Investigating the Social Sustainability of Immersive Virtual Technologies in Higher Educational Institutions: Students’ Perceptions toward Metaverse Technology
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
2.1. Educational Activities in the Metaverse: A Glimpse into the Future of Higher Education
2.2. Metaverse Technology and Pedagogical Frameworks in the HEIs
- (1)
- Constructivism: This approach highlights the learner’s proactive involvement in knowledge construction through first-hand experiences. Within the Metaverse, educators have the ability to generate immersive settings where students actively participate in creating their comprehension by engaging with the digital realm and working on projects or simulations.
- (2)
- Experiential Learning: Based on the theories of John Dewey and David Kolb, experiential learning emphasizes the acquisition of knowledge through direct encounters and subsequent reflection. The Metaverse provides prospects for immersive and practical education, enabling students to actively participate in virtual simulations, experiments, and role-playing scenarios.
- (3)
- Connectivism: Established by George Siemens, it underscores learning as a process that occurs within a network, wherein learners establish connections with resources, knowledge, and other learners. Within the Metaverse, students have the ability to collaborate without limitations, access a wide range of materials, and participate in interconnected learning communities.
- (4)
- Bloom’s Taxonomy is a framework that classifies cognitive abilities into different levels, ranging from basic thinking skills like remembering and understanding, to more advanced thinking skills like applying, analyzing, evaluating, and producing. Teachers have the ability to create tasks within the virtual reality world that are tailored to various levels of Bloom’s Taxonomy, promoting the development of analytical thinking and imaginative skills.
- (5)
- Universal Design for Learning (UDL) is an approach that fosters inclusive education through the provision of many methods for presenting information, engaging students, and expressing knowledge. Within the Metaverse, educators possess the ability to generate a wide range of educational resources, inclusive settings, and numerous methods of interaction to cater to various learning preferences and capabilities.
- (6)
- Game-Based Learning and Gamification: By utilizing components of games or concepts of game design, educators can employ the Metaverse to construct learning experiences that incorporate game-like characteristics. These experiences aim to enhance student engagement, motivation, and the acquisition of skills.
- (7)
- Learning Analytics: By harnessing data and analytics derived from students’ interactions in the Metaverse, educators can apply learning analytics frameworks to obtain insights into students’ advancement, preferences, and areas requiring enhancement. The utilization of data can provide valuable insights to enhance tailored learning experiences.
- (8)
- The utilization of Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR) in the field of Education: Although not a distinct theory, incorporating AR and VR technology into the Metaverse is consistent with pedagogical methods that prioritize immersive and experiential learning, enabling students to engage with knowledge in novel ways.
2.3. Theoretical Background and Hypotheses
2.3.1. Performance Expectancy (PE)
2.3.2. Effort Expectancy (EE)
2.3.3. Social Influence (SI)
2.3.4. Facilitating Conditions (FCs)
2.3.5. Perceived Curiosity (PC)
2.3.6. Extraversion (EXT) as a Critical Personality Trait
3. Research Methodology
3.1. Study Sample and Data Collection
- Demographic profiles of study respondents
3.2. Measurement
4. Data Analysis and Results
4.1. Descriptive Statistics
4.2. Measurement Model
4.3. Structural Model
5. Discussion, Implications, Limitations, and Future Research
5.1. Theoretical and Practical Implications
5.2. Limitations and Future Work
6. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Construct | Code | Measurement Item | Source (s) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance Expectancy | PE1 | I find the Metaverse technology to be useful for my study purposes. | [6,10,44] |
| PE2 | Using the Metaverse technology makes it easier for me to achieve my study goals. | ||
| PE3 | Using the Metaverse technology improves my learning efficiency. | ||
| Effort Expectancy | EE1 | My interaction with the Metaverse technology for educational purposes is clear and understandable. | [6,10,44] |
| EE2 | I think the Metaverse technology for educational purposes is easy to use. | ||
| EE3 | Learning to use the Metaverse technology for educational purposes is easy for me. | ||
| Facilitating Conditions | FC1 | There are online resources to show me how to use the Metaverse technology for educational purposes. | [6,10,44] |
| FC2 | There are online customer service providers to show me how to use the Metaverse technology for educational purposes. | ||
| FC3 | There are online customer service providers to help me when I have difficulties using the Metaverse technology for educational purposes. | ||
| FC4 | Using the Metaverse technology for educational purposes is compatible with other technology I use. | ||
| Social influence | SI1 | People who are important to me would think that I should use the Metaverse educational platform. | [6,10,44] |
| SI2 | People whose opinions I value would like me to use the Metaverse educational platform. | ||
| SI3 | People who influence my behavior would think that I should use the Metaverse educational platform. | ||
| Perceived Curiosity | PC1 | I follow the news about Metaverse out of curiosity. | [62,79] |
| PC2 | I cannot wait to try Metaverse. | ||
| PC3 | I enjoy spending hours on a question related to using Metaverse because I cannot be comfortable without getting an answer. | ||
| PC4 | I enjoy learning about subjects using Metaverse technology as this experience is new to me. | ||
| Extraversion | EXT1 | The Metaverse encourages university students to be outgoing and sociable. | [67,68,69,98] |
| EXT2 | The Metaverse encourages university students to be conversationalists. | ||
| EXT3 | The Metaverse promotes the cultivation of confidence and sociability among university students. | ||
| Social sustainability | SS1 | The use of Metaverse in the educational process ensures equal personal development and engagement opportunities for learners. | [96,97] |
