Exploring Extreme Voltage Events in Hydrogen Arcs within Electric Arc Furnaces
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methodology
3. Governing Equations
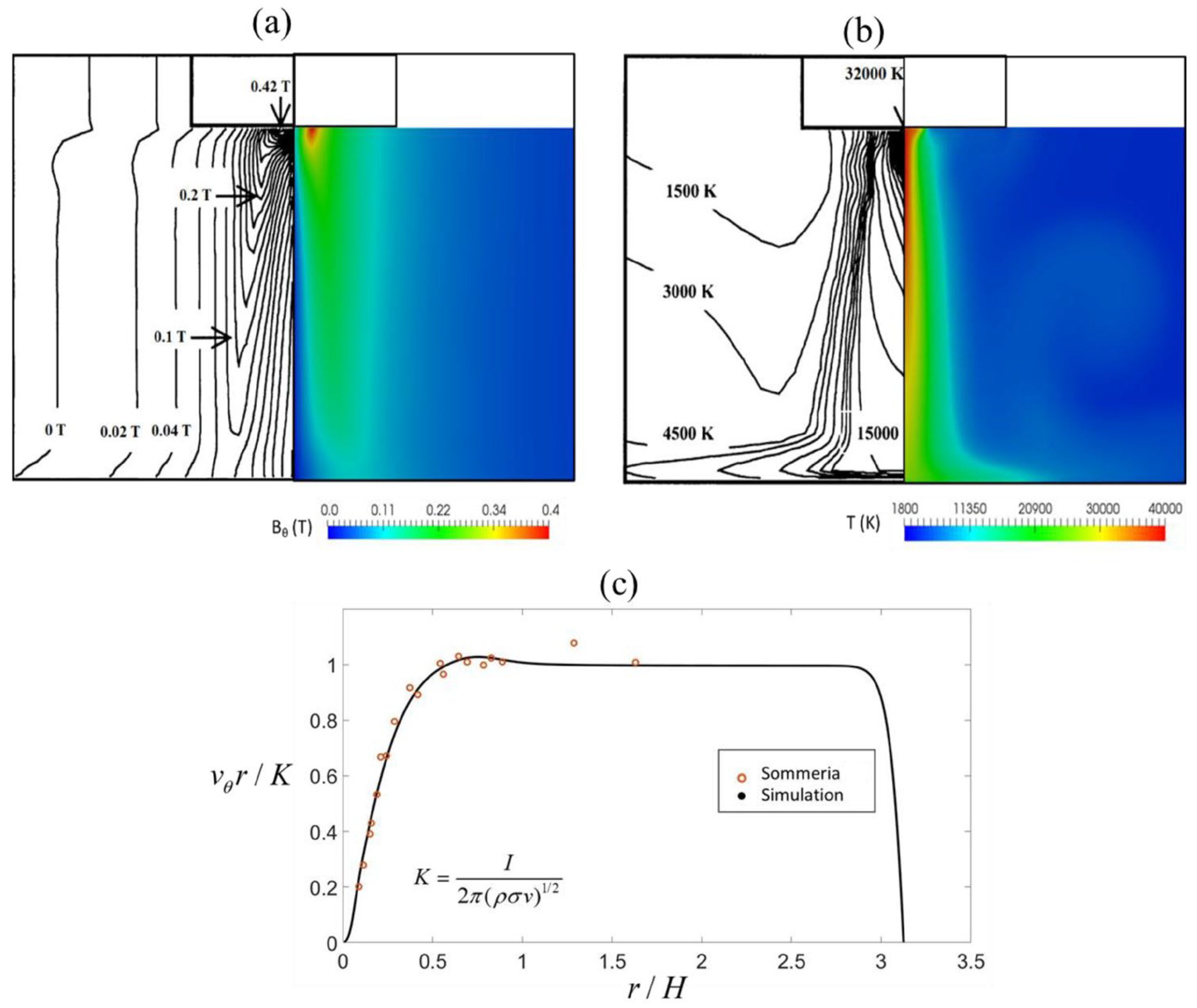
4. Boundary Conditions and Validation
5. Results and Discussion
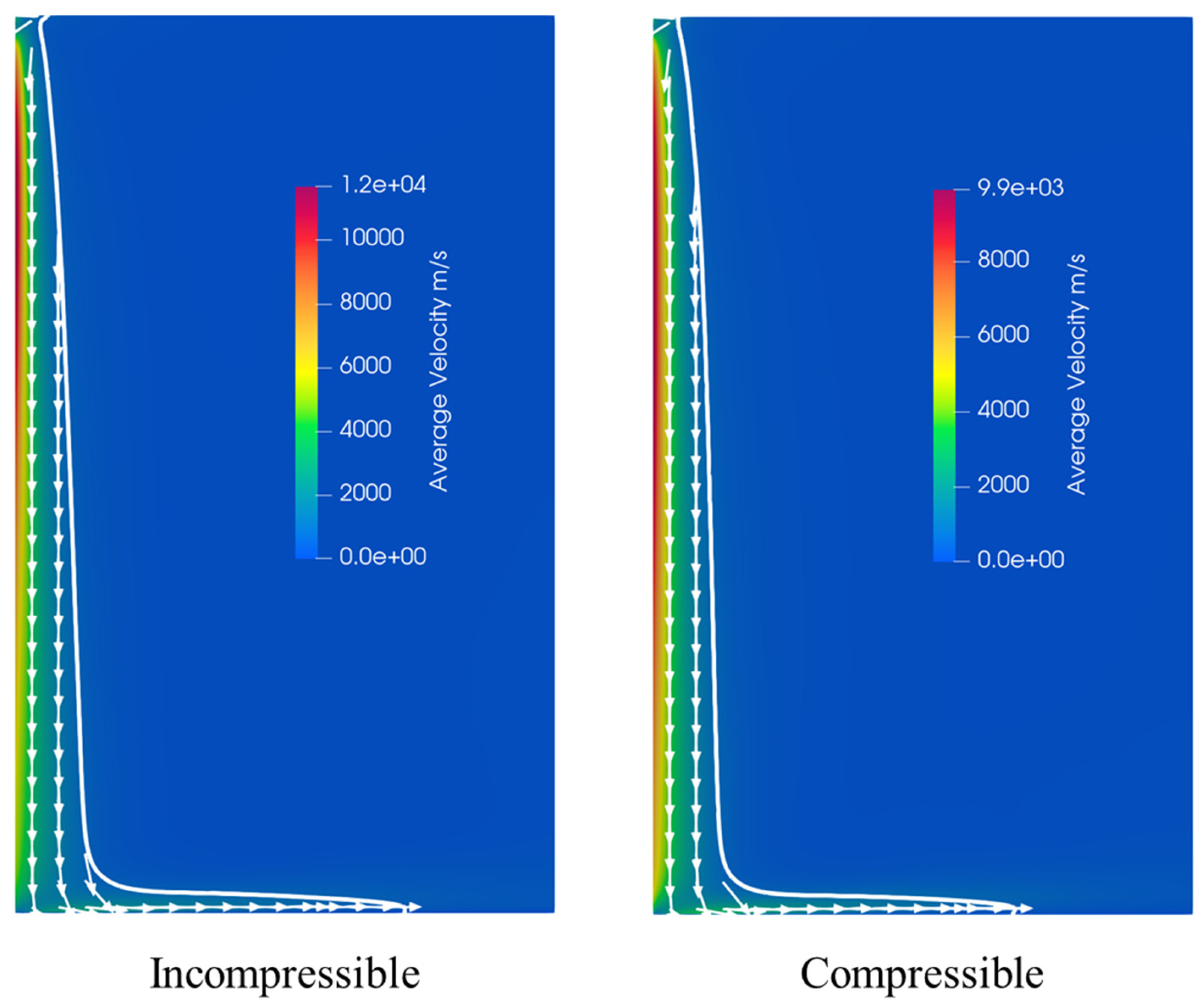
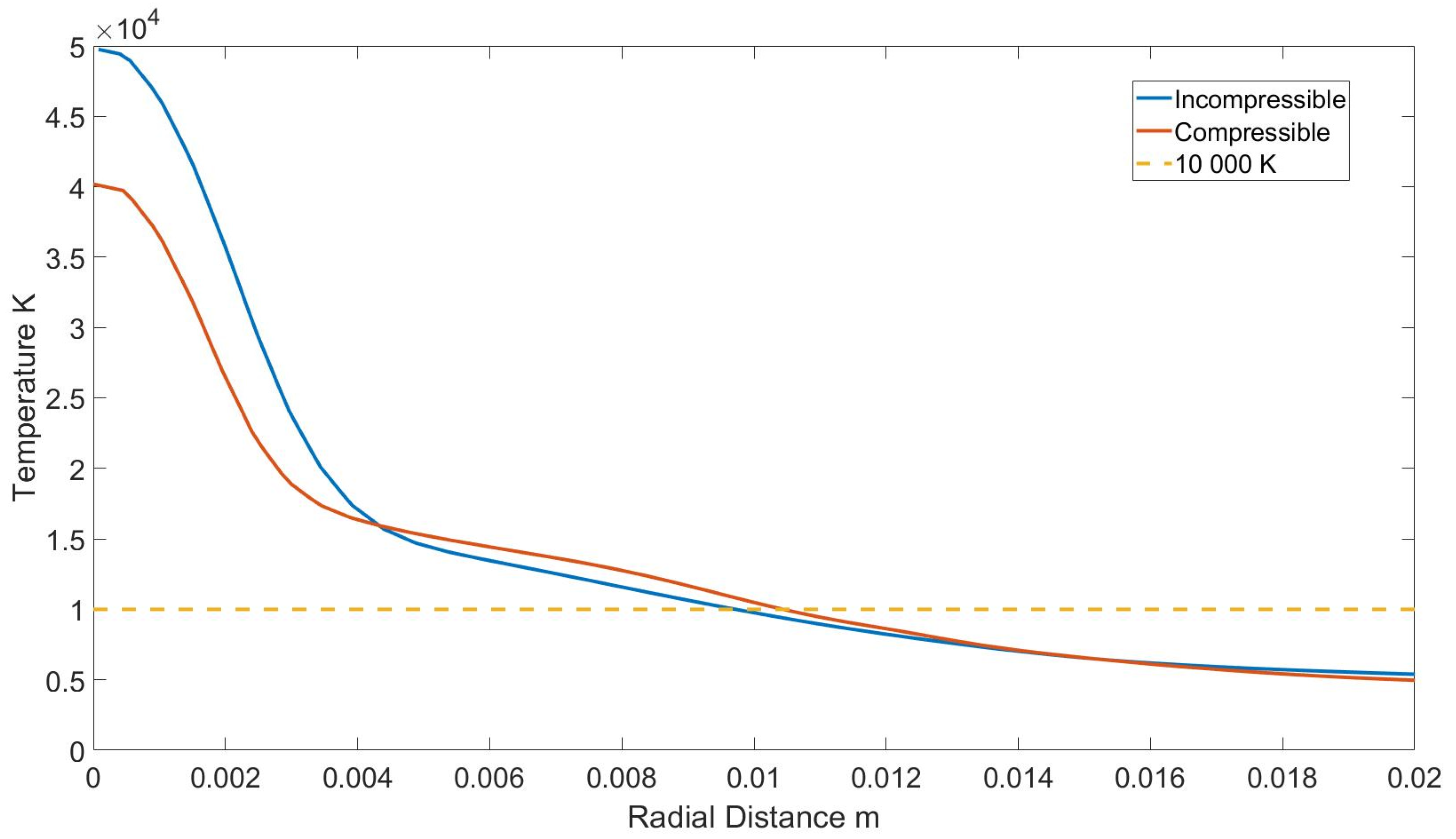
