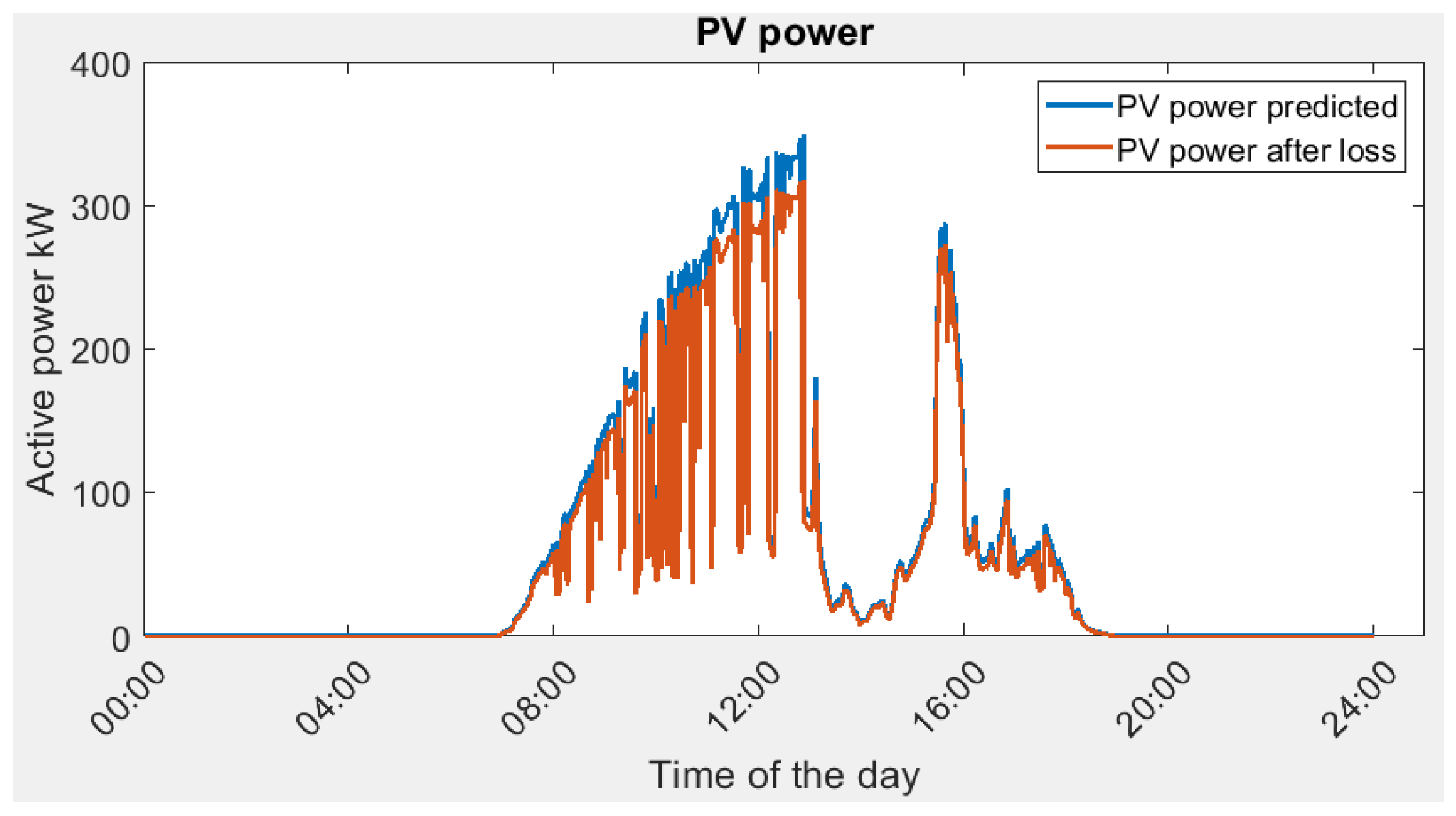
In both actual and predicted cases, the optimization process gives a lower power consumption from the main grid. In physical microgrids, energy conversion efficiency always introduces power loss in the system. In addition, there are various ancillary devices required for microgrid operation, such as industrial PC, controller, data servers, etc. Hence, the microgrid digital twin reveals the power consumption that is closer to the real-world application. Figure 14 shows the solar energy conversion efficiency. The actual power generated is lower as compared to the predicted PV power.