| SS2 | The use of Metaverse promotes social issues, including the development of communities, cultural competency, social equity, social assistance, responsibility for society, etc. | ||
| SS3 | In general, implementing Metaverse for the educational process contributes to taking aspects like equal opportunities and diversity management into consideration. |
References
- Arpaci, I.; Karatas, K.; Kusci, I.; Al-Emran, M. Understanding the social sustainability of the Metaverse by integrating UTAUT2 and big five personality traits: A hybrid SEM-ANN approach. Technol. Soc. 2022, 71, 102120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.; Yang, E.; Ryu, J. Work-in-progress—The effect of students’ perceptions on intention to use metaverse learning environment in higher education. In Proceedings of the IEEE 8th International Conference of the Immersive Learning Research Network (iLRN), Vienna, Austria, 30 May–4 June 2022; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, M.; Liu, S.; Hu, L.; Lee, J.-Y. A Study of Metaverse Exhibition Sustainability on the Perspective of the Experience Economy. Sustainability 2023, 15, 9153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephenson, N. Snow Crash: A Novel; Bantam Spectra: New York, NY, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Salar, H.C.; Başarmak, U.; Sezgin, M.E. Educational Integration of the Metaverse Environment in the Context of Web 3.0 Technologies: A Critical Overview of Planning, Implementation, and Evaluation. In Shaping the Future of Online Learning: Education in the Metaverse; IGI Global: Hershey, PA, USA, 2023; pp. 154–173. [Google Scholar]
- Teng, Z.; Cai, Y.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, X.; Li, X. Factors Affecting Learners’ Adoption of an Educational Metaverse Platform: An Empirical Study Based on an Extended UTAUT Model. Mob. Inf. Syst. 2022, 2022, 5479215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.-M.; Kim, Y.-G. A Metaverse: Taxonomy, components, applications, and open challenges. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 4209–4251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Needleman, S.E. The Amazing Things You’ll Do in the ‘Metaverse’ and What It Will Take to Get There. The Wall Street Journal, 16 October 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Huynh-The, T.; Gadekallu, T.R.; Wang, W.; Yenduri, G.; Ranaweera, P.; Pham, Q.-V.; da Costa, D.B.; Liyanage, M. Blockchain for the metaverse: A Review. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2023, 143, 401–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Ren, L.; Gu, C. A study of college students’ intention to use metaverse technology for basketball learning based on UTAUT2. Heliyon 2022, 8, e10562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salhab, H.A.; Allahham, M.; Abu-AlSondos, I.A.; Frangieh, R.H.; Alkhwaldi, A.F.; Ali, B.J.A. Inventory competition, artificial intelligence, and quality improvement decisions in supply chains with digital marketing. Uncertain Supply Chain. Manag. 2023, 11, 1915–1924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alharasis, E.E.; Alhadab, M.; Alidarous, M.; Jamaani, F.; Alkhwaldi, A.F. The impact of COVID-19 on the relationship between auditor industry specialization and audit fees: Empirical evidence from Jordan. J. Financ. Report. Account. 2023. ahead-of-print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alharasis, E.E.; Alidarous, M.; Alkhwaldi, A.F.; Haddad, H.; Alramahi, N.; Al-Shattarat, H.K. Corporates’ monitoring costs of fair value disclosures in pre-versus post-IFRS7 era: Jordanian financial business evidence. Cogent Bus. Manag. 2023, 10, 2234141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alharasis, E.; Alkhwaldi, A.; Hussainey, K. Key audit matters and auditing quality in the era of COVID-19 pandemic: The case of Jordan. Int. J. Law Manag. 2024, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Alkhwaldi, A.F.; Abu-Alsondos, I.; Abdulmuhsin, A.; Shehadeh, M.; Aldhmour, F.M. Toward an understanding of cutting edge technologies in financial industry: Cryptocurrency adoption. In Proceedings of the Conference on Sustainability and Cutting-Edge Business Technologies, Amman, Jordan, 22 May 2023; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; pp. 64–82. [Google Scholar]
- Shehadeh, M.; Almajali, D.; Abu-AlSondos, I.A.; Alkhwaldi, A.F.; Al-Gasaymeh, A.S. Digital Transformation and its Impact on Operational Efficiency and Competitive Advantage in Islamic Banks. In Proceedings of the 2023 International Conference on Business Analytics for Technology and Security (ICBATS), Dubai, United Arab Emiratesm, 7–8 March 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Alkhwaldi, A.; Kamala, M.; Qahwaji, R. Security Perceptions in Cloud-Based e-Govemment Services. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE 12th International Conference on Global Security, Safety and Sustainability (ICGS3), London, UK, 16–18 January 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Abu-AlSondos, I.A.; Abu-AlSondos, I.A.; Alkhwaldi, A.F.; Shehadeh, M.; Ali, B.J.; Al Nasar, M.R. The Role of Industry 4.0 Technologies in Enabling Knowledge Management Practices: United Arab Emirates Perspective. In The International Conference On Global Economic Revolutions; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Agarwal, S.; Kaushik, J.S. Student’s perception of online learning during COVID pandemic. Indian J. Pediatr. 2020, 87, 554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandez, C.B.; Hui, P. Life, the metaverse and everything: An overview of privacy, ethics, and governance in metaverse. In Proceedings of the IEEE 42nd International Conference on Distributed Computing Systems Workshops (ICDCSW), Bologna, Italy, 10 July 2022; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Alkhwaldi, A.F.; Abdulmuhsin, A.A. Crisis-centric distance learning model in Jordanian higher education sector: Factors influencing the continuous use of distance learning platforms during COVID-19 pandemic. J. Int. Educ. Bus. 2022, 15, 250–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Shin, C. Influencing Factors of Usage Intention of Metaverse Education Application Platform: Empirical Evidence Based on PPM and TAM Models. Sustainability 2022, 14, 17037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deloitte. The Metaverse and Its Potential for MENA. 2023. Available online: https://www2.deloitte.com/ (accessed on 14 August 2023).