5.1. Compressible and Incompressible Simulation
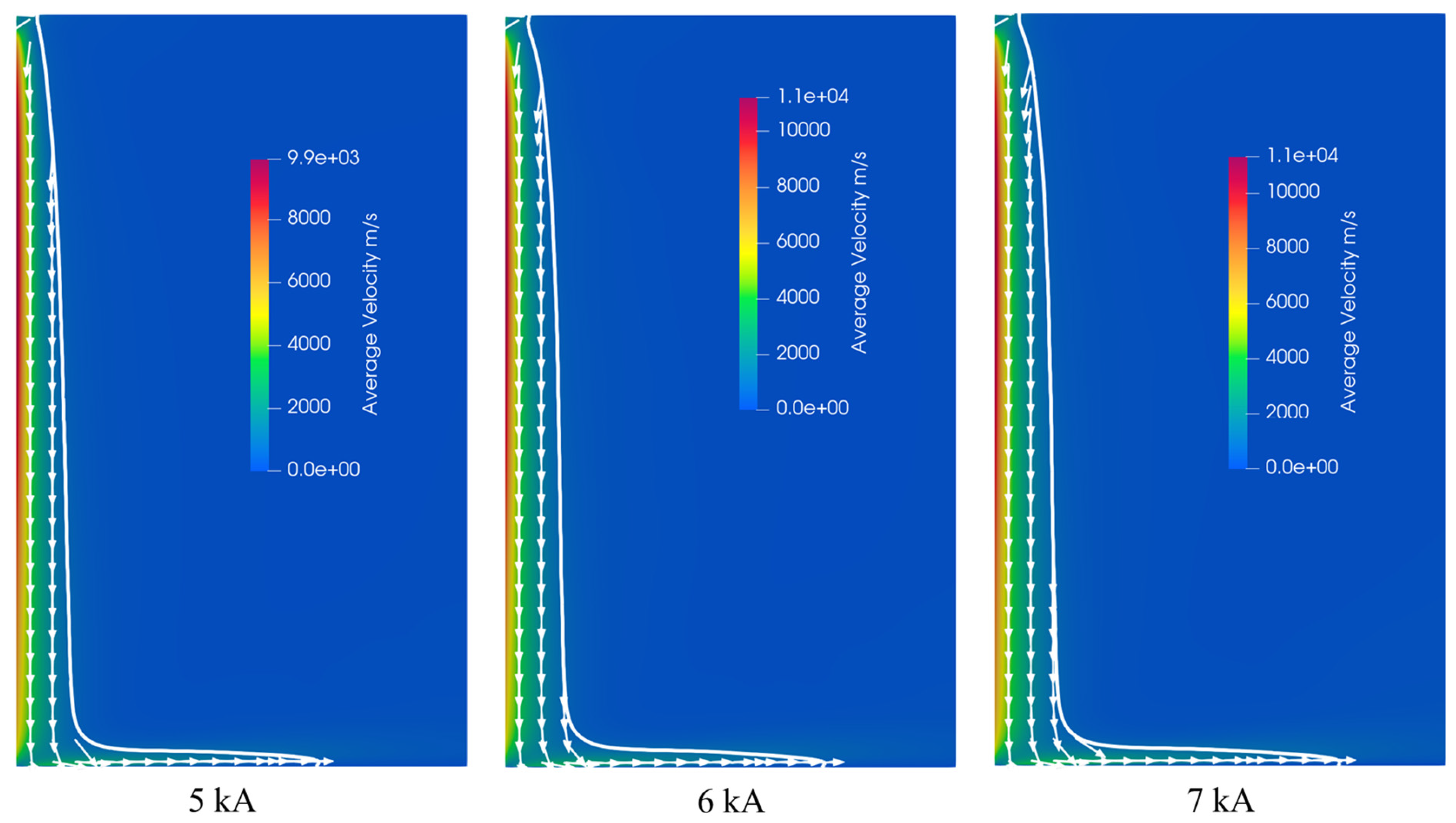
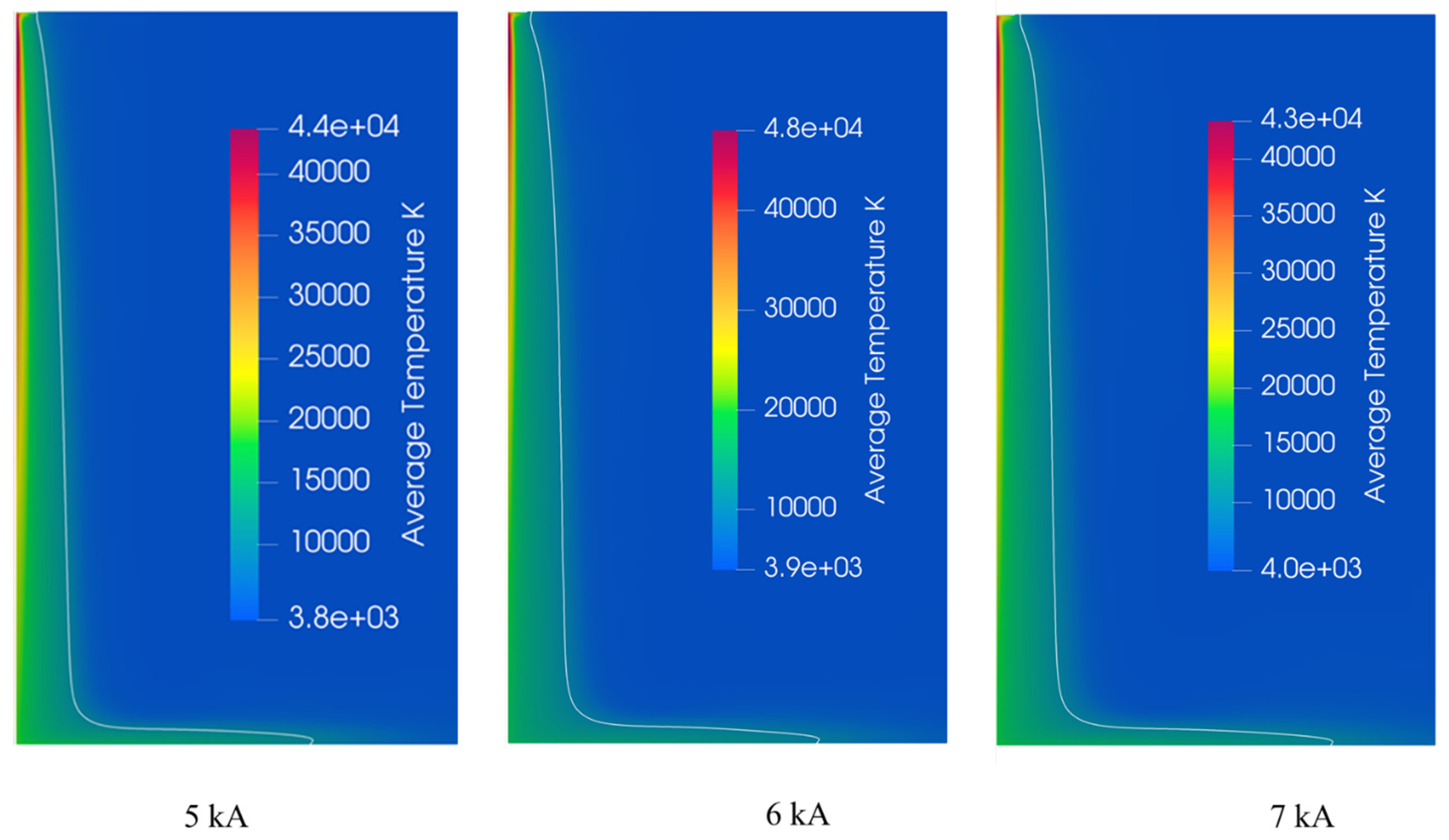
5.2. Effect of Applied Current
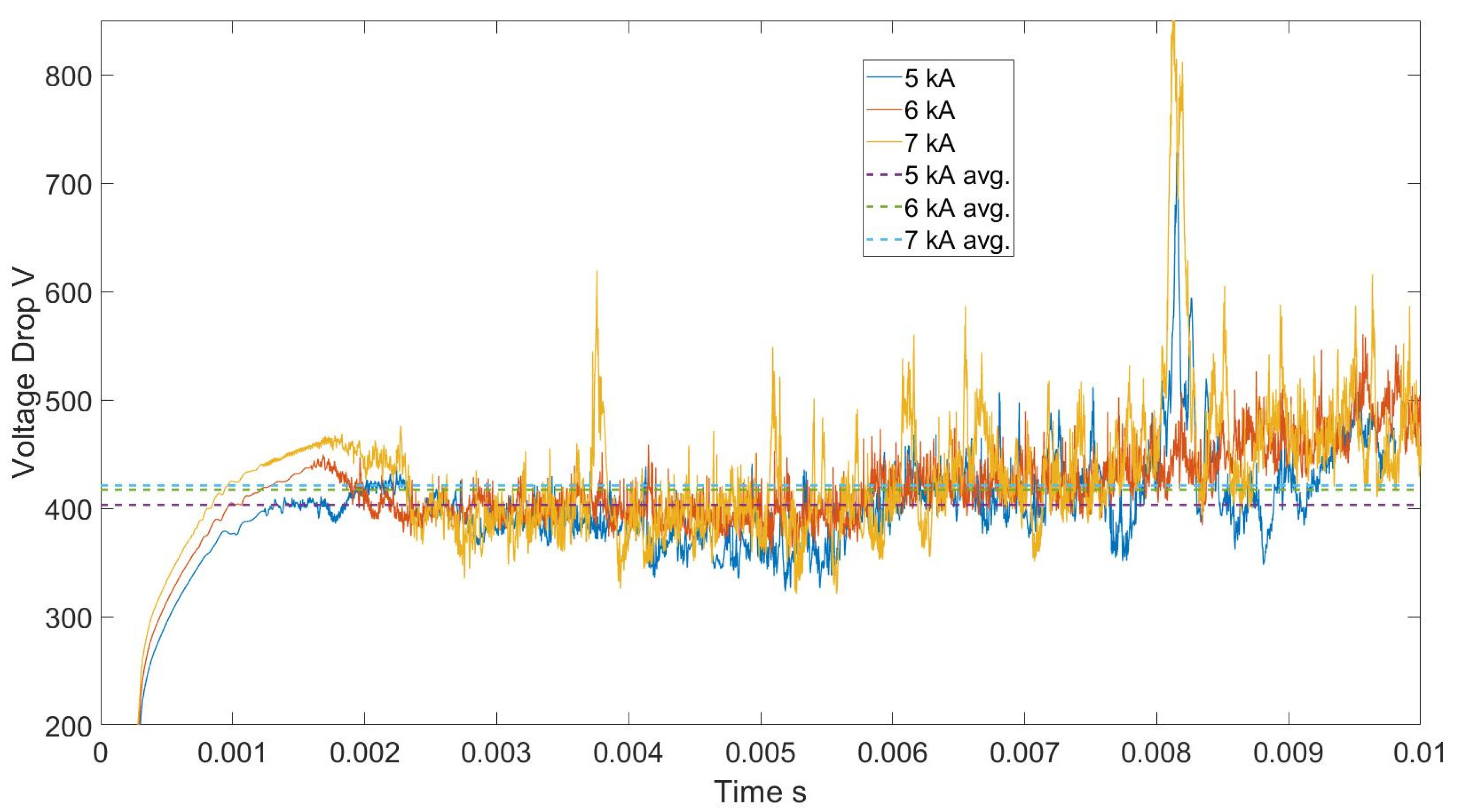
5.3. Analysis of Voltage Fluctuations
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| Velocity (m/s) | |
| Pressure (N/m2) | |