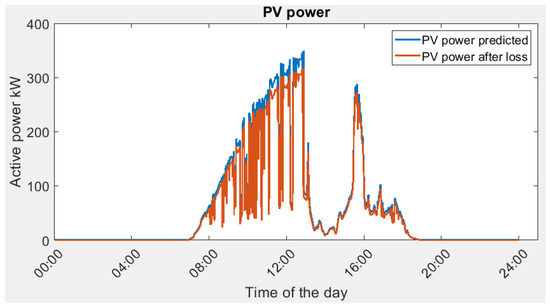
Figure 14.
Predicted PV power vs. actual PV power.
Scenario 1B: lowest cost (LC).
In this scenario, the actual power demand that is required from the grid is plotted as in Figure 15.
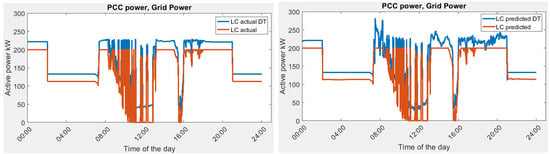
Figure 15.
Grid power demand in Scenario 1B, actual vs. predicted in optimization and DT simulation.
In this scenario, the initial battery SOC is flexible. After digital twin simulation, it was observed that the grid power demand has a similar trend as in Scenario 1A. There is additional power required from the grid. The battery is at 5% SOC in the beginning of the day and is charged early in the morning to take advantage of the lower electricity price in the off-peak hours.
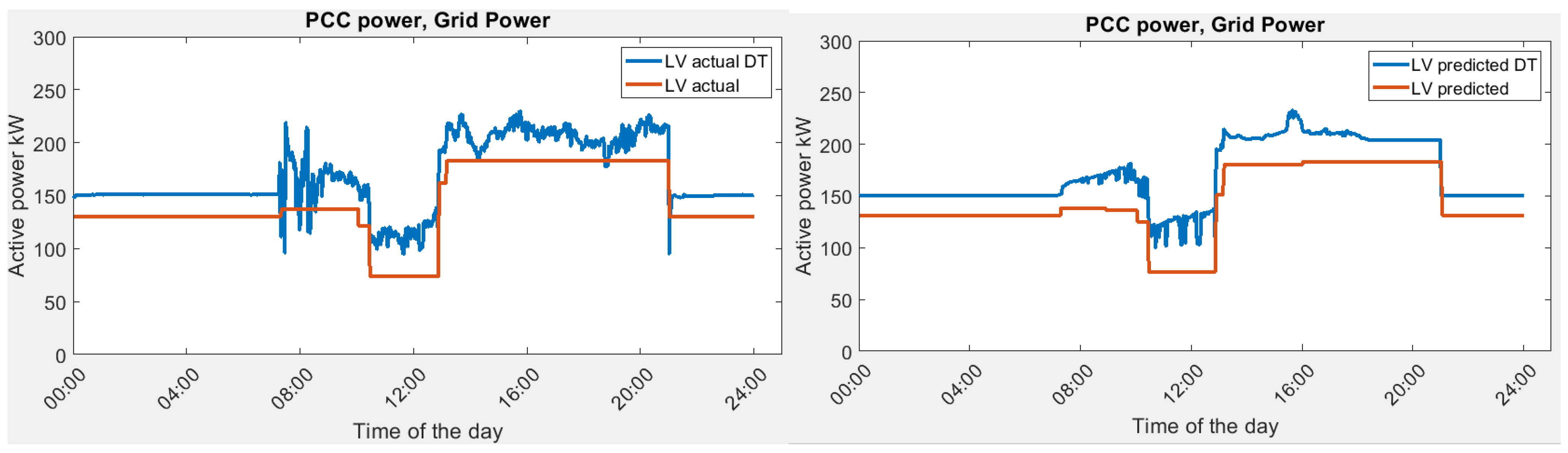
Scenario 2: lowest Variance (LV).