- JordanTimes. Metaverse Could Contribute up to $1.7 Billion to GDP in Jordan by 2035, Says Report. 2023. Available online: https://jordantimes.com/news/local/metaverse-could-contribute-17-billion-gdp-jordan-2035-says-report (accessed on 14 August 2023).
- AAU. Amman Arab University Is the First University In Metaviruses. 2022. Available online: https://www.aau.edu.jo/en/news/21157#:~:text=Amman%20Arab%20University%20has%20concluded,within%20the%20world%20of%20LivatVerse (accessed on 15 January 2023).
- PSUT. PSUT Creates an Experimental Course on the Metaverse. 2023. Available online: https://psut.edu.jo/en/news/psut-creates-an-experimental-course-on-the-metaverse-2 (accessed on 14 August 2023).
- Hwang, G.-J.; Chien, S.-Y. Definition, roles, and potential research issues of the metaverse in education: An artificial intelligence perspective. Comput. Educ. Artif. Intell. 2022, 3, 100082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abed, S.N.; Abdulmuhsin, A.A.; Alkhwaldi, A.F. The factors influencing the innovative performance of leaders in nurses’ professional: A developing country perspective. Leadersh. Health Serv. 2021, 35, 228–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akour, I.A.; Al-Maroof, R.S.; Alfaisal, R.; Salloum, S.A. A conceptual framework for determining metaverse adoption in higher institutions of gulf area: An empirical study using hybrid SEM-ANN approach. Comput. Educ. Artif. Intell. 2022, 3, 100052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Adwan, A.S.; Li, N.; Al-Adwan, A.; Abbasi, G.A.; Albelbisi, N.A.; Habibi, A. Extending the technology acceptance model (TAM) to Predict University Students’ intentions to use metaverse-based learning platforms. Educ. Inf. Technol. 2023, 28, 15381–15413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, R.; Yu, Z. Investigating Users’ Acceptance of the Metaverse with an Extended Technology Acceptance Model. Int. J. Hum.–Comput. Interact. 2023, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radianti, J.; Majchrzak, T.A.; Fromm, J.; Wohlgenannt, I. A systematic review of immersive virtual reality applications for higher education: Design elements, lessons learned, and research agenda. Comput. Educ. 2020, 147, 103778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvet, L.; Bourdin, P.; Prados, F. Immersive technologies in higher education: Applications, challenges, and good practices. In Proceedings of the 2019 3rd International Conference on Education and E-Learning, Barcelona, Spain, 5–7 November 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Pellas, N.; Mystakidis, S.; Kazanidis, I. Immersive Virtual Reality in K-12 and Higher Education: A systematic review of the last decade scientific literature. Virtual Real. 2021, 25, 835–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-AlSondos, I.A.; Salameh, A.A.; Alkhwaldi, A.F.; Mushtaha, A.S.; Shehadeh, M.; Al-Junaidi, A. Evaluating Mobile E-Learning Systems Acceptance: An Integrated Model. Int. J. Interact. Mob. Technol. 2023, 17, 30–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salloum, S.; Al Marzouqi, A.; Alderbashi, K.Y.; Shwedeh, F.; Aburayya, A.; Al Saidat, M.R.; Al-Maroof, R.S. Sustainability Model for the Continuous Intention to Use Metaverse Technology in Higher Education: A Case Study from Oman. Sustainability 2023, 15, 5257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nejad, M.C.; Mansour, S.; Karamipour, A. An AHP-based multi-criteria model for assessment of the social sustainability of technology management process: A case study in banking industry. Technol. Soc. 2021, 65, 101602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvanathan, R.G. Measuring Educational Sustainability. Int. J. High. Educ. 2013, 2, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouzguenda, I.; Alalouch, C.; Fava, N. Towards smart sustainable cities: A review of the role digital citizen participation could play in advancing social sustainability. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2019, 50, 101627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ario, M.K.; Santoso, Y.K.; Basyari, F.; Edbert; Fajar, M.; Panggabean, F.M.; Satria, T.G. Towards an implementation of immersive experience application for marketing and promotion through virtual exhibition. Softw. Impacts 2022, 14, 100439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Wu, J.; Jeon, G.