| Lorentz force per unit volume (N/m3) | |
| Source term per unit volume | |
| Effective viscosity (N.s/m2) | |
| Thermal conductivity (W/m.K) | |
| Ideal gas constant (J/mol·K) | |
| Molecular weight of the gas (g/mol) | |
| Operating pressure(N/m2) | |
| Temperature (K) | |
| Specific heat at constant pressure (J/kg.K) | |
| Current density (A/m2) | |
| Experimental radiation loss (w/m3) | |
| Magnetic field (T) | |
| Specific heat at constant volume (J/kg.K) | |
| Applied current (A) | |
| Control volume (m3) | |
| Greeks: | |
| Density (kg/m3) | |
| Electrical conductivity (S/m) | |
| Vacuum permeability (H/m) | |
| Ratio of specific heats (cp/cv) | |
| Voltage drop (V) | |
| Subscripts: | |
| Axial coordinates | |
| Radial coordinates | |
| Azimuthal coordinates | |
References
- Jones, R.T.; Reynolds, Q.G.; Curr, T.R.; Sager, D. Some Myths about DC Arc Furnaces. J. South. Afr. Inst. Min. Metall. 2011, 111, 665–673. [Google Scholar]
- Leonard Kzoa Electric Arc Furnace’s Development History. Available online: https://www.chnzbtech.com/electric-arc-furnace-s-development-history.html (accessed on 3 December 2023).
- Iea Global Crude Steel Production by Process Route and Scenario, 2019–2050. Available online: https://www.iea.org/data-and-statistics/charts/global-crude-steel-production-by-process-route-and-scenario-2019-2050 (accessed on 3 December 2023).