In this scenario, the focus is to reduce the power fluctuations so that the power variance is minimized. The result from the digital twin is plotted in Figure 16. The power fluctuation from the DT is much higher as compared with the ideal optimization. However, due to the additional power consumption in the microgrid, the variance is decreased in DT.
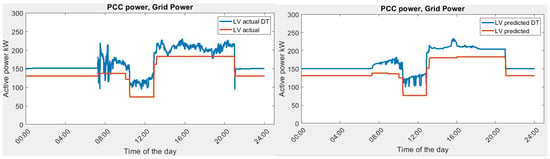
Figure 16.
Grid power demand in Scenario 2, actual vs. predicted in optimization and DT simulation.
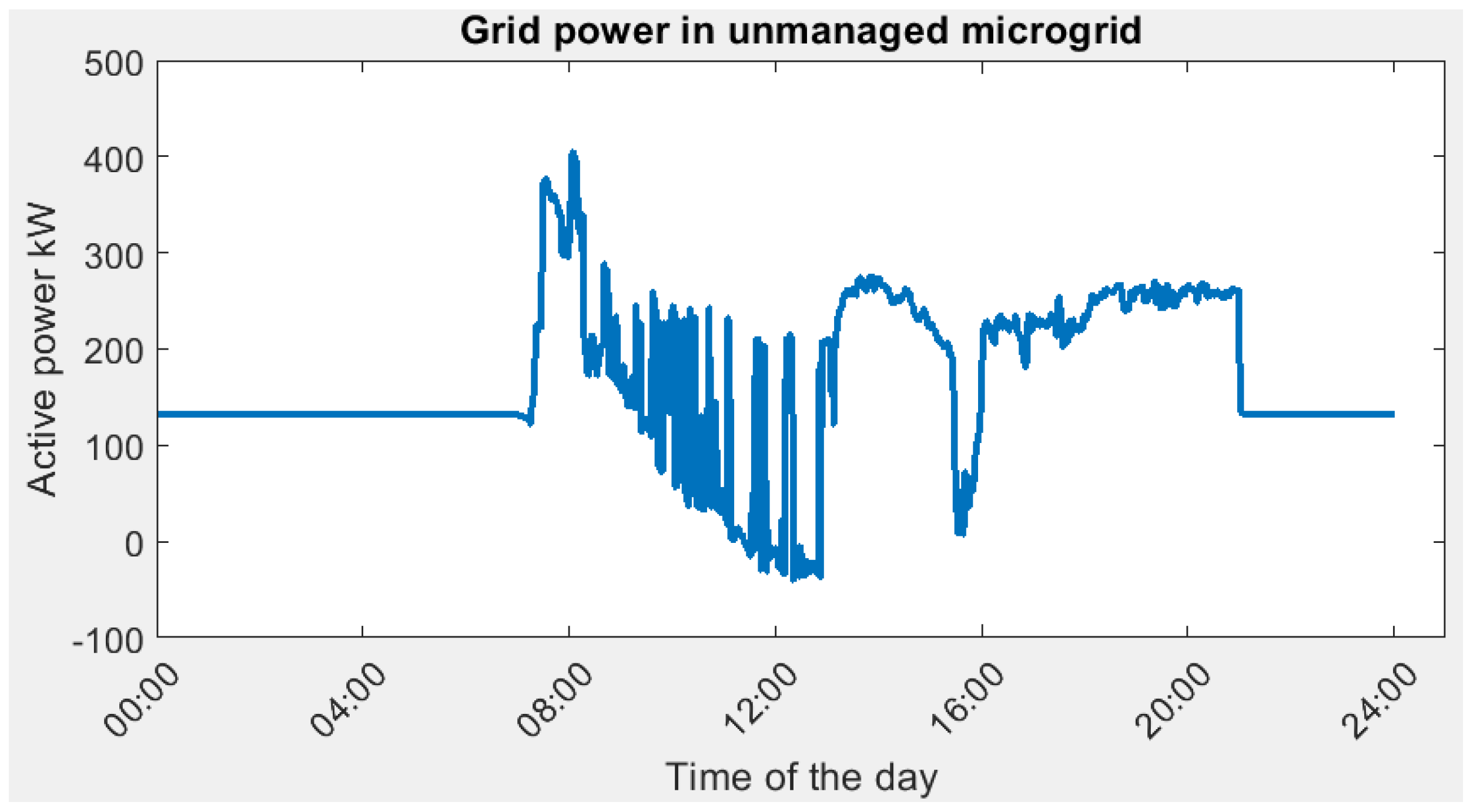
When the microgrid is unmanaged, namely, BESS is not active, the power drawn from the grid is shown in the figure below.