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Y.; Tan, M. Towards Understanding Metaverse Engagement Via Social Patterns and Reward Mechanism: A Case Study of Nova Empire; IEEE Transactions on Computational Social Systems: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Agyei, J.; Sun, S.; Abrokwah, E.; Penney, E.K.; Ofori-Boafo, R. Mobile banking adoption: Examining the role of personality traits. Sage Open 2020, 10, 2158244020932918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatesh, V.; Thong, J.Y.L.; Xu, X. Consumer acceptance and use of information technology: Extending the unified theory of acceptance and use of technology. MIS Q. 2012, 36, 157–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatesh, V.; Morris, M.G.; Davis, G.B.; Davis, F.D. User acceptance of information technology: Toward a unified view. MIS Q. 2003, 27, 425–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwivedi, Y.K.; Rana, N.P.; Jeyaraj, A.; Clement, M.; Williams, M.D. Re-examining the unified theory of acceptance and use of technology (UTAUT): Towards a revised theoretical model. Inf. Syst. Front. 2019, 21, 719–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, Y.; Leng, J.; Zhao, J.L. Demystifying metaverse as a new paradigm of enterprise digitization. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Big Data, Virtual Event, 10–14 December 2021; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 109–119. [Google Scholar]
- Onggirawan, C.A.; Kho, J.M.; Kartiwa, A.P.; Anderies; Gunawan, A.A.S. Systematic literature review: The adaptation of distance learning process during the COVID-19 pandemic using virtual educational spaces in metaverse. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2023, 216, 274–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, S.-N.; Kanematsu, H.; Barry, D.M.; Ogawa, N.; Yajima, K.; Nakahira, K.T.; Shirai, T.; Kawaguchi, M.; Kobayashi, T.; Yoshitake, M. Virtual Experiments in Metaverse and their Applications to Collaborative Projects: The framework and its significance. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2020, 176, 2125–2132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Zhao, B.; Ji, Z.; Liang, Z. On the Personalized Learning Space in Educational Metaverse Based on Heart Rate Signal. Int. J. Inf. Commun. Technol. Educ. IJICTE 2022, 18, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damaševičius, R.; Sidekersniene, T. Designing Immersive Gamified Experiences in the Metaverse for Enhanced Student Learning. In Proceedings of the 2023 International Conference on Intelligent Metaverse Technologies & Applications (iMETA), Tartu, Estonia, 8–20 September 2023; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2023; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, H.; Hwang, Y. Technology-enhanced education through VR-making and metaverse-linking to foster teacher readiness and sustainable learning. Sustainability 2022, 14, 4786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moschini, E. The second life researcher toolkit–an exploration of inworld tools, methods and approaches for researching educational projects in second life. In Researching Learning in Virtual Worlds; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; pp. 31–51. [Google Scholar]
- Mystakidis, S. Sustainable Engagement in Open and Distance Learning With Play and Games in Virtual Reality: Playful and Gameful Distance Education in VR. In Research Anthology on Virtual Environments and Building the Metaverse; IGI Global: Hershey, Pennsylvania, 2023; pp. 297–312. [Google Scholar]
- Ng, P.H.F.; Chen, P.Q.; Sin, Z.P.; Jia, Y.; Li, R.C.; Baciu, G.; Li, Q. From Classroom to Metaverse: A Study on Gamified Constructivist Teaching in Higher Education. In International Conference on Web-Based Learning; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2023; pp. 92–106. [Google Scholar]
- Sinha, E. ‘Co-creating’experiential learning in the metaverse-extending the Kolb’s learning cycle and identifying potential challenges. Int. J. Manag. Educ. 2023, 21, 100875. [Google Scholar]