- Fortune Electric Arc Furnaces Market Report Summaries. Available online: https://www.fortunebusinessinsights.com/electric-arc-furnaces-market-104745 (accessed on 3 December 2023).
- Odenthal, H.J.; Kemminger, A.; Krause, F.; Sankowski, L.; Uebber, N.; Vogl, N. Review on Modeling and Simulation of the Electric Arc Furnace (EAF). Steel Res. Int. 2018, 89, 1700098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dincer, I. Green Methods for Hydrogen Production. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2012, 37, 1954–1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordan, G.R.; Bowman, B.; Wakelam, D. Electrical and Photographic Measurements of High-Power Arcs. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 1970, 3, 1089–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowman, B. Properties of Arcs in DC Furnaces. In Proceedings of the 1994 Electric Furnace Conference, Nashville, TN, USA, 13–16 November 1994; pp. 111–120. [Google Scholar]
- Bowman, B.; Krüger, K. Arc Furnace Physics; Stahleisen: Düsseldorf, Germany, 2009; ISBN 978-3-514-00768-0. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, R.T.; Reynolds, Q.G.; Alport, M.J. DC Arc Photography and Modelling. Miner. Eng. 2002, 15, 985–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ushio, M.; Matsuda, F. Mathematical Modelling of Flow Field and Heat Transfer of Welding Arc. Int. Symp. Jpn. Weld. Soc. 1982, 1, 49–54. [Google Scholar]
- Szekely, J.; McKelliget, J.; Choudhary, M. Heat-transfer fluid flow and bath circulation in electric-arc furnaces and dc plasma furnaces. Ironmak. Steelmak. 1983, 10, 169–179. [Google Scholar]
- Ramírez-argáez, M.A. Mathematical Modeling of DC Electric Arc Furnace Operations. Ph.D. Thesis, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, MA, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Alexis, J.; Ramirez, M.; Trapaga, G.; Jönsson, P. Modeling of a DC Electric Arc Furnace—Heat Transfer from the Arc. ISIJ Int. 2000, 40, 1089–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Jin, Z.; Zhu, Z. Numerical Study of Dc Arc Plasma and Molten Bath in Dc Electric Arc Furnace. Ironmak. Steelmak. 2006, 33, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez-Argáez, M.A.; González-Rivera, C.; Trápaga, G. Mathematical Modeling of High Intensity Electric Arcs Burning in Different Atmospheres. ISIJ Int. 2009, 49, 796–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, Q.G.; Jones, R.T.; Reddy, B.D. Mathematical and Computational Modelling of the Dynamic Behaviour of Direct Current Plasma Arcs. Proc. 12th Int. Ferroalloys Congr. Sustain. Future 2010, 110, 789–801. [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds, Q.G. Computational Modelling of Shear-Layer Instabilities and Vortex Formation in DC Plasma Arcs. Miner. Eng. 2014, 63, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, Q.G. Computational Modeling of Arc–Slag Interaction in DC Furnaces. JOM 2017, 69, 351–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trelles, J.P. Computational Study of Flow Dynamics from a Dc Arc Plasma Jet. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2013, 46, 255201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Yin, S.; Liao, H.; Gu, S. Three-Dimensional Simulation of an Argon-Hydrogen DC Non-Transferred Arc Plasma Torch. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2015, 80, 644–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, A.B.; Uhrlandt, D. Foundations of High-Pressure Thermal Plasmas. Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 2018, 27, 063001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ernst, D.; Zarl, M.A.; Farkas, M.A.; Schenk, J. Effects of the Electrodes’ Shape and Graphite Quality on the Arc Stability during Hydrogen Plasma Smelting Reduction of Iron Ores. Steel Res. Int. 2023, 94, 2200818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Nasser, M.; Barati, H.; Redl, C.; Ishmurzin, A.; Voller, N.; Hackl, G.; Leuchtenmüller, M.; Wu, M.; Kharicha, A. Effect of Compressibility on Industrial DC Electric Arcs. Results Eng. 2023, 19, 101312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, A.B.; Tanaka, M.; Yamamoto, K.; Tashiro, S.; Sato, T.; Lowke, J.J. Modelling of Thermal Plasmas for Arc Welding: The Role of the Shielding Gas Properties and of Metal Vapour. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2009, 42, 194006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, C.; Jiang, Z.; Zhu, H.; Pan, T. Characteristics Analysis of Fluid Flow and Heating Rate of a Molten Bath Utilizing a Unified Model in a DC EAF. Metals 2022, 12, 390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, H.; Li, T.; Bai, C.; Jiang, Z.; Tan, M.; Gao, X.; Zhu, Y. Numerical Simulation of the Interaction between Arc Plasma and Molten Slag in Electric Arc Furnace for High-Titania Slag Smelting. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2023, 54, 1687–1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Parliament. Directorate General for Parliamentary Research Services. EU Energy System Transformation: Cost of Non Europe; European Parliament. Directorate General for Parliamentary Research Services: Maastricht, The Netherlands, 2021.