As compared to the unmanaged case (Figure 17), the peak power demand is reduced from 405.47 kW to (229.79 kW, 232.94 kW) in the digital twin verified result. This significant reduction in peak power will benefit both the building owner as well as the grid provider. The size of the equipment (such as transformer, protection device) can be reduced for the SIT@NYP building and the user can subscribe to smaller contracted capacity. Hence, it will bring economic benefits to stakeholders.
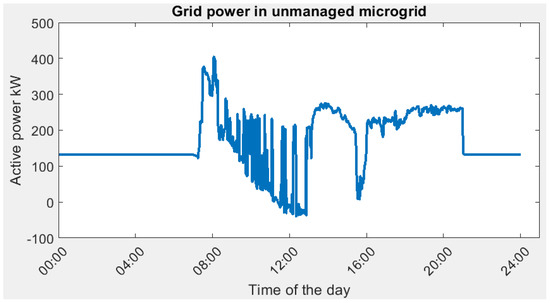
Figure 17.
Grid power demand in unmanaged microgrid scenario.
Figure 18 summarizes the reduction in variance and peak power in all cases of Scenario 2. The result reveals the capability of the proposed method in stabilizing the power fluctuation and decreasing the peak load or rated power of electrical assets needed.
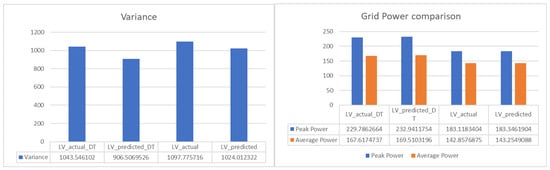
Figure 18.
Grid power demand comparison in Scenario 2.
Across three scenarios, there is a common observation of power loss within the microgrid, and higher power taken from the main grid. In the intricate web of a microgrid, power loss manifests through a spectrum of factors inherent in its diverse components and the intricacies of energy transmission and distribution. Noteworthy among these contributors are
- Conversion Inefficiencies: The transformation of energy from one form to another, such as the conversion between AC and DC, often incurs losses owing to the imperfect efficiency of devices like inverters, converters, and transformers operating within the microgrid.
- Transmission and Distribution Losses: In the journey of electricity through wires and cables, resistance along the transmission lines induces voltage drops and dissipates energy. These resistive losses amplify with increased transmission distances or diminished conductor quality.
- Component Degradation: Components like batteries, solar panels, inverters, and generators in the microgrid degrade over time. This decline reduces their efficiency, leading to increased internal resistance or lower energy conversion efficiency, contributing to power losses.
- Ancillary Equipment Consumption: Devices like controllers, sensors, monitoring systems, and auxiliary loads (such as equipment cooling systems) consume power for operation. While essential for microgrid functioning and monitoring, their power consumption adds to overall system power losses.
- The aforementioned losses can be reduced but cannot be eliminated. Hence, the authors suggest to include the losses in the optimization or the prediction process so that the proposed model can be applied in various types of buildings, geographical locations, and application constraints.
3.4. Discussion on the Practical Implementation Concerns of the Proposed Predictive Power Control Method
3.4.1. Building Operators Preference
When it comes to the selection of the objective of optimization, it is contingent upon a case-by-case evaluation. Building operators possess the autonomy to select operational strategies based on their preferences. This study investigates two prevalent objective functions. The first centers on optimizing economic benefits, specifically aiming for the lowest electricity cost. The second objective function prioritizes mitigating power fluctuation and minimizing peak demand. Other key objectives concerning building operator include:
- Sustainability and Environmental Stewardship: A priority for many proprietors is mitigating environmental impact by lowering energy usage, thereby reducing greenhouse gas emissions. This often involves integrating renewable energy sources and implementing eco-friendly practices.