- Tlili, A.; Huang, R.; Shehata, B.; Liu, D.; Zhao, J.; Metwally, A.H.S.; Wang, H.; Denden, M.; Bozkurt, A.; Lee, L.-H.; et al. Is Metaverse in education a blessing or a curse: A combined content and bibliometric analysis. Smart Learn. Environ. 2022, 9, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Yu, H.; Bell, Z.; Chu, X. Constructing an Edu-Metaverse Ecosystem: A New and innovative framework. IEEE Trans. Learn. Technol. 2022, 15, 685–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazdani, M.; Pamucar, D.; Erdmann, A.; Toro-Dupouy, L. Resilient sustainable investment in digital education technology: A stakeholder-centric decision support model under uncertainty. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2023, 188, 122282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatesh, V.; Thong, J.Y.L.; Xu, X. Unified theory of acceptance and use of technology: A synthesis and the road ahead. J. Assoc. Inf. Syst. 2016, 17, 328–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Rahmi, A.M.; Shamsuddin, A.; Wahab, E.; Al-Rahmi, W.M.; Alturki, U.; Aldraiweesh, A.; Almutairy, S. Integrating the Role of UTAUT and TTF Model to Evaluate Social Media Use for Teaching and Learning in Higher Education. Front. Public Health 2022, 10, 905968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahara, T.; Iyer, L.S.; Matta, V.; Alagarsamy, S. Effect of Organizational Culture during Crises on adoption of virtual classrooms: An extension of UTAUT model. J. Inf. Technol. Case Appl. Res. 2021, 23, 213–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aburbeian, A.M.; Owda, A.Y.; Owda, M. A Technology Acceptance Model Survey of the Metaverse Prospects. AI 2022, 3, 285–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manis, K.T.; Choi, D. The virtual reality hardware acceptance model (VR-HAM): Extending and individuating the technology acceptance model (TAM) for virtual reality hardware. J. Bus. Res. 2019, 100, 503–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acikgoz, F.; Elwalda, A.; De Oliveira, M.J. Curiosity on Cutting-Edge Technology via Theory of Planned Behavior and Diffusion of Innovation Theory. Int. J. Inf. Manag. Data Insights 2023, 3, 100152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaya, F.; Aydin, F.; Schepman, A.; Rodway, P.; Yetişensoy, O.; Kaya, M.D. The Roles of Personality Traits, AI Anxiety, and Demographic Factors in Attitudes toward Artificial Intelligence. Int. J. Hum. Comput. Interact. 2022, 40, 497–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, V.T. The perceptions of social media users of digital detox apps considering personality traits. Education and Information Technologies 2022, 27, 9293–9316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krey, N.; Chuah, S.H.W.; Ramayah, T. How functional and emotional ads drive smartwatch adoption: The moderating role of consumer innovativeness and extraversion. Internet Res. 2019, 29, 578–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.M.; Chiu, W.C.; Lin, H.H.; Wang, Y.S.; Wang, Y.Y.; Chen, I.F. Determinants of students’ adoption of virtual reality-based learning systems: An individual difference perspective. Innov. Educ. Teach. Int. 2022, 61, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.S.; Lin, H.H.; Liao, Y.W. Investigating the individual difference antecedents of perceived enjoyment in students’ use of blogging. Br. J. Educ. Technol. 2012, 43, 139–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkhwaldi, A.F.; Alobidyeen, B.; Abdulmuhsin, A.A.; Al-Okaily, M. Investigating the antecedents of HRIS adoption in public sector organizations: Integration of UTAUT and TTF. Int. J. Organ. Anal. 2022, 31, 3251–3274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkhwaldi, A.F.; Al-Ajaleen, R.T. Toward a Conceptual Model for Citizens’ Adoption of Smart Mobile Government Services during the COVID-19 Pandemic in Jordan. Inf. Sci. Lett. 2022, 11, 573–579. [Google Scholar]
- Alkhwaldi, A.F.; Al Eshoush, A.S. Towards A model for Citizens’ Acceptance of E-Payment Systems for Public Sector Services in Jordan: Evidence from Crisis Era. Inf. Sci. Lett. 2022, 11, 657–663. [Google Scholar]
- Alkhwaldi, A.F. Understanding the Patients’ Usage of Contactless Healthcare Services: Evidence from the Post-COVID-19 Era. In The Role of Digital Technologies in Shaping the Post-Pandemic World, Proceedings of the 21st IFIP WG 6.11 Conference on e-Business, e-Services and e-Society, I3E 2022, Newcastle upon Tyne, UK, 13–14 September 2022; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Papagiannidis, S., Alamanos, E., Gupta, S., Dwivedi, Y.K., Mäntymäki, M., Pappas, I.O., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; Volume 13454, pp. 356–373. [Google Scholar]