- Kmecova, M.; Sikula, O.; Krajcik, M. Circular Free Jets: CFD Simulations with Various Turbulence Models and Their Comparison with Theoretical Solutions. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 471, 062045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, J.C.; Bach, G.R.; Krey, R.U.; Liebermann, R.W.; Yos, J.M. Continuum Radiated Power for High-Temperature Air and Its Components. AIAA J. 1966, 4, 1223–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKelliget, J.W.; Szekely, J. A Mathematical Model of the Cathode Region of a High Intensity Carbon Arc. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 1983, 16, 1007–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haidar, J.; Farmer, A.J.D. Surface Temperature Measurements for Tungsten-Based Cathodes of High-Current Free-Burning Arcs. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 1995, 28, 2089–2094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barati, H.; Kharicha, A.; Al-Nasser, M.; Kreuzer, D.; Hackl, G.; Gruber, M.; Ishmurzin, A.; Redl, C.; Teplyakov, I.O.; Wu, M.; et al. MHD Instability at the Cathode Spot as the Origin of the Vortex Formation in High-Intensity Plasma Arcs. J. Phys. Commun. 2022, 6, 015008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kharicha, A.; Al-Nasser, M.; Barati, H.; Karimi-Sibaki, E.; Vakhrushev, A.; Abdi, M.; Ludwig, A.; Wu, M. Tornados and Cyclones Driven by Magneto-Hydrodynamic Forces. Eur. J. Mech. B/Fluids 2022, 94, 90–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Nasser, M.; Kharicha, A.; Barati, H.; Pichler, C.; Hackl, G.; Gruber, M.; Ishmurzin, A.; Redl, C.; Wu, M.; Ludwig, A. Toward a Simplified Arc Impingement Model in a Direct-Current Electric Arc Furnace. Metals 2021, 11, 1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommeria, J. Electrically Driven Vortices in a Strong Magnetic Field. J. Fluid Mech. 1988, 189, 553–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Boundary | Flow | Temperature | Magnetic Field |
|---|---|---|---|
| Electrode | |||
| Top air | |||
| Side air | |||
| Flat and static surface | |||
| Axis of symmetry |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Al Nasser, M.; Alrasheedi, N.; Karimi-Sibaki, E.; Vakhrushev, A.; Ahmadein, M.; Ataya, S.; Kharicha, A. Exploring Extreme Voltage Events in Hydrogen Arcs within Electric Arc Furnaces. Sustainability 2024, 16, 2831. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16072831
Al Nasser M, Alrasheedi N, Karimi-Sibaki E, Vakhrushev A, Ahmadein M, Ataya S, Kharicha A. Exploring Extreme Voltage Events in Hydrogen Arcs within Electric Arc Furnaces. Sustainability. 2024; 16(7):2831. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16072831
Chicago/Turabian StyleAl Nasser, Mohamad, Nashmi Alrasheedi, Ebrahim Karimi-Sibaki, Alexander Vakhrushev, Mahmoud Ahmadein, Sabbah Ataya, and Abdellah Kharicha. 2024. "Exploring Extreme Voltage Events in Hydrogen Arcs within Electric Arc Furnaces" Sustainability 16, no. 7: 2831. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16072831
APA StyleAl Nasser, M., Alrasheedi, N., Karimi-Sibaki, E., Vakhrushev, A., Ahmadein, M., Ataya, S., & Kharicha, A. (2024). Exploring Extreme Voltage Events in Hydrogen Arcs within Electric Arc Furnaces. Sustainability, 16(7), 2831. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16072831