- Regulatory Compliance: Adherence to energy efficiency standards, building codes, and governmental regulations is imperative to ensure legal compliance and promote energy-conservation measures.
- Resilience and Reliability: Ensuring a dependable power supply is vital. Some proprietors prioritize systems capable of withstanding power disruptions, often incorporating backup power sources like generators or battery storage for resilience. This can impose additional constraints on SOC in order to maintain sufficient reserve.
Each of the objectives can formulate its objective functions for optimization. For complicated scenarios, the building operator may pursue more than one objective. In such cases, weighted factors or coefficients can be applied using the following objective function.
where is the overall objective, is the weighing factor for ith objective, is the ith objective function.
3.4.2. The Cost-Effectiveness
It is crucial to prioritize economic considerations in practical implementation. The additional costs associated with the proposed method, such as computation/simulation hardware, software, and configuration manpower expenses, are quantifiable and relatively limited. Notably, these costs remain consistent regardless of the scale of power, which stands as a notable advantage of employing a digital twin. In addition, the implementation has low marginal cost and wide application scope due to the low sensitivity of the applied scenario.
The cost-effectiveness of the proposed method relies heavily on the economic benefits it generates, which can stem from various aspects:
- Cost Reduction and Optimization: The method outlined in this paper demonstrates a capacity for substantial energy optimization, promising considerable cost savings over an extended period.
- Operational Efficiency: Leveraging virtual models allows for real-time monitoring and analysis of assets or processes, fostering optimized operations. By simulating diverse scenarios and strategies, organizations can pinpoint the most efficient and cost-effective approaches.
- Improved Decision-Making: Digital twins furnish data-driven insights and simulations, enhancing decision-making. This can translate into reduced risks, optimized resource allocation, and more informed investments, positively impacting the overall financial performance.
- Insight Provision: In certain implementation scenarios, digital twin-based control systems can offer vital insights even before the physical installation of assets. The provision of insights through simulation aids in informed decision-making and planning.
These economic benefits highlight the potential of the proposed method to yield substantial returns by optimizing energy usage, enhancing operational efficiency, improving decision-making, and offering valuable insights. The quantification of various economic benefits may be challenging and vary case-by-case. Once quantified, the cost-effectiveness can be determined. This will promote energy resilience and sustainability as based on the operational strategies of the building operators’ preference for cost-effectiveness.
3.4.3. Technical Feasibility
The practicality of the suggested approach has been demonstrated via the SIT@NYP scenario. The AI, energy optimization, and digital twin components have been tested and showcased the proposed method’s functionality or effectiveness. Consequently, its technical readiness level stands high, making it prepared for implementation.
4. Conclusions
In summary, the authors present a systematic way of combining AI, optimization, and the microgrid digital twin to form a novel method of predictive power control to buildings. The results show promising accuracy and accountability. In the prediction analysis, the result reveals that for buildings with cyclic power demand, the load is highly predictable and the one-layer LSTM can provide sufficiently good prediction regardless of training data date (pre COVID-19 or during COVID-19). The optimization process shows performance improvement from 22% to 82% depending on the building operator’s preference. In future, or when the physical microgrid is implemented, the real-time digital twin can provide online energy prediction and optimization, which can operate in real-time with the building’s electrical and cooling systems. It will further unleash the power of the microgrid digital twin in predictive power control to sustainable buildings. Additional deliberation regarding the practical implementation concerns is provided, encompassing various building operators’ preferences, cost efficiency, and technical readiness. The suggested predictive power control exhibits remarkable adaptability to accommodate diverse building scenarios, offers a broad spectrum of economic advantages, and holds significant promise for practical implementation.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, C.B.S. and R.T.; methodology, K.J.T.; software, H.J. and R.T.; validation, K.T.T. and S.B.K.; formal analysis, H.J., D.C.L.S. and R.T.; investigation, H.J. and S.C.; data curation, H.J.; writing—original draft preparation, R.T.; writing—review and editing, C.B.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This project is supported by the National Research Foundation, Singapore, and the Energy Market Authority, under the Exploiting Distributed Generation (“EDGE”) Programme and administered by the EDGE Programme Office (EDGE Programme Award EDGE-GC2018-001). Any opinions, findings, and conclusions or recommendations expressed in this material are those of the author(s) and do not reflect the views of the Energy Market Authority, Singapore.