- Alkhwaldi, A.F.; Al-Qudah, A.A.; Al-Hattami, H.M.; Al-Okaily, M.; Al-Adwan, A.S.; Abu-Salih, B. Uncertainty avoidance and acceptance of the digital payment systems: A partial least squares-structural equation modeling (PLS-SEM) approach. Glob. Knowl. Mem. Commun. 2023. ahead-of-print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Okaily, M.; Alkhwaldi, A.F.; Abdulmuhsin, A.A.; Alqudah, H.; Al-Okaily, A. Cloud-based accounting information systems usage and its impact on Jordanian SMEs’ performance: The post-COVID-19 perspective. J. Financ. Report. Account. 2023, 21, 126–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkhwaldi, A.F. Understanding the acceptance of business intelligence from healthcare professionals’ perspective: An empirical study of healthcare organizations. Int. J. Organ. Anal. 2024. ahead-of-print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dbesan, A.H.; Abdulmuhsin, A.A.; Alkhwaldi, A.F. Adopting knowledge-sharing-driven blockchain technology in healthcare: A developing country’s perspective. VINE J. Inf. Knowl. Manag. Syst. 2023. ahead-of-print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litman, J.A. Relationships between measures of I-and D-type curiosity, ambiguity tolerance, and need for closure: An initial test of the wanting-liking model of information-seeking. Personal. Individ. Differ. 2010, 48, 397–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litman, J.A. Interest and deprivation factors of epistemic curiosity. Personal. Individ. Differ. 2008, 44, 1585–1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halder, S.; Roy, A.; Chakraborty, P.K. The influence of personality traits on information seeking behaviour of students. Malays. J. Libr. Inf. Sci. 2010, 15, 41–53. [Google Scholar]
- Irfan, M.; Ahmad, M. Relating consumers’ information and willingness to buy electric vehicles: Does personality matter? Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2021, 100, 103049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, Y. Personalization and personality: Some effects of customizing message style based on consumer personality. J. Consum. Psychol. 2002, 12, 313–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shumanov, M.; Cooper, H.; Ewing, M. Using AI predicted personality to enhance advertising effectiveness. Eur. J. Mark. 2022, 56, 1590–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camadan, F.; Reisoglu, I.; Ursavas, F.; Mcilroy, D. How teachers’ personality affect on their behavioral intention to use tablet PC. Int. J. Inf. Learn. Technol. 2018, 35, 12–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terzis, V.; Moridis, C.N.; Economides, A.A. How student’s personality traits affect Computer Based Assessment Acceptance: Integrating BFI with CBAAM. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2012, 28, 1985–1996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, P.T., Jr.; McCrae, R.R. The five-factor model, five-factor theory, and interpersonal psychology. In Handbook of Interpersonal Psychology: Theory, Research, Assessment, and Therapeutic Interventions; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2010; pp. 91–104. [Google Scholar]
- McCrae, R.R.; Costa, P.T., Jr. Understanding persons: From stern’s personalistics to Five-factor theory. Personal. Individ. Differ. 2021, 169, 109816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, P.T.; McCrae, R.R. Normal personality assessment in clinical practice: The NEO Personality Inventory. Psychol. Assess. 1992, 4, 5–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCrae, R.R.; Costa, P.T. Validation of the five-factor model of personality across instruments and observers. J. Personal. Soc. Psychol. 1987, 52, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matz, S.C.; Kosinski, M.; Nave, G.; Stillwell, D.J. Psychological targeting as an effective approach to digital mass persuasion. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 12714–12719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shumanov, M.L.; Johnson, L. Making conversations with chatbots more personalized. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2021, 117, 106627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.N.; Cao, X.; Pitafi, A.H. Personality traits as predictor of M-payment systems: A SEM-neural networks approach. J. Organ. End User Comput. JOEUC 2019, 31, 89–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikbin, D.; Iranmanesh, M.; Foroughi, B. Personality traits, psychological well-being, Facebook addiction, health and performance: Testing their relationships. Behav. Inf. Technol. 2021, 40, 706–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, G.; Singh, D. Personality matters: Does an individual’s personality affect adoption and continued use of green banking channels? Int. J. Bank Mark. 2022, 40, 746–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnett, T.; Pearson, A.W.; Pearson, R.; Kellermanns, F.W. Five-factor model personality traits as predictors of perceived and actual usage of technology. Eur. J. Inf. Syst. 2015, 24, 374–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelletier, L.G.; Legault, L.R.; Tuson, K.M. The environmental satisfaction scale: A measure of satisfaction with local environmental conditions and government environmental policies. Environ. Behav. 1996, 28, 5–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staniškienė, E.; Stankevičiūtė, Ž. Social sustainability measurement framework: The case of employee perspective in a CSR-committed organisation. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 188, 708–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Lu, Y. The effects of personality traits on user acceptance of mobile commerce. Intl. J. Hum.–Comput. Interact. 2011, 27, 545–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- In, J. Introduction of a pilot study. Korean J. Anesthesiol. 2017, 70, 601–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nick, T.G. Descriptive statistics. In Topics Biostatistics; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007; pp. 33–52. [Google Scholar]
- Byrne, B.M. Structural Equation Modeling with AMOS: Basic Concepts, Applications, and Programming; Routledge: London, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Hair, J.F.; Black, W.C.; Babin, B.J.; Anderson, R.E. Multivariate Data Analysis: Pearson New International Edition; Always Learning; Pearson Harlow: Essex, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Kline, R.B. Principles and Practice of Structural Equation Modeling; Guilford Publications: New York, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Hair, J.F., Jr.; Lomax, R.G. An introduction to structural equation modeling. In Partial Least Squares Structural Equation Modeling (PLS-SEM) Using R: A Workbook; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 1–29. [Google Scholar]
- Faqih, K.M.; Jaradat, M.-I.R.M. Integrating TTF and UTAUT2 theories to investigate the adoption of augmented reality technology in education: Perspective from a developing country. Technol. Soc. 2021, 67, 101787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkhwaldi, A.F. Understanding learners’ intention toward Metaverse in higher education institutions from a developing country perspective: UTAUT and ISS integrated model. Kybernetes 2023. ahead-of-print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molla, A.; Licker, P.S. An analysis of the factors affecting mobile commerce adoption in developing countries: Towards an integrated model. Rev. Int. Bus. Strategy 2019, 10, 83–110. [Google Scholar]
- Tarhini, A.; El-Masri, M.; Ali, M.; Serrano, A. Extending the UTAUT model to understand the customers’ acceptance and use of internet banking in Lebanon: A structural equation modeling approach. Inf. Technol. People 2016, 29, 830–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkhwaldi, A.F.; Abdulmuhsin, A.A. Understanding User Acceptance of IoT Based Healthcare in Jordan: Integration of the TTF and TAM. In Digital Economy, Business Analytics, and Big Data Analytics Applications; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 191–213. [Google Scholar]
- Venkatesh, V.; Zhang, X. Unified theory of acceptance and use of technology: US vs. China. J. Glob. Inf. Technol. Manag. 2010, 13, 5–27. [Google Scholar]