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Mtibaa, F.; Nguyen, K.-K.; Azam, M.; Papachristou, A.; Venne, J.-S.; Cheriet, M. LSTM-based indoor air temperature prediction framework for HVAC systems in smart buildings. Neural Comput. Appl. 2020, 32, 17569–17585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.F.; Alam, S.B.; Hassan, M.; Rozbu, M.R.; Ishtiak, T.; Rafa, N.; Mofijur, M.; Ali, A.B.M.S.; Gandomi, A.H. Deep learning modelling techniques: Current progress, applications, advantages, and challenges. Artif. Int. Rev. 2023, 56, 13521–13617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, H.S.; Kim, G. Prediction model of Cooling Load considering time-lag for preemptive action in buildings. Energy Build. 2017, 151, 53–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zeng, Y.; Starly, B. Recurrent neural networks with long term temporal dependencies in machine tool wear diagnosis and prognosis. SN Appl. Sci. 2021, 3, 442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Peng, R.-Q.; Wang, J.-Q.; Li, Z.; Qu, H.-B. NEWLSTM: An Optimized Long Short-Term Memory Language Model for Sequence Prediction; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2020; pp. 65395–65401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Fang, Z.; Xu, X.; Zhang, X.; Ding, Y.; Jiang, X.; Ji, Y. Using long short-term memory networks to predict energy consumption of air-conditioning systems. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2020, 55, 10200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mavsar, M.; Deniša, M.; Nemec, B.; Ude, A. Intention Recognition with Recurrent Neural Networks for Dynamic Human-Robot Collaboration. In Proceedings of the 2021 20th International Conference on Advanced Robotics (ICAR), Ljubljana, Slovenia, 6–10 December 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Chalapathy, R.; Khoa, N.L.D.; Sethuvenkatraman, S. Comparing multi-step ahead building cooling load prediction using shallow machine learning and deep learning models. Sust. Energy Grids Netw. 2021, 28, 100543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, T.; Khitab, Z.; Girbau, F.; Sumper, A. Energy Management System for Optimal Operatioin of Microgrids Network. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Smart Energy Grid Engineering (SEGE), Oshawa, ON, Canada, 12–15 August 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, Y.; Xiao, F.; Wang, W.; He, X.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, Y. Digital Twin for Power System Steady-state Modelling, Simulation, and Analysis. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE 4th Conference on Energy Internet and Energy System Integration (EI2), Wuhan, China, 30 October–1 November 2020. [Google Scholar]
- IEC 60870S-5-104; Telecontrol Equipment and Systems—Part 5-104: Transmission Protocols—Network Access for IEC 60870-5-101 Using Standard Transport Profiles. International Electrotechnical Commission: Geneva, Switzerland, 2006.
- Jiang, H.; Tjandra, R.; Lim, W.J.; Cao, S.; Soh, C.B.; Tan, K.T.; Krishnan, S.B. Unleashing the Potential of Digital Twin Technology in Microgrid—A Case Study of a Tropical Microgrid. In Proceedings of the 2023 6th International Conference on Electrical Engineering and Green Energy (CEEGE), Grimstad, Norway, 6–9 June 2023; pp. 165–170. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, F.; Chen, X.; Cao, S.; Soh, C.B.; Cai, Z.; Tseng, K.; Jet, D.; Mahinda, V. MPC Based Dynamic Voltage Regulation Using Grid-Side BESPS With the Consideration of Communication Delay. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2023, 38, 838–848. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Wang, J.; Tian, J.; Lu, J.; Xiong, R. Application of Digital Twin in Smart Battery Management Systems. Chin. J. Mech. Eng. 2021, 34, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).