- Cech, E.A. Culture of disengagement in engineering education? Sci. Technol. Hum. Values 2014, 39, 42–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.A.; Rahman, S. Investigating the success of OGB in China: The influence of personality traits. Inf. Syst. Front. 2021, 23, 543–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatesh, V.; Sykes, T.A.; Venkatraman, S. Understanding egovernment portal use in rural India: Role of demographic and personality characteristics. Inf. Syst. J. 2014, 24, 249–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schepman, A.; Rodway, P. The General Attitudes towards Artificial Intelligence Scale (GAAIS): Confirmatory validation and associations with personality, corporate distrust, and general trust. Int. J. Hum. Comput. Interact. 2023, 39, 2724–2741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, C.; Zhang, C.; Wang, S. Social anxiety as a moderator in consumer willingness to accept AI assistants based on utilitarian and hedonic values. J. Retail. Consum. Serv. 2022, 65, 102878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwivedi, Y.K.; Hughes, L.; Baabdullah, A.M.; Ribeiro-Navarrete, S.; Giannakis, M.; Al-Debei, M.M.; Dennehy, D.; Metri, B.; Buhalis, D.; Cheung, C.M.; et al. Metaverse beyond the hype: Multidisciplinary perspectives on emerging challenges, opportunities, and agenda for research, practice and policy. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2022, 66, 102542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Ramirez, M.; Arroyo-Figueroa, G.; Ayala, A. The use of a virtual reality training system to improve technical skill in the maintenance of live-line power distribution networks. Interact. Learn. Environ. 2021, 29, 527–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Demographics | No. | (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Gender | ||
| 215 | 50.1% |
| 207 | 49.9% |
| Age | ||
| 346 | 82% |
| 37 | 8.8% |
| 30 | 7.1% |
| 9 | 2.1% |
| Academic level | ||
| 368 | 87.2% |
| 36 | 8.5% |
| 18 | 4.3% |
| Majors | ||
| 114 | 27% |
| 101 | 24% |
| 46 | 11% |
| 17 | 4% |
| 51 | 12% |
| 21 | 5% |
| 34 | 8% |
| 38 | 9% |
| Competency levels of using virtual IT and/or Metaverse | ||
| 114 | 27% |
| 198 | 47% |
| 110 | 26% |
| Variables | Mean | SD | α |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance Expectancy (PE) | 3.69 | 1.17 | 0.903 |
| Effort Expectancy (EE) | 3.66 | 1.16 | 0.898 |
| Social Influence (SI) | 3.69 | 1.33 | 0.818 |
| Facilitating Conditions (FC) | 3.52 | 1.09 | 0.796 |
| Perceived Curiosity (PC) | 3.43 | 1.33 | 0.910 |
| Extraversion (EXT) | 3.67 | 1.32 | 0.849 |
| Social sustainability of MVTECH (SS) | 3.53 | 1.19 | 0.797 |
| CR | AVE | PE | EE | SI | FC | PC | EXT | SS | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PE | 0.734 | 0.526 | 0.725 | ||||||
| EE | 0.830 | 0.688 | 0.413 | 0.829 | |||||
| SI | 0.788 | 0.570 | 0.485 | 0.529 | 0.754 | ||||
| FC | 0.756 | 0.507 | 0.505 | 0.506 | 0.547 | 0.712 | |||
| PC | 0.801 | 0.618 | 0.396 | 0.424 | 0.449 | 0.536 | 0.786 | ||
| EXT | 0.846 | 0.765 | 0.413 | 0.457 | 0.458 | 0.608 | 0.467 | 0.810 | |
| SS | 0.758 | 0.523 | 0.410 | 0.448 | 0.477 | 0.468 | 0.519 | 0.507 | 0.723 |
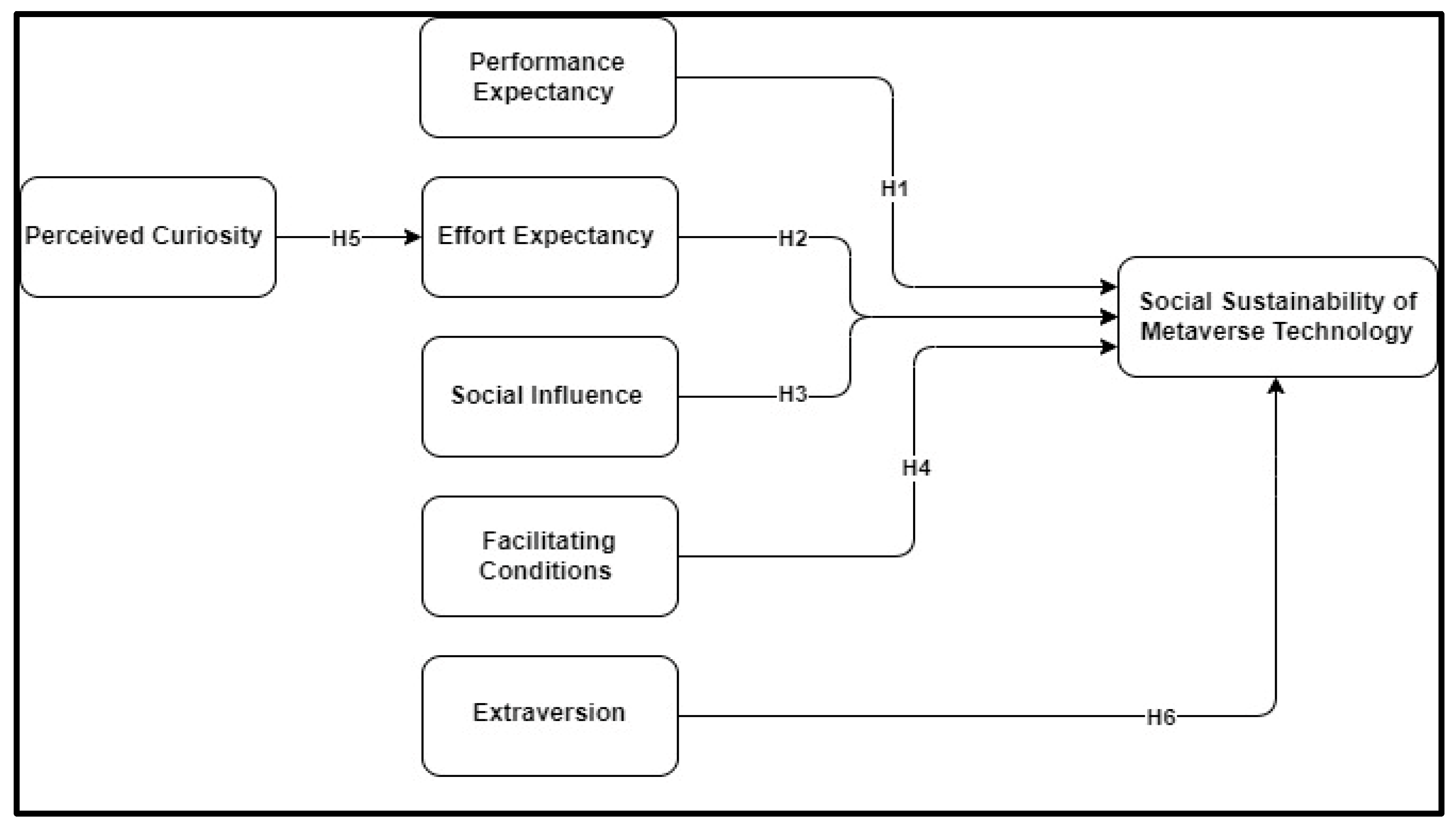
| Hypotheses | Path | Path Coefficient (β) | Supported |
|---|---|---|---|
| H1 | PE >> SS | 0.172 * | Yes |
| H2 | EE >> SS | 0.042 | No |
| H3 | SI >> SS | 0.034 | No |
| H4 | FC >> SS | 0.151 * | Yes |
| H5 | PC >> EE | 0.235 ** | Yes |
| H6 | EXT >> SS | 0.193 * | Yes |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alkhwaldi, A.F. Investigating the Social Sustainability of Immersive Virtual Technologies in Higher Educational Institutions: Students’ Perceptions toward Metaverse Technology. Sustainability 2024, 16, 934. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16020934
Alkhwaldi AF. Investigating the Social Sustainability of Immersive Virtual Technologies in Higher Educational Institutions: Students’ Perceptions toward Metaverse Technology. Sustainability. 2024; 16(2):934. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16020934
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlkhwaldi, Abeer F. 2024. "Investigating the Social Sustainability of Immersive Virtual Technologies in Higher Educational Institutions: Students’ Perceptions toward Metaverse Technology" Sustainability 16, no. 2: 934. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16020934
APA StyleAlkhwaldi, A. F. (2024). Investigating the Social Sustainability of Immersive Virtual Technologies in Higher Educational Institutions: Students’ Perceptions toward Metaverse Technology. Sustainability, 16(2), 934. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16020934







